Influence of Farming Intensity and Climate on Lowland Stream Nitrogen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Farming Intensity
2.2. Hydrochemistry Monitoring
- Fortnightly grab-sampling in benchmark streams: Sub-surface grab samples were taken from a well-mixed section with no macrophytes in the center of the stream channel during the daytime. This instantaneous sampling was used for the analysis of conservative and non-conservative N fractions (i.e., TN, TDN, NO3−, DON, and NH4+).
- Automatic pooled sampling in benchmark streams: High-frequency monitoring using automated equipment was conducted during the same two-year period. Glacier refrigerated automatic samplers (ISCO-Teledyne) collected an equal water volume every four hours from the same sampling point, and the pooled samples were collected fortnightly. The final nutrient concentration in the only sampler carboy thus represented a time-proportional average for the fortnightly sampling period. As this sampling involved refrigerated storage of pooled samples for up to two weeks, the emphasis was placed on the analysis of TN.
- Snapshot grab-sampling in the series of streams was made once in winter and once in summer. Sub-surface grab samples were taken in a well-mixed section with no macrophytes from the center of the stream channels during the daytime. This instantaneous sampling was used for the analysis of different N fractions, with emphasis on dissolved compounds (i.e., TDN, NO3−, DON, and NH4+).
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Climate and Hydrology
3.2. Total Nitrogen Concentrations and Losses in Benchmark Streams
3.3. Influence of Temperature and Discharge on Total Nitrogen Concentrations
3.4. Influence of Climate/Hydrology and Farming Intensity on Nitrogen Species
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Farming Intensity
4.2. Influence of Climate
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, L.J.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennet, E.M. Agricultural modifications of hydrological flows create ecological surprises. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erisman, J.W.; Sutton, M.A.; Galloway, J.; Klimont, Z.; Winiwarter, W. How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, N.; Galloway, J.N. An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 2008, 451, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M. Beyond global warming: Ecology and global change. Ecology 1994, 75, 1861–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sagrario, M.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Goma, J.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Lankildehus, F. Does high nitrogen loading prevent clear-water conditions in shallow lakes at moderately high phosphorus concentrations? Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.; Fisher, J.; Russell, V.; Collings, S.; Moss, B. Nitrate availability and plant species richness: Implications for management of freshwater lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; de Vries, W.; de Wit, C.A.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bormann, F.H.; Likens, G.E. Nutrient cycling. Science 1967, 155, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulêtreau, S.; Salvo, E.; Lyautey, E.; Mastrorillo, S.; Garabetian, F. Temperature dependence of denitrification in phototrophic river biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deelstra, J.; Iital, A.; Povilaitis, A.; Kyllmar, K.; Greipsland, I.; Blicher-Mathiesen, G.; Jansons, V.; Koskiaho, J.; Lagzdins, A. Hydrological pathways and nitrogen runoff in agricultural dominated catchments in Nordic and Baltic countries. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner-Kittridge, M.; Strauss, P.; Blöschl, G.; Eder, A.; Saracevic, E.; Zessner, M. The seasonal dynamics of the stream sources and input flow paths of water and nitrogen of an Austrian headwater agricultural catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542 Pt A, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durand, P.; Breuer, L.; Johnes, P.J.; Billen, G.; Butturini, A.; Pinay, G.; van Grinsven, H.; Garnier, J.; Rivett, M.; Reay, D.S.; et al. Nitrogen processes in aquatic ecosystems. In The European Nitrogen Assessment—Sources, Effects and Policy Perspectives; Sutton, M.A., Howard, C.M., Erisman, J.W., Billen, G., Bleeker, A., Grennfelt, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; p. 664. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.C.; Lee, T.Y.; Lin, T.C.; Hein, T.; Lee, L.C.; Shih, Y.T.; Kao, S.J.; Shiah, F.K.; Lin, N.H. Effects of different N sources on riverine DIN export and retention in a subtropical high-standing island, Taiwan. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, S.J.; Naney, J.W. Environmental impact of agricultural nitrogen and phosphorus use. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1987, 35, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; Volume 12-03, p. 153. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Res. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potter, P.; Ramankutty, N.; Bennett, E.M.; Donner, S.D. Characterizing the spatial patterns of global fertilizer application and manure production. Earth Interact. 2010, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, P.; Ramankutty, N.; Bennett, E.M.; Donner, S.D. Global Fertilizer and Manure, Version 1: Nitrogen Fertilizer Application; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.D.; Castillo, M.M. Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; p. 436. [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon, D. Tropical Stream Ecology; Academic Press/Elsevier: London, UK, 2008; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante, M.M.C.; Martinelli, L.A.; Pérez, T.; Rasse, R.; Ometto, J.P.; Pacheco, F.S.; Lins, S.R.M.; Marquina, S. Nitrogen management challenges in major watersheds of South America. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gücker, B.; Silva, R.C.S.; Graeber, D.; Monteiro, J.A.F.; Brookshire, E.N.J.; Chaves, R.C.; Boëchat, I.G. Dissolved nutrient exports from natural and human-impacted Neotropical catchments. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, R. Chapter 2. Transformation and transport processes of nitrogen in agricultural systems. In Nitrogen in the Environment: Sources, Problems, and Management, 2nd ed.; Hatfield, J.L., Follett, R.F., Eds.; Academic Press/Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 19–50. [Google Scholar]
- Phalan, B.; Bertzky, M.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Donald, P.F.; Scharlemann, J.P.W.; Stattersfield, A.J.; Balmford, A. Crop expansion and conservation priorities in tropical countries. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurance, W.F.; Sayer, J.; Cassman, K.G. Agricultural expansion and its impacts on tropical nature. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W. Replication versus realism: The need for ecosystem-scale experiments. Ecosystems 1998, 1, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyenola, G.; Meerhoff, M.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; Graeber, D.; Fosalba, C.; Vidal, N.; Mazzeo, N.; Ovesen, N.B.; Jeppesen, E.; et al. Monitoring strategies of stream phosphorus under contrasting climate-driven flow regimes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4099–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graeber, D.; Goyenola, G.; Meerhoff, M.; Zwirnmann, E.; Ovesen, N.B.; Glendell, M.; Gelbrecht, J.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; Jeppesen, E.; et al. Interacting effects of climate and agriculture on fluvial DOM in temperate and subtropical catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blicher-Mathiesen, G.; Rasmussen, A.; Grant, R.; Jensen, P.G.; Hansen, B.; Thorling, L. Landovervågningsoplande 2012. NOVANA; Aarhus Universitet, DCE—Nationalt Center for Miljø og Energi, 2013; p. 154, Videnskabelig Rapport fra DCE—Nationalt Center for Miljø og Energi nr. 174; Available online: http://dce152.au.dk/pub/SR74.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Ciganda, V. Instituto Nacional de Investigación Agropecuaria, La Estanzuela; Personal Communication: Colonia, Uruguay, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.T.; Vivas, M.B. Landscape development intensity index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 101, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Dormann, C.F.; Prati, D.; Klaus, V.H.; Kleinebecker, T.; Hölzel, N.; Alt, F.; Boch, S.; Gockel, S.; Hemp, A.; et al. A quantitative index of land-use intensity in grasslands: Integrating mowing, grazing and fertilization. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2012, 13, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaby, M. Grasslands; Chelsea House: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Valderrama, J.C. The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Mar. Chem. 1981, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Weidemann, O. Die bestimmung des Nitrat-ions in wasser. Wasser 1955, 22, 247. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, M.I.C.; Ferreira, F.N.; de Oliveira, N.M.M.; Avila, A.K. Simplified version of the sodium salicylate method for analysis of nitrate in drinking waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 477, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO13395. Water Quality—Determination of Nitrite Nitrogen and Nitrate Nitrogen and the Sum of Both by Flow Analysis (CFA and FIA) and Spectrometric Detection. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=21870 (accessed on 26 April 2016).
- Zwirnmann, E.; Krüger, A.; Gelbrecht, J. Analytik im Zentralen Chemielabor des IGB, Berichte des IGB, Heft 9; Institut Für Gewa¨Ssero¨Kologie und Binnenfischerei: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Westerhoff, P. Dissolved organic nitrogen measurement using dialysis pretreatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graeber, D.; Gelbrecht, J.; Kronvang, B.; Gücker, B.; Pusch, M.T.; Zwirnmann, E. Technical Note: Comparison between a direct and the standard, indirect method for dissolved organic nitrogen determination in freshwater environments with high dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 4873–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, S.; Balz, A.; Abert, M.; Pronk, W. Characterisation of aquatic humic and non-humic matter with size-exclusion chromatography—Organic carbon detection—Organic nitrogen detection (LC-OCD-OND). Water Res. 2011, 45, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D.; Carliell-Marquet, C.; Ward, D. Changes in freshwater organic matter fluorescence intensity with freezing/ thawing and dehydration/rehydration. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114, G00F08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koroleff, F. Direct Determination of Ammonia in Natural Water as Indophenol-Blue; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1970; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Allen, P.M.; Muttiah, R.; Bernhardt, G. Automated base flow separation and recession analysis techniques. Ground Water 1995, 33, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronvang, B.; Bruhn, A.J. Choice of sampling strategy and estimation method for calculating nitrogen and phosphorus transport in small lowland streams. Hydrol. Process. 1996, 10, 1483–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.V.; Swaney, D.P.; Buddemeier, R.W.; Scarsbrook, M.R.; Weatherhead, M.A.; Humborg, C.; Eriksson, H.; Hannerz, F. River nutrient loads and catchment size. Biogeochemistry 2005, 75, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.S.; Horsburgh, J.S.; Mesner, N.O.; Ryel, R.J.; Stevens, D.K. Influence of sampling frequency on estimation of annual total phosphorus and total suspended solids loads. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2012, 48, 1258–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferroni, C.E. Teoria statistica delle classi e calcolo delle probabilità. Pubbl. Ist. Super. Sci. Econ. Commer. Firenze 1936, 8, 3–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.; Ruedy, R.; Sato, M.; Lo, K. Global surface temperature change. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GISTEMP Team. GISS Surface Temperature Analysis (GISTEMP). Available online: http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/ (accessed on 16 May 2016).
- DMI. Decadal Mean Weather. Available online: http://www.dmi.dk/en/vejr/arkiver/decadal-mean-weather/ (accessed on 26 April 2016).
- INUMET. Cilimatological Statistics. Available online: http://www.meteorologia.com.uy/ServCli/caracteristicasClimaticas (accessed on 26 April 2016).
- DMI. Denmark’s Future Climate. Available online: https://www.dmi.dk/en/klima/fremtidens-klima/danmark-og-groenland/ (accessed on 4 November 2016).
- Kronvang, B.; Windolf, J.; Larsen, S.E.; Bøgestrand, J. Background concentrations and loadings of nitrogen in Danish surface waters. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant 2015, 65, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; Dalgaard, T.; Thorling, L.; Sørensen, B.; Erlandsen, M. Regional analysis of groundwater nitrate concentrations and trends in Denmark in regard to agricultural influence. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 3277–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLauchlan, K. The nature and longevity of agricultural impacts on soil carbon and nutrients: A review. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 1364–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesoriero, A.J.; Duff, J.H.; Saad, D.A.; Spahr, N.E.; Wolock, D.M. Vulnerability of streams to legacy nitrate sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3623–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.; Laubel, A.; Kronvang, B.; Andersen, H.E.; Svendsen, L.M.; Fuglsang, A. Loss of dissolved and particulate phosphorus from arable catchments by subsurface drainage. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2633–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.E.; Windolf, J.; Kronvang, B. Leaching of dissolved phosphorus from tile-drained agricultural areas. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoumans, O.F.; Chardon, W.J.; Bechmann, M.E.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Hofman, G.; Kronvang, B.; Rubæk, G.H.; Ulén, B.; Dorioz, J.M. Mitigation options to reduce phosphorus losses from the agricultural sector and improve surface water quality: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windolf, J.; Thodsen, H.; Troldborg, L.; Larsen, S.E.; Bøgestrand, J.; Ovesen, N.B.; Kronvang, B. A distributed modelling system for simulation of monthly runoff and nitrogen sources, loads and sinks for ungauged catchments in Denmark. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 2645–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. World Fertilizer Trends and Outlook to 2018; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CDKN. The IPCC’s Fifth Assessment Report What’s in it for Latin America? Executive Summary. Available online: https://cdkn.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/IPCC-AR5-Whats-in-it-for-Latin-America.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Madsen, H.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Steen-Mikkelsen, P. Update of regional intensity–duration–frequency curves in Denmark: Tendency towards increased storm intensities. Atmos. Res. 2009, 92, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.; Rusticucci, M.; Penalba, O.; Renom, M.; Laborbe, R. An intercomparison of observed and simulated extreme rainfall and temperature events during the last half of the twentieth century: Part 2: Historical trends. Clim. Chang. 2010, 98, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olesen, J.E.; Carter, T.R.; Díaz-Ambrona, C.H.; Fronzek, S.; Heidmann, T.; Hickler, T.; Holt, T.; Minguez, M.I.; Morales, P.; Palutikof, J.P.; et al. Uncertainties in projected impacts of climate change on European agriculture and terrestrial ecosystems based on scenarios from regional climate models. Clim. Chang. 2007, 81, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.E.; Kronvang, B.; Larsen, S.E.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Jensen, T.S.; Rasmussen, E.K. Climate-change impacts on hydrology and nutrients in a Danish lowland river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 365, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Kronvang, B.; Olesen, J.; Audet, J.; Søndergaard, M.; Hoffmann, C.; Andersen, H.; Lauridsen, T.; Liboriussen, L.; Larsen, S.; et al. Climate change effects on nitrogen loading from cultivated catchments in Europe: Implications for nitrogen retention, ecological state of lakes and adaptation. Hydrobiologia 2011, 663, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
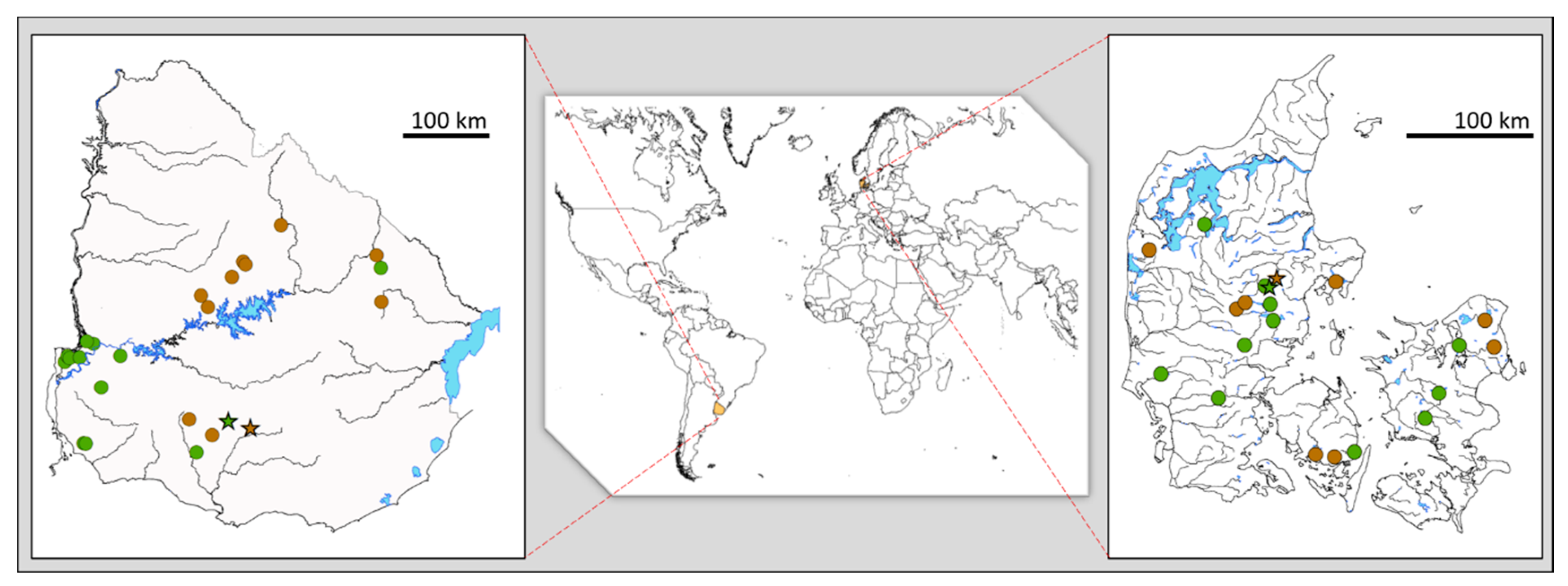
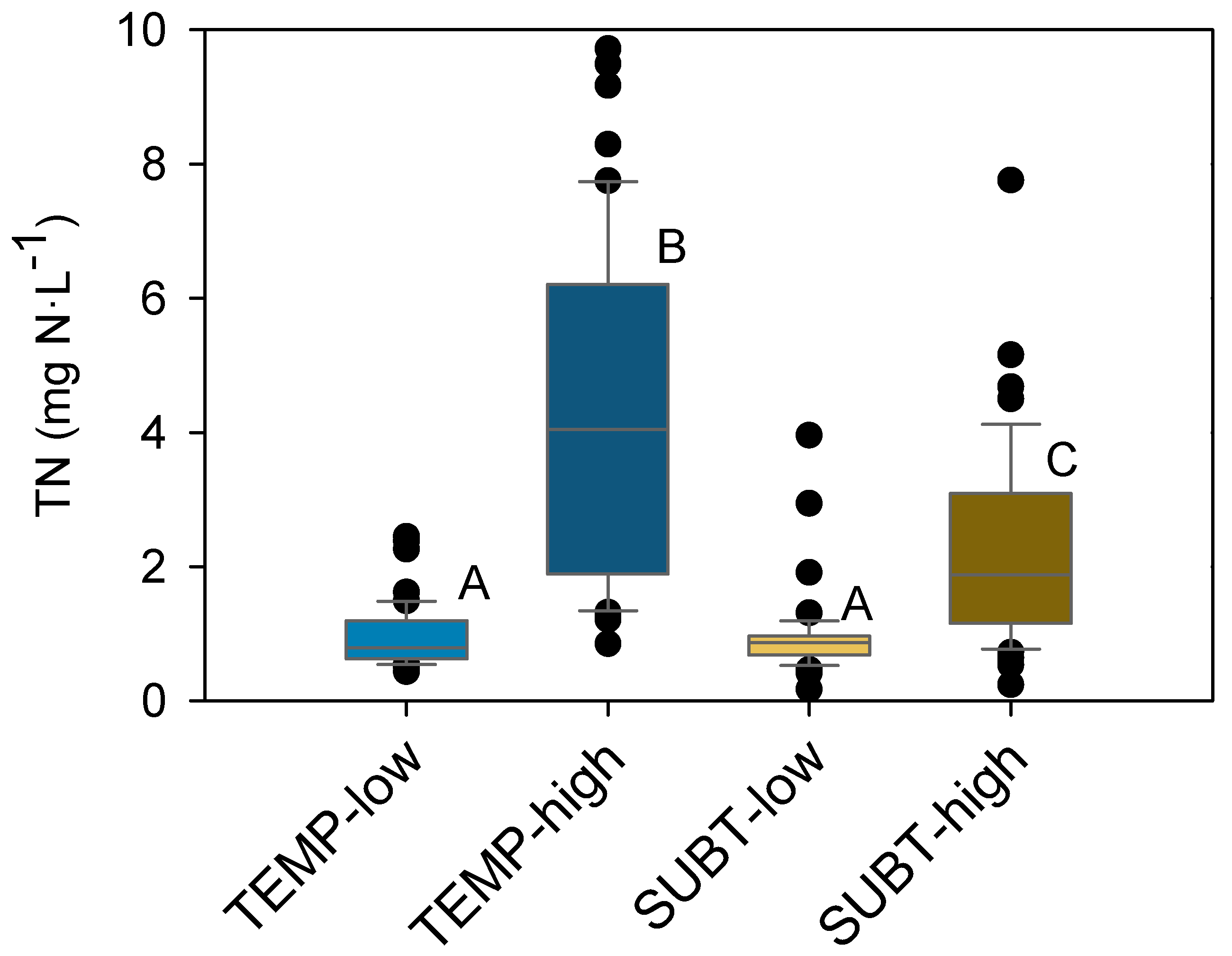
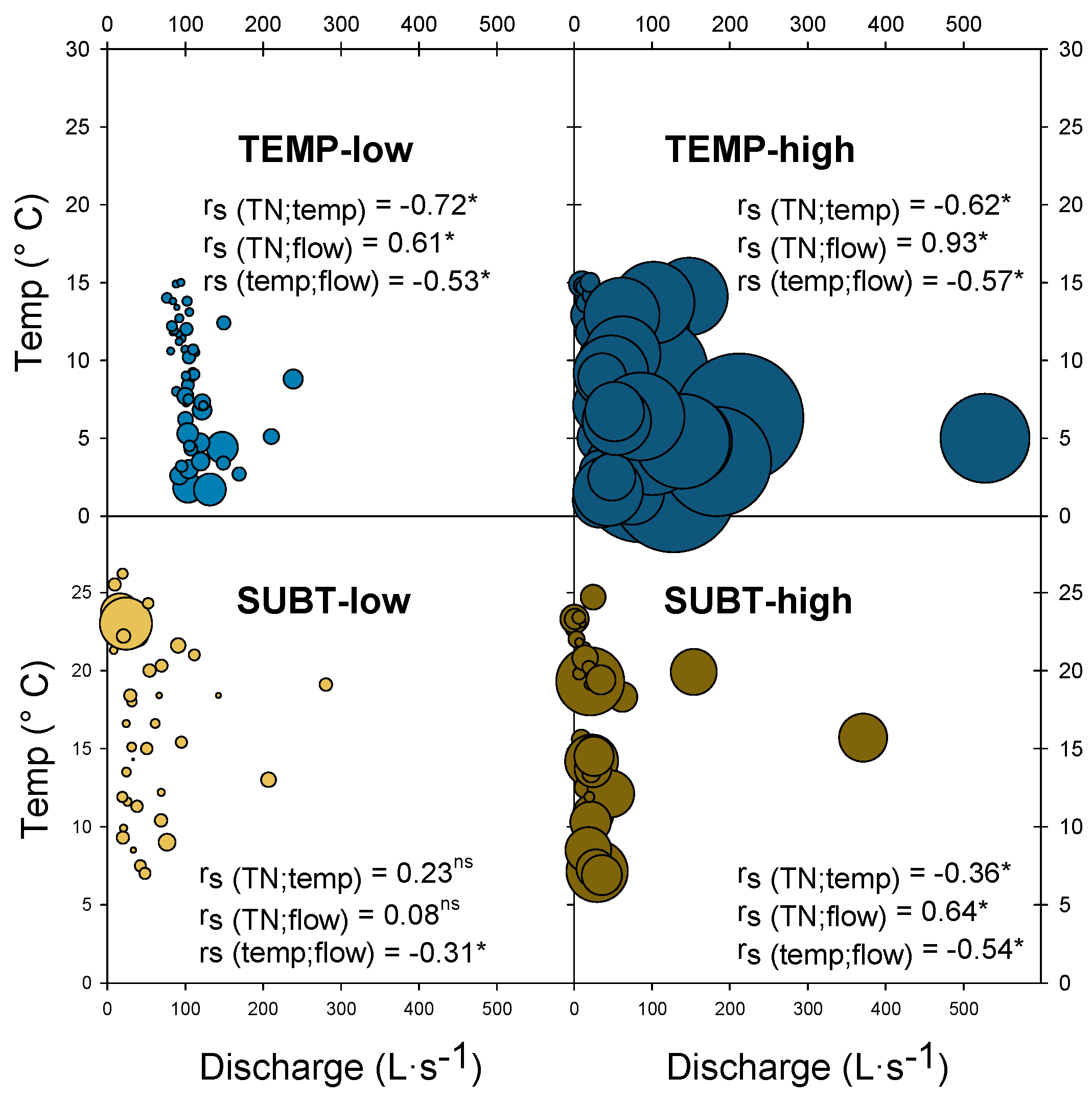

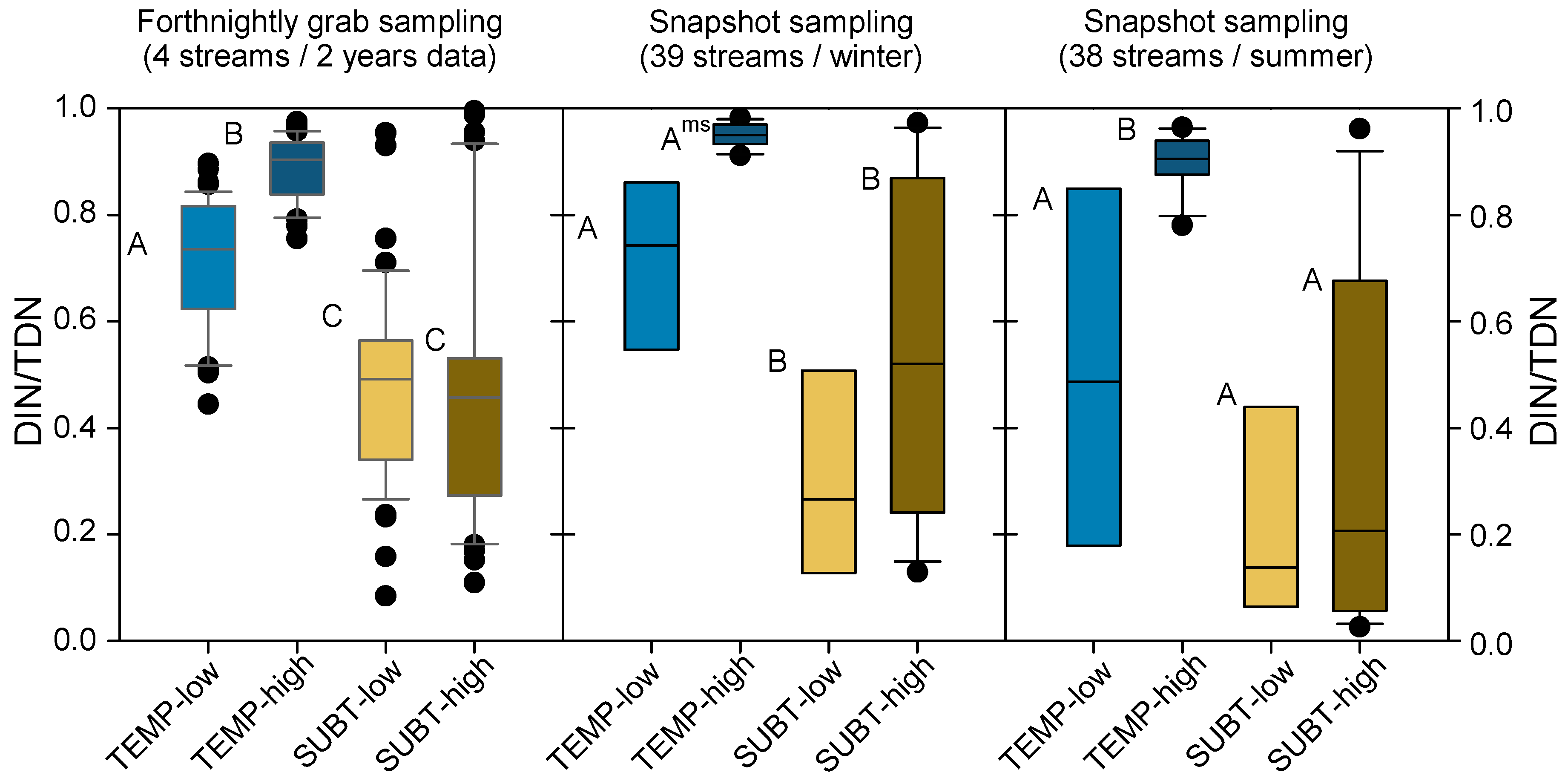
| Climate & Farming Intensity | Benchmark Streams | Snapshot Grab-Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| TEMP Low | Granslev stream Haplic Luvisols # O.M. = 5% F.A.= 29%; mean L.U. = 0.25 ha−1 N fertilizer = 45 kg N·ha−1·year−1 (45 % fertilizers; 55% manure) | Mainly Luvisols and Podsols; Arenosols # O.M. < 5%. Range F.A. = 0%–26% |
| TEMP High | Gelbæk stream Gleyic Luvisols # O.M. < 5% F.A.= 92%; mean L.U. = 0.79 ha−1 N fertilizer = 143 kg N·ha−1·year−1 (45 % fertilizers; 55% manure) | Mainly Luvisols and Podsols, some Albeluvisols Arenosols and Cambisols # O.M. < 5%. Range F.A. = 74%–93% |
| SUBT Low | Chal-Chal stream Luvic Phaeozem and Eutric Vertisols * O.M. = 5.2% F.A.= 30%; mean L.U. = 0.62 ha−1 N fertilizer = 76 kg N·ha−1·year−1 (18% fertilizers; 82% manure) | Phaeozem and Vertisols * O.M. = 5% ± 1.5 Range F.A. = 0%–25% |
| SUBT High | Pintado Stream Eutric Regosols * O.M. = 4% to 5% F.A.= 90%; mean L.U. = 2.00 ha−1 N fertilizer = 242 kg N·ha−1·year−1 (17% fertilizers; 83% manure) | Mainly Phaeozem * O.M. = 5% ± 1.5 Range F.A. = 75%–100% |
| Total n | nstreams = 4 | nstreams = 39 (w), 38 (s) |
| Sampling | grab and pooled sampling 2 years | 1 sample in (w) and 1 in (s) |
| Characteristic | TEMP Low | TEMP High | SUBT Low | SUBT High |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accumulated rainfall of each study year (mm·y−1) | 756–770 | 766–778 | 1010–1030 | 1196–1405 |
| Mean regional accumulated rainfall (mm·y−1) | 765 a | 1100–1200 b | ||
| Base Flow Index (BFI) | 0.88 | 0.64 | 0.39 | 0.29 |
| Region | Year | Low-Farming Intensity | High-Farming Intensity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN Loss | FWC TN | TN Loss | FWC TN | ||
| SUBT | 1 | 1.39 | 0.82 | 4.67 | 1.99 |
| SUBT | 2 | 2.12 | 0.72 | 9.17 | 2.13 |
| TEMP | 1 | 6.11 | 1.2 | 13.16 | 6.28 |
| TEMP | 2 | 4.68 | 0.98 | 12.65 | 6.23 |
| N Form | Benchmark Streams | Snapshot Sampling | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fortnightly Sampling | Winter | Summer | |
| Comparison between Climate/Hydrology Conditions (TEMP vs. SUBT) | |||
| TDN | F(1, 181) = 38.16 *** | F(1, 35) = 29.97 *** | F(1, 34) = 19.60 *** |
| NO3− | F(1, 186) = 78.25 *** | F(1, 35) = 29.99 *** | F(1, 34) = 30.58 *** |
| DON | F(1, 181) = 27.27 *** | F(1, 35) = 1.44, p = 0.24 ns | F(1, 34) = 4.90 * |
| NH4+ | F(1, 186) = 0.19, p = 0.66 ns | F(1 35) = 7.72 ** | F(1, 34) = 2.31, p = 0.14 ns |
| DIN/TDN | F(1, 181) = 179.67 *** | F(1, 35) = 30.06 *** | F(1, 34) = 23.67 *** |
| Comparison between Farming Intensity Conditions (Low & High) Nested in Climate/Hydrology | |||
| TDN | F(2, 181) = 71.85 *** | F(2, 35) = 30.30 *** | F(2, 34) = 20.78 *** |
| NO3− | F(2, 186) = 80.12 *** | F(2, 35) = 28.48 *** | F(2, 34) = 20.49 *** |
| DON | F(2, 181) = 24.42 *** | F(2, 35) = 0.232, p = 0.79 ns | F(2, 34) = 1.19, p = 0.31 ns |
| NH4+ | F(2, 186) = 10.05 *** | F(2, 35) = 2.75, p = 0.08 ms | F(2, 34) = 3.09, p = 0.08 ms |
| DIN/TDN | F(2, 181) = 14.67 *** | F(2, 35) = 6.26 ** | F(2, 34) = 5.50** |
| Interaction between Farming Intensity and Climate/Hydrology | |||
| TDN | F(1, 181) = 307.1 *** | F(1, 35) = 85.0 *** | F(1, 34) = 116.4 *** |
| NO3- | F(1, 186) = 193.6 *** | F(1, 35) = 57.5 *** | F(1, 34) = 52.33 *** |
| DON | F(1, 181) = 255.1 *** | F(1 35) = 103.0 *** | F(1, 34) = 59.9 *** |
| NH4+ | F(1, 186) = 140.3 *** | F(1, 35) = 106.0 *** | F(1, 34) = 21.6 *** |
| DIN/TDN | F(1, 181) = 2744.1 *** | F(1, 35) = 299.3 *** | F(1, 34) = 132.9*** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goyenola, G.; Graeber, D.; Meerhoff, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Vidal, N.; Fosalba, C.; Ovesen, N.B.; Gelbrecht, J.; Mazzeo, N.; et al. Influence of Farming Intensity and Climate on Lowland Stream Nitrogen. Water 2020, 12, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041021
Goyenola G, Graeber D, Meerhoff M, Jeppesen E, Teixeira-de Mello F, Vidal N, Fosalba C, Ovesen NB, Gelbrecht J, Mazzeo N, et al. Influence of Farming Intensity and Climate on Lowland Stream Nitrogen. Water. 2020; 12(4):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041021
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoyenola, Guillermo, Daniel Graeber, Mariana Meerhoff, Erik Jeppesen, Franco Teixeira-de Mello, Nicolás Vidal, Claudia Fosalba, Niels Bering Ovesen, Joerg Gelbrecht, Néstor Mazzeo, and et al. 2020. "Influence of Farming Intensity and Climate on Lowland Stream Nitrogen" Water 12, no. 4: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041021







