Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Blackwater for Different Practical Application Scenarios in Decentralized Scale: From Wastes to Energy Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Sources of Substrate and Inoculum
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.2.1. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Tests of Different Substrate Ratios
2.2.2. Effect of Blackwater Initial Total Ammonia Nitrogen Concentration on Codigestion
2.3. Analysis and Calculations
2.3.1. Analytical Methods
2.3.2. Kinetic Data Analysis
2.3.3. Synergistic Effect
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Different Ratios of Two Substrates on Anaerobic Codigestion
3.1.1. Methane Production
3.1.2. Degradation of Organic Matter
3.1.3. System Stability Analysis
3.1.4. Kinetics of Anaerobic Codigestion
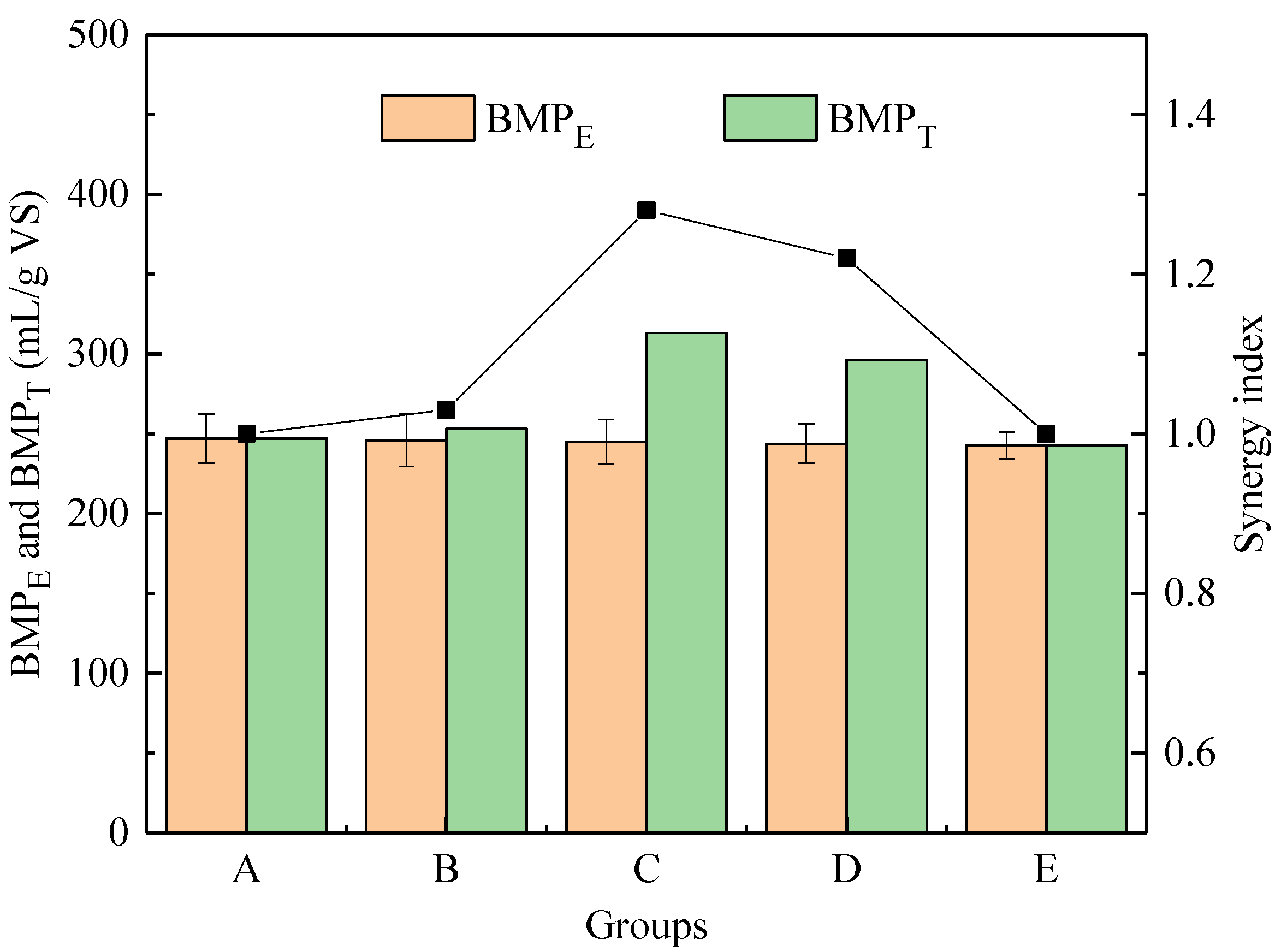
3.1.5. Synergistic Effect
3.2. Effect of Blackwater Initial Total Ammonia Nitrogen Concentration
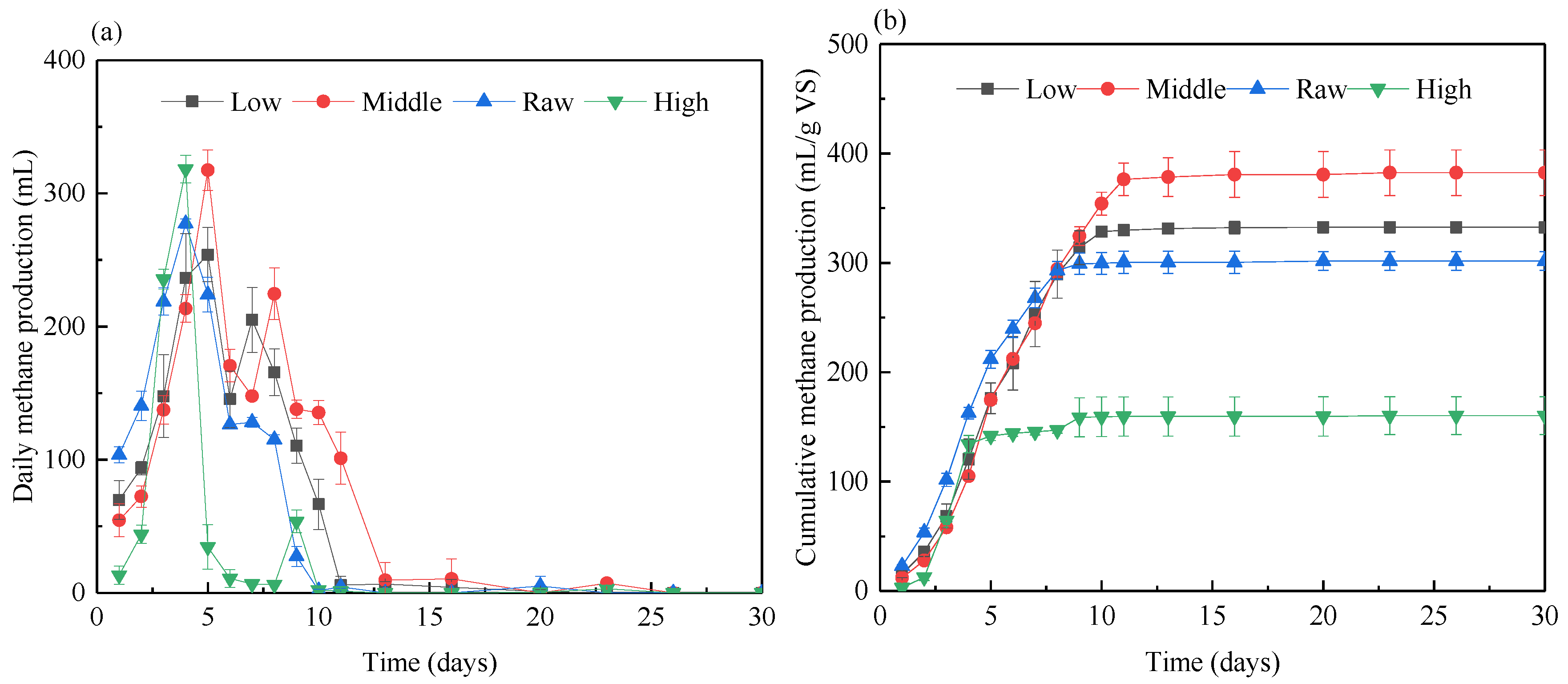
3.2.1. Methane Production
3.2.2. System Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2017; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawa, K.; Elmitwally, T.A.; Gaillard, A.; Leeuwen, V.M.; Zeeman, G. Co-digestion of concentrated black water and kitchen refuse in an accumulation system within the DESAR (decentralized sanitation and reuse) concept. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. Effects of thermal pretreatment on the biomethane yield and hydrolysis rate of kitchen waste. Appl. Energy 2016, 172, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, K.; Tan, L.; Tang, Y.; Kida, K. Development of an efficient anaerobic co-digestion process for garbage, excreta, and septic tank sludge to create a resource recycling-oriented society. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y. A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic digestion: Research updates and tendencies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, G.; Rodríguez-Abalde, A.; Fernández, B.; Flotats, X.; Bonmatí, A. Biomass adaptation over anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and trapped grease waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6830–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yu, M.; Song, N.; Xu, B.; Gao, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q. Effect of ethanol pre-fermentation on organic load rate and stability of semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Xu, S.; Florentino, A.P.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. Enhancing blackwater methane production by enriching hydrogenotrophic methanogens through hydrogen supplementation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.W.; Chiam, J.A.; Wang, J. Microbial community structure reveals how microaeration improves fermentation during anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Guo, B.; Liu, Y. Mesophiles outperform thermophiles in the anaerobic digestion of blackwater with kitchen residuals: Insights into process limitations. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Elmitwalli, T.A.; Zeeman, G. Enhanced primary treatment of concentrated black water and kitchen residues within DESAR concept using two types of anaerobic digesters. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luostarinen, S.; Rintala, J. Anaerobic on-site treatment of kitchen waste in combination with black water in UASB-septic tanks at low temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavagnolo, M.C.; Girotto, F.; Hirata, O.; Cossu, R. Lab-scale co-digestion of kitchen waste and brown water for a preliminary performance evaluation of a decentralized waste and wastewater management. Waste Manag. 2017, 66, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gabauer, W.; Li, Z.; Ortner, M.; Fuchs, W. Improving exploitation of chicken manure via two-stage anaerobic digestion with an intermediate membrane contactor to extract ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Microbial community dynamics in anaerobic digesters treating conventional and vacuum toilet flushed blackwater. Water Res. 2019, 160, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhen, G.; Liu, Y.; Hojo, T.; Estrada, A.L.; Li, Y. Long-term effect of the antibiotic cefalexin on methane production during waste activated sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Chufo, W.A.; Jaffar, M.; Li, X. Promoting anaerobic biogasification of corn stover through biological pretreatment by liquid fraction of digestate (LFD). Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. Effects of liquid digestate pretreatment on biogas production for anaerobic digestion of wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Energy production from different organic wastes by anaerobic co-digestion: Maximizing methane yield versus maximizing synergistic effect. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Tao, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, K. Synergistic methane production from the anaerobic co-digestion of Spirulina platensis with food waste and sewage sludge at high solid concentrations. Renew. Energy 2019, 142, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Q.; Florentino, A.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Co-digestion of blackwater with kitchen organic waste: Effects of mixing ratios and insights into microbial community. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Lim, J.W.; Mao, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of source segregated brown water (feces-without-urine) and food waste: For Singapore context. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendland, C.; Deegener, S.; Behrendt, J.; Toshev, P.; Otterpohl, R. Anaerobic digestion of blackwater from vacuum toilets and kitchen refuse in a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR). Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Song, N.; Chang, Q.; Gao, M.; Sonomoto, K. Effect of ethanol pre-fermentation and inoculum-to-substrate ratio on methane yield from food waste and distillers’ grains. Appl. Energy 2015, 155, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, W.; Wang, X.; Gabauer, W.; Ortner, M.; Li, Z. Tackling ammonia inhibition for efficient biogas production from chicken manure: Status and technical trends in Europe and China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M. Ammonia Inhibition in High-Solids Biogasification: An Overview and Practical Solutions. Environ. Technol. 1999, 20, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, P.; Horan, N.J. Optimising the biogas production from leather fleshing waste by co-digestion with MSW. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4117–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, G.; Illa, J.; Fernández, B.; Bonmatí, A. Thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge with grease waste: Effect of long chain fatty acids in the methane yield and its dewatering properties. Appl. Energy 2014, 117, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Su, H.; Baeyens, J.; Tan, T. Reviewing the anaerobic digestion of food waste for biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhi, Z.; Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Bakonyi, P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Rajesh Banu, J. Synergistic effect and biodegradation kinetics of sewage sludge and food waste mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion and the underlying stimulation mechanisms. Fuel 2019, 253, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehariya, S.; Patel, A.K.; Obulisamy, P.K.; Punniyakotti, E.; Wong, J.W.C. Co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge for methane production: Current status and perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, Q.; Wu, S.; Qi, D.; Li, W.; Zuo, Z.; Dong, R. Batch anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure with dewatered sewage sludge under mesophilic conditions. Appl. Energy 2014, 128, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mashad, H.M. Kinetics of methane production from the codigestion of switchgrass and Spirulina platensis algae. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Saino, M.; Bai, X. Study on the bio-methane yield and microbial community structure in enzyme enhanced anaerobic co-digestion of cow manure and corn straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassab, G.; Khater, D.; Odeh, F.; Shatanawi, K.; Halalsheh, M.; Arafah, M.; van Lier, J.B. Impact of Nanoscale Magnetite and Zero Valent Iron on the Batch-Wise Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Waste-Activated Sludge. Water 2020, 12, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| KW | BW | Inoculum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TS (%) | 25.1 | 6.7 | 6.0 |
| VS/TS (%) | 90.2 | 78.5 | 48.8 |
| C (%) | 46.7 | 43.2 | / |
| H (%) | 6.6 | 6.1 | / |
| O (%) | 44.2 | 45.8 | / |
| N (%) | 2.2 | 4.0 | / |
| S (%) | 0.3 | 0.9 | / |
| C/N | 21.2 | 10.8 | / |
| pH | 4.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 |
| COD (g/L) | 192.9 | 143.2 | / |
| TAN (mg/L) | 635 | 4488 | / |
| VFA (g/L) | 0.72 | 20.27 | / |
| A | B | C | D | E | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KW:BW based on TS | 4:0 | 3:1 | 1:1 | 1:3 | 0:4 | / |
| Mixture (g) | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| KW (g) | 20.3 | 15.7 | 10.7 | 5.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| BW (g) | 0.0 | 19.7 | 40.5 | 62.5 | 85.7 | 0.0 |
| Inoculum (g) | 314.8 | 312.6 | 310.2 | 308.1 | 305.4 | 400 |
| Water (g) | 64.9 | 52.0 | 38.6 | 23.9 | 8.9 | 0.0 |
| TS of mixture (%) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| VS of mixture (g) | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.5 | / |
| pH of mixture | 7.9 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| Low | Middle | Raw | High | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAN (mg/L) | 1541 | 2388 | 4488 | 6318 |
| pH | 6.2 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 6.2 |
| A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CODinitial (g/L) | 4.8 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 6.6 |
| CODfinal (g/L) | 2.9 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 3.2 |
| CODrr (%) | 39.6 | 46.9 | 49.1 | 56.1 | 51.5 |
| TSinitial (g/L) | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 |
| TSfinal (g/L) | 15.2 | 25.4 | 23.3 | 32.2 | 35.6 |
| TSrr (%) | 74.7 | 57.7 | 61.2 | 46.3 | 40.7 |
| VSinitial (g/L) | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.3 |
| VSfinal (g/L) | 2.9 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 4.3 | 5.1 |
| VSrr (%) | 74.8 | 72.2 | 74.8 | 62.6 | 54.9 |
| Bm (mL/g VS) | Rm (mL/g VS/d) | λ (d) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 246.55 | 28.86 | 3.20 | 0.9970 |
| B | 251.79 | 31.56 | 1.83 | 0.9987 |
| C | 309.98 | 59.80 | 1.04 | 0.9975 |
| D | 292.91 | 57.85 | 0.81 | 0.9965 |
| E | 239.20 | 42.32 | 0.63 | 0.9955 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zuo, S. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Blackwater for Different Practical Application Scenarios in Decentralized Scale: From Wastes to Energy Recovery. Water 2020, 12, 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092556
Wang H, Li Z, Zhou X, Wang X, Zuo S. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Blackwater for Different Practical Application Scenarios in Decentralized Scale: From Wastes to Energy Recovery. Water. 2020; 12(9):2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092556
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huihui, Zifu Li, Xiaoqin Zhou, Xuemei Wang, and Siqi Zuo. 2020. "Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Blackwater for Different Practical Application Scenarios in Decentralized Scale: From Wastes to Energy Recovery" Water 12, no. 9: 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092556
APA StyleWang, H., Li, Z., Zhou, X., Wang, X., & Zuo, S. (2020). Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Blackwater for Different Practical Application Scenarios in Decentralized Scale: From Wastes to Energy Recovery. Water, 12(9), 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092556





