Abstract
The effect of total organic carbon (TOC) on the prokaryotic community structure in situ has been rarely known. This study aimed to determine the effect of TOC level on the composition and networks of archaeal and bacterial communities in the sediments of Dianchi Lake, one of the most eutrophic lakes in China. Microbial assemblages showed significantly associations with TOC. Moreover, relatively high and low TOC formed taxonomic differences in prokaryotic assemblages. According to the results, the most abundant bacteria across all samples were identified as members of the phyla Proteobacteria, Nitrospirae, Chloroflexi, Firmicutes and Ignavibacteriae. The dominant groups of archaea consisted of Euryarchaeota, Woesearchaeota DHVEG-6, Bathyarchaeota and WSA2. Lastly, the meta-analysis results highlighted that the low TOC (LT) prokaryotic community structure is larger and more complex compared to moderate TOC (MT). On the whole, the prokaryotic community structure is obviously distinct among groups with different TOC levels, and LT communities may interact with each other strongly in the Dianchi Lake sediment. This study can provide more insights into prokaryotic assemblages in eutrophic lake sediment and provide suggestions for the restoration and maintenance of sediment ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Microbial consortia harbored in the sediment are at the hub of ecological processes, which play a pivotal role in the biogeochemical cycling of nutrients, biotransformation and biodegradation of pollutants, as well as the restoration and maintenance of sediment ecosystems [1,2,3]. Insights into prokaryotic communities in lake sediment ecosystems can indicate the directions of ecosystem management and biodiversity preservation. It has been of particular interest to more comprehensively clarify the mechanisms driving the assembly and interactions of freshwater-sediment microbial communities [4,5,6,7].
Over the past few years, numerous studies reported that both variations in physicochemical properties and in biotic factors can form sediment ecosystems communities [8]. According to Swan et al. (2010), salinity in the sediments of a California hypersaline lake impacts the distribution of bacteria and archaea [9]. Pollution levels act as significant environmental variables of bacterial communities in lake sediments [10]. Furthermore, most studies suggested that the spatial variation model of prokaryotic communities in lake sediment may be unique [11,12,13]. For example, Yu et al. illustrated the spatiotemporal variation of sediment bacterial assemblages between Dianchi Lake and Erhai Lake [11].
All of the mentioned conclusions are drawn in terms of the comparing inter-lake. However, the existing studies primarily overlooked the significant effect of geographical distance [13,14]. Sediments with a longer geographical distance are subject to distinct ambient conditions (e.g., hydrological properties, climatic influences, geological settings and catchment area). Jinbo et al. collected sediment samples in 15 lakes to examine the effect of geographic distance on microbial community structure. The larger-scale (4–1670 km) study revealed that geographic distance was the dominant factors in shaping community variation compared to any other factor [13]. Thus, the impact of environmental factors cannot be expounded, and the exploration of some ecological rules is hindered.
Moreover, the more comprehensive mechanism of environmental factors driving the assembly of lake-sediment prokaryotic communities remains elusive. Some existing studies revealed that environmental factors, such as sediment pH [13], nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) [15], total organic carbon (TOC) [14] and dissolved oxygen (DO) [16] was extensively considered to critically determine the lake sediment microbial communities. Thus far, the effect of a specific environmental factor level on the prokaryotic structure in situ has been rarely studied. Dianchi Lake stretches 39 km length from North to South and extends 13.5 km width in the West–East direction. Sediments of Dianchi Lake considered an ideal model system to address ecological principles exhibit large variations of physical and chemical parameters.
Microbial communities form ecological networks with each other to perform ecosystem functions [17,18,19]. To maintain homeostasis, the microbes establish a stable network via nutrient cycling and niche competition processes. Thus, the interactions of microbial systems should be expounded since their environmental niches, functional roles, or ecological interactions in the ecosystem may be clarified. With the analytical procedure of network analysis, considerable studies have explored the complex links in many microbial ecosystems (e.g., lake [20], stream soil [21] and hydrothermal vents [22]). Thus far, only a few existing studies investigated the microbial community networks in freshwater lake sediments. Nevertheless, effects of environmental factors on the interactions of microorganisms in lake-sediments have not been determined.
Previously, several studies reported that TOC influenced community compositions of sediment prokaryotes more than other environmental factors [14,23]. Furthermore, the concentrations of TOC clearly varied in the Dianchi Lake sediment [24]. The present study hypothesized that the distribution and co-occurrence of prokaryotes in Dianchi Lake sediment will change for differences in responses to TOC gradient. To determine the effect of TOC level on the composition, structure and networks of archaea and bacteria, a relatively high-density sampling in situ was performed at Dianchi Lake in China. Only in the lake, thirteen representative sediments were taken spanning the entire lake. Subsequently, Illumina MiSeq sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene hypervariable V3–V4 portion of prokaryotic communities was performed. The present study aimed to solve the following questions: (i) whether prokaryotic communities structure varies among different TOC levels; (ii) whether there is an obvious difference in the prokaryotic network associated with different TOC levels.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the composition and structure dynamics of bacteria and archaea associated with TOC level, and to adopt network thinking and network analysis tools to research microbial communities in a lake sediment ecosystem.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites Description and Sampling Procedure
In October 2014, a relatively high-density sampling in situ was performed at Dianchi Lake in China. Spanning the lake, thirteen representative surface sediments were taken, in which no palpable difference was identified in geographical distance (Figure 1). Triplicate samples retrieved from respective site were packed into a 50 mL sterile Eppendorf tube and then transferred on ice to the laboratory to undergo molecular analyses.
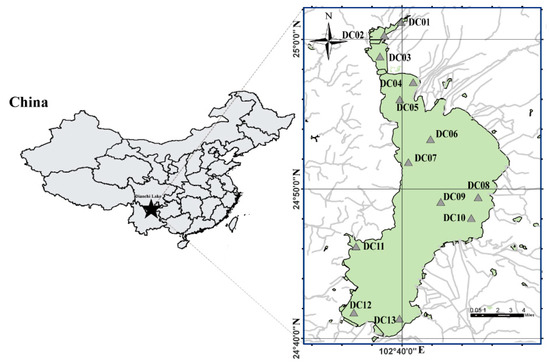
Figure 1.
The distribution and location map of the 13 sediments sampling stations across the Dianchi Lake region. Grey lines refer to rivers. The map was created using ArcGis version 10.2.
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
Total DNA was extracted immediately from the sediment with the Power Soil DNA Isolation Kit (MOBIO Laboratories, Inc., Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s manual. The extracted DNA purification and quantity were determined by NanoDrop 2000 UV-vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, NC, USA), and DNA quality was checked with 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The V3–V4 regions of the 16S rRNA gene fragments were PCR amplified with the universal primers for prokaryotes (archaea and bacteria) 341F: (5′-CCTAYGGGRBGCASCAG-3′) and the primer 806R (5′-GGACTACNNGGGTATCTAAT-3′) [25] and 50 ng of DNA template under the running conditions (i.e., initial denaturation at 98 °C for 1 min, 30 cycles of 10 sec at 94 °C, 30 sec at 50 °C, 30 sec at 72 °C, and a final elongation step for 5 min at 72 °C. PCR reactions were performed in triplicate 20 μL mixture supplemented by 4 μL of 5 × FastPfu Buffer, 2 μL of 2.5 mM dNTPs, 0.8 μL of each primer (5 μM), 0.4 μL of FastPfu Polymerase and 10 ng of template DNA. The resulted PCR products were extracted from a 2% agarose gel and further purified with the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA) and quantified with QuantiFluor™-ST (Promega, Wisconsin, WI, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.3. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
The purified amplicons from respective triplicate sediment sample were pooled in equimolar and Illumina MiSeq sequenced (2 × 250) on an Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) at the Ramaciotti Centre for Genomics (UNSW) in line with the standard protocols by Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The raw reads were deposited into the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database with project number PRJNA608846.
2.4. Sequencing Data Processing
Raw fastq files were demultiplexed, quality-filtered by Trimmomatic and merged into Raw Tags by FLASH based on the following criteria: (i) the reads were truncated at any site receiving an average quality score < 20 over a 50 bp sliding window; (ii) Primers were exactly matched allowing 2 nucleotide mismatching, and reads supplemented by ambiguous bases were removed; (iii) sequences overlapping longer than 10 bp were merged in accordance with their overlap sequence.
Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered with 97% similarity cutoff with UPARSE (version 7.1 http://drive5.com/uparse/) and chimeric sequences were identified and then removed with UCHIME. Subsequently, the taxonomy of each 16S rRNA gene sequence was analyzed by RDP Classifier algorithm (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/) against the Silva (SSU138) 16S rRNA database with confidence threshold of 70%. Plots were all visualized with the “ggplot2” package in R.
2.5. Detection and Visualization of Microbiological Interactions
Network relationships were calculated, respectively according to the relative abundance of each OTU applying the R package WGCNA [26]. After pairwise Spearman’s rank correlations are calculated, the correlation matrix was designed to assess the p-values. Multiple testing was performed to regulate the p-values with “mt.rawp2adjp” function in package “multtest” [27]. The correlations with a significance threshold (Spearman’s correlation coefficient (ρ) more than 0.8 and p-value below 0.05) were retrieved. The mentioned final network was revealed and suitably edited with Gephi [28].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
RDA (redundancy analysis) was conducted by R package vegan. Taxonomic variations in Dianchi Lake sediments in response to TOC were detected with Partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). PLS-DA was conducted with mixOmics package. LEfSe tool [29] were performed to discriminate different taxa among groups. Only the LDA scores > 3.0 were identified as discriminatory groups. Other statistical analyses were conducted in R environment.
3. Results
3.1. Variability of Cardinal Environmental Factors of the Sediments
Limnological parameters in sediments of Dianchi Lake were measured at the Tongchuan Agricultural Analysis and Testing Technology Co. Ltd. (Kunming, China), including the water (WT), temperature (Temp), total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) and nitrite nitrogen (NO2−-N) of each sampling site. The physicochemical properties are listed in Table 1. Some parameters of Dianchi Lake sediment exhibited horizontal heterogeneity. On the whole, the sediment temperature values were relatively high at sites DC06 and DC07, while they were low at sites DC01 and DC02. The NO2−-N, and NO3−-N values ranged from 0.87 to 15.74 and from 0.009 to 0.046 mg/kg, respectively. Besides, the TP (0.084–0.477%) content reached the highest point at site DC01 and a bottom at site DC09. The contents of TN (0.24–0.92%) also fluctuated significantly (Table 1). A significant level in sediment TOC (32.5–131.2 g/kg) content from respective sampling site was identified. On the whole, the TOC contents in Caohai were found to be higher than those collected from Waihai.

Table 1.
Geographical locations and physicochemical composition of sediment samples.
3.2. Prokaryotic Community Richness and Diversity
Perfectly unbiased profiling procedure to illustrate the shifts in relative abundance and diversity of microbial communities was provided based on 16S rRNA gene amplicons generated from Illumina MiSeq sequencing. A total of 375,170 quality-controlled sequences of 16S rRNA gene were achieved from 13 sediment samples (Table 2), with an average of 28,859 gene fragments (21,952–36,735) in respective sample (Table 2). The Good’s Coverage for the observed OTUs reached over 0.96, and the rarefaction curves (Figure S1) indicated that the number of individuals analyzed was reasonable to almost represent the diversity of the 13 samples. To avoid the biases of sequencing depths among samples, 15,251 sequences were subsampled randomly in respective sample and all reads (at least two sequences in one sample) were clustered into 3312 operational taxonomic units (OTUs) exhibiting 97% similarity by high-throughput sequencing. Simpson values ranged from 0.008 to 0.036 (Table 2). Among a range of samples, the Shannon value in the DC04 was found the highest. The highest Chao index was identified in DC09. The ACE estimators of microbial communities ranged from 1919.384 to 2377.044 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Summary of high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA gene libraries in sediment samples.
3.3. Prokaryotic Community Overall Variation in Sediments
To analyze prokaryotes in sediment, the Dianchi Lake bacterial community structure was analyzed based on high throughput sequencing technology. For phylum level, the dominant taxa hailing from the 13 sites were also analyzed. A total of 10 bacterial phyla and 8 archaeal phyla (a relative abundance totaling > 1%) were detected across all the samples (i.e., 46 and 13 genera, respectively). The relative abundances of bacterial and archaeal populations at the phylum and genus levels are presented in Figure 2 and Figure S2.
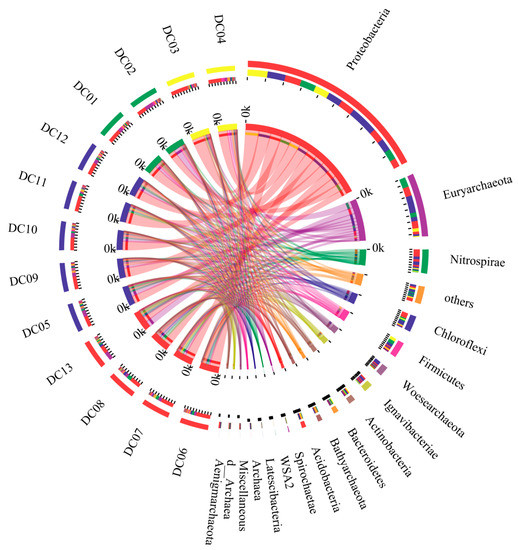
Figure 2.
Relative abundances of dominant bacteria and archaea at the phylum level derived from sediment samples. The data were depicted with Circos. The left half circle and the right half circle indicate the taxonomic composition in respective sample and the distribution of species in different samples at the phylum level, respectively. The width of the bars complies with the relative abundance.
At the phylum level, Proteobacteria was the dominant bacterial group among the samples (Figure 2), taking up 27.4–64.4% of the total reads in respective sample, followed by Nitrospirae (1.2–15.8%), Chloroflexi (3.3–8.7%), Firmicutes (0.9–11.7%), Ignavibacteriae (0.5–5.7%), Actinobacteria (0.8–4.7%), Bacteroidetes (0.6–4.9%), Acidobacteria (0.8–2.9%), Spiprochaetae (0.4–2.1%), and Latescibacteria (0.3–1.5%). On the whole, the mentioned bacterial phyla took up more than 94.6% of the total reads (Figure 2). In the genera of bacteria, Nitrospira (1.2–15.8%) Thiobacillus (1.3–9.9%), a genus of the order Sva0485 (2.4–5.8%) and a genus pertaining to the family Xanthomonadales Incertae Sedis (1.0–5.0%) had highly abundant in most samples (Figure S2). Candidatus Competibacter (0.7–6.1%), Ignavibacterium (0.1–5.0%), a genus belonging to the family Syntrophaceae (1.1–3.3%), Desulfatiglans (0.9–3.2%) and Crenothrix (0.5–4.6%) are at the end of the list.
The phylum level scatter of archaeal communities across the samples is also presented in Figure 2, i.e., Euryarchaeota (3.3–32.2%), Woesearchaeota DHVEG-6 (0.6–5.5%), Bathyarchaeota (0.3–3.5%), and WSA2 (0.1–3.9%), sequences that could not be matched with a known phylum (0.1–1.0%). Moreover, the phyla that could not be identified in all samples covered miscellaneous Euryarchaeotic group (MEG), norank Archaea and Aenigmarchaeota. To observe the structure of Archaea at the genus level, the communities with higher relative abundances were analyzed. As shown in Figure S2, Methanosaeta (1.0–19.7%) was the dominant archaeal genus, followed by a genus pertaining to the phylum Woesearchaeota DHVEG-6 (0.6–5.5%), Methanoregula (0.7–6.2%), a genus belonging to the family ASC21 (0.1–8.9%), Methanolinea (0.4–6.8%) and a genus of the phylum Bathyarchaeota (0.3–3.5%).
3.4. Linking Sediment Prokaryotic Communities to Environmental Factors
RDA was performed to illustrate the correlation between prokaryotic community structure and relevant environmental factors in the sediment (Figure 3). This study aimed to determine the critical environmental factors facilitating the distribution of prokaryotes. The sediment environmental factors in the first and second axes took up 54.39% of the variance for OTU composition (RDA 1: 40.07%; RDA 2: 14.32%). Total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN) and NO3−-N (N5) exhibited most significant correlations (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01) with the prokaryotic composition structure in Dianchi Lake sediment (Figure 3 and Table S1). However, TOC acted as the more robust factor determining prokaryotic community composition (r2 = 0.728, p = 0.02) compared with all environmental variables tested. It is noteworthy that TOC displayed significant negative correlations with the community structures of almost all the samples.
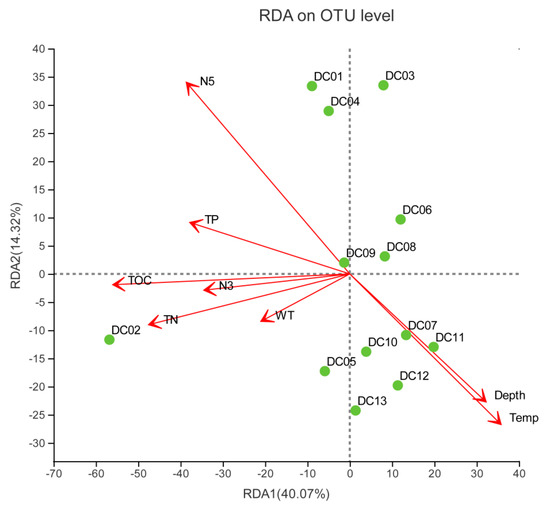
Figure 3.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of dominant operational taxonomic units (OTUs) as affected by sediment environmental variables. Points in the graph represent the samples. The length and angle of red arrows represent the impact of environmental factors on prokaryotic community in respective sample.
3.5. Prokaryotic β-Diversity among Samples
To characterize the potential effect of TOC on the prokaryotic community composition and structure, Partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) was performed to assess the community similarity of all samples (Figure 4A). As suggested from the PLS-DA results at the OTU level, the assemblages could be parsed into four major subgroups (i.e., G1, G2, G3 and G4). Group G1 contained four samples (i.e., DC06, DC07, DC08, and DC13), Group G2 consisted of five samples (i.e., DC05, DC09, DC10, DC11, and DC12), Group G3 contained two samples (i.e., DC01 and DC02), and Group G4 covered two samples (i.e., DC03 and DC04 adjacent to the dam). The prokaryotic communities of each group were clustered together, respectively, indicating significant differences in the total community structures. The mentioned distinct clustered subgroups were also demonstrated by hierarchical cluster analysis based on OTU level (Figure 4B). Meantime, the results of Anosim (p = 0.001) analysis revealed that the difference among groups was more obvious than that within groups (Figure S3). Moreover, the Groups G1, G2 and G3 exhibited three distinct levels, representing TOC levels for low (36.1–45 g/kg), moderate (49–56.9 g/kg), and high (87.3–131.2 g/kg) concentration, respectively (Table 1). All the mentioned results suggested that TOC level may be the most relevant abiotic factor affecting the prokaryotic community structures in Dianchi Lake sediment ecosystems.
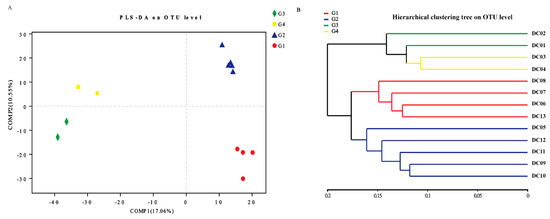
Figure 4.
(A) Partial least square discriminant score analysis for the distance of prokaryotic communities of sediment microbiota among all the samples; (B) hierarchical clustering analysis on the similarity/diversity among the groups G1, G2, G3 and G4. Points exhibiting various colors and shapes represent different groups according to TOC level. Group G1 contained four samples (i.e., DC06, DC07, DC08, and DC13 from low TOC areas (36.1–45 g/kg)), group G2 consisted of five samples (i.e., DC05, DC09, DC10, DC11, and DC12 from moderate total organic carbon (TOC) areas (49–56.9 g/kg)), group G3 contained two samples (i.e., DC01 and DC02 from high TOC areas (87.3–131.2 g/kg)), and group G4 covered two samples (i.e., DC03 and DC04 adjacent to the dam).
3.6. Diversity of the Prokaryotic Communities among Groups
Next, this study aimed to delve into which prokaryotes TOC impacted. Thus, Redundancy analysis was executed between G1 with low TOC (LT) and G2 with moderate TOC (MT) samples using the LEfSe tool. Only LDA scores of 3 or greater are shown in cladograms (Figure 5 and Figure S4). The bacteria that were significantly enriched in Group G1 included 5 groups (Figure 5), covering a genus pertaining to the orders MSBL5, 43F 1404R and Sva0485, respectively (e.g., the genus and their order and family), as well as two families Syntrophobacteraceae and Alcaligenaceae (e.g., the family and its unknown genus). In archaea, G1 was primarily composed of two groups (Figure 5), covering Bathyarchaeota (from phylum to genus), the family Desulfobacteraceae and its unknown genus. In the G2 samples, 6 bacterial groups were significantly enriched, which covered Bacteroidetes vadinHA17 (from Class to genus), Leptolinea in Anaerolineaceae, Napoli_4B_65 (from order to genus), a genus Dechloromonas in Rhodocyclaceae, Desulfarculales and its family Desulfarculaceae and its genus Desulfatiglans, order Xanthomonadales and its family Xanthomonadales Incertae Sedis.
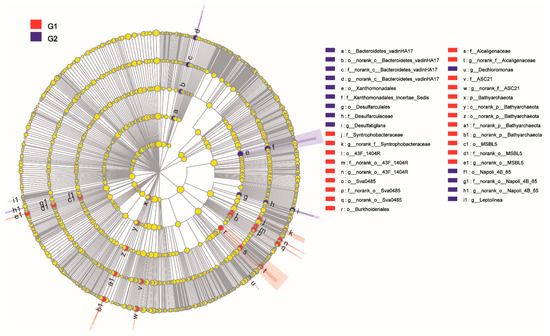
Figure 5.
LEfSe analysis (LDA) of the bacteria and archaea inhabited in Dianchi Lake sediments exhibiting different TOC levels. Prokaryotic taxa that are differentially abundant (LDA score > 3.0) between G1 and G2 samples were visualized by Circos. Letter and number combinations indicate different taxonomic groups (from order to genus). The size of circle is proportional to the relative occurrence in respective community.
3.7. Prokaryotic Interaction Network
As revealed from the results of species–species association network analysis (Figure 6), the co-occurrence patterns displayed a significantly different trend between a low TOC level (LT) and a moderate TOC level (MT). The more interactions (edges) of the LT community than the MT community were harbored despite the comparable number of vertexes. For instance, this study reported that the LT community network exhibited a total of 146 nodes connected with 931 edges, whereas 121 nodes and 154 edges were retrieved in the MT community. Furthermore, our analyzed results revealed that Average degree (AD), a robust indicator of network topology [29], was significantly higher in LT (12.8 and 2.5, respectively). The comparisons with the other common topologies in network analysis are summarized in Supplementary Table S2. Note that the mentioned network parameters suggested that the LT network was more complex. LT and MT network shared only 11 common edges (Figure S5). The mentioned results suggested LT communities with lower TOC levels tended to establish larger and more sophisticated co-occurrences compared with MT communities.
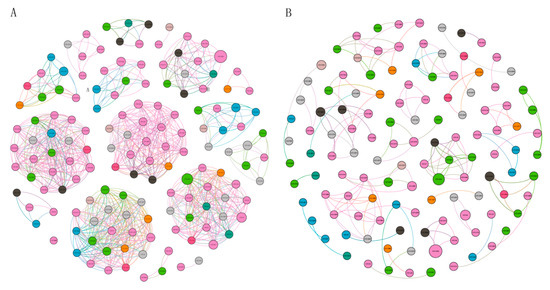
Figure 6.
Co-occurrence patterns of phylotypes exhibiting robust pairwise correlation (ρ > 0.8, p-value < 0.01). (A) Network of group G1 with low TOC level (LT); (B) network of group G2 with moderate TOC level (MT). The nodes represent individual OTUs, and colors indicate different phyla. The pink line and the blue line represent the positive and negative correlations, respectively. The circle diameter is proportional to the mean abundance of different phyla. Colors of dots represent the species at different phylum levels.
4. Discussion
Thus far, A growing body of studies suggested that pH [13,30], organic matter [31], nitrogen [15], TOC [5], phosphorus [32] and heavy metal [33] were the critical drivers of microbial communities in lake sediments. However, the mentioned conclusions were drawn in terms of the comparing inter-lake, which have overlooked the significant effect of geographical distance. Sediments with a longer geographical distance are subject to distinct ambient conditions (e.g., hydrological properties, climatic influences, geological settings and catchment area). Furthermore, the effect of a specific environmental variables level on the prokaryotic structure in situ has been rarely studied. Dianchi Lake considered an ideal model system to address ecological principles exhibit large variations of physical and chemical parameters. Here, we compared bacterial and archaeal communities’ structure and networks associated with different TOC levels in Dianchi lake. To the best of the our knowledge, this is the first study to determine the effect of TOC levels on the dynamics of prokaryotic composition and adopt network thinking to research microbial communities in a lake sediment ecosystem.
More comprehensively clarifying the environmental factors that driving the assembly of prokaryotic communities is of great importance for ecosystem management and biodiversity preservation in complex lake-sediment environments [2]. We found that TOC is an important driver for the composition of bacterial and archaeal communities in Dianchi Lake sediment. This was a result same as a previous study [34], in which Xiong et al. observed the remarkably organic matter’s effect on change of sediment prokaryotes in Erhai Lake. Our study reported that the most abundant bacteria across all samples were identified as members of the phyla Proteobacteria, Nitrospirae, Chloroflexi, Firmicutes and Ignavibacteriae and the dominant groups of archaea consisted of Euryarchaeota, Woesearchaeota DHVEG-6, Bathyarchaeota and WSA2. However, Bai et al. suggested that Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes and Chloroflexi were dominant bacterial groups in Dianchi Lake sediment [5]. This difference may be due to our broader sampling and deeper sequencing compared to the former research. Numerous existing studies suggested striking spatial heterogeneity in the prokaryotic community in freshwater lake sediment [1,15,30,34,35,36]. In the earlier study on Dianchi Lake, Bai et al. reported that the microbial communities obviously clustered into two groups (Caohai and Waihai) [5]. However, whether prokaryotic communities structure varies among different TOC levels is unclear. In the present study, the results of UPGMA cluster and PLS-DA analysis demonstrated that sediment samples were split into three groups (G1, G2 and G3) and samples with similar TOC levels tend to be grouped together (Figure 4). The above results indicated that the structure of bacterial and archaeal communities was homologous within individual groups, and exhibited significant variations among three groups (G1, G2 and G3). DC03 and DC04 (with different TOC levels) clustered together, which might be affected by the dam (Figure 1). As confirmed from the mentioned results, the prokaryotic community structure varies among different TOC levels in the Dianchi Lake sediment. A previous study [37] demonstrated that marine benthic community composition responded variably to different TOC levels and this was consistent with our results.
In the present study, two groups were taken to assess the relationships between TOC levels and the co-occurrence of prokaryotic communities by a network analysis. Certain topological indexes of the observed network were calculated to identify the co-occurrence patterns between LT and MT. Given the co-occurrence results, LT (i.e., 433 positive correlations and 498 negative correlations) interacted stronger with other than MT (73 positive correlations and 81 negative correlations). The mentioned findings are relatively illogical: why are there larger and more sophisticated interactions associated with LT networks than MT? Environmental conditions can significantly impact the interactions among prokaryotes. MT communities might primarily be colonized with higher number of phylotypes exhibiting a larger genome with versatile functional traits related to substantial nutrients synthesis and mediate interactions. The nutrient rich status in MT could enable them to exploit available nutrients efficiently without being required to develop relationships with neighboring members. Thus, there were few connections between individuals in MT. While in the case of resource scarcity (LT), microbes with small genomes might dominate the community. Existing studies assumed that the streamlined genome size provide a competitive advantage for prokaryotes in a nutritionally deficient environment [38]. However, the mentioned members with small genomes often lack complete access to some of the necessary genomic traits to produce nutrients. Microbial communities are capable of exchanging metabolites in different habitats [39]. “Beneficiaries” supplemented by streamlined genome can obtain essential metabolites from the “helper” for their survival [40]. Indeed, they can also, in turn, provide other metabolites for their helpers, which may be the reason for the more interactions and complicated network in LT community.
Overall, our results showed that TOC level may be an important driver for the composition and networks of bacterial and archaeal communities in Dianchi Lake sediment. Prokaryotic communities structure varies among different TOC levels and there is an obvious difference in the prokaryotic network associated with different TOC levels. This study set up a starting point for provide insights into microbial assemblages in a eutrophic lake. Next, we will elucidate the potential mechanisms underlying response to the TOC level in prokaryotes using metagenomic and metatranscriptomic data.
5. Conclusions
TOC level might be a key determinant to shape sediment microbial communities in Dianchi Lake. The prokaryotic community structure is obviously distinct among different TOC levels in Dianchi Lake sediment. Interestingly, LT communities interacted with each other stronger when compared to MT communities. Overall, this study could enhance our knowledge of microbial assemblages in eutrophic lake sediment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/12/9/2557/s1. Figure S1: Rarefaction curves depicted in a random sampling of 16S rRNA gene sequences. Figure S2: Relative abundances of the dominant bacteria and archaea at the genus level derived from sediment samples. Figure S3: Inter-group difference analysis with ANOSIM. Figure S4: Histogram of LDA scores for bacteria exhibiting richness differences between G1 and G2. Different colored regions represent different groups (red, G1; blue, G2). Figure S5: Venn diagram presenting overlaps of edges between the LT network and MT network. Table S1: Redundancy analysis (RDA) analysis of environmental variables and dominant communities. Table S2: Common topological properties extensively applied in network analysis.
Author Contributions
Data curation, Y.-P.L., Q.-Q.H., W.X., Y.-X.W. and X.-L.C.; formal analysis, C.-P.L.; funding acquisition, C.-Q.D., Y.-X.W. and X.-L.C.; visualization, C.-P.L.; writing—original draft, C.-P.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.-X.W. and X.-L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (National Key Sciences and Technology Program for Water Solutions, 2012ZX07102-003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (31660001, 31660089, 31660042 and 31960220), and the Yunnan Provincial Sciences and Technology Department (2018BC001).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, F.H.; Lin, G.H.; Gao, G.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhao, G.P.; Zhou, Z.H.; Shen, J.H. Bacterial and archaeal assemblages in sediments of a large shallow freshwater lake, Lake Taihu, as revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, N.; Herndl, G.J.; Hansell, D.A.; Benner, R.; Kattner, G.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Kirchman, D.L.; Weinbauer, M.G.; Luo, T.; Chen, F. Microbial production of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter: Long-term carbon storage in the global ocean. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Song, C.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y. Shifts between ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in relation to nitrification potential across trophic gradients in two large Chinese lakes (Lake Taihu and Lake Chaohu). Water Res. 2013, 47, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmonen, E.; Haukka, K.; Rantala-Ylinen, A.; Rajaniemi-Wacklin, P.; Lepistö, L.; Sivonen, K. Bacterioplankton community composition in 67 Finnish lakes differs according to trophic status. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wen, D.; Li, Z.; Jefferson, W.A.; Feng, C.; Tang, X. Bacterial communities in the sediments of Dianchi Lake, a partitioned eutrophic waterbody in China. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7, e37796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. Colonization Characteristics of Bacterial Communities on Plastic Debris Influenced by Environmental Factors and Polymer Types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10763–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, G.; Jiang, J. Spatial-Temporal Variation of Bacterial Communities in Sediments in Lake Chaohu, a Large, Shallow Eutrophic Lake in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.Z.; Xie, S.G.; Liu, Y. Distribution of sediment bacterial and archaeal communities in plateau freshwater lakes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, B.; Ehrhardt, C.; Reifel, K.; Moreno, L.; Valentine, D. Archaeal and Bacterial Communities Respond Differently to Environmental Gradients in Anoxic Sediments of a California Hypersaline Lake, the Salton Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, B.; Hose, G.C.; Harford, A.J.; Midgley, D.J.; Greenfield, P.; Paulsen, I.T.; Chariton, A.A. Microbial communities are sensitive indicators for freshwater sediment copper contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhen, W.; Feng, Q.; Xie, S.; Yong, L. Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4161–4175. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Ruiz, M.D.R.; Cifuentes, A.; Font-Verdera, F.; Perez-Fernandez, C.; Farias, M.E.; Gonzalez, B.; Orfila, A.; Rossello-Mora, R. Biogeographical patterns of bacterial and archaeal communities from distant hypersaline environments. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, J.; Hou, J.; Yang, Y.; Yao, T.; Knight, R.; Chu, H. Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.J.; Pan, J.; Duan, C.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, H.C.; Song, X.; Li, M. Prokaryotic Diversity in Mangrove Sediments across Southeastern China Fundamentally Differs from That in Other Biomes. mSystems 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Yang, J.S.; Qu, J.H.; Li, H.F.; Liu, W.J.; Li, B.Z.; Wang, E.T.; Yuan, H.L. Sediment prokaryote communities in different sites of eutrophic Lake Taihu and their interactions with environmental factors. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Ding, K.; Chen, R.; Liu, S. Joint response of chemistry and functional microbial community to oxygenation of the reductive confined aquifer. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Simon, P.N.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, J.; Igarashi, Y.; Pan, X.; et al. Distinct Network Interactions in Particle-Associated and Free-Living Bacterial Communities during a Microcystis aeruginosa Bloom in a Plateau Lake. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lu, T.; Paerl, H.W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Qian, H. Feedback Regulation between Aquatic Microorganisms and the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lin, F.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Shen, M.; Park, M.S.; Li, T.; Zhao, J. A Large-Scale Comparative Metagenomic Study Reveals the Functional Interactions in Six Bloom-Forming Microcystis-Epibiont Communities. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, T.G. Coordinated Metacommunity Assembly and Spatial Distribution of Multiple Microbial Kingdoms within a Lake. Microb. Ecol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Guo, Z.; Gu, X.; Gao, H.; Weng, S.; Zhou, J.; Gu, D.; Lu, H.; Zhou, X. Rare rather than abundant microbial communities drive the effects of long-term greenhouse cultivation on ecosystem functions in subtropical agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 706, 136004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchinski, K.; Moyer, C.L.; Hager, K.; Fullerton, H. Fine-Scale Biogeography and the Inference of Ecological Interactions Among Neutrophilic Iron-Oxidizing Zetaproteobacteria as Determined by a Rule-Based Microbial Network. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippini, G.; Bugnot, A.B.; Johnston, E.L.; Ruszczyk, J.; Potts, J.; Scanes, P.; Ferguson, A.; Ostrowski, M.; Varkey, D.; Dafforn, K.A. Sediment bacterial communities associated with environmental factors in Intermittently Closed and Open Lakes and Lagoons (ICOLLs). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.-Y.; Han, X.-X.; Huang, X.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, H.; Huang, T.; Yu, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-C. Distribution Characteristics of n-alkanes in Sediment Core and Implication of Environment in Different Lakes of Dianchi. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2016, 37, 4605–4614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S. Group-specific primer and probe sets to detect methanogenic communities using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoav, B.; Krieger, A.M.; Daniel, Y. Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika 2006, 3, 491–507. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the Third International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, L.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, L.J.; Zhao, D.Y. Spatial distribution of bacterial communities in sediment of a eutrophic lake revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and multivariate analysis. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B. Characterization of sediment bacterial communities in plain lakes with different trophic statuses. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.; Gao, G.; Qin, B.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chi, K.; Dai, J. Comparing sediment bacterial communities in the macrophyte-dominated and algae-dominated areas of eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Ge, G. Effects of Heavy Metal and Nutrients on Benthic Microbial Communities in Freshwater Sediment of Poyang Lake (China). J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Xie, P.; Wang, S.; Niu, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, W. Sources of organic matter affect depth-related microbial community composition in sediments of Lake Erhai, Southwest China. J. Limnol. 2015, 74, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, H.; Mauro, T.; Jakob, Z.; Raffaele, P.; Walter, W.; John, P. Composition of bacterial and archaeal communities in freshwater sediments with different contamination levels (Lake Geneva, Switzerland). Water Res. 2011, 45, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Li, Z.; Du, B.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y. Bacterial communities in sediments of the shallow Lake Dongping in China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 112, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, H.S.; Peterson, C.H.; Kim, S.L.; Conlan, K.E.; Fairey, R.; McDonald, C.; Grabowski, J.H.; Oliver, J.S. Variation in marine benthic community composition allows discrimination of multiple stressors. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 261, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, S.J.; Cameron Thrash, J.; Temperton, B. Implications of streamlining theory for microbial ecology. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1553–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, A.; Comte, J.; Babin, M.; Forest, A.; Matsuoka, A.; Lovejoy, C. Oceanographic structure drives the assembly processes of microbial eukaryotic communities. ISME J. 2015, 9, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, A.; Jamshidi, S.; Lagadeuc, Y.; Eveillard, D.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P. Beyond the Black Queen Hypothesis. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).