Comparing Rainfall Erosivity Estimation Methods Using Weather Radar Data for the State of Hesse (Germany)
Abstract
1. Introduction
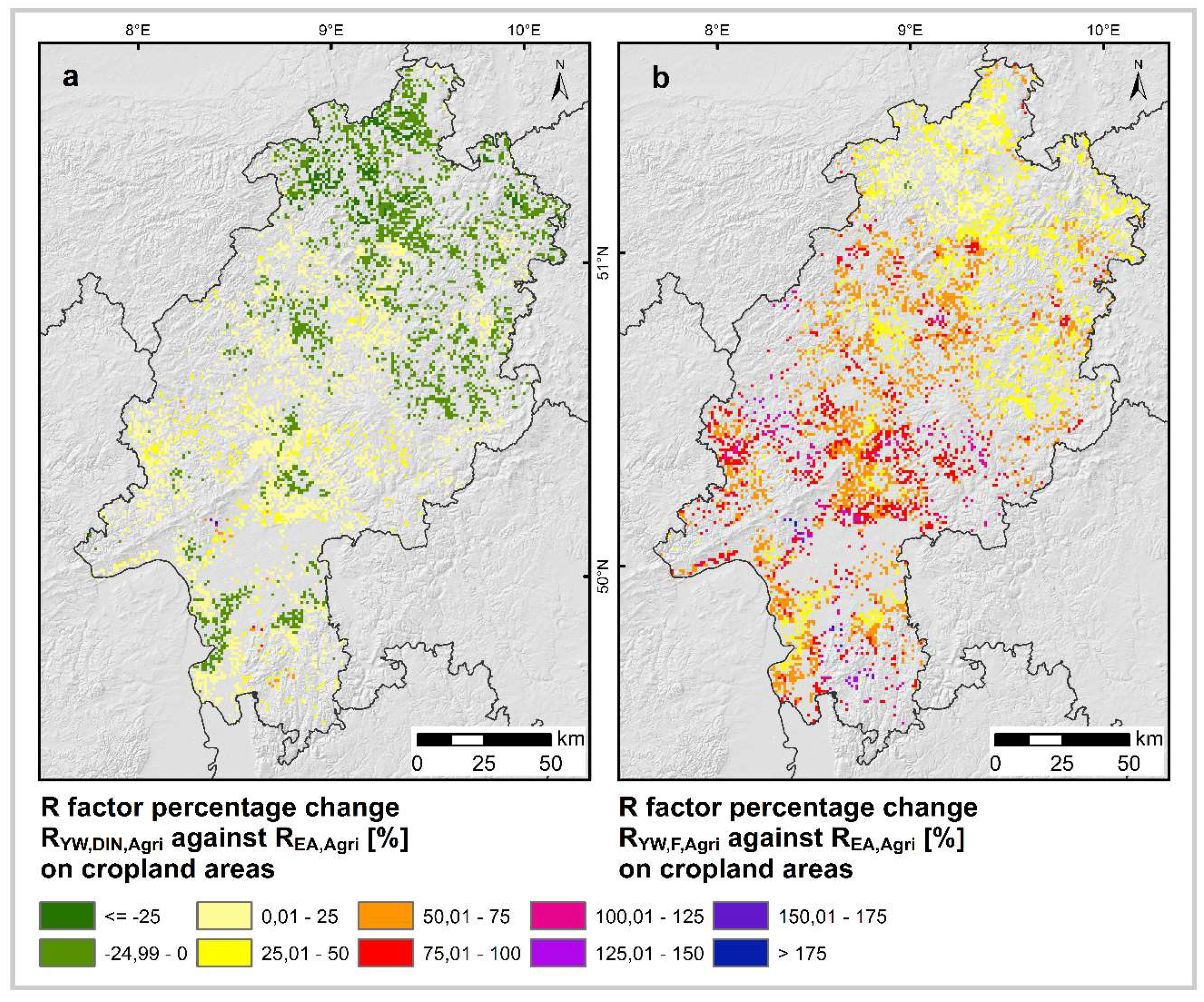
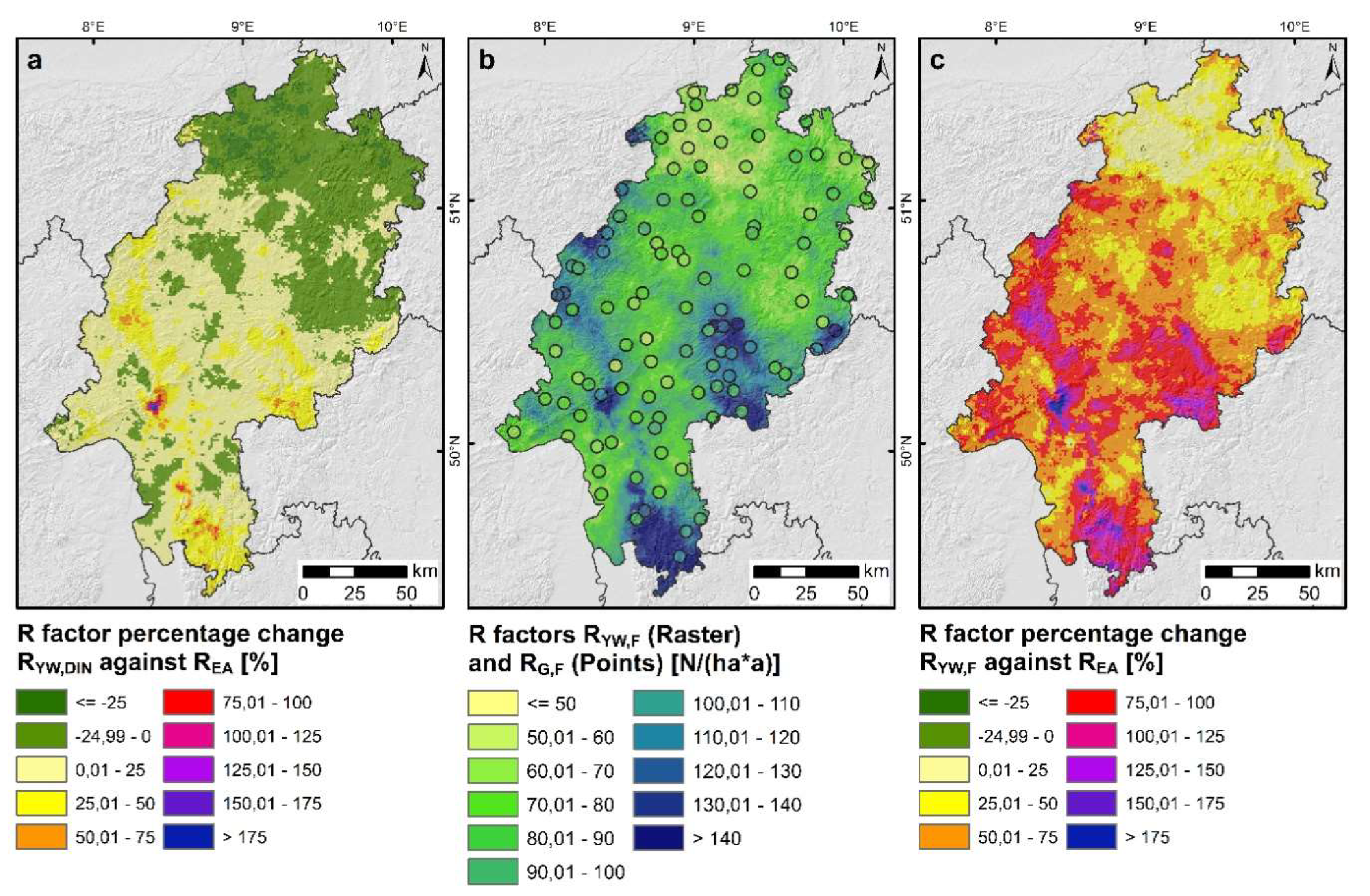
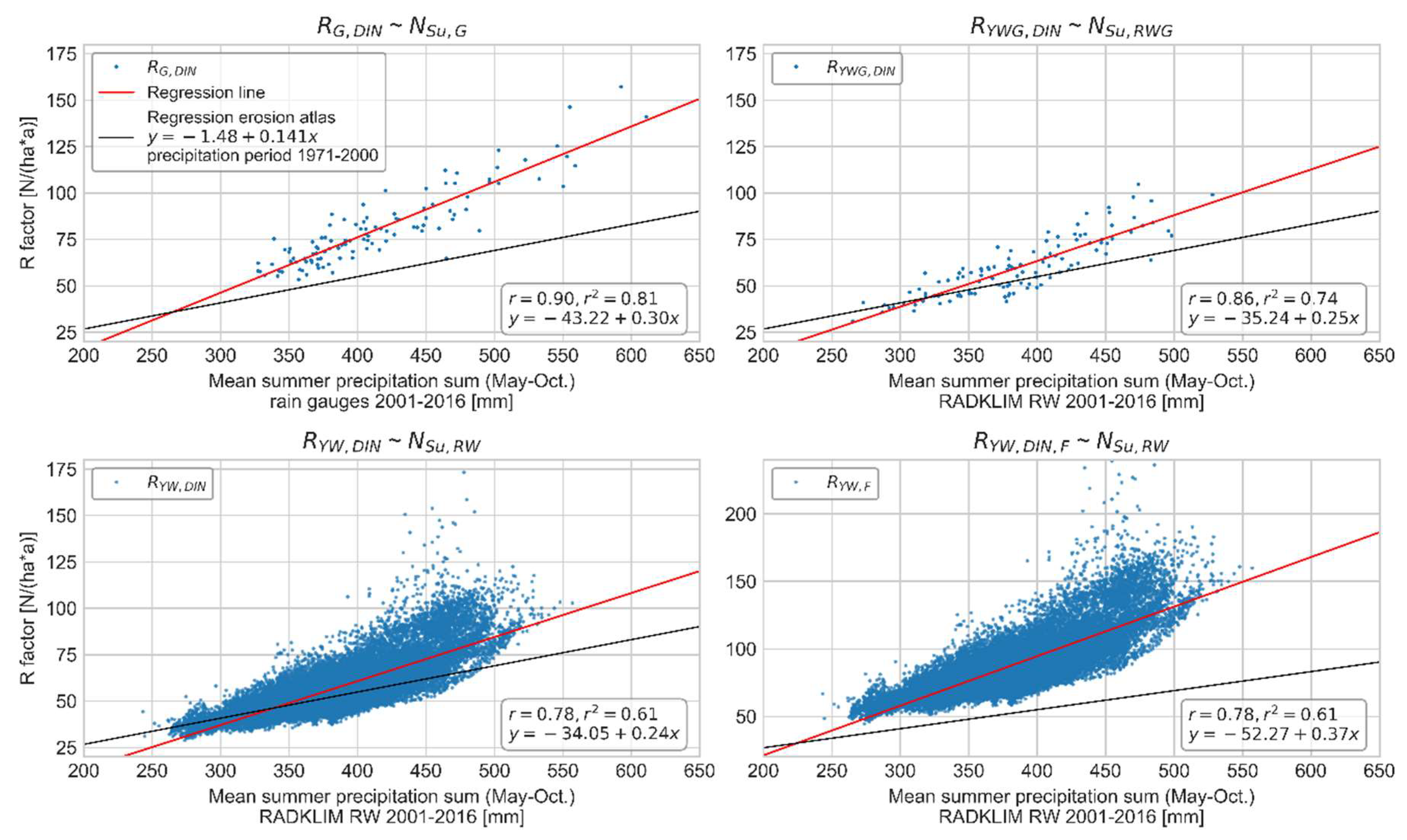
- The newly calculated R-factors from both datasets are higher than the R-factors from earlier calculations due to changes in climate, interannual rainfall distribution and rainfall intensity.
- Since radar data include small-scale convective cells without gaps, the R-factors derived from the radar climatology should be higher on average than those calculated from rain gauge measurements. At the same time, the radar measurements underestimate the maximum precipitation intensities. The latter can be compensated by the correction factors according to Fischer et al. [22].
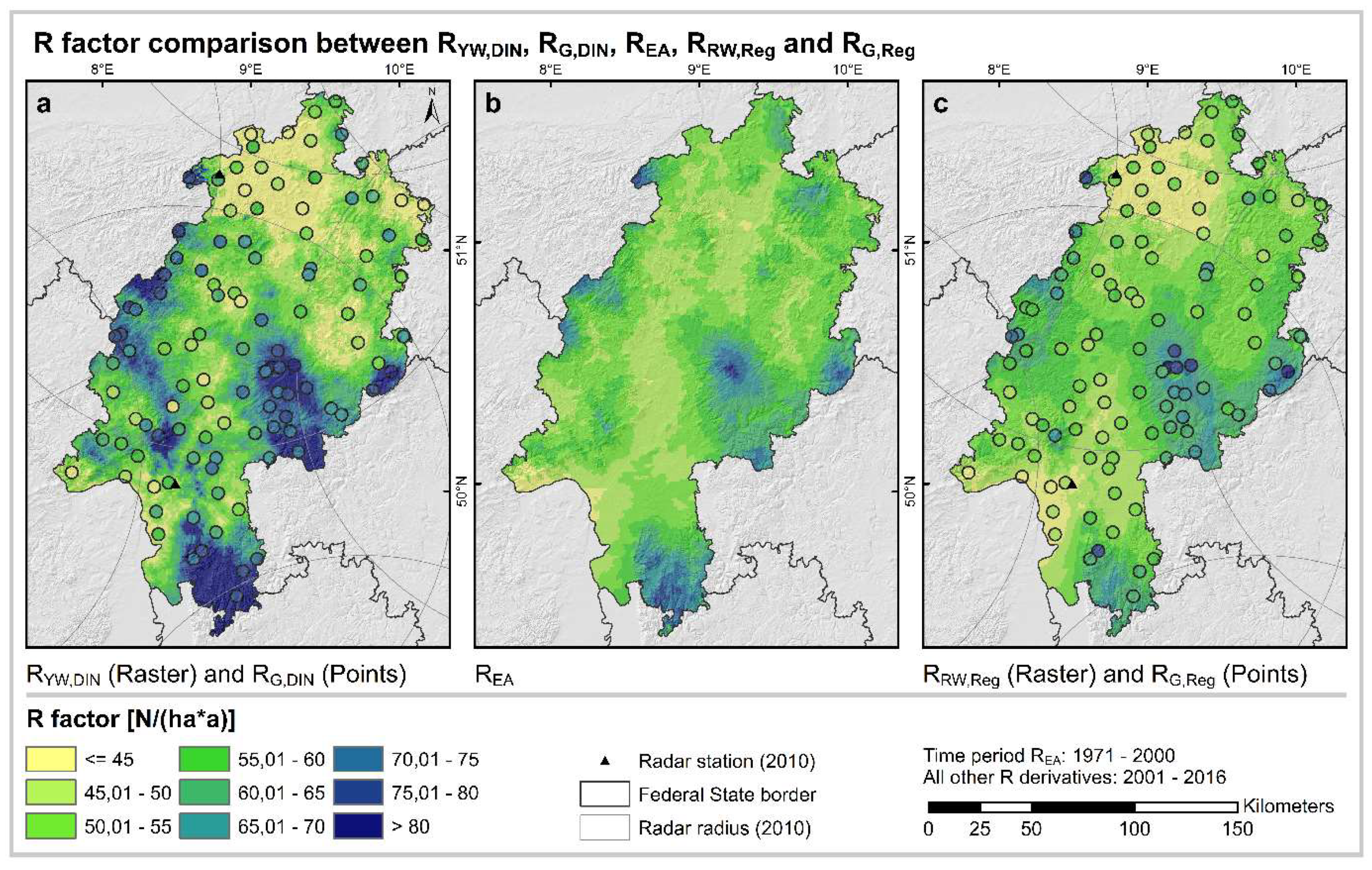
- The spatial distribution of the R-factors derived from the radar climatology deviates from the patterns of the R-factors calculated and interpolated by means of the regression equation due to the comprehensive coverage of all heavy rainfall events.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Basis
2.2.1. Radar Climatology Data
2.2.2. Rain Gauge Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. R-factor Calculation According to DIN 19708
| 5-min interval of the rainfall event | |
| kinetic energy of the rainfall in period i [kJ/m2] | |
| rainfall depth in period i, [mm] | |
| rainfall intensity in period i, [mm/h], that is |
2.3.2. R-factor Calculation Using Regression
- (a)
- all 1 km2 pixels within Hesse (n = 23,320)
- (b)
- all pixels containing at least ten hectares of cropland (n = 11,555)
- (c)
- all rain gauge stations (n = 110)
2.3.3. Application of Scaling Factors
3. Results
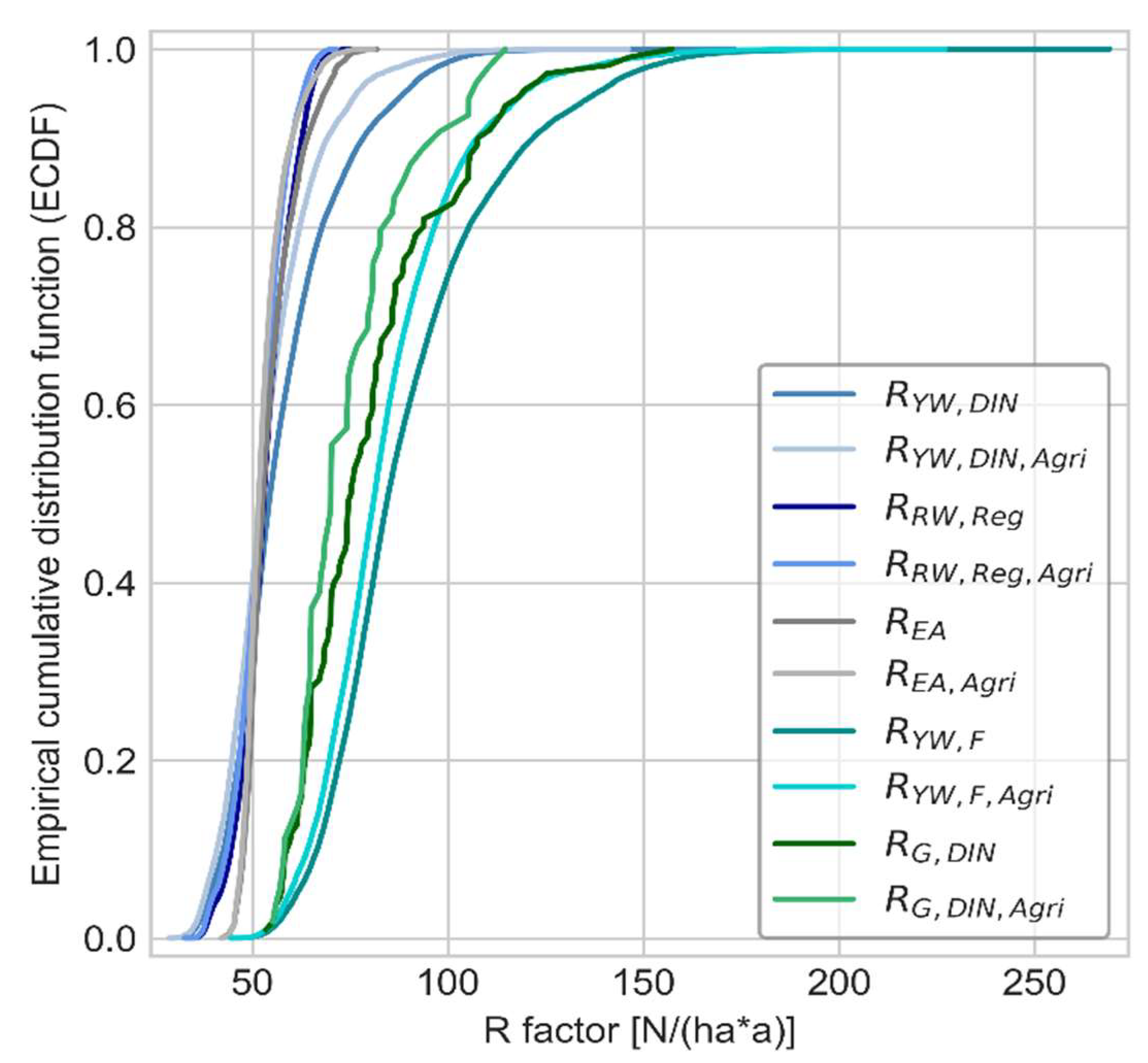
3.1. Statistical Comparison of the Calculated R-factors
3.2. Spatial Distribution
3.3. Derivation of Updated Regression Equations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses. A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture handbook number 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Schwertmann, U.; Vogl, W.; Kainz, M. Bodenerosion durch Wasser. Vorhersage des Abtrags und Bewertung von Gegenmaßnahmen, 2. Aufl.; Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germany, 1990; ISBN 3800130882. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung. DIN 19708. Bodenbeschaffenheit—Ermittlung der Erosionsgefährdung von Böden durch Wasser mithilfe der ABAG; Normenausschuss Wasserwesen im DIN: Berlin, Germany, 2005; (19708). [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadic, M.P.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalikova, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, F.; Hauck, J.; Brandhuber, R.; Weigl, E.; Maier, H.; Auerswald, K. Spatio-temporal variability of erosivity estimated from highly resolved and adjusted radar rain data (RADOLAN). Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, K.; Fischer, F.K.; Winterrath, T.; Brandhuber, R. Rain erosivity map for Germany derived from contiguous radar rain data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1819–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, B.; Friedrich, K.; Vorderbrügge, T.; Vereecken, H.; Wendland, F. Distributed modelling of mean annual soil erosion and sediment delivery rates to surface waters. CATENA 2013, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung. DIN 19708. Bodenbeschaffenheit—Ermittlung der Erosionsgefährdung von Böden durch Wasser mit Hilfe der ABAG, 2017–08; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sauerborn, P. Die Erosivität der Niederschläge in Deutschland. Ein Beitrag zur quantitativen Prognose der Bodenerosion durch Wasser in Mitteleuropa. Ph.D. Thesis, Inst. für Bodenkunde, Bonn, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Elhaus, D. Erosionsgefährdung. Informationen zu den Auswertungen der Erosionsgefährdung durch Wasser, Germany. 2015. Available online: https://www.gd.nrw.de/zip/erosionsgefaehrdung.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Burt, T.; Boardman, J.; Foster, I.; Howden, N. More rain, less soil: Long-term changes in rainfall intensity with climate change. Earth Surface Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiener, P.; Neuhaus, P.; Botschek, J. Long-term trends in rainfall erosivity–analysis of high resolution precipitation time series (1937–2007) from Western Germany. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171-172, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K.; Schmanke, M.; Tetzlaff, B.; Vorderbrügge, T. Erosionsatlas Hessen. In Proceedings of the Tagungsband d. Jahrestagung der DBG/BGS, Kommission VI, “Erd-Reich und Boden-Landschaft“, Bern, Switzerland, 24–27 August 2019. DBG/BGS, Ed.. [Google Scholar]
- Hessisches Landesamt für Naturschutz, Umwelt und Geologie (HLNUG). BodenViewer Hessen. Available online: http://bodenviewer.hessen.de/mapapps/resources/apps/bodenviewer/index.html?lang=de (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Rogler, H.; Schwertmann, U. Erosivität der Niederschläge und Isoerodentkarte Bayerns. Z. für Kult. und Flurberein. 1981, 22, 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hessisches Landesamt für Naturschutz, Umwelt und Geologie (HLNUG). R-Faktor. Available online: https://www.hlnug.de/themen/boden/auswertung/bodenerosionsbewertung/bodenerosionsatlas/r-faktor (accessed on 16 January 2020).
- Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V.; Yang, H.; Durre, I.; Vose, R.; Dunn, R.J.H.; Willett, K.M.; Aguilar, E.; Brunet, M.; Caesar, J.; et al. Updated analyses of temperature and precipitation extreme indices since the beginning of the twentieth century: The HadEX2 dataset. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2098–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterrath, T.; Brendel, C.; Hafer, M.; Junghänel, T.; Klameth, A.; Lengfeld, K.; Walawender, E.; Weigl, E.; Becker, A. Radar climatology (RADKLIM) version 2017.002 (YW); gridded precipitation data for Germany. Available online: https://search.datacite.org/works/10.5676/dwd/radklim_yw_v2017.002 (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Winterrath, T.; Brendel, C.; Hafer, M.; Junghänel, T.; Klameth, A.; Walawender, E.; Weigl, E.; Becker, A. Erstellung einer radargestützten Niederschlagsklimatologie; Berichte des Deutschen Wetterdienstes No. 251; 2017; Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/pbfb_verlag_berichte/pdf_einzelbaende/251_pdf.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2 (accessed on 29 March 2019).
- Kreklow, J.; Tetzlaff, B.; Burkhard, B.; Kuhnt, G. Radar-Based Precipitation Climatology in Germany—Developments, Uncertainties and Potentials. Atmosphere 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstert, A.; Agarwal, A.; Boessenkool, B.; Crisologo, I.; Fischer, M.; Heistermann, M.; Köhn-Reich, L.; López-Tarazón, J.A.; Moran, T.; Ozturk, U.; et al. Forensic hydro-meteorological analysis of an extreme flash flood: The 2016-05-29 event in Braunsbach, SW Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.K.; Winterrath, T.; Auerswald, K. Temporal- and spatial-scale and positional effects on rain erosivity derived from point-scale and contiguous rain data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6505–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Spinoni, J.; Ballabio, C.; Meusburger, K.; Beguería, S.; Klik, A.; Michaelides, S.; Petan, S.; Hrabalíková, M.; et al. Monthly Rainfall Erosivity: Conversion Factors for Different Time Resolutions and Regional Assessments. Water 2016, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmel, A. Hessisches Bergland. In Physische Geographie Deutschlands, 2nd ed.; Liedtke, H., Marcinek, J., Eds.; Justus Perthes Verlag: Gotha, Germany, 1995; pp. 340–352. ISBN 3-623-00840-0. [Google Scholar]
- Winterrath, T.; Brendel, C.; Hafer, M.; Junghänel, T.; Klameth, A.; Lengfeld, K.; Walawender, E.; Weigl, E.; Becker, A. Radar climatology (RADKLIM) version 2017.002 (RW); gridded precipitation data for Germany. Available online: https://search.datacite.org/works/10.5676/dwd/radklim_rw_v2017.002 (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Deutscher Wetterdienst Open Data Portal. Rain Gauge Precipitation Observations in 1-Minute Resolution. Available online: https://opendata.dwd.de/climate_environment/CDC/observations_germany/climate/1_minute/precipitation/ (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Kreklow, J.; Tetzlaff, B.; Kuhnt, G.; Burkhard, B. A Rainfall Data Intercomparison Dataset of RADKLIM, RADOLAN, and Rain Gauge Data for Germany. Data 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The HDF Group. Hierarchical Data Format. Available online: https://portal.hdfgroup.org (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Mckinney, W. pandas: A Foundational Python Library for Data Analysis and Statistics. Python High-Perform. Sci. Comput. 2011, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Kreklow, J. Facilitating radar precipitation data processing, assessment and analysis: A GIS-compatible python approach. J. Hydroinformatics 2019, 21, 652–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreklow, J.; Tetzlaff, B.; Burkhard, B.; Kuhnt, G. Radar-Based Precipitation Climatology in Germany - Developments, Uncertainties and Potentials. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202002.0044/v1 (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.R.; Dokken, D.J.; Mach, K.J.; Mastrandrea, M.D. Climate Change 2014 – Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects; Working Group II Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/climate-change-2014-impacts-adaptation-and-vulnerability-part-a-global-and-sectoral-aspects/1BE4ED76F97CF3A75C64487E6274783A (accessed on 7 February 2018).
- Giorgi, F.; Bi, X.; Pal, J. Mean, interannual variability and trends in a regional climate change experiment over Europe. II: climate change scenarios (2071–2100). Clim. Dyn. 2004, 23, 839–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, T.; Jacob, D. Modeling extreme precipitation events—A climate change simulation for Europe. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2004, 44, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, C.; Schöll, R.; Fukutome, S.; Schmidli, J.; Vidale, P.L. Future change of precipitation extremes in Europe: Intercomparison of scenarios from regional climate models. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyselý, J.; Beranová, R. Climate-change effects on extreme precipitation in central Europe: Uncertainties of scenarios based on regional climate models. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2009, 95, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirmbach, M.; Einfalt, T.; Langstädtler, G.; Janßen, C.; Reinhardt, C.; Mehlig, B. Extremwertstatistische Untersuchung von Starkniederschlägen in NRW (ExUS). Korresp. Abwasser und Abfall 2013, 60, 591–599. [Google Scholar]
- Fiener, P.; Auerswald, K. Comment on “The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe” by Panagos et al. (Environmental Science & Policy 54 (2015) 438–447). Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 57, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Beguería, S.; Klik, A.; Rymszewicz, A.; Michaelides, S.; Olsen, P.; Tadić, M.P.; et al. Reply to the comment on "Rainfall erosivity in Europe" by Auerswald et al. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name | Derivation Method | Input Dataset | Spatial Extent | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RYW,DIN | DIN 19708 | RADKLIM YW (5 min) | All radar pixels in Hesse (1 × 1 km) | 23,320 |
| RYW,DIN, Agri | DIN 19708 | RADKLIM YW (5 min) | Radar pixels containing ≥ 10 ha of cropland | 11,555 |
| RG,DIN | DIN 19708 | Rain gauge data (5 min) | All rain gauges | 110 |
| RYWG,DIN | DIN 19708 | RADKLIM YW (5 min) | Pixels containing a rain gauge | 110 |
| REA | Interpolated rain gauge data (1971–2000) | 1 × 1 km grid for Hesse | 23,320 | |
| REA,Agri | Interpolated rain gauge data (1971–2000) | Grid cells containing ≥ 10 ha of cropland | 11,555 | |
| RRW,Reg | RADKLIM RW (1 h) | All radar pixels in Hesse | 23,320 | |
| RRW,Reg,Agri | RADKLIM RW (1 h) | Radar pixels containing ≥ 10 ha of cropland | 11,555 | |
| RG,Reg | Rain gauge data | All rain gauges in Hesse | 110 | |
| RRWG,Reg | RADKLIM RW (1 h) | Pixels containing a rain gauge | 110 | |
| REAG | Interpolated rain gauge data (1971–2000) | Grid cells containing a rain gauge | 110 | |
| RYW,F | RADKLIM YW (5 min) | All radar pixels in Hesse | 23,320 | |
| RYW,F,Agri | RADKLIM YW (5 min) | Radar pixels containing ≥ 10 ha of cropland | 11,555 | |
| RG,F | Rain gauge data | All rain gauges | 110 | |
| RYWG,F | RADKLIM YW (5 min) | Pixels containing a rain gauge | 110 | |
| RG,P | Rain gauge data | All rain gauges | 110 |
| R-factor | n | Method | Data Source | Mean | Standard Deviation | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RYW,DIN | 23,320 | DIN 19708 | RADKLIM | 58.0 | 14.7 | 28.8 | 54.6 | 173.2 |
| RYW,DIN,Agri | 11,555 | DIN 19708 | RADKLIM | 54.2 | 12.0 | 28.8 | 52.3 | 146.1 |
| RG,DIN | 110 | DIN 19708 | Gauges | 80.6 | 20.6 | 53.4 | 75.3 | 157.2 |
| RYWG,DIN | 110 | DIN 19708 | RADKLIM | 60.1 | 15.8 | 31.0 | 57.8 | 104.7 |
| REA | 23,320 | Regression | Erosion atlas | 54.5 | 6.6 | 42.1 | 52.8 | 81.8 |
| REA,Agri | 11,555 | Regression | Erosion atlas | 52.8 | 5.3 | 42.1 | 51.7 | 81.0 |
| RRW,Reg | 23,320 | Regression | RADKLIM | 53.2 | 6.8 | 32.8 | 53.0 | 77.0 |
| RRW,Reg,Agri | 11,555 | Regression | RADKLIM | 51.9 | 6.4 | 32.8 | 52.1 | 71.4 |
| RG,Reg | 110 | Regression | Gauges | 57.0 | 8.8 | 44.7 | 55.0 | 84.7 |
| RRWG,Reg | 110 | Regression | RADKLIM | 53.1 | 7.8 | 35.9 | 52.4 | 73.0 |
| REAG | 110 | Regression | Erosion atlas | 55.9 | 8.1 | 45.2 | 53.7 | 81.8 |
| RYW,F | 23,320 | DIN scaled | RADKLIM | 90.1 | 22.8 | 44.5 | 84.8 | 269.1 |
| RYW,F,Agri | 11,555 | DIN scaled | RADKLIM | 84.2 | 18.6 | 44.5 | 81.3 | 227.0 |
| RG,F | 110 | DIN scaled | Gauges | 84.6 | 21.6 | 56.1 | 79.1 | 165.1 |
| RYWG,F | 110 | DIN scaled | RADKLIM | 93.4 | 24.6 | 48.0 | 89.8 | 162.7 |
| RG,P | 110 | DIN scaled | Gauges | 64.4 | 16.4 | 42.6 | 60.1 | 125.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kreklow, J.; Steinhoff-Knopp, B.; Friedrich, K.; Tetzlaff, B. Comparing Rainfall Erosivity Estimation Methods Using Weather Radar Data for the State of Hesse (Germany). Water 2020, 12, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051424
Kreklow J, Steinhoff-Knopp B, Friedrich K, Tetzlaff B. Comparing Rainfall Erosivity Estimation Methods Using Weather Radar Data for the State of Hesse (Germany). Water. 2020; 12(5):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051424
Chicago/Turabian StyleKreklow, Jennifer, Bastian Steinhoff-Knopp, Klaus Friedrich, and Björn Tetzlaff. 2020. "Comparing Rainfall Erosivity Estimation Methods Using Weather Radar Data for the State of Hesse (Germany)" Water 12, no. 5: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051424
APA StyleKreklow, J., Steinhoff-Knopp, B., Friedrich, K., & Tetzlaff, B. (2020). Comparing Rainfall Erosivity Estimation Methods Using Weather Radar Data for the State of Hesse (Germany). Water, 12(5), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051424





