Seasonal and Long-Term Connections between Trophic Status, Sestonic Chlorophyll, Nutrients, Organic Matter, and Monsoon Rainfall in a Multipurpose Reservoir
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Sites
2.3. Field Sampling and Rainfall Data
2.4. Water Quality Analyses
2.5. Trophic Status Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Role of Monsoon and Water Chemistry Variability
3.2. Long-Term Trends in the Water Quality Parameters
3.3. Spatio-Seasonal Links between Nutrients, Ambient Ratios, and Sestonic CHL-a
3.4. Conditional Plotting
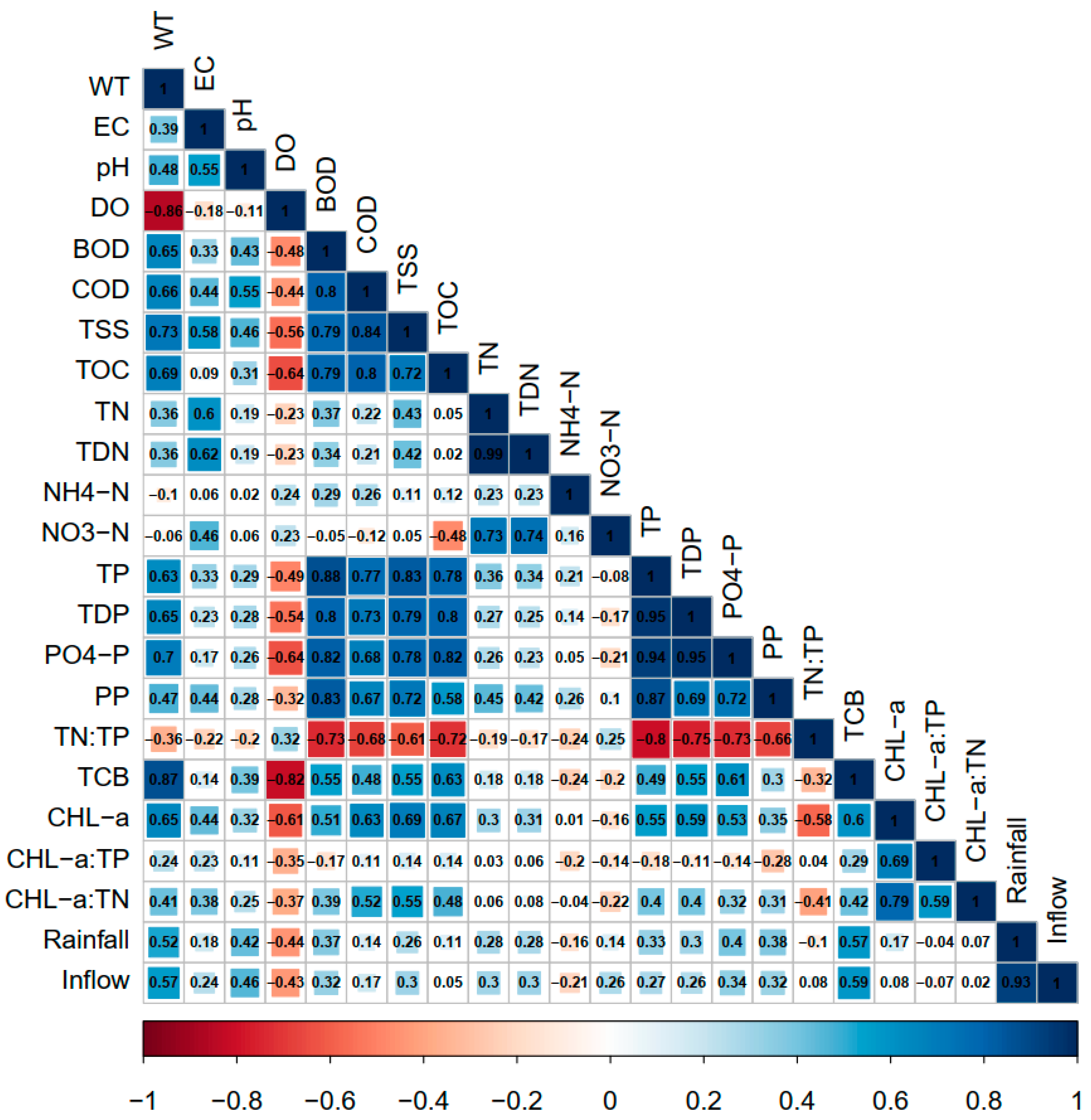
3.5. Co-Relating Water Chemistry Parameters
3.6. Predominant Links between Water Chemistry Parameters
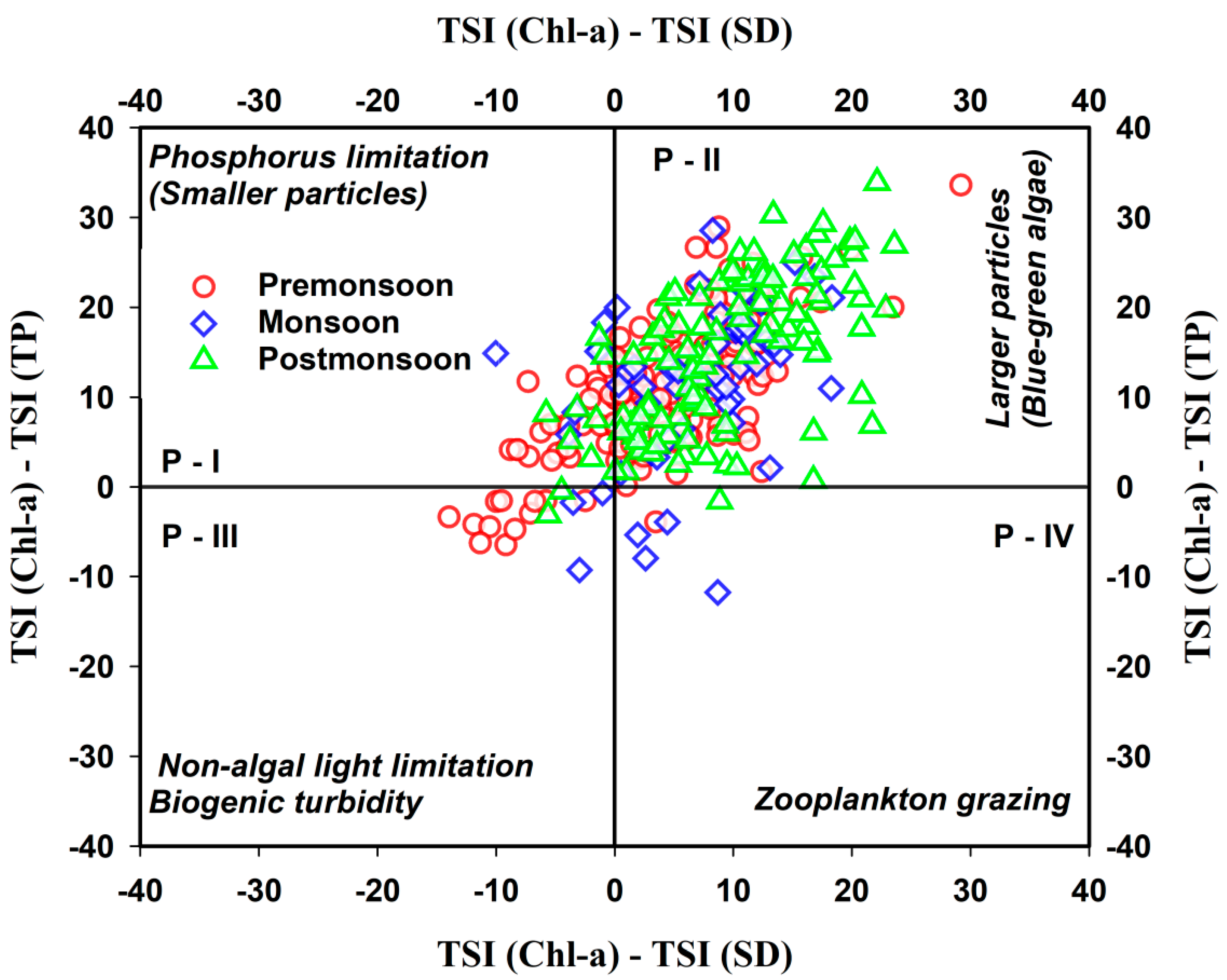
3.7. Trophic State Index Deviation (TSID)
4. Conclusions and Management Strategies
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Stream health evaluation using a combined approach of multi-metric chemical pollution and biological integrity models. Water 2018, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Seasonal Pattern of Nutrient Limitation in a Eutrophic Lake and Quantitative Analysis of the Impacts from Internal Nutrient Cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 13675–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zou, R.; Jiang, Q.; Elser, J.J.; Zhao, L.; Ye, R.; Liu, Y. What maintains seasonal nitrogen limitation in hyper-eutrophic Lake Dianchi? Insights from stoichiometric three-dimensional numerical modeling. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Landscape heterogeneity impacts water chemistry, nutrient regime, organic matter and chlorophyll dynamics in agricultural reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-J.; Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Long-Term Ecological Health Assessment of a Restored Urban Stream Based on Chemical Water Quality, Physical Habitat Conditions and Biological Integrity. Water 2019, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.-G. Long-Term Interannual and Seasonal Links between the Nutrient Regime, Sestonic Chlorophyll and Dominant Bluegreen Algae under the Varying Intensity of Monsoon Precipitation in a Drinking Water Reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E.; Havens, K.E. Simple graphical methods for the interpretation of relationships between trophic state variables. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Ansari, A.A. Eutrophication: An Ecological Vision. Bot. Rev. 2005, 71, 449–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Water quality and Trophic state index analysis in relation to Land use patterns in Agricultural Reservoirs. Korea Soc. Environ. Ecol. Proc. 2019, 2, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Havens, K.E.; James, R.T.; East, T.L.; Smith, V.H. N:P ratios, light limitation, and cyanobacterial dominance in a subtropical lake impacted by non-point source nutrient pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Atique, U.; Paul, A.K.; Iqbal, S. Seasonal and spatial variation of flagellate communities in a tropical river. Limnologica 2020, 85, 125824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chislock, M.F.; Doster, E.; Zitomer, R.A.; Wilson, A.E. Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences, and Controls in Aquatic Ecosystems. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2013, 4, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Reservoir Water Quality Assessment Based on Chemical Parameters and the Chlorophyll Dynamics in Relation to Nutrient Regime. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, K.W. Perspectives on reservoir limnology. In Reservoir Limnology: Ecological Perspectives; Thornton, K.W., Kimmel, B.L., Payne, F.E., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Gao, J. When and where to reduce nutrient for controlling harmful algal blooms in large eutrophic lake Chaohu, China? Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.H.; Walker, W.W. Reservoir Nutrient Dynamics. In Reservoir Limnology: Ecological Perspectives; Thornton, K.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, J.; Atique, U.; An, K.G. Multiyear links between water chemistry, algal chlorophyll, drought-flood regime, and nutrient enrichment in a morphologically complex reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nõges, T. Relationships between morphometry, geographic location and water quality parameters of European lakes. Hydrobiologia 2009, 633, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.E.; An, K.G. Evaluation of algal chlorophyll and nutrient relations and the N:P ratios along with trophic status and light regime in 60 Korea reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.G.; Park, S.S. Indirect influence of the summer monsoon on chlorophyll-total phosphorus models in reservoirs: A case study. Ecol. Model. 2002, 152, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, G.; Jun, M.S.; Choi, K. Eutrophication of reservoirs in South Korea. Limnology 2001, 2, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, D.S.; Hwang, S.J.; An, K.G. Nutrients and chlorophyll-a dynamics in a temperate reservoir influenced by Asian monsoon along with in situ nutrient enrichment bioassays. Limnology 2010, 11, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R.; Knowlton, M.F.; An, K.G. Trophic state, seasonal patterns and empirical models in South Korean Reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2003, 19, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Soranno, P.A.; Wagner, T. The role of phosphorus and nitrogen on chlorophyll a: Evidence from hundreds of lakes. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.S.; Lei, T.C. Reservoir trophic state evaluation using Landsat TM images. JAWRA 2001, 37, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T.Y.; Gerunsin, N.; Soo, C.L.; Nyanti, L.; Sim, S.F.; Grinang, J. Seasonal changes and spatial variation in water quality of a large young tropical reservoir and its downstream river. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 8153246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markad, A.T.; Landge, A.T.; Nayak, B.B.; Inamdar, A.B.; Mishra, A.K. Trophic state modeling for shallow freshwater reservoir: A new approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, F.E.; North, R.L.; McEachern, P.; Obrecht, D.V.; Gurung, T.B.; Jones, S.B.; Jones, J.R. Phytoplankton nutrient deficiencies vary with season in sub-tropical lakes of Nepal. Hydrobiologia 2019, 833, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunbabu, E.; Ravichandran, S.; Sreeja, P. Sedimentation and internal phosphorus loads in Krishnagiri Reservoir, India. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2014, 19, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Downing, J.A. Relationship of chlorophyll to phosphorus and nitrogen in nutrient-rich lakes. Inl. Waters 2017, 7, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; Iqbal, S.; Khan, N.; Qazi, B.; Javeed, A.; Anjum, K.M.; Haider, M.S.; Khan, T.A.; Mahmood, S.; Sherzada, S. Multivariate Assessment of Water Chemistry and Metals in a River Impacted by Tanning Industry. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 3013–3025. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, M.A.; Paul, S.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Atique, U.; Ahmed, Z.; Paul, A.K.; Iqbal, S.; Mahboob, S. Seasonal analysis of food items and feeding habits of endangered riverine catfish Rita rita (Hamilton, 1822). Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, J.M.; Özkundakci, D.; Hamilton, D.; Miller, S. Relationships between land use and nitrogen and phosphorus in New Zealand lakes. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atique, U.; Byungjin, L.; Johee, Y.; An, K.-G. Biological Health Assessments of Lotic Waters by Biotic Integrity Indices and their Relations to Water Chemistry. Water 2019, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, D.-Y.; Atique, U.; Yoon, J.; Lim, B.; An, K.-G. Ecological Risk Assessment of Urban Streams Using Fish Biomarkers of DNA Damages and Physiological Responses. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, M.F.; Jones, J.R. Temporal and spatial dynamics of suspended sediment, nutrients, and algal biomass in Mark Twain Lake, Missouri. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1995, 135, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Jia, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Shi, K.; Gao, Y. Changes in chlorophyll a and its response to nitrogen and phosphorus characteristics over the past three decades in Poyang Lake, China. Ecohydrology 2020, 14, e2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W. On the phosphorus limitation paradigm for lakes. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.P.; Lewis, W.M. Phytoplankton nutrient limitation in Colorado mountain lakes. Freshw. Biol. 1988, 20, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maberly, S.C.; Pitt, J.A.; Davies, P.S.; Carvalho, L. Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation and the management of small productive lakes. Inl. Waters 2020, 10, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzialowski, A.R.; Wang, S.-H.; Lim, N.-C.; Spotts, W.W.; Huggins, D.G. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in central plains reservoirs, USA. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourg, P.; North, R.L.; Hunter, K.; Vandergucht, D.M.; Abirhire, O.; Silsbe, G.M.; Guildford, S.J.; Hudson, J.J. Light and nutrient co-limitation of phytoplankton communities in a large reservoir: Lake Diefenbaker, Saskatchewan, Canada. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Zipper, C.; Shabman, L.; Younos, T. A Literature Review for Use in Nutrient Criteria Development for Freshwater Streams and Rivers in Virginia; SR28-2006; Virginia Water Resources Research Center: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Klippel, G.; Macêdo, R.L.; Branco, C.W.C. Comparison of different trophic state indices applied to tropical reservoirs. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2020, 25, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kim, J.Y.; An, K.-G. Trophic Responses of the Asian Reservoir to Long-Term Seasonal and Interannual Dynamic Monsoon. Water 2020, 12, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingole, N.P.; An, K.-G. Modifications of nutrient regime, chlorophyll-a, and trophic state relations in Daechung Reservoir after the construction of an upper dam. J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 40, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, K.-G. Long-term Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Epilimnetic Nutrients (N, P), Chlorophyll-a, and Suspended Solids at the Dam Site of Yongdam Reservoir and Empirical Models. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 44, 214–225. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nürnberg, G.K. Trophic state of clear and colored, soft- and hardwater lakes with special consideration of nutrients, anoxia, phytoplankton and fish. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1996, 12, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; Watson, S.B.; McCauley, E. Predicting cyanobacteria dominance in lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; ISBN 0419239308. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Qiao, B.; Li, J.; Tu, J. First flush characteristics of rainfall runoff from a paddy field in the Taihu Lake watershed, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8336–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Marín, L.A.; Wheater, H.S.; Lindenschmidt, K.E. Assessment of nutrient loadings of a large multipurpose prairie reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Relative Abundance and Invasion Dynamics of Alien Fish Species Linked to Chemical Conditions, Ecosystem Health, Native Fish Assemblage, and Stream Order. Water 2021, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, W.-K.; Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Ecological risk assessments and eco-toxicity analyses using chemical, biological, physiological responses, DNA damages and gene-level biomarkers in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) in an urban stream. Chemosphere 2019, 239, 124754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, U.; Kwon, S.; An, K.-G. Linking weir imprints with riverine water chemistry, microhabitat alterations, fish assemblages, chlorophyll-nutrient dynamics, and ecological health assessments. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, R.; Filazzola, A.; Mahdiyan, O.; Shuvo, A.; Blagrave, K.; Ewins, C.; Moslenko, L.; Gray, D.K.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Relationships of total phosphorus and chlorophyll in lakes worldwide. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 66, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharip, Z.; Zaki, A.T.A.; Shapai, M.A.H.M.; Suratman, S.; Shaaban, A.J. Lakes of Malaysia: Water quality, eutrophication and management. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2014, 19, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.S. Environmental and Ecological Statistics with R, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781498728720. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Xia, C.; Xu, M.; Guo, J.; Sun, G. Application of modified water quality indices as indicators to assess the spatial and temporal trends of water quality in the Dongjiang River. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Yu, S.; Rhew, D. Relationships between water quality parameters in rivers and lakes: BOD5, COD, NBOPs, and TOC. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, S.; Joseph, A. Assessment of physico-chemical properties of water and phytoplankton bloom formation in a eutrophic pond using multivariate analysis. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2019, 24, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.B.; Brattebo, S.K.; Overland, C. Four decades of diluting phosphorus to maintain lake quality. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
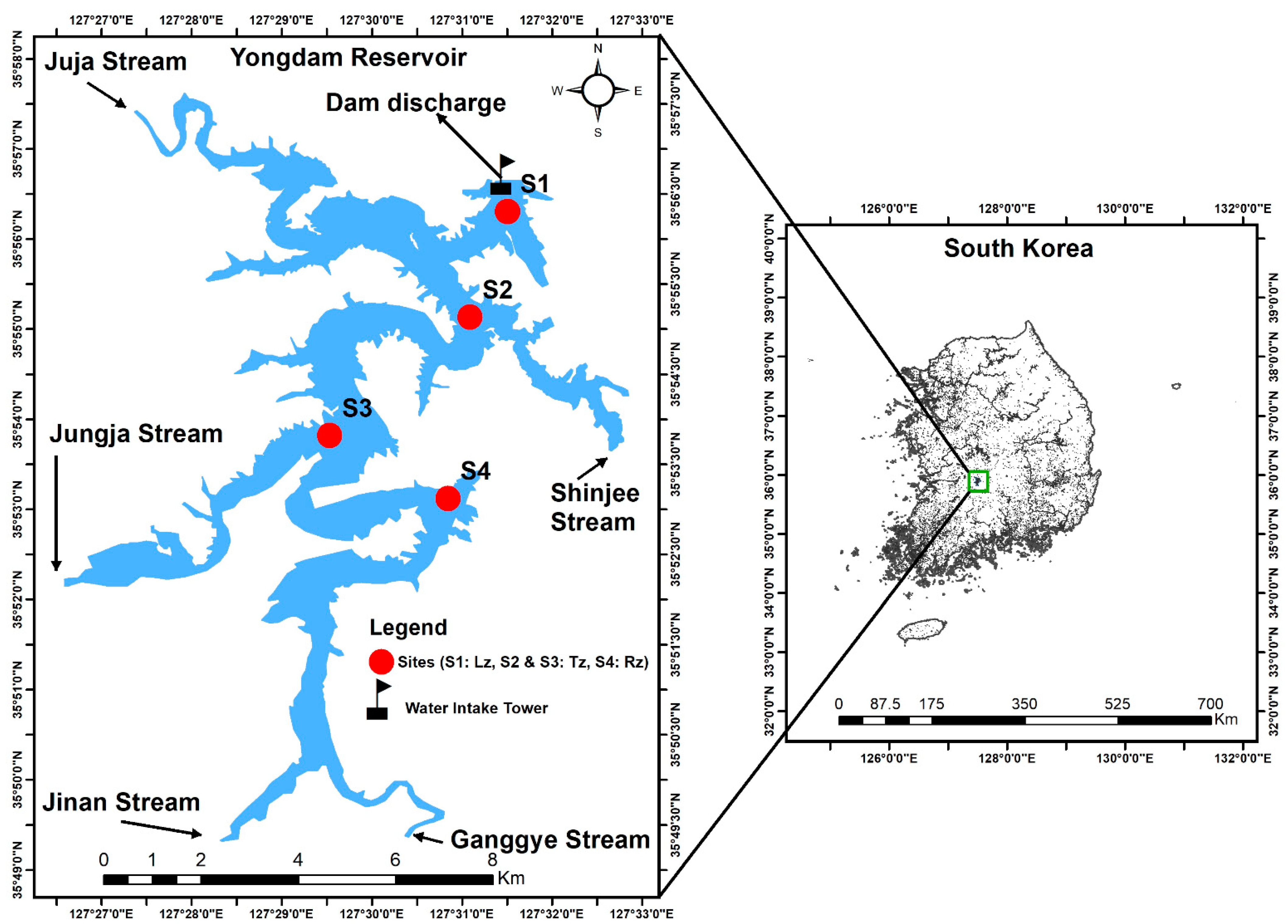
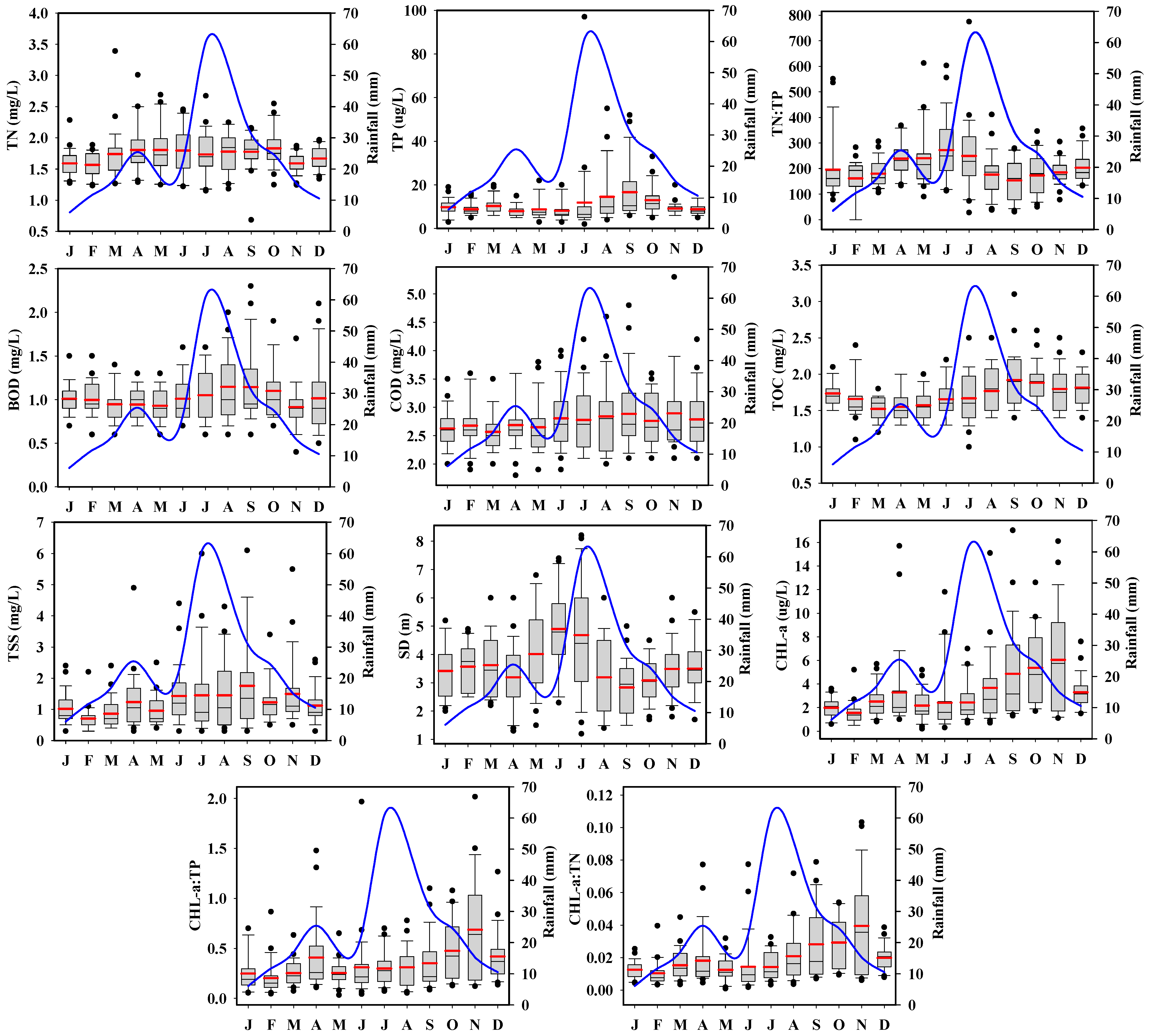
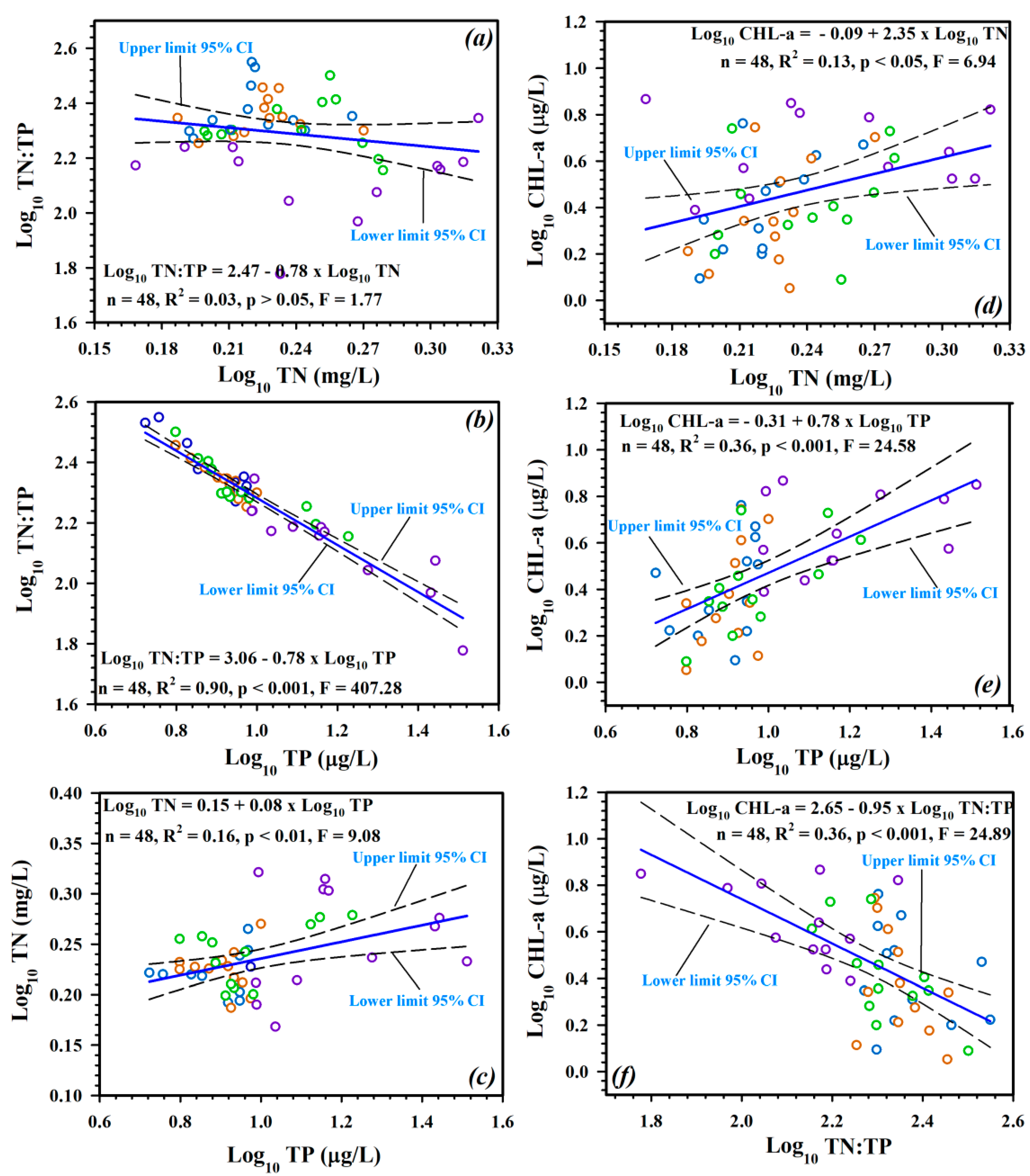
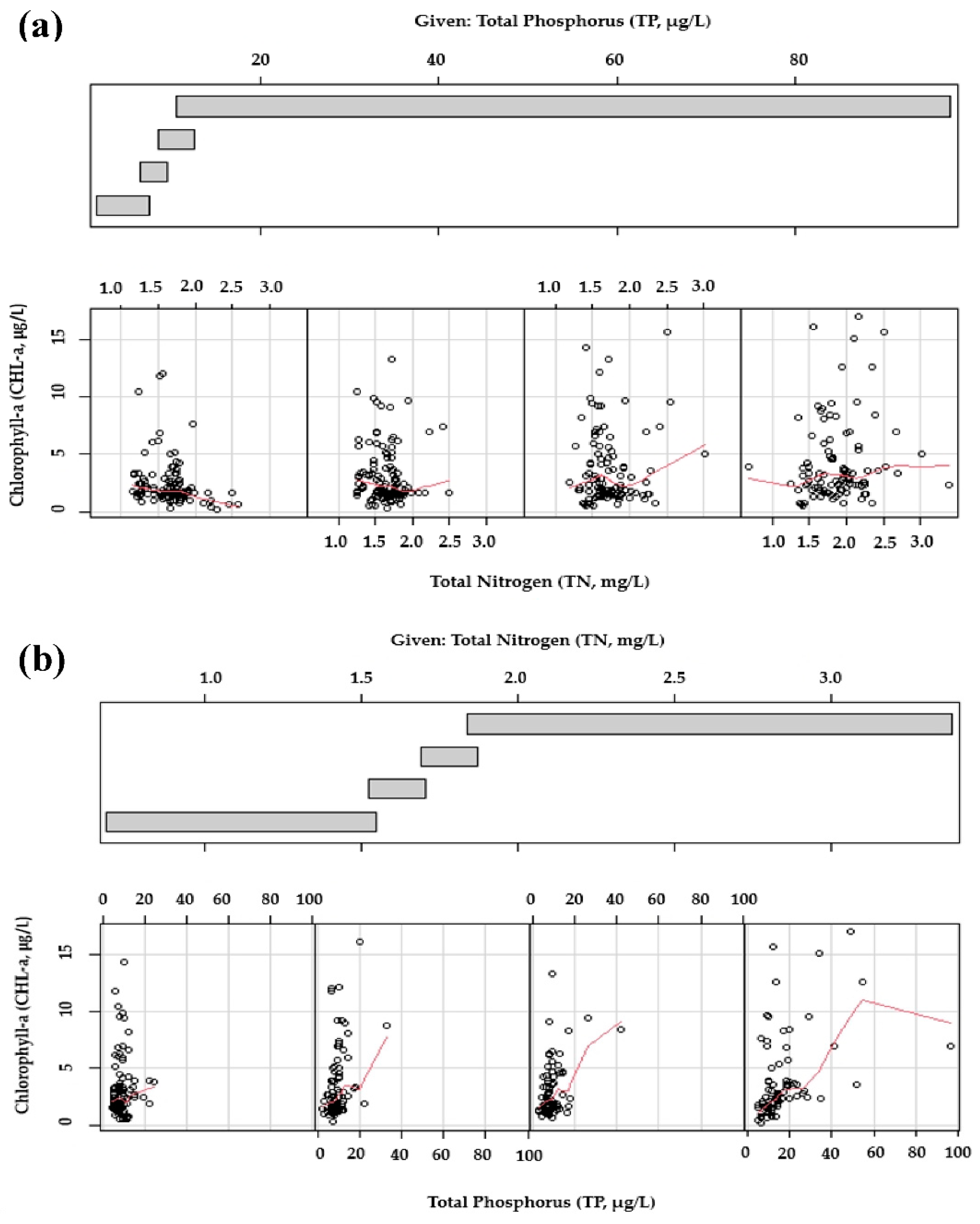


| Water Quality Parameter | Lz | Tz | Rz | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | (Min–Max) | Mean ± SD | (Min–Max) | Mean ± SD | (Min–Max) | Mean ± SD | (Min–Max) | |
| WT (℃) | 9.39 ± 3.08 | 3.0–16.7 | 9.55 ± 3.19 | 3.0–17.7 | 11.08 ± 4.28 | 3.0–19.8 | 13.57 ± 6.06 | 3.7–24.3 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 126.4 ± 3.59 | 90–161 | 126.4 ± 3.77 | 90–156 | 127.6 ± 4.86 | 76–171 | 135.9 ± 8.21 | 82–210 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 0.92 ± 0.21 | 0.3–2.9 | 1.03 ± 0.23 | 0.3–3.8 | 1.10 ± 0.29 | 0.3–4.6 | 1.89 ± 0.65 | 0.3–6.1 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 0.94 ± 0.07 | 0.5–1.9 | 0.95 ± 0.05 | 0.5–1.8 | 1.00 ± 0.08 | 0.4–1.9 | 1.18 ± 0.14 | 0.7–2.3 |
| COD (mg/L) | 2.61 ± 0.08 | 1.9–3.7 | 2.61 ± 0.08 | 1.9–3.9 | 2.71 ± 0.12 | 1.8–3.9 | 3.05 ± 0.20 | 2–5.3 |
| TOC (mg/L) | 1.64 ± 0.08 | 1.2–2.2 | 1.63 ± 0.08 | 1.1–2.2 | 1.71 ± 0.15 | 1–2.6 | 1.88 ± 0.22 | 1.2–3.1 |
| DO (mg/L) | 9.45 ± 1.30 | 5.6–12.5 | 9.53 ± 1.42 | 5.6–12.5 | 9.38 ± 1.67 | 4.3–12.7 | 9.23 ± 2.12 | 4.1–13.4 |
| pH | 7.39 ± 0.11 | 6.0–8.1 | 7.40 ± 0.10 | 5.8–8.3 | 7.46 ± 0.08 | 6.6–8.1 | 7.56 ± 0.09 | 6.4–8.4 |
| TN (mg/L) | 1.67 ± 0.08 | 1.15–2.22 | 1.68 ± 0.08 | 1.18–2.41 | 1.74 ± 0.11 | 1.17–2.57 | 1.81 ± 0.20 | 0.68–3.39 |
| TDN (mg/L) | 1.59 ± 0.08 | 1.01–2.16 | 1.60 ± 0.08 | 1.01–2.16 | 1.66 ± 0.11 | 1.04–2.55 | 1.73 ± 0.20 | 0.64–3.29 |
| NH4-N (mg/L) | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0–0.46 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.00–2.41 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.00–0.46 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.003–0.32 |
| NO3-N (mg/L) | 1.29 ± 0.08 | 0.53–1.92 | 1.29 ± 0.10 | 0.73–1.98 | 1.34 ± 0.15 | 0.69–2.20 | 1.33 ± 0.25 | 0.32–2.91 |
| TP (µg/L) | 8.02 ± 1.38 | 2.0–16 | 8.10 ± 1.13 | 3–16 | 9.76 ± 2.64 | 3–35 | 17.09 ± 7.59 | 6–97 |
| TDP (µg/L) | 4.74 ± 1.00 | 0–29 | 4.43 ± 1.26 | 0–15 | 5.85 ± 2.53 | 0–26 | 9.89 ± 5.37 | 1–61 |
| PO4-P (µg/L) | 1.48 ± 0.80 | 0–7 | 1.51 ± 0.69 | 0–7 | 2.36 ± 2.18 | 0–20 | 4.39 ± 3.59 | 0–43 |
| TN:TP | 243 ± 52 | 192–354 | 231 ± 30 | 183–278 | 212 ± 54 | 141–324 | 141 ± 39 | 62–221 |
| TCB (CFU/100mL) | 124.5 ± 91.2 | 2–1409 | 159.7 ± 111.2 | 2–1708 | 156.2 ± 124.7 | 1–1656 | 192.9 ± 137.3 | 4–1870 |
| CHL-a (µg/L) | 2.88 ± 1.10 | 0.4–12.2 | 2.68 ± 1.41 | 0.2–14.3 | 2.90 ± 1.33 | 0.6–9.6 | 4.89 ± 1.73 | 0.5–17 |
| Parameters | Kruskal–Wallis Test (A) | Mean ± Standard Deviation (Range) | Kruskal–Wallis Test (B) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premonsoon | Monsoon | Postmonsoon | |||
| TSS (mg/L) | H = 16.5 *** | 1.04 ± 0.69 (0.3–4.9) | 1.45 ± 1.20 (0.3–6) | 1.40 ± 1.02 (0.3–6.1) | H = 13.10 ** |
| BOD (mg/L) | H = 14.9 ** | 0.97 ± 0.20 (0.6–1.6) | 1.09 ± 0.35 (0.6–2) | 1.04 ± 0.37 (0.4–2.3) | H = 3.45 |
| TOC (mg/L) | H = 11.9 * | 1.61 ± 0.24 (1.1–2.4) | 1.72 ± 0.33 (1–2.5) | 1.85 ± 0.30 (1.4–3.1) | H = 42.58 *** |
| CHL-a (ug/L) | H = 10.4 * | 2.33 ± 2.06 (0.2–15.7) | 3.05 ± 2.47 (0.7–15.1) | 4.90 ± 3.52 (1.1–17) | H = 59.64 *** |
| TN (mg/L) | H = 4.5 | 1.72 ± 0.35 (1.22–3.39) | 1.76 ± 0.34 (1.15–2.67) | 1.72 ± 0.26 (0.68–2.55) | H = 2.11 |
| TP (ug/L) | H = 22.6 *** | 8.98 ± 3.71 (3–22) | 13.20 ± 15.23 (2–97) | 11.92 ± 7.94 (5–52) | H = 12.75 ** |
| TN:TP | H = 21. 2 ** | 222 ± 93.2 (81–612) | 214 ± 121.4 (34–363) | 182 ± 72.3 (30–361) | H = 9.59 * |
| Variable | S | Z | p-Value | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 1620 | 6.255 | <0.001 | + |
| EC | 438 | 1.688 | 0 | |
| TSS | 786 | 3.034 | <0.01 | + |
| BOD | 469 | 1.811 | 0 | |
| COD | 624 | 2.408 | <0.05 | + |
| TOC | 1608 | 6.216 | <0.001 | + |
| DO | −1790 | −6.912 | <0.001 | − |
| pH | 704 | 2.718 | <0.01 | + |
| TN | −11 | −0.038 | 0 | |
| TDN | −36 | −0.135 | 0 | |
| NH4-N | 151 | 0.579 | 0 | |
| NO3-N | −732 | −2.824 | <0.01 | − |
| TP | 299 | 1.152 | 0 | |
| TDP | 576 | 2.223 | <0.05 | + |
| PO4-P | 637 | 2.48 | <0.05 | + |
| PP | −190 | −0.731 | 0 | |
| TCB | 1089 | 4.203 | <0.001 | + |
| CHL-a | 1218 | 4.702 | <0.001 | + |
| Empirical Model | Season | Size | Equation | R2 | F Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log10 (TN:TP) vs. Log10 (TP, ug/L) | Premonsoon | 24 | TN:TP = 0.134 − (0.860 * TP) | 0.896 | 190.48 *** |
| Monsoon | 8 | TN:TP = 0.0219 − (0.702 * TP) | 0.944 | 100.84 *** | |
| Postmonsoon | 16 | TN:TP = 0.112 − (0.845 * TP) | 0.913 | 147.17 *** | |
| Log10 (TN:TP) vs. Log10 (TN, mg/L) | Premonsoon | 24 | TN:TP = −0.565 − (0.460 * TN) | 0.003 | 0.40 |
| Monsoon | 8 | TN:TP = 1.066 − (7.278 * TN) | 0.746 | 17.62 ** | |
| Postmonsoon | 16 | TN:TP = −0.784 + (0.0727 * TN) | 0.000 | 0.002 |
| Parameters | PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 | PC 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT (℃) | 0.77 | 0.24 | −0.43 | −0.12 |
| Cond (µS/cm) | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.44 |
| pH | 0.50 | 0.24 | ||
| DO (mg/L) | −0.75 | 0.47 | 0.21 | |
| BOD (mg/L) | 0.85 | −0.16 | 0.30 | −0.17 |
| COD (mg/L) | 0.82 | −0.22 | 0.14 | 0.16 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 0.87 | 0.20 | ||
| TOC (mg/L) | 0.80 | −0.52 | ||
| TN (mg/L) | 0.49 | 0.69 | 0.34 | |
| TDN (mg/L) | 0.48 | 0.72 | 0.32 | 0.11 |
| NH4-N (mg/L) | 0.12 | −0.14 | 0.71 | 0.13 |
| NO3-N (mg/L) | 0.84 | 0.41 | ||
| TP (ug/L) | 0.87 | −0.23 | 0.36 | −0.10 |
| TDP (ug/L) | 0.84 | −0.29 | 0.17 | −0.15 |
| PO4-P (ug/L) | 0.79 | −0.28 | −0.34 | |
| PP (ug/L) | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.49 | |
| TCB (Bact/100mL) | 0.70 | −0.59 | −0.22 | |
| CHL-a (ug/L) | 0.78 | −0.28 | 0.42 | |
| TN:TP | −0.79 | 0.42 | −0.32 | |
| CHL-a:TP | 0.21 | 0.13 | −0.67 | 0.59 |
| CHL-a:TN | 0.42 | −0.11 | −0.26 | 0.53 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 0.44 | 0.65 | −0.25 | −0.43 |
| Inflow (cm/s) | 0.46 | 0.45 | −0.24 | −0.46 |
| Eigenvalue | 9.85 | 3.49 | 2.99 | 1.72 |
| % variance | 48.31 | 16.68 | 15.17 | 8.13 |
| Cumulative % variance | 48.31 | 64.99 | 80.16 | 88.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jargal, N.; Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.-G. Seasonal and Long-Term Connections between Trophic Status, Sestonic Chlorophyll, Nutrients, Organic Matter, and Monsoon Rainfall in a Multipurpose Reservoir. Water 2021, 13, 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131720
Jargal N, Atique U, Mamun M, An K-G. Seasonal and Long-Term Connections between Trophic Status, Sestonic Chlorophyll, Nutrients, Organic Matter, and Monsoon Rainfall in a Multipurpose Reservoir. Water. 2021; 13(13):1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131720
Chicago/Turabian StyleJargal, Namsrai, Usman Atique, Md Mamun, and Kwang-Guk An. 2021. "Seasonal and Long-Term Connections between Trophic Status, Sestonic Chlorophyll, Nutrients, Organic Matter, and Monsoon Rainfall in a Multipurpose Reservoir" Water 13, no. 13: 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131720
APA StyleJargal, N., Atique, U., Mamun, M., & An, K.-G. (2021). Seasonal and Long-Term Connections between Trophic Status, Sestonic Chlorophyll, Nutrients, Organic Matter, and Monsoon Rainfall in a Multipurpose Reservoir. Water, 13(13), 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131720









