Establishing a Smart Farm-Scale Piggery Wastewater Treatment System with the Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
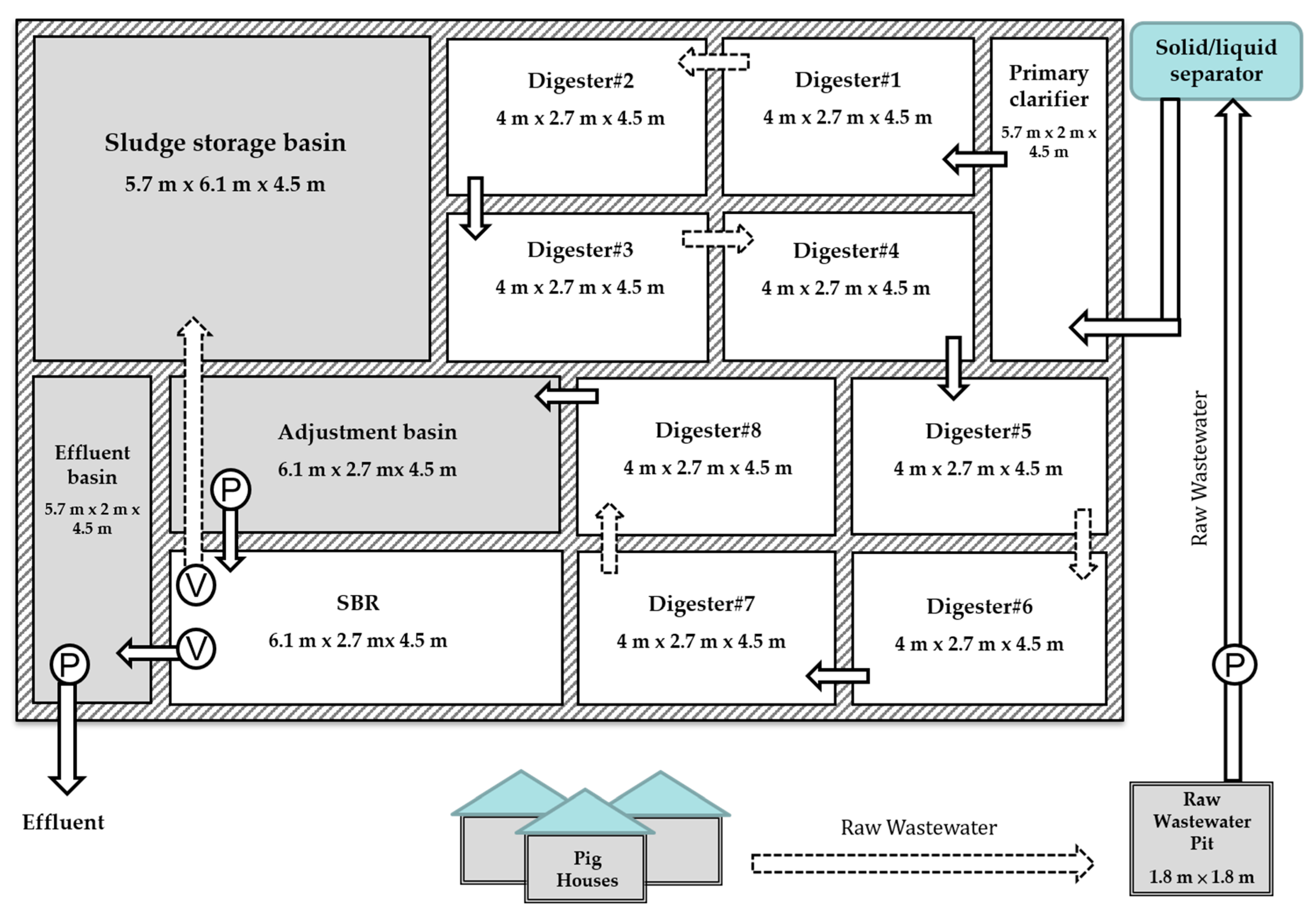
2.1. Design of a Piggery Wastewater Treatment System on a Selected Pig Farm
2.2. Automatic Control Mode of Piggery Wastewater Treatment System
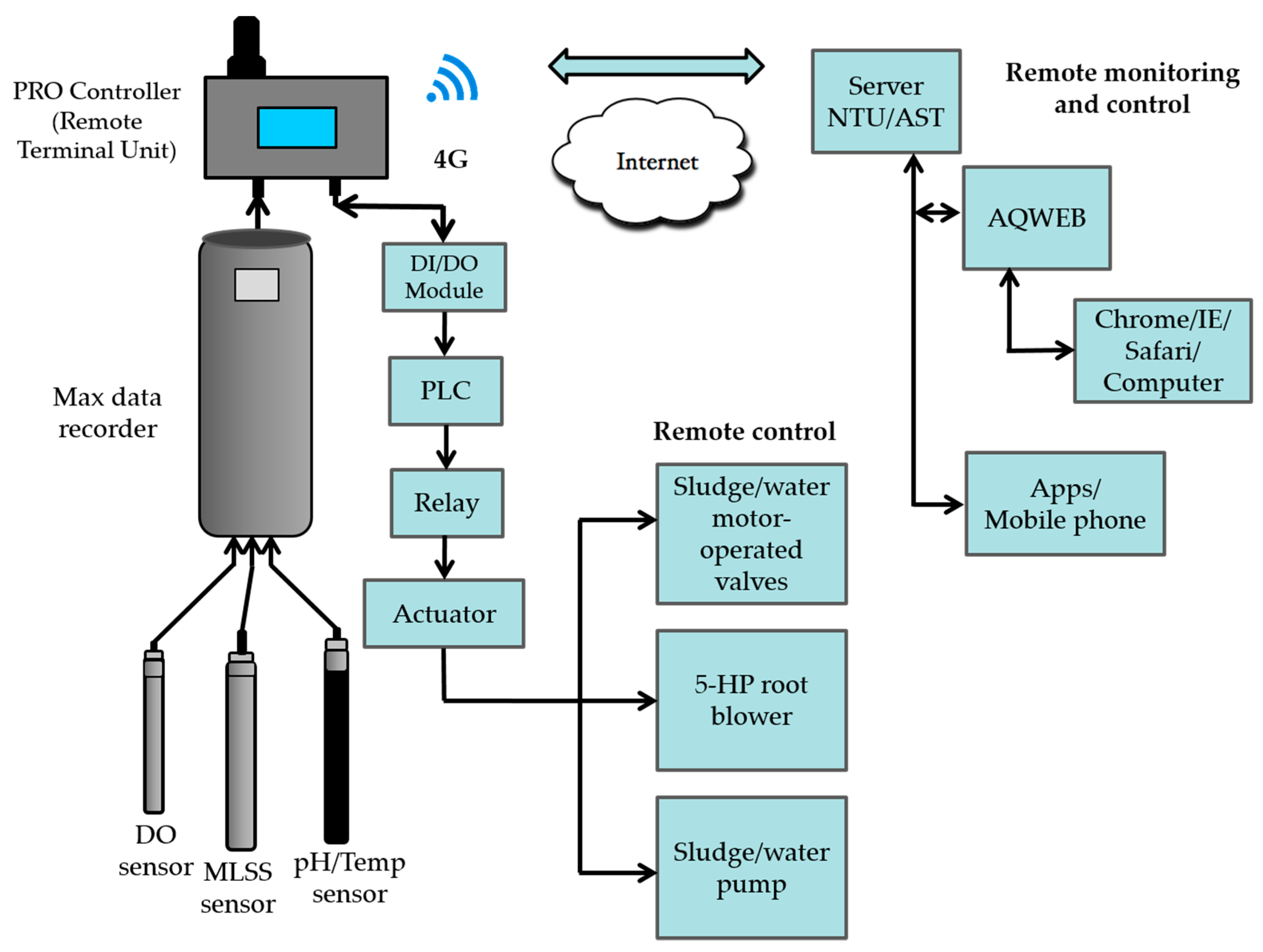
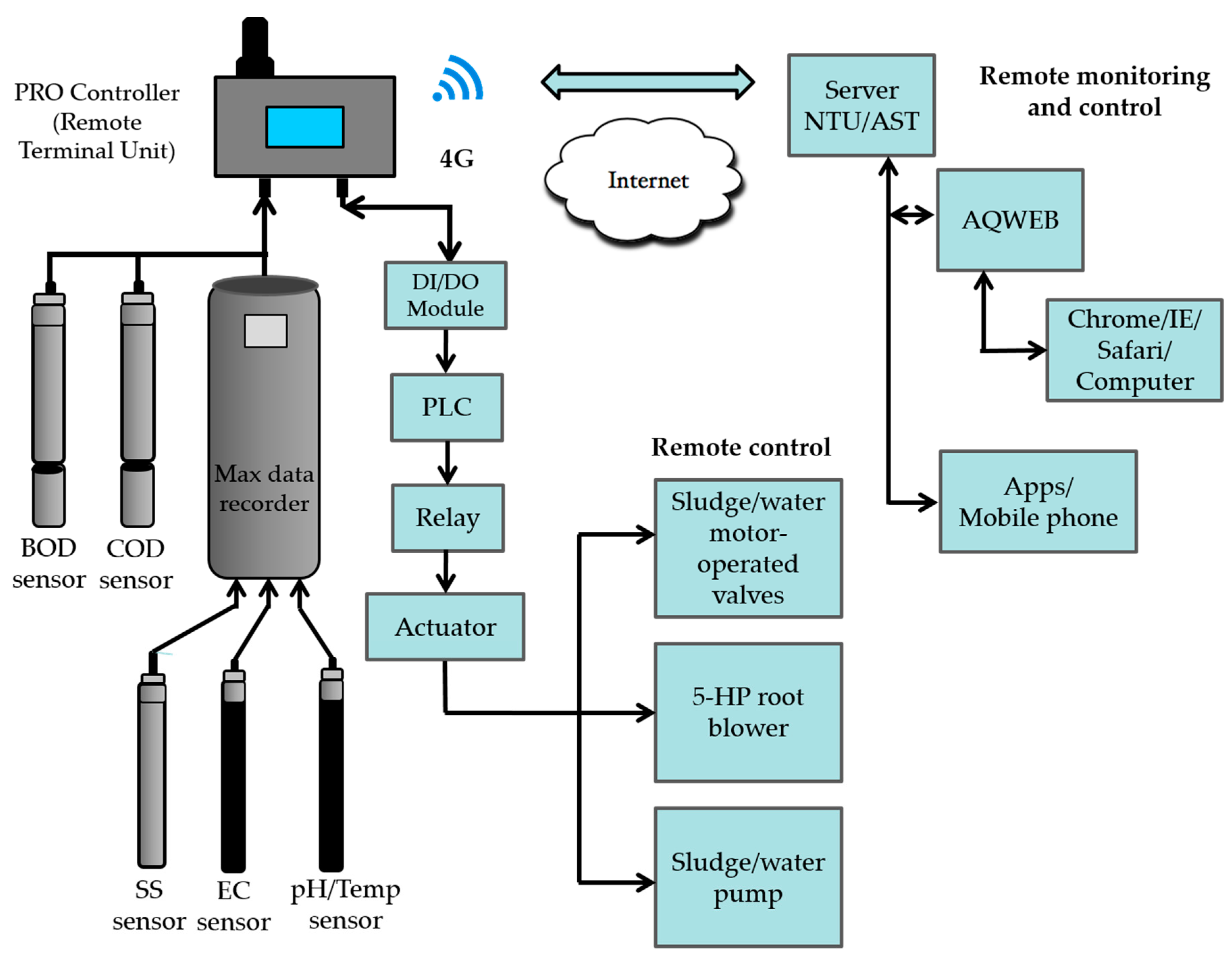
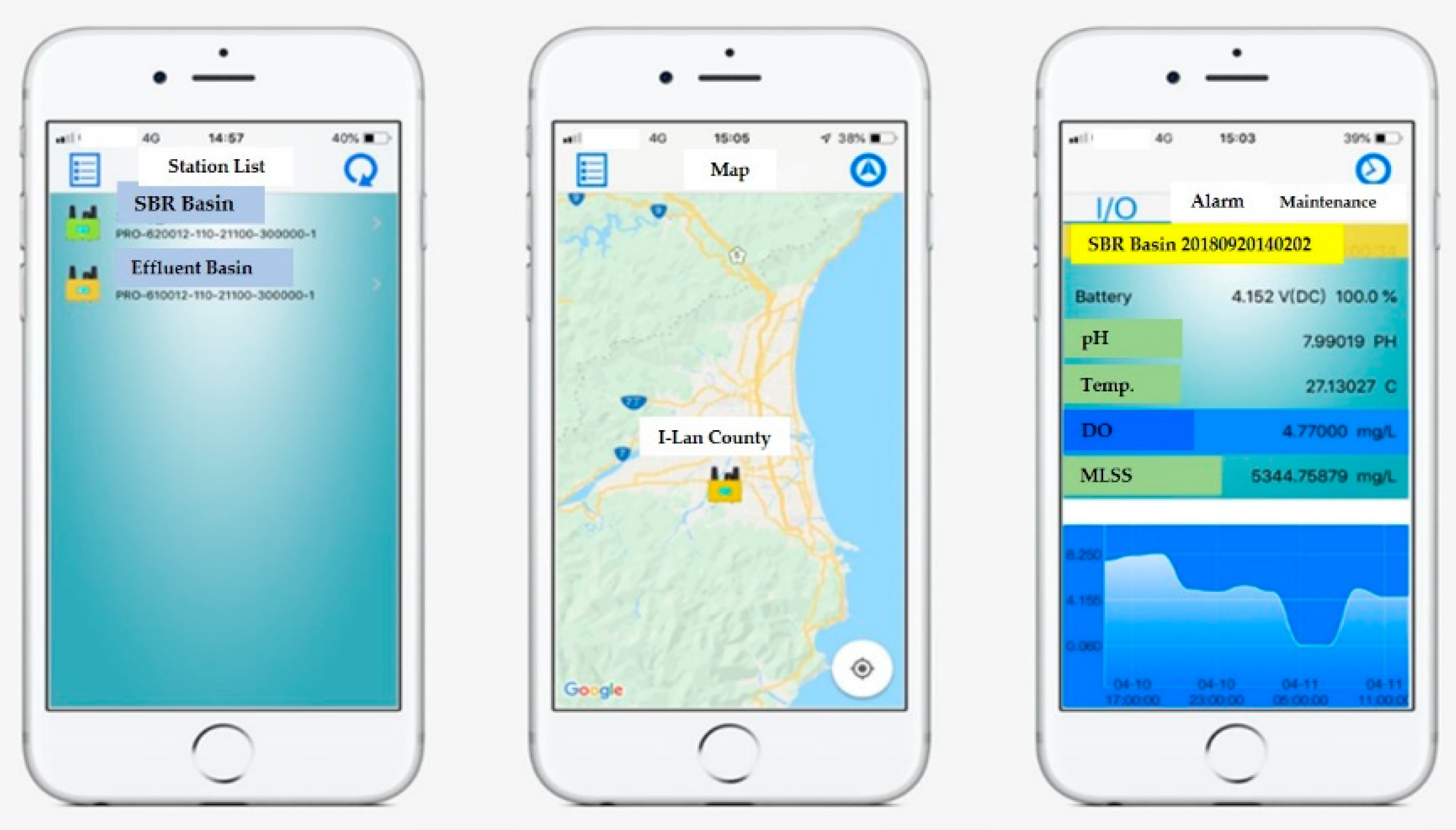
2.3. Smart Piggery Wastewater Treatment System with the Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
2.4. Calibration of Water Quality Sensors
2.5. Analysis of Water Quality
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Operation of the Smart Piggery Wastewater Treatment System
3.1.1. The Efficiency of Piggery Wastewater Treatment Based on the Analytical Chemical Data
3.1.2. The Efficiency of Piggery Wastewater Treatment Based on the Water Quality Sensors
3.2. Promotion of the Novel Piggery Wastewater Treatment System
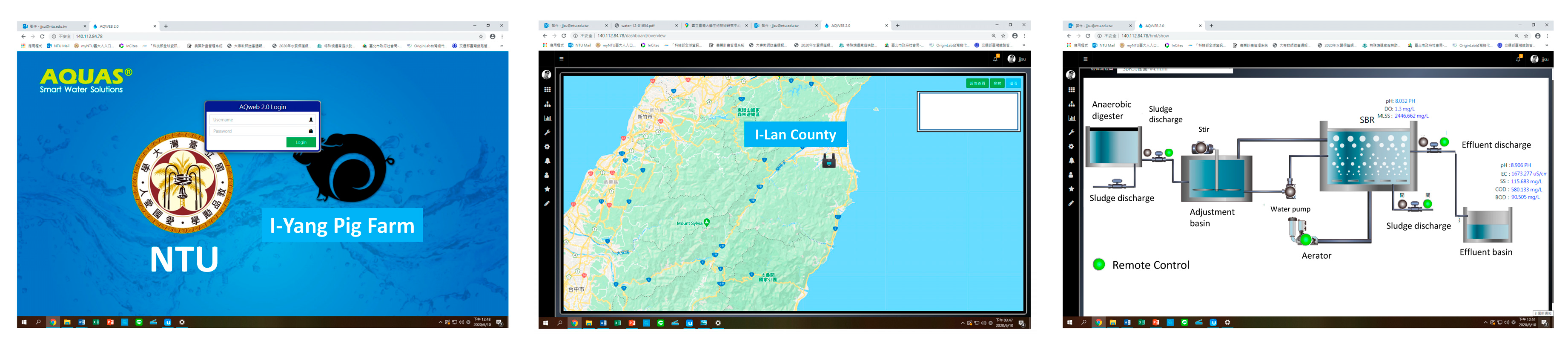
3.2.1. Set-Up Remote Monitoring Alarm and Feedback Control
3.2.2. Reducing Daily Wastewater Volume, Increasing Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT), and Maintaining Mesophilic Conditions of Wastewater Treatment Basins
3.3. The Advantages and Disadvantages of the Smart Piggery Wastewater Treatment System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berckmans, D. General introduction to precision livestock farming. Anim. Front. 2017, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.J.; Kung, C.M.; Lin, J.; Lian, W.C.; Wu, J.F. Utilization of sequencing batch reactor for in situ piggery wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. 1997, 32, 391–405. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.J.; Lian, W.C.; Wu, J.F. Studies on piggery wastewater treatment by a full-scale sequencing batch reactor after anaerobic fermentation. J. Agric. Assoc. China 1999, 188, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Huang, S.M. Ammonium reduction from piggery wastewater using immobilized ammonium-reducing bacteria with a full-scale sequencing batch reactor on farm. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, G. Automation development in water and wastewater systems. Environ. Eng. Res. 2007, 12, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, G.; Carlsson, B.; Comas, J.; Copp, J.; Gernaey, K.V.; Ingildsen, P.; Jeppsson, U.; Kim, C.; Rieger, L.; Rodríguez-Roda, I.; et al. Instrumentation, control, and automation in wastewater—From London 1973 to Narbonne 2013. In Proceedings of the 11th IWA Conference on Instrumentation, Control, and Automation (ICA 2013), Narbonne, France, 18–20 September 2013; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bortone, G. Integrated anaerobic and aerobic biological treatment for intensive swine production. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5424–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, T.; Zhang, X. Bioprocessing for slaughterhouse wastewater and its computerized control and supervisory system. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1999, 27, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.J.; Huang, J.F.; Wang, Y.L.; Hong, Y.Y. Treatment of duck house wastewater by a pilot-scale sequencing batch reactor system for sustainable duck production. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3870–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangitrao, R.R. Automation of sewage treatment plant using PLC & SCADA. Int. J. Adv. Res. Electr. Electr. Instr. Eng. 2016, 5, 8627–8637. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, G. Remote monitoring system of pig motion behavior and piggery environment based on Internet of Things. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agri. Eng. 2015, 31, 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson, V.; Cerny, M.; Lim, M.; Gledson, B.; Lockley, S.; Woodward, J. A smart sewer asset information model to enable an ‘Internet of Things’ for operational wastewater management. Automat. Constr. 2018, 91, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.H.; Kumar, W.; Memon, A.R.; Chowdhry, B.S.; Adamir, M.; Kumar, P. Internet of Things (IoT) enabled smart animal farm. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development, New Delhi, India, 16–18 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghe, D. IoT application to sustainable animal production. Annals of the University of Oradea, Fascicle. Ecotoxicol. Anim. Husb. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 16, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Sendhil Kumar, K.S.; Siva Shanmugam, G.; Rayavel, P.; RuchiKushwaha. Smart environmental waste water monitoring system and analysis using big data. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Chen, S. Application of environmental Internet of Things on water quality management of urban scenic river. Int. J. Sust. Dev. World Ecol. 2013, 20, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, C.; Turcu, C.; Gaitan, V. An Internet of Things oriented approach for water utility monitoring and control. pp. 175–180. Available online: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1811/1811.12807.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 5-3–5-6, 5-12–5-16, 2-53–2-58. [Google Scholar]
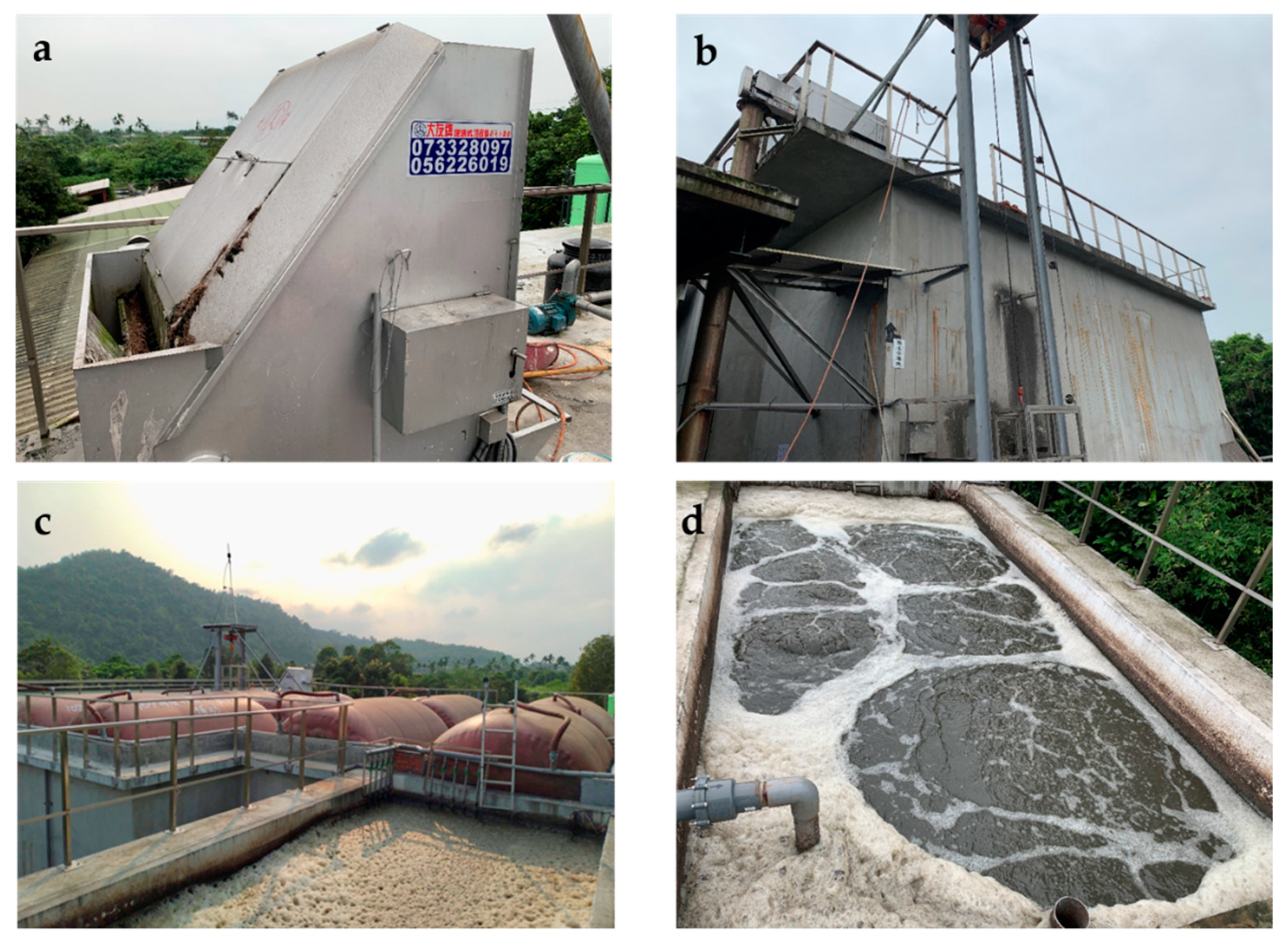
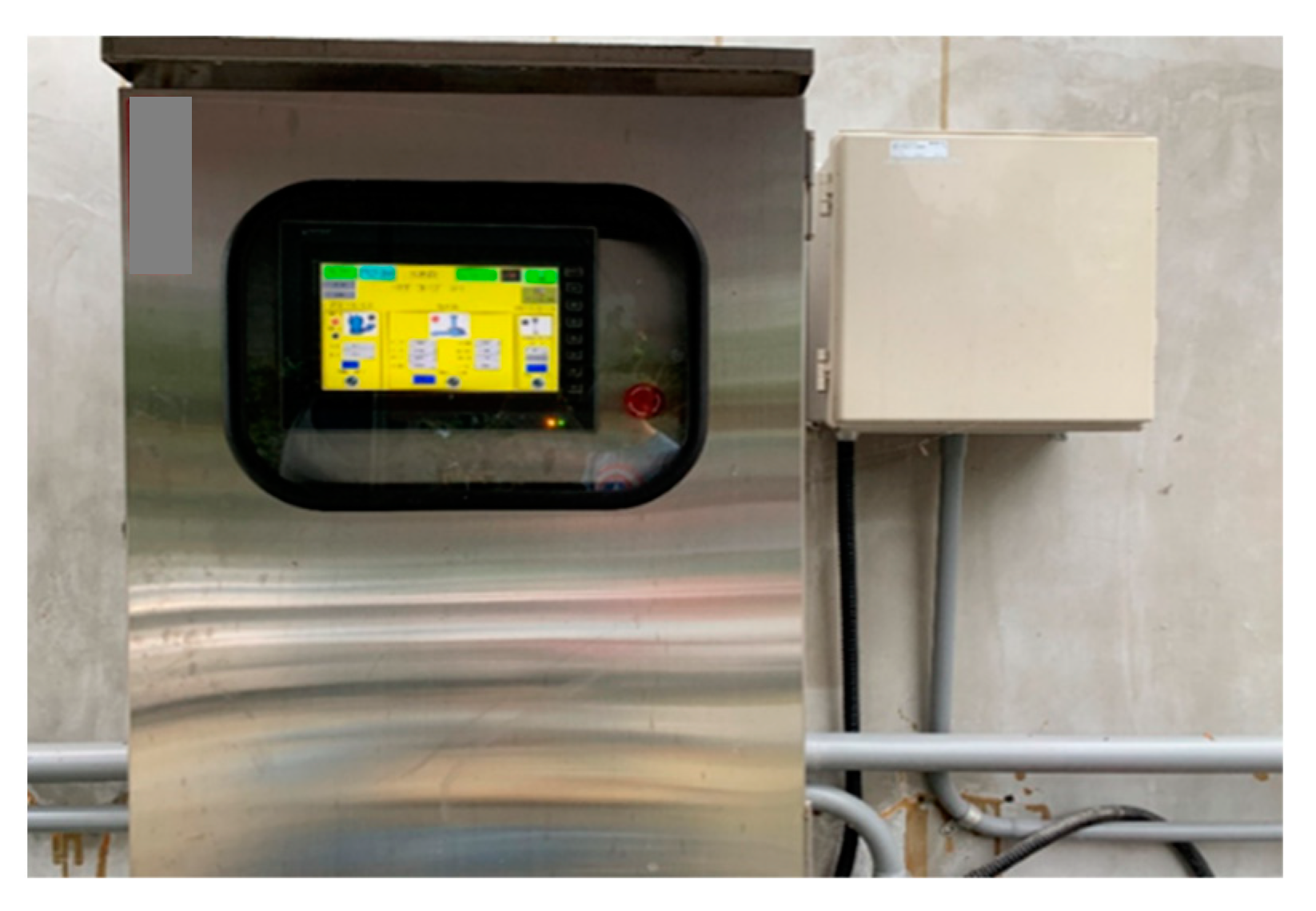



| Operation Sequence | Beginning Time (h:min) | End Time (h:min) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pumping influent | 09:58 | 10:48 | 50 |
| SBR/aeration on | 10:50 | 14:20 | 210 |
| SBR/aeration off | 14:21 | 15:40 | 80 |
| SBR/aeration on | 15:41 | 20:10 | 270 |
| SBR/aeration off | 20:11 | 21:29 | 78 |
| Effluent discharge | 21:30 | 21:55 | 25 |
| Pumping influent | 21:58 | 22:48 | 50 |
| SBR/aeration on | 22:50 | 02:20 | 210 |
| SBR/aeration off | 02:21 | 03:40 | 80 |
| SBR/aeration on | 03:41 | 08:10 | 270 |
| SBR/aeration off | 08:11 | 09:28 | 78 |
| Sludge discharge | 09:29 | 1 | |
| Effluent discharge | 09:30 | 09:55 | 25 |
| Indexes | Sensor Data | Analytical Data | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data before calibration (n = 5897) | |||
| pH | 8.74 ± 2.45 | 8.13 ± 0.43 | |
| EC (μS/cm) | 2767 ± 403 | 2194 ± 476 | <0.05 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 128 ± 73 | 79 ± 24 | <0.05 |
| COD (mg/L) | 245 ± 183 | 448 ± 187 | <0.05 |
| SS (mg/L) | 228 ± 206 | 121 ± 52 | <0.05 |
| Data after calibration (n = 9648) | |||
| pH | 8.24 ± 0.46 | 7.81 ± 0.33 | |
| EC (μS/cm) | 2456 ± 479 | 2634 ± 635 | NS |
| BOD (mg/L) | 69 ± 9 | 66 ± 16 | NS |
| COD (mg/L) | 575 ± 46 | 563 ± 25 | NS |
| SS (mg/L) | 146 ± 16 | 149 ± 15 | NS |
| Water Samples | pH | EC (μS/cm) | MLSS (mg/L) | BOD (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | SS (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw wastewater | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 2597 ± 614 | NA | 1127 ± 178 | 4077 ± 21 | 3676 ± 166 |
| Pre-separated wastewater | 7.0 ± 0.6 | 2498 ± 540 | NA | 492 ± 112 | 858 ± 242 | 978 ± 18 |
| SBR | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 2007 ± 189 | 2013 ± 1040 | 153 ± 21 | 689 ± 176 | NA |
| Effluent | 8.0 ± 0.4 | 2411 ± 579 | NA | 70 ± 17 | 523 ± 121 | 140 ± 34 |
| Removal (%) | 94 | 87 | 96 |
| Indexes | Analytical Data of Water Samples | |
|---|---|---|
| Before Sensor Calibration | After Sensor Calibration | |
| EC (μS/cm) | 2625 ± 691 | 2477 ± 633 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 322 ± 61 | 336 ± 55 |
| PO43− (mg/L) | 125 ± 40 | 112 ± 47 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 66 ± 24 | 62 ± 20 |
| NO2− (mg/L) | 96 ± 57 | 100 ± 52 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 62 ± 39 | 60 ± 22 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 251 ± 27 | 235 ± 21 |
| NH4+ (mg/L) | 122 ± 17 | 114 ± 12 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 703 ± 18 | 715 ± 26 |
| K+ (mg/L) | 276 ± 10 | 260 ± 22 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 109 ± 7 | 101 ± 6 |
| Indexes | Sensor Data | Analytical Data | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data before calibration (n = 8273) | |||
| pH | 8.03 ± 0.73 | 7.76 ± 0.28 | |
| Water Temp. (°C) | 24.92 ± 0.01 | - | |
| DO (mg/L) | 2.5 ± 0.01 | - | |
| BOD (mg/L) | NA | 161 ± 23 | |
| COD (mg/L) | NA | 583 ± 149 | |
| MLSS (mg/L) | 1089 ± 530 | 885 ± 56 | <0.05 |
| Data after calibration (n = 9873) | |||
| pH | 7.73 ± 0.73 | 7.84 ± 0.19 | |
| Water Temp. (°C) | 25.77 ± 2.07 | - | |
| DO (mg/L) | 2.00 ± 0.68 | - | |
| BOD (mg/L) | NA | 146 ± 18 | |
| COD (mg/L) | NA | 771 ± 156 | |
| MLSS (mg/L) | 2760 ± 653 | 2891 ± 211 | NS |
| Samples. | pH | EC (μS/cm) | MLSS (mg/L) | BOD (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | SS (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical data (n = 144) | ||||||
| Raw wastewater | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 2597 ± 614 | NA | 1127 ± 178 | 4077 ± 21 | 3676 ± 166 |
| SBR | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 2007 ± 189 | 2013 ± 1040 | 153 ± 21 | 689 ± 176 | NA |
| Sensor data before sensor calibration (n = 14170) | ||||||
| SBR | 8.0 ± 0.7 | NA | 1089 ± 530 | NA | NA | NA |
| Effluent | 8.7 ± 2.5 | 2766 ± 403 | 128 ± 73 | 245 ± 183 | 228 ± 206 | |
| Removal (%) | 89 | 94 | 93 | |||
| Sensor data after sensor calibration (n = 19521) | ||||||
| SBR | 7.73 ± 0.73 | NA | 2759 ± 652 | NA | NA | NA |
| Effluent | 8.2 ± 0.5 | 2456 ± 479 | 69 ± 9 | 575 ± 46 | 146 ± 16 | |
| Removal (%) | 94 | 86 | 96 | |||
| Samples | pH | EC (μS/cm) | MLSS (mg/L) | BOD (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | SS (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical data (n = 144) | ||||||
| Raw wastewater | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 2597 ± 614 | NA | 1127 ± 178 | 4077 ± 21 | 3676 ± 166 |
| SBR | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 2007 ± 189 | 2013 ± 1040 | 153 ± 21 | 689 ± 176 | NA |
| Analytical data before sensor calibration (n = 42) | ||||||
| SBR | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 1979 ± 159 | 865 ± 56 | 161 ± 23 | 583 ± 149 | NA |
| Effluent | 8.1 ± 0.4 | 2194 ± 476 | NA | 79 ± 24 | 448 ± 187 | 121 ± 52 |
| Removal (%) | 93 | 89 | 97 | |||
| Analytical data after sensor calibration (n = 66) | ||||||
| SBR | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 2064 ± 257 | 2891 ± 211 | 146 ± 18 | 771 ± 156 | NA |
| Effluent | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 2634 ± 635 | NA | 66 ± 16 | 563 ± 24 | 149 ± 15 |
| Removal (%) | 94 | 86 | 96 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, J.-J.; Ding, S.-T.; Chung, H.-C. Establishing a Smart Farm-Scale Piggery Wastewater Treatment System with the Internet of Things (IoT) Applications. Water 2020, 12, 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061654
Su J-J, Ding S-T, Chung H-C. Establishing a Smart Farm-Scale Piggery Wastewater Treatment System with the Internet of Things (IoT) Applications. Water. 2020; 12(6):1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061654
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Jung-Jeng, Shih-Torng Ding, and Hsin-Cheng Chung. 2020. "Establishing a Smart Farm-Scale Piggery Wastewater Treatment System with the Internet of Things (IoT) Applications" Water 12, no. 6: 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061654
APA StyleSu, J.-J., Ding, S.-T., & Chung, H.-C. (2020). Establishing a Smart Farm-Scale Piggery Wastewater Treatment System with the Internet of Things (IoT) Applications. Water, 12(6), 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061654





