Riparian Ground Beetles (Coleoptera) on the Banks of Running and Standing Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
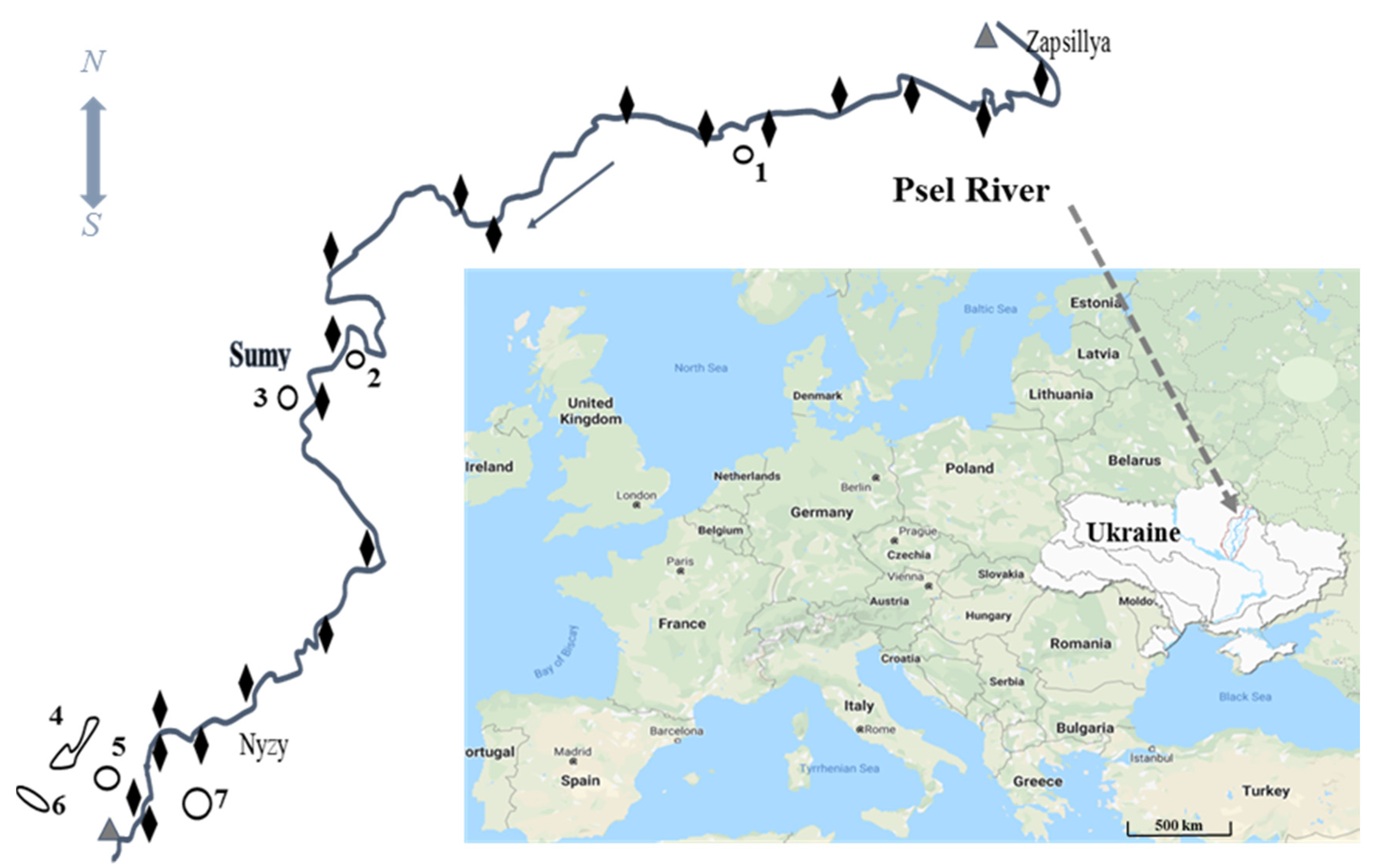
2.1. Study Area
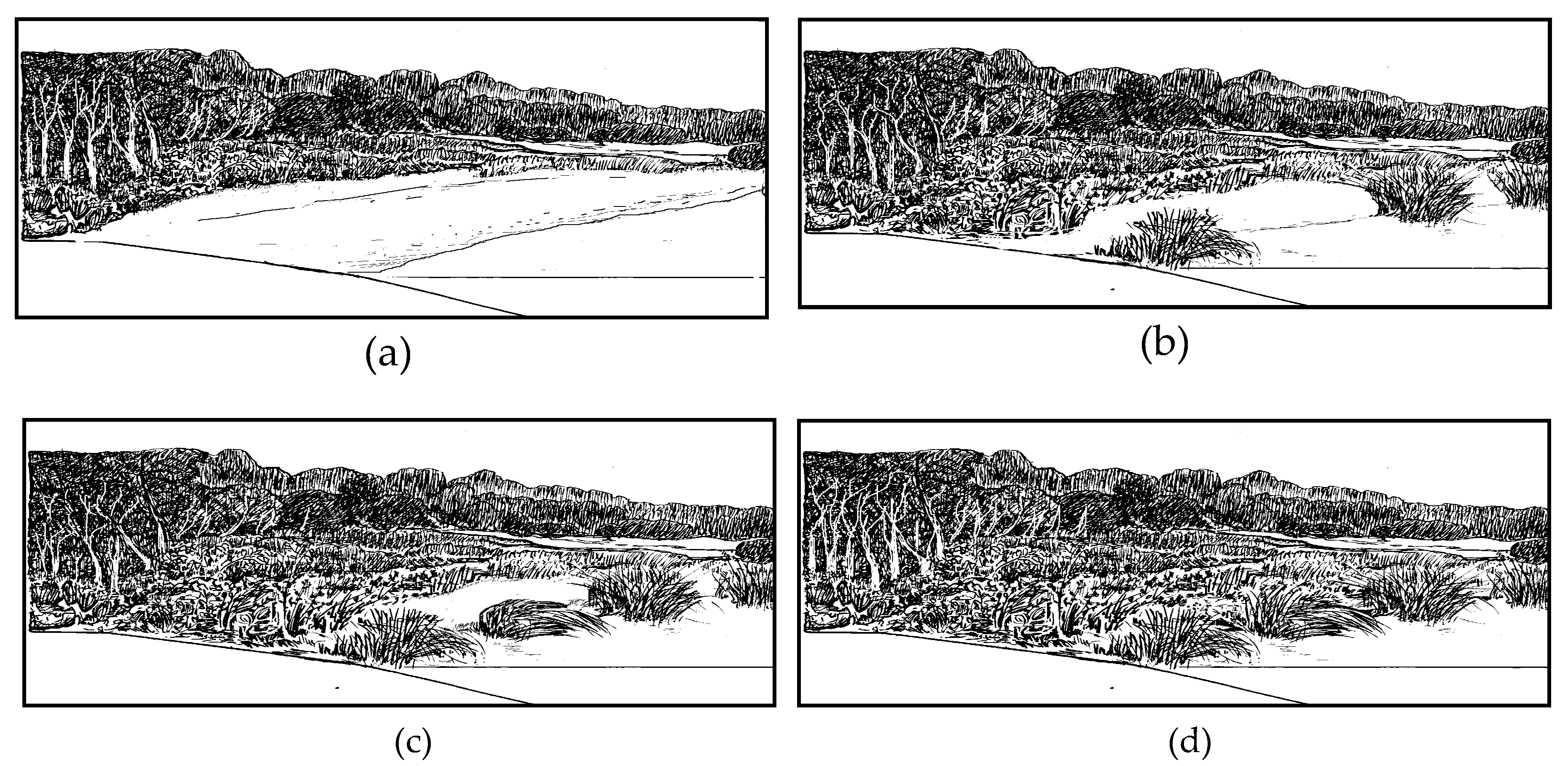
2.2. Sampling Methods
2.3. Data Analysis
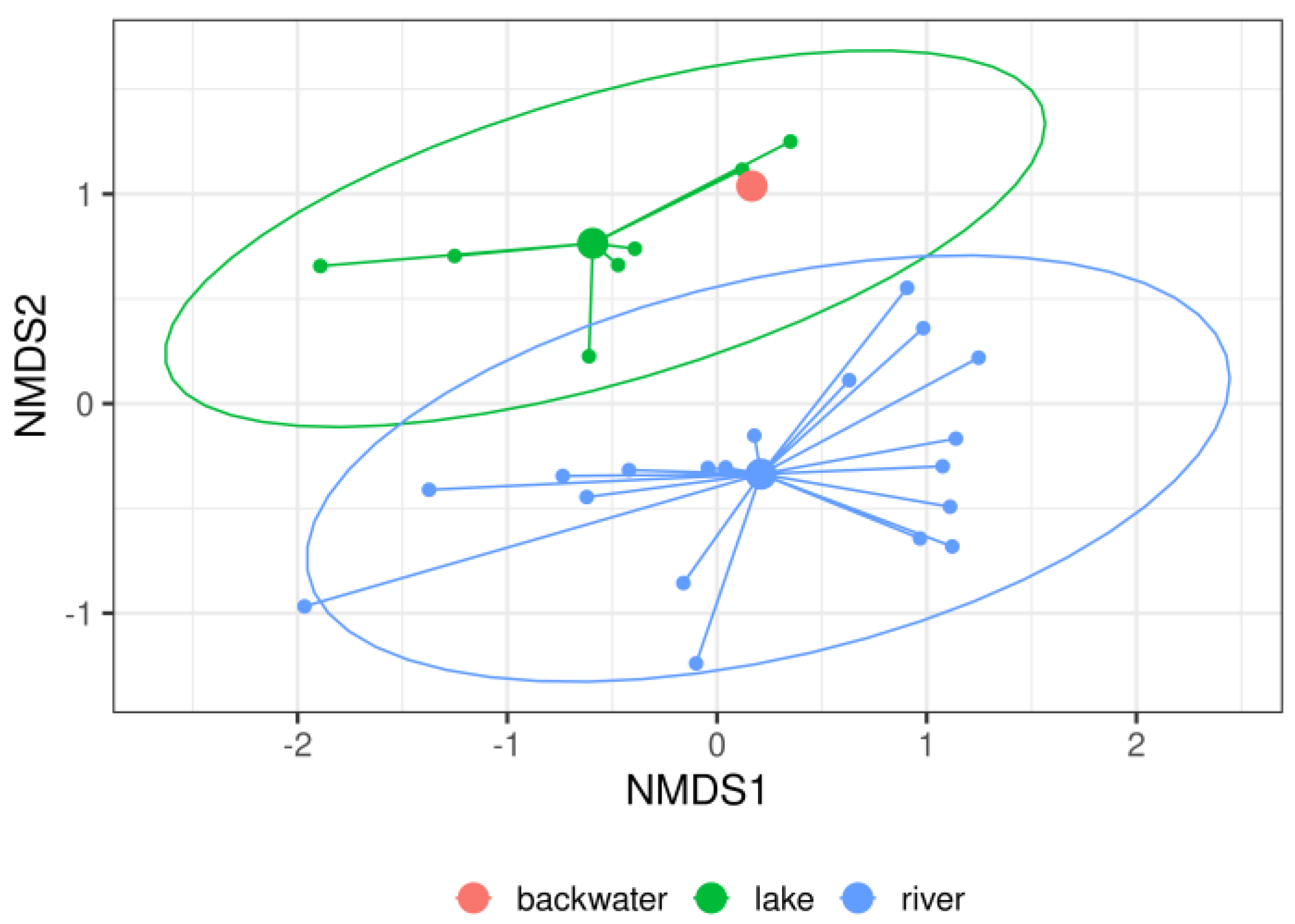
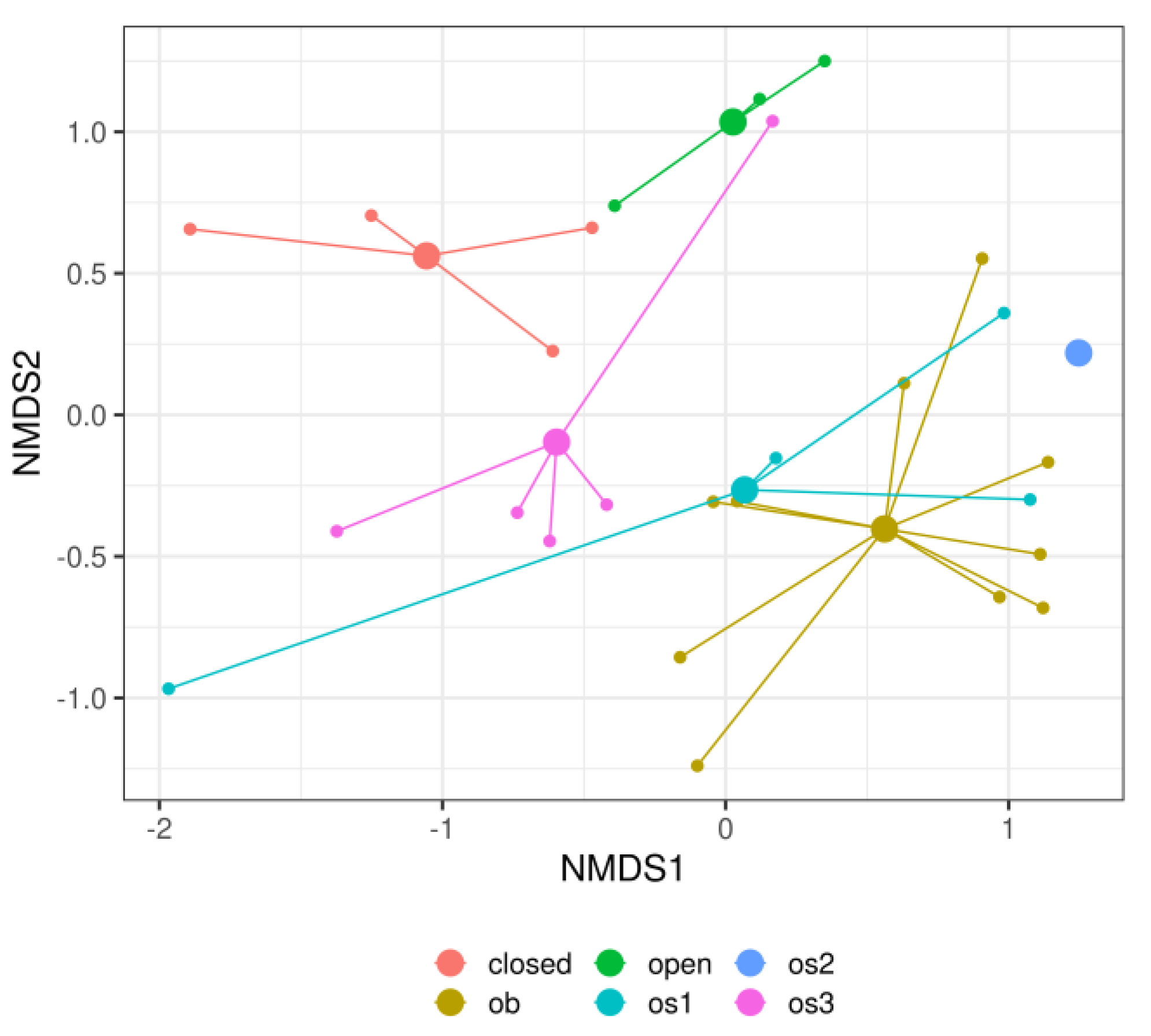
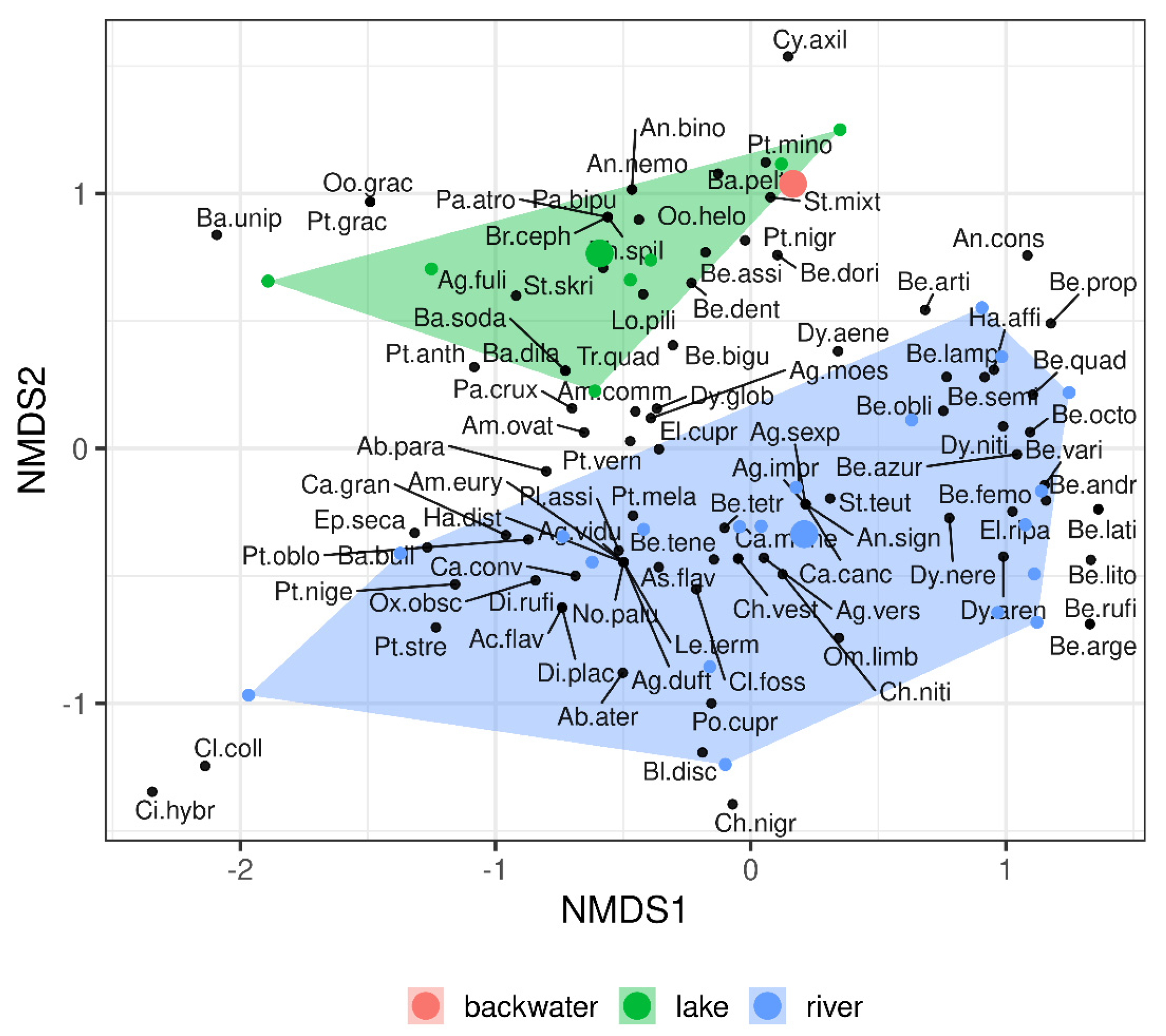
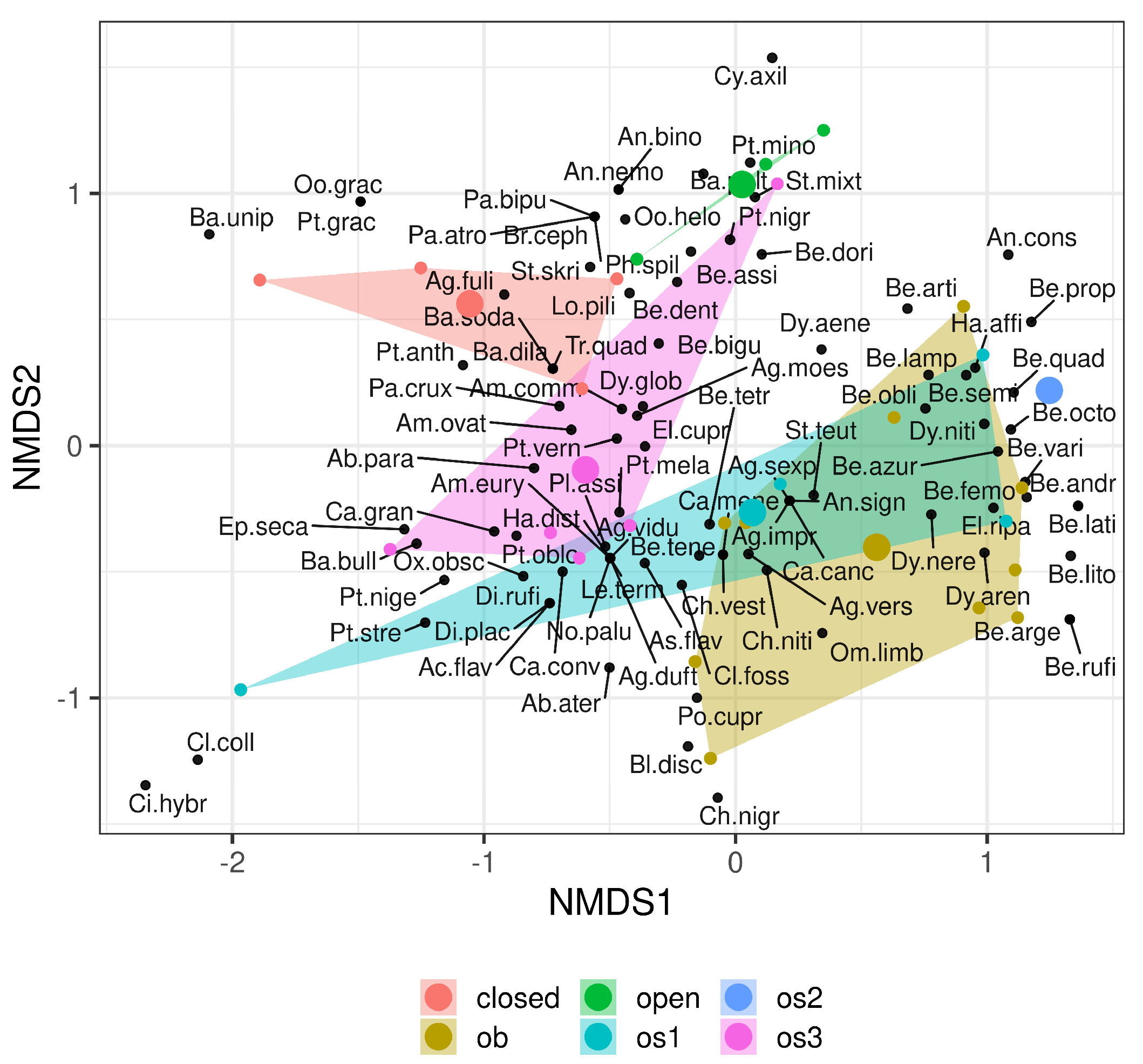
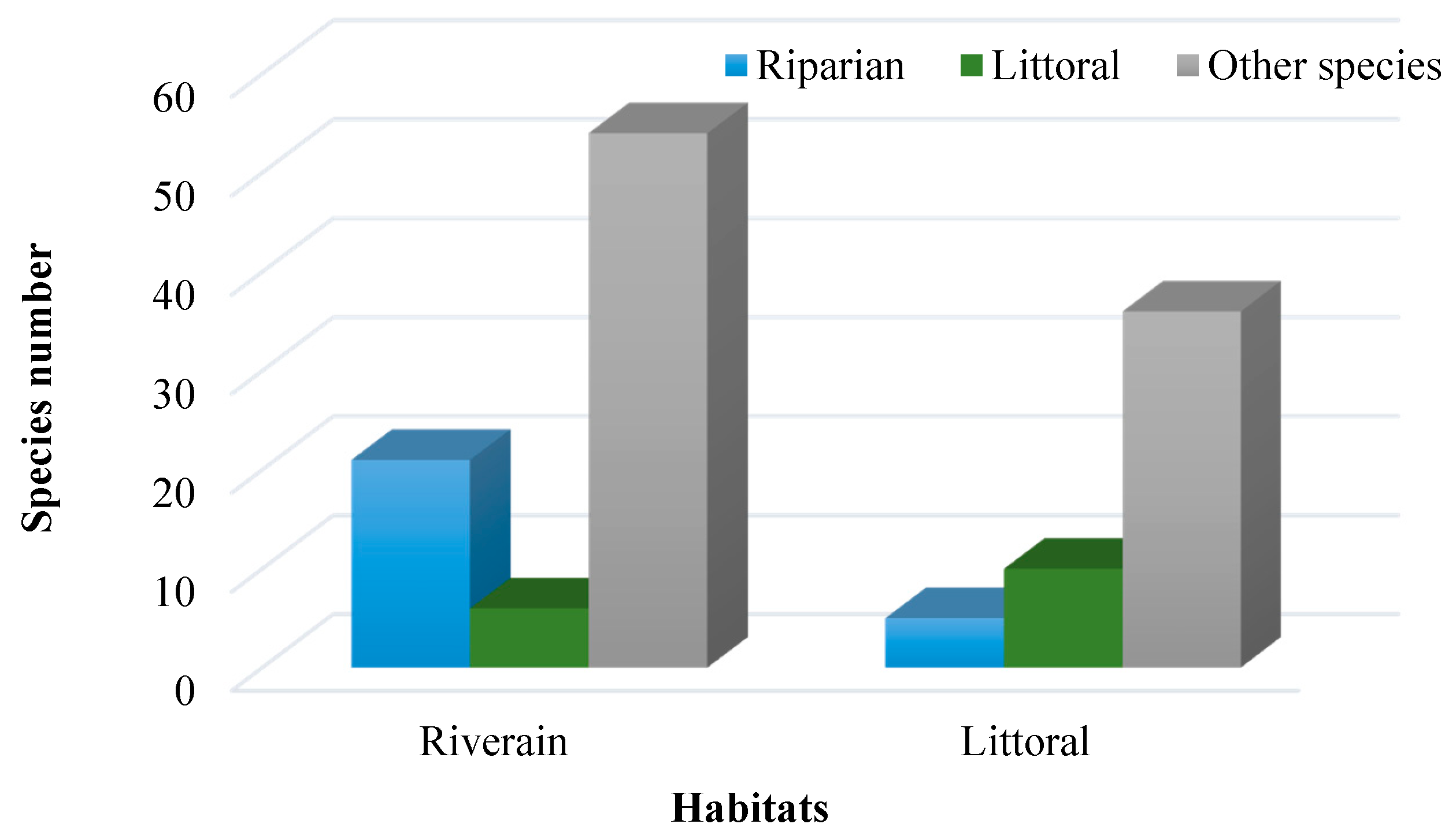
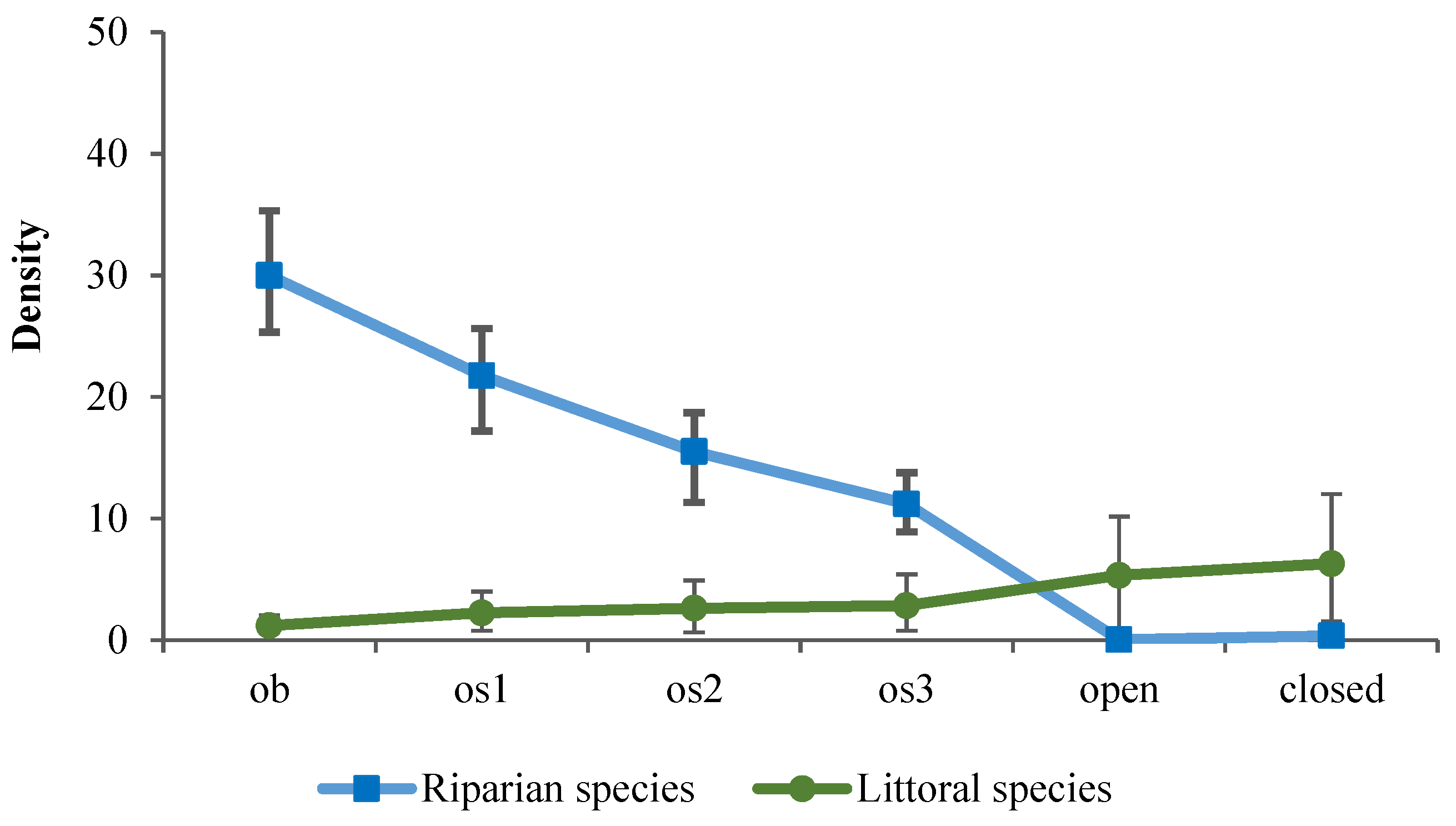
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petts, G.E.; Amoros, C. (Eds.) Fluvial Hydrosystems; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D.T.; Tockner, K.; Wad, J.V. The fauna of dynamic riverine landscapes. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V. Riverine landscapes: Biodiversity patterns, disturbance regimes, and aquatic conservation. Biol. Conserv. 1998, 83, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Décamps, H.; McClain, M.E. Riparia: Ecology, Conservation, and Management of Streamside Communities; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sabo, J.L.; Sponseller, R.; Dixon, M.; Gade, K.; Harms, T.; Heffernan, J.; Jani, A.; Katz, G.; Soykan, C.; Watts, J.; et al. Riparian zones increase regional species richness by harboring different, not more, species. Ecology 2005, 86, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNECE. River Convention. In Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes; Vlaams Parlement, Stuk 263 (No. 1); United Nations Economic Commission for Europe Geneva: Genève, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K.; Schiemer, F. Biodiversity of floodplain river ecosystems: Ecotones and connectivity. Regul. Rivers Res. Mgmt. 1999, 15, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscaini, A.; Franceschini, A.; Maiolini, B. River ecotones: Carabid beetles as a tool for quality assessment. Hydrobiologia 2000, 422, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Décamps, H. (Eds.) The Ecology and Management of Aquatic Terrestrial Ecotones; Pearl River: New York, NY, USA; Parthenon, Greece, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.V.; Wiens, J.A. Ecotones of riverine ecosystems: Role and typology, spatio-temporal dynamics, and river regulation. In Fish and Land/Inland Water Ecotones—The Need for Integration of Fisheries Science, Limnology and Landscape Ecology; Zalewski, M., Thorpe, J.E., Schiemer, F., Eds.; Pearl River: New York, NY, USA; Parthenon, Greece, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger, A.; Mac Nally, R.; Lake, P.S. Immediate and longer-term effects of managed flooding on floodplain invertebrate assemblages is south-eastern Australia: Generation and maintenance of a mosaic landscape. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1190–12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, J.A.; Lorang, M.S.; Hauer, F.R. The shifting habitat mosaic of river ecosystems. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 2005, 29, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Platcher, H. Riparian ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) preying on aquatic invertebrates: A feeding strategy in alpine floodplains. Oecologia 1997, 111, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, I.L.; Power, M.E. River-Watershed Exchange: Effects of Riverine Subsidies on Riparian Lizards and Their Terrestrial Prey. Ecology 2002, 83, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paetzold, A.; Schubert, C.J.; Tockner, K. Aquatic-terrestrial linkages along a braided –river: Riparian arthropods feeding on aquatic insects. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähnig, S.C.; Brunzel, S.; Gacek, S.; Lorenz, A.W.; Hering, D. Effects of re-braiding measures on hydromorphology, floodplain vegetation, ground beetles and benthic invertebrates in mountain rivers. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonn, A.; Kleinwächter, M. Microhabitat distribution of spider and ground beetle assemblages (Araneae, Carabidae) on frequently inundated river banks of the River Elbe. Z. Ökolgie Nat. 1999, 8, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Manderbach, R.; Hering, D. Typology of riparian ground beetle communities (Coleoptera, Carabidae, Bembidion spec.) in Central Europe and adjacent areas. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2001, 152, 583–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeets, K.; Lewylle, I.; Bonte, D.; Maelfait, J.-P. The spider fauna (Aranea) from gravel banks along the Common Meuse: Riparian assemblages and species conservation. Nieuwsbr. Belg. Arachnol. Ver. 2007, 22, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, J.; Hanssen, O. Riparian beetles, a unique, but vulnerable element in the fauna of Fennoscandia. Biodivers. Conserv. 2005, 14, 3497–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, M.D.; Lott, D.A. Invertebrates of Exposed Riverine Sediments; R&D Technical Report Wll; National Rivers Authority: Marlow, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Manderbach, R.; Reich, M. Auswirkungen großer Querbauwerke auf die Laufkäferzönosen (Coleoptera, Carabidae) von Umlagerungsstrecken der Oberen Isar. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 1995, 101, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, S.; Reich, M.; Plachter, H. Ground beetle communities (Coleoptera: Carabidae) on the banks of two rivers in the eastern Carpathians, the Ukraine. Verhandl. Gesellsch. Ökol. 1997, 27, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Marggi, W.A. Faunistik der Sandlaukäfer und Laukäfer der Schweiz (Cicindelidae and Carabidae) Coleoptera. Teil 1/Text. Doc. Faun. Helv. 1992, 13, 463. [Google Scholar]
- Trautner, J.; Müller-Motzfeld, G.; Bräunicke, M. Rote Liste der Sandlaufkäfer und und Laukäfer Deutschlands (Coleoptera: Cicindelidae et Carabidae). 2. Fassung. Stand Dezember. Nat. Landsch. 1996, 29, 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bräunicke, M.; Trautner, J. Die Ahlenläufer-Arten der Bembidion-Untergattungen Bracteon und Odontonium—Verbreitung, Bestandssituation, Habitate und Gefährdung charakteristischer Flussaue-Arten in Deutschland. Angewande Carabidol. Suppl. 1999, 1, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, J.P.; Bell, D.; Fowles, A. The hydroecological controls and conservation value of beetles on exposed riverine sediments in England and Wales. Biol. Cons. 2004, 118, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, M. Methods and preliminary results from a study on the habitat functions of the gravel bar interior in alluvial floodplains. Verhandl. Gesellsch. Ökol. 1996, 26, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Antvogel, H.; Bonn, A. Environmental parameters and microspatial distribution of insects: A case study of carabids in an alluvial forest. Ecography 2001, 24, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adis, J.; Junk, W.J. Terrestrial invertebrates inhabiting lowland river floodplains of Central Amazonia and Central Europe: A review. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonn, A.; Hagen, K.; Wohlgemuth-von Reiche, D. The significanse of flood regimes for carabid beetle and spider communities in riparian habitats–a comparison of three major rivers in Germany. River Res. Appl. 2002, 18, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerisch, M.; Schanowski, A.; Figura, W.; Gerken, B.; Dziock, F.; Henle, K. Carabid beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) as indicators of hydrological site conditions in floodplain grasslands. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2006, 91, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, M.; Fontaneto, D. Biodiversity of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in different habitats of the Italian Po lowland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 127, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.; Poff, N. Adaptation to natural flow regimes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, A.J.; Sadler, J.P.; Fowles, A.P. Condition-dependent dispersal of a patchily distributed riparian ground beetle in response to disturbance. Oecologia 2006, 150, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeets, K.; Vandegehuchte, M.; Maelfait, J.-P.; Bonte, D. Understanding the impact of flooding on trait-displacements and shifts in assemblage structure of predatory arthropods on river banks. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paetzold, A.; Yoshimura, C.; Tockner, K. Riparian arthropod responses to flow regulation and river channelization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, D. Ground beetles and rove beetles be associated with temporary ponds in England. Freshw. Forum 2001, 17, 40–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gunter, J.; Assmann, T. Restoration ecology meets carabidology: Effects of floodplain restitution on ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Biodivers. Conserv. 2005, 14, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, M.B.; Babko, R.V. Assemblages of ground beetles in the riverside reservoirs of Kyiv. In Ecological State of the Reservoirs of Kyiv; Phytocenter: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2005; pp. 68–74. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Brauns, M.; Garcia, X.; Pusch, M.T. Potential effects of water-level fluctuations on littoral invertebrates in lowland lakes. Hydrobiologia 2008, 613, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šustek, Z. Succession of carabid communities in different types of reed stands in Central Europe. Oltenia. Stud. Comunicări Ştiinţele Nat. 2010, 26, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kirichenko, M.B. The Carabid Fauna (Coleoptera, Carabidae) of the River Banks, Lakes Shores and Marshes of the Forest and Forest-Steppe of Eastern Part of the Ukraine. Ph.D. Thesis, Schmalhausen Institute of Zoology NAS of Ukraine, Kiev, Ukraine, 1999. (In Ukrainian). [Google Scholar]
- Hůrka, K. Carabidae of the Czech and Slovak Republics; Kabourek: Zlín, Czech Republic, 1996; 565p. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorenko, D. Reclassification of World Dyschiriini with a Revision of the Palearctic Fauna (Coleoptea, Carabidae); Pensoft, Sofia, Moscow & ST: Sofia, Petersburg, 1996; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- Eyre, M.D.; Luff, M.L.; Phillips, D.A. The ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) of exposed riverine sediments in Scotland and northern England. Biodivers. Conserv. 2001, 10, 403–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, R.H.G.; Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Van Tongeren, O.F.R. Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Beals, M.L. Understanding community structure: A data-driven multivariate approach. Oecologia 2006, 150, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, R.N. The analysis of proximities: Multidimensional scaling with an unknown distance function. I. Psychometrica 1962, 27, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrica 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Williams, W.P.; Bark, A.W. Similarity measure bias in river benthic Aufwuchs community analysis. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountford, M.D. An index of similarity and its application to classification problems. In Progress in Soil Zoology; Butterworths: London, UK, 1962; pp. 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Faith, D.P.; Minchin, P.R.; Belbin, L. Compositional dissimilarity as a robust measure of ecological distance. Vegetatio 1987, 69, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.M.; Yang, M.S.; Hung, W.L. New similarity measures of intuitionistic fuzzy sets based on the Jaccard index with its application to clustering. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2018, 33, 1672–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, J.; Mou, X.X.; Xu, B.D.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Ren, Y.P. Interannual changes in fish community structure in the northern part of the coastal waters of Jiangsu Province, China in spring. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.4-6. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 13 September 2019).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, B. Flood Pulsing and Disturbance Dynamics; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Junk, W.J. Flood pulsing and linkages between terrestrial, aquatic, and wetland systems. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 2005, 29, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Tockner, K. Biodiversity: Towards a unifying theme for river ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerken, B.; Dörfer, K.; Buschmann, M.; Kamps-Schwob, S.; Berthelmann, J.; Gertenbach, D. Composition and distribution of carabid communities along rivers and ponds in the region of Upper Were (NW/NDS/FRG) with respect to protection and management of a floodplain ecosystem. Reg. Riv. Res Mngm. 1991, 6, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshall, S.E.; Sadler, J.P.; Hannah, D.M.; Bates, A.J. The role of microhabitat and food availability in determining riparian invertebrate distributions on gravel bars: A habitat manipulation experiment. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, A.; Bonacci, T.; Zetto, T.; Brandmayr, P. La carabidofauna dell’ecotopo fluviale del crati (Cosenza, Italia) (Coleoptera Carabidae). Nat. Sicil. 2010, 34, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Naiman, R.J.; Décamps, H. The ecology of interfaces: Riparian zones. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 621–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K.; Arscott, D.B.; Claret, C. Riverine landscape diversity. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 517–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J. Ecomorphological adaptations of Riparian Bembidiini species (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Ecol. Generalis 1985, 11, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desender, K.; Turin, H. Loss of habitats and changes in the composition of the ground and tiger beetle fauna in four west European countries since 1950 (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Biol. Conserv. 1989, 48, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desender, K. Ecomorphological adaptations of riparian carabid beetles. In Verhandelingen Van Het Symposium ‘Invertebraten Van België’; Royal Institute of Natural Sciences: Brussels, Belgium, 1989; pp. 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Desender, K.; Maelfait, J.-P.; Stevens, J.; Allemeersch, L. Loopkevers langs de Grensmaas (carabid beetles along the Common Meuse). Jaarb. LIKONA 1993, 3, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Van Looy, K.; Vanacker, S.; Jochems, H.; de Blust, G.; Dufrêne, M. Ground beetle habitat templets and riverbank integrity. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachertz, H.; Januschke, K.; Hering, D. The role of large-scale descriptors and morphological status in shaping ground beetle (Carabidae) assemblages of floodplains in Germany. Ecol. Indicat. 2019, 103, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C. Conservation management of riparian communities. In Ecological Principles of Nature Conservation; Hansson, L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 352–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.V.; Stanford, J.A. Ecological connectivity in alluvial river ecosystems and its disruption by flow regulation. Reg. Rivers Res. Mgmt. 1995, 11, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, M.; Babko, R. The spatial population distribution of Omophron limbatum Fabricius 1777 (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the condition of regulated rivers. Teka Kom. Ochr. Kszt. Srod. Przyr. 2009, 6, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Januschke, K.; Brunzel, S.; Haase, P.; Hering, D. Effects of stream restorations on riparian mesohabitats, vegetation and carabid beetles. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 3147–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, M.; Łagód, G.; Majerek, D.; Franus, M.; Babko, R. The effect of landscape on the diversity in urban green areas. Ecol Chem Eng S 2017, 24, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species and Their Codes | River Banks | Shores of Lakes | Habitat Requirements | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Bars | Stages 1–3, Backwaters | Open | Closed | |||
| Agonum impressum | Ag.impr | - | 100 | - | - | rip |
| Asaphidion flavipes | As.flav | 22.1 | 77.4 | - | 0.5 | rip |
| Bembidion argenteolum | Be.arge | 100 | - | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion azurescens | Be.azur | 55.7 | 44.3 | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion cruciatum | Be.andr | 100 | - | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion femoratum | Be.femo | 86.8 | 13.2 | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion laticolle | Be.lati | 100 | - | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion litorale | Be.lito | 96.5 | 3.5 | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion ruficolle | Be.rufi | 100 | - | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion semipunctatum | Be.semi | 66.7 | 33.3 | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion tenellum | Be.tene | 25.0 | 75.0 | - | - | rip |
| Bembidion tetracolum | Be.tetr | 43.4 | 54.1 | - | 2.4 | rip |
| Bembidion varium | Be.vari | 73.1 | 27.7 | - | 0.9 | rip |
| Chlaenius nitidulus | Ch.niti | 43. | 57 | - | - | rip |
| Cicindela hybrida | Ci.hybr | - | 100 | - | - | rip |
| Dyschirius aeneus | Dy.aene | 7.3 | 53.3 | 39.5 | - | rip |
| Dyschirius arenosus | Dy.aren | 82.5 | 16.7 | - | 0.8 | rip |
| Dyschirius neresheimeri | Dy.nere | 100 | - | - | - | rip |
| Dyschirius nitidus | Dy.niti | 72.7 | 27.3 | - | - | rip |
| Elaphrus riparius | El.ripa | 75.6 | 24.4 | - | - | rip |
| Omophron limbatum | Om.limb | 65.4 | 34.6 | - | - | rip |
| Badister dilatatus | Ba.dila | - | - | - | 100 | lit |
| Badister peltatus | Ba.pelt | - | 47.3 | 29.5 | 23.2 | lit |
| Badister sodalis | Ba.soda | - | - | - | 100 | lit |
| Bembidion assimile | Be.assi | 1.1 | 7.1 | 85.6 | 6.1 | lit |
| Bembidion biguttatum | Be.bigu | 0.7 | 6.7 | - | 92.6 | lit |
| Bembidion dentellum | Be.dent | 10.6 | 9.2 | - | 80.2 | lit |
| Bembidion doris | Be.dori | 11.4 | 13.6 | 49.2 | 25.8 | lit |
| Elaphrus cupreus | El.cupr | 9.2 | 6.9 | 20.6 | 63.3 | lit |
| Philorhizus spilotus | Ph.spil | - | - | - | 100 | lit |
| Stenolophus skrimshiranus | St.skri | - | - | 66.7 | 33.3 | lit |
| Abax parallelopipedus | Ab.ater | - | 59.0 | - | 41.0 | |
| Abax parallelus | Ab.para | - | 19.4 | - | 80.6 | |
| Acupalpus flavicollis | Ac.flav | 31.0 | 69.0 | - | - | |
| Agonum duftschmidi | Ag.duft | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Agonum fuliginosum | Ag.fuli | 1.8 | 2.3 | 19.2 | 76.7 | |
| Agonum moestum | Ag.moes | - | 23.1 | - | 76.9 | |
| Agonum sexpunctatum | Ag.sexp | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Agonum versutum | Ag.vers | 100 | - | - | - | |
| Agonum viduum | Ag.vidu | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Amara communis | Am.comm | - | 48.7 | 51.3 | - | |
| Amara eurynota | Am.eury | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Amara ovata | Am.ovat | - | 21.1 | - | 78.9 | |
| Anisodactylus binotatus | An.bino | - | - | 100 | - | |
| Anisodactylus nemorivagus | An.nemo | - | - | 100 | - | |
| Anisodactylus signatus | An.sign | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Anthracus consputus | An.cons | 47.8 | 52.2 | - | - | |
| Badister bullatus | Ba.bull | - | 62.7 | - | 37.3 | |
| Badister unipustulatus | Ba.unip | - | - | - | 100 | |
| Bembidion articulatum | Be.arti | 45.1 | 30.3 | 23.8 | 0.7 | |
| Bembidion lampros | Be.lamp | 33.9 | 66.1 | - | - | |
| Bembidion octomaculatum | Be.octo | 26.4 | 73.6 | - | - | |
| Bembidion obliquum | Be.obli | 100 | - | - | - | |
| Bembidion properans | Be.prop | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Bembidion quadrimaculatum | Be.quad | 23.5 | 76.5 | - | - | |
| Blemus discus | Bl.disc | 37.2 | 62.8 | - | - | |
| Broscus cephalotes | Br.ceph | - | - | - | 100 | |
| Carabus cancellatus | Ca.canc | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Carabus convexus | Ca.conv | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Carabus granulatus | Ca.gran | - | 51.6 | 13.3 | 35.1 | |
| Carabus menetriesi | Ca.mene | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Chlaenius nigricornis | Ch.nigr | 89.6 | 10.4 | - | - | |
| Chlaenius vestitus | Ch.vest | 34.7 | 65.3 | - | - | |
| Clivina collaris | Cl.coll | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Clivina fossor | Cl.foss | 41.1 | 38.4 | - | 20.5 | |
| Cymindis axillaris | Cy.axil | - | - | 100 | - | |
| Dyschiriodes globosus | Dy.glob | 23.0 | 23.5 | 6.0 | 47.6 | |
| Epaphius secalis | Ep.seca | 2.0 | 10.9 | - | 87.1 | |
| Harpalus affinis | Ha.affi | 50 | 50 | - | - | |
| Harpalus distinguendus | Ha.dist | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Leistus terminatus | Le.term | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Loricera pilicornis | Lo.pili | - | 18.0 | 51.3 | 30.8 | |
| Notiophilus palustris | No.palu | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Oodes gracilis | Oo.grac | - | - | - | 100 | |
| Oodes helopioides | Oo.helo | 1.0 | 8.3 | 70.3 | 20.4 | |
| Oxypselaphus obscurum | Ox.obsc | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Panagaeus bipustulatus | Pa.bipu | - | - | - | 100 | |
| Panagaeus cruxmajor | Pa.crux | - | 30.9 | 27.6 | 41.4 | |
| Patrobus atrorufus | Pa.atro | - | - | - | 100 | |
| Poecilus cupreus | Po.cupr | 100 | - | - | - | |
| Platynus assimile | Pl.assi | 4.4 | 64.0 | 3.5 | 32.5 | |
| Pterostichus anthracinus | Pt.anth | 8.9 | 23.0 | 14.7 | 53.4 | |
| Pterostichus gracilis | Pt.grac | - | - | - | 100 | |
| Pterostichus melanarius | Pt.mela | - | 69.2 | - | 30.8 | |
| Pterostichus minor | Pt.mino | 5.0 | 17.0 | 52.6 | 25.3 | |
| Pterostichus niger | Pt.nige | 1.7 | 98.3 | - | - | |
| Pterostichus nigrita | Pt.nigr | 1.4 | 17.2 | 32.4 | 50.0 | |
| Pterostichus oblongopunctatus | Pt.oblo | 1.8 | 59.4 | - | 39.8 | |
| Pterostichus strenuus | Pt.stre | 5.8 | 72.6 | - | 21.6 | |
| Pterostichus vernalis | Pt.vern | - | 15.6 | - | 84.4 | |
| Stenolophus mixtus | St.mixt | 11.2 | 13.8 | 75.0 | - | |
| Stenolophus teutonus | St.teut | 54.5 | - | - | 45.5 | |
| Trechus quadristriatus | Tr.quad | - | - | - | 100 | |
| Trichocellus placidus | Di.plac | - | 100 | - | - | |
| Trichocellus rufithorax | Di.rufi | - | 100 | - | - | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirichenko-Babko, M.; Danko, Y.; Franus, M.; Stępniewski, W.; Babko, R. Riparian Ground Beetles (Coleoptera) on the Banks of Running and Standing Waters. Water 2020, 12, 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061785
Kirichenko-Babko M, Danko Y, Franus M, Stępniewski W, Babko R. Riparian Ground Beetles (Coleoptera) on the Banks of Running and Standing Waters. Water. 2020; 12(6):1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061785
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirichenko-Babko, Marina, Yaroslav Danko, Małgorzata Franus, Witold Stępniewski, and Roman Babko. 2020. "Riparian Ground Beetles (Coleoptera) on the Banks of Running and Standing Waters" Water 12, no. 6: 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061785
APA StyleKirichenko-Babko, M., Danko, Y., Franus, M., Stępniewski, W., & Babko, R. (2020). Riparian Ground Beetles (Coleoptera) on the Banks of Running and Standing Waters. Water, 12(6), 1785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061785






