Impact Assessment of Urban Flood on Traffic Disruption using Rainfall–Depth–Vehicle Speed Relationship
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Materials
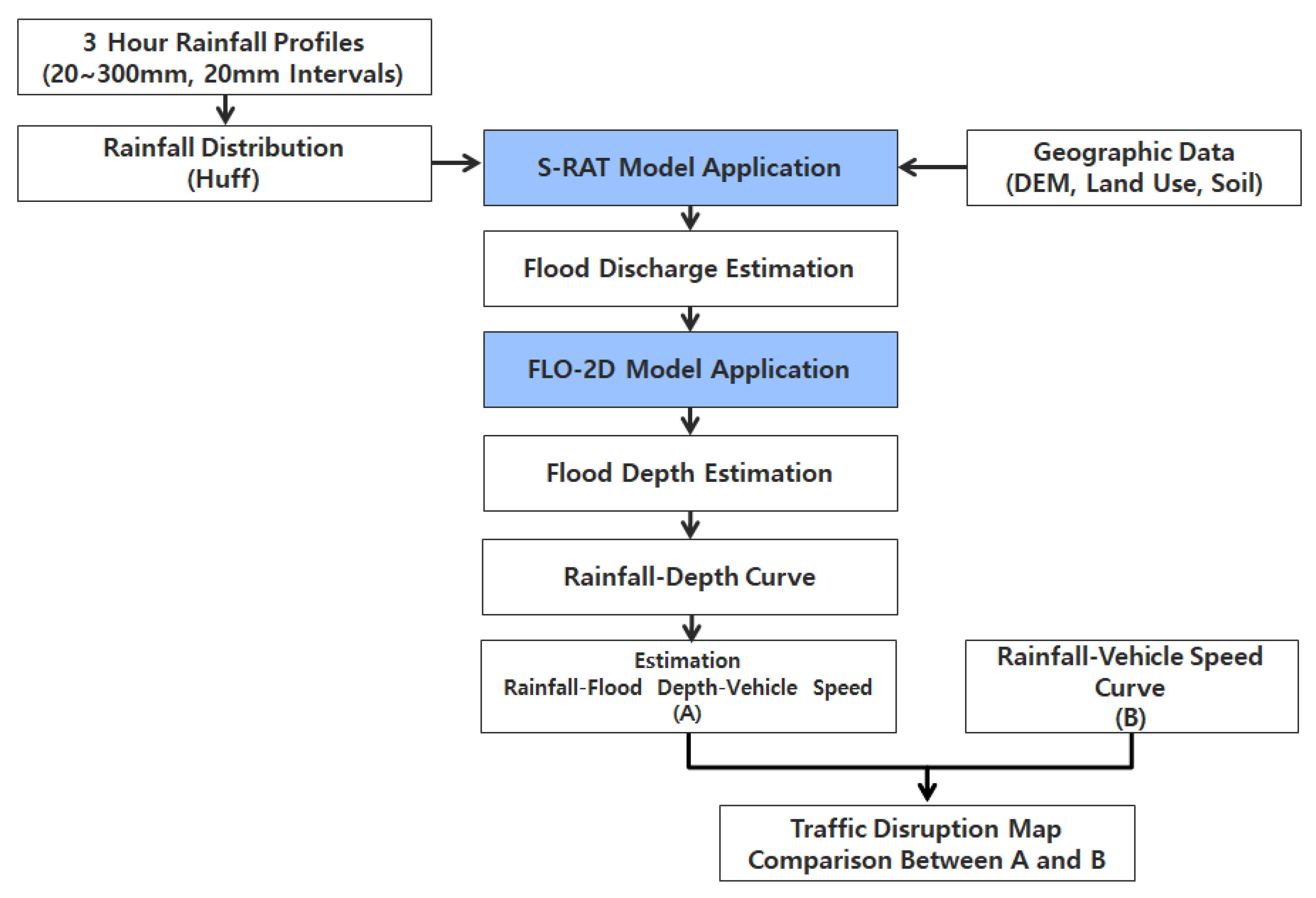
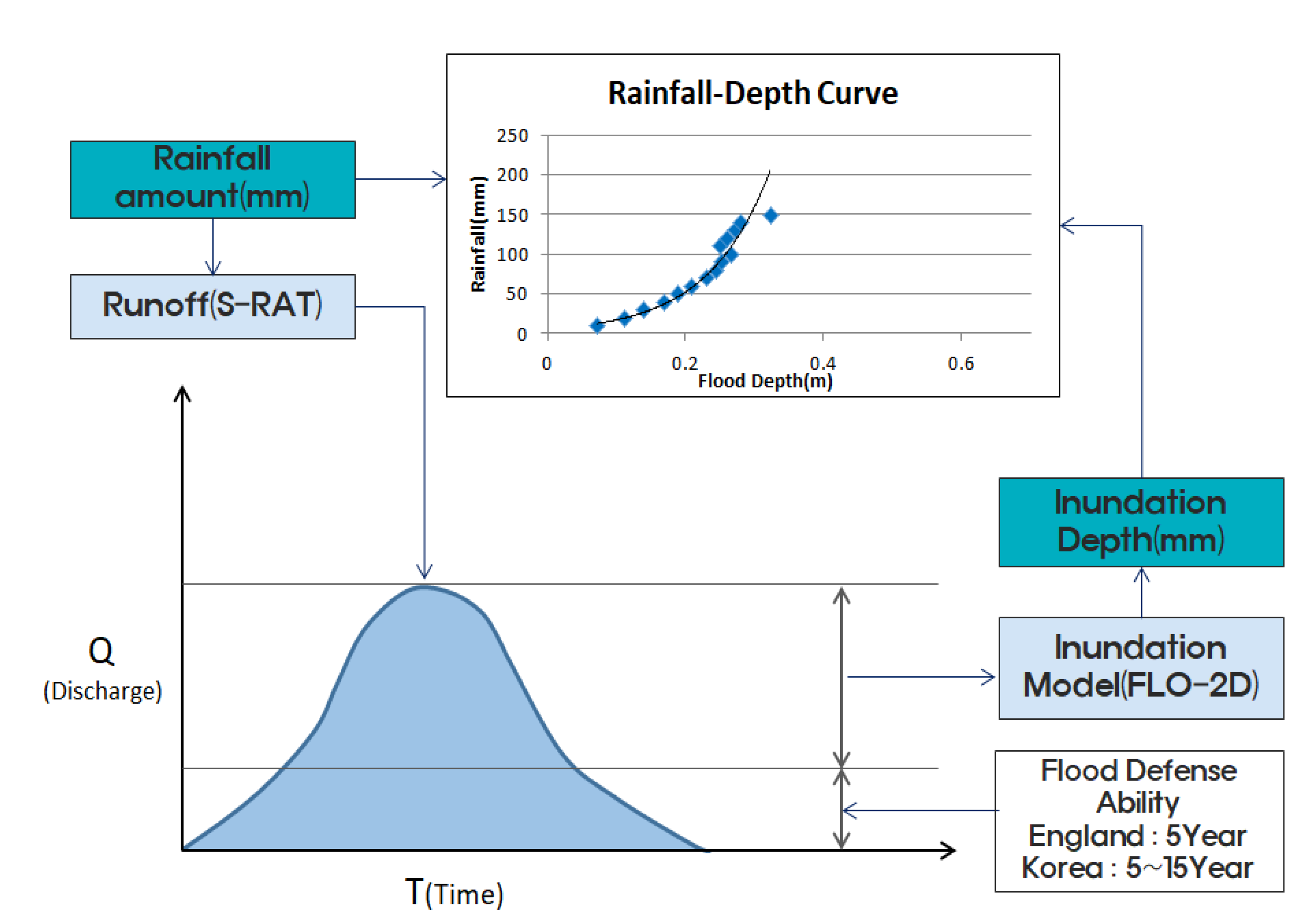
2.1. Methodology
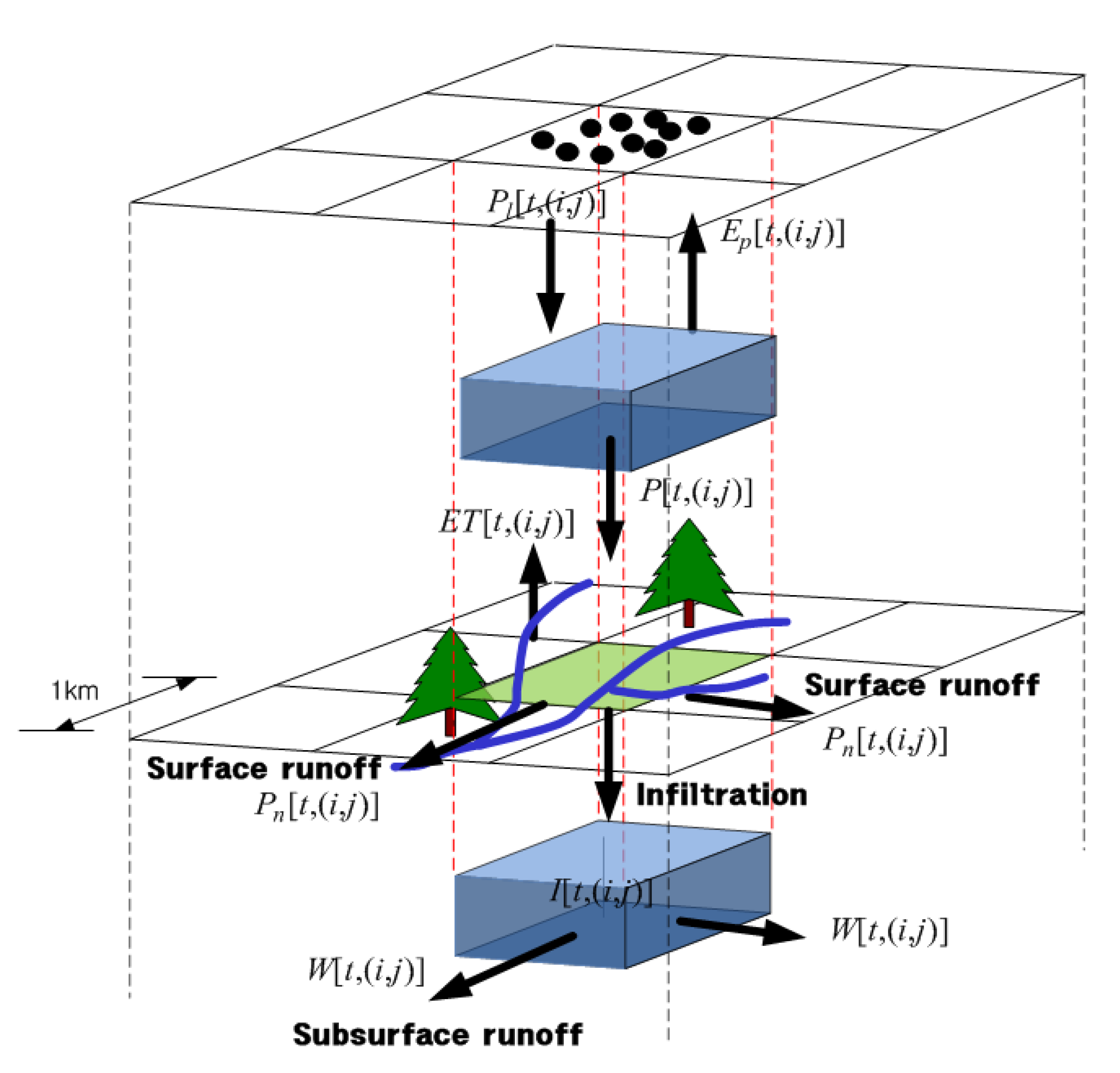
2.2. Distributed Rainfall–Runoff Model (S-RAT)
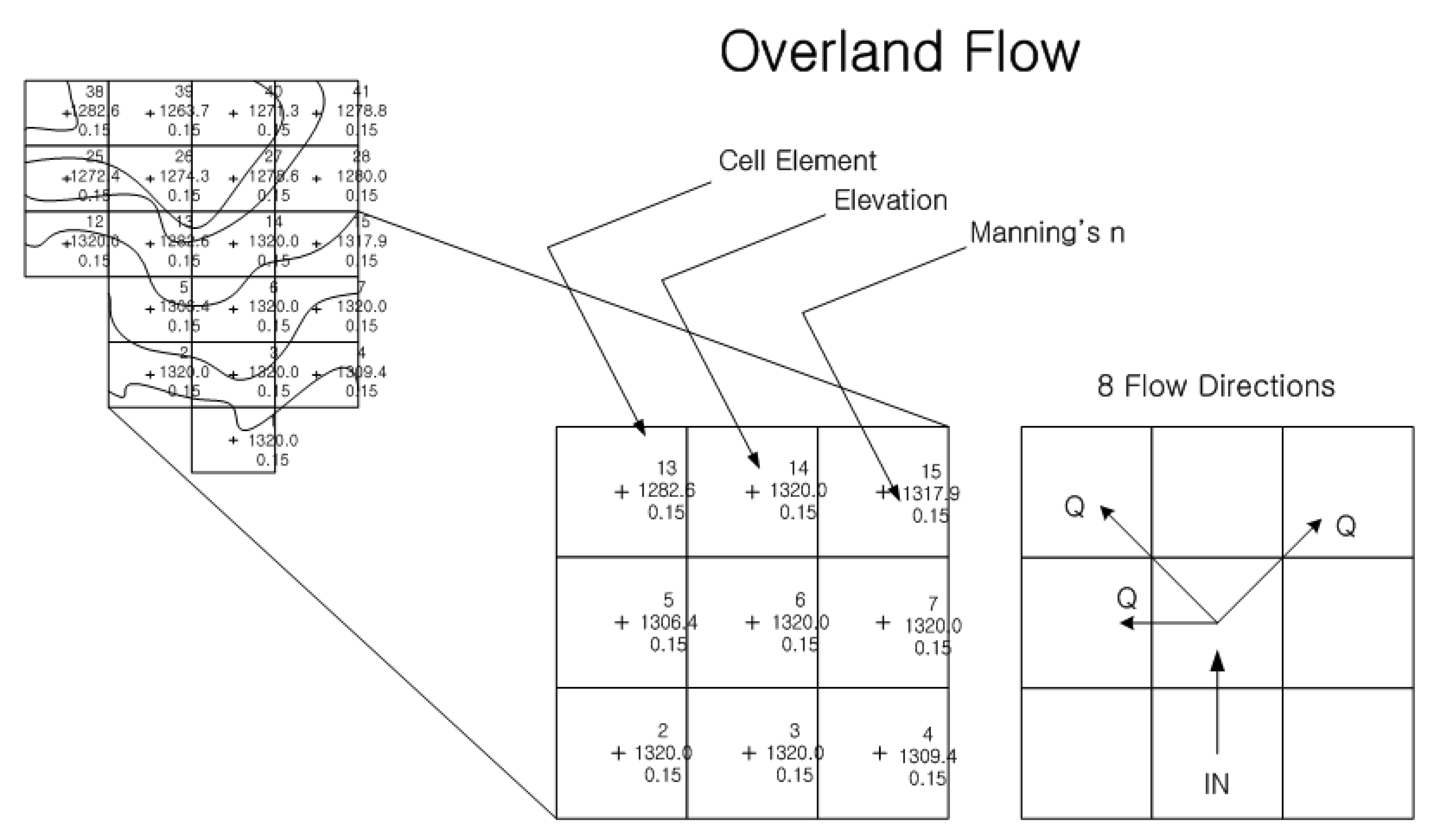
2.3. Flood Inundation Model (Flo-2D)
The Background and Review of Model Selection
2.4. Study Area and Input Data Construction (Rainfall Data, S-RAT, and FLO-2D)
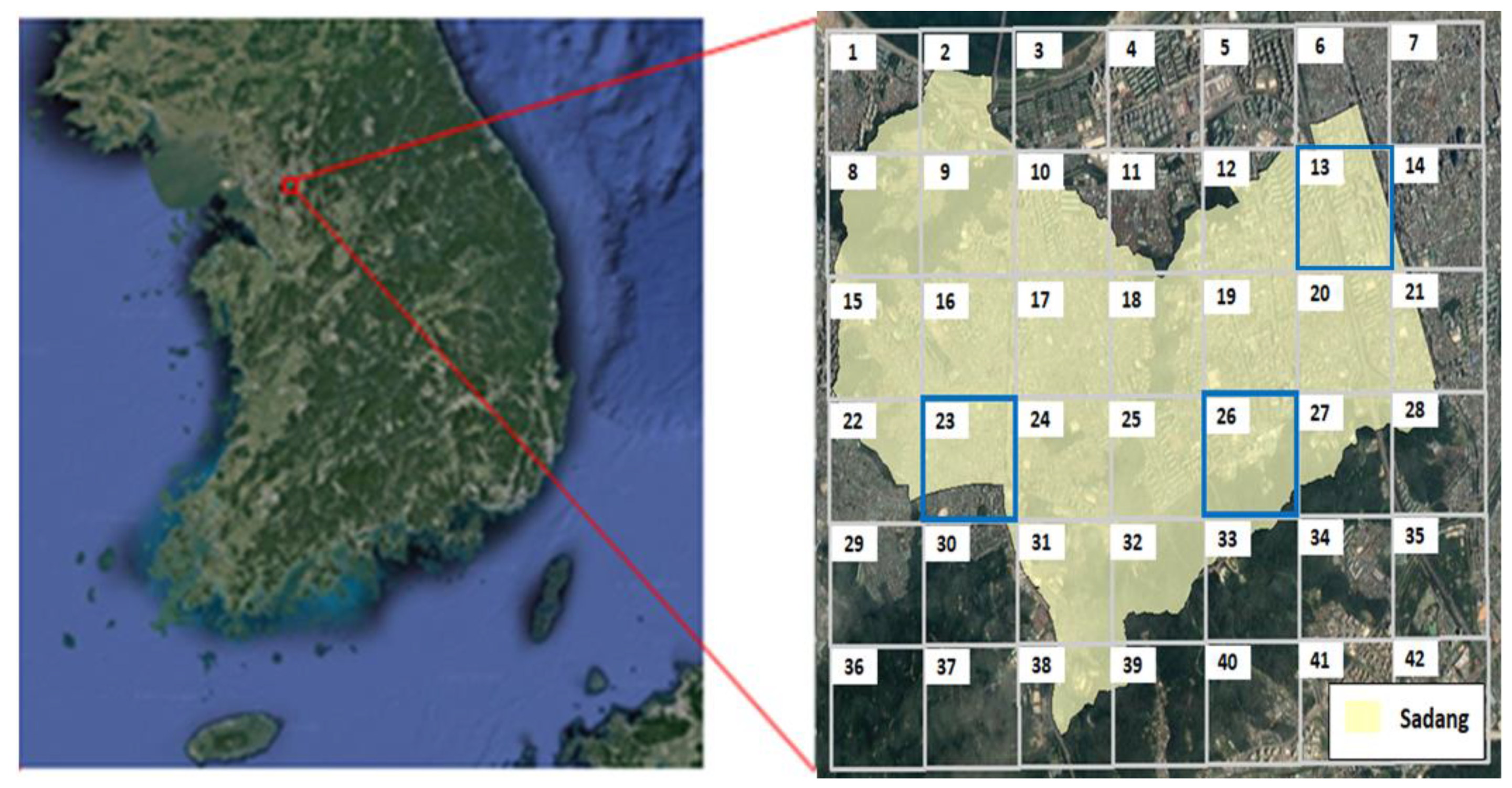
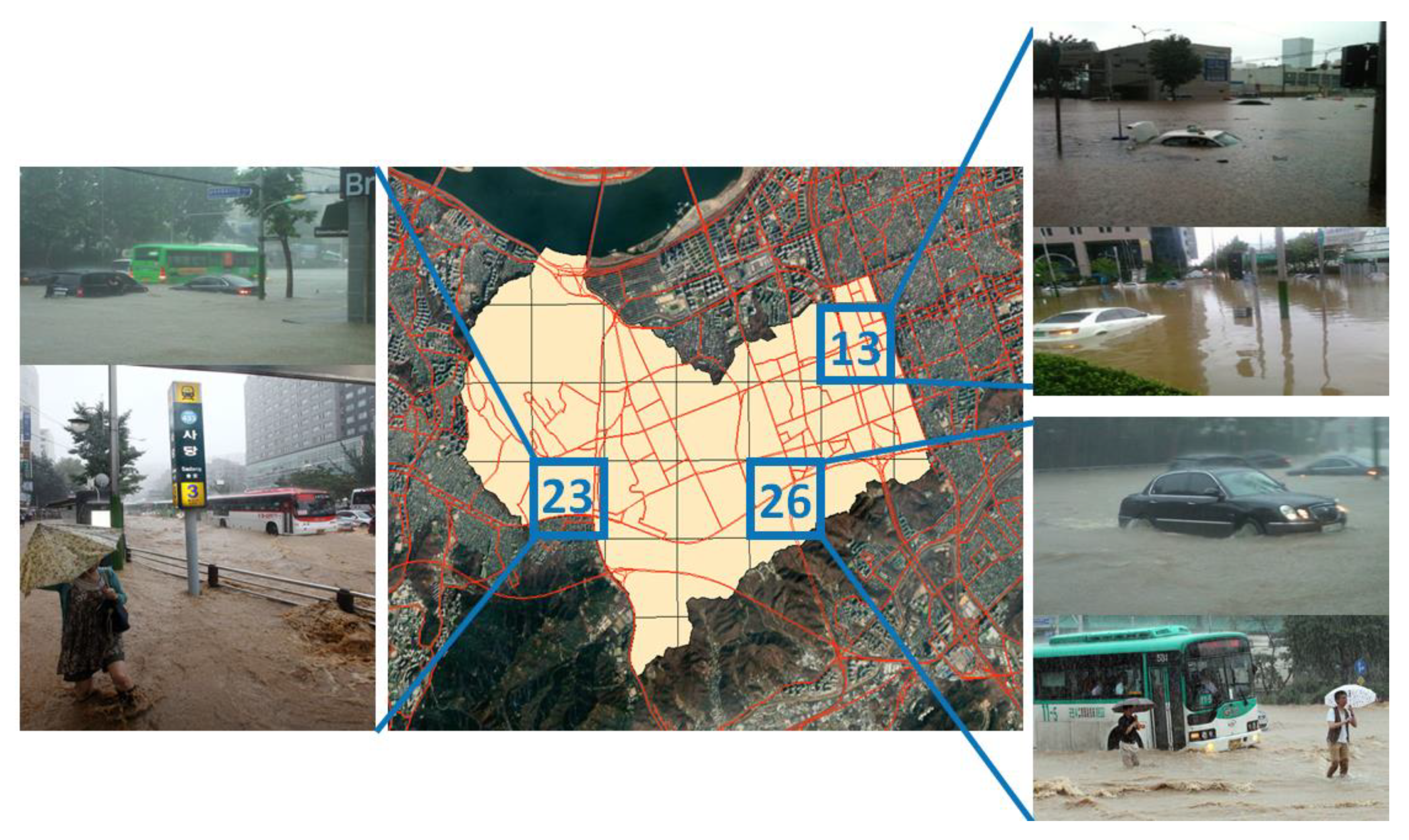
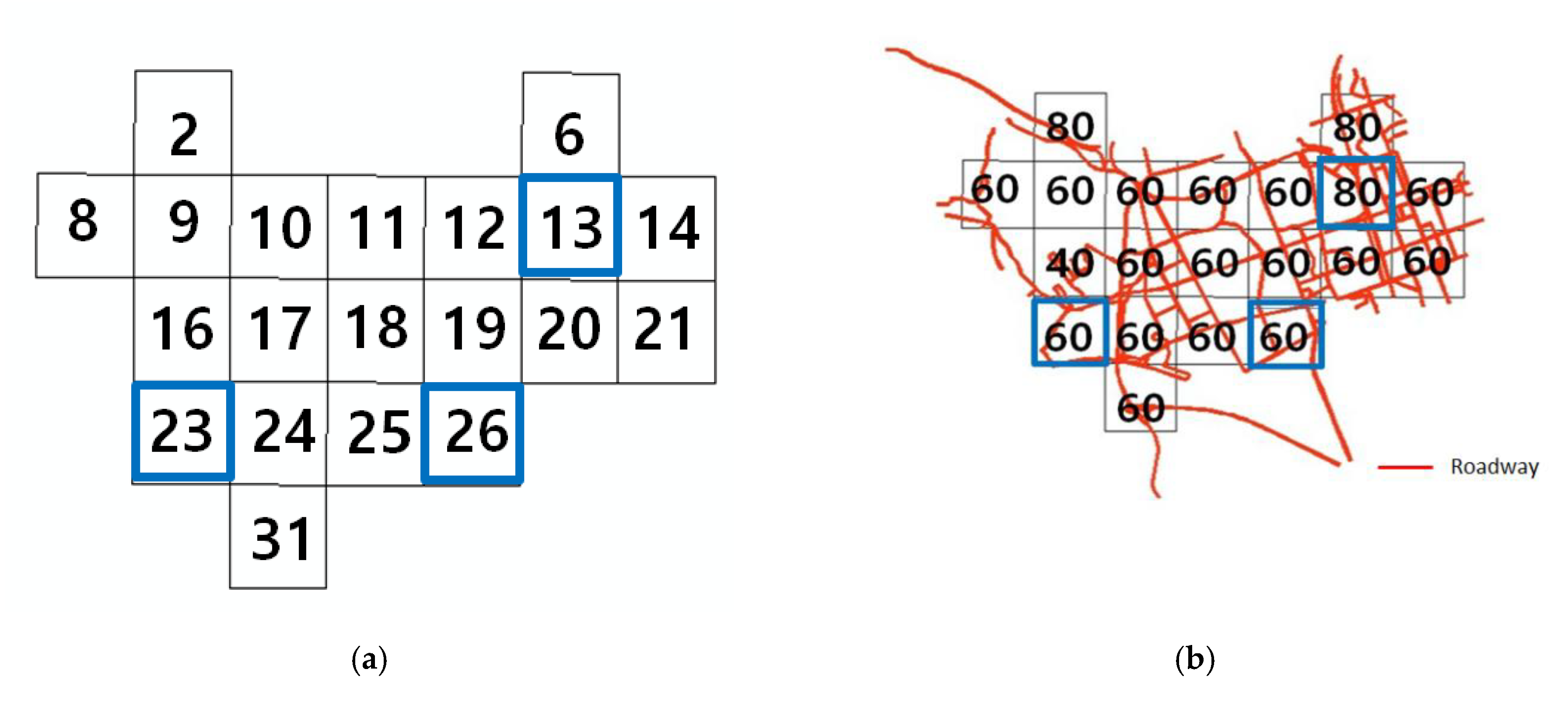
2.4.1. Study Area
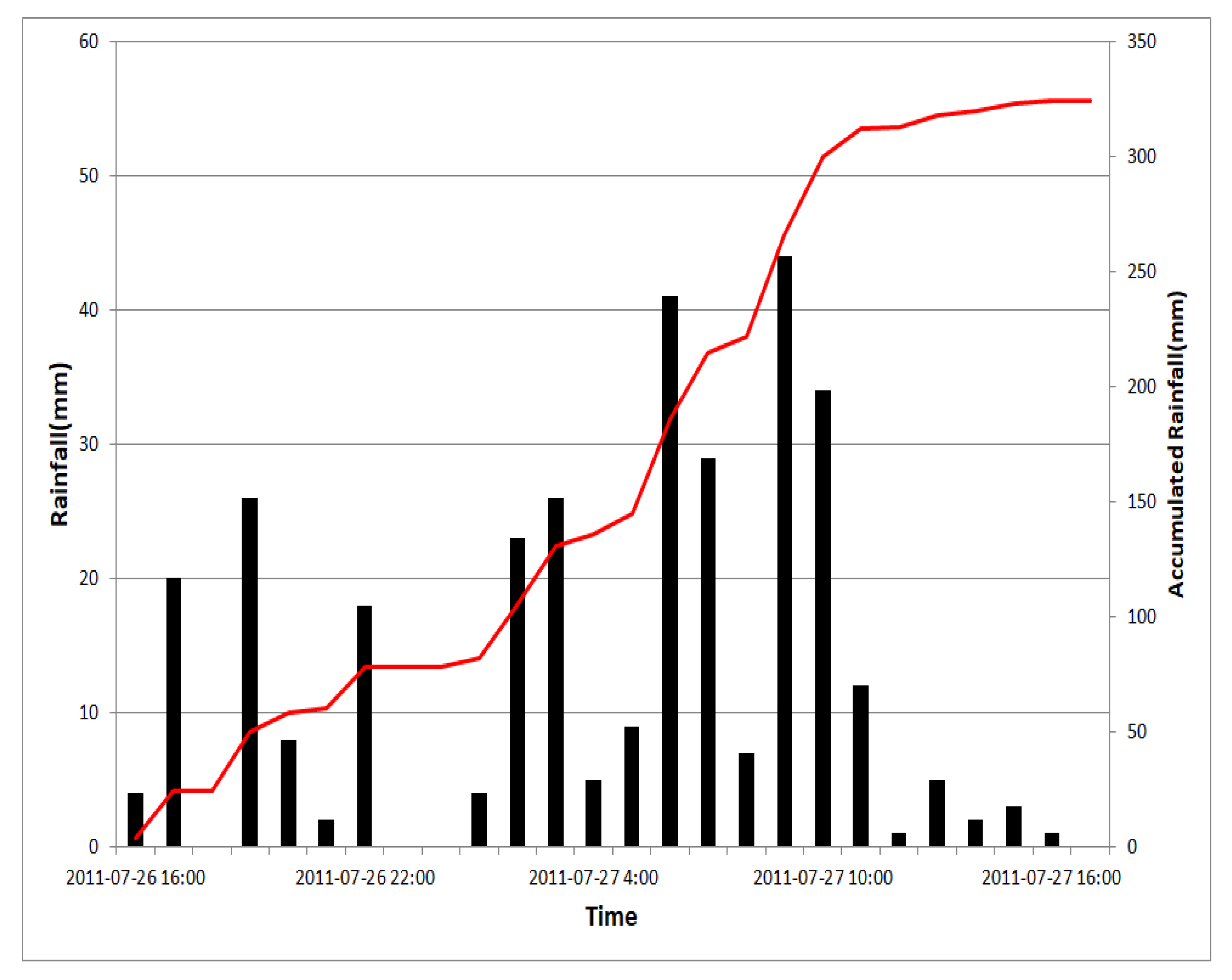
2.4.2. Input Data Construction
2.5. Rainfall–Depth Curve
2.6. Depth–Vehicle Speed Curve
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results of the Application
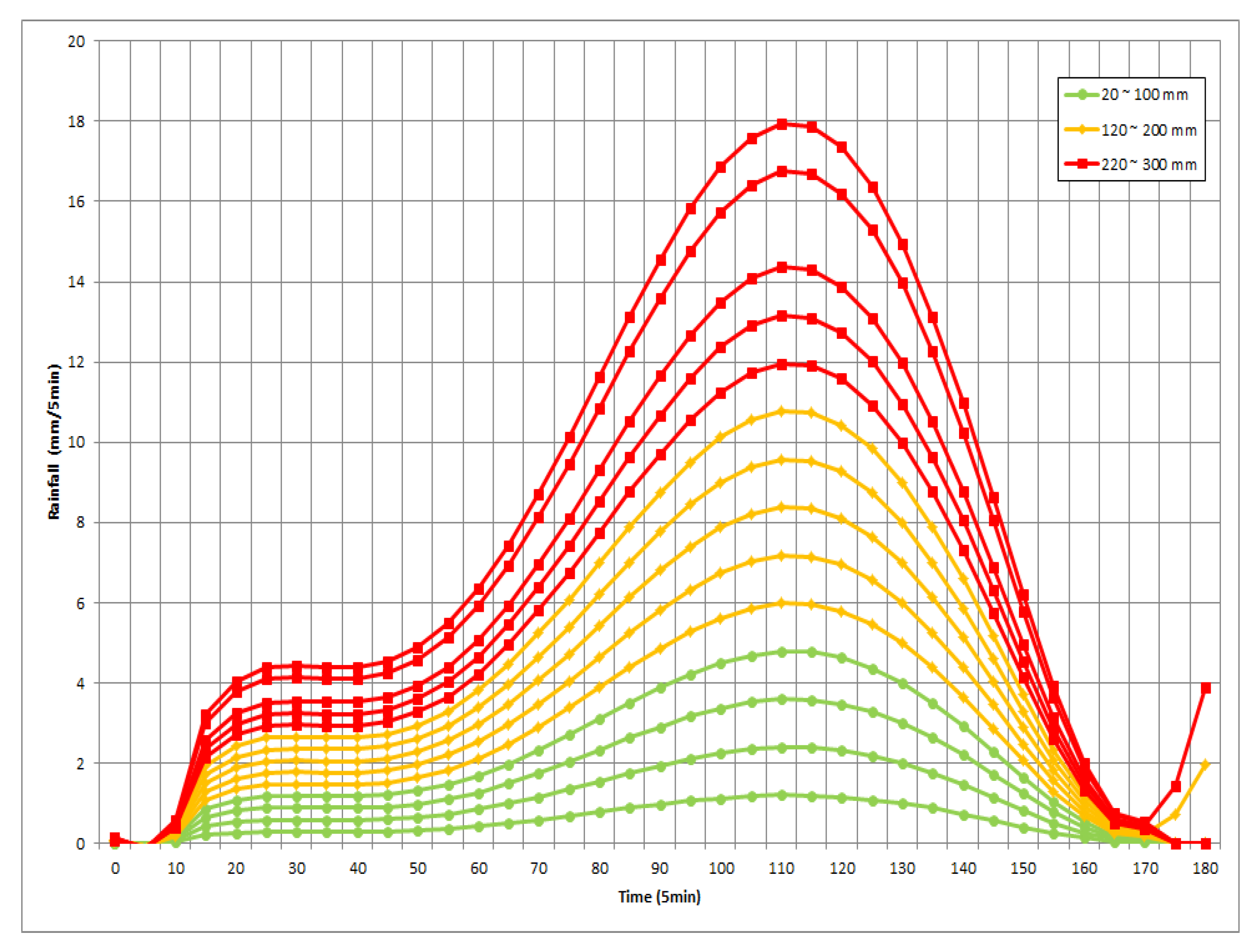
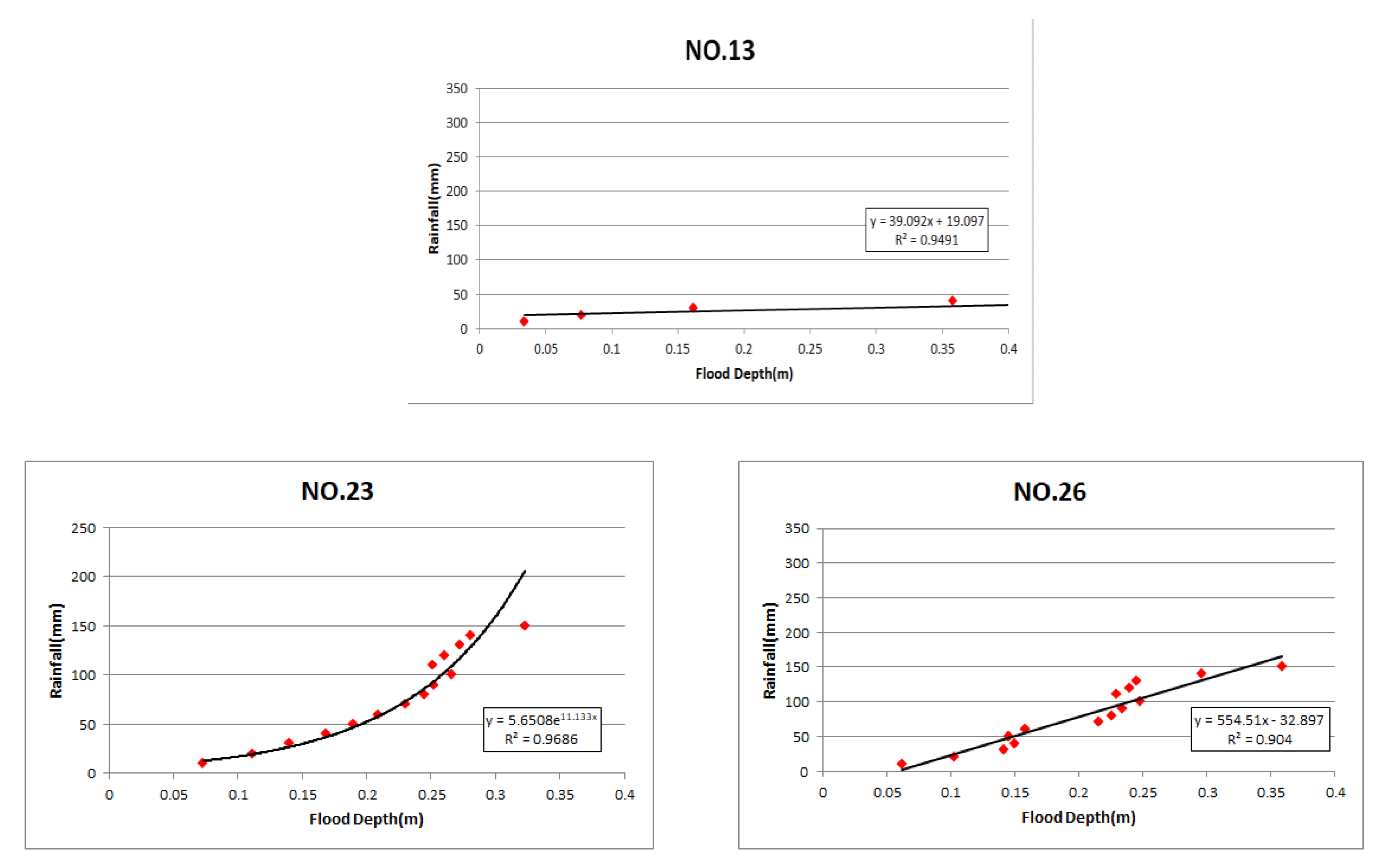
3.2. Creation of Rainfall–Depth Curve
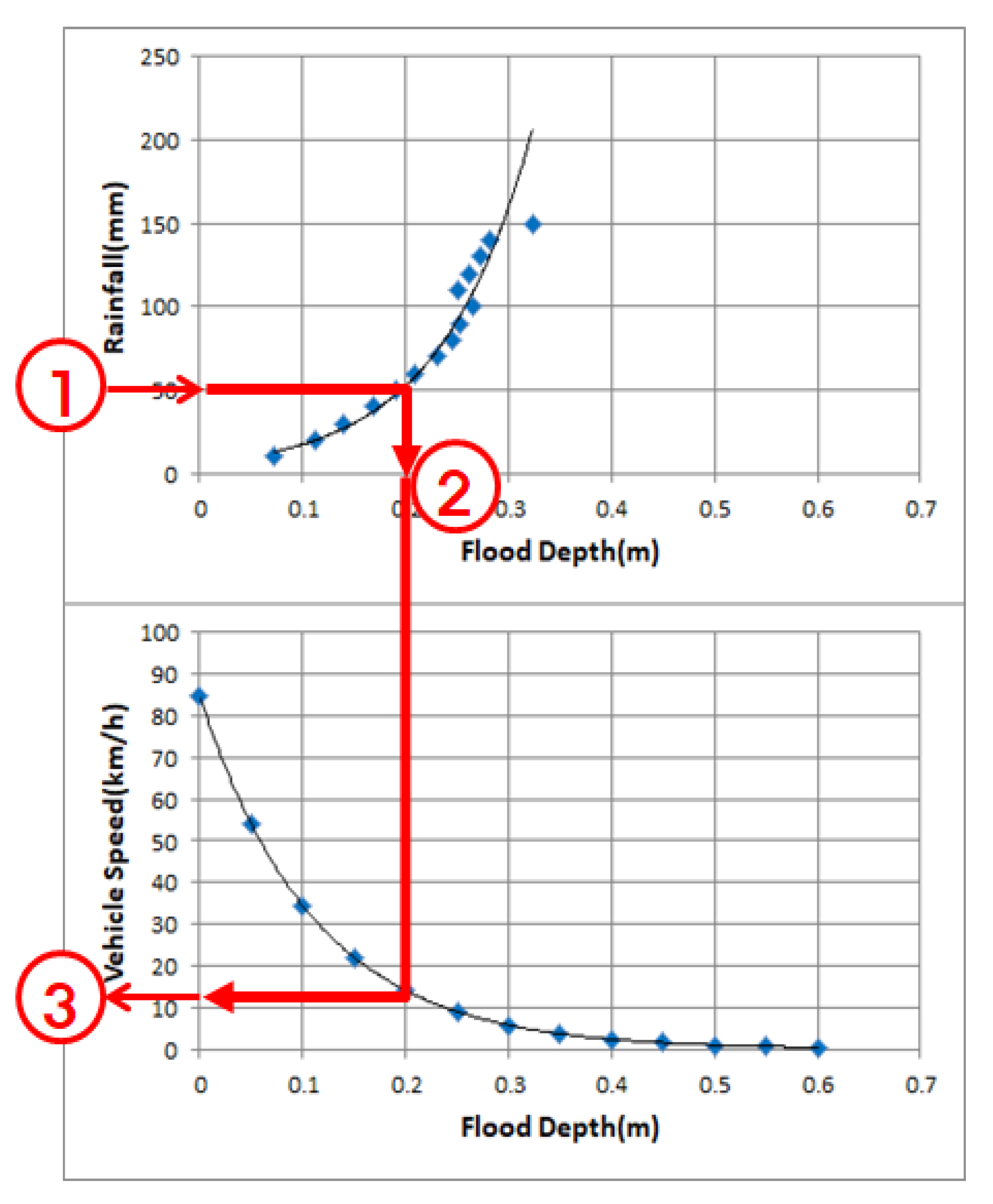
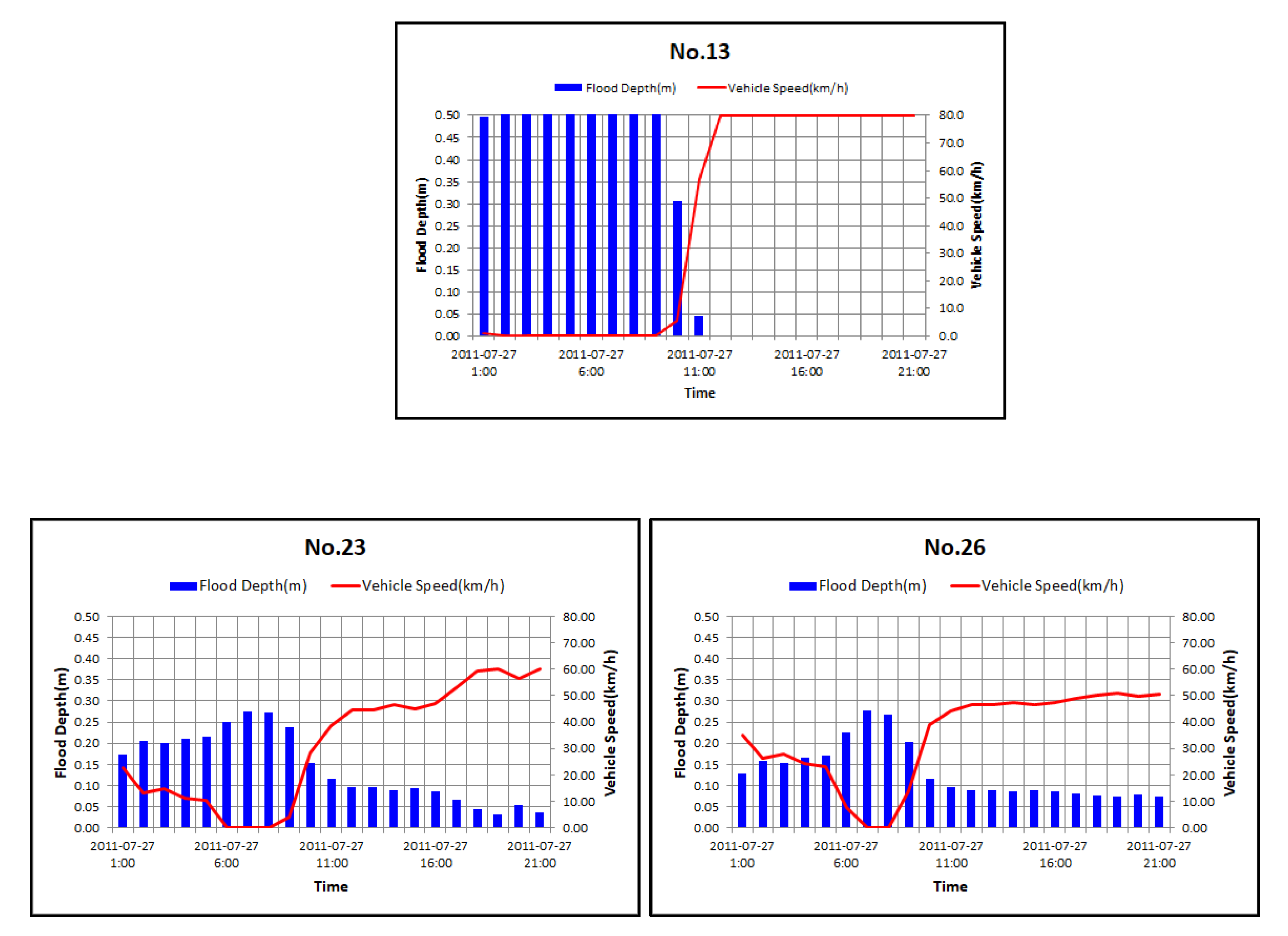
3.3. Results of Calculation by the Relationship between Rainfall–Flood Depth–Vehicle Speed
3.4. Result of Calculation by Rainfall–Vehicle Speed Curve
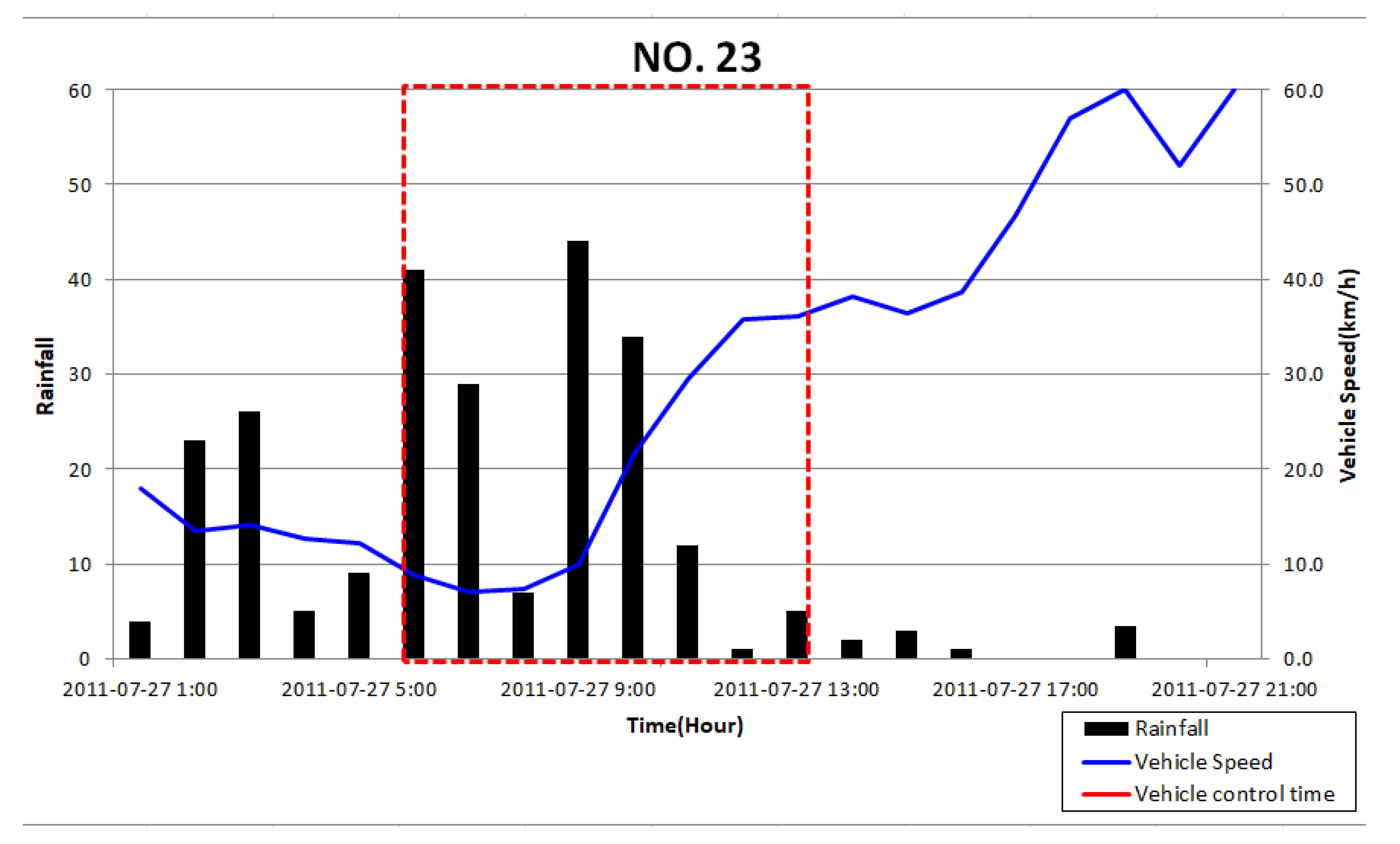
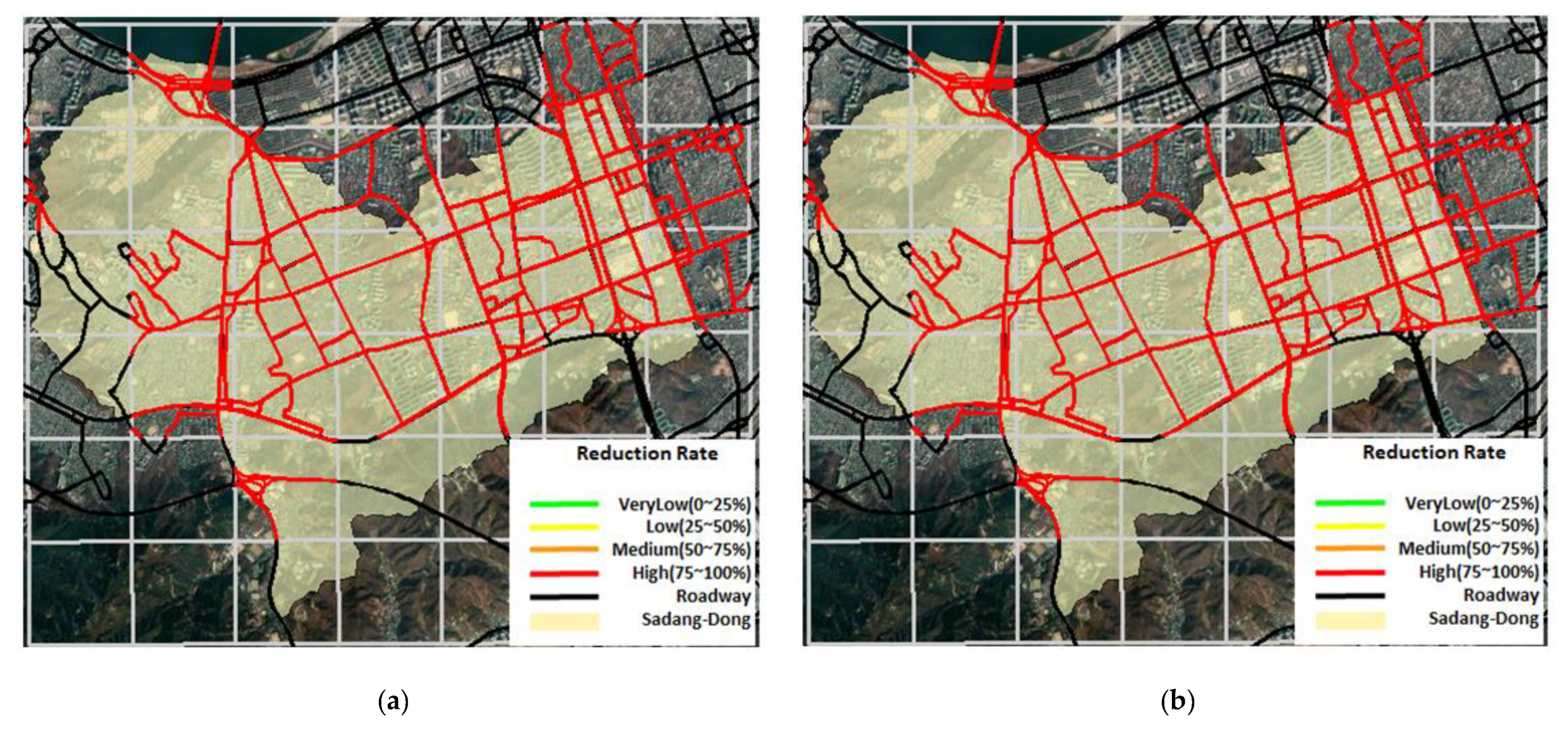
3.5. Traffic Disruption Simulation using Relationship of Rainfall–Depth–Vehicle Speed
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kendon, E.J.; Roberts, N.M.; Senior, C.A.; Roberts, M.J. Realism of Rainfall in a Very High-Resolution Regional Climate Model. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 5791–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Available online: http://ipcc-wg2.gov/AR5/ (accessed on 2 October 2015).
- Kim, E.; Hwang, H.S.; Kim, C.S. A Study on the Development of the Flood Risk Index for Roads Considering Real-time Rainfall. J. Korea Multimed. Soc. 2013, 16, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetse, M.J.; Rietveld, P. The impact of climate change and weather on transport: An overview of empirical findings. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2009, 14, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guideline on Multi-Hazard Impact-Based Forecast and Warning System; WMO-No. 1150; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Meteorological Administration. Meteorological Technology & Policy 9; Korea Meteorological Administration: Seoul, Korea, 2016; p. 74.
- Flood Forecasting Centre. Flood Guidance Statement User Guide, version 4; Flood Forecasting Centre: Exeter, UK, 2017; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Arkell, B.P.; Darch, G.J.C. Impact of climate change on London’s transport network. Munic. Eng. 2006, 169, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, E.; Chapman, L.; Quinn, A. Investigating the impact of precipitation on vehicle speeds on UK motorways. Meteorol. Appl. 2012, 21, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregnolato, M.; Ford, A.; Glenis, V.; Wilkinson, S.; Dawson, R. Impact of Climate Change on Disruption to Urban Transport Networks from Pluvial Flooding. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, 04017015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, K.Y. Impact Forecast Vision and Direction Meteorological Technology & Policy. Nat. Inst. Meterol. Sci. 2016, 9, 6–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.-W.; Oh, J.-S. Analysis of Provincial road in National Highway Average Speed Variation According to Rainfall Intensity. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2015, 15, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tae, K.; Oh, J. Provincial Road in National Highway Traffic Volume Variation According to Rainfall Intensity. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2015, 15, 406–414. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.K.; Do, M.S.; Choi, P.S.; Kim, M.S. The Effects of Weather Condition and Speed Regulation Cameras on Vehicles’ Speed. J. Civ. Eng. 2003, 2003, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.M.; Park, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.J. A Study on the Mitigation of Inundation Damage Using Flood Inundation Analysis Model Flumen. J. Korean Soc. Civ. Eng. 2007, 11, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, N.E.; Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Wang, L.-P.; Pina, R.D.; Marques, A.S.; Onof, C.; Leitão, J.P. Stochastic Urban Pluvial Flood Hazard Maps Based upon a Spatial-Temporal Rainfall Generator. Water 2015, 7, 3396–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, S.; Shi, P.; Chen, X.; Xue, F.; Gou, J.; Zhang, W. Development and Integration of Sub-Daily Flood Modelling Capability within the SWAT Model and a Comparison with XAJ Model. Water 2018, 10, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, D.; Urich, C.; Liu, S.; Gu, S. Application of CityDrain3 in Flood Simulation of Sponge Polders: A Case Study of Kunshan, China. Water 2018, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burger, G.; Bach, P.M.; Urich, C.; Leonhardt, G.; Kleidorfer, M.; Rauch, W. Designing and implementing a multi-core capable integrated urban drainage modelling Toolkit: Lessons from CityDrain3. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 100, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Lee, M.-H. The Development and Application of the Urban Flood Risk Assessment Model for Reflecting upon Urban Planning Elements. Water 2019, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, H.-Y.; Pan, T.-Y.; Chang, H.-K.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Lai, J.-S.; Tan, Y.-C.; Su, M.-D. Using Tabu Search Adjusted with Urban Sewer Flood Simulation to Improve Pluvial Flood Warning via Rainfall Thresholds. Water 2019, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delft Hydraulics. SOBEK Software User’s Manual; WL|Delft Hydraulics: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, P.; Liu, R.; Ma, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, D. Flash Flood Simulation for Ungauged Catchments Based on the Distributed Hydrological Model. Water 2019, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, E.; Oh, C.; Hong, S. Prediction of Speed by Rain Intensity using Road Weather Information System and Vehicle Detection System data. J. Korea Inst. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 12, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.; Tam, M.L.; Cao, X.; Li, X. Modeling the Effects of Rainfall Intensity on Traffic Speed, Flow, and Density Relationships for Urban Roads. J. Transp. Eng. 2013, 139, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashros, N.; Ben-Edigbe, J.; Alhassan, H.M.; Hassan, S.A. Investigating the Impact of Rainfall on Travel Speed. J. Teknol. 2014, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H. Short-Term Traffic Prediction Using Rainfall. Int. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2014, 2, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.; Kelvin, L.; Kumar, S.; Li, X.; Victor, H.Y.T.; Nikola, M.; Asif, T.; Justin, D.; Patrick, J. Improving Traffic Prediction by Including Rainfall Data; ITS Asia-Pacific Forum: Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Wu, J.; Ben-Akiva, M.; Seshadri, R.; Du, Y. Rainfall-integrated traffic speed prediction using deep learning method. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 11, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.J. Analysis on inundation characteristics for flood impact forecasting in Gangnam drainage basin. Atmosphere 2017, 27, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Pregnolato, M.; Ford, A.; Wilkinson, S.M.; Dawson, R.J. The impact of flooding on road transport: A depth-disruption function. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 55, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-S.; Yoon, S.-K.; Yang, D.-M.; Kwon, H. Development of Grid-Based Conceptual Hydrologic Model. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 43, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, V.M.; Hawkins, R.H. Runoff curve number: Has it reached maturity? J. Hydrol. Eng. 1996, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Software Packages FLO-2D Manual. 2009. Available online: https://www.flo-2d.com/download/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Lee, S.H.; Kang, N.H.; Sik, B.S.B. A Study on the Method of Calculating the Threshold Rainfall for Rainfall Impact Forecasting. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2018, 18, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Go, D.-H.; Lee, K.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, S.-W. FLO-2D Simulation of the Flood Inundation Zone in the Case of Failure of the Sandae Reservoir Gyeongju, Gyeongbuk. J. Eng. Geol. 2015, 25, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Paik, J.; Kim, K.S. Run-out Modeling of Debris Flows in Mt. Umyeon using FLO-2D. J. Korean Soc. Civ. Eng. 2013, 33, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.; Kim, B. Modeling for Debris Flow Behavior on Expressway Using FLO-2D. J. Korean Soc. Civ. Eng. 2019, 39, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Kyong-Hoon, K.; Park, J. Analysis of Optimal Evacuation Route for Flood Disaster. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2018, 18, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Javier, F.; Daniel, C. Pilar García-Navarro Rainfall/runoff simulation with 2D full shallow water equations: Sensitivity analysis and calibration of infiltration parameters. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 496–513. [Google Scholar]
- Bout, B.; Jetten, V. The validity of flow approximations when simulating catchment-integrated flash floods. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liang, Q.; Ming, X. A full-scale fluvial flood modelling framework based on a high-performance integrated hydrodynamic modelling system (HiPIMS). Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 132, 103392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, G.-T.; Shih, D.-S.; Cheng, J.-R.C. An integrated media, integrated processes watershed model. Comput. Fluids 2011, 45, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, L.; Castellet, E.B. A simple and efficient unstructured finite volume scheme for solving the shallow water equations in overland flow applications. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5464–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellos, V.; Tsakiris, G. A hybrid method for flood simulation in small catchments combining hydrodynamic and hydrological techniques. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liang, Q. A new efficient implicit scheme for discretising the stiff friction terms in the shallow water equations. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 117, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, P.; Costanzo, C.; De Bartolo, S.; Gangi, F.; Macchione, F.; Tomasicchio, G. Hydraulic Characterization of River Networks Based on Flow Patterns Simulated by 2-D Shallow Water Modeling: Scaling Properties, Multifractal Interpretation, and Perspectives for Channel Heads Detection. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7717–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Choi, H.; Jee, H. Estimation of the flash flood index by the probable rainfall data for ungauged catchments. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2010, 10, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.K.; Kim, B.S. A Study on the development of a heavy rainfall risk impact evaluation matrix. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 52, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, F.A. Time distribution of rainfall in heavy storms. Water Resour. Res. 1967, 3, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, B.; Notley, S.; Boddington, K.; Rees, T. External Factors Affecting Motorway Capacity. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 16, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallaway, B.M.; Ivey, D.L.; Hayes, G.G.; Ledbetter, W.G.; Olson, R.M.; Woods, D.L.; Schiller, R.E. Pavement and Geometric Design Criteria for Minimizing Hydroplaning; Report No. FHWA-RD-79-31; Federal Highway Administration: Springfield, IL, USA, 1979; p. 302.
- Ong, G.P.; Fwa, T.F. Hydroplaning Risk Management for Grooved Pavements. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Managing Pavement Assets, Calgary, AB, Canada, 23–28 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Galatioto, F.; Glenis, V.; Roberts, R.; Kilsby, C. Exploring and modelling the impacts of rainfall and flooding on transport network. The case study of Newcastle upon Tyne. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Urban Sustainability and Resilience (USAR 2014), London, UK, 5–7 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- YouTube. Video: UK Flood Observation, Perth. 2012. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tCqEARMI-_k (accessed on 22 September 2016).
- Electric Vehicle Safety Task Forces. EVS GTR on Protection Against Water. 8th EVS GTR IWG Meeting, Electric Vehicle Safety Task Forces (EVSTF), Changchun (China). 2015. Available online: https://globalautoregs.com/documents/11234 (accessed on 23 September 2016).
- English, A. How to Drive Through Floods. Available online: http://www.telegraph.co.uk/cars/advice/how-to-drive-through-floods/ (accessed on 22 September 2016).
- Greenflag.com. Expert Advice: Driving Through Flood Water. 2015. Available online: http://blog.greenflag.com/2015/expert-advice-driving-through-flood-water/ (accessed on 22 September 2016).
- Koo, S. An Observation on the Concept of Shape Grammar through the Body Proportion of the Mid-size Sedans. Arch. Des. Res. 2005, 5, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.G.; Jang, S.K. Decision of System Layout and Package Layout for Medium-Sized Low Floor BusEnglish Title of The Paper (Times New Roman 14pt). In Proceedings of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering Conference, Jeju, Korea, 26–28 May 2010; pp. 1455–1456. [Google Scholar]
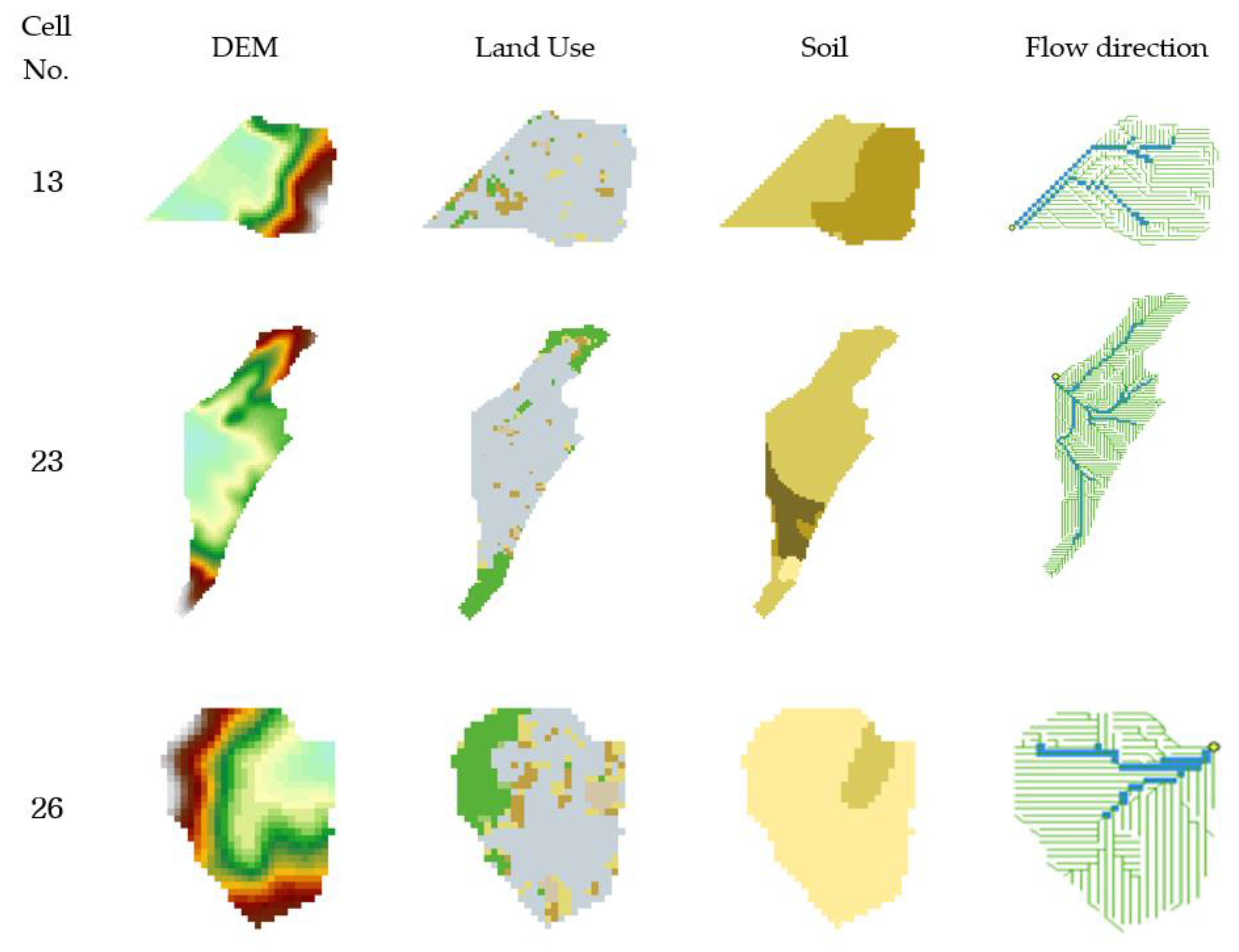
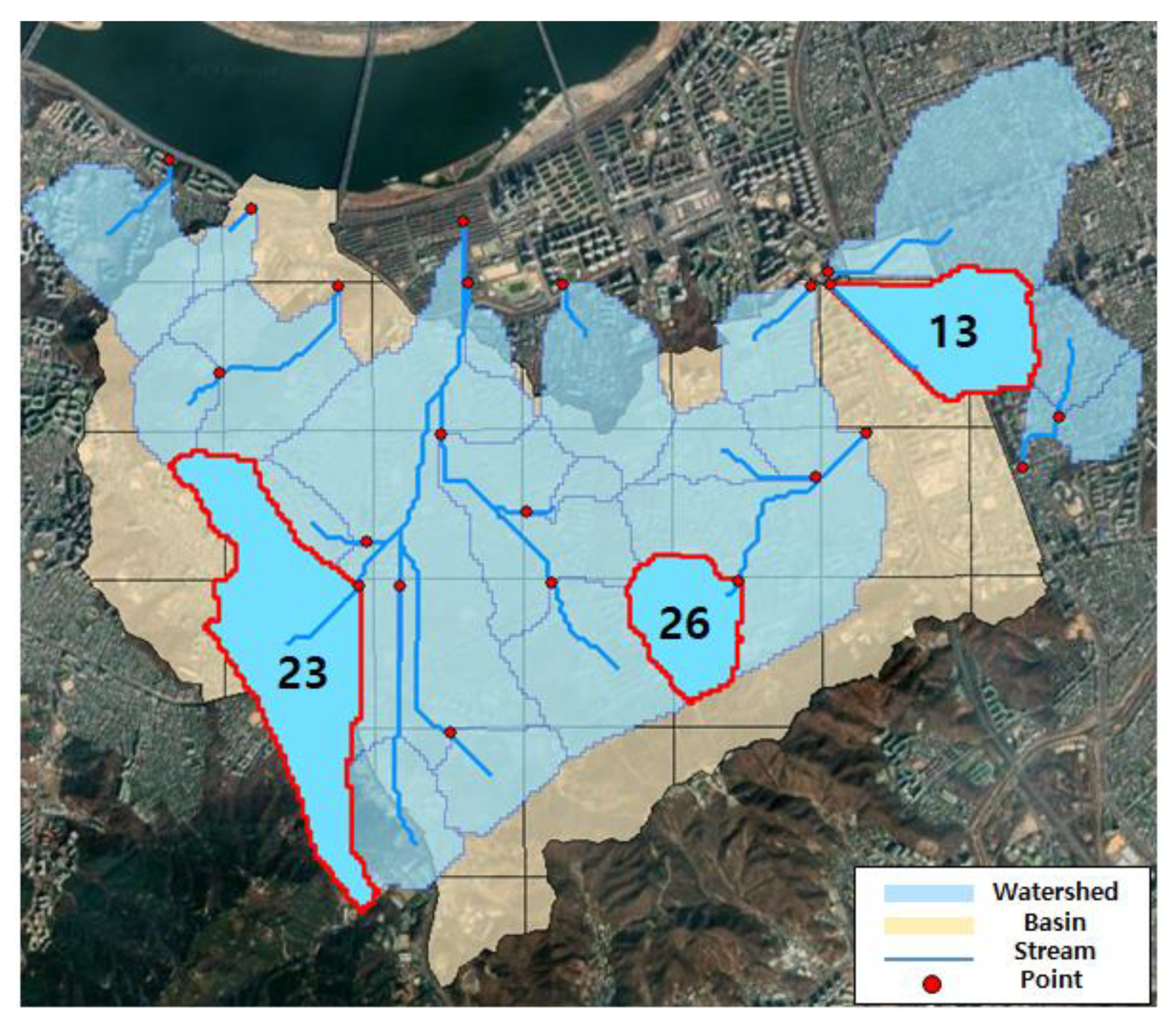
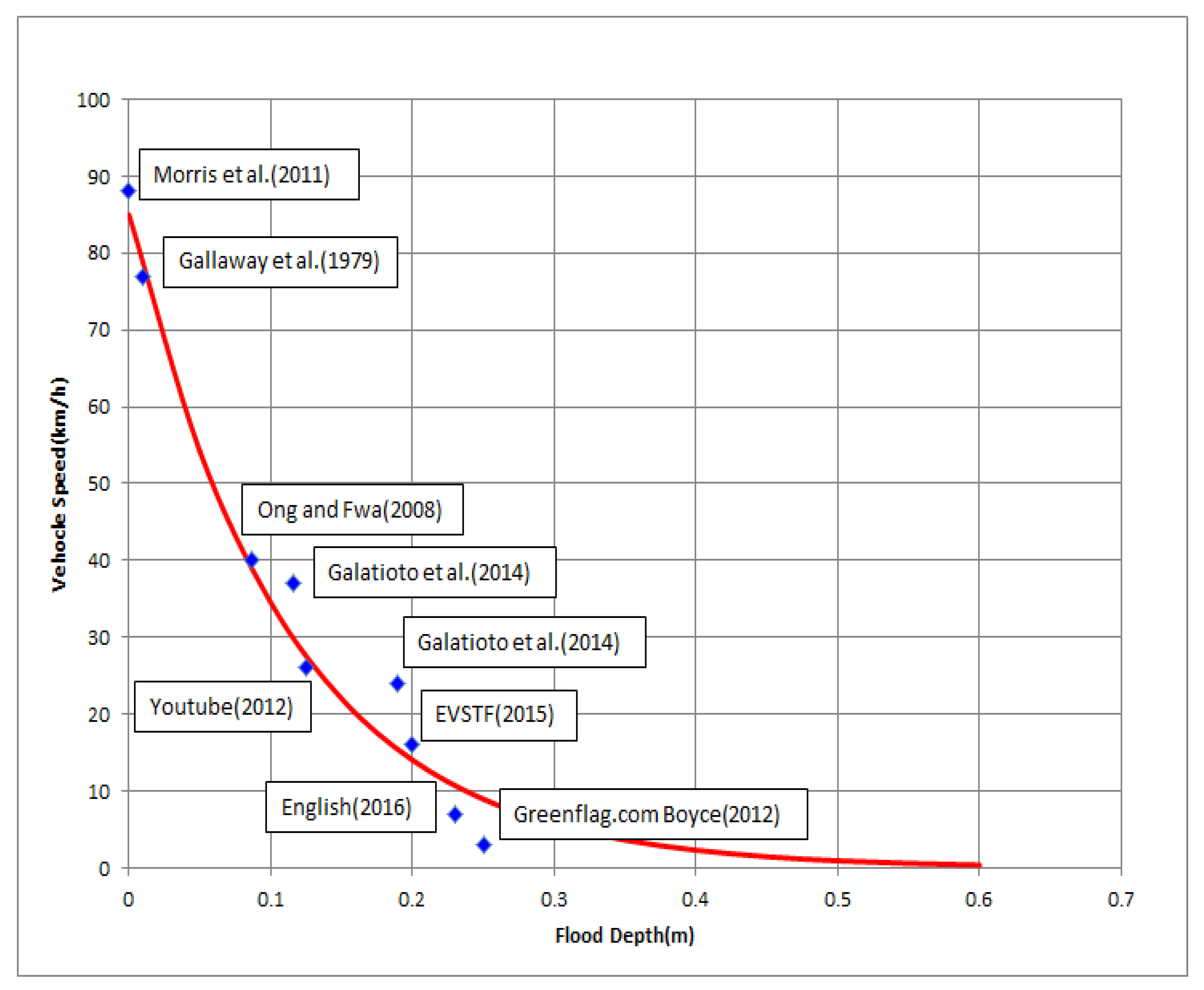




| Point No. | Flood Depth (m) | Vehicle Speed (km/h) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 [51] | 0 | 88 |
| 2 [52] | 0.01 | 77 |
| 3 [53] | 0.087 | 40 |
| 4 [54] | 0.116 | 37 |
| 5 [55] | 0.125 | 26 |
| 6 [54] | 0.189 | 24 |
| 7 [56] | 0.200 | 16 |
| 8 [57] | 0.230 | 7 |
| 9 [58] | 0.250 | 3 |
| Cell No | Rainfall–Depth Curve | Threshold Rainfall |
|---|---|---|
| Transport (20 cm) | ||
| 2,6 | 35.3 mm | |
| 8 | 79.3 mm | |
| 9,10 | 47.6 mm | |
| 11 | 49.3 mm | |
| 12 | 68.8 mm | |
| 13 | 26.9 mm | |
| 14 | 54.4 mm | |
| 16,17 | 105.4 mm | |
| 18,19,20 | 45.3 mm | |
| 21 | 25.7 mm | |
| 23 | 52.4 mm | |
| 24 | 118.6 mm | |
| 25 | 57.4 mm | |
| 26 | 78.0 mm | |
| 31 | 132.8 mm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choo, K.-S.; Kang, D.-H.; Kim, B.-S. Impact Assessment of Urban Flood on Traffic Disruption using Rainfall–Depth–Vehicle Speed Relationship. Water 2020, 12, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040926
Choo K-S, Kang D-H, Kim B-S. Impact Assessment of Urban Flood on Traffic Disruption using Rainfall–Depth–Vehicle Speed Relationship. Water. 2020; 12(4):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040926
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoo, Kyung-Su, Dong-Ho Kang, and Byung-Sik Kim. 2020. "Impact Assessment of Urban Flood on Traffic Disruption using Rainfall–Depth–Vehicle Speed Relationship" Water 12, no. 4: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040926





