Seasonal Succession of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Driving Factors of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Subtropical Reservoir in South China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
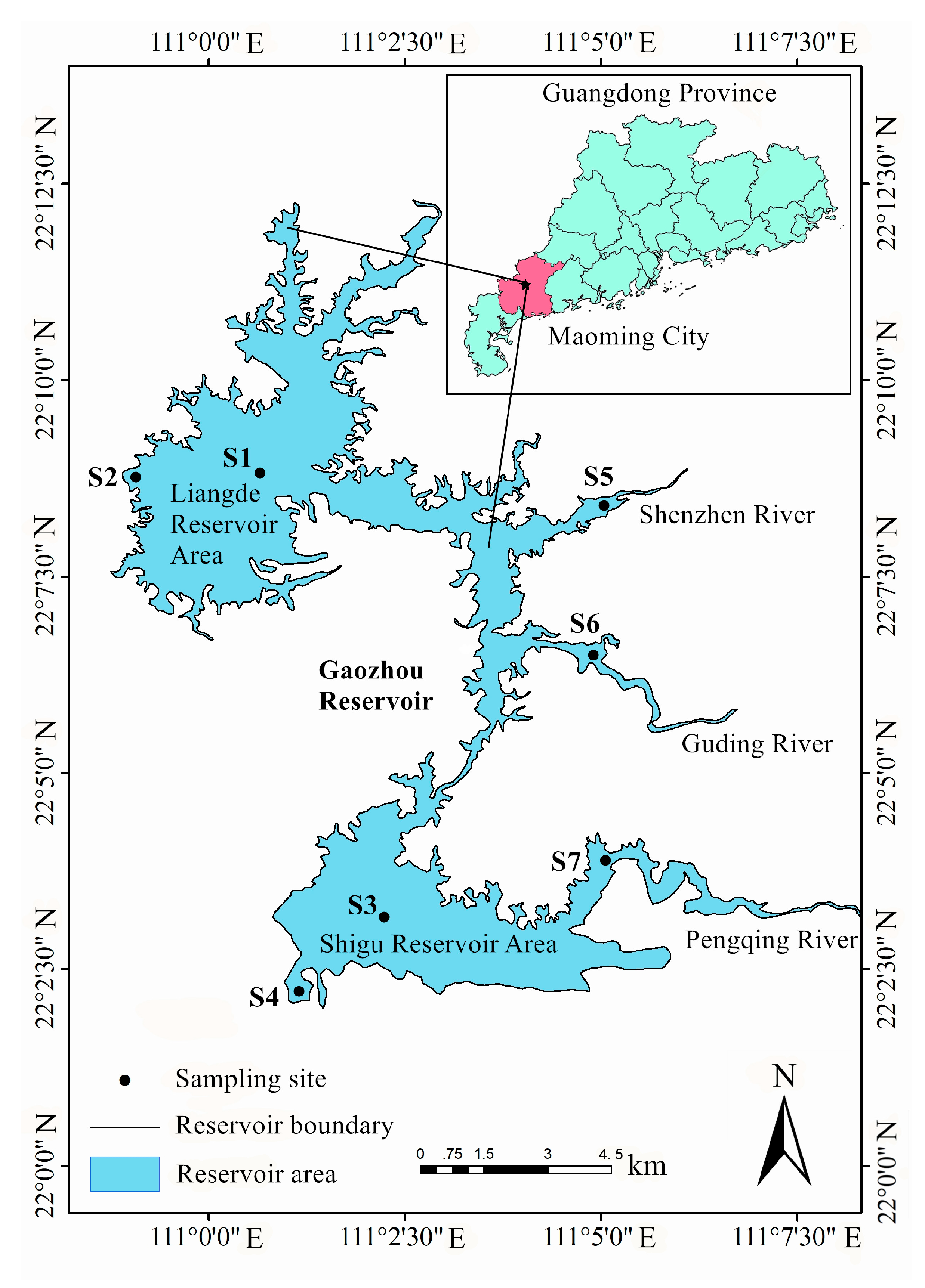
2.1. Study Period and Site Description
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
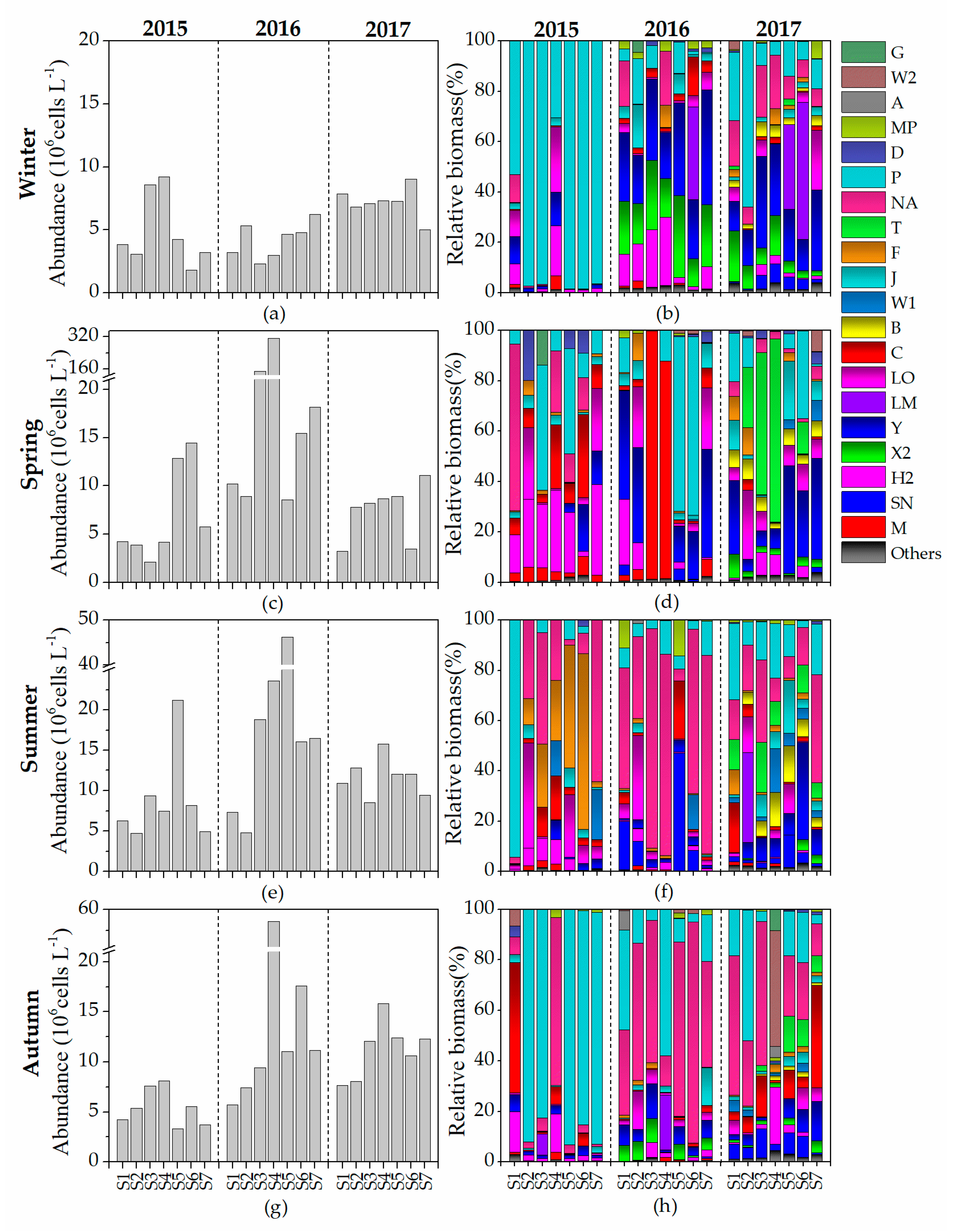
3.1. Phytoplankton Dynamics
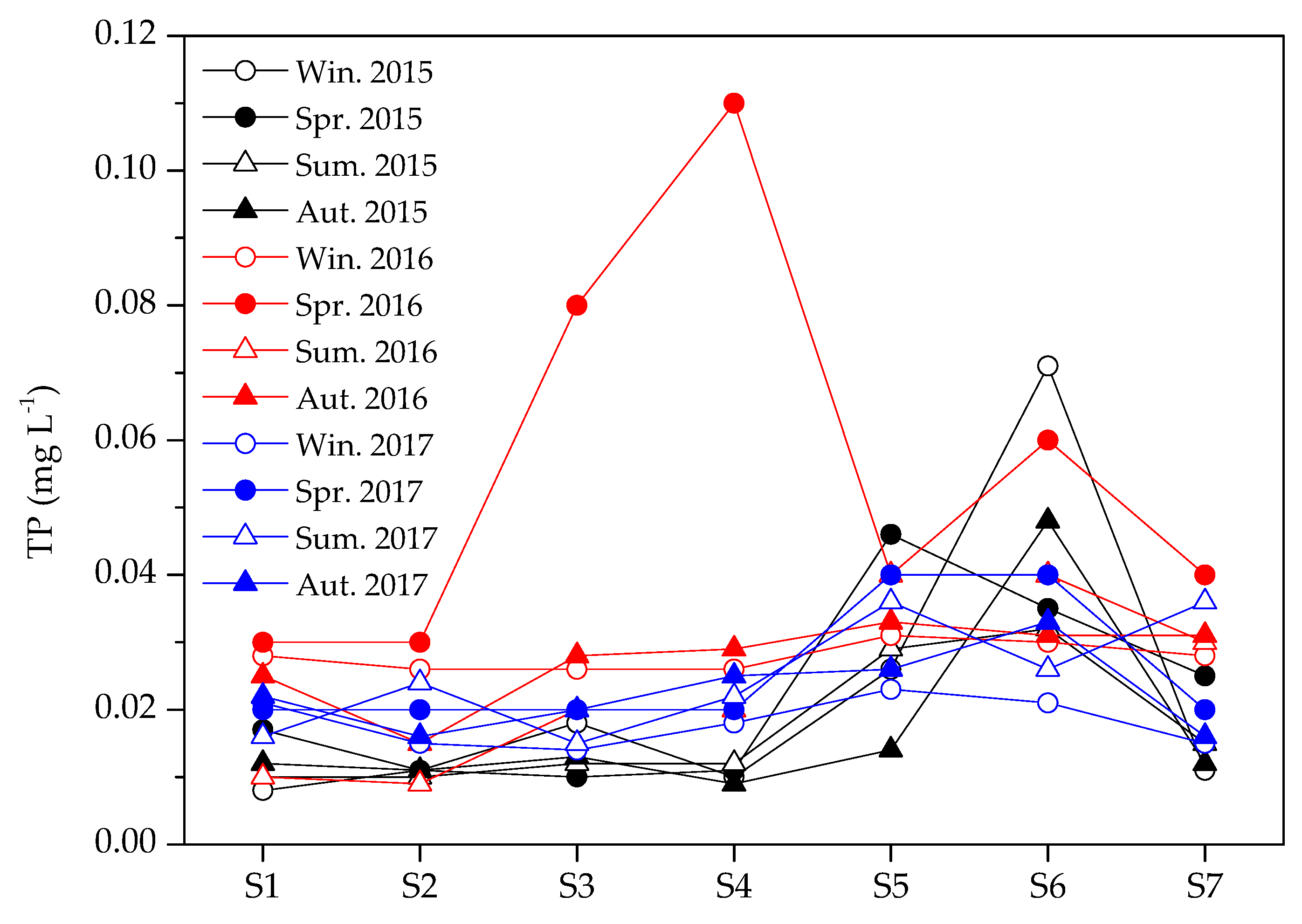
3.2. Variations in Environmental Factors
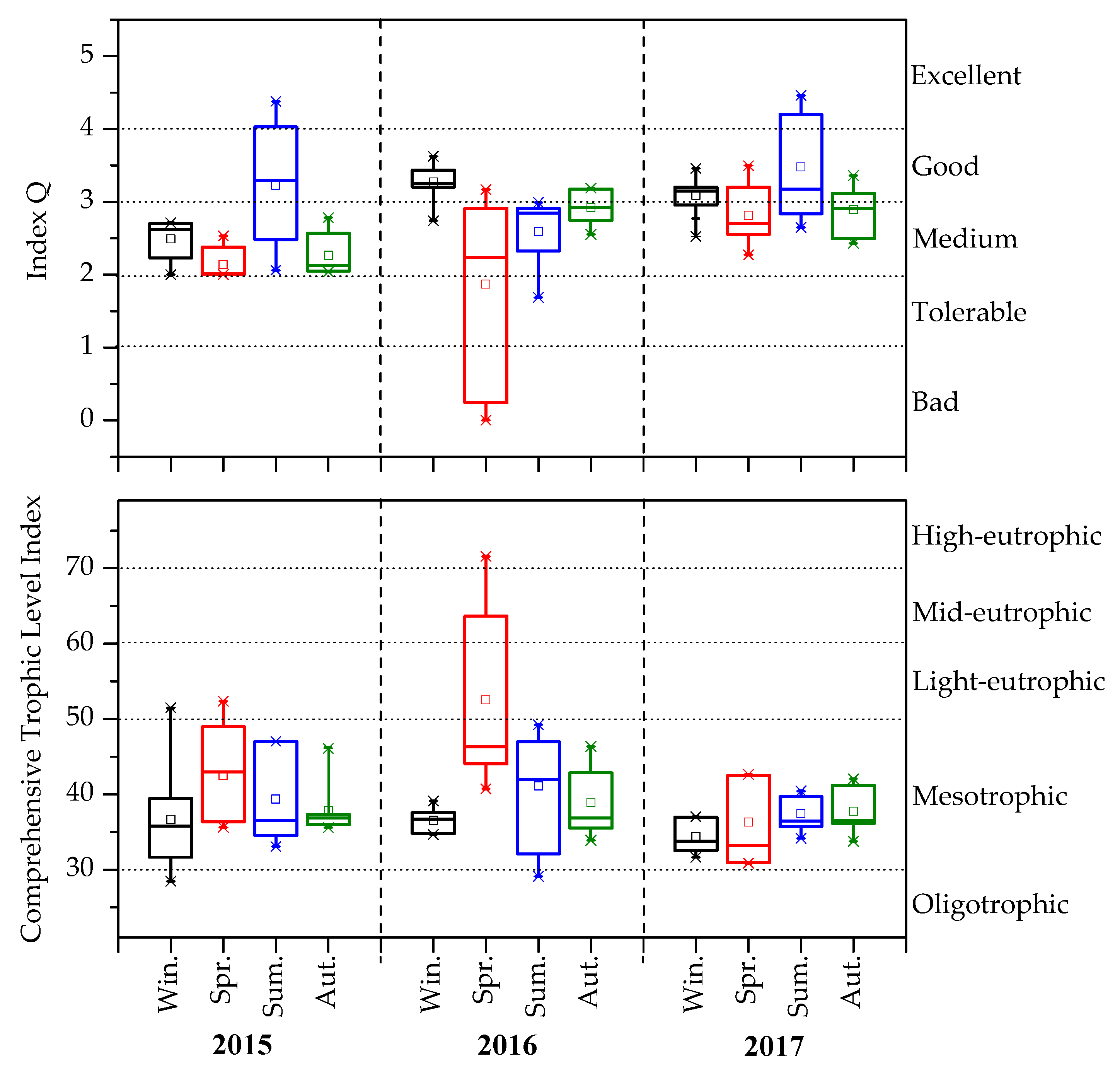
3.3. Changes in Q and TLI (Σ)
3.4. Redundancy Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Phytoplankton Seasonal Dynamics
4.2. Environmental Driving Factors
4.3. Analysis of Cyanobacterial Blooms
4.4. Environmental Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilken, S.; Soares, M.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Ratcovich, J.; Ekvall, M.K.; Donk, E.V.; Hansson, L.A. Primary producers or consumers? Increasing phytoplankton bacterivory along a gradient of lake warming and browning: Increasing phytoplankton bacterivory. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, S142–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Drakare, S.; Johnson, R.K. Use of taxon-specific models of phytoplankton assemblage composition and biomass for detecting impact. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 97, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, R.M.D.C.; Dolbeth, M.; de Lucena Barbosa, J.E.; Patrício, J. Narrowing the gap: Phytoplankton functional diversity in two disturbed tropical estuaries. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 86, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Li, B.; He, F.; Gu, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, H.; Tan, L.; Xiao, W.; Liu, S.; Cai, Q. Flow directionality, mountain barriers and functional traits determine diatom metacommunity structuring of high mountain streams. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chirico, N.; António, D.C.; Pozzoli, L.; Marinov, D.; Malagó, A.; Sanseverino, I.; Beghi, A.; Genoni, P.; Dobricic, S.; Lettieri, T. Cyanobacterial Blooms in Lake Varese: Analysis and Characterization over Ten Years of Observations. Water 2020, 12, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalak, A.M. Study role of climate change in extreme threats to water quality. Nature 2016, 535, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, A.; Budzyńska, A.; Dondajewska-Pielka, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R. Functional Groups of Phytoplankton and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Restored Uzarzewskie Lake. Water 2020, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Qian, K.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J. A comparison of factors influencing the summer phytoplankton biomass in China’s three largest freshwater lakes: Poyang, Dongting, and Taihu. Hydrobiologia 2017, 792, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; von Fumetti, S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. The importance of small waterbodies for biodiversity and ecosystem services: Implications for policy makers. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Huszar, V.; Kruk, C.; Naselliflores, L.; Melo, S. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padisák, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Naselli-Flores, L. Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: A critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 2009, 621, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.S.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Ovalle, A.R. Phytoplankton Functional Groups in a Tropical Estuary: Hydrological Control and Nutrient Limitation. Estuar. Coast. 2009, 32, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, C.; Devercelli, M.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Hernández, E.; Beamud, G.; Diaz, M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Segura, A.M. Classification of Reynolds phytoplankton functional groups using individual traits and machine learning techniques. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.C.; Pivato, B.M.; Vieira, L.C.G.; Bovo-Scomparin, V.M.; Bortolini, J.C.; Pineda, A.; Train, S. Use of phytoplankton functional groups as a model of spatial and temporal patterns in reservoirs: A case study in a reservoir of central Brazil. Hydrobiologia 2018, 805, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, V.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Crossetti, L.O. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to the mixing regime in a deep subtropical reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2009, 628, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, V.; Caputo, L.; Ordóñez, J.; Marcé, R.; Armengol, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Huszar, V.L.M. Driving factors of the phytoplankton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean reservoir. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.D.C.D.; Crossetti, L.O.; Becker, V. Effects of temperature increase and nutrient enrichment on phytoplankton functional groups in a Brazilian semi-arid reservoir. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2018, 30, e215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Hou, Z.; Li, Z.; Chu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zheng, B. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups and their driving factors in a subtropical plateau lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L.M.; Crossetti, L.O.; Ferragut, C. Ecological status assessment of tropical reservoirs through the assemblage index of phytoplankton functional groups. Braz. J. Bot. 2017, 40, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupertino, A.; Gücker, B.; Von Rückert, G.; Figueredo, C.C. Phytoplankton assemblage composition as an environmental indicator in routine lentic monitoring: Taxonomic versus functional groups. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Liu, J.; King, L. A comprehensive model for assessing lake eutrophication. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Trolle, D.; Spigel, B.; Hamilton, D.P.; Norton, N.; Sutherland, D.; Plew, D.; Allan, M.G. Application of a Three-Dimensional Water Quality Model as a Decision Support Tool for the Management of Land-Use Changes in the Catchment of an Oligotrophic Lake. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.; Ma, C.; Xi, B.; Su, J.; Zan, F.; Ji, D.; He, Z. Establishing eutrophication assessment standards for four lake regions, China. J. Environ. Sci. China 2013, 25, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padisák, J.; Borics, G.; Grigorszky, I.; Soróczki-Pintér, É. Use of Phytoplankton Assemblages for Monitoring Ecological Status of Lakes within the Water Framework Directive: The Assemblage Index. Hydrobiologia 2006, 553, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Nan, J.; Li, J. Driving Factors and Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in an Estuary Reservoir in the Yangtze River, China. Water 2019, 11, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Song, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Jenkins, A. Response of the phytoplankton community to water quality in a local alpine glacial lake of Xinjiang Tianchi, China: Potential drivers and management implications. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Ni, W.; Luo, Y.; Jan Stevenson, R.; Qi, J. Response of freshwater algae to water quality in Qinshan Lake within Taihu Watershed, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Q.; Liang, R.; Xia, B.; Zhuo, Q. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Adsorption Characteristics of Suspended Solids Input into a Drinking Water Reservoir via Typhoon Heavy Rainfall. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Q.; Liang, R.; Xia, B.; Gou, T. Simulation of the impact of typhoon-induced suspended solids precipitation on water quality in a reservoir for drinking water. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 27, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, L. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton morphological characters and driving factors in tropical reservoirs: A case study from Gaozhou Reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 825–836. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Han, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yao, L.; Wei, D.; Zhang, J.; Hu, F. Study on the Structure of Phytoplankton Community and Its Relationships with Environmental Factors in Gaozhou reservoir. J. Hydroecology 2013, 34, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, G.; Wanyan, H.; Cai, L.; Hu, G.; Xu, Z. Preliminary regulating factors of spring cyanobacterial bloom in Gaozhou Reservoir, Guangdong Province. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Huang, Y. Characteristics change of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients and water strategies in Gaozhou Reservoir. Ecol. Sci. 2015, 34, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Hu, R.; Peng, L.; Lei, L.; Feng, Y.; Han, B. Dissimilarity of phytoplankton assemblages in two connected tropical reservoirs: Effects of water transportation and environmental filtering. Hydrobiologia 2016, 764, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Environmental Protection Administration. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Method, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Qin, L.; Bao, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Critical nutrient thresholds needed to control eutrophication and synergistic interactions between phosphorus and different nitrogen sources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21008–21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.W.G.; Kipling, C.; Cren, E.D.L. The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers and the statistical basis of estimations by counting. Hydrobiol 1958, 11, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Du Rselen, C.; Kirschtel, D.; Zohary, U.P.A.T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nixdorf, B.; Rektins, A.; Mischke, U. Standards and Thresholds of the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD)—Phytoplankton and Lakes. In Standards and Thresholds for Impact Assessment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Q.; Jin, X. The Standard Methods in Lake Eutrophication Investigation, 2nd ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Y. Primary study on enacting the lake nutrient control standard. Environ.Sci. 2009, 30, 2497–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenard, T.; Ejankowski, W.; Poniewozik, M. Responses of Phytoplankton Communities in Selected Eutrophic Lakes to Variable Weather Conditions. Water 2019, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Xue, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F.; Chen, D. Effects of Water Diversion from Yangtze River to Lake Taihu on the Phytoplankton Habitat of the Wangyu River Channel. Water 2018, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardikar, R.; Haridevi, C.K.; Chowdhury, M.; Shinde, N.; Ram, A.; Rokade, M.A.; Rakesh, P.S. Seasonal distribution of phytoplankton and its association with physico-chemical parameters in coastal waters of Malvan, west coast of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, D. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups in a reservoir in central China. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. /Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 2018, 192, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, J.; Ma, C.; Qin, X. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton functional groups and its relationship with the environment in river: A case study in northeast China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2012, 27, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, M. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on phytoplankton composition and biomass in 15 subtropical, urban shallow lakes in Wuhan, China. Limnologica 2011, 41, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, C.; Hao, D.; Pei, H.; Doblin, M.A.; Ren, Y.; Wei, J.; Feng, Y. Phytoplankton Functional Groups Variation and Influencing Factors in a Shallow Temperate Lake. Water Environ. Res. 2018, 90, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, T.; Hu, R.; Han, B.; Wang, S.; Qian, X.; Padisák, J. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups regulated by monsoonal hydrology in a large canyon-shaped reservoir. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5099–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Lv, J.; Liu, Q.; Nan, F.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Xie, S.; Feng, J. Interactive effects of temperature and nutrients on the phytoplankton community in an urban river in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Du, P.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Shou, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, J. Oyster farming control on phytoplankton bloom promoted by thermal discharge from a power plant in a eutrophic, semi-enclosed bay. Water Res. 2019, 159, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Feng, M.; Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Ke, F.; Chen, X.; Li, W. The establishment of preliminary safety threshold values for cyanobacteria based on periodic variations in different microcystin congeners in Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Sci. Proc. Imp. 2015, 17, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, Q.; Peng, X.; Liu, C. Principle of Vernalization in Microcystis aeruginosa in Dianchi Lake and Improvement of Gene Model on Controlling the Vernalization. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 2028–2034. [Google Scholar]

| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | All seasons | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Proportion | Taxa | Proportion | Taxa | Proportion | Taxa | Proportion | Taxa | Proportion | |
| Cyanobacteria | 10 | 9.71% | 15 | 13.76% | 19 | 15.08% | 15 | 12.50% | 20 | 12.90% |
| Cryptophytes | 4 | 3.88% | 4 | 3.67% | 4 | 3.17% | 4 | 3.33% | 4 | 2.58% |
| Dinoflagellates | 4 | 3.88% | 5 | 4.59% | 5 | 3.97% | 5 | 4.17% | 5 | 3.23% |
| Chrysophytes | 1 | 0.97% | 1 | 0.92% | 1 | 0.79% | 1 | 0.83% | 1 | 0.65% |
| Diatoms | 26 | 25.24% | 26 | 23.85% | 29 | 23.02% | 28 | 23.33% | 30 | 19.35% |
| Euglenophytes | 2 | 1.94% | 3 | 2.75% | 3 | 2.38% | 3 | 2.50% | 3 | 1.94% |
| Chlorophytes | 56 | 54.37% | 55 | 50.46% | 65 | 51.59% | 64 | 53.33% | 92 | 59.35% |
| Total taxa | 103 | 100% | 109 | 100% | 126 | 100% | 120 | 100% | 155 | 100% |
| Functional Groups | Phytoplankton Species | Taxonomic Group | F Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | Microcystis aeruginosa a | Cyanobacteria | 0 |
| S1 | Pseudanabaena sp. | Cyanobacteria | 0 |
| SN | Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii | Cyanobacteria | 0 |
| H1 | Aphanizomenon flos-aquae | Cyanobacteria | 0 |
| H2 | Dolichospermum circinale | Cyanobacteria | 2.0 |
| X1 | Ankistrodesmus falcatus, Monoraphidium sp. | Chlorophytes | 3.5 |
| X2 | Chroomonas acutaa | Cryptophytes | 5.0 |
| X3 | Schroederia sp. | Chlorophytes | 5.0 |
| Y | Cryptomonas ovataa, Cryptomonas erosaa, | Cryptophytes | 3.0 |
| Gymnodinium aeruginosuma | Dinoflagellates | ||
| LM | Ceratium hirundinella | Dinoflagellates | 4.0 |
| LO | Peridiniopsis borgei a | Dinoflagellates | 4.0 |
| Chroococcus sp., Merismopedia glauca | Cyanobacteria | ||
| K | Aphanocapsa sp. | Cyanobacteria | 0 |
| TC | Gloeocapsa punctata | Cyanobacteria | 4.0 |
| E | Dinobryon divergens | Chrysophytes | 5.0 |
| D | Synedra acus, Nitzschia sublinearis | Diatoms | 2.0 |
| C | Cyclotella meneghiniana, Cymbella perpusilla, Navicula sp., Diploneis sp. | Diatoms | 3.0 |
| B | Cyclotella bodanica | Diatoms | 4.0 |
| A | Rhizosolenia sp., Attheya zachariasi | Diatoms | 4.0 |
| MP | Achnanthes exigua, Cocconeis placentula | Diatoms | 4.0 |
| W1 | Euglena sp., Phacus sp. | Euglenophytes | 0 |
| W2 | Trachelomonas sp. | Euglenophytes | 1.0 |
| WO | Chlamydomonas globosa | Chlorophytes | 0 |
| G | Eudorina elegans, Pandorina morum | Chlorophytes | 2.0 |
| J | Tetraëdron trigonum a, Pediastrum duplex var. gracillimum, Scenedesmus sp., Chodatella sp., Crucigenia sp., Coelastrum sp. | Chlorophytes | 2.0 |
| F | Haematococcus pluvialis, Planktosphaeria gelotinosa, Quadrigula chodatii, Elakatothrix gelatinosa a, Selenastrum dibraianum, Kirchneriella lunaris, Oocystis lacustis | Chlorophytes | 5.0 |
| T | Mougeotia gracillima a | Chlorophytes | 5.0 |
| NA | Cosmarium sp. a, Staurodesmus sp. a, Euastrum sp., | Chlorophytes | 3.0 |
| P | Staurastrum sp. a, Closterium acerosum a | Chlorophytes | 2.0 |
| Melosira varians a, Fragilaria sp. a | Diatoms |
| Winter | Sping | Summer | Autumn | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Range | Mean | Range | Mean | Range | Mean | Range | |
| WT (°C) | 20.8 | 17.8–23.9 | 28.0 | 22.9–32.2 | 31.2 | 28.8–33.3 | 26.5 | 24.8–27.8 |
| pH | 7.33 | 6.73–8.36 | 7.32 | 6.29–8.33 | 8.63 | 8.10–9.28 | 7.61 | 6.84–8.93 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 8.11 | 6.12–10.71 | 10.03 | 8.14–14.38 | 8.78 | 7.74–9.90 | 7.40 | 5.54–9.25 |
| EC (μs cm−1) | 58.7 | 54.4–67.0 | 66.1 | 59.8–88.3 | 58.8 | 53.1–64.7 | 56.9 | 53.8–60.9 |
| SS (mg L−1) | 2.1 | 0.3–5.2 | 9.0 | 2.0–59.0 | 3.5 | 1.4–8.0 | 2.5 | 1.4–5.0 |
| TN (mg L−1) | 0.58 | 0.37–0.95 | 0.94 | 0.36–2.60 | 0.58 | 0.20–1.06 | 0.56 | 0.38–0.85 |
| NH4–N (mg L−1) | 0.064 | 0.028–0.154 | 0.069 | 0.013–0.135 | 0.060 | 0.027–0.178 | 0.055 | 0.029–0.097 |
| NO3–N (mg L−1) | 0.35 | 0.19–0.68 | 0.38 | 0.08–0.85 | 0.22 | 0.08–0.62 | 0.25 | 0.12–0.49 |
| TP (mg L−1) | 0.023 | 0.008–0.071 | 0.035 | 0.010–0.110 | 0.022 | 0.009–0.040 | 0.022 | 0.009–0.048 |
| CODMn (mg L−1) | 1.9 | 0.8–4.2 | 3.3 | 0.6–12.2 | 2.2 | 1.4–3.5 | 1.9 | 1.2–2.8 |
| Chla (mg m−3) | 8.9 | 3.1–36.3 | 25.8 | 5.2–193.3 | 16.8 | 4.4–53.8 | 14.8 | 6.8–32.4 |
| WL (m) | 60.6 | 60.3–61.3 | 61.0 | 60.4–61.8 | 60.7 | 60.4–61.2 | 60.7 | 60.2–61.2 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 239 | 50–428 | 504 | 428–684 | 888 | 633–1116 | 337 | 210–517 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, G.-J.; Liang, R.; Gou, T.; Xia, B.; Li, S.; Liu, C. Seasonal Succession of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Driving Factors of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Subtropical Reservoir in South China. Water 2020, 12, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041167
Yao L, Zhao X, Zhou G-J, Liang R, Gou T, Xia B, Li S, Liu C. Seasonal Succession of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Driving Factors of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Subtropical Reservoir in South China. Water. 2020; 12(4):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041167
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Lingai, Xuemin Zhao, Guang-Jie Zhou, Rongchang Liang, Ting Gou, Beicheng Xia, Siyang Li, and Chang Liu. 2020. "Seasonal Succession of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Driving Factors of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Subtropical Reservoir in South China" Water 12, no. 4: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041167
APA StyleYao, L., Zhao, X., Zhou, G.-J., Liang, R., Gou, T., Xia, B., Li, S., & Liu, C. (2020). Seasonal Succession of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Driving Factors of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Subtropical Reservoir in South China. Water, 12(4), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041167





