Influences of Land-Use Dynamics and Surface Water Systems Interactions on Water-Related Infectious Diseases—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Conceptual Linkages among Land Use, Water Quality, and WRID
2.1. LULC and Surface Water Quality
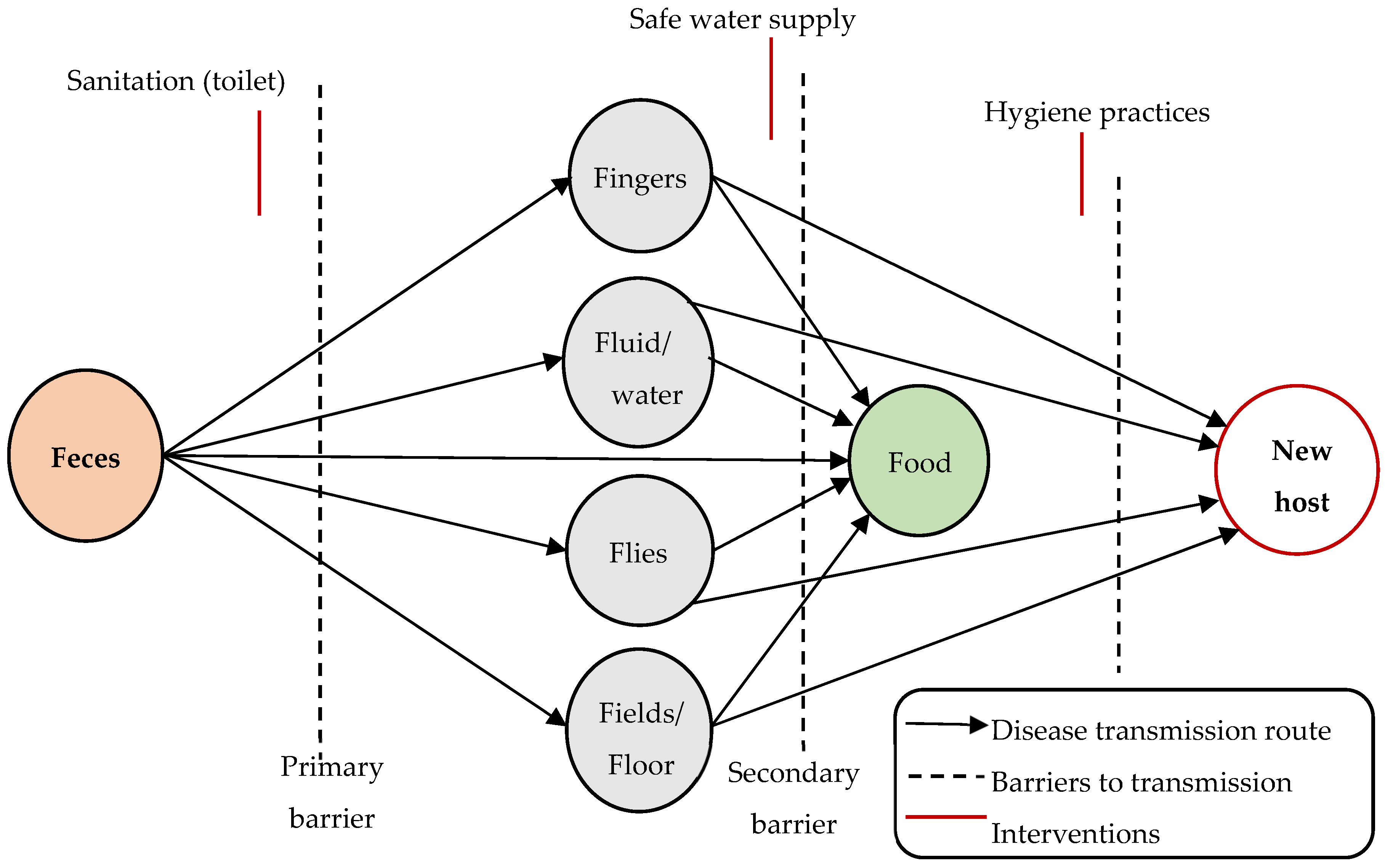
2.2. Water-Related Infectious Diseases (WRID)
2.3. Influences of Water Quality on WRID
3. Methodology
3.1. Identification of the Key Research Question
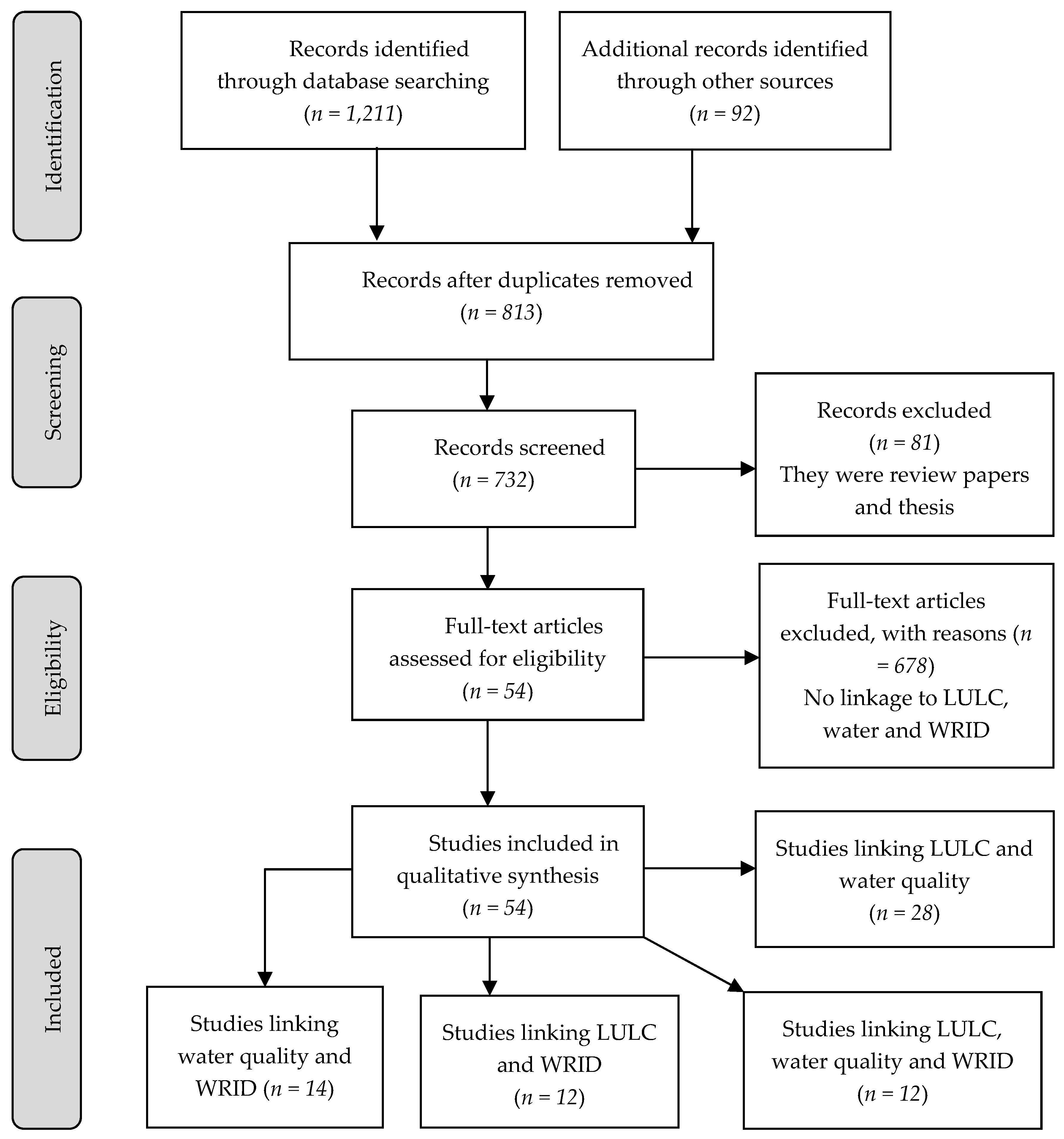
3.2. Identification of Relevant Articles
3.3. Selection of the Relevant Articles: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
3.4. Charting and Tabulating of Data
3.5. Reporting and Summarizing of the Results
4. Results
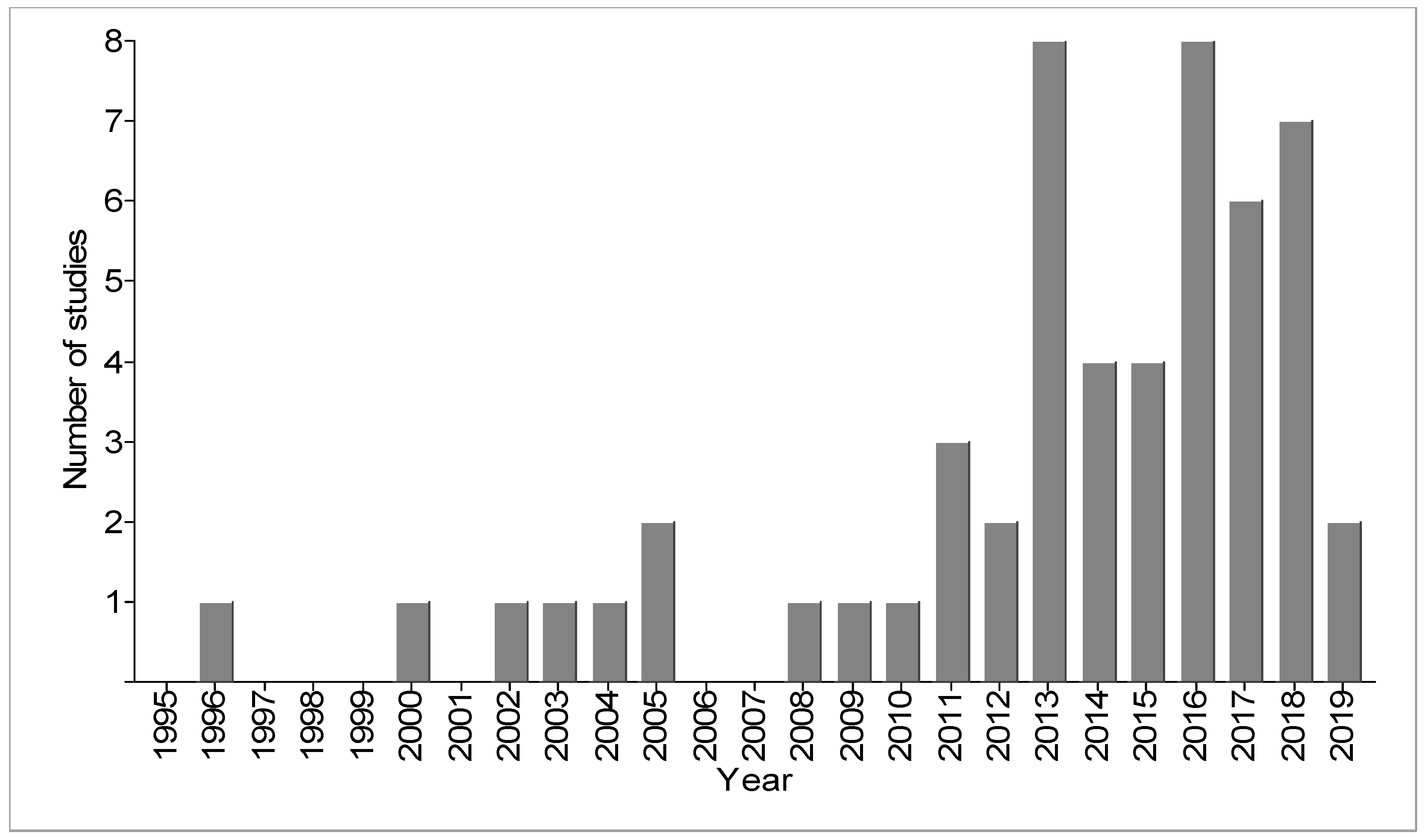
4.1. Trends in the Scientific Studies on LULC, Surface Water Quality, and WRID
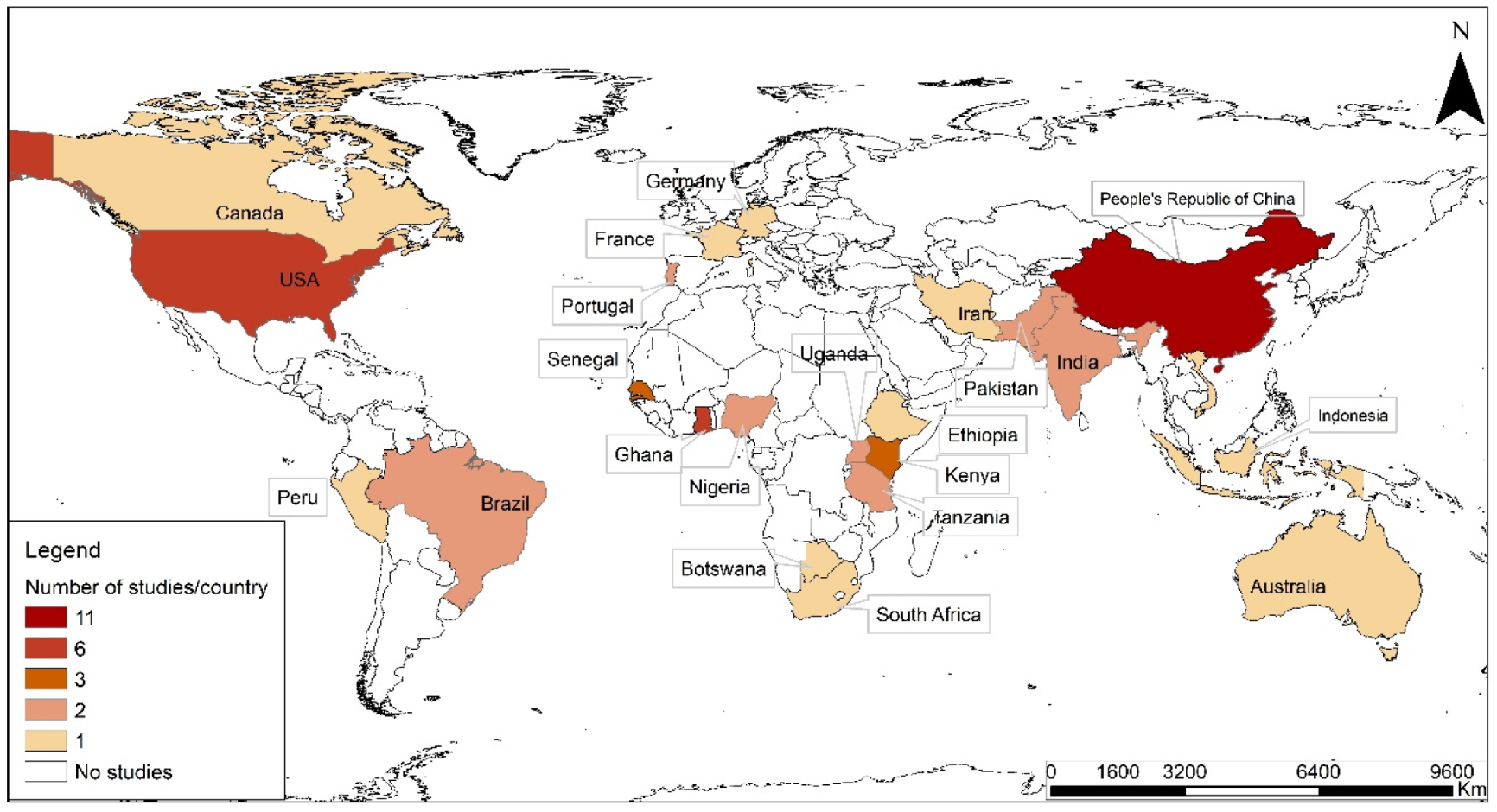
4.2. Distribution of studies by country/region
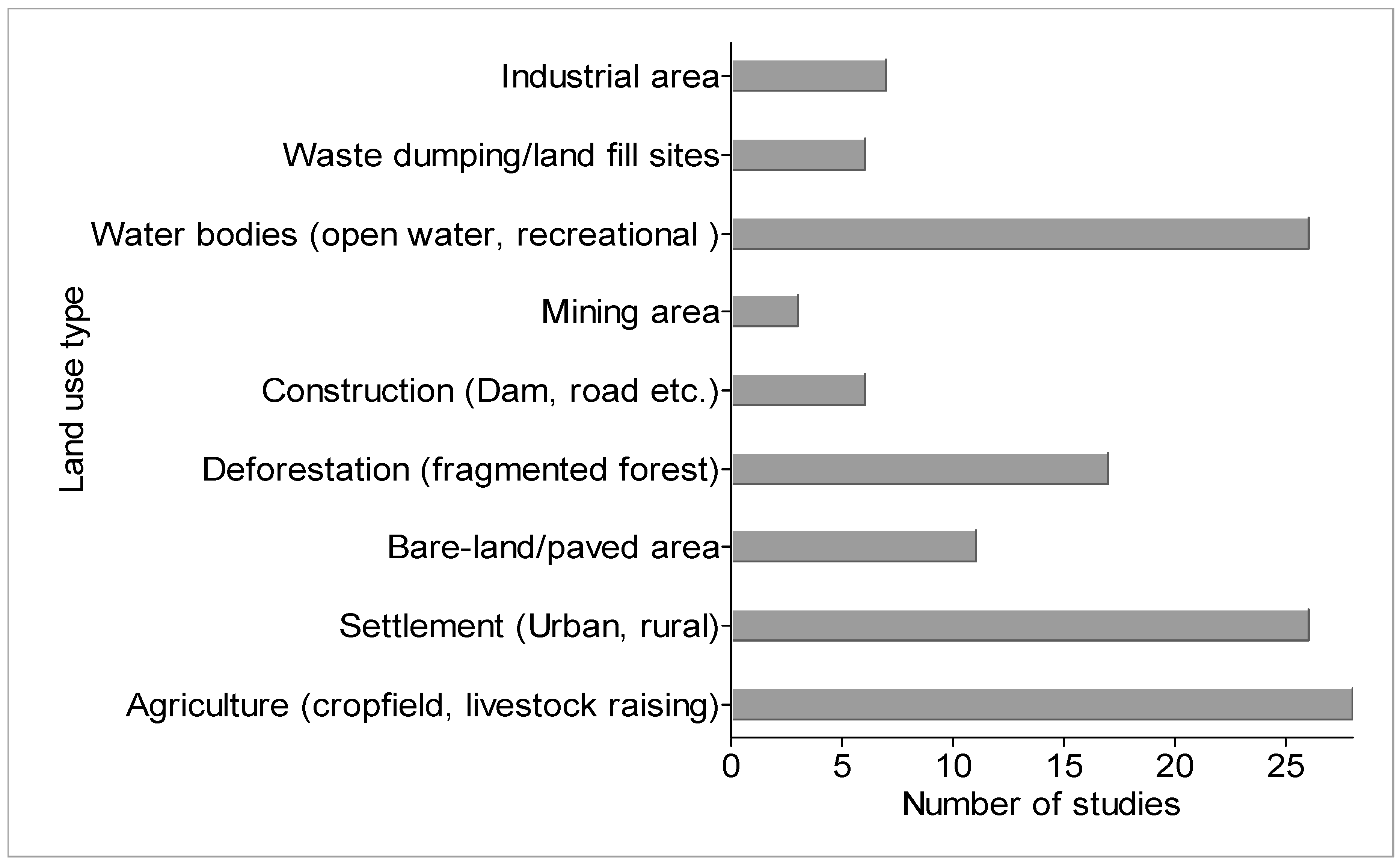
4.3. Land Use and Land Cover Classification
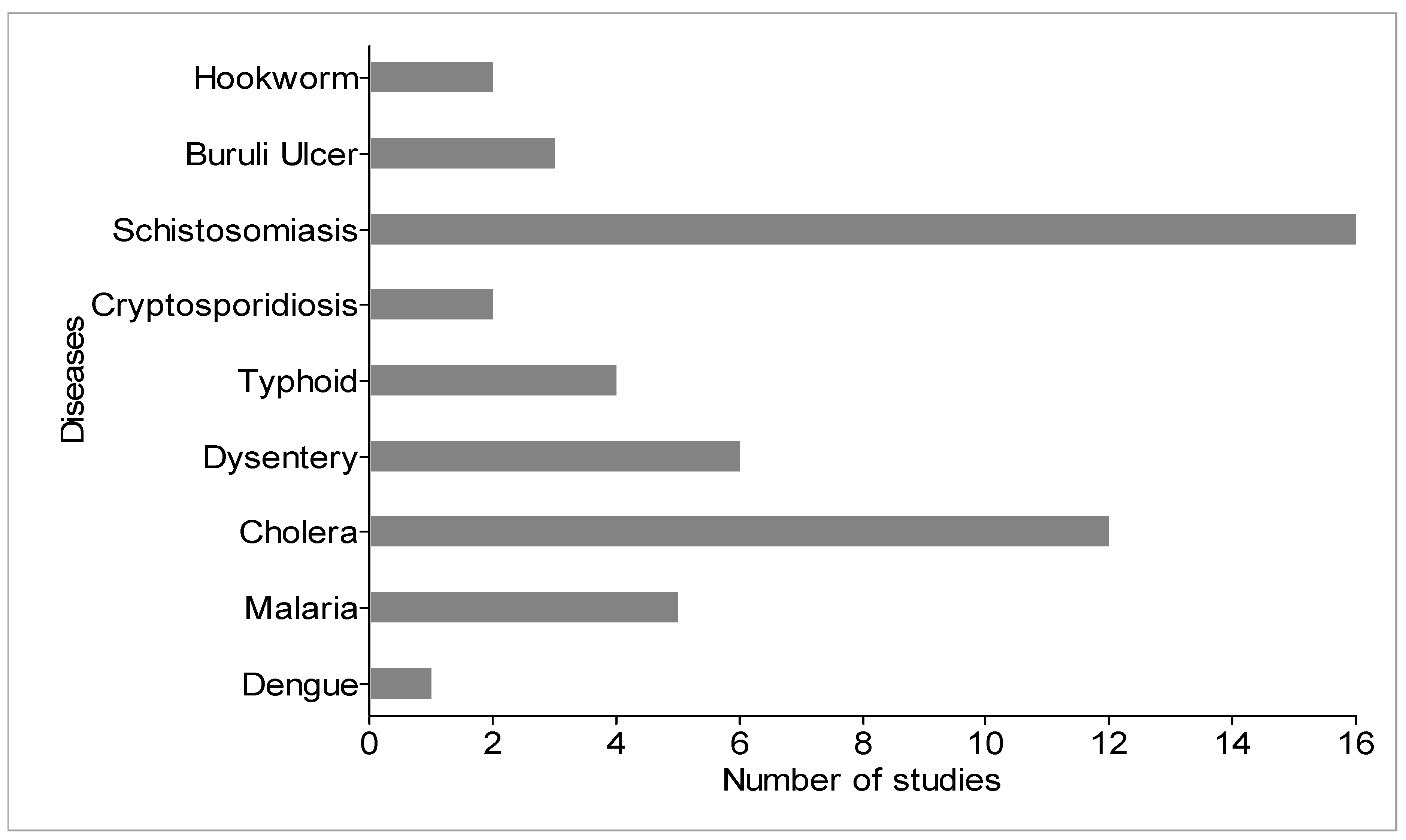
4.4. Identified Water-Related Infectious Diseases
4.5. Land-Use Change and Surface Water Pollution Pathways
4.6. Water Quality Parameters and the Potential Water-Related Infectious Diseases
4.7. Studies Linking Land Use, Water, and Major WRID
5. Discussion
5.1. Influences of Water Quality on WRID
5.2. Directions for Further Research
5.3. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adedire, F.M. Differentials in Metropolitanisation Trends in Lagos Peri-Urban Settlements. J. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Briassoulis, H. Analysis of Land Use Change: Theoretical and Modeling Approaches; Chapter on; Regional Research Institute, West Virginia University: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dwarakish, G.S.; Ganasri, B.P.; De Stefano, L. Impact of land use change on hydrological systems: A review of current modeling approaches. Gis Appl. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. Ed. Aquat. Procedia Ms. B.P. Dwarakish Ganasri Cogent Geosci. 2015, 1, 1115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpa, D.; Nunes, J.P.; Keizer, J.J.; Abrantes, N. Impacts of climate and land use changes on the water quality of a small Mediterranean catchment with intensive viticulture. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Hoven, C.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E.; van der Merwe, B.; Loubser, M.; Abia, A.L.K. The impact of various land uses on the microbial and physicochemical quality of surface water bodies in developing countries: Prioritisation of water resources management areas. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 8, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.; Mahoney, C.; Mcclelland, C.; Myers, A. The Effect of Land Use and Land Cover on Water Quality in Urban Environments, Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences; Kansas State University: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.O. Land use/land cover water quality nexus: Quantifying anthropogenic influences on surface water quality. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Hutchins, M. The impacts of urbanisation and climate change on urban flooding and urban water quality: A review of the evidence concerning the United Kingdom. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 12, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, J.; Inkoom, J.N.; Thiel, M.; Shankar, S.; Lautenbach, S.; Fürst, C. Peri-urban land use pattern and its relation to land use planning in Ghana, West Africa. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 165, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations; Department of Economic and Social Affairs; Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-92-1-148319-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gerten, C.; Fina, S.; Rusche, K. The Sprawling Planet: Simplifying the Measurement of Global Urbanization Trends. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T.; von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. Global Water Pollution and Human Health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monney, I. Urbanization and Pollution of Surface Water Resources in the Two Largest Cities in Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Monit. Anal. 2013, 1, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, L.C.; Siri, J.G.; Chakravarty, I.; Arsénio, A.M.; Biswas, R.; Chatterjee, A. Improving health in cities through systems approaches for urban water management. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2016, 15, S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamba, F.; Sangija, F.; Wei, S. Impact of water pollution on human health in the Central African Republic. Adv. Soc. Sci. Res. J. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Shafique, I. Perception of household in regards to water pollution: An empirical evidence from Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8543–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Water. Towards a Worldwide Assessment of Freshwater Quality: A UN-Water Analytical Brief; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mackinnon, E.; Ayah, R.; Taylor, R.; Owor, M.; Ssempebwa, J.; Olago, L.D.; Kubalako, R.; Dia, A.T.; Gaye, C.C.; Campos, L.; et al. 21st century research in urban WASH and health in sub-Saharan Africa: Methods and outcomes in transition. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, L.; Casagrandi, R.; Rinaldo, A.; Gatto, M. Epidemicity thresholds for water-borne and water-related diseases. J. Biol. 2018, 447, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastel, M.; Bussalleu, A.; Paz-Soldan, V.A.; Salmon-Mulanovixh, G.; Valdes-Vaelasquez, A.; Hartinger, S.M. Critical linkages between land use change and human health in the Amazon region: A scoping review. PLoS Negl. TROP. Dis. 2018, 13, e0196414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalande, N.; Cernesson, F.; Decherf, A.; Tournoud, M.G. Implementing the DPSIR framework to link water quality of rivers to land use: Methodological issues and preliminary field test. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rain, D.; Engstrom, R.; Ludlow, C.; Antos, S. Accra Ghana: A City Vulnerable to Flooding and Drought-Induced Migration. Case study prepared for Cities and Climate Change: Global Report on Human Settlements, 2011. Available online: http://www.unhabitat.org/grhs/2011 (accessed on 26 February 2020).
- Hwang, S.-A.; Hwang, S.-J.; Park, S.-R.; Lee, S.-W. Examining the Relationships between Watershed Urban Land Use and Stream Water Quality Using Linear and Generalized Additive Models. Water 2016, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, H. Land use planning and health and well-being. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry-Shields, J.; Bartram, J. Human health and the water environment: Using the DPSEEA framework to identify the driving forces of disease. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deilami, K.; Hayes, J.F.; McGree, J.; Goonetilleke, A. Application of landscape epidemiology to assess potential public health risk due to poor sanitation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kulinkina, V.A.; Shinee, E.; Rafael, B.; Herrador, G.; Nygård, K.; Schmoll, O. The situation of water-related infectious diseases in the pan-European region; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; p. 42. ISBN 9 789289 052023. [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for drinking water quality. In Managing Chemical Hazards in Drinking-Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 145–196.
- White, G.; Bradley, D.; White, A. Reproduced by permission of The University of Chicago Press, # 1972. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 80, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kulinkina, V.A.; Mohan, V.R.; Francis, M.R.; Kattula, D.; Sarkar, R.; Plummer, J.D.; Ward, H.; Kang, G.; Balraj, V.; Naumova, E.N. Seasonality of water quality and diarrheal disease counts in urban and rural settings in south India. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.; Kolotelo, P.; Schang, C.; Osborne, C.A.; Coleman, R.; Deletic, A.; Mccarthy, D.T. Escherichia coli concentrations and loads in an urbanised catchment: The Yarra River, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2013, 497, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gara, T.; Fengting, L.; Nhapi, I.; Makate, C.; Gumindoga, W. Health Safety of Drinking Water Supplied in Africa: A Closer Look Using Applicable Water-Quality Standards as a Measure. Expo. Health 2017, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Ganguli, B.; Sen Roy, S.; Halder, B.; Banerjee, N.; Banerjee, M.; Samanta, M.; Giri, A.K.; Polya, D.A. Diarrhoeal health risks attributable to water-borne-pathogens in arsenic-mitigated drinking water in west Bengal are largely independent of the microbiological quality of the supplied water. Water 2014, 6, 1100–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyarko, R.; Torpey, K.; Ankomah, A. Schistosoma haematobium, Plasmodium falciparum infection and anaemia in children in Accra, Ghana. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previsich, N.; Narayanan, A.; Fleury, M.D. One Health, Climate Change and Water Related Issues: A Canadian Public Health Perspective, Global Bioethics. Taylor Fr. Group 2017, 7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clasen, T.; Pruss-ustun, A.; Mathers, C.D.; Cumming, O.; Cairncross, S.; John, M. Estimating the impact of unsafe water, sanitation and hygiene on the global burden of disease: Evolving and alternative methods. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholera. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cholera (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Wagner, E.G.; Lanoix, J.N. Excreta Disposal for Rural Areas and Small Communities; World Organization Monograph series; no. 39; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1958; p. 187. [Google Scholar]
- Falkenberg, T.; Saxena, D.; Kistemann, T. Impact of Wastewater-Irrigation on In-Household Water Contamination. A Cohort Study Among Urban Farmers in Ahmedabad, India Science of the Total Environment. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.117 (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Water1st International F-Diagram. Available online: http://water1st.org/problem/f-diagram/ (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Forstinus, N.O.; Ikechukwu, N.E.; Emenike, M.P.; Christiana, A.O. Water and Waterborne Diseases: A Review. Int. J. Trop. Dis. Health 2016, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonj, C.; Diekkrüger, B.; Borgemeister, C. Thomas Kistemann Health risk perceptions and local knowledge of water-related infectious disease exposure among Kenyan wetland communities. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soller, J.A.; Schoen, M.E.; Varghese, A.; Ichida, A.M.; Boehm, A.B.; Eftim, S.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Ravenscroft, J.E. Human health risk implications of multiple sources of faecal indicator bacteria in a recreational waterbody. Water Res. 2014, 66, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, B.; Nafees, M.; Baig, S.A. Assessment of Drinking Water Quality and Water Born Diseases in Post Flood Scenario in District Swat, Pakistan Sustainable Water Sanitation Health and Development Program; World Health Organization (WHO): Abbottabad, Pakistan, 2016; Volume 34, pp. 1238–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Vrebos, D.; Beauchard, O.; Meire, P. Science of the Total Environment The impact of land use and spatial mediated processes on the water quality in a river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näschen, K.; Diekkrüger, B.; Leemhuis, C.; Steinbach, S.; Seregina, L.S.; Thonfeld, F.; van der Linden, R. Hydrological modeling in data-scarce catchments: The Kilombero floodplain in Tanzania. Water 2018, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.; Byrne, J. The benefits of publishing systematic quantitative literature reviews for PhD candidates and other early-career researchers. Sage 2014, 33, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottdenker, N.L.; Streicker, D.G.; Faust, C.L.; Carroll, C.R. Anthropogenic Land Use Change and Infectious Diseases: A Review of the Evidence. EcoHealth 2014, 11, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework Scoping Studies: Towards a Methodological Framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.A.; Gundry, S.; Wright, J.; Conroy, R. A systematic review of the health outcomes related to household water quality in developing countries household water quality in developing countries. J. Water Health 2004, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Zhou, X.; Guo, M.; Wu, W. Land use change and its effects on water quality in typical inland lake of arid area in China. J. Environ. Biol. 2016, 37, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wijesiri, B.; Deilami, K.; Goonetilleke, A. Evaluating the relationship between temporal changes in land use and resulting water quality. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribolzi, O.; Cuny, J.; Sengsoulichanh, P.; Mousquès, C.; Soulileuth, B.; Pierret, A.; Huon, S.; Sengtaheuanghoung, O. Land use and water quality along a mekong tributary in Northern Lao P.D.R. Environ. Manag. 2011, 47, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, L. Influence of spatial variation in land-use patterns and topography on water quality of the rivers inflowing to Fuxian Lake, a large deep lake in the plateau of southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Tran, A.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Linard, C.; Soti, V. Pathogenic landscapes: Interactions between land, people, disease vectors, and their animal hosts. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2010, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, V.S. Urbanizing diseases: Contested institutional terrain of water- and vector-borne diseases in Ahmedabad, India. Water Int. 2013, 38, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, J.A.; Daszak, P.; Tabor, G.M.; Aguirre, A.A.; Pearl, M.; Epstein, J.; Wolfe, N.D.; Kilpatrick, A.M.; Foufopoulos, J.; Molyneux, D.; et al. Unhealthy landscapes: Policy recommendations on land use change and infectious disease emergence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, B.M.; Reis, R.; Vale, M.J.; Saraiva, R. Land use and land cover changes in Zêzere watershed (Portugal)-Water quality implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Lu, Y.; Saeed, M.A.; Bilal, H.; Sher, H.; Khan, H.; Ali, J.; Wang, P.; Uwizeyimana, H.; Baninla, Y.; et al. Prevalent fecal contamination in drinking water resources and potential health risks in Swat, Pakistan. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntoke, O.; Aboderin, O.J.; Bankole, A.M. Association of water-borne diseases morbidity pattern and water quality in parts of Ibadan City, Nigeria. Tanzan. J. Health Res. 2009, 11, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ohene-Adjei, K.; Kenu, E.; Bandoh, D.A.; Addo, P.N.O.; Noora, C.L.; Nortey, P.; Afari, E.A. Epidemiological link of a major cholera outbreak in Greater Accra region of Ghana, 2014. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarcoo, G.; Hodgson, I.O.A.; Ampofo, J.A.; Cobbina, S.J.; Koku, J.E. Assessment of quality of drinking water in Amasaman, Accra (Ghana). J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 19, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, J.P.; Gower, C.M.; Knowles, S.C.L.; Molyneux, D.H.; Fenton, A. One health-an ecological and evolutionary framework for tackling Neglected Zoonotic Diseases. Evol. Appl. 2016, 9, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, J.E.T.; Tadesse, G.; Mekete, K.; Wuletaw, Y.; Gebretsadik, A.; French, M.D.; Harrison, W.E.; Drake, L.J.; Gardiner, I.A.; Yard, E.; et al. School Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene, Soil-Transmitted Helminths, and Schistosomes: National Mapping in Ethiopia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, J.S.; Mazumder, A. Influence of seasonal and inter-annual hydro- meteorological variability on surface water fecal coliform concentration under varying land-use composition. Water Res. 2013, 48, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, N.B.; Foster, D.; Groffman, P.; Grove, J.M.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Pataki, D.E.; Peters, D.P.C. The changing landscape: Ecosystem responses to urbanization and pollution across climatic and societal gradients. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Liu, K.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.X. Relationship of land use/cover on water quality in the Liao River basin, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistemann, T.; Rind, E.; Koch, C.; Claßen, T.; Lengen, C.; Exner, M.; Rechenburg, A. Effect of sewage treatment plants and diffuse pollution on the occurrence of protozoal parasites in the course of a small river. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, N.T.; Hoover, C.M.; Arakala, A.; Civitello, D.J.; De Leo, G.A.; Gambhir, M.; Johnson, S.A.; Jouanard, N.; Loerns, K.A.; McMahon, T.A.; et al. Agrochemicals increase risk of human schistosomiasis by supporting higher densities of intermediate hosts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attua, E.M.; Ayamga, J.; Pabi, O. International Journal of River Basin Management Relating land use and land cover to surface water quality in the Densu River basin, Ghana Relating land use and land cover to surface water quality in the Densu River basin. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglanu, L.M.; Appiah, D.O. The Korle Lagoon in Distress: The Stress of Urban Solid Waste on Water Bodies in Accra, Ghana. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. Issn 2014, 7, 2028–9324. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, M. Science of the Total Environment Impacts of land use and population density on seasonal surface water quality using a modi fi ed geographically weighted regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindblade, K.A.; Walker, E.D.; Onapa, A.W.; Katungu, J.; Wilson, M.L. Land use change alters malaria transmission parameters by modifying temperature in a highland area of Uganda. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2000, 5, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyona, D.N.; Matano, A.; Abuom, P.O.; Adoka, S.O.; Ouma, C.; Kanangire, C.K.; Owuor, P.O.; Ofulla, A.V.O. Distribution and abundance of schistosomiasis and fascioliasis host snails along the Mara River in Kenya and Tanzania. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2014, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Head, J.R.; Chang, H.; Li, Q.; Hoover, C.M.; Wilke, T.; Clewing, C.; Carlton, E.J.; Liang, S.; Lu, D.; Zhong, B.; et al. Genetic Evidence of Contemporary Dispersal of the Intermediate Snail Host of Schistosoma japonicum: Movement of an NTD Host Is Facilitated by Land Use and Landscape Connectivity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Shuai, J.; Tao, F.; Shi, P. River discharge, land use change, and surface water quality in the Xiangjiang River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4130–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvani, J.; Boustani, F.; Tabiee, O.; Hashemi, M. The effects of human activity in yasuj area on the health of stream city. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 50, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, P.; Henry, A.; Meheut, G.; Charni-ben-tabassi, N.; Ingrand, V.; Helmi, K. Health Risk Assessment Related to Waterborne Pathogens from the River to the Tap. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 2967–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.G.F.; Sabogal-Paz, L.P.; Dodds, W.K. Land use influence on raw surface water quality and treatment costs for drinking supply in São Paulo State (Brazil). Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciddio, M.; Mari, L.; Sokolow, S.H.; De Leo, G.A.; Casagrandi, R.; Gatto, M. The spatial spread of schistosomiasis: A multidimensional network model applied to Saint-Louis region, Senegal. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 108, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codjoe, S.N.A.; Larbi, R.T. Climate change/variability and schistosomiasis transmission in Ga district, Ghana. Clim. Dev. 2016, 8, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picquet, M.; Ernould, J.C.; Vercruysse, J.; Southgate, V.R.; Mbaye, A.; Sambou, B.; Niang, M.; Rollinson, D. The epidemiology of human schistosomiasis in the Senegal River basin. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 90, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.P.; Johansen, M.V.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wang, F.F.; Wu, W.D.; Zhang, G.H.; Pan, X.P.; Yang, J.; Ørnbjerg, N. Transmission of Schistosoma japonicum by humans and domestic animals in the Yangtze River valley, Anhui province, China. Acta Trop. 2005, 96, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.S. Ecological Systems and Complexity Theory: Toward an Alternative Model of Accountability in Education. Complicity Int. J. Complex. Educ. 2008, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, K.A.; Heaney, A.K.; Shaman, J. Hydrometeorology and flood pulse dynamics drive diarrheal disease outbreaks and increase vulnerability to climate change in surface-water-dependent populations: A retrospective analysis. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A. GIS and Remote Sensing for Malaria Risk Mapping, Ethiopia. Isprs Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh-quarcoo, P.B.; Attah, S.K.; Donkor, E.S.; Nyako, M.; Minamor, A.A.; Afutu, E.; Hervie, E.T.; Ayeh-kumi, P.F. Urinary Schistosomiasis in Children—Still a Concern in Part of the Ghanaian Capital City. Open J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, T.; Buza, J.; Kinung’Hi, S.M.; Kariuki, H.C.; Mwanga, J.R.; Munisi, D.Z.; Wilson, S. Geographical and behavioral risks associated with Schistosoma haematobium infection in an area of complex transmission. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadeka, E.A.; Nagi, S.; Sunahara, T.; Cheruiyot, N.B.; Bahati, F.; Ozeki, Y.; Inoue, M.; Osada-Oka, M.; Okabe, M.; Hirayama, Y.; et al. Spatial distribution and risk factors of Schistosoma haematobium and hookworm infections among schoolchildren in Kwale, Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Making a Difference: Indicators to Improve Children’s Environmental Health/ prepared by David Briggs; World Health Organization: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Q.; Kang, M. Impacts of Land Use on Surface Water Quality in a Subtropical River Basin: A Case Study of the Dongjiang River Basin, Southeastern China. Water 2015, 7, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabiri, G.; Leemhuis, C.; Diekkrüger, B.; Näschen, K.; Steinbach, S.; Thonfeld, F. Modelling the impact of land use management on water resources in a tropical inland valley catchment of central Uganda, East Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marale, S.M.; Mahajan, D.M.; Gavali, R.S.; Roa, K.R. Evaluation of Water Quality with Waterborne Diseases for Assessing Pilgrimage Impact along. Int. J. Environ. Prot. 2012, 2, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization Country Office. Ghana Situation: Report on Cholera Outbreak in Ghana; World Health Organizatio: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 2015, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
| Land use | Water Quality | Infectious WRID | Combined Search |
|---|---|---|---|
| “land use” OR “land use change” OR “built-up areas” OR “bare-grounds” OR “cultivated areas” OR “farm” AND. | “water pollution” OR “Physicochemical” OR “fecal pollution” OR “solid wastes” OR “wastewater” AND. | “health” OR “water-borne” OR “water-related” OR “diarrhea” OR “cholera” OR “fever” OR “malaria” OR “schistosomiasis” OR “Buruli ulcer” OR “bacteria” OR “parasite” OR “pathogen” AND. | “1” AND “2” AND “3” |
| Land-Use Classifications | Mechanisms of Water Pollution | Water Quality Parameters Tested. | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture (cropland, livestock raising) | Pollution with sediments and nutrients from farms, through stormwater runoff and flooding. | pH, EC, DO, N, K, TN, TP, TSS | [8,55,70,71,72] |
| Settlement (Urban, rural) | Point-source and non-point-source pollution due to poor sanitation and waste management | Heavy metals, fecal coliform, E. coli, temperature, | [8,32,67,73,74] |
| Deforestation (fragmented forest) | A decrease in vegetation cover exposed water to extreme heat, led to sedimentation and eutrophication | Temperature, turbidity, pH, COD, BOD, DO, TSS, EC heavy metals | [8,75,76,77] |
| Industrial area | Industrial and domestic effluents pollute water | Turbidity, pH, COD, BOD, DO, TSS | [8,61,78] |
| Bare-land/paved area | Pollution of water through stormwater | N, P, fecal coliform, E. coli | [79,80] |
| Water bodies (open water, recreational) | Pollution with fecal matter | E. coli, fecal matter, C. parvum oocysts, Giardia duodenalis cysts | [32,35,79,81] |
| Mining area | Point-source pollution through stormwater runoff from mining areas | N, P, COD, DO, heavy metals | [74,76,82] |
| Waste dumping/landfill sites | Wastewater solid waste disposal | EC, pH, DO, Cu, lead | [6,73] |
| Water Quality Parameters | Diseases | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature, turbidity, pH | Dengue | [75] |
| Temperature | Malaria | [59,75,87] |
| E. coli, fecal coliform | Cholera | [45,61,62,81,88] |
| E. coli, fecal coliform, turbidity, pH | Dysentery | [61,62,89] |
| E.coli, fecal coliform | Typhoid fever | [61,62] |
| E. coli, fecal coliform, BOD, temperature, DO | Cryptosporidiosis | [70,81] |
| Fecal coliform | Schistosomiasis | [76,77,83,85,90,91,92] |
| E. coli, fecal coliform, temperature, turbidity | Buruli ulcer | [85] |
| E.coli, fecal coliform, temperature, DO, BOD, TSS, turbidity | Hookworm | [92] |
| LULC | Water Quality Parameters | WRID | Summary Of Key Findings | Country | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated lands, swamp, forest, open water | Temperature | Malaria | Replacement of natural swamp vegetation with irrigated rice and vegetable farms led to an increase in temperature and breeding of Anopheles mosquitos. LULC also reduced the breeding of mosquito. | Uganda | [75,95] |
| Cropland, urban expansion | pH, turbidity, TDS, DO, BOD, COD, E. coli | Cholera | A high concentration of E. coli correlated with cholera cases in areas along the river, with a high rate of urbanization and wastes disposal into the river. | India | [58,96] |
| Dam construction, streamside pool, swamps | Temperature, turbidity, DO, EC, pH | Schistosomiasis | The distribution of the intermediate snails varied with the variation in vegetation cover, turbidity, and pH of water and soil. | Tanzania | [76,91] |
| Grassland, croplands forest, livestock farming | Clostridium perfringens and E. coli | Cryptosporidiosis | The erratic occurrence of Cryptosporidium in the streams was mainly attributed to diffuse pollution. Recreational activities increased the exposure and risk factors | Germany | [70,81] |
| Cropland, forest, urban area, water bodies | Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts, Giardia duodenalis cysts, E. coli. | Cholera | Pollution of surface water with C. parvum and G. duodenalis, due to fecal pollution from wastewater treatment plants and croplands. | France | [81] |
| Croplands, recreational waters | Fecal coliform | Schistosomiasis | Recreational activity was the major exposure and risk factor of schistosomiasis transmission | Ghana | [35,90] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ntajal, J.; Falkenberg, T.; Kistemann, T.; Evers, M. Influences of Land-Use Dynamics and Surface Water Systems Interactions on Water-Related Infectious Diseases—A Systematic Review. Water 2020, 12, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030631
Ntajal J, Falkenberg T, Kistemann T, Evers M. Influences of Land-Use Dynamics and Surface Water Systems Interactions on Water-Related Infectious Diseases—A Systematic Review. Water. 2020; 12(3):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030631
Chicago/Turabian StyleNtajal, Joshua, Timo Falkenberg, Thomas Kistemann, and Mariele Evers. 2020. "Influences of Land-Use Dynamics and Surface Water Systems Interactions on Water-Related Infectious Diseases—A Systematic Review" Water 12, no. 3: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030631
APA StyleNtajal, J., Falkenberg, T., Kistemann, T., & Evers, M. (2020). Influences of Land-Use Dynamics and Surface Water Systems Interactions on Water-Related Infectious Diseases—A Systematic Review. Water, 12(3), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030631






