Treatment of Winery Wastewater with a Multistage Constructed Wetland System for Irrigation Reuse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
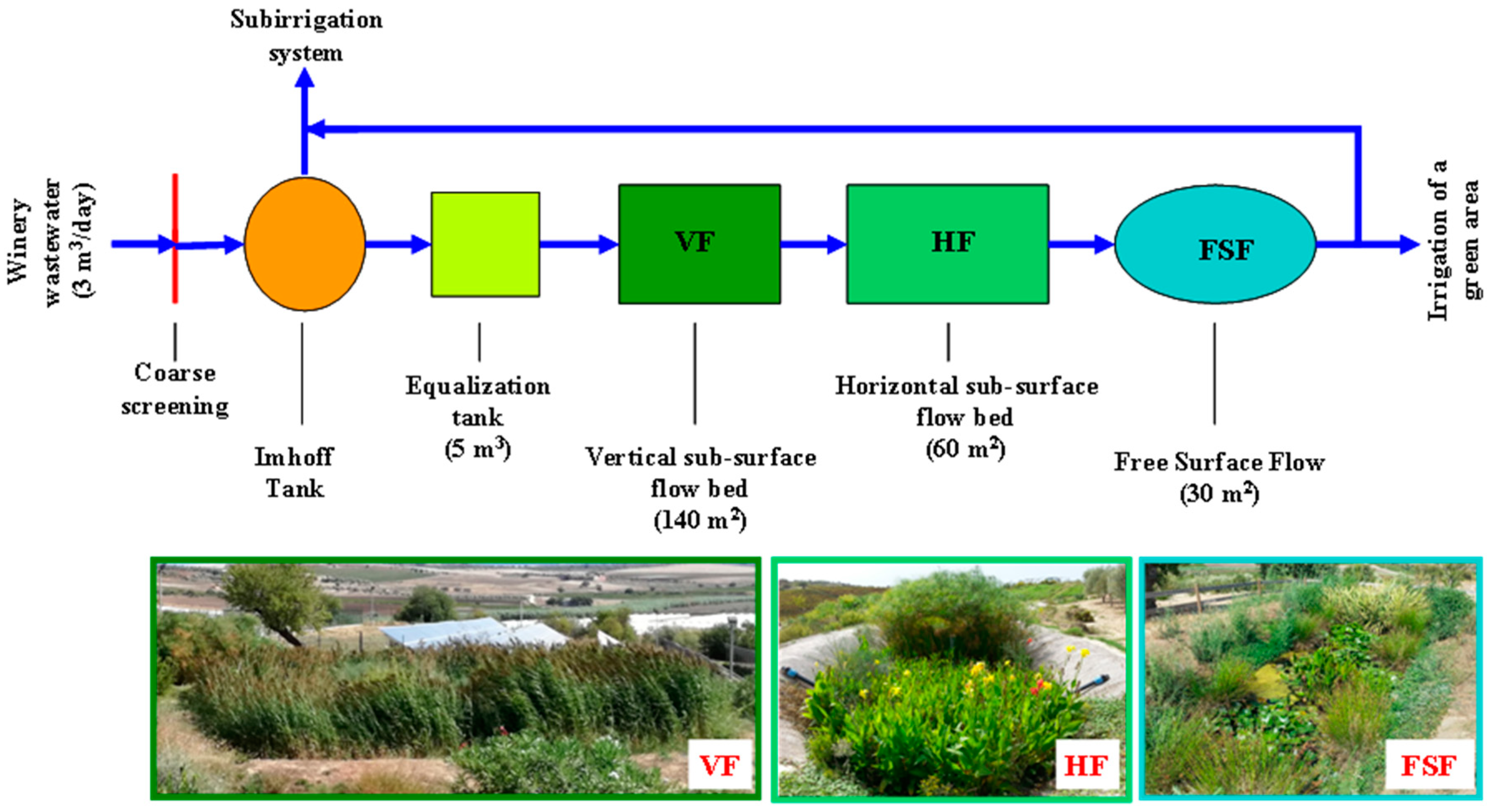
2.1. The Experimental Multistage CW System
2.2. Wastewater Quality Characterization
2.3. Plant Measurements
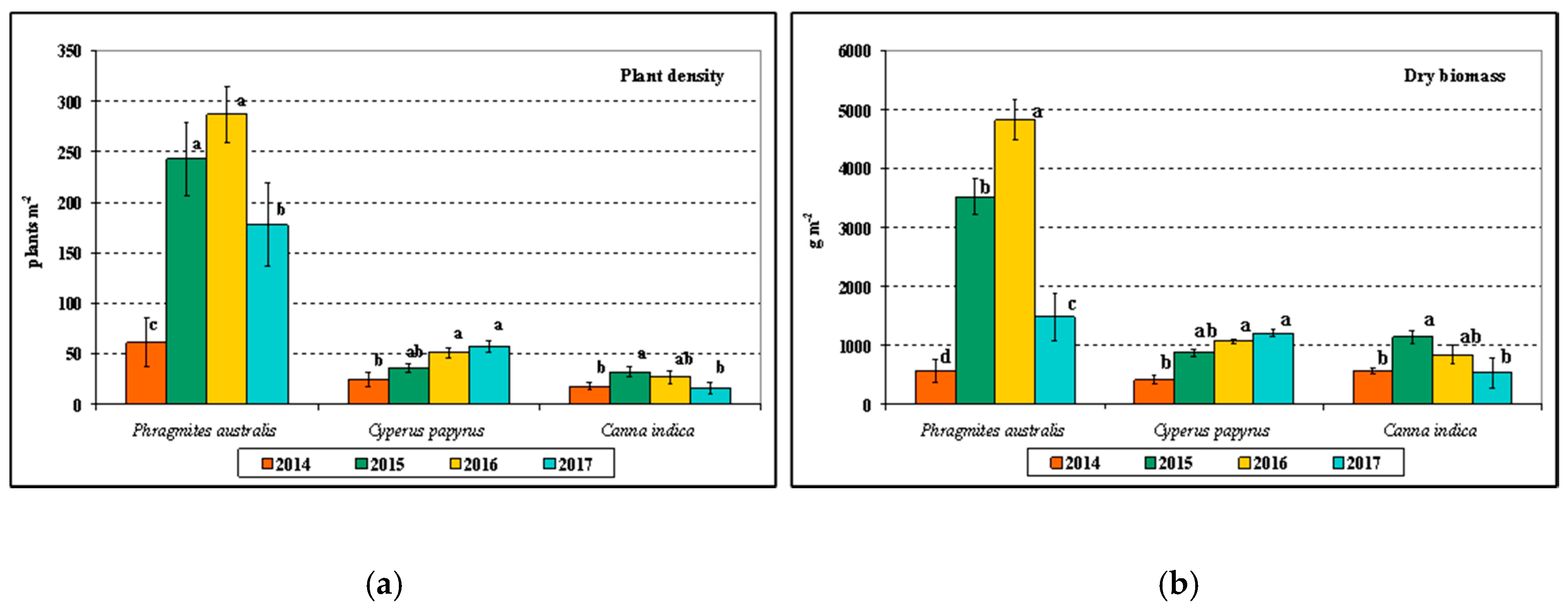
3. Results and Discussion
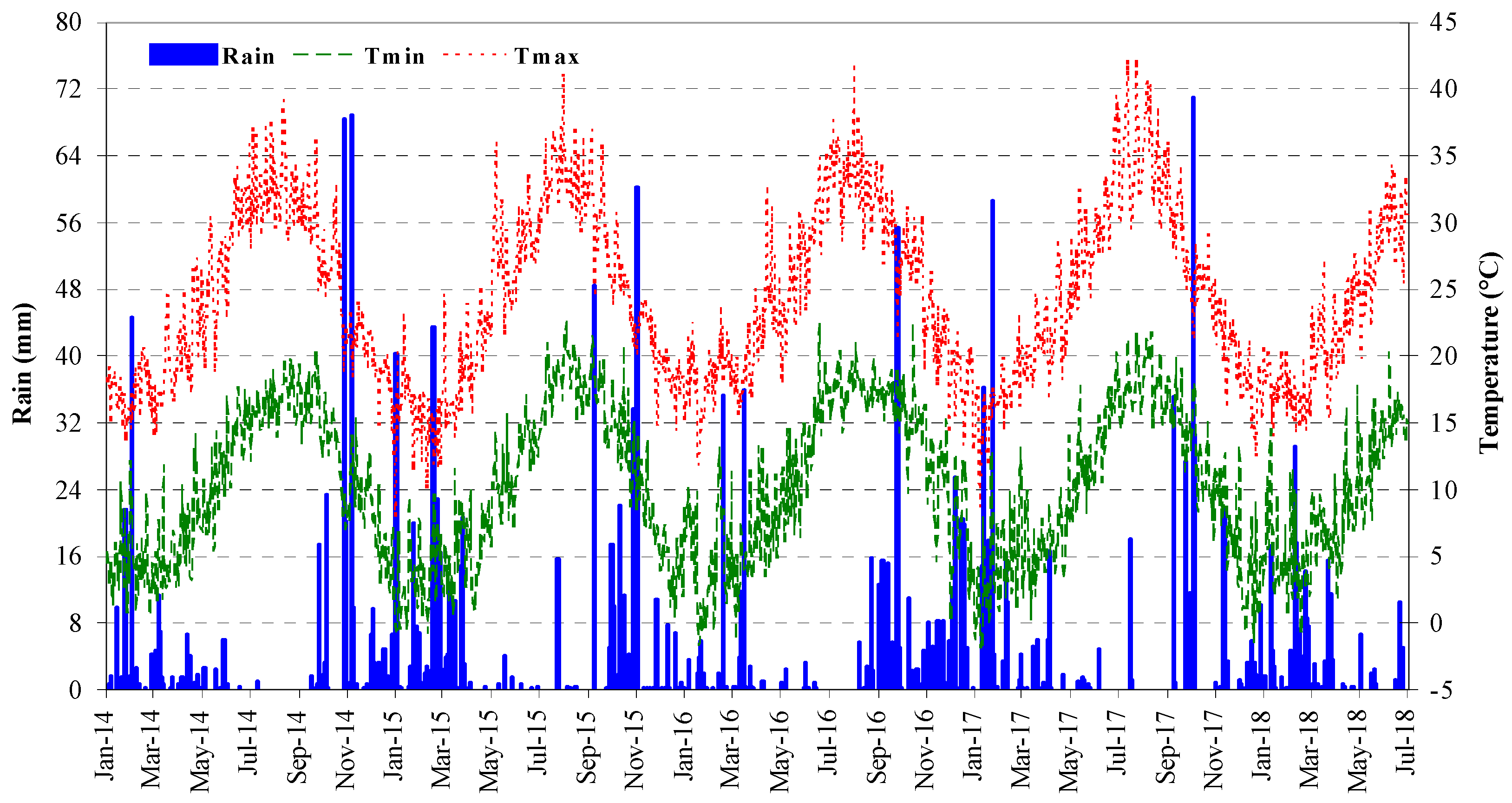
3.1. Weather Data at the Experimental Site
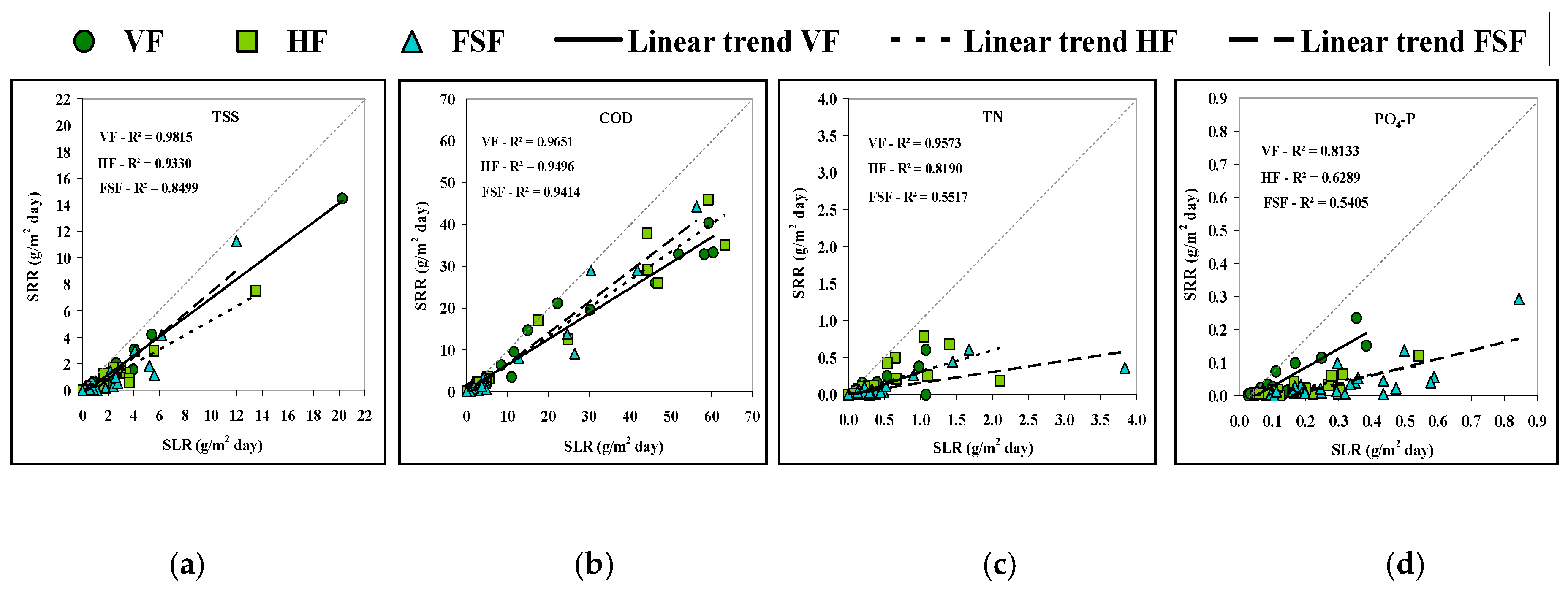
3.2. Wastewater Physico-Chemical Parameters
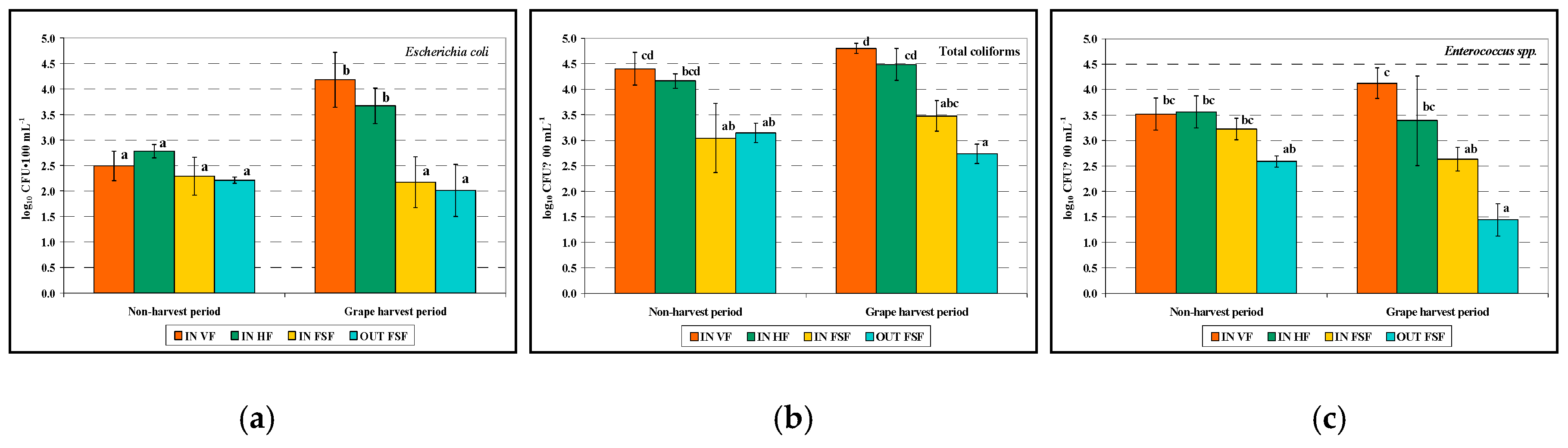
3.3. Microbiological Parameters
3.4. Winery Wastewater Reuse Option
3.5. Characteristics of Vegetated Areas in the Multistage CW
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Organization of Vine and Wine. Available online: http://www.oiv.int/public/medias/7044/ppt-oiv-2019-october-press-conference.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2020).
- Masi, F.; Rochereau, J.; Troesch, S.; Ruiz, I.; Soto, M. Wineries wastewater treatment by constructed wetlands: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreottola, G.; Foladori, P.; Ziglio, G. Biological treatment of winery wastewater: An overview. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ioannou, L.A.; Li Puma, L.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Treatment of winery wastewater by physicochemical, biological and advanced processes: A review. J. Hazards Mater. 2015, 286, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, L.; de la Varga, D.; Ruiz, I.; Soto, M. Winery wastewater treatment in a hybrid constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, H.L.; Grismer, M.E.; Tchobanoglous, G. Treatment of high-strength winery wastewater using a subsurface flow constructed wetland. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradie, A.; Sigge, G.O.; Cloete, T.E. Influence of winemaking practices on the characteristics of winery wastewater and water usage of wineries. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2014, 35, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Arienzo, M.; Christen, E.W.; Quayle, W.C. Phytotoxicity testing of winery wastewater for constructed wetlands treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruccioli, M.; Duarte, J.C.; Eusebio, A.; Federici, F. Aerobic treatment of winery wastewater using a jet-loop activated sludge reactor. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, P.J.; Burgess, J.E. Treatment methods for wine-related ad distillery wastewaters: A review. Bioremediat. J. 2008, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Recommendation of 6 May 2003 Concerning the Definition of Micro, Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises; 2003/361/EC. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/AUTO/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2003.124.01.0036.01.ENG (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Litaor, M.I.; Meir-Dinar, N.; Castro, B.; Azaizeh, H.; Rytwo, G.; Levi, N.; Levi, M.; MarChaim, U. Treatment of winery wastewater with aerated cells mobile system. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2015, 4, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheridan, C.M.; Glasser, D.; Hildebrandt, D. Estimating rate constants of contaminant removal in constructed wetlands treating winery effluent: A comparison of three different methods. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. The use constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow for various types of wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulidzi, A.R. Winery and distillery wastewater treatment by constructed wetland with shorter retention time. Water. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2611–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grismer, M.E.; Shepherd, H.L. Plants in constructed wetlands help to treat agricultural processing wastewaters. Calif. Agric. 2011, 65, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decree of Ministry for Environment, n. 185, 23/07/2003, Gazzetta Ufficiale n. 169. Italian Technical Guidelines for Wastewater Reuse. Available online: http://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2003/07/23/003G0210/sg (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Marzo, A.; Ventura, D.; Cirelli, G.L.; Aiello, R.; Vanella, D.; Rapisarda, R.; Barbagallo, S.; Consoli, S. Hydraulic reliability of a horizontal wetland for wastewater treatment in Sicily. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, A.C.; Cirelli, G.L.; Di Silvestro, I.; Pacifici, P.; Castiglione, V.; Toscano, A.; Milani, M. Growth and biomass production of different plant species in two different constructed wetland systems in Sicily. Desalination 2009, 246, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatti, S. Flora d’Italia; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- APHA/AWWA/WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Baltimore: American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water-Works Association (AWWA), and American Environment Federation (AEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water; American Public Health Association: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, N.; Marzo, A.; Randazzo, C.; Caggia, C.; Toscano, A.; Cirelli, G.L. Constructed wetlands combined with disinfection systems for removal of urban wastewater contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO. Water quality—Detection and enumeration of Escherichia coli and coliform bacteria—Part 1: Membrane filtration method 9308-1:2001; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and on the Council on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse. 28.5.2018 COM (2018) 337 final 2018/0169 (COD). 2018. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/pdf/water_reuse_regulation.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Grismer, M.E.; Carr, M.A.; Shepherd, H.L. Evaluation of constructed wetland treatment performance for winery wastewater. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanieri, L.; Bracali, M.; Bresciani, R.; Masi, F. Multi-stage CW system for winery wastewater treatment. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Wetland Systems for Water Pollution Control, Venice, Italy, 4–9 October 2010; Masi, F., Nivala, J., Eds.; International Water Association: London, UK, 2010; pp. 1139–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Rochard, J.; Oldano, A.; Marengo, D. Environmental innovation in winery effluent management: Use of reed beds. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Wetland Systems for Water Pollution Control, Venice, Italy, 4–9 October 2010; Masi, F., Nivala, J., Eds.; International Water Association: London, UK, 2010; pp. 1454–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Gautier, M.; Prost Boucle, S.; Molle, P.; Michel, P.; Gourdon, R. Performance evaluation of partially saturated vertical-flow constructed wetland with trickling filter and chemical precipitation for domestic and winery wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masi, F.; Conte, G.; Martinuzzi, N.; Pucci, B. Winery high organic content wastewater treated by constructed wetland in Mediterranean climate. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Wetland System for Water Pollution Control, Arusha, Tanzania, 16–19 September 2002; IWA and University of Dar El Salaam: Arusha, Tanzania, 2002; pp. 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Knight, R.L. Treatment Wetlands; Lewis Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shingare, R.P.; Thawale, P.R.; Raghunathan, K.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, S. Constructed wetland for wastewater reuse: Role and efficiency in removing enteric pathogens. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeters, G.A.; Stuart, D.G. Survival of coliform bacteria in natural waters—field and laboratory studies with membrane-filter chambers. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jourjon, F.; Khaldi, S.; Reveiller, M.; Thibault, C.; Poulard, A.; Chretien, P.; Bednar, J. Microbiological characterization of winery effluents: An inventory of the sites for different treatment systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozema, E.R.; Rozema, L.R.; Zheng, Y. A vertical flow constructed wetland for the treatment of winery process water and domestic sewage in Ontario, Canada: Six years of performance data. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 86, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgot, M.; Oron, G.; Cirelli, G.L.; Dalezios, N.R.; Díaz, A.; Angelakis, A.N. Criteria for wastewater treatment and reuse under water scarcity (Chapter 14). In Handbook of Drought and Water Scarcity: Environmental Impacts and Analysis of Drought and Water Scarcity; Eslamian, S., Eslamian, F.A., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 252–272. [Google Scholar]
- Barbera, A.C.; Maucieri, C.; Ioppolo, A.; Milani, M.; Cavallaro, V. Effects of olive mill wastewater physico-chemical treatments on polyphenol abatement and Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.) germinability. Water Res. 2014, 52, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maucieri, C.; Cavallaro, V.; Caruso, C.; Borin, M.; Milani, M.; Barbera, A.C. Sorghum biomass production for energy purpose using treated urban wastewater and different fertilization in a mediterranean environment. Agriculture 2016, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milani, M.; Toscano, A. Evapotranspiration from pilot-scale constructed wetland planted with Phragmites australis in a Mediterranean environment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2013, 48, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, M.; Marzo, A.; Toscano, A.; Consoli, S.; Cirelli, G.L.; Ventura, D.; Barbagallo, S. Evapotranspiration from horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with different perennial plant species. Water 2019, 11, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanner, C.C. Growth and nutrition of Schoenoplectus validus in agricultural wastewaters. Aquat. Bot. 1994, 47, 131–153. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, R.; Cirelli, G.L.; Consoli, S. Effect of reclaimed wastewater irrigation on soil and tomato fruits: A case study in Sicily (Italy). Agr. Water Manag. 2007, 93, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, S.; Barbera, A.C.; Cirelli, G.L.; Milani, M.; Toscano, A. Reuse of constructed wetland effluents for irrigation of energy crops. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| WW Main Quality Characteristics and Location | Minimum | Average | Maximum | Standard Deviation | Removal (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Each Stage | All CW | |||||
| pH | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 4.67 | 6.82 | 11.06 | 1.34 | ||
| Outlet VF | 5.08 | 6.96 | 8.32 | 0.66 | ||
| Outlet HF | 6.20 | 7.02 | 7.66 | 0.37 | ||
| Outlet FSF | 6.57 | 7.19 | 7.82 | 0.33 | ||
| Electrical Conductivity (μS·cm−1) | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 561 | 1086 | 2930 | 584 | ||
| Outlet VF | 510 | 990 | 2040 | 459 | ||
| Outlet HF | 462 | 983 | 1974 | 451 | ||
| Outlet FSF | 433 | 943 | 986 | 411 | ||
| TSS (mg·L−1) | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 8 | 86 | 630 | 130 | ||
| Outlet VF | 5 | 36 | 180 | 40 | 42 | |
| Outlet HF | 2 | 14 | 170 | 20 | 34 | |
| Outlet FSF | 2 | 11 | 31 | 7 | 24 | 69 |
| BOD5 (mg·L−1) | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 4 | 316 | 1,243 | 418 | ||
| Outlet VF | 2 | 122 | 500 | 166 | 45 | |
| Outlet HF | 2 | 34 | 144 | 43 | 47 | |
| Outlet FSF | 2 | 17 | 65 | 20 | 29 | 78 |
| COD (mg·L−1) | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 6 | 587 | 2020 | 730 | ||
| Outlet VF | 5 | 221 | 882 | 301 | 45 | |
| Outlet HF | 4 | 74 | 393 | 112 | 51 | |
| Outlet FSF | 3 | 28 | 94 | 37 | 40 | 81 |
| NH4-N (mg·L−1) | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 0.6 | 3.5 | 15.2 | 3.7 | ||
| Outlet VF | 0.3 | 2.0 | 10.5 | 2.6 | 31 | |
| Outlet HF | 0.2 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 0.6 | 28 | |
| Outlet FSF | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 16 | 57 |
| TN (mg·L−1) | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 2.7 | 13.3 | 39.6 | 11.9 | ||
| Outlet VF | 2.1 | 8.3 | 29.4 | 7.1 | 30 | |
| Outlet HF | 1.7 | 5.3 | 26.8 | 5.4 | 29 | |
| Outlet FSF | 1.5 | 4.2 | 24.3 | 4.5 | 15 | 56 |
| PO4-P (mg·L−1) | ||||||
| Inlet VF | 1.7 | 4.9 | 12.5 | 3.1 | ||
| Outlet VF | 1.5 | 3.4 | 7.6 | 1.5 | 22 | |
| Outlet HF | 1.3 | 3.0 | 5.9 | 1.2 | 11 | |
| Outlet FSF | 1.2 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 0.9 | 11 | 38 |
| WW Main Quality Characteristics and Location | WW Italian Law Limits for Agricultural Reuse | % Samples under Reuse Italian Law Limits | EU Proposal Regulation | % Samples Compliant with EU Regulation Requirements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Requirements | Water Quality Class a | ||||
| TSS | 10 mg·L−1 | 10–35 mg·L−1 | A–B, C, D | ||
| Inlet VF | 16 | 16–22 | |||
| Outlet VF | 40 | 40–56 | |||
| Outlet HF | 58 | 58–76 | |||
| Outlet FSF | 66 | 66–100 | |||
| BOD5 | 20 mg·L−1 | 10–25 mg·L−1 | A–B, C, D | ||
| Inlet VF | 24 | 16–24 | |||
| Outlet VF | 46 | 32–52 | |||
| Outlet HF | 68 | 48–68 | |||
| Outlet FSF | 82 | 64–86 | |||
| COD | 100 mg·L−1 | - | |||
| Inlet VF | 48 | ||||
| Outlet VF | 64 | ||||
| Outlet HF | 86 | ||||
| Outlet FSF | 100 | ||||
| TN | 35 mg·L−1 | - | |||
| Inlet VF | 96 | ||||
| Outlet VF | 100 | ||||
| Outlet HF | 100 | ||||
| Outlet FSF | 100 | ||||
| E. coli | 50 b–200 c CFU·100 mL−1 | 10–100–1000–10,000 CFU·100 mL−1 | A–B–C–D | ||
| Inlet VF | 20–40 | 20–40–40–40 | |||
| Outlet VF | 20–40 | 20–40–60–100 | |||
| Outlet HF | 20–60 | 20–40–80–100 | |||
| Outlet FSF | 40–60 | 40–40–100–100 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milani, M.; Consoli, S.; Marzo, A.; Pino, A.; Randazzo, C.; Barbagallo, S.; Cirelli, G.L. Treatment of Winery Wastewater with a Multistage Constructed Wetland System for Irrigation Reuse. Water 2020, 12, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051260
Milani M, Consoli S, Marzo A, Pino A, Randazzo C, Barbagallo S, Cirelli GL. Treatment of Winery Wastewater with a Multistage Constructed Wetland System for Irrigation Reuse. Water. 2020; 12(5):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051260
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilani, Mirco, Simona Consoli, Alessia Marzo, Alessandra Pino, Cinzia Randazzo, Salvatore Barbagallo, and Giuseppe Luigi Cirelli. 2020. "Treatment of Winery Wastewater with a Multistage Constructed Wetland System for Irrigation Reuse" Water 12, no. 5: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051260
APA StyleMilani, M., Consoli, S., Marzo, A., Pino, A., Randazzo, C., Barbagallo, S., & Cirelli, G. L. (2020). Treatment of Winery Wastewater with a Multistage Constructed Wetland System for Irrigation Reuse. Water, 12(5), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051260










