Characteristics and Source of Dissolved Organic Matter in Lake Hulun, A Large Shallow Eutrophic Steppe Lake in Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
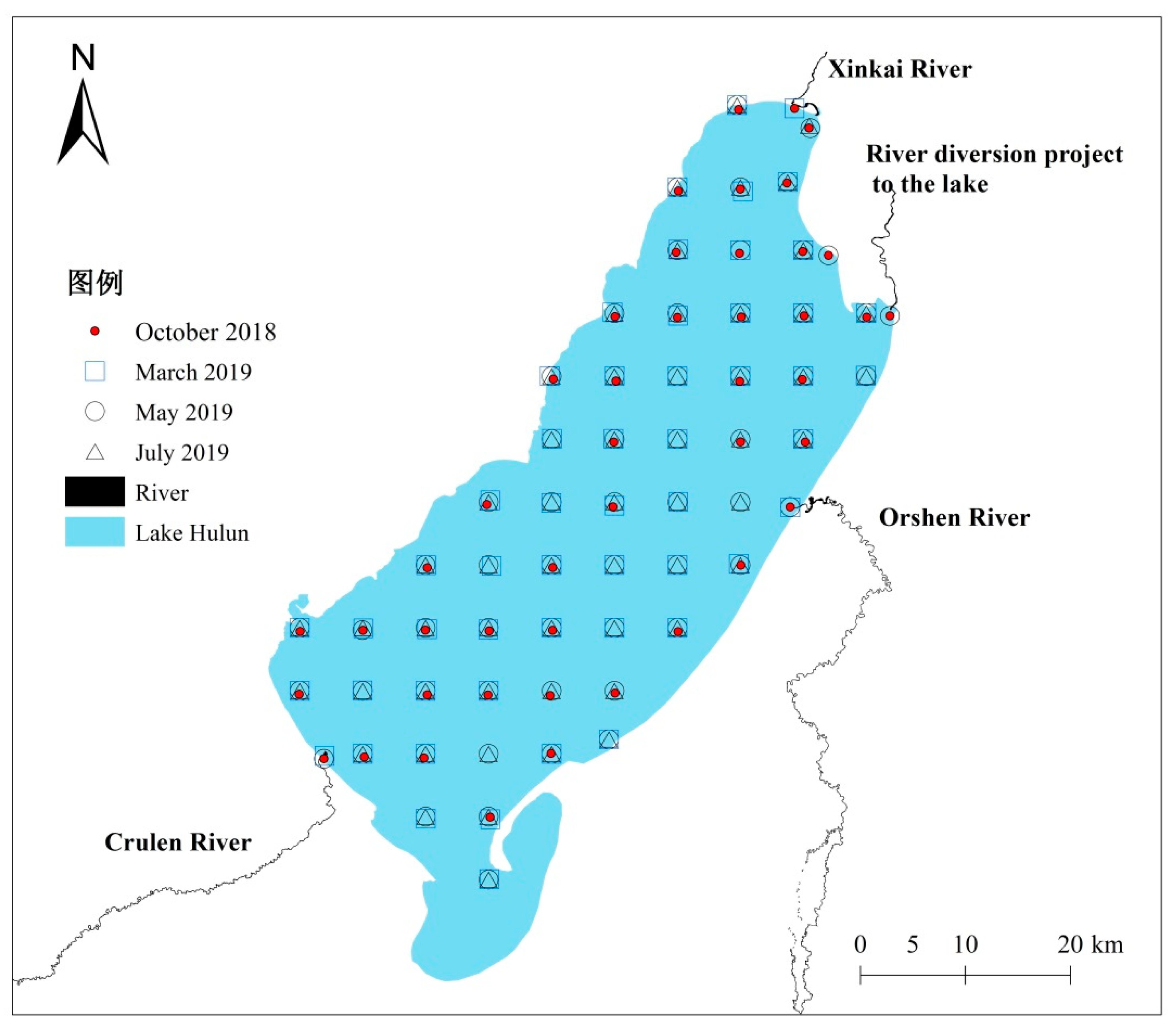
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.3.1. Basic Physical and Chemical Index Analysis
2.3.2. Chromophoric DOM Absorption Analysis
2.3.3. Fluorescence EEMs-PARAFAC Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of the Lake Water
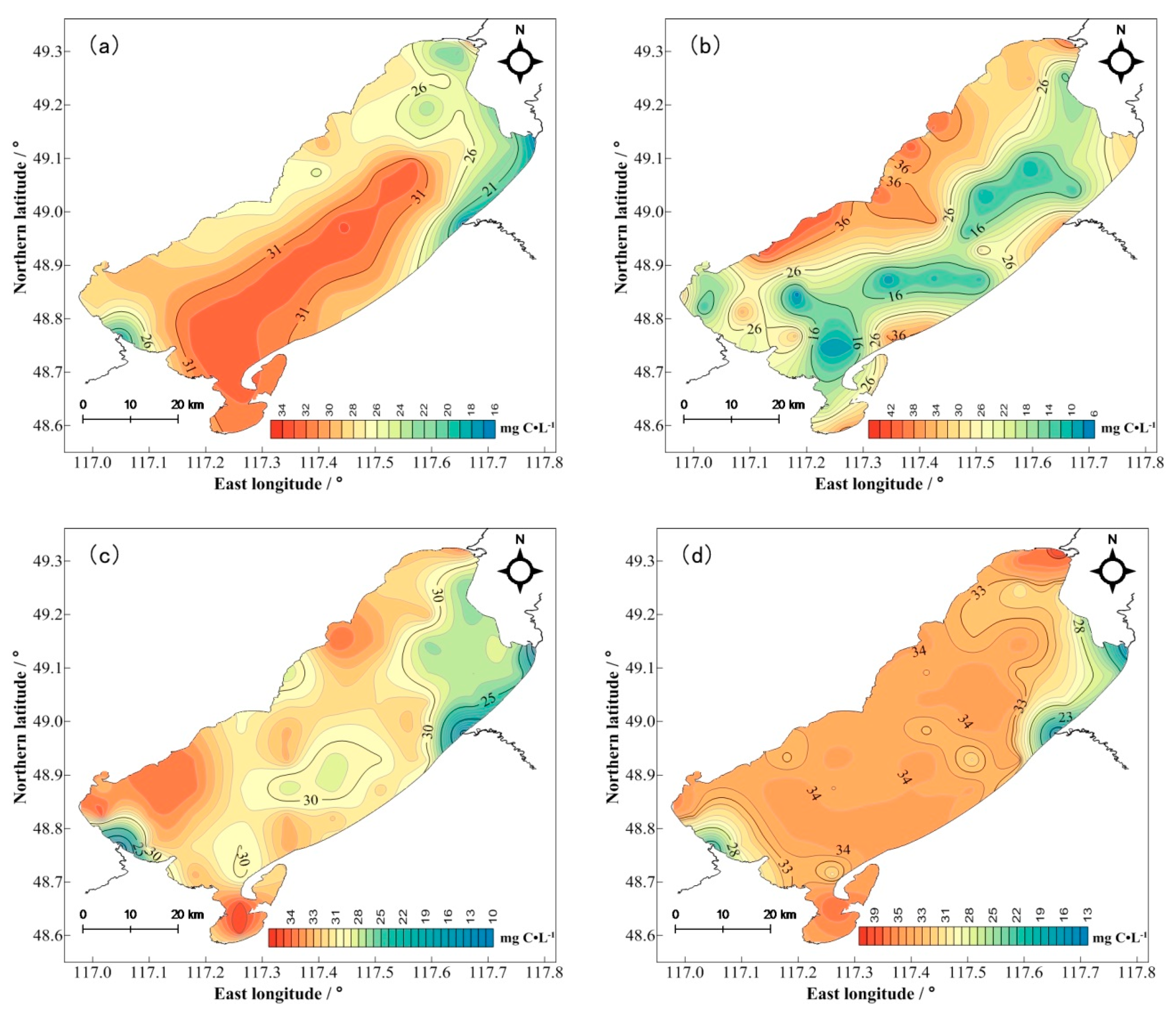
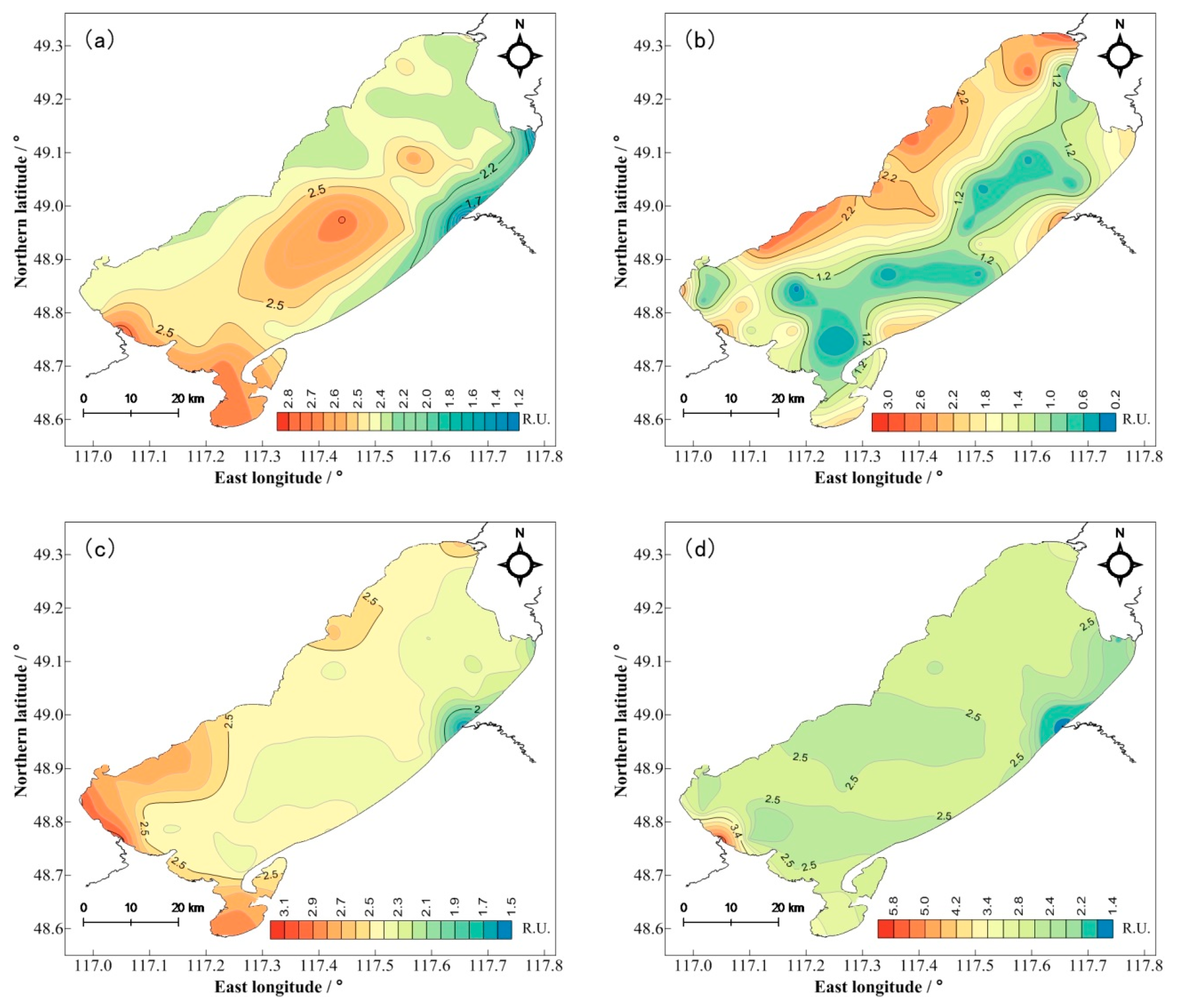
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of DOM
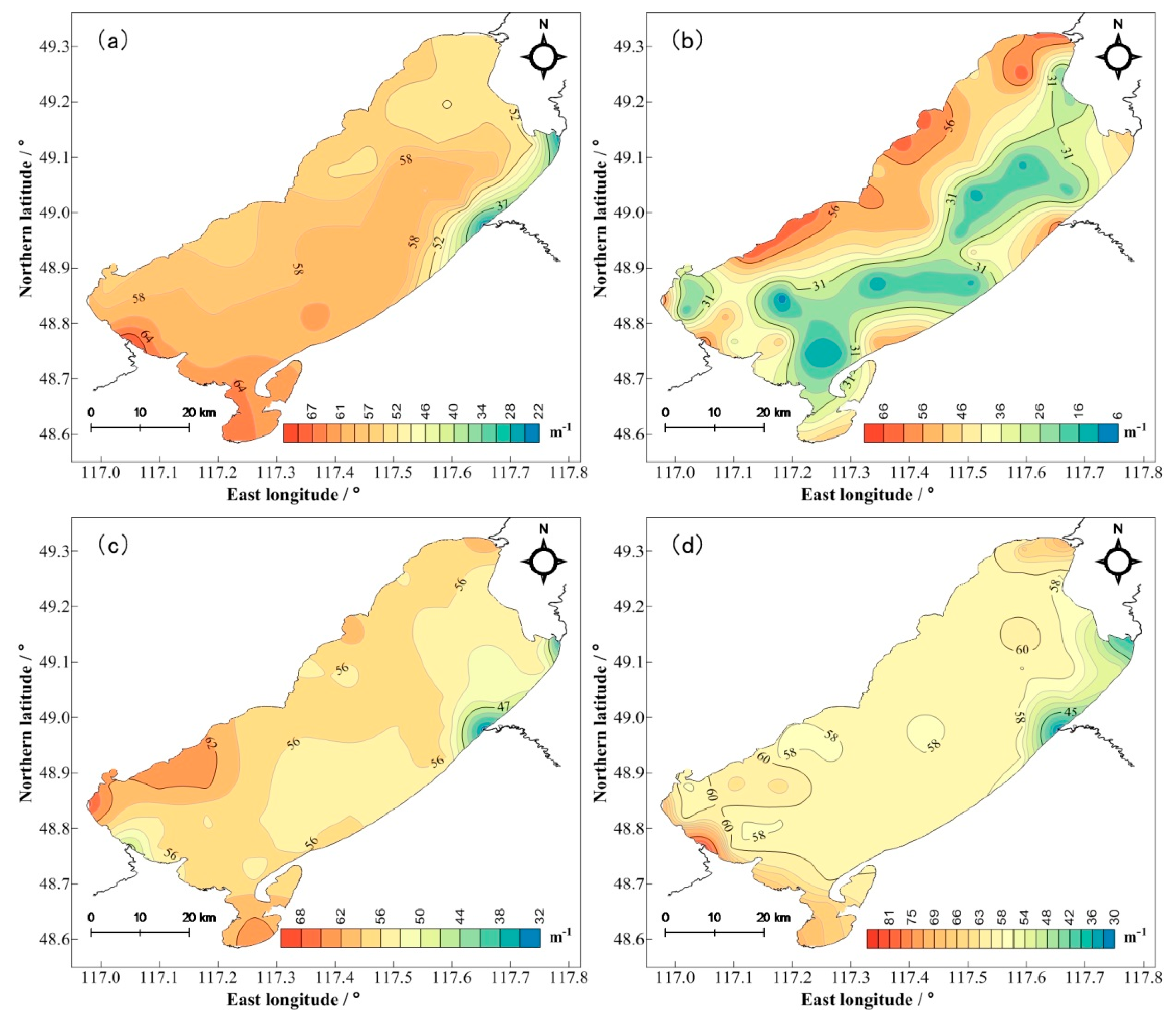
3.3. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of CDOM
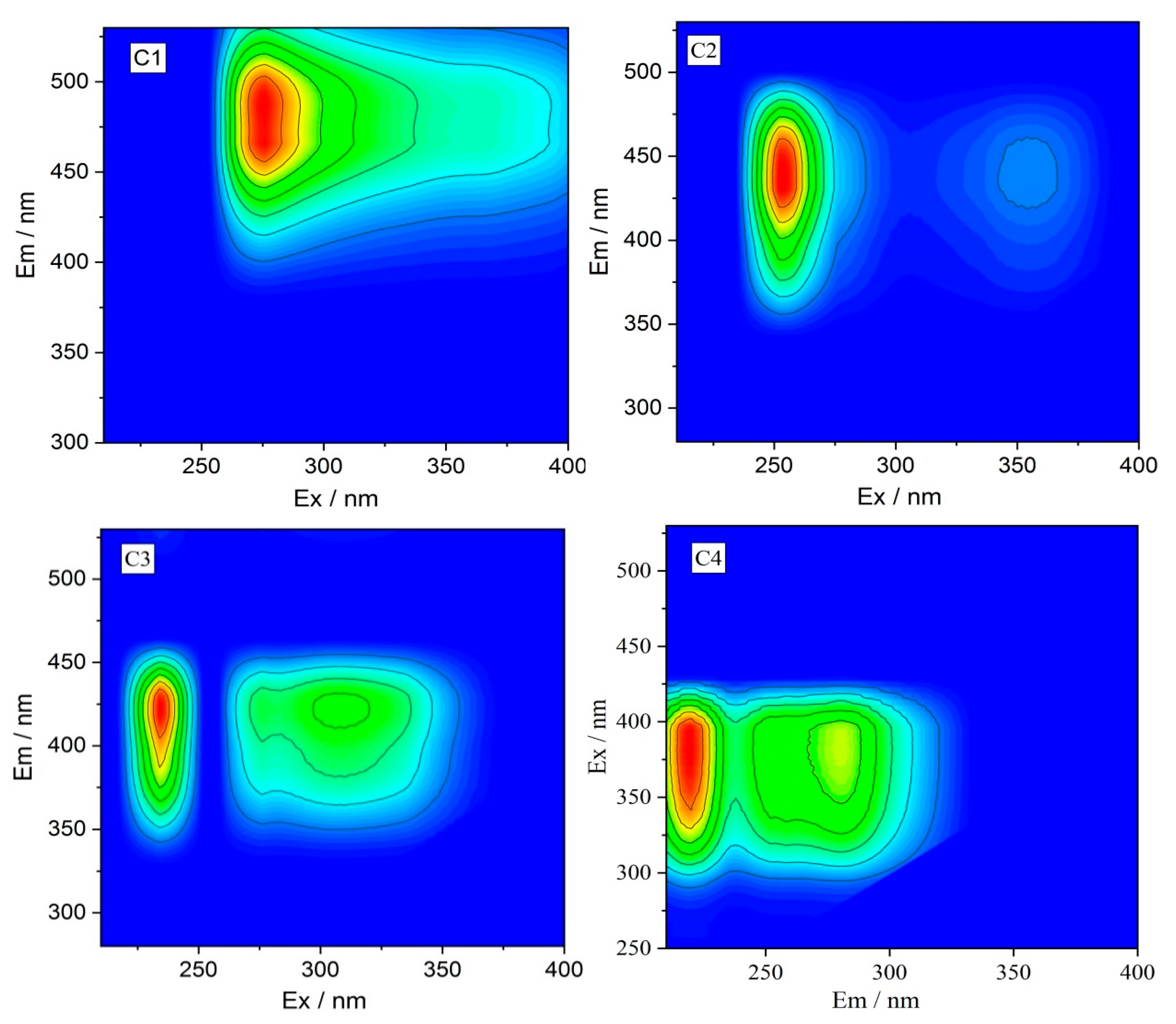
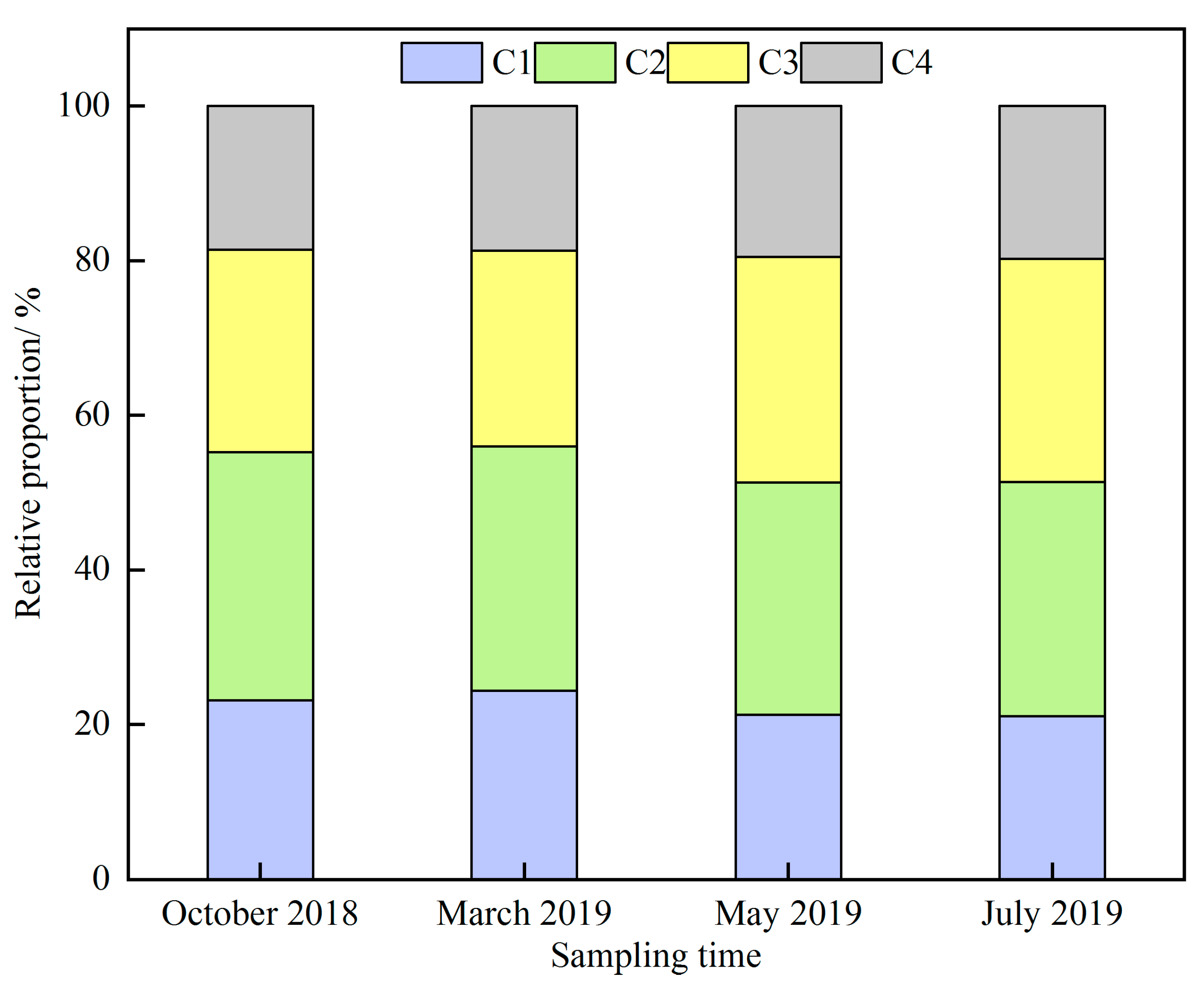
3.4. Fluorescence Characteristics and Components of DOM
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparative Analysis of DOM Concentration in Lake Hulun and Other Lakes
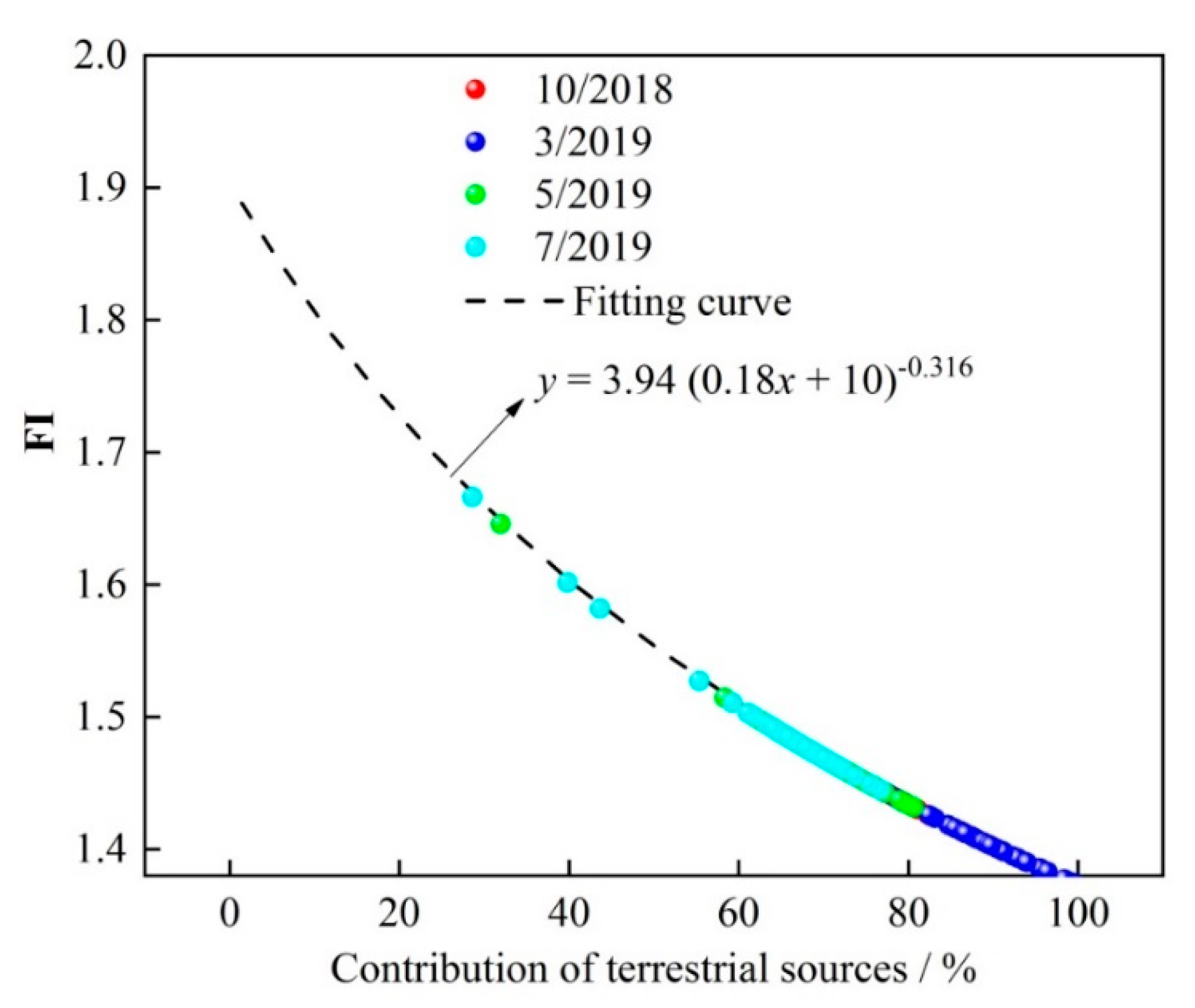
4.2. Source Apportionment of DOM in Overlying Water of Lake Hulun
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herzsprung, P.; Von Tuempling, W.; Wendt-Potthoff, K.; Hertkorn, N.; Harir, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Friese, K. High field FT-ICR mass spectrometry data sets enlighten qualitative DOM alteration in lake sediment porewater profiles. Org. Geochem. 2017, 108, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Bravo, A.G.; Skyllberg, U.; Bjorn, E.; Wang, D.; Yan, H.; Green, N.W. Influence of dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics on dissolved mercury (Hg) species composition in sediment porewater of lakes from southwest China. Water Res. 2018, 146, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.D.; Song, K.S.; Shang, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, C.; Lyu, L.L. Differences in the distribution and optical properties of DOM between fresh and saline lakes in a semi-arid area of Northern China. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, D.T.; Stoddard, J.L.; Evans, C.D.; De Wit, H.A.; Forsius, M.; Hogasen, T.; Wilander, A.; Skjelkvale, B.L.; Jeffries, D.S.; Vuorenmaa, J.; et al. Dissolved organic carbon trends resulting from changes in atmospheric deposition chemistry. Nature 2007, 450, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Z. Photochemical reactivities of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in a sub-alpine lake revealed by EEM-PARAFAC: An insight into the fate of allochthonous DOM in alpine lakes affected by climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipczynska-Kochany, E. Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.C.; Wu, Z.F.; Yao, S.C.; Xue, B. Climate change has weakened the ability of Chinese lakes to bury polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Hu, Y.; Cai, J.; Bai, C.R.; Shao, K.Q.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.L.; Jeppesen, E.; Tang, X.M. Hydraulic connectivity and evaporation control the water quality and sources of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Lake Bosten in arid northwest China. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Jin, Z.D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Major ion chemistry, weathering process and water quality of natural waters in the Bosten Lake catchment in an extreme arid region, NW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Perry, L.; Li, W.H. Implications of climate change for water management of an arid inland lake in Northwest China. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2015, 31, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.D.; Song, K.S.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, X.L. Carbon dioxide and methane supersaturation in lakes of semi-humid/semi-arid region, Northeastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.J.; Xue, B.; Yao, S.C.; Gui, Z.F. Organic carbon burial from multi-core records in Hulun Lake, the largest lake in northern China. Quat. Int. 2018, 475, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, J.P.; Xiang, J.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.L. Water level changes of Hulun Lake in Inner Mongolia derived from Jason satellite data. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 58, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chuai, X.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H. Climatic warming and overgrazing induced the high concentration of organic matter in Lake Hulun, a large shallow eutrophic steppe lake in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.N.; Liang, L.E. Spatial and temporal variation of water quality in Hulun Lake. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2016, 43, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, P.G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Mar. Chem. 1996, 51, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Zhuang, W.E.; Chen, C.T.A.; Wang, B.J.; Kuo, F.W. Unveiling the transformation and bioavailability of dissolved organic matter in contrasting hydrothermal vents using fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC. Water Res. 2017, 111, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.L.; Xiao, J.L.; Chang, Z.G.; Zhai, D.Y.; Xu, Q.H.; Li, Y.C.; Itoh, S.; Lomtatidze, Z. Holocene climate changes in the mid-high-latitude-monsoon margin reflected by the pollen record from Hulun Lake, northeastern Inner Mongolia. Quat. Res. 2017, 73, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEP of PRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China). Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method (HJ 636-2012); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- MEP of PRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China). Water Quality—Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen—Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry (HJ 535-2009); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- MEP of PRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China). Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method (GB 11893-89); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1989.
- MEP of PRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China). Water Quality—Determination of Permanganate Index; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1989.
- MEP of PRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China). Water Quality—Determination of Chlorophyll—A Spectrophotometric Method; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Song, K.; Shang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Liu, G.; Lyu, L.; Fang, C. Characterization of CDOM in saline and freshwater lakes across China using spectroscopic analysis. Water Res. 2019, 150, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J. Differences in fluorescence characteristics and bioavailability of water-soluble organic matter (WSOM) in sediments and suspended solids in Lihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 12648–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Bro, R. Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: A tutorial. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2008, 6, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.M.; Boyer, E.W.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Doran, P.T.; Kulbe, T.; Andersen, D.T. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, P.F.; Qian, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N.N.; Cui, X.A. Characteristics, sources, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in large and shallow Hongze Lake, China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Zhao, Y.; Du, J. Dissolved carbon and CDOM in lake ice and underlying waters along a salinity gradient in shallow lakes of Northeast China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zepp, R.G.; Erickson, D.J., III; Paul, N.D.; Sulzberger, B. Interactive effects of solar UV radiation and climate change on biogeochemical cycling. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Photochem. Assoc. Eur. Soc. Photobiol. 2007, 6, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartisano, C.M.; Del Vecchio, R.; Bianca, M.R.; Blough, N.V. Investigating the sources and structure of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the North Pacific Ocean (NPO) utilizing optical spectroscopy combined with solid phase extraction and borohydride reduction. Mar. Chem. 2018, 204, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effler, S.W.; Perkins, M.; Peng, F.; Strait, C.; Weidemann, A.D.; Auer, M.T. Light-absorbing components in Lake Superior. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Laor, Y.; Raviv, M.; Medina, S.; Saadi, I.; Krasnovsky, A.; Vager, M.; Levy, G.J.; Bar-Tal, A.; Borisover, M. Compositional characteristics of organic matter and its water-extractable components across a profile of organically managed soiL. Geoderma 2017, 286, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Markager, S.; Bro, R. Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy. Mar. Chem. 2003, 82, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, J.F.; Del Giorgio, P.A. Partial coupling and differential regulation of biologically and photochemically labile dissolved organic carbon across boreal aquatic networks. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 5969–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalá, T.S.; Reche, I.; Fuentes-Lema, A.; Romera-Castillo, C.; Nieto-Cid, M.; Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Calvo, E.; Álvarez, M.; Marrasé, C.; Stedmon, C.A.; et al. Turnover time of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the dark global ocean. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonnelli, M.; Galletti, Y.; Marchetti, E.; Mercadante, L.; Brogi, R.S.; Ribotti, A.; Sorgente, R.; Vestri, S.; Santinelli, C. Dissolved organic matter dynamics in surface waters affected by oil spill pollution: Results from the Serious Game exercise. Deep Sea Res. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2016, 133, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünsch, U.J.; Murphy, K.R.; Stedmon, C.A. The one-Sample PARAFAC approach reveals molecular size distributions of fluorescent components in dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11900–11908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schittich, A.R.; Wunsch, U.J.; Kulkarni, H.V.; Battistel, M.; Bregnhoj, H.; Stedmon, C.A.; McKnight, U.S. Investigating Fluorescent Organic-Matter Composition as a Key Predictor for Arsenic Mobility in Groundwater Aquifers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13027–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, K.C.; Wang, S.R.; Wang, S.G.; Li, Y.P.; Li, Q.C.; Meng, Z. Characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in overlying water of typical lakes of Yunnan Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, S.; Wen, Z.; Lyu, L.; Shang, Y. Characterization of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in lakes across the Tibet-Qinghai Plateau using spectroscopic analysis. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, D.; Meng, B.; Chi, J.; Laudon, H.; Liu, J. The concentrations and characteristics of dissolved organic matter in high-latitude lakes determine its ambient reducing capacity. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queimalinos, C.; Reissig, M.; Perez, G.L.; Soto Cardenas, C.; Gerea, M.; Garcia, P.E.; Garcia, D.; Dieguez, M.C. Linking landscape heterogeneity with lake dissolved organic matter properties assessed through absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy: Spatial and seasonal patterns in temperate lakes of Southern Andes (Patagonia, Argentina). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Guo, L.D.; Minor, E.C. Characterization of bulk and chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Laurentian Great Lakes during summer 2013. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, Z.D.; Song, K.S.; Liu, G.; Shang, Y.X.; Hou, J.B.; Lyu, L.L.; Fang, C. Impact factors of dissolved organic carbon and the transport in a river-lake continuum in the Tibet Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.C. Lakes in China-Research of Their Emvironment; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jiao, R.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Yan, W. Dissolved organic carbon content and characteristics in relation to carbon dioxide partial pressure across Poyang Lake wetlands and adjacent aquatic systems in the Changjiang basin. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Feng, L.Q.; Cai, L.L.; Gao, G. Resolving the variability of CDOM fluorescence to differentiate the sources and fate of DOM in Lake Taihu and its tributaries. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Zhang, Y.C.; Duan, H.T.; Ma, R.H. Variability of light absorption properties in optically complex inland waters of Lake Chaohu, China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yuan, D.H.; Guo, X.J.; He, L.S.; He, J.W.; Li, H.Y.; Li, J.Q. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in Lake Baiyangdian using spectroscopic techniques and multivariate statistical analysis. Clean Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, S.R. New insights into the source of decadal increase in chemical oxygen demand associated with dissolved organic carbon in Dianchi Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J. Study on dissolved organic matter leached from water and sediment pore water in Wuliangsuhai Lake. In Proceedings of the International Symposium and Industrialization Forum on Biogas, Technology and Environment Engineering, Chengdu, China, 26–28 October 2011; pp. 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Kida, M.; Kojima, T.; Tanabe, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Kudoh, S.; Maie, N.; Fujitake, N. Origin, distributions, and environmental significance of ubiquitous humic-like fluorophores in Antarctic lakes and streams. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Kojima, R.; Wada, C.; Suzuki, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Takei, N.; Bamba, D. Distribution and characteristics of ultraviolet absorption and fluorescenceof dissolved organic matter in a large lake (Lake Biwa, Japan). J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Murillo, J.C.; Filella, M. Temporal evolution of organic carbon concentrations in Swiss lakes: Trends of allochthonous and autochthonous organic carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 520, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepp, M.; Koiv, T.; Noges, P.; Noges, T. The role of catchment soils and land cover on dissolved organic matter (DOM) properties in temperate lakes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J. Dissolved organic matter and its optical properties in a blackwater tributary of the upper Orinoco river, Venezuela. Org. Geochem. 1998, 28, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Silva, S.R.; Kelly, V.J. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter in four large river systems across the United States. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1301–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.L.; Shi, X.Y.; Wu, X.D.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Li, D.M.; Kong, F.X. Dynamics of dissolved organic carbon after a cyanobacterial bloom in hypereutrophic Lake Taihu (China). Limnologica 2011, 41, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Parameters | October 2018 | March 2019 | May 2019 | July 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water temperature (°C) | 6.45 ± 2.04 | 0.05 ± 0.08 | 11.18 ± 1.72 | 24.20 ± 2.60 |
| pH | 8.52 ± 0.45 | 9.17 ± 0.29 | 8.68 ± 0.25 | 8.95 ± 0.10 |
| EC (ms·m−1) | 102.35 ± 36.53 | 155.83 ± 36.22 | 165.17 ± 20.53 | 143.28 ± 40.08 |
| SD (cm) | 19.0 ± 3.7 | - | 22.5 ± 9.1 | 11.67 ± 2.58 |
| Salinity (mg·L−1) | 646.83 ± 198.34 | 762.33±224.04 | 1088.00 ± 160.19 | 874.00 ± 194.59 |
| CODMn (mg·L−1) | 12.24 ± 2.36 | 8.52 ± 3.53 | 12.80 ± 1.70 | 13.47 ± 1.92 |
| NH4+-N (mg·L−1) | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 0.24 ± 0.13 | 0.16 ± 0.04 |
| TN (mg·L−1) | 1.71 ± 0.31 | 1.77 ± 0.55 | 1.85 ± 0.23 | 2.30 ± 0.50 |
| TP (mg·L−1) | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.08 |
| COD (mg·L−1) | 74.30 ± 12.10 | 71.30 ± 26.65 | 81.22 ± 17.63 | 85.40 ± 16.37 |
| chl a (mg·m−3) | 5.5 ± 3.2 | 5.8 ± 1.8 | 10.7 ± 0.8 | 19.7 ± 25.4 |
| Component | Exmax (nm) | Emmax (nm) | Comparison with other Studies in Open Fluor Database | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 260 | 488 | C2: Exmax = 275(340), Emmax = 484 [36]; C1: Exmax = 270(370), Emmax = 478 [37] | Terrestrially derived humic-like substances with high molecular weight |
| C2 | 254, 356 | 440 | C2: Exmax = 325, Emmax=430 [38]; C3: Exmax = 275 (345), Emmax = 436 [36] | Terrestrially derived humic-like substances |
| C3 | 234, 320 | 420 | C3: Emmax = 430 [39]; C2: Exmax = 305, Emmax = 390 [40] | Terrestrial humic-like substances |
| C4 | 220, 280 | 384 | C5: Exmax = 280(<240), Emmax = 368 [35]; C3: Exmax = 275, Emmax = 384 [34] | A possible mix of humic-like and tryptophan-like substances produced as a result of biological production |
| Country/Region | Lake | Lake Type | Nutrition Status | Altitude (m) | Area (km2) | Water Depth (m) | DOC (mg C/L) | Sampling Time | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | ERL | Lake Poyang | Shallow freshwater lake | Light eutropher | 1–12 | 3886 | 12–20 | 3.71 ± 1.65 | 2013.6 | [48] |
| Lake Taihu | Shallow freshwater lake | Light eutropher | 1.1 | 2338 | 1.9 | 2.19 ± 0.99 | 2010.2 | [49] | ||
| Lake Hongze | Shallow freshwater lake | Light eutropher | >13 | 1960 | 1.77 | 13.9 ± 0.7 | 2016.4 | [29] | ||
| Lake Chao | Shallow freshwater lake | Light eutropher | 5–10 | 770 | 3.0 | 0.013 ± 0.001 | 2013.3–2015.4 | [50] | ||
| Lake Baiyangdian | Shallow freshwater lake | Light eutropher | 4.1–4.6 | 336 | - | 11.52 ± 2.95 | 2012.6 | [51] | ||
| NLR | Lake Chagan | Shallow freshwater lake | Light eutropher | 126 | 375.2 | 2.3 | 15 | 2011, 2014, 2015 | [30] | |
| YGR | Lake Tiancai | Alpine freshwater lake | Oligotropher | 3880 | 0.2 | 6.5* | 10.33 | 2013.6 | [5] | |
| Lake Dianchi | Plateau freshwater lake | Light eutropher | 1886 | 298 | 4.1 | 15.15 | 2013 | [52] | ||
| Lake Erhai | Plateau freshwater lake | Mesotropher | 1974 | 256.5 | 15 | 34.54 ± 4.26 | 2016.4 | [41] | ||
| TQR | Lake Qinghai | Plateaus, saltwater lake | Light eutropher | 3199 | 4349.9 | 21 | 17.2 | 2014.9 | [42] | |
| Lake Yangzhuoyongcuo | Plateaus saltwater lake | Oligotropher | 4447 | 571.4 | 20–40 | 8.1 | 2015.6 | [42] | ||
| Lake Keluke | Plateau freshwater lake | Mesotropher | 2817 | 54.7 | 5 | 5.8 | 2014.9 | [42] | ||
| Lake Bangongcuo | Plateau freshwater lake | Oligotropher | 4244 | 451.1 | 57 | 3.1 | 2015.7 | [42] | ||
| MXR | Lake Bosten | Inland freshwater lake | Mesotropher | 1048 | 1000 | 9 | 13.16 ± 3.63 | 2015.6 | [8] | |
| Lake Wuliangsuhai | Shallow freshwater lake | Eutropher | 1018 | 300 | 0.5–1.5 | 57.11 ± 7.35 | 2009.11 | [53] | ||
| Lake Daihai | Inland brackish lake | Eutropher | 1220 | 55 | 4 | 44.56 ± 2.44 | 2018 | Unpublished research results of the research team | ||
| Lake Hulun | Inland brackish lake | Eutropher | 545.6 | 2339 | 5.75 | 32.30 ± 4.62 | 2019.7 | This paper | ||
| Antarctica | Lake Richardson | Freshwater lake | Oligotropher | - | 5.44 | - | 1.16 | 2017.2 | [54] | |
| Argentina | Lake Schmoll | Shallow lake | Oligotropher | 1950 | 0.028 | 5 * | 0.401 ± 0.000 | 2013–2015 | [44] | |
| Lake Toncek | Shallow lake | Oligotropher | 1750 | 0.05 | 9 * | 0.732 ± 0.027 | 2013–2015 | [44] | ||
| Lake Juventus | Shallow lake | Oligotropher | 1010 | 0.046 | 12.0 * | 2.079 ± 0.007 | 2013–2015 | [44] | ||
| Lake Morenito | Shallow lake | Oligotropher | 770.8 | 0.365 | 10.5 * | 1.45 | 2019 | [44] | ||
| Lake Moreno | Deep lake | Oligotropher | 770.8 | 6.1 | 90–106 * | 0.73–0.74 | 2019 | [44] | ||
| Lake Escondido | Shallow lake | Oligotropher | 772.8 | 0.09 | 8.3 * | 4.04–4.29 | 2019 | [44] | ||
| America, Canada | Lake Superior | Freshwater lake | Oligotropher | 180 | 82000 | 147 | 1.188 | 2013.9 | [45] | |
| Canada | Lake Huron | Freshwater lake | Oligotropher | 177 | 59600 | 60 | 1.872 | 2013.8 | [45] | |
| America | Lake Michigan | Freshwater lake | Oligotropher | 177 | 58016 | 85 | 2.1936 | 2013.8 | [45] | |
| America, Canada | Lake Erie | Freshwater lake | Eutropher | 174 | 25744 | 19 | 2.574 | 2013.9 | [45] | |
| Lake Ontario | Freshwater lake | Oligotropher | 85 | 19554 | 86 | 2.337 | 2013.9 | [45] | ||
| America, Canada | Lake Saint Clair | Freshwater lake | Eutropher | 175 | 1210 | 7.8 | 1.848 | 2013.8 | [45] | |
| Japan | Biwa Lake | Freshwater lake | Mesotropher | 84.371 | 670.25 | 41.2 | 1.47 | 2006 | [55] | |
| Switzerland | Lake Bienne | Freshwater lake | - | 429 | 39.50 | 74 * | 3.16 | 1987–2010 | [56] | |
| Lake Constance-Obersee | Freshwater lake | - | 395 | 473.00 | 254 * | 1.3 | 2000–2009 | [56] | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zheng, B.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, S. Characteristics and Source of Dissolved Organic Matter in Lake Hulun, A Large Shallow Eutrophic Steppe Lake in Northern China. Water 2020, 12, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040953
Wang W, Zheng B, Jiang X, Chen J, Wang S. Characteristics and Source of Dissolved Organic Matter in Lake Hulun, A Large Shallow Eutrophic Steppe Lake in Northern China. Water. 2020; 12(4):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040953
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenwen, Binghui Zheng, Xia Jiang, Junyi Chen, and Shuhang Wang. 2020. "Characteristics and Source of Dissolved Organic Matter in Lake Hulun, A Large Shallow Eutrophic Steppe Lake in Northern China" Water 12, no. 4: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040953
APA StyleWang, W., Zheng, B., Jiang, X., Chen, J., & Wang, S. (2020). Characteristics and Source of Dissolved Organic Matter in Lake Hulun, A Large Shallow Eutrophic Steppe Lake in Northern China. Water, 12(4), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040953







