Using Isotopes (H, O, and Sr) and Major Ions to Identify Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in the Hongjiannao Lake Basin, Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
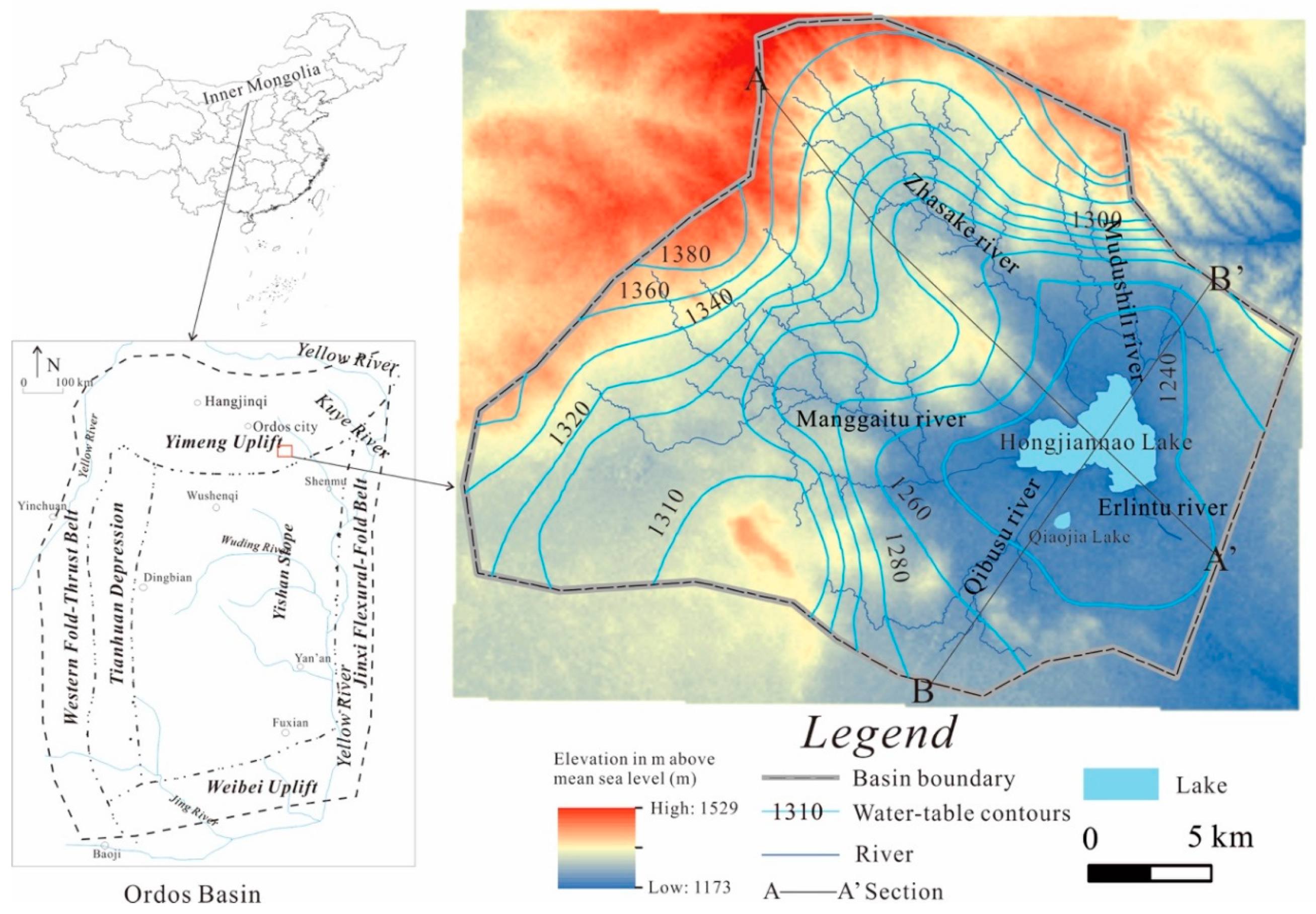
2. Description of the Study Area
2.1. Study Location and Climate
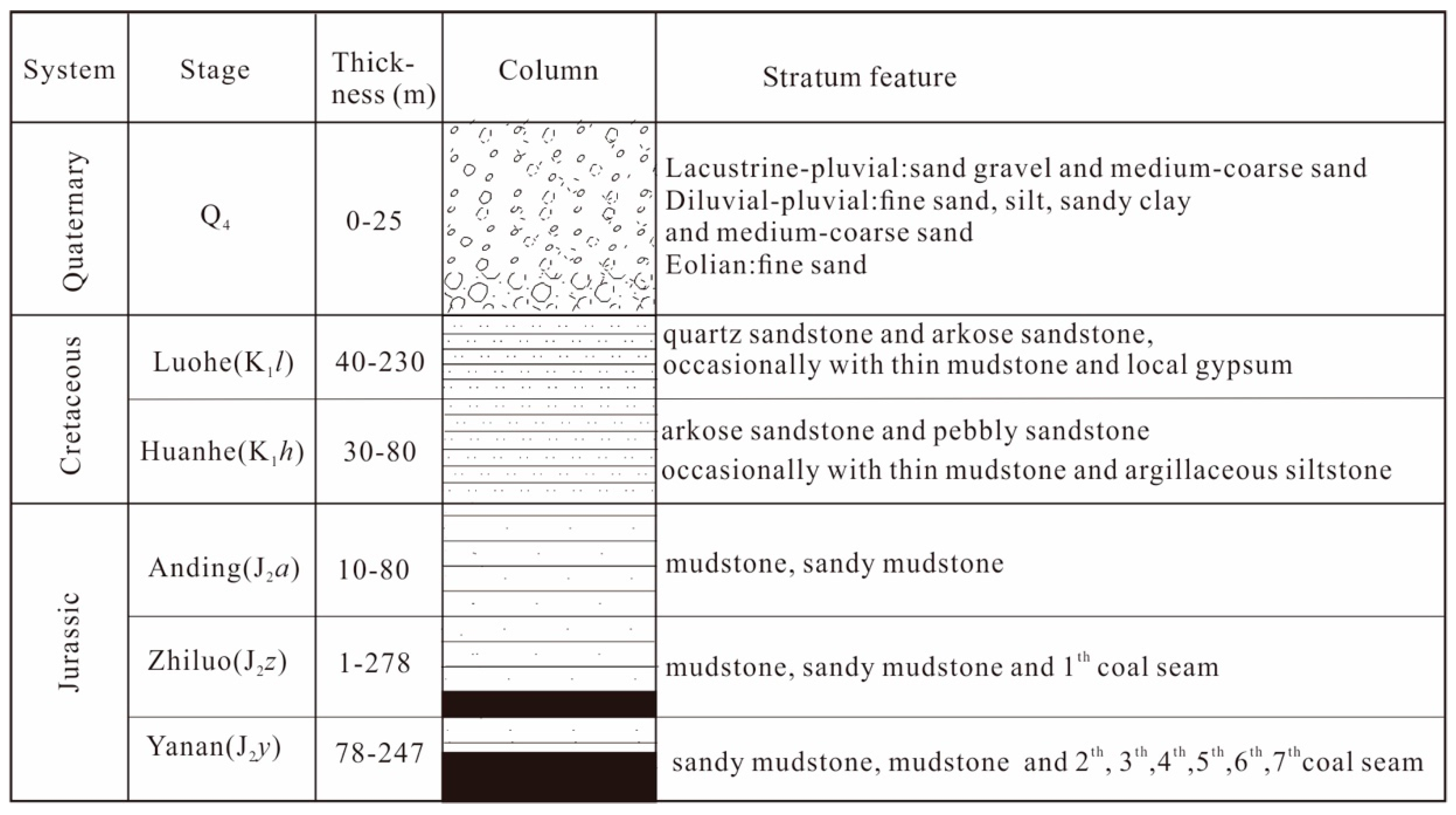
2.2. Hydrological, Geological and Hydrogeological Setting
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
3.2. Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemical Characterization
4.2. TDS Concentration Variations
4.3. Hydrochemical Variations along Groundwater Flow Path
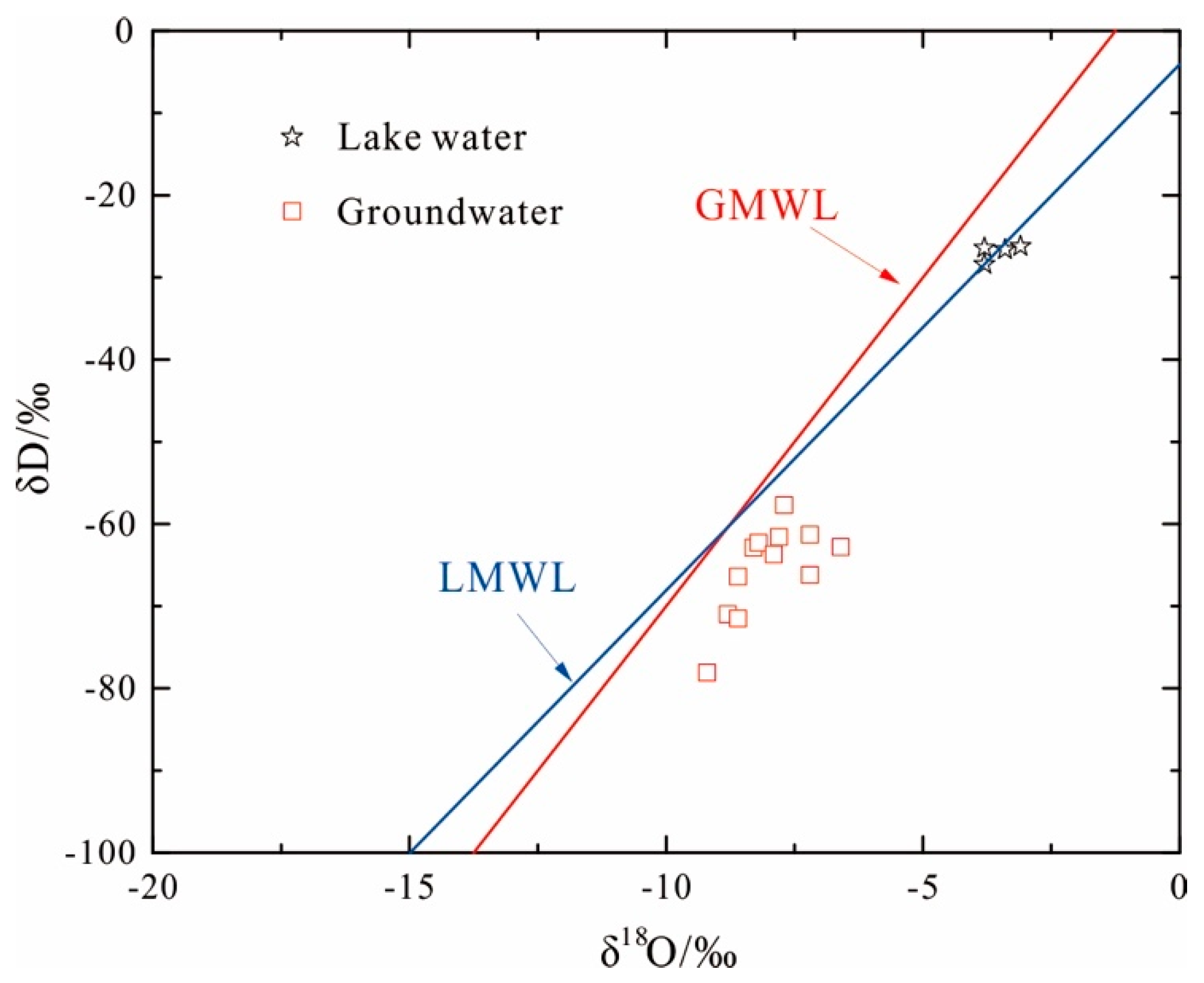
4.4. Stable Water Isotopes (δD and δ18O)
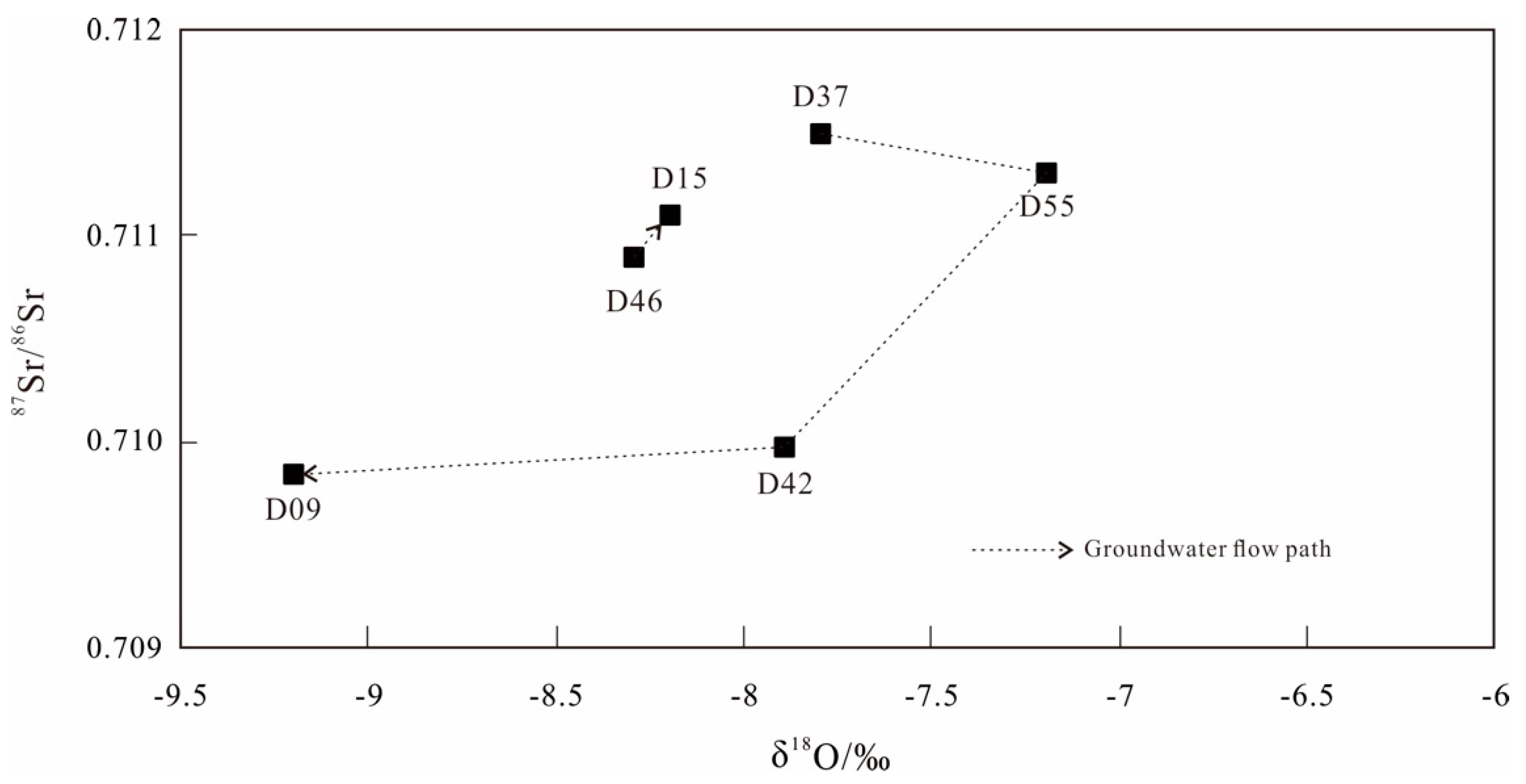
4.5. Sr Concentration and Sr Isotopic Characterization
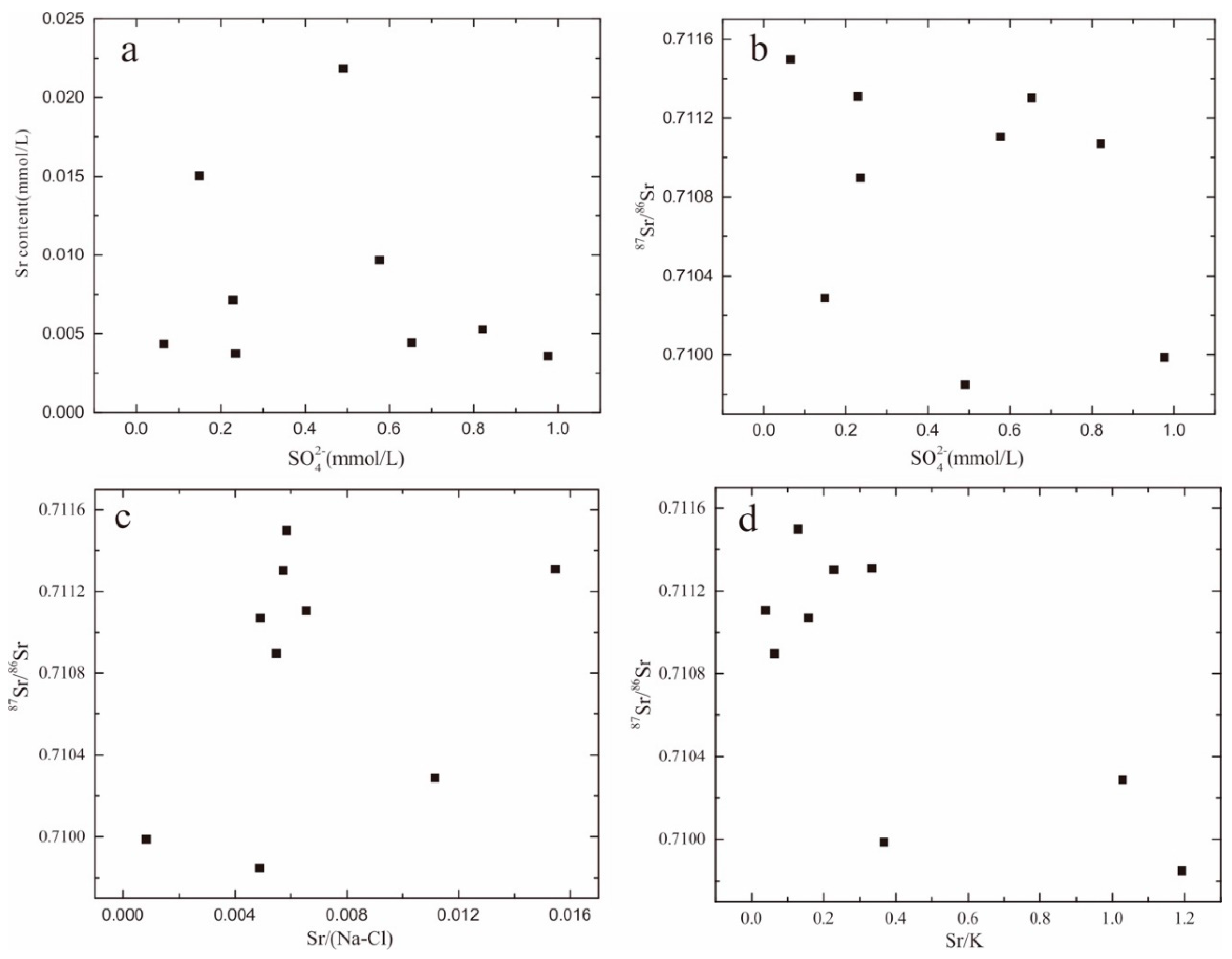
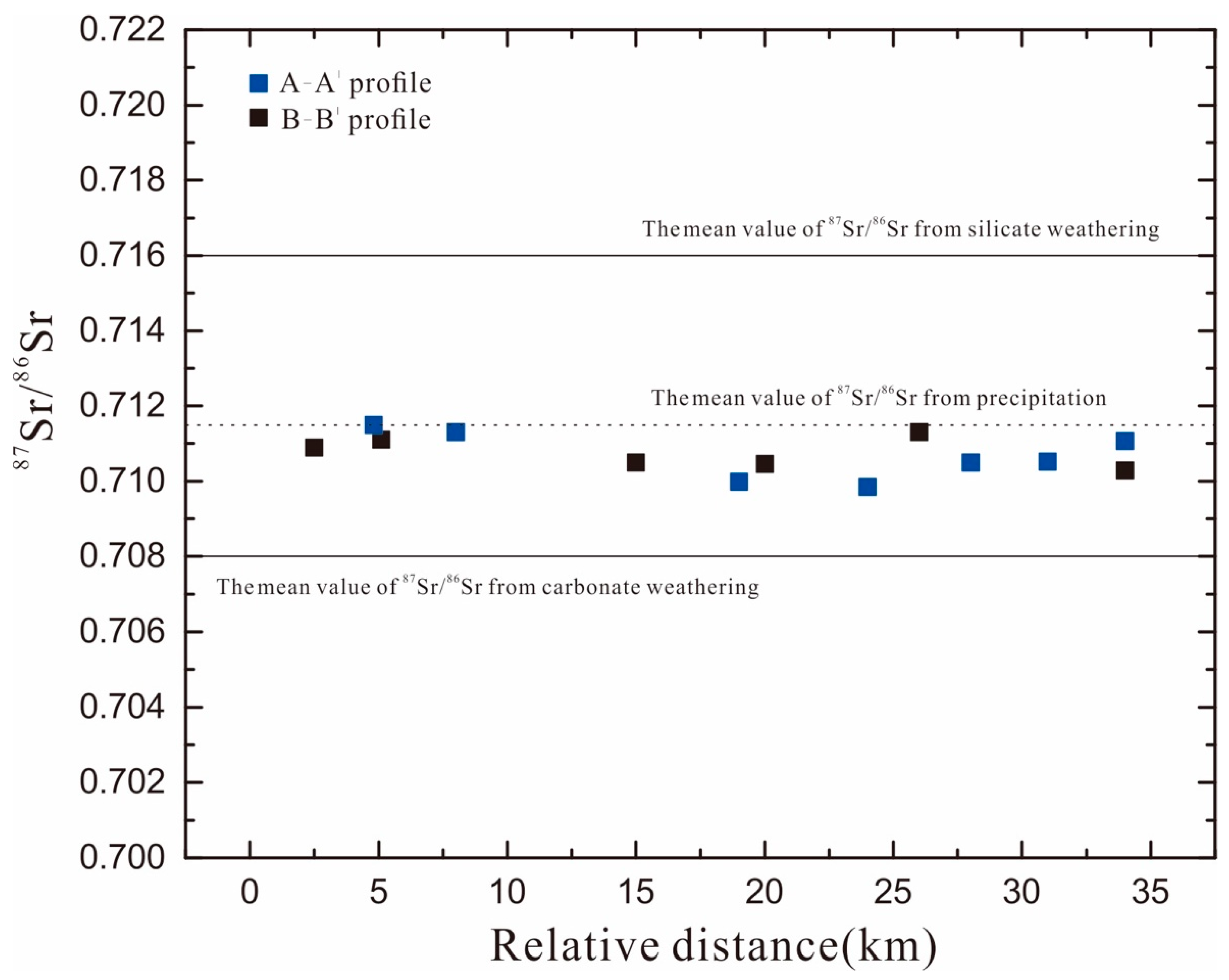
4.5.1. Sr Isotope and Concentrations
4.5.2. Sr Isotope Characterization in Groundwater
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sample | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | HCO3− | CO32− | TDS | pH | δD | δ18O | 87Sr/86Sr | Sr2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | μg/L | ||||||||||||||
| D46 | 22.1 | 2.31 | 11.7 | 54.4 | 9.92 | 20 | 22.6 | 236 | 0 | 380 | 7.38 | −62.9 | −8.3 | 0.710897 | 327 |
| D15 | 64.2 | 9.73 | 40 | 87.7 | 46.6 | 2.12 | 55.4 | 481 | 0 | 787 | 7.59 | −62.3 | −8.2 | 0.711106 | 848 |
| D04 | 10.1 | 1.55 | 10.1 | 49.3 | 4.98 | 3.71 | 23.5 | 182 | 0 | 285 | 8.05 | −57.7 | −7.7 | / | / |
| D12 | 24.2 | 0.76 | 13.1 | 89.5 | 9.85 | 26.2 | 62.7 | 277 | 0 | 503 | 7.34 | −71 | −8.8 | 0.711303 | 389 |
| D23 | 152 | 0.95 | 11.4 | 67.1 | 89.1 | 48.4 | 112 | 301 | 0 | 782 | 7.63 | −80.6 | −10.6 | / | / |
| D20 | 34.3 | 0.57 | 9.47 | 36 | 5.08 | 28.5 | 14.3 | 192 | 0 | 320 | 7.66 | −62.8 | −6.6 | 0.710288 | 1318 |
| D30 | 2308 | 43.8 | 78.1 | 7.53 | 1929 | 13.8 | 670 | 1402 | 536 | 6991 | 9.14 | −26.6 | −3.4 | 0.710491 | 281 |
| D34 | 2336 | 44.4 | 80.6 | 6.88 | 1981 | 13.8 | 679 | 1439 | 544 | 7129 | 9.5 | −25.4 | −3.2 | 0.710454 | 273 |
| D37 | 24.2 | 1.33 | 21.6 | 40.1 | 10.9 | 0.69 | 6.26 | 252 | 6.29 | 364 | 8.25 | −61.6 | −7.8 | 0.711498 | 382 |
| D55 | 22.7 | 0.84 | 21.9 | 56.4 | 18.6 | 48.5 | 22 | 231 | 0 | 422 | 7.82 | −66.2 | −7.2 | 0.71131 | 627 |
| D42 | 132 | 0.38 | 1.18 | 2.51 | 50.8 | 8.57 | 93.8 | 198 | 11 | 498 | 8.84 | −63.7 | −7.9 | 0.709986 | 314 |
| D26 | 55.9 | 0.59 | 15.7 | 55.4 | 21.1 | 77.8 | 30.6 | 247 | 0 | 505 | 7.67 | −71.5 | −8.6 | / | / |
| D09 | 122 | 0.72 | 5.45 | 10.5 | 29.1 | 10.7 | 47.1 | 261 | 0 | 487 | 8.03 | −78.1 | −9.2 | 0.709848 | 1914 |
| D01 | 32.9 | 1.31 | 14.8 | 88 | 12.5 | 37 | 78.9 | 270 | 0 | 536 | 7.83 | −61.3 | −7.2 | 0.711069 | 463 |
| D28 | 2323 | 48.4 | 80.6 | 6.88 | 1967 | 13.8 | 677 | 1406 | 563 | 7090 | 9.16 | −28.4 | −3.8 | 0.710522 | 291 |
| D32 | 2305 | 44.3 | 79.3 | 5.61 | 1942 | 13.8 | 673 | 1406 | 551 | 7023 | 9.18 | −27 | −3.2 | 0.710491 | 307 |
References
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, C.; Zhu, G. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Chen, L. Coincidence probability of precipitation for the middle route of south-to-north water transfer project in China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ma, R.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; McCarter, C. Groundwater sustainability and groundwater/surface-water interaction in arid Dunhuang Basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, F.; Xue, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wu, P. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in the salt chemical industrial base of Guyuan City, northwestern China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 8, 3427–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Wu, X.; Mu, W.; Fu, R.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D. Hydrogeochemical characterization and suitability assessment of groundwater in an agro-pastoral area, Ordos Basin, NW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, G.; Liang, X.; Cui, L. Hydrochemical and stable isotope (δD and δ18O) characteristics of groundwater and hydrogeochemical processes in the Ningtiaota Coalfield, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ. 2018, 37, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Su, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Ji, R.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Xinchang preselected site and their implications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusi, S.; Di Curzio, D.; Palmucci, W.; Petaccia, R. Detection of the natural origin hydrocarbon contamination in carbonate aquifers (central Apennine, Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15577–15596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomo, M.; Vermeulen, D. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of a flooded underground coal mine groundwater system. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 92, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, A.; Sönmez, S. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of the Ilica geothermal system (Erzurum, Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4451–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdag, A. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of Kavak (Seydisehir-Konya) geothermal field, Turkey. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 121, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ako, A.; Shimada, J.; Hosono, T.; Ichiyanagi, K.; Nkeng, G.; Eyong, G.; Roger, N. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Mbanga, Njombe and Penja (Banana Plain)-Cameroon. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2012, 75, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K. Quantifying streamflow variations in ungauged lake basins by integrating remote sensing and water balance modelling: A case study of the erdos larus relictus national nature reserve, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, K.; Yan, G. Application of landsat imagery to investigate lake area variations and relict gull habitat in hongjian lake, Ordos Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, E.; Yang, B.; Ji, J. Paleosandstorm characteristics and lake evolution history deduced from investigation on lacustrine sediments-The case of Hongjiannao Lake, Shaanxi Province. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Gao, F. Monitoring spatio-temporal changes of water area in Hongjiannao Lake from 1957 to 2015 and its driving forces analysis. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, K. A multi-method study of regional groundwater circulation in the Ordos Plateau, NW China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y. Groundwater Investigation in the Ordos Basin; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liotta, M.; Alessandro, W.; Arienzo, I.; Longo, M. Tracing the circulation of groundwater in volcanic systems using the 87sr/86sr ratio: Application to Mt. Etna. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 331, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Hou, G.; Qian, H. Groundwater circulation by hydrochemistry and isotope method. In Water Resources Environment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Awaleh, M.; Baudron, P.; Soubaneh, Y.; Boschetti, T.; Hoch, F.; Egueh, N.; Mohamed, J.; Dabar, O.; Masse-Dufresne, J.; Gassani, J. Recharge, groundwater flow pattern and contamination processes in an arid volcanic area: Insights from isotopic and geochemical tracers (Bara aquifer system, Repulic of Djibouti). J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 175, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, J.; Dotson, S.; Hart, E.; Kreamer, D. Water circulation in karst systems: Comparing physicochemical and environmental isotopic data interpretation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaris, C.; Mezga, K.; Slejko, F.; Urbanc, J.; Zini, L. Groundwater characterization by means of conservative (δ18O and δ2H) and non-Conservative (87Sr/86Sr) isotopic values: The classical Karst region aquifer case (Italy-Slovenia). Geosci. J. 2018, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Wu, C.; Dong, W.; Hou, G. Strontium isotope evolution mechanism of the Cretaceous groundwater in Ordos Desert Plateau. J. Chendu Univ. Technol. 2011, 3, 348–358. [Google Scholar]
- Palmucci, W.; Rusi, S.; Pennisi, M.; Curzio, D. Contribution of B and Sr Isotopes to assess boron contamination of groundwater: Case studies in Central Italy. Rend. Online Soc. Geol. Ital. 2016, 41, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, H. Geochemistry of groundwater. In Groundwater Studies-an International Guide for Research and Practice; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1984; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Tian, L.; Biggs, T.; Rong, W. Deuterium-excess determination of evaporation to inflow ratios of an alpine lake: Implications for water balance and modeling. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, X.; Liang, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H. Groundwater Science Monograph; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, I.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotope in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 58–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zeng, Q.; Zeng, C.; Chen, B.; Chen, C.; He, H.; Cai, X.; Ou, Y.; et al. Using deuterium excess, precipitation and runoff data to determine evaporation and transpiration: A case study from the Shawan Test Site, Puding, Guizhou, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 242, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Jing, L.; Yu, P. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, F.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. The variations of stable isotopes (δD and δ18O) in the precipitation in Baotou area. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, X. Isotopic enrichment of liquid water during evaporation from water surfaces. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, V.; Nakhaei, M.; Lak, R.; Kholghi, M. Geophysical, isotopic, and hydrogeochemical tools to identify potential impacts on coastal groundwater resources from Urmia hypersaline Lake, NW Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 16738–16760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Occurrence, genesis and travertine deposition of the Adong hot springs in northwestern Yunnan of China. Geothermics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettayfi, N.; Bouchaou, L.; Michelot, J.; Tagma, T.; Warner, N.; Boutaleb, S.; Massault, M.; Lgourna, Z.; Vengosh, A. Geochemical and isotopic (oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, strontium) constraints for the origin, salinity, and residence time of groundwater from a carbonate aquifer in the Western Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco. J. Hydrol. 2012, 438–439, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahib, L.; Marandi, A.; Schüth, C. Strontium isotopes as an indicator for groundwater salinity sources in the Kirkuk region, Iraq. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Pang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Gu, W.; Zhou, L.; Yu, D.; Xu, C. Geochemical and isotopic evidence on the recharge and circulation of geothermal water in the Tangshan Geothermal System near Nanjing, China: Implications for sustainable development. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1705–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterman, Z.; Thamke, J.; Futa, K.; Preston, T. Strontium isotope systematics of mixing groundwater and oil-field brine at Goose Lake in northeastern Montana, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2403–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y. Strontium isotope geochemistry of groundwater affected by human activities in Nandong underground river system, China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Ellis, A.; Su, C.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Duan, M. Delineation of groundwater flow paths using hydrochemical and strontium isotope composition: A case study in high arsenic aquifer systems of the Datong basin, northern China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakari, S.; Aagaard, P.; Vogt, R.; Ruden, F.; Johansen, I.; Vuai, S. Strontium isotopes as tracers for quantifying mixing of groundwater in the alluvial plain of a coastal watershed, south-eastern Tanzania. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 130, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Jin, K.; Jiang, S.; Tan, H.; Han, L.; Tang, Q. Chemical and strontium isotopic characteristics of shallow groundwater in the Ordos Desert Plateau, North China: Implications for the dissolved sr source and water-rock interactions. Geochemistry 2015, 75, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, M.; Banner, J.; Sharp, J. Regional groundwater flow paths in Trans-Pecos, Texas inferred from oxygen, hydrogen, and strontium isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoo, Y.; Nakano, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Hao, Q. Mineralogical variation of Sr-Nd isotopic and elemental compositions in loess and desert sand from the central loess plateau in China as a provenance tracer of wet and dry deposition in the northwestern Pacific. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hou, G.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, Z.; Yin, L.; Wang, D.; Su, X. Formation of mud springs in the Cretaceous Ordos groundwater basin, China and their hydrogeological significance. Geol. Bull. China 2008, 27, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Dotsika, E.; Poutoukis, D.; Kloppmann, W.; Guerrot, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouimtzis, T. The use of O, H, B, Sr and S isotopes for tracing the origin of dissolved boron in groundwater in Central Macedonia, Greece. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, T.; Krabbenhoft, D.; Kendall, C. Kinetic and mineralogic controls on the evolution of groundwater chemistry and 87sr/86sr in a sandy silicate aquifer, northern Wisconsin, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, P.; Petelet-Giraud, E. Strontium isotopes as tracers of groundwaterinduced floods: The Somme case study (France). J. Hydrol. 2005, 305, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaga, A. Chemical kinetics of water-rock interactions. J. Geophys. Res. 1974, 89, 4009–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.; Ma, J.; Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Kipfer, R.; Darbyshire, D. Groundwater recharge history and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Minqin Basin, North West China. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 2148–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Hydrochemical | Saturation Index | CAI-1 | d-Index (‰) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Calcite | Gypsum | Dolomite | |||
| D46 | HCO3–Ca | 0.11 | −2.32 | −0.1 | −1.46 | 3.5 |
| D15 | HCO3–Ca | 0.74 | −1.89 | 1.49 | −0.59 | 3.3 |
| D04 | HCO3–Ca | 0.63 | −2.31 | 0.93 | −1.34 | 3.9 |
| D12 | HCO3–Ca | 0.31 | −1.74 | 0.13 | −1.53 | −0.6 |
| D23 | HCO3–Ca | 0.37 | −1.82 | 0.65 | 0.35 | 4.2 |
| D20 | HCO3–Ca–Na | 0.14 | −2.66 | 0.04 | −5.86 | −10 |
| D37 | HCO3–Ca | 0.86 | −2.99 | 1.5 | −1.34 | 0.8 |
| D55 | HCO3–Ca | 0.53 | −2.37 | 0.99 | −0.27 | −8.6 |
| D42 | HCO3–Ca–Na | 0.05 | −3.06 | −0.1 | −1.61 | −0.5 |
| D26 | HCO3–Ca–Na | 0.39 | −2.24 | 0.57 | −1.68 | −2.7 |
| D09 | HCO3–Na | 0.06 | −2.7 | 0.19 | −3.22 | −4.5 |
| D01 | HCO3–Ca | 0.76 | −1.67 | 1.1 | −1.74 | −3.7 |
| Sample | Sr2+ (μg/g) | 87Sr/86Sr |
|---|---|---|
| T01 | 282 | 0.713994 |
| T02 | 530 | 0.712538 |
| T03 | 225 | 0.715187 |
| T04 | 450 | 0.712705 |
| Silicate minerals weathering | 0.716–0.720 | |
| Carbonate minerals weathering | 0.708 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Mu, W.; Zhu, G. Using Isotopes (H, O, and Sr) and Major Ions to Identify Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in the Hongjiannao Lake Basin, Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051467
Wu C, Wu X, Mu W, Zhu G. Using Isotopes (H, O, and Sr) and Major Ions to Identify Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in the Hongjiannao Lake Basin, Northwest China. Water. 2020; 12(5):1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051467
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chu, Xiong Wu, Wenping Mu, and Ge Zhu. 2020. "Using Isotopes (H, O, and Sr) and Major Ions to Identify Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in the Hongjiannao Lake Basin, Northwest China" Water 12, no. 5: 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051467
APA StyleWu, C., Wu, X., Mu, W., & Zhu, G. (2020). Using Isotopes (H, O, and Sr) and Major Ions to Identify Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in the Hongjiannao Lake Basin, Northwest China. Water, 12(5), 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051467




