α- and β-Diversity Patterns of Macrophytes and Freshwater Fishes are Driven by Different Factors and Processes in Lakes of the Unexplored Southern Balkan Biodiversity Hotspot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. α-Diversity
2.3. β-Diversity
2.4. α-Diversity Patterns—Generalized Linear Models (GLMs)
2.5. β-Diversity Patterns—Generalised Dissimilarity Modeling (GDM)
3. Results
3.1. Predictors of α-Diversity
3.2. Components of β-Diversity
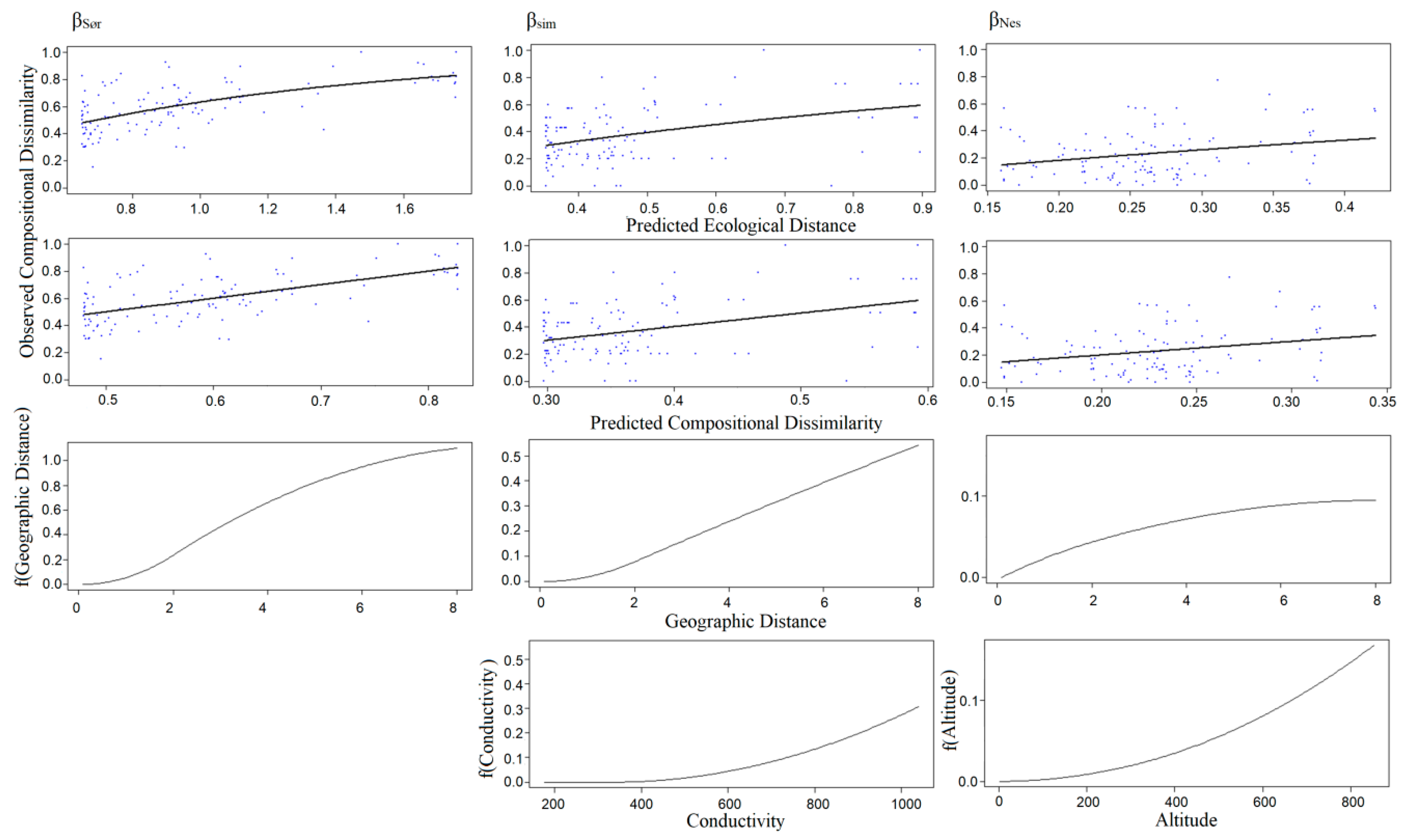
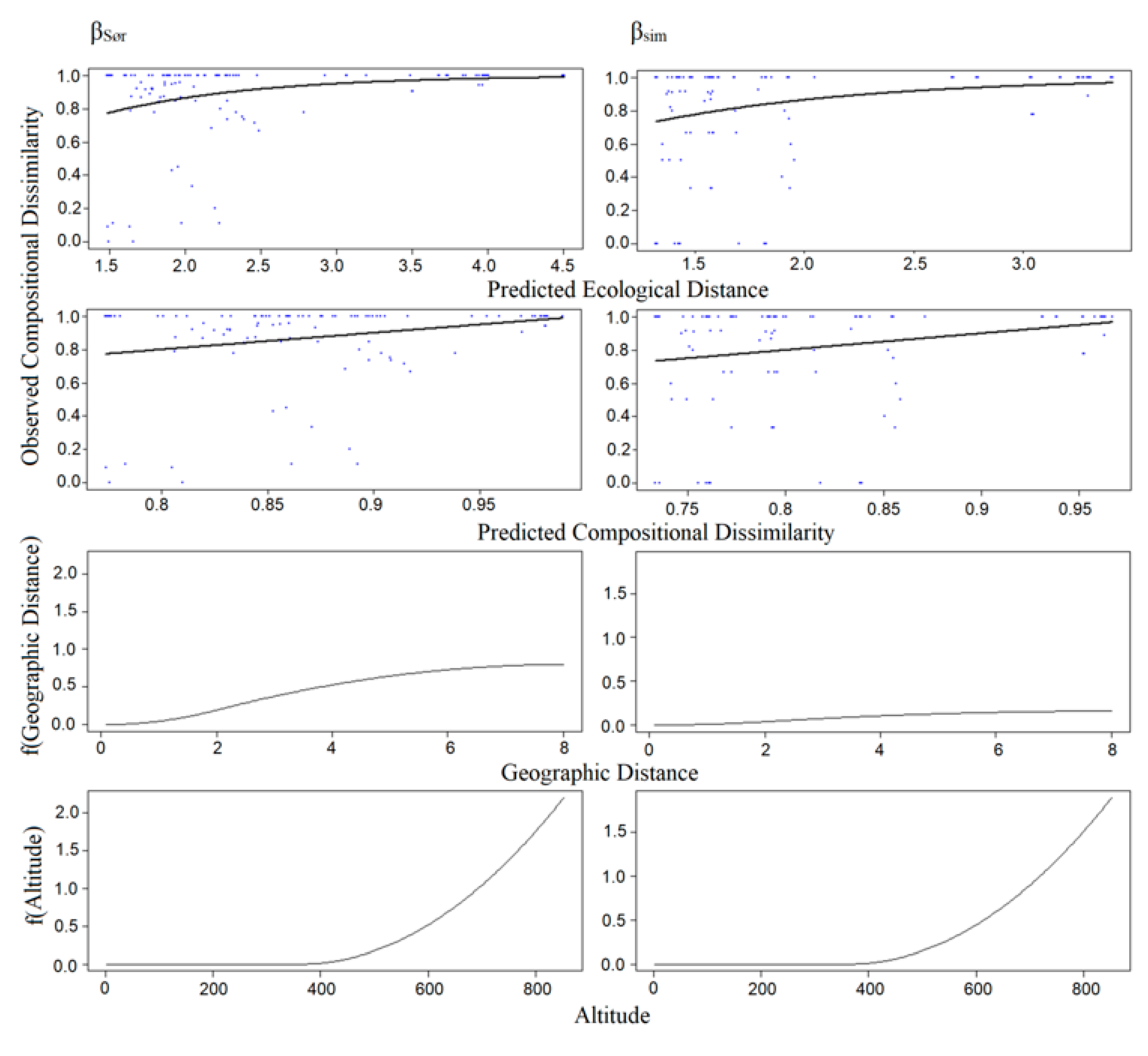
3.3. Patterns of Dissimilarity/GDM Models of β-Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. α-Diversity
4.2. β-Diversity
4.3. Conservation Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darwin, C. The Voyage of the Beagle. Natural History Library; Anchor Press: Norwell, MA, USA, 1839. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, A.R. Tropical Nature, and Other Essays; Macmillan & Co.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1878; p. 356. [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur, R.H. Geographical Ecology: Patterns in the Distribution of Species; Harper and Row: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Ricklefs, R.E.; Jenkins, D.G. Biogeography and ecology: Towards the integration of two disciplines. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J.; Crist, T.O.; Chase, J.M.; Vellend, M.; Inouye, B.D.; Freestone, A.L.; Sanders, N.J.; Cornell, H.V.; Comita, L.S.; Davies, K.F.; et al. Navigating the multiple meanings of b diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, J.; Alahuhta, J.; Fattorini, S. Phylogenetic diversity of regional beetle faunas at high latitudes: Patterns, drivers and chance along ecological gradients. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 2751–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veech, J.A.; Summerville, K.S.; Crist, T.O.; Gering, J.C. The additive partitioning of species diversity: Recent revival of an old idea. Oikos 2002, 99, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligeiro, R.; Melo, A.S.; Callisto, M. Spatial scale and the diversity of macroinvertebrates in a Neotropical catchment. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco-Ramos, V.; Arias-González, J.E. Additive Partitioning of Coral Reef Fish Diversity across Hierarchical Spatial Scales throughout the Caribbean. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, J.T.; Martens, K.; Higuti, J. Diversity of ostracod communities (Crustacea, Ostracoda) across hierarchical spatial levels in a tropical floodplain. Hydrobiologia 2015, 762, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, G.G. Community Ecology; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MS, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Simberloff, D.; Connor, E.F. Missing Species Combinations. Am. Nat. 1981, 118, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, R.E. Community Diversity: Relative Roles of Local and Regional Processes. Science 1987, 235, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H.; Ruokolainen, K.; Aguilar, M.; Sarmiento, A. Floristic patterns along a 43-km long transect in an Amazonian rain forest. J. Ecol. 2003, 91, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibold, M.A.; Holyoak, M.; Mouquet, N.; Amarasekare, P.; Chase, J.M.; Hoopes, M.F.; Holt, R.D.; Shurin, J.B.; Law, R.; Tilman, D.; et al. The metacommunity concept: A framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, B.; Lechowicz, M.J. Neutrality, niches, and dispersal in a temperate forest understory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7651–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottenie, K. Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, A.S.; Rangel, T.F.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F. Environmental drivers of beta-diversity patterns in New-World birds and mammals. Ecography 2009, 32, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekola, J.C.; White, P. The distance decay of similarity in biogeography and ecology. J. Biogeogr. 1999, 26, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Baselga, A. The relationship between species replacement, dissimilarity derived from nestedness, and nestedness. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Ricklefs, R.E.; White, P.S. Beta diversity of angiosperms in temperate floras of eastern Asia and eastern North America. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, N.; Comita, L.; Chase, J.M.; Sanders, N.J.; Swenson, N.G.; Crist, T.O.; Stegen, J.C.; Vellend, M.; Boyle, B.L.; Anderson, M.J.; et al. Disentangling the drivers of β diversity along latitudinal and elevational gradients. Science 2011, 333, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Yang, Q.; Quan, Q.; Xia, L.; Ge, D.; Lv, X. Multiscale partitioning of small mammal?-diversity provides novel insights into the Quaternary faunal history of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Hengduan Mountains. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 1412–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.H.; Reeves, J.H. On the meaning and measurement of nestedness of species assemblages. Oecologia 1992, 92, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A. Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 19, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J. A macroecological perspective of diversity patterns in the freshwater realm. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 1703–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisner, B.; Neto, P.P.; Lindström, E.S.; Barnett, A.; Longhi, M.L. The role of environmental and spatial processes in structuring lake communities from bacteria to fish. Ecology 2006, 87, 2985–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; Mc Donald, R.; Hillebrand, H. The distance decay of similarity in ecological communities. Ecography 2007, 30, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaris, A.D.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Michaloudi, E.; Bobori, D.C. Biogeographical patterns of freshwater micro- and macroorganisms: A comparison between phytoplankton, zooplankton and fish in the eastern Mediterranean. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Soininen, J.; Alahuhta, J.; Lappalainen, J.; Virtanen, R. Metacommunity ecology meets biogeography: Effects of geographical region, spatial dynamics and environmental filtering on community structure in aquatic organisms. Oecologia 2017, 183, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceschin, F.; Bini, L.M.; Padial, A.A. Correlates of fish and aquatic macrophyte beta diversity in the Upper Paraná River floodplain. Hydrobiologia 2018, 805, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Heino, J.; Quirino, B.A.; Moresco, G.A.; Peláez, O.; Meira, B.R.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Jati, S.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A.; Velho, L.F.M.; et al. Differently dispersing organism groups show contrasting beta diversity patterns in a dammed subtropical river basin. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 691, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stendera, S.; Adrian, R.; Bonada, N.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hugueny, B.; Januschke, K.; Pletterbauer, F.; Hering, D. Drivers and stressors of freshwater biodiversity patterns across different ecosystems and scales: A review. Hydrobiologia 2012, 696, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryštufek, B.; Reed, J.M. Pattern and Process in Balkan Biodiversity—An overview. In Balkan Biodiversity, Pattern and Process in the European Hotspot; Griffiths, H.J., Kryštufek, B., Reed, J.M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsikos, N.; Leprieur, F.; Leonardos, I.D. Biogeography of freshwater fishes of the Balkan Peninsula. Hydrobiologia 2014, 738, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănărescu, P.M. Distribution Pattern of the Aquatic Fauna of the Balkan Peninsula. In Balkan Biodiversity, Pattern and Process in the European Hotspot; Griffiths, H.J., Kryštufek, B., Reed, J.M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Radoman, P. Hydrobioidea, a Superfamily of Prosobranchia (Gastropoda) II: Origin, Zoogeography, Evolution in the Balkans and Asia Minor. Monographs of the Institute of Zoology; Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Belgrade: Belgrade, Serbia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Alahuhta, J. Geographic patterns of lake macrophyte communities and species richness at regional scale. J. Veg. Sci. 2015, 26, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, J.W. Lakemorpho: Lake Morphometry Metrics. R package Version 1.1.1. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lakemorpho (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- GMAO. MERRA-2 tavg1_2d_slv_Nx: 2d,1-Hourly,Time-Averaged,Single-Level,Assimilation,Single-Level Diagnostics V5.12.4, Greenbelt, MD, USA, Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC). Available online: http://www.soda-pro,com/el/web-services/meteo-data/ (accessed on 1 May 2018). [CrossRef]
- Koumpli-Sovantzi, L. The aquatic flora of Aetoloakarnania (W Greece). Willdenowia 1989, 18, 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Papastergiadou, E.; Babalonas, D. Aquatic flora of N. Greece I. Hydrophytes. Wildenowia 1993, 23, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Sarika–Hatzinikolaou, M.; Yannitsaros, A.; Babalonas, D. The macrophytic vegetation of seven aquatic ecosystems of Epirus (NW Greece). Phytocoenologia 2003, 33, 93–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valchev, V.; Georgiev, V.; Ivanova, D.; Tsoneva, S.; Janauer, G. Conservationally Important Macrophytes in the Bulgarian Stretch of the danube River and the Near Water Bodies. In Proceedings of the 36th international conference of IAD, Austrian Committee Danube Research, Ed, Vienna, Austria, 4–8 September 2006; pp. 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidis, K.; Papastergiadou, E. Aquatic vegetation and related abiotic environment in a shallow urban lake of Greece. Belg. J. Bot. 2007, 140, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Talevska, M.; Petrovic, D.; Milosevic, D.; Talevski, T.; Maric, D.; Talevska, A. Biodiversity of macrophyte vegetation from Lake Prespa, Lake Ohrid and Lake Skadar. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2009, 23, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolaki, P.; Tsakiri, E.; Papastergiadou, E. Inventory of aquatic and riparian flora of Acheron and Louros rivers, and Zirou Lake in western Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 861–874. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidis, K. Ecological Assessment of Lakes of NW Greece with Emphasis on the Associations between Aquatic Macrophytes, Zooplankton and Water Quality. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Biology, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprieur, F.; Oikonomou, A. The need for richness-independent measures of turnover when delineating biogeographical regions. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, A.; Orme, D.; Villeger, S.; Bortoli, D.; Leprieur, F. Betapart: Partitioning Beta Diversity Into Turnover and Nestedness Components. R Package Version 1.3. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/betapart/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Wei, T.; Simko, V.; Levy, M.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zemla, J. Corrplot: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. R Package Version 0.84. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/corrplot/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S.; Price, B.; Adler, D.; Bates, D.; Baud-Bovy, G.; Bolker, B.; Ellison, S.; Firth, D.; Friendly, M.; et al. R-Core. Car: Companion to Applied Regression. R Package Version 3.0-6. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/car/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Quinn, G.P.; Keough, M.G. Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference. R Package Version 1.42.1. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mazerolle, M.J. AICcmodavg: Model Selection and Multimodel Inference Based on (Q) AIC(c). R Package Version 1.27. 2013. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/AICcmodavg/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Ferrier, S.; Guisan, A. Spatial modelling of biodiversity at the community level. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, S.; Manion, G.; Elith, J.; Richardson, K. Using generalized dissimilarity modelling to analyse and predict patterns of beta diversity in regional biodiversity assessment. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolar, J.B.; Gilroy, J.J.; Kunin, W.E.; Edwards, D.P. How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, R.; Lin, Q.; Hou, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, B.-P.; Naselli-Flores, L. Spatial structure and β-diversity of phytoplankton in Tibetan Plateau lakes: Nestedness or replacement? Hydrobiologia 2017, 808, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guareschi, S.; Abellan, P.; Laini, A.; Green, A.J.; Sanchez-Zapata, J.A.; Velasco, J.; Millan, A. Cross-taxon congruence in wetlands: Assessing the value of waterbirds as surrogates of macroinvertebrate biodiversity in Mediterranean Ramsar sites. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, N.; Legras, G.; Kulbicki, M.; Mérigot, B.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; Mazouni, N.; Galzin, R.; Gaertner, J. Multi-component β-diversity approach reveals conservation dilemma between species and functions of coral reef fishes. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 44, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rørslett, B. Principal determinants of aquatic macrophyte richness in northern European lakes. Aquat. Bot. 1991, 39, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.I.; Arnott, S.E.; Cottingham, C.L. The relationship in lake communities between primary productivity and species richness. Ecology 2000, 81, 2662–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.I.; Li, W.; Maberly, S.C. Area, altitude and aquatic plant diversity. Ecography 2003, 26, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahuhta, J.; Kosten, S.; Akasaka, M.; Auderset, D.; Azzella, M.M.; Bolpagni, R.; Bove, C.P.; Chambers, P.A.; Chappuis, E.; Clayton, J.; et al. Global variation in the beta diversity of lake macrophytes is driven by environmental heterogeneity rather than latitude. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, H.; Huttunen, P. Aquatic macrophytes and ecological gradients in 57 small lakes in southern Finland. Aquat. Bot. 1995, 51, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, C.D.; Brown, J.H. Fish species diversity in lakes. Am. Nat. 1974, 108, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, U.S.; Welcomme, R.L. An Analysis of Fish Species Richness in Natural Lakes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 65, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakou, E.; Bobori, D.C.; Kallimanis, A.S.; Mazaris, A.D.; Sgardelis, S.P.; Pantis, J.D. Freshwater fish community structured more by dispersal limitation than by environmental heterogeneity. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2009, 18, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Pédron, S.; Mehner, T.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Argillier, C.; Winfield, I.J.; Volta, P.; Emmrich, M.; Hesthagen, T.; Holmgren, K.; et al. Fish diversity in European lakes: Geographical factors dominate over anthropogenic pressures. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, J.M.; Keast, A. Resource heterogeneity and fish species diversity in lakes. Can. J. Zool. 1984, 62, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, O.; Sand-Jensen, K. Aquatic macrophyte richness in Danish lakes in relation to alkalinity, transparency, and lake area. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, T.; Jeppesen, E.; Declerck, S.A.J.; De Meester, L.; Conde-Porcuna, J.M.; Rommens, W.; Brucet, S. The importance of environmental variables for submerged macrophyte community assemblage and coverage in shallow lakes: Differences between northern and southern Europe. Hydrobiologia 2014, 744, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elo, M.; Alahuhta, J.; Kanninen, A.; Meissner, K.K.; Seppälä, K.; Mönkkönen, M. Environmental Characteristics and Anthropogenic Impact Jointly Modify Aquatic Macrophyte Species Diversity. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K.; Papastergiadou, E. Relationships between lake morphometry, water quality and aquatic macrophytes in Greek lakes. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar]
- Lacoul, P.; Freedman, B. Relationships between aquatic plants and environmental factors along a steep Himalayan altitudinal gradient. Aquat. Bot. 2006, 84, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuis, E.; Gacia, E.; Ballesteros, E. Environmental factors explaining the distribution and diversity of vascular aquatic macrophytes in a highly heterogeneous Mediterranean region. Aquat. Bot. 2014, 113, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Aláez, C.; Fernández-Aláez, M.; García-Criado, F.; García-Girón, J. Environmental drivers of aquatic macrophyte assemblages in ponds along an altitudinal gradient. Hydrobiologia 2016, 812, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrivnák, R.; Ot’Ahel’Ová, H.; Kochjarová, J.; Pal’Ove-Balang, P. Effect of environmental conditions on species composition of macrophytes—Study from two distinct biogeographical regions of Central Europe. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2013, 411, 09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, E.; Neubauer, T.A.; Harzhauser, M.; Kroh, A.; Mandic, O. Distribution patterns of European lacustrine gastropods—A result of environmental factors and deglaciation history. Hydrobiologia 2016, 775, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukács, B.A.; Vojtkó, A.E.; Mesterházy, A.; Molnar V., A. Süveges, K.; Végvári, Z.; Brusa, G.; Cerabolini, B.E.L. Growth-form and spatiality driving the functional difference of native and alien aquatic plants in Europe. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, P.A.; Lacoul, P.; Murphy, K.J.; Thomaz, S.M. Global diversity of aquatic macrophytes in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahuhta, J.; Lindholm, M.; Bove, C.; Chappuis, E.; Clayton, J.; De Winton, M.; Feldmann, T.; Ecke, F.; Gacia, E.; Grillas, P.; et al. Global patterns in the metacommunity structuring of lake macrophytes: Regional variations and driving factors. Oecologia 2018, 188, 1167–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radinger, J.; Wolter, C. Patterns and predictors of fish dispersal in rivers. Fish Fish. 2013, 15, 456–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahuhta, J.; Johnson, L.B.; Olker, J.; Heino, J. Species sorting determines variation in the community composition of common and rare macrophytes at various spatial extents. Ecol. Complex. 2014, 20, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Melo, A.S.; Jyrkänkallio-Mikkola, J.; Petsch, D.K.; Saito, V.S.; Tolonen, K.T.; Bini, L.M.; Landeiro, V.L.; Silva, T.S.F.; Pajunen, V.; et al. Subtropical streams harbour higher genus richness and lower abundance of insects compared to boreal streams, but scale matters. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleith, R.S.; Wehr, J.D.; Karol, K.G. Untangling climate and water chemistry to predict changes in freshwater macrophyte distributions. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 2802–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanidis, K.; Sarika, M.; Papastegiadou, E. Exploring environmental predictors of aquatic macrophytes in water-dependent Natura 2000 sites of high conservation value: Results from a long-term study of macrophytes in Greek lakes. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, J.; Heino, J.; Bini, L.M.; Padial, A.A. The strength of species sorting of phytoplankton communities is temporally variable in subtropical reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 2017, 800, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, T.; Levi, E.E.; Bezirci, G.; Özuluğ, M.; Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N.; Özcan, S.; Brucet, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Beklioğlu, M.; Çakıroğlu, A.I. Fish assemblage and diversity in lakes of western and central Turkey: Role of geo-climatic and other environmental variables. Hydrobiologia 2016, 771, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J. Are indicator groups and cross-taxon congruence useful for predicting biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems? Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Ouyang, S. Beta diversity patterns of fish and conservation implications in the Luoxiao Mountains, China. ZooKeys 2019, 817, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
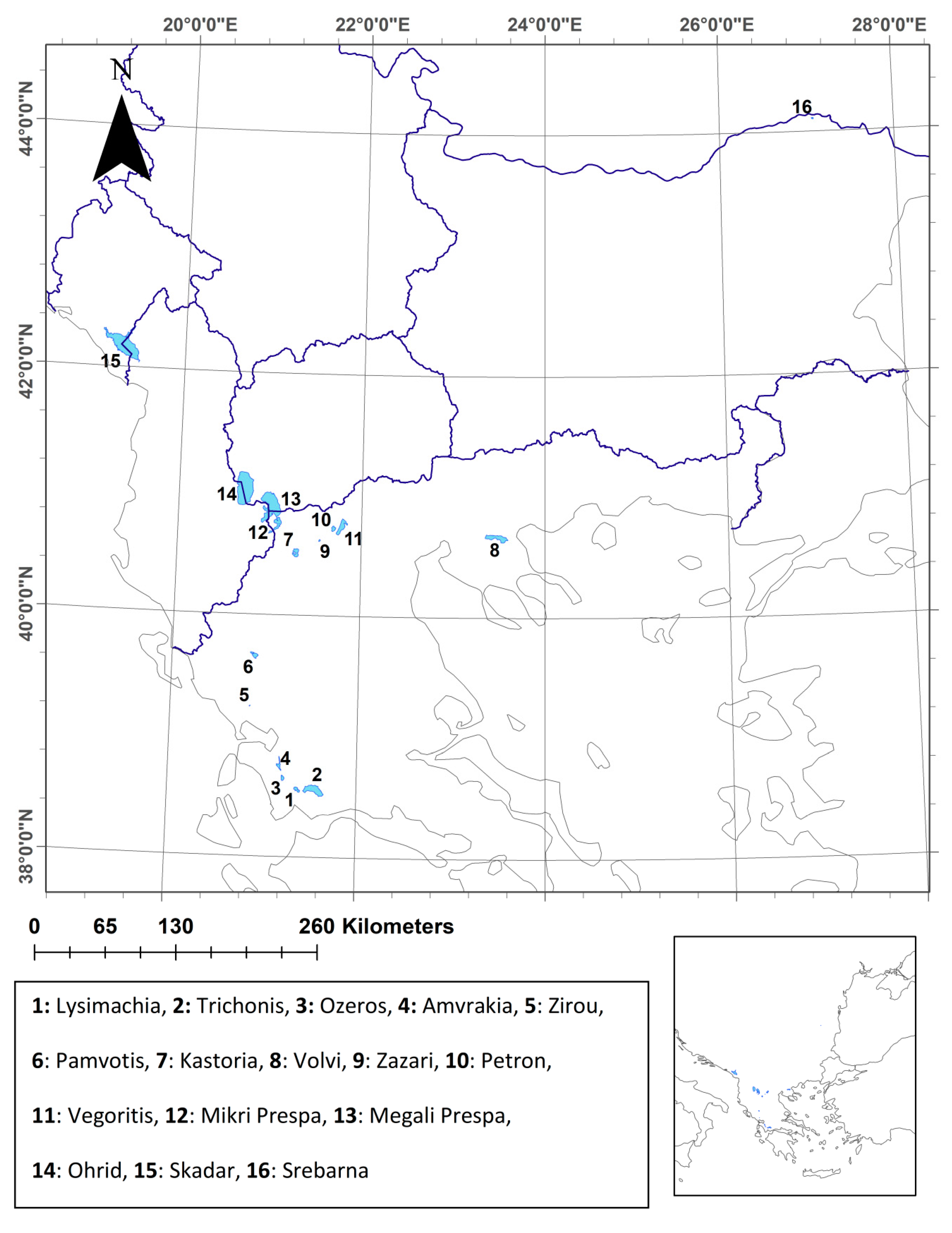
| Environmental Descriptor | Variable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat heterogeneity | Lake surface | The area of the surface of the lake (km2) |
| Fetch | The longest unbroken stretch of open water on a lake (km) | |
| Shoreline length | The lake perimeter/length of the shoreline of the lake (km) | |
| Shoreline development | The ratio of the shoreline length to the length of the circumference of a circle of area equal to that of the lake | |
| Maximum depth | The depth of the deepest point in the lake (m) | |
| Climate | Average monthly air temperature | Average monthly air temperature calculated by monthly air temperatures for 2017 (°C) |
| Maximum monthly air temperature | Maximum monthly air temperature of 2017 (°C) | |
| Minimum monthly air temperature | Minimum monthly air temperature of 2017 (°C) | |
| Rainfall | Annual rainfall (mm) | |
| Precipitation | Annual precipitation (rainfall and snowfall, mm) | |
| Altitude | Height of the lake location above sea level (m) | |
| Water quality | Conductivity | Average electrical conductivity (μS/cm) based on available measurements |
| pH | Average pH based on available measurements |
| Predictor | Estimate | Std. Error | Z Value | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macrophytes | ||||
| (Intercept) | −74.638 | 29.411 | −20.538 | * |
| Altitude | 0.2810 | 0.1036 | 2.714 | ** |
| Surface | 0.4878 | 0.1267 | 3.851 | *** |
| pH | 97.756 | 32.260 | 3.030 | ** |
| Residual deviance: 14.041 | ||||
| Fish | ||||
| (Intercept) | 20.357 | 0.2482 | 8.202 | *** |
| Altitude | −0.5151 | 0.1133 | −4.548 | *** |
| Shoreline development | 0.8385 | 0.1513 | 5.540 | *** |
| Surface | 0.6423 | 0.1673 | 3.838 | *** |
| Residual deviance: 7.6345 | ||||
| Biota | Component | Min | 1st Qu | Median | Mean | 3rd Qu | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macrophytes | βSør | 0.152 | 0.470 | 0.600 | 0.601 | 0.738 | 1.000 |
| βSim | 0.000 | 0.222 | 0.333 | 0.371 | 0.500 | 1.000 | |
| βNes | 0.000 | 0.095 | 0.186 | 0.230 | 0.326 | 0.771 | |
| Fish | βSør | 0.000 | 0.875 | 1.000 | 0.881 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| βSim | 0.000 | 0.778 | 1.000 | 0.824 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
| βNes | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.056 | 0.056 | 0.444 |
| Macrophytes | Null Deviance | GDM Deviance | %Deviance Explained | Variables | Coefficients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| βSør | 16.489 | 10.462 | 36.547 | Geographical distance | 1.103 |
| βSim | 24.438 | 19.057 | 22.019 | Conductivity | 0.311 |
| Geographical distance | 0.559 | ||||
| βNes | 21.163 | 19.462 | 8.032 | Altitude | 0.170 |
| Geographical distance | 0.095 | ||||
| Fish | |||||
| βSør | 51.272 | 45.680 | 10.910 | Altitude | 2.245 |
| Geographical distance | 0.796 | ||||
| βSim | 72.574 | 65.983 | 9.082 | Altitude | 1.931 |
| Geographical distance | 0.158 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oikonomou, A.; Stefanidis, K. α- and β-Diversity Patterns of Macrophytes and Freshwater Fishes are Driven by Different Factors and Processes in Lakes of the Unexplored Southern Balkan Biodiversity Hotspot. Water 2020, 12, 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071984
Oikonomou A, Stefanidis K. α- and β-Diversity Patterns of Macrophytes and Freshwater Fishes are Driven by Different Factors and Processes in Lakes of the Unexplored Southern Balkan Biodiversity Hotspot. Water. 2020; 12(7):1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071984
Chicago/Turabian StyleOikonomou, Anthi, and Konstantinos Stefanidis. 2020. "α- and β-Diversity Patterns of Macrophytes and Freshwater Fishes are Driven by Different Factors and Processes in Lakes of the Unexplored Southern Balkan Biodiversity Hotspot" Water 12, no. 7: 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071984
APA StyleOikonomou, A., & Stefanidis, K. (2020). α- and β-Diversity Patterns of Macrophytes and Freshwater Fishes are Driven by Different Factors and Processes in Lakes of the Unexplored Southern Balkan Biodiversity Hotspot. Water, 12(7), 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071984






