Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Sea Level Change in Saronikos Gulf (Aegean Sea, Greece): Evidence from the Piraeus Coastal Plain and Elefsis Bay Sedimentary Records
Abstract
1. Introduction
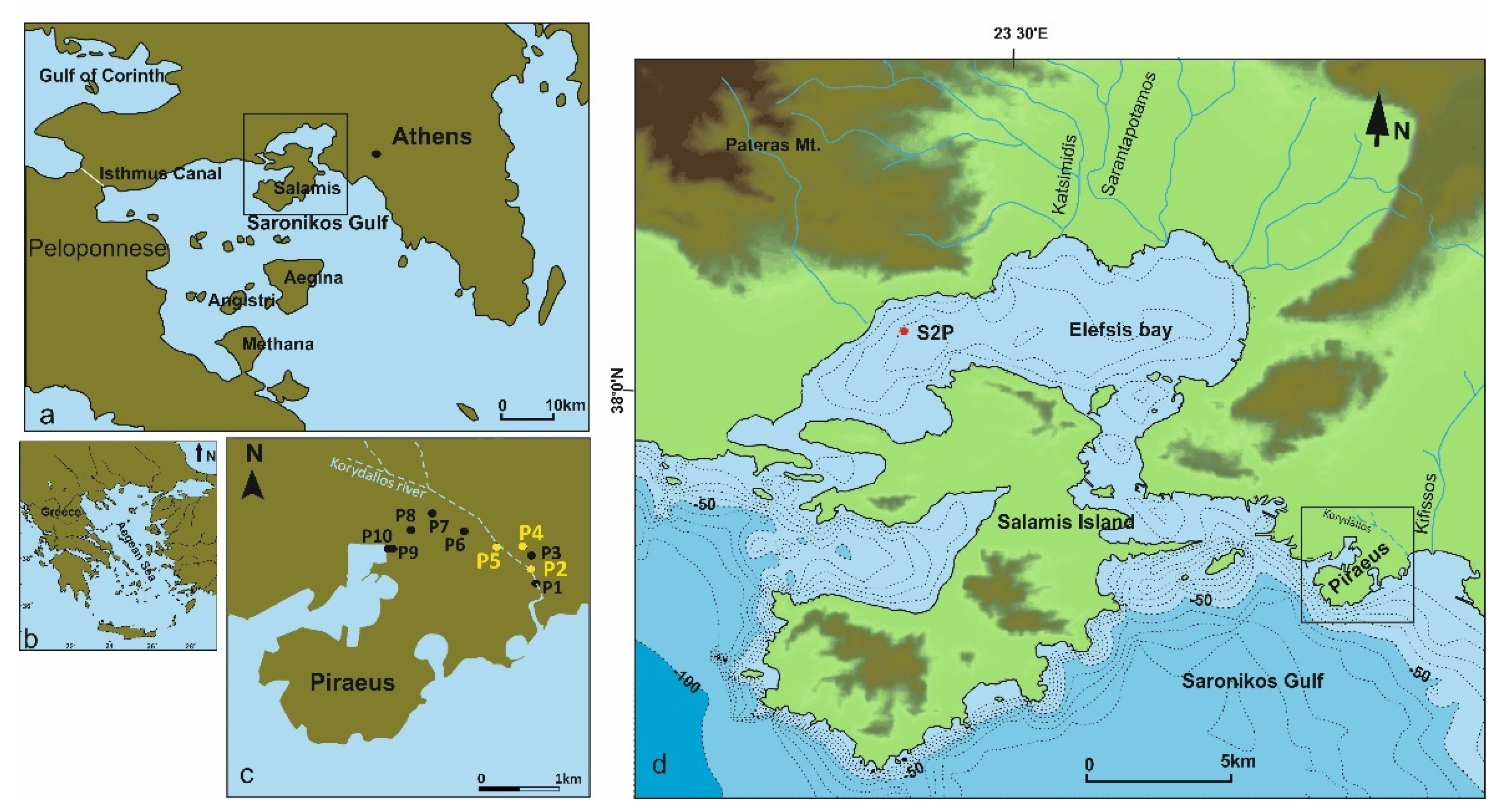
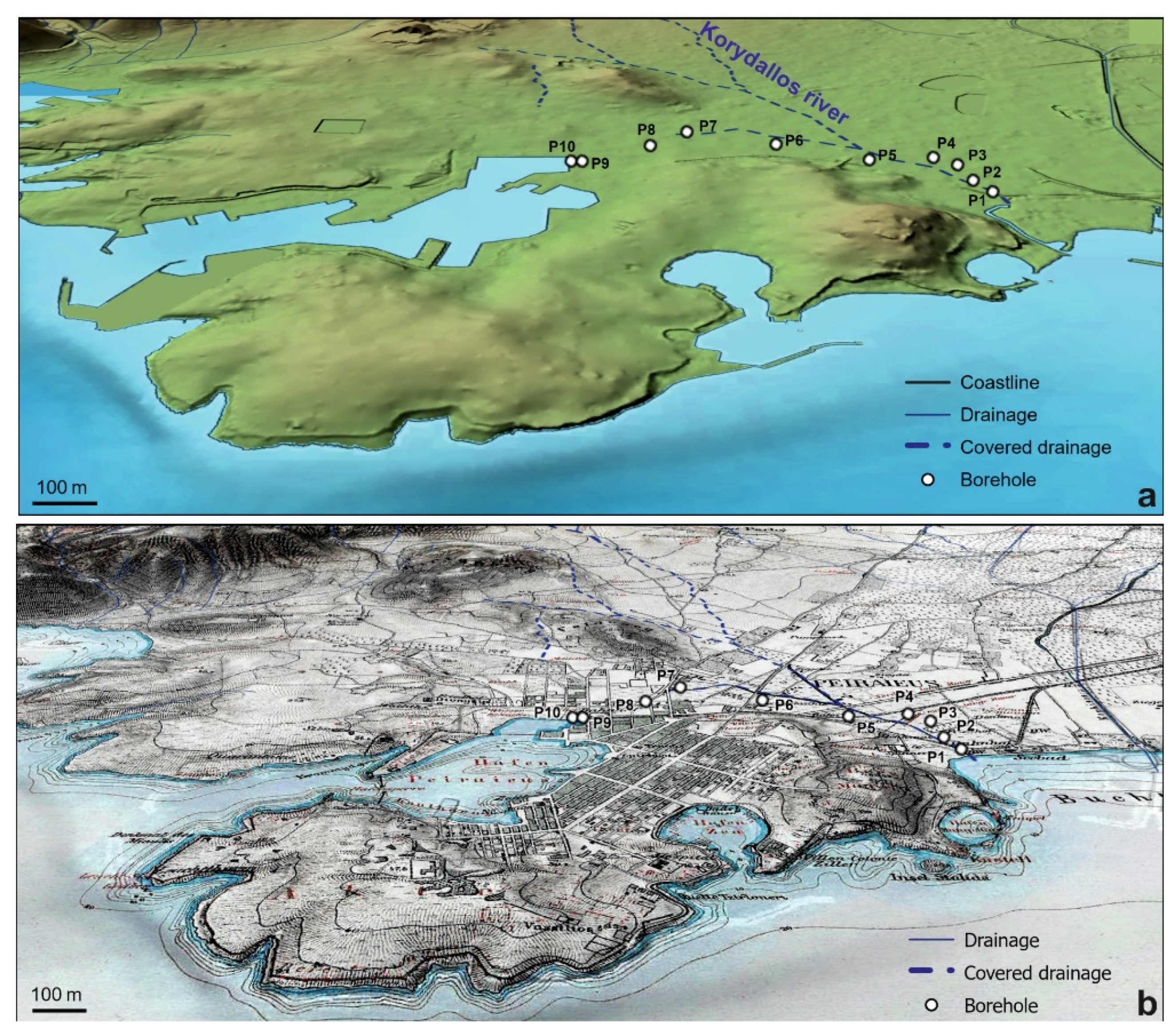
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
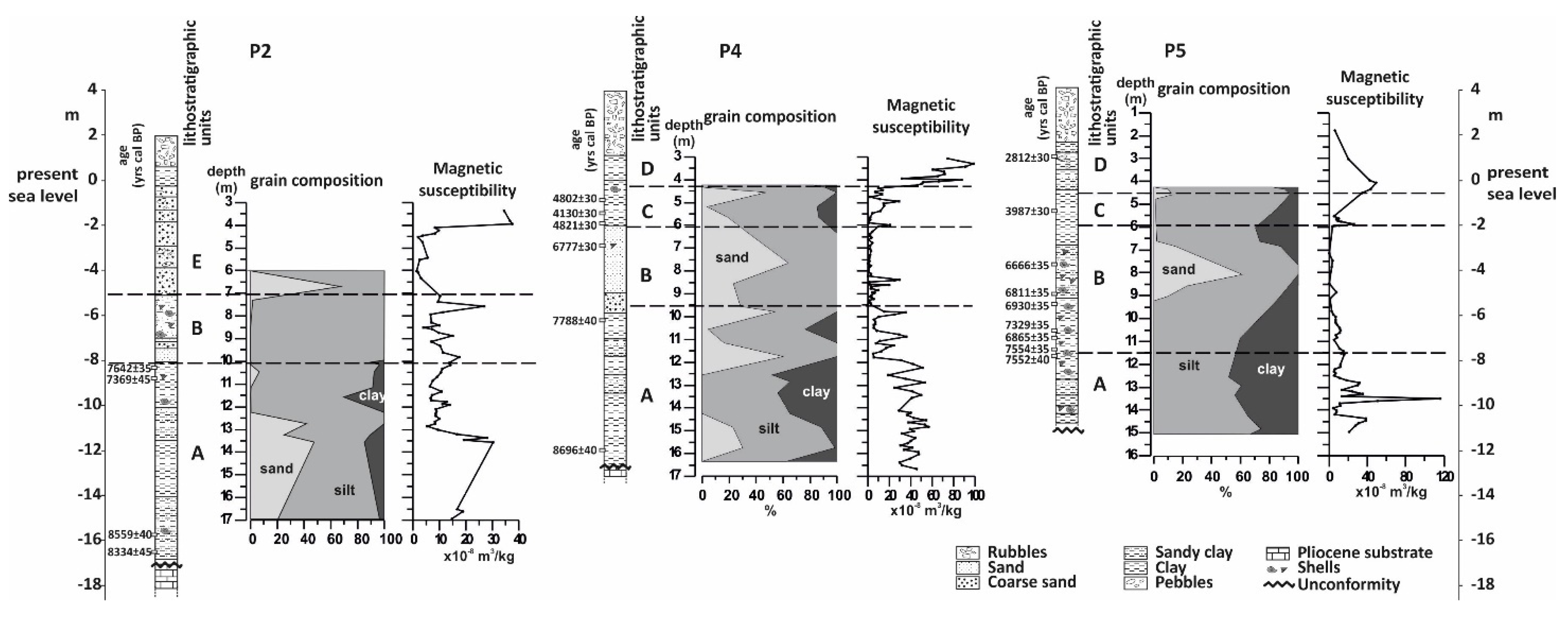
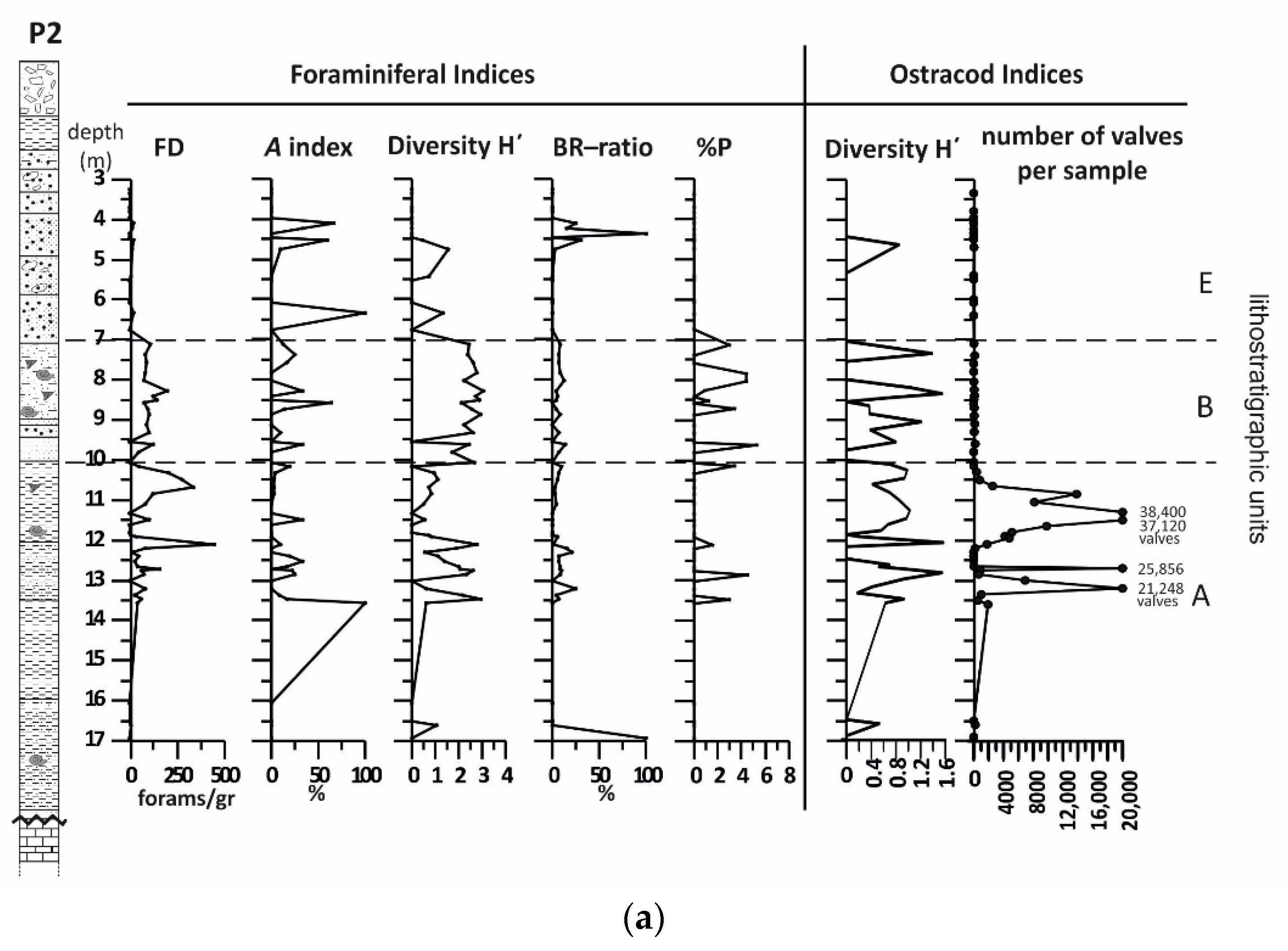
4.1. Borehole P2
4.1.1. Lithology and Magnetic Susceptibility
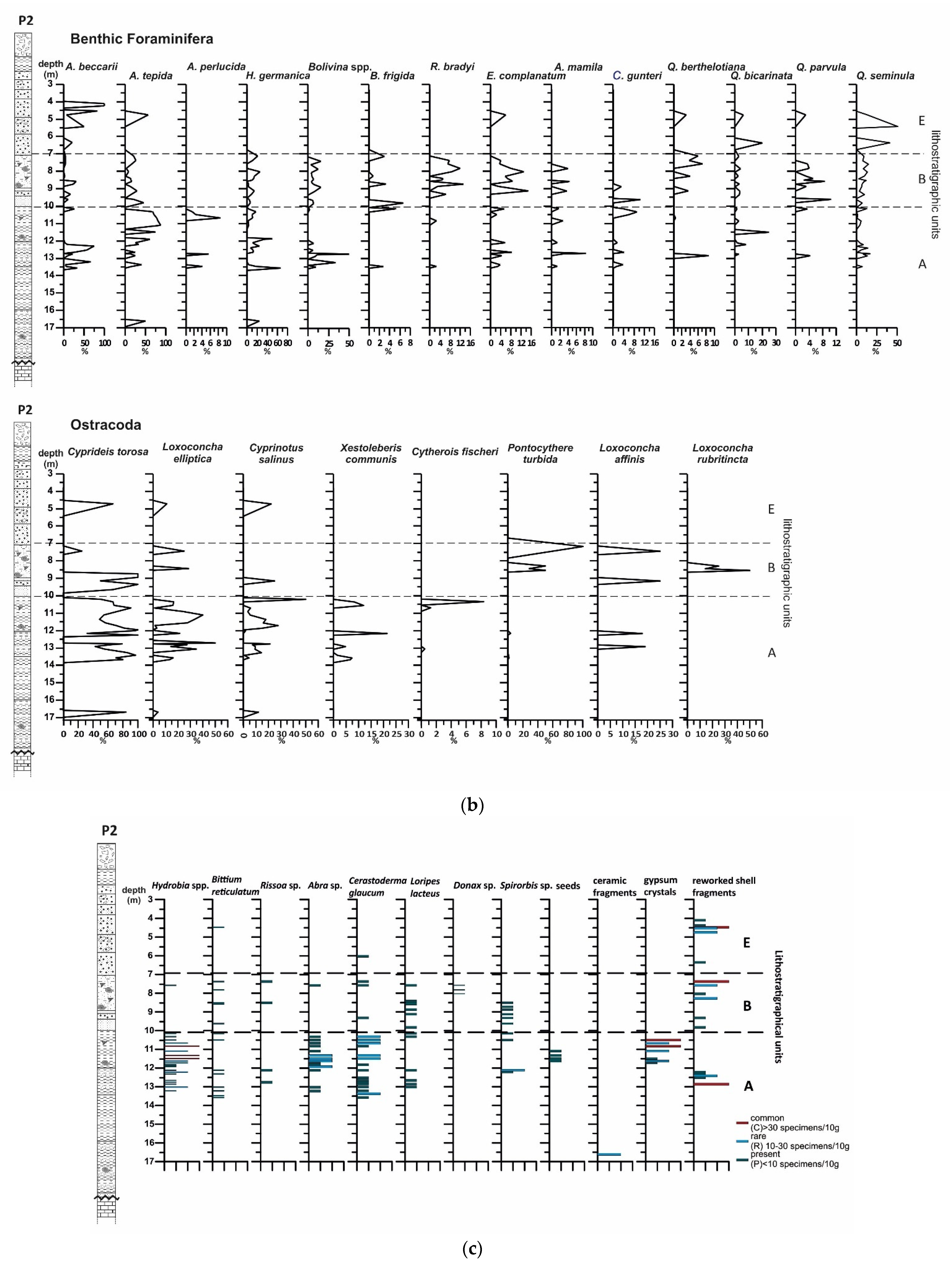
4.1.2. Benthic Foraminifera
4.1.3. Ostracods
4.1.4. Mollusc Assemblages
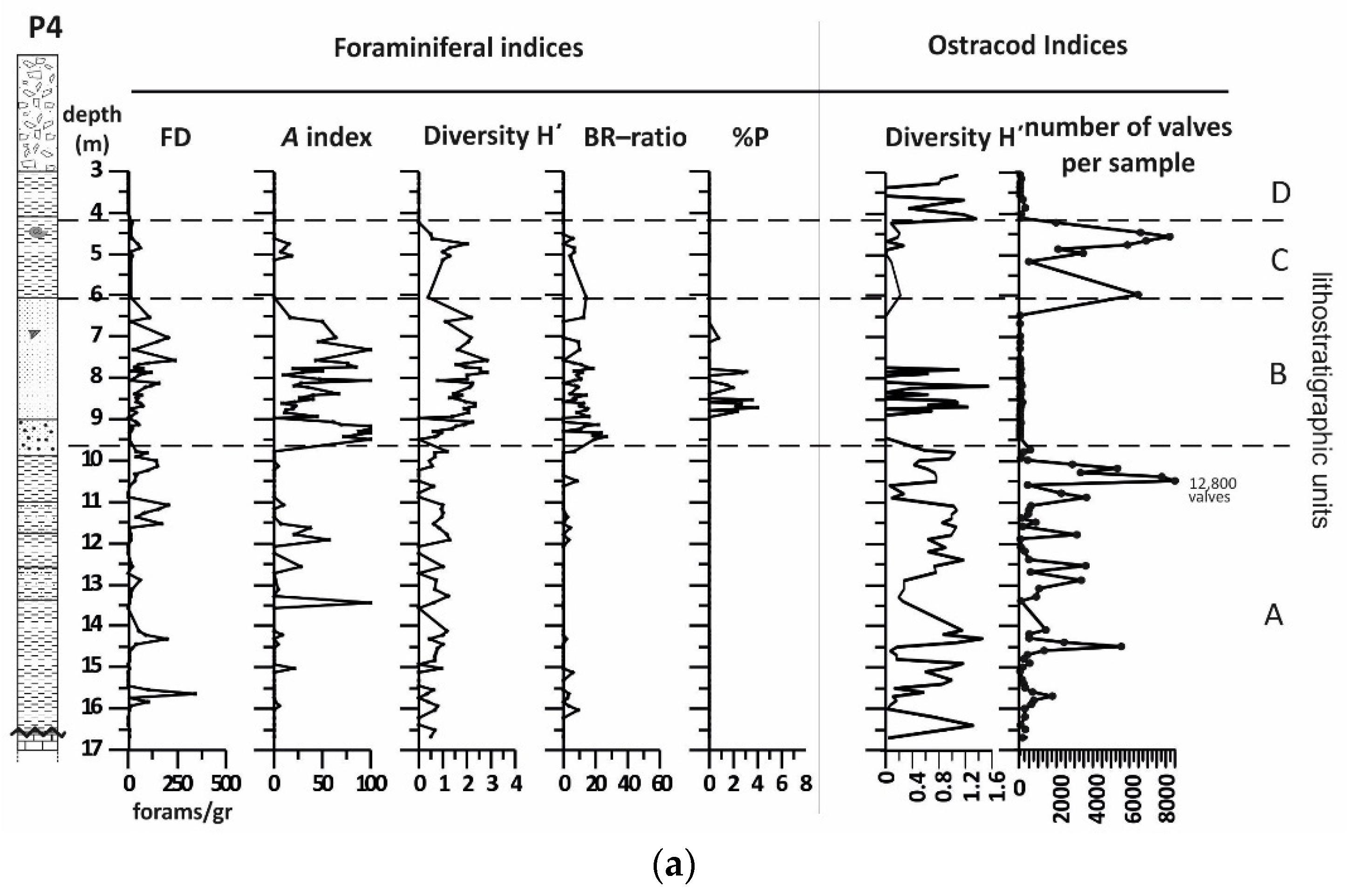
4.2. Borehole P4
4.2.1. Lithology and Magnetic Susceptibility
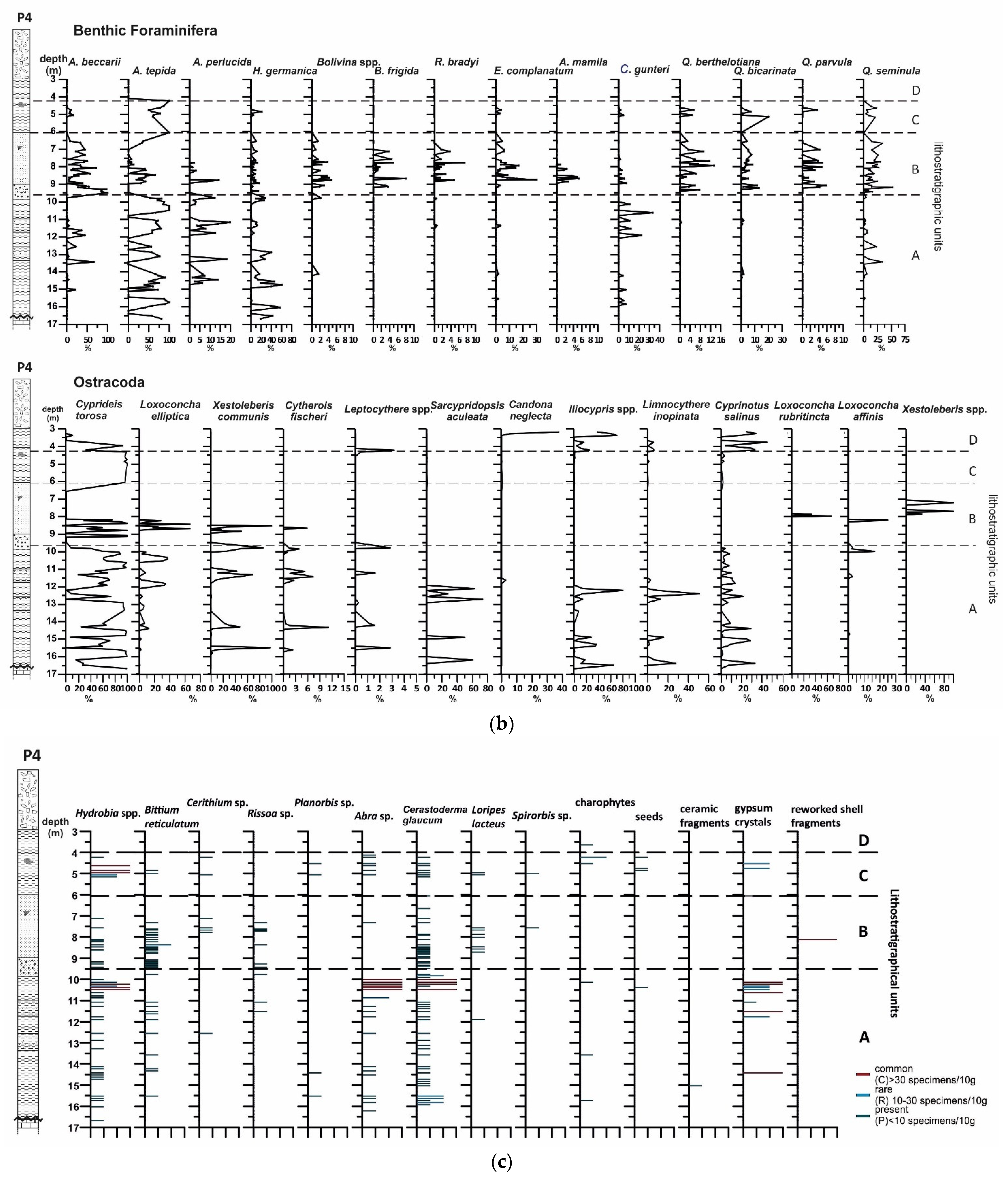
4.2.2. Benthic Foraminifera
4.2.3. Ostracods
4.2.4. Mollusc Assemblages
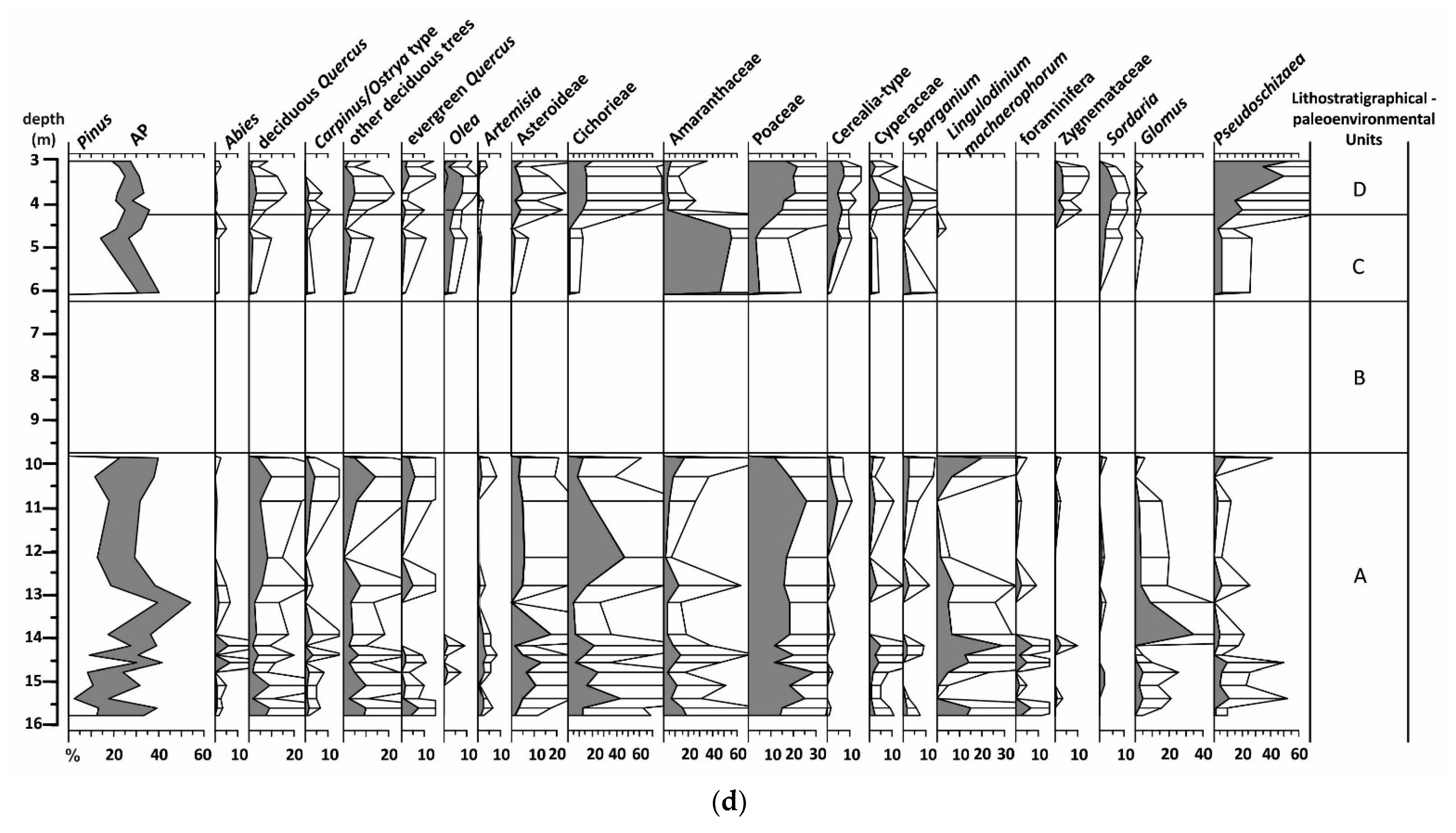
4.2.5. Palynological Analysis
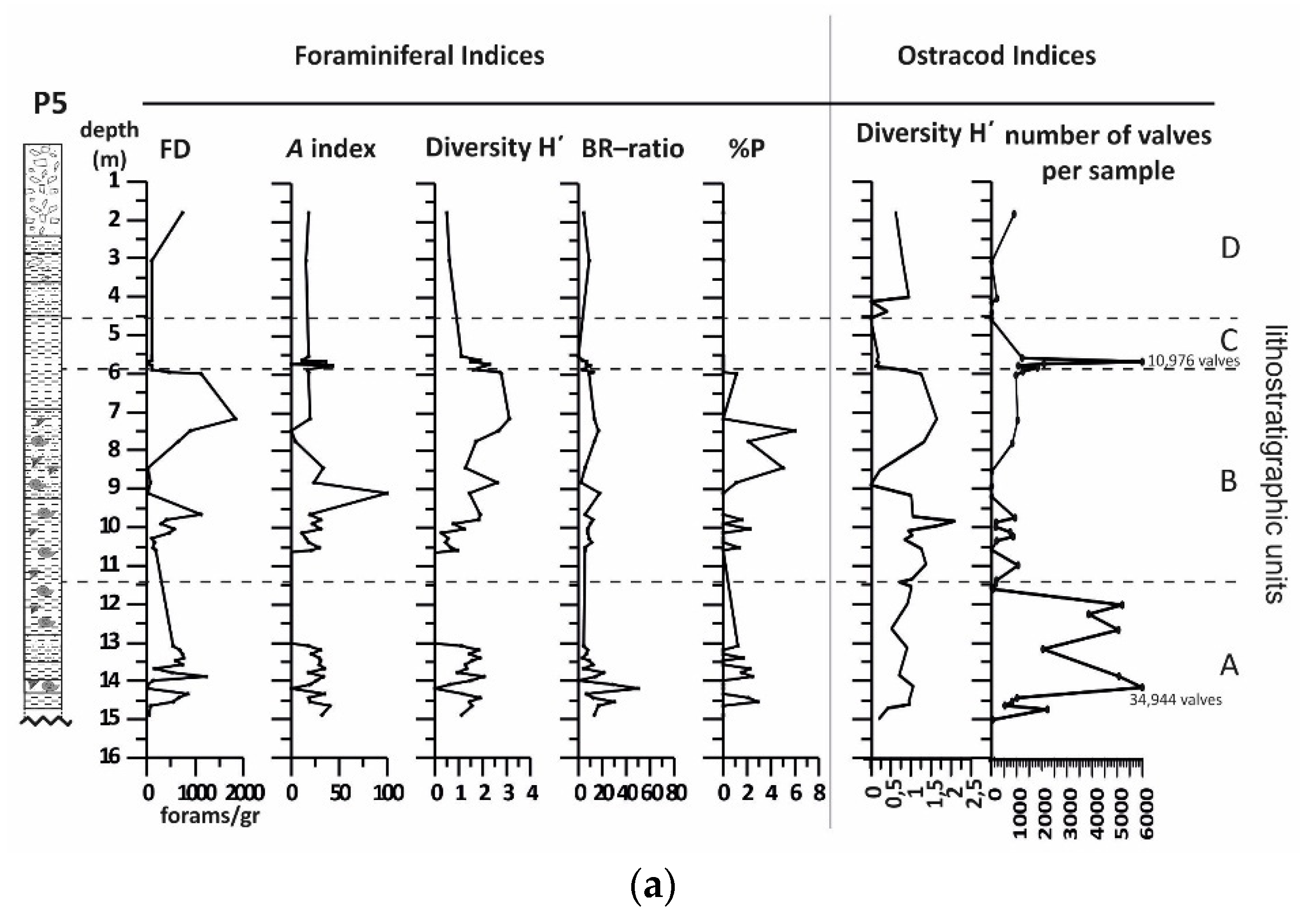
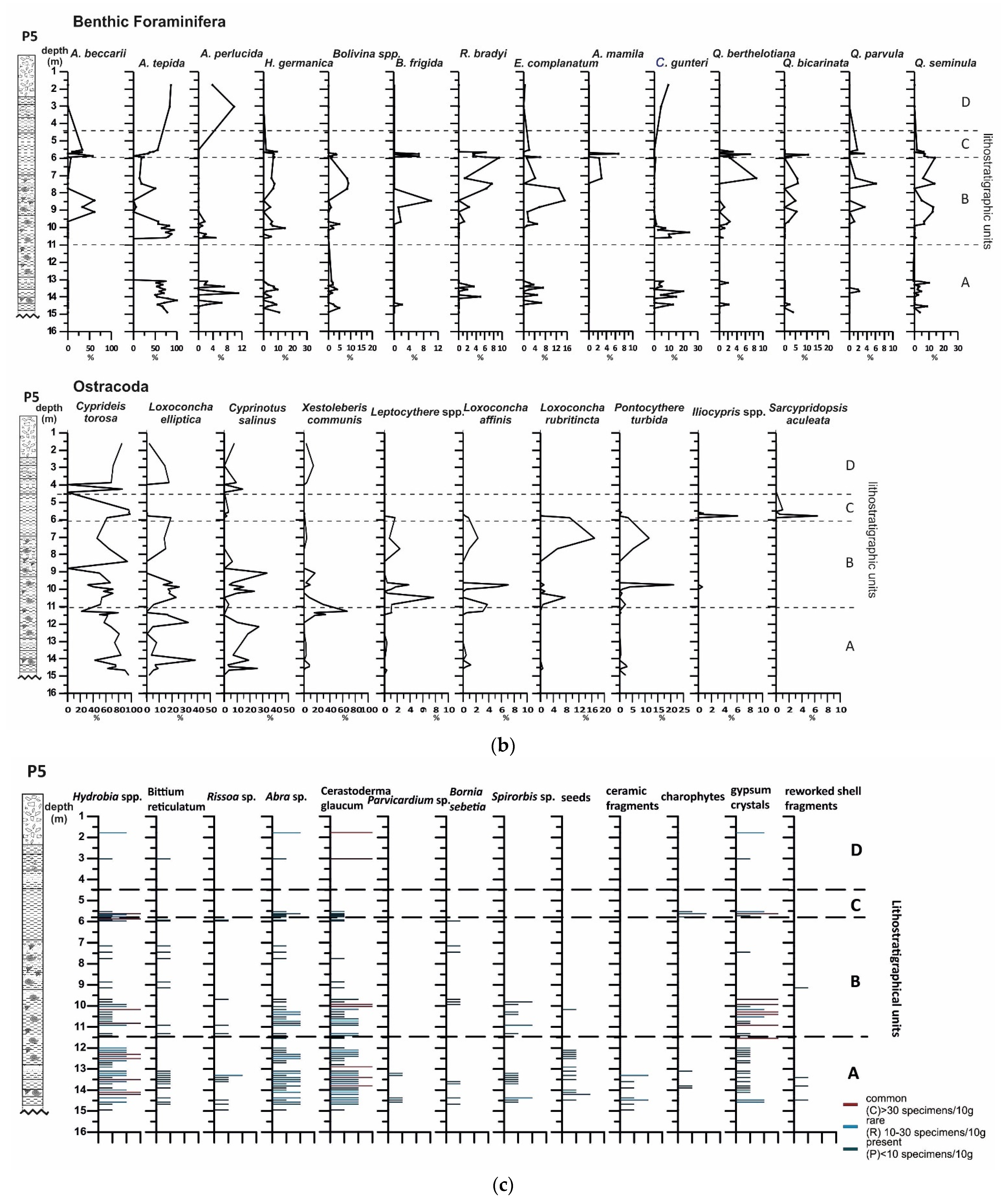
4.3. Borehole P5
4.3.1. Lithology and Magnetic Susceptibility
4.3.2. Benthic Foraminifera
4.3.3. Ostracods
4.3.4. Mollusc Assemblages
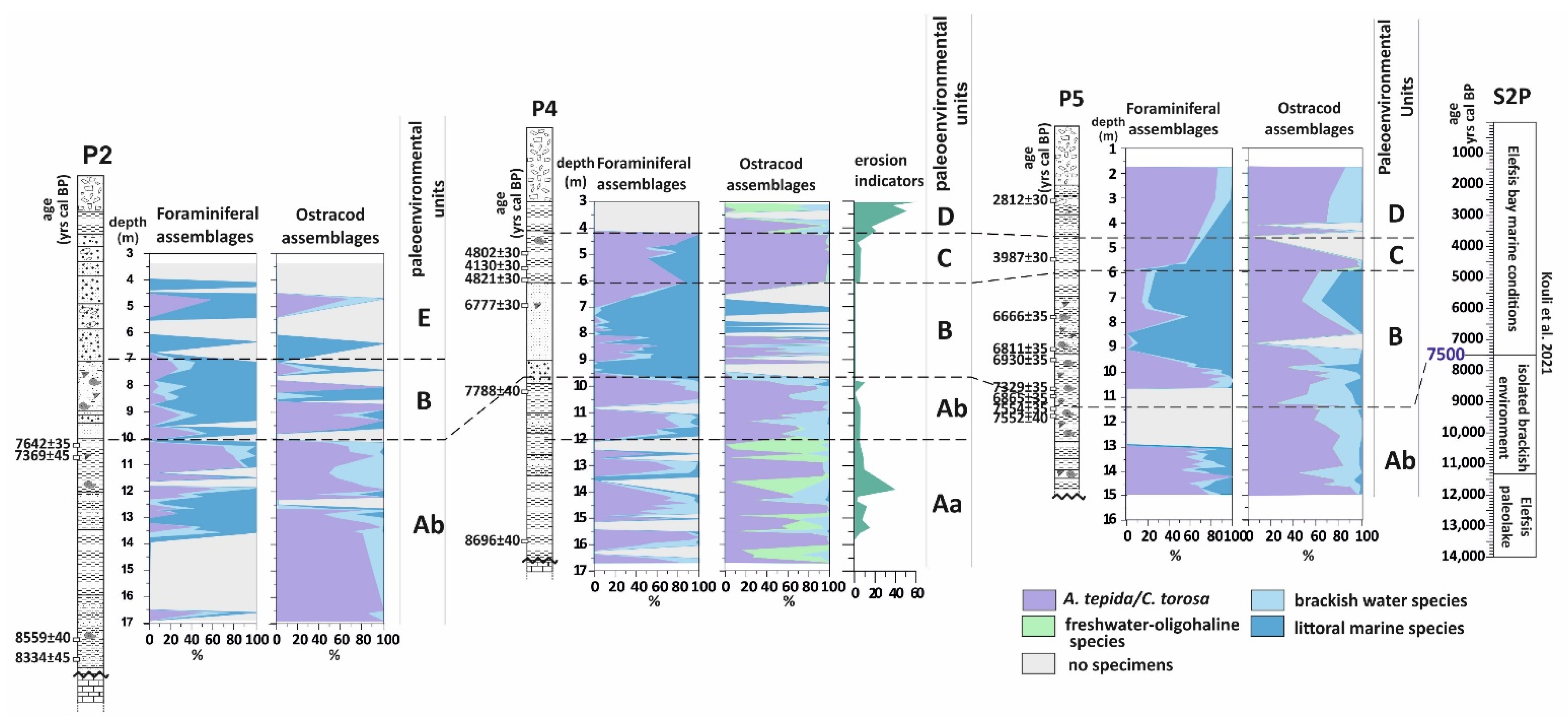
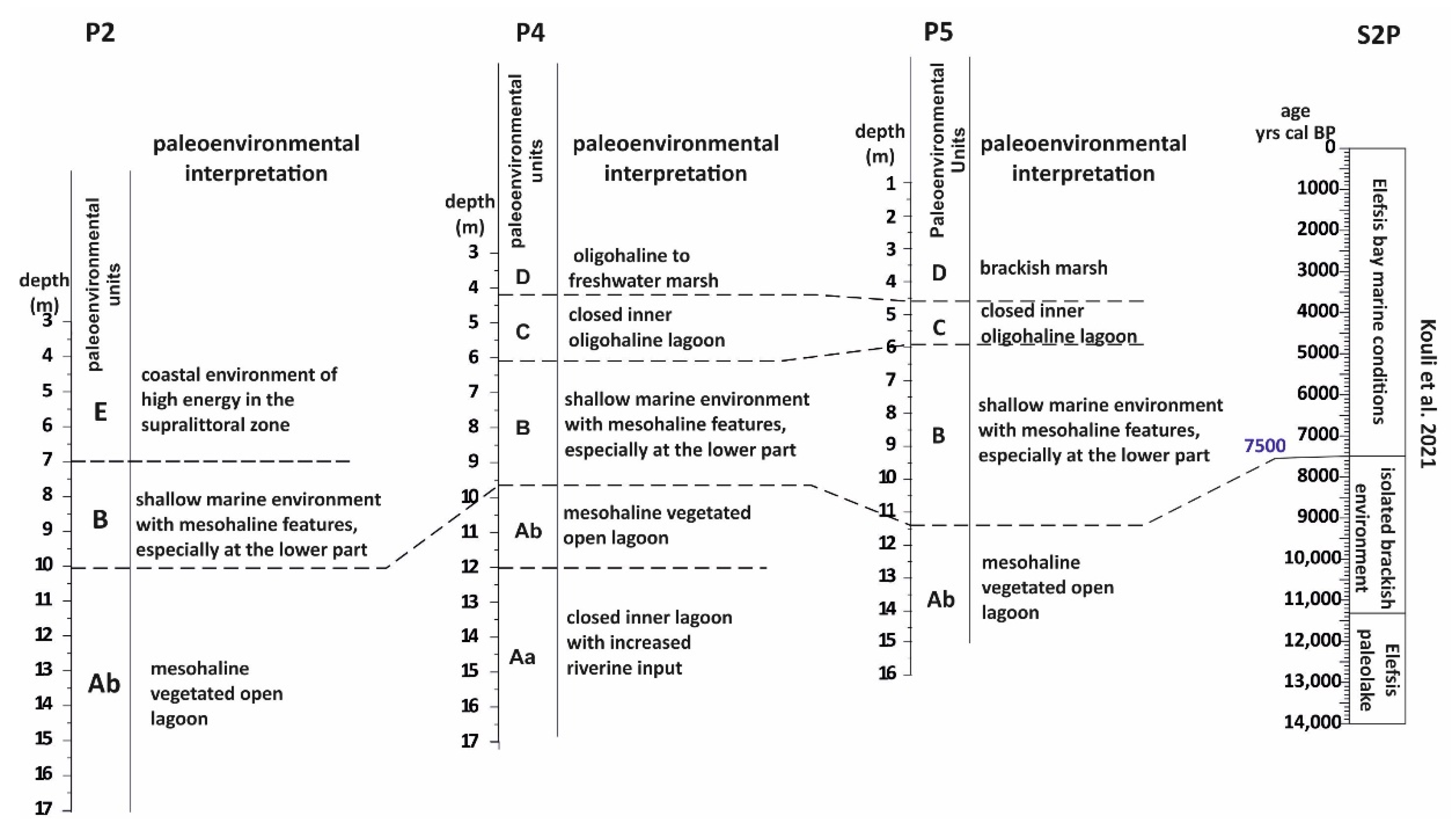
5. Discussion
5.1. Paleoenvironmental Interpretations
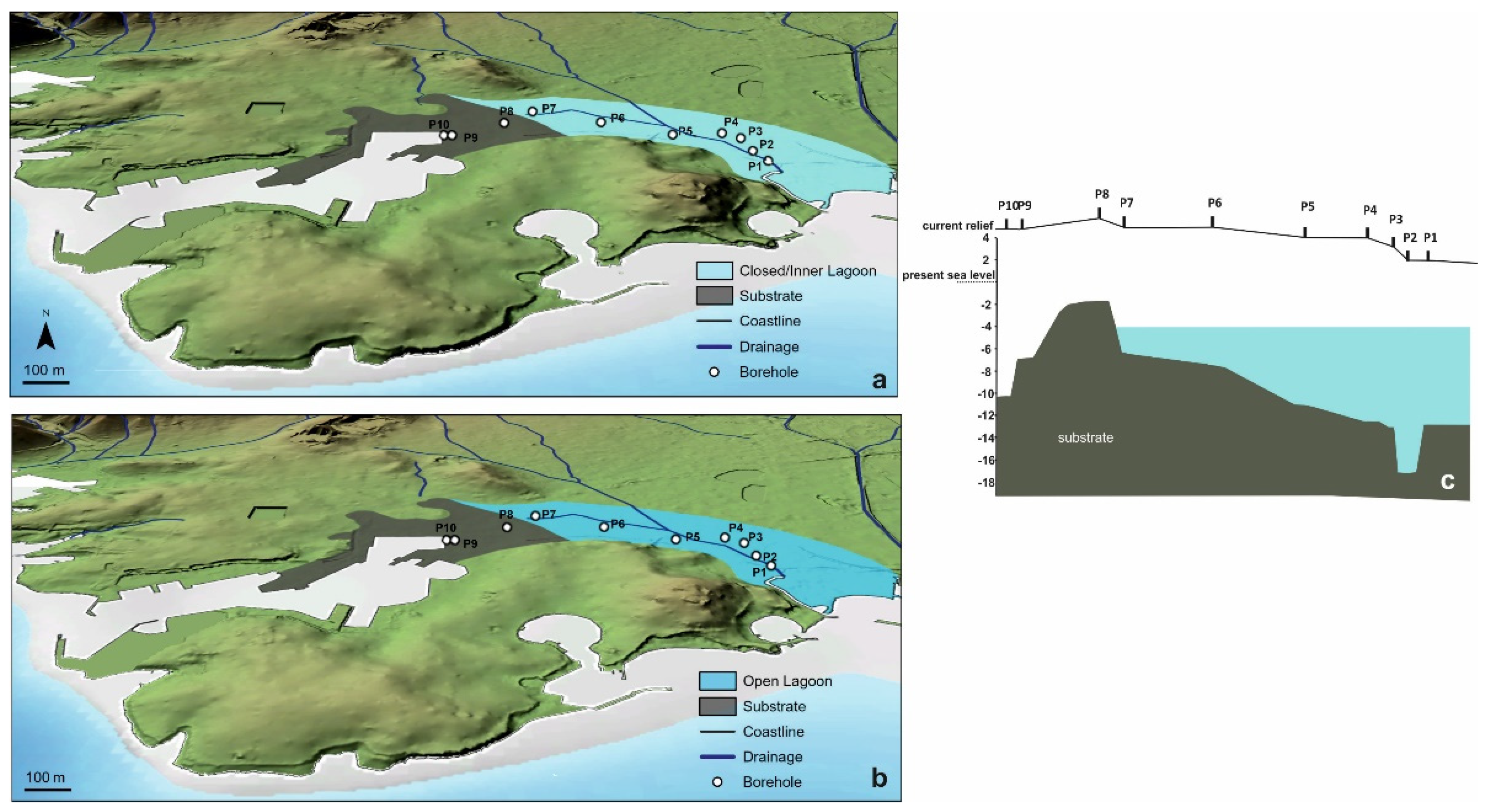
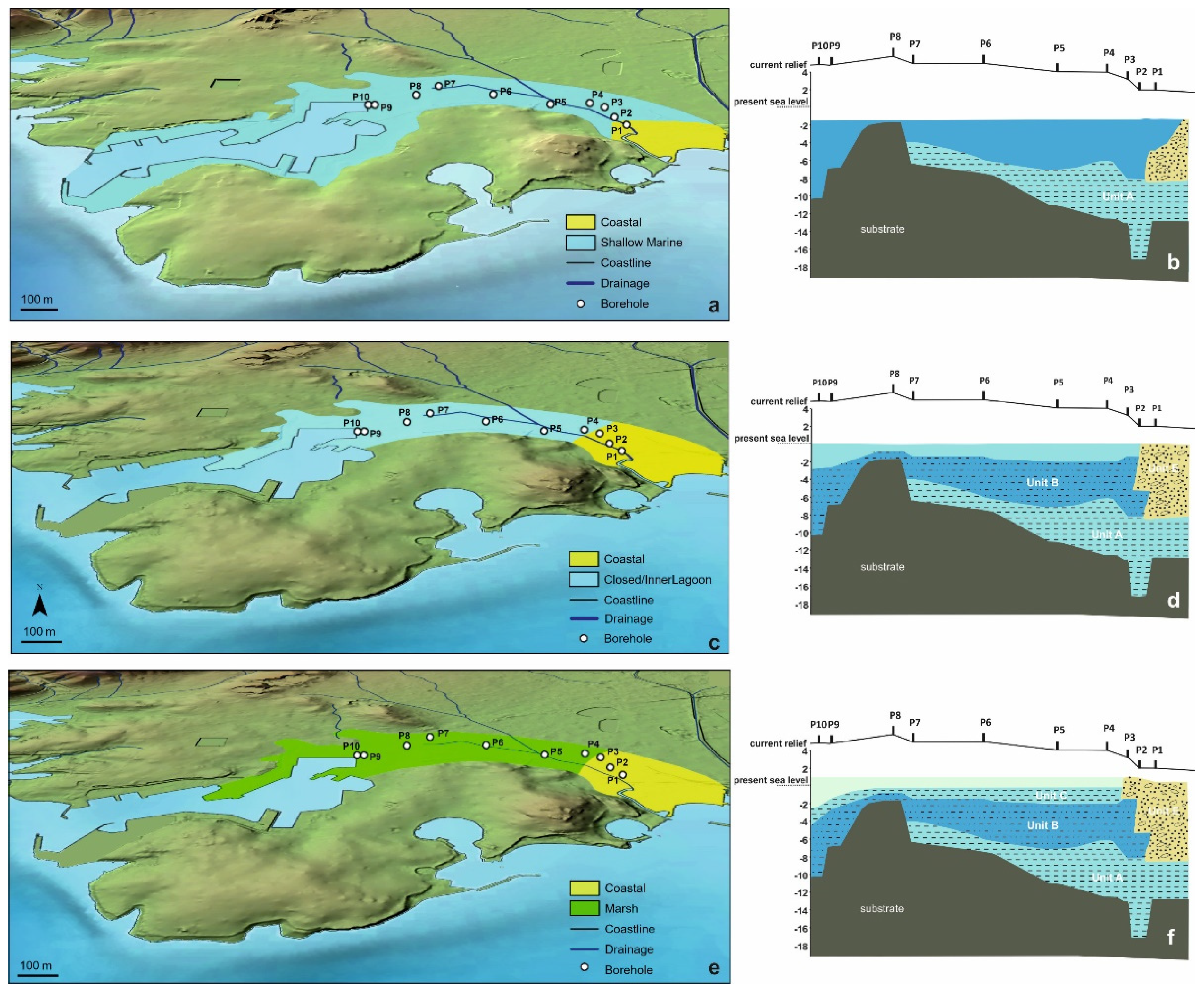
5.1.1. The First Stage of the Piraeus Lagoon (Unit A)
5.1.2. The Shallow Marine Bay and the Island of Piraeus (Unit B)
5.1.3. The Second Stage of the Piraeus Lagoon (Unit C)
5.1.4. The Piraeus Marsh (Unit D)
5.1.5. The Piraeus Coast (Unit E; ca. 3400–2500 cal BP)
5.2. Absolute Sea Level Rise Scenario for the Inner Saronikos Gulf during Mid-Holocene
6. Conclusions
- During 8700–7500 cal BP the first stage of the Piraeus Lagoon was established, reflected in the Unit A deposit of the local sedimentary archive. However, based on the data of this study, two sub-stages in the evolution of the lagoonal environment are identified:
- (i)
- a closed lagoon system, resulting in the formation of the Unit Aa Paleoenvironment (the older part of Unit A) and restricted to the eastern part of the coastal plain; and
- (ii)
- a mesohaline open lagoon system, resulting in the deposition of the Unit Ab Paleoenvironment and still remaining confined to the eastern part of the plain, due to a topographic high formed by the Pliocene substrate. Since the sea level position at ca. 8000 yr BP was at −17 m, the marine influence should have been established either via channels incised in the fluvio-deltaic area of Kifissos and Korydallos rivers or due to the salinization of the unconfined aquifer. The increased occurrence of Cerealia-type pollen in Unit Ab may be indicative of the first activities of the farming Neolithic communities in the area.
- During 7500–5400 cal BP a shallow marine bay was developed (reflected in the Unit B deposit of the local sedimentary archive), being the result of the Holocene sea level rise. At that time, Piraeus was a tied island connected to the mainland through a sandy isthmus.
- During 4800–3500 cal BP the second stage in the Piraeus Lagoon evolution occurred (reflected in the Unit C deposit of the local sedimentary archive), featured by a restricted environment with oligohaline conditions. The lagoon was delimited in the western part of the Piraeus plain, partly affected by the warm and humid climate conditions associated with the ongoing Mid-Holocene African monsoon forcing during 5400–4300 yr BP. To the east, the fluvio-deltaic deposits of Kifissos and Korydallos rivers were configuring the Piraeus Coast (reflected in the Unit E deposit of the local sedimentary archive; ca. 3400–2500 cal BP). During this stage, the borderlands of Piraeus Lagoon were used for cultivation and grazing activities, as evidenced by the palynological data.
- After 2800 cal BP the Piraeus Marsh was formed (reflected in the Unit D deposit of the local sedimentary archive), being confined to the western part of the coastal plain, while the Piraeus Coast continued to expand to the east. The increased occurrence of cultivars, such as Cerealia-type and Olea, in Unit D provides good evidence for human activities during the Archaic and Classical Periods.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benoit, G.; Comeau, A. A Sustainable Future for the Mediterranean: The Blue Plan’s Environment and Development Outlook; Benoit, G., Comeau, A., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2005; ISBN 9781844072590. [Google Scholar]
- Zenetos, A.; Arianoutsou, M.; Bazos, I.; Balopoulou, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Dimiza, M.; Drakopoulou, P.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kondylatos, G.; Koutsikos, N.; et al. ELNAIS: A collaborative network on Aquatic Alien Species in Hellas (Greece). Manag. Biol. Invasions 2015, 6, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethoux, J.; Gentili, B.; Morin, P.; Nicolas, E.; Pierre, C.; Ruiz-Pino, D. The Mediterranean Sea: A miniature ocean for climatic and environmental studies and a key for the climatic functioning of the North Atlantic. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomer, I.; Eisenhauer, G. Ostracod faunas as palaeoenvironmental indicators in marginal marine environments. In Geophysical Monograph Series; Wiley-Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 131, pp. 135–149. ISBN 9781118668689. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.W. Ecology and Applications of Benthic Foraminifera; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Frontalini, F.; Coccioni, R. Benthic foraminifera for heavy metal pollution monitoring: A case study from the central Adriatic Sea coast of Italy. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukousioura, O.; Dimiza, M.D.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Hallock, P. Living benthic foraminifera as an environmental proxy in coastal ecosystems: A case study from the Aegean Sea (Greece, NE Mediterranean). J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 88, 189–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Kouli, K.; Tsourou, T.; Koukousioura, O.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Dermitzakis, M.D. Paleoenvironmental changes since 3000 BC in the coastal marsh of Vravron (Attica, SE Greece). Quat. Int. 2010, 216, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukousioura, O.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dimiza, M.D.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Syrides, G.; Vouvalidis, K. Benthic foraminiferal evidence and paleoenvironmental evolution of Holocene coastal plains in the Aegean Sea (Greece). Quat. Int. 2012, 261, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, M.G.; Bergamin, L.; Di Bella, L.; Esu, D.; Cerone, E.P.; Antonioli, F.; Verrubbi, V. Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of late Quaternary foraminifera and molluscs from the ENEA borehole (Versilian plain, Tuscany, Italy). Quat. Res. 2010, 74, 165–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.S.; Medioli, F.S. Quantitative Studies of Marsh Foraminiferal Distributions in Nova Scotia and Comparison with Those in Other Parts of the World: Implications for Sea Level Studies; A Special Publication of the Cushman Foundation for Foraminiferal Research, no 17: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlopoulos, K.; Theodorakopoulou, K.; Bassiakos, Y.; Hayden, B.; Tsourou, T.; Triantaphyllou, M.; Kouli, K.; Vandarakis, D. Paleoenvironmental evolution of Istron (N.E Crete), during the last 6000 years: Depositional environment, climate and sea level changes. Geodin. Acta 2007, 20, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pavlopoulos, K.; Triantaphyllou, M.; Karkanas, P.; Kouli, K.; Syrides, G.; Vouvalidis, K.; Palyvos, N.; Tsourou, T. Paleoenvironmental evolution and prehistoric human environment, in the embayment of Palamari (Skyros Island, Greece) during Middle-Late Holocene. Quat. Int. 2010, 216, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, P.; Boomer, I. The use of ostracods from marginal marine, brackish waters as bioindicators of modern and Quaternary environmental change. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 225, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, K.; Karkanas, P.; Triantaphyllou, M.; Karymbalis, E.; Tsourou, T.; Palyvos, N. Paleoenvironmental Evolution of the Coastal Plain of Marathon, Greece, during the Late Holocene: Depositional Environment, Climate, and Sea Level Changes. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 222, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakopoulou, K.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Kouli, K.; Tsourou, T.; Bassiakos, Y.; Zacharias, N.; Hayden, B.; Tsourou, T.; Bassiakos, Y.; et al. Geoarchaeological studies in the coastal area of Istron-Kalo Chorio (Gulf of Mirabello- Eastern Crete): Landscape evolution and paleoenvironmental reconstruction. Z. Geomorphol. 2009, 53, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsourou, T.; Drinia, H.; Anastasakis, G. Ostracod assemblages from Holocene Middle Shelf Deposits of southern Evoikos Gulf (Central Aegean Sea, Greece) and their palaeoenvironmental implications. Micropaleontology 2015, 61, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Tsourou, T.; Dermitzakis, M.D. Brackish marsh benthic microfauna and paleoenvironmental changes during the last 6.000 years on the coastal plain of Marathon (SE Greece). Riv. Ital. Paleontol. Strat. 2003, 109, 539–547. [Google Scholar]
- West, C.F.; Burchell, M.; Andrus, C.F.T. Molluscs and Paleoenvironmental Reconstruction in Island and Coastal Settings: Variability, Seasonality, and Sampling. In Zooarchaeology in Practice; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Syrides, G.; Albanakis, K.; Vouvalidis, K.; Pilali-Papasteriou, A.; Papaefthimiou-Papanthimou, A.; Ghilardi, M.; Fouache, E.; Paraschou, T.; Psomiadis, D. Holocene Palaeogeography of the Northern Margins of Giannitsa Plain in Relation to the Prehistoric Site of Archontiko (Macedonia—Greece). Z. Geomorphol. Suppl. Issues 2009, 53, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouvalidis, K.; Syrides, G.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Papakonstantinou, M.; Tsourlos, P. Holocene palaeoenvironmental changes in Agia Paraskevi prehistoric settlement, Lamia, Central Greece. Quat. Int. 2010, 216, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukousioura, O.; Dimiza, M.D.; Kyriazidou, E.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Syrides, G.; Aidona, E.; Vouvalidis, K.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Papadopoulou, L. Environmental evolution of the Paliouras coastal lagoon in the eastern Thermaikos gulf (Greece) during Holocene. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukousioura, O.; Kouli, K.; Vouvalidis, K.; Aidona, E.; Karadimou, G.; Syrides, G. A multi-proxy approach for reconstructing environmental dynamics since the mid Holocene in Lake Ismarida (Thrace, N. Greece). Rev. Micropaléontologie 2020, 68, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, K.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Tsourou, T.; Karkanas, P.; Dermitzakis, M.D.D. Palynological investigation of Holocene palaeoenvironmental changes in the coastal plain of Marathon (Attica, Greece). Geobios 2009, 42, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsodendris, A.; Brauer, A.; Zacharias, I.; Putyrskaya, V.; Klemt, E.; Sangiorgi, F.; Pross, J. Ecosystem response to human- and climate-induced environmental stress on an anoxic coastal lagoon (Etoliko, Greece) since 1930 AD. J. Paleolimnol. 2015, 53, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadori, L.; Giardini, M.; Giraudi, C.; Mazzini, I. The plant landscape of the imperial harbour of Rome. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, K. Vegetation development and human activities in Attiki (SE Greece) during the last 5000 years. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2012, 21, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiran, J.-P.; Pavlopoulos, K.P.; Fouache, E.; Triantaphyllou, M.; Etienne, R. Piraeus, the ancient island of Athens: Evidence from Holocene sediments and historical archives. Geology 2011, 39, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, F.C.; Reinhardt, E.G.; Rothaus, R. Foraminifera and tidal notches: Dating neotectonic events at Korphos, Greece. Mar. Geol. 2009, 257, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Roberts, A.P.; Larrasoaña, J.C.; Banerjee, S.K.; Guyodo, Y.; Tauxe, L.; Oldfield, F. Environmental magnetism: Principles and applications. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, F.; Yu, L. The influence of particle size variations on the magnetic properties of sediments from the north-eastern Irish Sea. Sedimentology 1994, 41, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verosub, K.L.; Roberts, A.P. Environmental magnetism: Past, present, and future. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1995, 100, 2175–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, M.; Kunesch, S.; Styllas, M.; Fouache, E. Reconstruction of Mid-Holocene sedimentary environments in the central part of the Thessaloniki Plain (Greece), based on microfaunal identification, magnetic susceptibility and grain-size analyses. Geomorphology 2008, 97, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Grapes, R.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J. Magnetic properties of sediments from the Pearl River Delta, South China: Paleoenvironmental implications. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, G.; Oguchi, T.; He, H.; Shen, H. Discrimination in magnetic properties of different-sized sediments from the Changjiang and Huanghe Estuaries of China and its implication for provenance of sediment on the shelf. Mar. Geol. 2009, 260, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiza, M.D.; Koukousioura, O.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dermitzakis, M.D. Live and dead benthic foraminiferal assemblages from coastal environments of the Aegean Sea (Greece): Distribution and diversity. Rev. Micropaléontologie 2016, 59, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, A.; Simboura, N.; Pagou, Κ.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Gerakaris, V.; Hatzianestis, I.; Panayotidis, P.; Pantazi, M.; Papadopoulou, N.; Reizopoulou, S.; et al. Using a holistic ecosystem-integrated approach to assess the environmental status of Saronikos Gulf, Eastern Mediterranean. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simboura, N.; Zenetos, A.; Pancucci-Papadopoulou, M.A. Benthic community indicators over a long period of monitoring (2000–2012) of the Saronikos Gulf, Greece, Eastern Mediterranean. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidou, A.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Anagnostou, C.; Siokou–Frangou, I.; Pagou, K.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Zervoudaki, S.; Zeri, C.; Chatzianestis, J.; et al. Biogeochemical Characteristics in the Elefsis Bay (Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean) in Relation to Anoxia and Climate Changes. In Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, Chemical Structure of Pelagic Redox Interfaces: Observation and Modeling; Yakushev, E.V., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 161–202. ISBN 978-3-642-32125-2. [Google Scholar]
- Foutrakis, P.M.; Anastasakis, G. Quaternary continental shelf basins of Saronikos Gulf, Aegean Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2020, 40, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, G.; Botfalvai, G.; Ősi, A. Mapping the past: GIS and intrasite spatial analyses of fossil deposits in paleontological sites and their applications in taxonomy, taphonomy and paleoecology. Palaeontol. Electron. 2018, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazachos, B.C. Seismicity of the Aegean and surrounding area. Tectonophysics 1990, 178, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E. The Athens earthquake (7 September 1999): Intensity distribution and controlling factors. Eng. Geol. 2001, 59, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, D.; Basi, E.K.; Kranis, H.; Danamos, G. Paleogeographic evolution of the Athens Basin from the Upper Miocene to present. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2004, 36, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, G.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Goiran, J.-P.; Fouache, E. Was the Piraeus peninsula (Greece) a rocky island? Detection of pre-Holocene rocky relief with borehole data and resistivity tomography analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, C.T. Le Pirée. Étude économique et historique depuis les temps les plus anciens jusqu’à la fin de l’Empire romain. Rev. Etud. Grec. 1968, 83, 219–220. [Google Scholar]
- Economidou, E. The Attic landscape throughout the centuries and its human degradation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1993, 24, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandarakis, D.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Vouvalidis, K.; Fouache, E. Holocene lithostratigraphy and its implementation in the geoarchaeological research of the Athenian Basin, Greece. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2016, 8, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeblich, A.R.; Tappan, H. Foraminiferal Genera and Their Classification; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 2, ISBN 978-1-4899-5760-3. [Google Scholar]
- Loeblich, A.R.; Tappan, H. Foraminifera of the Sahul Shelf and Timor Sea; Cushman Foundation for Foraminiferal Research Special Publication, 31: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1994; ISBN 9781970168204. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past Paleontological statistics software. Package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Melis, R.; Violanti, D. Foraminiferal biodiversity and Holocene evolution of the Phetchaburi coastal area (Thailand Gulf). Mar. Micropaleontol. 2006, 61, 94–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zwaan, G.; Jorissen, F.; de Stigter, H. The depth dependency of planktonic/benthic foraminiferal ratios: Constraints and applications. Mar. Geol. 1990, 95, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnaim-Katav, S.; Almogi-Labin, A.; Sandler, A.; Sivan, D. Benthic foraminifera as palaeoenvironmental indicators during the last million years in the eastern Mediterranean inner shelf. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 386, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallikarakis, A.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Papanikolaou, I.; Dimiza, M.D.; Reicherter, K.; Migiros, G. Age Constraints and Paleoenvironmental Interpretation of a Borehole Sedimentary Sequence along the Eastern Part of the Corinth Isthmus, Greece. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 34, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geslin, E.; Debenay, J.-P.; Duleba, W.; Bonetti, C. Morphological abnormalities of foraminiferal tests in Brazilian environments: Comparison between polluted and non-polluted areas. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2002, 45, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, K.; Koukousioura, O.; Triantaphyllou, M.; Vandarakis, D.; Marion de Procé, S.; Chondraki, V.; Fouache, E.; Kapsimalis, V. Geomorphological changes in the coastal area of Farasan Al-Kabir Island (Saudi Arabia) since mid Holocene based on a multi-proxy approach. Quat. Int. 2018, 493, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, D.J.; Cohen, A.; Martens, K. Taxonomy, morphology and biology of quaternary and living ostracoda. In Geophysical Monograph Series; Wiley-Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 131, pp. 5–36. ISBN 9781118668689. [Google Scholar]
- Barbeito-Gonzalez, P.J. Die Ostracoden des Kustenbereiches von Naxos (Griechenland) und ihre Lebensbereiche. Mitt. Hamburg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1971, 67, 255–326. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaduce, G.; Ciampo, G.; Masoli, M. Distribution of Ostracoda in the Adriatic Sea; Olschki, L.S., Ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Meisch, C. Freshwater Ostracoda of Western and Central Europe (Süßwasserfauna von Mitteleuropa 8/3); Schwoerbel, J., Zwick, P., Eds.; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag GmbH: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2000; ISBN 9783827410016. [Google Scholar]
- Stambolidis, E.A. Subrezente Ostracoden aus dem Evros-Delta (Griechenland) Einschliesslich der Entwicklung des Schlosses Gewisser Arten; Faculty of Science: Uppsala, Sweden, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Athersuch, J.; Whittaker, J.E. On Loxoconcha elliptica (Brady). Stereo-Atlas Ostracod Shells 1976, 3, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Beug, H.-J. Leitfaden der Pollenbestimmung für Mitteleuropa und Angrenzende Gebiete; Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil: München, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Reille, M. Pollen et Spores d’ Europe et d’ Afrique du Nord; Laboratoire de Botanique Historique et Palynologie: Marseille, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Van Geel, B.; Coope, G.R.; Van Der Hammen, T. Palaeoecology and stratigraphy of the lateglacial type section at Usselo (the Netherlands). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 1989, 60, 25–38, 41–42, 45–46, 48–49, 51–60, 63–64, 67–68, 75–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geel, B.; Buurman, J.; Brinkkemper, O.; Schelvis, J.; Aptroot, A.; van Reenen, G.; Hakbijl, T. Environmental reconstruction of a Roman Period settlement site in Uitgeest (The Netherlands), with special reference to coprophilous fungi. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2003, 30, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadori, L. The Lateglacial and Holocene vegetation and climate history of Lago di Mezzano (central Italy). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 202, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtius, E.; Kaupert, J.A. Karten von Attika. Berlin, Germany 1895–1903 Heidelberger Historische Bestände—Digital. Available online: https://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/curtius1895a/0003 (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Pavlopoulos, K.P.; Kouli, K.; Koukousioura, O.; Dimiza, M.D.; Aidona, E.; Syrides, G.; Pallikarakis, A.; Goiran, J.P.; Fouache, E. Μultiproxy paleoenvironmental reconstruction: The Piraeus coastal plain case study. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2016, 50, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontalini, F.; Buosi, C.; Da Pelo, S.; Coccioni, R.; Cherchi, A.; Bucci, C. Benthic foraminifera as bio-indicators of trace element pollution in the heavily contaminated Santa Gilla lagoon (Cagliari, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alve, E.; Murray, J.W. Ecology and taphonomy of benthic foraminifera in a temperate mesotidal inlet. J. Foraminifer. Res. 1994, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debenay, J.-P.; Guillou, J.-J. Ecological transitions indicated by foraminiferal assemblages in paralic environments. Estuaries 2002, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciuto, F. Distribution of some species of fresh and brackish-water Ostracoda from the lower Pleistocene of SE Sicily. Biogeogr. J. Integr. Biogeogr. 2011, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, I.; Anadon, P.; Barbieri, M.; Castorina, F.; Ferreli, L.; Gliozzi, E.; Mola, M.; Vittori, E. Late Quaternary sea-level changes along the Tyrrhenian coast near Orbetello (Tuscany, central Italy): Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction using ostracods. Mar. Micropaleontol. 1999, 37, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavé, B.; Massé, L.; Carbonel, P.; Tastet, J.-P. Holocene coastal changes and infilling of the La Perroche marsh (French Atlantic coast). Oceanol. Acta 2001, 24, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisch, C.; Broodbakker, N.W. Freshwater Ostracoda (Crustacea) collected by Prof. J.H. Stock on the Canary and Cape Verde Islands. With an annotated checklist of the freshwater Ostracoda of the Azores, Madeira, the Canary, the Selvagens and Cape Verde Islands. Trav. Sci. Musée Natl. d’histoire Nat. Luxemb. 1993, 19, 3–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaidou, A.; Bourgoutzani, F.; Zenetos, A.; Guelorget, O.; Perthuisot, J.-P. Distribution of molluscs and polychaetes in coastal lagoons in Greece. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1988, 26, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevrekidis, T.; Gouvis, N.; Koukouras, A. Bionomy of Macrobenthic Molluscs in Evros Delta (North Aegean Sea). Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1996, 81, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrides, G.E. Marine mollusk fauna and Holocene stratigraphy of the marsh of Agia Paraskevi, (Lamia, Fthiotida) Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2008, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Morzadec-Kerfourn, M.T. Interaction between sea-level changes and the development of littoral herbaceous vegetation and autotrophic dinoflagellates. Quat. Int. 2005, 133–134, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, S.A.G.; Lahijani, H.A.K.; Reyss, J.-L.; Chalié, F.; Haghani, S.; Shah-Hosseini, M.; Shahkarami, S.; Tudryn, A.; Arpe, K.; Habibi, P.; et al. A two-step expansion of the dinocyst Lingulodinium machaerophorum in the Caspian Sea: The role of changing environment. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 77, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, K.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Koukousioura, O.; Dimiza, M.; Parinos, C.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Gogou, A.; Kyrikou, S.; Mavrommatis, N.; Syrides, G.; et al. Late Glacial marine transgression and ecosystem response in the landlocked Elefsis Bay. Water 2021, 13, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K. Sea-level change and shore-line evolution in Aegean Greece since upper palaeolithic time. Antiquity 1996, 70, 588–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombani, N.; Osti, A.; Volta, G.; Mastrocicco, M. Impact of Climate Change on Salinization of Coastal Water Resources. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athersuch, J.; Horne, D.J.; Whittaker, J.E. Marine and brackish water ostracods (superfamilies Cypridacea and Cytheracea). Keys and notes for the identification of species. Synopses Br. Fauna New Ser. No 1989, 43, 1–343. [Google Scholar]
- Neale, J.W. Ostracods and palaeosalinity reconstruction. In Ostracoda in the Earth Sciences; Deckker, P., Colin, J.P., Peypouquet, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 125–157. [Google Scholar]
- Van Morkhoven, F.P.C.M. Post-Paleozoic Ostracoda. Their Morphology, Taxonomy and Economic Use; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1962; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Carboni, M.G.; Bergamin, L.; Di Bella, L.; Iamundo, F.; Pugliese, N. Palaeoecological evidences from foraminifers and ostracods on Late Quaternary sea-level changes in the Ombrone river plain (central Tyrrhenian coast, Italy). Geobios 2002, 35, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, M.C.; Freitas, M.C.; Andrade, C.; Cruces, A. Coastal evolution and Holocene ostracods in Melides lagoon (SW Portugal). Mar. Micropaleontol. 2006, 60, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, M.C.; Fatela, F.; Lopes, V.; Freitas, M.C.; Andrade, C. Cyprideis torosa (Jones, 1850) in mainland Portugal: What do we know? J. Micropalaeontol. 2017, 36, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Abad, M.; Galán, E.; González, I.; Aguilá, I.; Olías, M.; Ariza, J.L.G.; Cantano, M. The present environmental scenario of El Melah Lagoon (NE Tunisia) and its evolution to a future sabkha. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 44, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W. Ecology and Palaeoecology of Benthic Foraminifera; Longman: Harlow/Essex, UK; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Athersuch, J. The ecology and distribution of the littoral ostracods of Cyprus. J. Nat. Hist. 1979, 13, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsourou, T. Composition and Distribution of Recent Marine Ostracod Assemblages in the Bottom Sediments of Central Aegean Sea (SE Andros Island, Greece). Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2012, 97, 276–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraga, M.; Tsaila-Monopolis, S.; Ioakim, C.; Papatheodorou, G.; Ferentinos, G. Evaluation of palaeoenvironmental changes during the last 18,000 years in the Myrtoon basin, SW Aegean Sea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2000, 156, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, E.; Bevan, A.; Kouli, K.; Katsianis, M.; Woodbridge, J.; Bonnier, A.; Engel, M.; Finné, M.; Fyfe, R.; Maniatis, Y.; et al. Long-term trends of land use and demography in Greece: A comparative study. Holocene 2019, 29, 742–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrikou, S.; Kouli, K.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dimiza, M.D.; Gogou, A.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Anagnostou, C.; Karageorgis, A.P. Late Glacial and Holocene vegetation patterns of Attica: A high-resolution record from Elefsis Bay, southern Greece. Quat. Int. 2020, 545, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarrella, F.; Moncharmont Zei, M. Benthic Foraminifera of the Gulf of Naples (Italy): Systematics and autoecology. Boll. Della Soc. Paleontol. Ital. 1993, 32, 145–264. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaidou, A.; Petrou, K.; Kormas, K.A.; Reizopoulou, S. Inter-Annual Variability of Soft Bottom Macrofaunal Communities in Two Ionian Sea Lagoons. Hydrobiologia 2006, 555, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castejón-Silvo, I.; Terrados, J. Experimental assessment of Posidonia oceanica -associated gastropods grazing on an early successional biofilm community: Nutrient availability and species-specific effects. Mar. Ecol. 2017, 38, e12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouvalidis, K.G.; Syrides, G.E.; Albanakis, K.S. Holocene morphology of the Thessaloniki Bay: Impact of sea level rise. Z. Geomorphol. Suppl. 2005, 137, 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Ziveri, P.; Gogou, A.; Marino, G.; Lykousis, V.; Bouloubassi, I.; Emeis, K.-C.C.; Kouli, K.; Dimiza, M.; Rosell-Melé, A.; et al. Late Glacial-Holocene climate variability at the south-eastern margin of the Aegean Sea. Mar. Geol. 2009, 266, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Gogou, A.; Bouloubassi, I.; Dimiza, M.; Kouli, K.; Rousakis, G.; Kotthoff, U.; Emeis, K.C.; Papanikolaou, M.; Athanasiou, M.; et al. Evidence for a warm and humid Mid-Holocene episode in the Aegean and northern Levantine Seas (Greece, NE Mediterranean). Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 1697–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, A.M.; Bandini Mazzanti, M.; Florenzano, A.; Montecchi, M.C.; Rattighieri, E. Olea, Juglans and Castanea: The OJC group as pollen evidence of the development of human-induced environments in the Italian peninsula. Quat. Int. 2013, 303, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, A.M.; Sadori, L. Mediterranean Culture and climatic change: Past patterns and future trends. In The Mediterranean Sea: Its History and Present Challenges; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 507–527. ISBN 978-94-007-6703-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jahns, S. On the Holocene vegetation history of the Argive Plain (Peloponnese, southern Greece). Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 1993, 2, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.; Knipping, M.; Brückner, H.; Kiderlen, M.; Kraft, J.C. Reconstructing middle to late Holocene palaeogeographies of the lower Messenian plain (southwestern Peloponnese, Greece): Coastline migration, vegetation history and sea level change. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2009, 284, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, M.; Koutsios, A.; Kontopoulos, N. Holocene vegetation history of the Kotihi lagoon (northwest Peloponnesus, Greece). Quat. Int. 2012, 261, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, E.; Unkel, I.; Kouli, K.; Holmgren, K.; Avramidis, P.; Bonnier, A.; Dibble, F.; Finné, M.; Izdebski, A.; Katrantsiotis, C.; et al. The socio-environmental history of the Peloponnese during the Holocene: Towards an integrated understanding of the past. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 136, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebski, A.; Słoczyński, T.; Bonnier, A.; Koloch, G.; Kouli, K. Landscape Change and Trade in Ancient Greece: Evidence from Pollen Data. Econ. J. 2020, 130, 2596–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiza, M.D.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dermitzakis, M.D. Seasonality and ecology of living coccolithophores in Eastern Mediterranean coastal environments (Andros Island, Middle Aegean Sea). Micropaleontology 2008, 54, 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lambeck, K.; Purcell, A. Sea-level change in the Mediterranean Sea since the LGM: Model predictions for tectonically stable areas. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 1969–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, K.; Kapsimalis, V.; Theodorakopoulou, K.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P. Vertical displacement trends in the Aegean coastal zone (NE Mediterranean) during the Holocene assessed by geo-archaeological data. Holocene 2012, 22, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgeley, J.; Steig, E.J.; Hakim, G.J. The Holocene Thermal Maximum as an analog for future warming: Insights from paleoclimate data assimilation. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2018, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 December 2018; p. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jevrejeva, S.; Jackson, L.P.; Riva, R.E.M.; Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C. Coastal sea level rise with warming above 2 °C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13342–13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Tsourou, T.; Kouli, K.; Koukousioura, O.; Dimiza, M.D.; Aidona, E.V.; Syrides, G.; Antoniou, V.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Vandarakis, D.; et al. Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Sea Level Change in Saronikos Gulf (Aegean Sea, Greece): Evidence from the Piraeus Coastal Plain and Elefsis Bay Sedimentary Records. Water 2021, 13, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121621
Triantaphyllou MV, Tsourou T, Kouli K, Koukousioura O, Dimiza MD, Aidona EV, Syrides G, Antoniou V, Panagiotopoulos IP, Vandarakis D, et al. Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Sea Level Change in Saronikos Gulf (Aegean Sea, Greece): Evidence from the Piraeus Coastal Plain and Elefsis Bay Sedimentary Records. Water. 2021; 13(12):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121621
Chicago/Turabian StyleTriantaphyllou, Maria V., Theodora Tsourou, Katerina Kouli, Olga Koukousioura, Margarita D. Dimiza, Elina V. Aidona, George Syrides, Varvara Antoniou, Ioannis P. Panagiotopoulos, Dimitris Vandarakis, and et al. 2021. "Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Sea Level Change in Saronikos Gulf (Aegean Sea, Greece): Evidence from the Piraeus Coastal Plain and Elefsis Bay Sedimentary Records" Water 13, no. 12: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121621
APA StyleTriantaphyllou, M. V., Tsourou, T., Kouli, K., Koukousioura, O., Dimiza, M. D., Aidona, E. V., Syrides, G., Antoniou, V., Panagiotopoulos, I. P., Vandarakis, D., Pallikarakis, A., Cheilaris, S., Skampa, E., Goiran, J.-P., Fouache, E., & Pavlopoulos, K. P. (2021). Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Sea Level Change in Saronikos Gulf (Aegean Sea, Greece): Evidence from the Piraeus Coastal Plain and Elefsis Bay Sedimentary Records. Water, 13(12), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121621










