Abstract
The spatial complexity of floodplains is a function of several processes: hydrodynamics, flow direction, sediment transportation, and land use. Sediments can bind toxic elements, and as there are several pollution sources, the risk of heavy metal accumulation on the floodplains is high. We aimed to determine whether fluvial forms have a role in metal accumulations. Topsoil samples were taken from point bars and swales in the floodplain of the Tisza River, North-East Hungary. Soil properties and metal concentrations were determined, and correlation and hypothesis testing were applied. The results showed that fluvial forms are important drivers of horizontal metal patterns: there were significant differences (p < 0.05) between point bars and swales regarding Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn. Vertical distribution also differed significantly by fluvial forms: swales had higher metal concentrations in all layers. General Linear Models had different results for macro and micro elements: macro element concentrations were determined by the organic matter, while for micro elements the clay content and the forms were significant explanatory variables. These findings are important for land managers and farmers because heavy metal concentration has a direct impact on living organisms, and the risk of bioaccumulation can be high on floodplains.
1. Introduction
Floodplains are relatively flat but spatially complex landforms adjacent to river channels in all alluvial valleys [1,2]. They are formed by the river and are ordinarily inundated [3,4]. Their microtopography acts on several processes, e.g., hydrodynamic, flow direction, and sediment transportation, land uses, and land cover; therefore, they play a crucial role in flood control [5]. During floods, it is not only water and sediments which are conveyed by rivers to floodplains, but also heavy metals [6,7], which get into the water due to natural processes (e.g., weathering) or human activities (e.g., mining) [8,9,10], either in soluble form, or with suspended matter [11]. Heavy metals can be dangerous for living organisms: if these metals are taken up by crops or grass in pastures, they can get into food chains and can pose a serious health threat through bioaccumulation and biomagnification [12,13]. Consequently, it is important to map and monitor the quantity and the spatial distribution of metals accumulated in the floodplains of rivers.
Hungary is in a special situation: the country lies in the middle of the Carpathian basin and 90% of the surface water discharge comes from outside its boundaries [14]; thus, there is a high dependence on the environmental practice(s) of the neighboring countries. Some rivers (especially the Tisza River and its tributaries such as the Kraszna, Szamos, and Túr which arrive from Romania and Ukraine) carry potentially polluted water, in soluble form and bound to the fine fraction of the suspended sediments (i.e., clay has the potential to bind heavy metals [15,16,17], as in their catchment area there are several pollution sources (ore mines, industrial plants, sewage treatment plants etc. [18,19]). Thus, their floodplains are occasionally polluted with different amounts of heavy metals during flooding events [20]. The risk varies over time, e.g., there were two toxic sedimentation events, both of which occurred due to relevant increases in melting snow and heavy rains in 2000 (cyanide and heavy metal pollution), most of the sources of which are still active [21,22]. The rate of the overbank sedimentation processes varies in space and time between 1 and 20 mm annually [23,24,25,26,27]. Furthermore, the rate depends on the distance from the riverbank (sediments become finer as a function of distance), hydrodynamic processes (i.e., slow speed generates higher rates of sedimentation), vegetation density (dense vegetation slows down the speed), the shape of the active floodplain (dykes along the river are not parallel, and therefore there are narrow and wide areas which have direct effects on the speed) and the fluvial forms [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
Examples of heavy metals on floodplains derived from mining have been described by many authors [6,36,37,38,39,40] as has the use of metals to determine the timing and stratigraphy of floodplain alluvium [41,42,43,44]. Furthermore, there are studies on geomorphology as a driver of heavy metal accumulation in alluvial areas [13,45,46,47,48,49,50], but their number is limited in relation to how the pattern of heavy metals alters among floodplain forms [51,52,53,54]. However, this is an important topic as different fluvial forms can generate very diverse accumulation patterns and a better knowledge of this can help to produce better maps of the distribution of metals. As floodplains are often areas of intensive or extensive agricultural production, having more information about the horizontal and vertical pattern of the concentration of the metals is also an important task.
The aim of our work was to reveal the role of fluvial geomorphic forms—point bars and swales—on heavy metal patterns. The main questions were the following: (1) Are there significant differences in the heavy metal concentration between swales and point bars? (2) Which soil properties have a relevant influence on heavy metal accumulation? (3) Is there a trend in the vertical distribution of heavy metals? And (4) is there a statistical interaction between swales and point bars and the vertical distribution of metals?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The study area is in the floodplain of the Tisza River NE-Hungary, near Rakamaz (Figure 1). The Tisza River enters the country from the Carpathians and meanders through its floodplain forming sinuous loops. It was intensively regulated in the 19th–20th century, many of the meanders were cut and dykes were built [55]. Despite the river regulation works, the Tisza River Valley is acknowledged as one of the most natural river valleys in Europe [56]. The floodplain, which lies exactly below the confluence of the Bodrog and Tisza River, belongs to the Natura 2000 network, and is a Ramsar site. Here, the floodplain is wide and rich in landforms. The main landforms of the study site are point bars and swales. The key process behind their formation is a horizontal floodplain evolution caused by the continuously shifting central line of the Tisza River. There are more than a hundred swales and point bars in the floodplain between the Nagy-Morotva Lake, which is an oxbow lake emerged by natural cut off process [57,58], and the Tisza River. The different position of the point bar and swale series and the landforms—paleo channel, levee—which enclave between the series show that they emerged at different periods of time [59]. The sampled point bar and swale series form a line, occurring approximately 3–25 m one after another, making the floodplain surface wavy with their 0.3–0.5 m height differences. Swales have denser vegetation than the point bars [60] and in some cases they have water cover. The study area serves as pasture and grazing land.
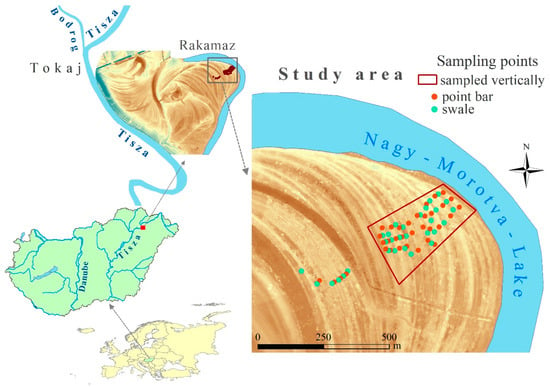
Figure 1.
The location of the study area and the points of the soil sampling (the background is a LiDAR-based digital terrain model).
Usually, there are two flood events a year in the Tisza River when the water can overrun the floodplain: the first occurring in spring after the snow melt and the second in early summer due to heavy rainfall. Floods do not occur every year and they depend on the winter precipitation and the distribution and amount of rainfall in the spring and early summer [61].
In 2000, due to mining activities in the Romanian Maramures region, the Tisza River was loaded with several pollutants, and received two severe cyanide and heavy metal contaminations [19]. Following this, much research focused on the contamination level of the water and the sediments which had accumulated on the floodplain, and it was found that before the well-known mining accident there had been further contaminations conveyed by the river at different times [9,62]. The study site was also affected by these contaminations.
2.2. Soil Samplings
Soil samples were collected from the top 0–25 cm layer from 14 swales and 14 point bars next to the Nagy-Morotva-Lake (Figure 1). 34 samples were collected from point bars and 30 samples from swales. In addition, we also conducted vertical sampling from the top 25 cm at 5 cm intervals (sampling locations are marked by the red polygon in Figure 1); the total number of these samples was 270. The sampling was conducted at a distance of 2500–3000 m from the Tisza riverbed. Furthermore, areas closer to the river had been disturbed by previous agricultural activity (ploughing) and the forms occurring were not restricted to swales and point bars.
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
Soil properties were determined in the laboratory of the Institute of Geosciences (University of Debrecen) according to current Hungarian standards. The soils were first oven-dried at 40–60 °C and then disaggregated in a porcelain mortar. The organic matter content was determined following Tyurin’s scheme with dichromate digestion and titration with Fe(NH4)2(SO4) 6H2O Kononova’s version (1966) in [63]. The pH[H2O] and pH[KCl] were measured with the electrometric method [64]. The granulometric composition was carried out with the Köhn-pipette approach, where soil samples were put in suspension, and the sedimentation of the particles by gravity gave the basis of the measurements; specifically, the settling time of 10 cm-s was applied for measurement [65,66]. For the determination of metal concentrations, soil samples were treated with the HNO3/H2O2 acid digestion method at 130 °C for 2 h, then passed through 12–15 μm filter paper [20,67]; then the concentrations of Al, Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn were measured with an MP-AES 4200 Microwave Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy device [68] in the Department of Inorganic and Analytical Chemistry (University of Debrecen). Al, Ca and Mg are not heavy metals [69]; thus, when we refer to heavy metals, we do not include these elements in the interpretations. Furthermore, we refer to metal concentrations with a term of accumulation, too, as the sampled 0–25 cm layers are the result of several years of accumulation processes [27,70].
2.4. Terrain Dataset and Analysis
For auxiliary data we used a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) point cloud and a Digital Terrain Model (DTM) created from the LiDAR bare earth point cloud with 1 m geometric resolution. The survey was carried out in the framework of flood protection projects (Swiss-Hungarian Program [71]). The dataset provided the basis for the visual interpretation of the geomorphological forms, and for the vectorization and cross-section generation, which were performed in the ESRI ArcGIS 10.3 software environment [72].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
We applied hypothesis testing to reveal whether the sampling site had significant differences in its heavy metal distributions. According to the Shapiro-Wilk test, most variables did not follow the normal distribution; thus, we applied robust methods. We applied the robust Two-Sample t-test (Yuen’s test) combined with trimmed means (with a trim proportion of 0.2) and bootstrapping (599 replications), which does not require normal distribution [73]. The main factor which was applied was the fluvial forms (point bar, swale). Our H0 was that mean concentrations of heavy metal were the same at the fluvial forms, while H1 predicted differences in the concentrations. We also determined the effect size (r), which is a standardized measure of the magnitude of differences: similarly to correlation, its range is between 0 and 1 (the sign is not important, it depends on the categorical variable), and values tending to 1 mean large differences, while values close to 0 refer to negligible effects [74]. The vertical distribution of heavy metals was analyzed with a robust two-way factorial ANOVA (analysis of variance). We aimed to reveal the effect of depth layers and fluvial forms on heavy metal concentrations. The relationship between heavy metals and soil properties was analyzed with correlation analysis, and the result was visualized as a correlation plot. We applied dimension reduction to the metals studied; a standardized Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was performed using the correlation matrix and Varimax rotation. Our primary aim was to separate the metals into correlating groups (i.e., rotated principal components, RCs) to obtain fewer variables, keeping the explained variance at the maximum level. Then, we analyzed the RCs as dependent variables to explore whether the soil properties and landforms had significant effects with General Linear Models. For GLMs, we calculated the effect size (ω2), which is the estimate of how much variance in the dependent variable is accounted for by the independent variables [75]. According to [74], the effect is considered very small when ω2 is <0.01; it is small between 0.01–0.06, medium between 0.06–0.14, and large when >0.14.
Statistical analysis was conducted in R 3.5.3 [76] with the ggcorrplot [77], and the WRS2 [78] packages. GLM was performed in Jamovi 1.1.7 with the General Analyses for Linear Models module [79].
3. Results
3.1. Basic Soil Properties and the Concentrations of Heavy Metals
Samples with the largest fraction of sandy sediments belonged to the positive landforms, i.e., point bars, while clayey samples originated from the negative forms, i.e., swales (Table 1).

Table 1.
The soil characteristics of the analyzed samples, according to the two landforms.
The granulometric composition—the mixture of sand, silt, and clay particles—was the most diverse in the point bars. The samples of the bars belonged to 5 texture classes: clay loam (8 samples), loam (2 samples), silt loam (4 samples), silty clay (4 samples), and silty clay loam (16 samples). Samples from swales were characterized by silty clay (5 samples) and silty clay loam (25 samples) textures. Soils were rich in organic matter (3–7%). The pH of the samples was neutral in the floodplain.
Regarding heavy metals (Figure 2), Zn was the only element for which the amount was above the contamination level in 10 samples (200 mg/kg, 6/2009 IV.14. KöM-EüM-FVM-KHVM regulation) in 4 point bars and 6 swales. Its content varied from 129.2 to 256.4 mg/kg, with an average of 184.9 mg/kg. The highest concentration (256.4 mg/kg) appeared in the concave-upward forms.
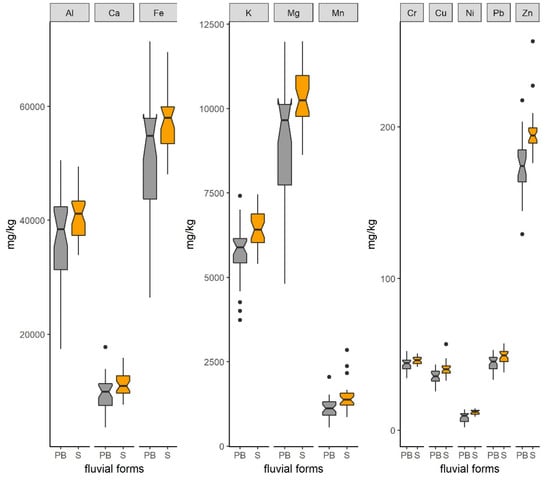
Figure 2.
The accumulation differences between the two landforms (unit: mg/kg; PB: point bar—grey, S: swale—orange; whiskers: 1.5 × interquartile range, •: outliers; box: lower quartile, median, upper quartile; notch: 95% confidence interval of the median).
3.2. Horizontal Pattern of Heavy Metals
In the floodplain the higher metal concentrations belonged to the swales. There were significant differences (p < 0.05) between point bars and swales in each of the studied metals (Table 2).

Table 2.
Differences of heavy metals by point bars and swales according to the Robust Independent Samples (Yuen’s) T-Test (t: t-statistic, df: degree of freedom, p: significance, mean diff.: mean difference between heavy metal content, ξ: effect size; p < 0.05 highlighted with bold).
3.3. Vertical Distribution of Heavy Metals
Vertical distributions of the metals did not show a clear overall trend (Figure 3). Ca, Cu and Zn had a continuously decreasing concentration towards the deeper layers in both the point bars and swales, with the highest concentration in the top 5 cm. Mn and K showed the same pattern at the point bar samples, but not in the case of the swales. Al, Fe, Mg, and Cr had increasing concentrations in swales in the deeper layers, but in point bars they started to decrease after a maximum depth of 5–15 cm. According to the two-way factorial ANOVA, the depth did not have significant effect on the vertical distribution of Ni in the top 25 cm layer, while the geomorphology of the floodplain (i.e., swales and point bars) caused significant differences in each metal’s concentration: swales had a higher concentration in each depth layer. There were only two metals (Ca and Cu) where the interaction of the two factors (depth and fluvial form type) did not have a significant effect on the distribution, i.e., concentrations depended both on the depth and landform (swale or point bar) for all other metals (Table 3).
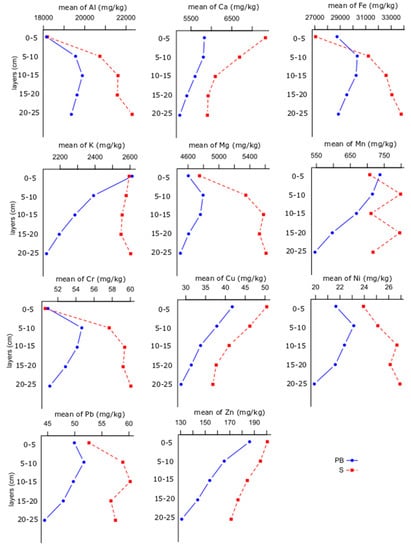
Figure 3.
Interaction plot of the vertical distribution of metals (unit: mg/kg; PB: point bar—blue; S: swale—red).

Table 3.
Result of two-way factorial ANOVA by depth layers and landforms (highlighted with bold: p < 0.05).
3.4. Relationship between Soil Properties and Heavy Metals
First, we conducted correlation analysis. There were negative correlations between the heavy metals and the sand fraction, and the distance from the Tisza riverbank, while soil properties were in a positive relationship with the metals (Figure 4). The clay content had a role in binding metals with moderate correlations. Additionally, correlations between heavy metals, e.g., Zn/Cu, Cu/Pb, Fe/Mg, Mg/Ca, Fe/Al, Ni/Cr were high (r > 0.7). Al had a strong connection with Cr, Cu, Ni from among the micro elements; Fe also correlated with these elements and, additionally, with Zn.
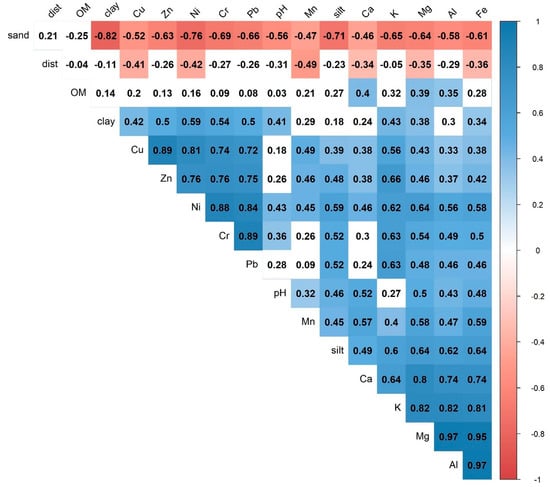
Figure 4.
Connections between heavy metals (mg/kg) and soil properties (OM: Organic matter, %; dist: distance from the Tisza riverbank).
As the next step we used the RCs of the PCA in the analysis. The PCA performed on the metals was justified by the fact RMSR = 0.03, which indicated that the quality of the adjustment was good; the result explained 92% of the total variance. RC1 accounted for 41% and was in strong correlation with Al, Ca, Fe, K, and Mg, while RC2 accounted for 40% of the variance and correlated with Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn. RC3 accounted for 11% and correlated with Mn. Accordingly, RC1 referred to the macro, while RC2 to the micro elements (and were heavy metals at the same time).
Combining the possible influencing factors of the metal distribution using the RCs as aggregated variables, we found that RC1 (macro elements) as a dependent variable resulted in a model where soil properties and the two landforms accounted for 14.5% of the variance (adj. R2 = 0.145), but had a significant relationship only with the organic matter content, and all other factors had only weak effect on them according to the partial ω2 (Table 4). However, in the case of heavy metals (RC2), the fluvial landforms and the clay content had significant (p < 0.05) and considerable (ω2 < 0.01) effects, and the model explained 30.8% of the variance (adj. R2 = 0.308). While the clay content had a large effect, fluvial forms had only a small effect on the metal distribution (Table 5).

Table 4.
Summary of GLM performed with RC1 (SS: Sum of Squares, df: degree of freedom, F: F-statistic, p: significance, ω2: effect size; p < 0.05 is highlighted with bold).

Table 5.
Summary of GLM performed with RC2 (SS: Sum of Squares, df: degree of freedom, F: F-statistic, p: significance, ω2: effect size; p < 0.05 is highlighted with bold).
4. Discussion
Accumulation patterns have strong relationship with the distance from the riverbank, but it cannot be explained directly by this factor, as the hydrodynamic conditions change even on an annual time scale in relation to the magnitude of floods (i.e., water discharge, speed and depth) and also as the land cover changes (conversions of land, e.g., from forest to plough land or from plough land to abandoned site; [24,80,81]). Unlike a soil horizon where the evolution of soil formation is a unified process (e.g., Chernozems), Fluvisols are regularly inundated, causing reductive circumstances and new layers of sediments being deposited on the top layer; all flood events can have unique features in terms of granulometric composition and metal content. Thus, the variation in the horizontal pattern is also the consequence of the heterogeneous state of the sampled top 25 cm. According to [23] the deposition rate is greater close to the river (~10–20 mm/year) and only a few millimeters per year from the riverbank at about 1000 m distance; thus our sampled layer may be the result of 50–100 (or even more) flood events with different sediments and metal contents.
At the study site, the correlations between the metals and the distances from the Tisza riverbed were weak or moderate with a negative sign (from −0.26 to −0.49). The weak correlation and the negative sign are in accordance with [82], and are the consequence of the decreasing amount of depositing sediments: water only inundates the area during floods and most suspended sediment deposits are close to the river; our study area was at a distance of 2500–3000 m from the Tisza riverbed.
The granulometric composition of the landforms is in accordance with the findings of [83], i.e., that point bars had a higher ratio of coarser fraction than swales: point bars had a sand fraction of 17.6 ± 7.9%, and swales of 10.6 ± 2.2%; furthermore, the clay content was 33.4 ± 5.5 and 36.8 ± 3.2%, respectively. It is due to point bars emerged higher water discharge, when river sediment transportation capacity is higher, thus more sand sediments would be accumulate; and also the flow velocity is greater over bars, thus fewer clay sediments would be deposited here, than swales lying in slow-moving depositional environment. Metals are bound by inorganic and organic colloids. Clay, as an inorganic colloid, was one of the most important factors determining the micro elements’ (RC2) concentration besides the fluvial forms. However, the clay was not a significant variable for macro elements (RC1). The reason is that clay (i.e., clay minerals) bound the micro elements and deposited them in greater amounts in the deeper swales, but macro elements are often the building elements of the crystal structure of the clay minerals (as Al-, Fe and Mg-octahedral sheets; [84]. Soil formation, in this area is influenced by soil moisture and regular water coverage, which controls the adsorption-desorption of the metal concentration through the pH, organic matter transformation and humic substance formation, and is strongly linked to the concave and convex fluvial forms [85].
Concave forms with better water supply support denser vegetation, and this is reflected in the higher organic matter content of the swale samples 4.9 ± 1.3%, while in the bars it was lower, at 4.2 ± 1%. The organic matter was the significant explanatory variable which determined the concentration of macro elements (RC1) in the GLM. This connection is confirmed by several authors [86,87] as Fe, Al, and Ca are key regulators of soil organic matter stability. However, pairwise correlations only varied between 0.3 and 0.5: it is known that floodplains do not provide favorable locations for humus formation; usually the first stages of transformation, the fulvic acids, are dominant, and these have an acidic character, few binding locations and poor binding capacity [88].
As a consequence of the number of colloids, point bars had lower metal concentrations (Figure 2, Table 2). Furthermore, there is another process which can have a relevant effect on the concentration, i.e., leaching and erosion [54]. Point bars have better infiltration capacity because of their higher sand content, their higher position between the swales, and the downward erosion of the finest particles (which bind heavy metals). Thus, both the infiltrating water of rains and floods and the surface runoff (generated by precipitation) reduce the metal concentration. Accordingly, in the study area where swales and point bars form a series of concave and convex forms, a simple regular pattern can be observed (Figure 5a,b): swales as depressions usually had higher heavy metal concentrations, while in point bars the values were lower. Although the differences were significant between point bars and swales regarding each metal, this was not true for all forms. When the relative situation resulted in point bars at lower terrain heights (i.e., a point bar swale series between higher point bars, Figure 5c), the difference in heavy metal concentrations did not followed the pattern which was characteristic in all other locations (Figure 5d). In this case, the vegetation density counter-balanced the sediment trap effect of swales as dense grass decreases flow speed and intensifies deposition [30,89].
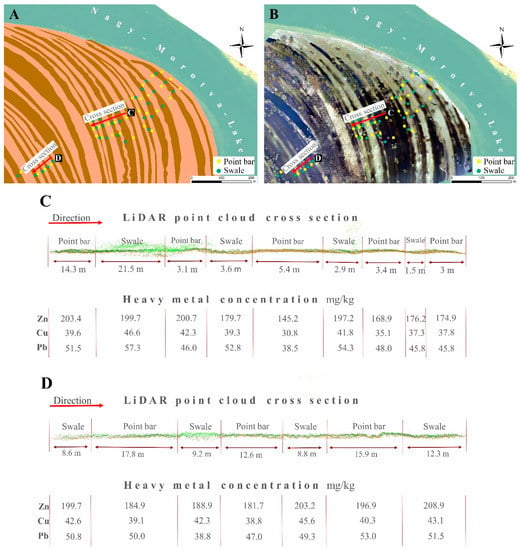
Figure 5.
Point bar and swale topography, and their heavy metal accumulation pattern. (A) The digitized fluvial forms in a LiDAR-based digital terrain model; (B) point bar-swale series in an aerial image during flood; (C,D) cross sections of point bars and swales in a LiDAR point cloud (z exaggeration: 2) and their metal concentrations. When point bars have denser vegetation and they are in lower position their metal concentrations were higher, as it reflected in case of Figure 5C in the first two point bars.
Vertical metal distribution had a varying trend regarding the metals studied. This can be explained partly by natural processes (erosion, leaching, pH or organic matter), but also by a close connection with anthropogenic activities. Due to ore mining sites in the Maramures Mounts there was two large accidents when the dams broke, and the sludge reached the Tisza River in 2000 [90]. One of them coincided with a flood, and the heavy metal pollution, bound to suspended colloids (i.e., clay), was deposited in the floodplain. This pollution can be identified in swales, in the 5–10 layer in the case of Pb. This means that there was about 5 cm of accumulation in the area due to the sedimentation, but the reason for this was not only the deposition of the suspended sediment carried by the river, but the erosion from the point bars and the accumulation of decaying organic matter, too.
5. Conclusions
We conducted a geomorphology-based heavy metal analysis to determine the relationship between two fluvial forms—point bars and swales—and metal concentrations. We revealed that macro and micro elements formed two non-correlating principal components, for the following reasons: micro elements are bound to clayey sediments while clays consist of Fe, Al, Mg, the macro elements. Fluvial forms, i.e., the concave swales and the convex point bars, are important influencing factors of the horizontal heavy metal patterns: swales had significantly (p < 0.05) higher concentrations for each studied metal in the examined floodplain. Vertical distribution also differed significantly by forms: swales had higher metal concentrations in all layers. While concentrations of Al, Fe, Mg, and Cr gradually increased, all the other metals had a decreasing trend in the deeper layers. These findings are important for land managers and farmers because heavy metal concentration has a direct impact on living organisms, and floodplains are important scenes of agricultural activities, here for example grazing and harvesting are presented. Principles drawn from a better understanding of heavy metal accumulation pattern help to identify the hotspot areas of severe metal contents.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.S. and S.S.; methodology, E.B., P.H. and J.P.; software, Z.S., T.T. and S.S.; validation, C.A.T.; formal analysis, Z.S.; investigation, E.B., P.H., B.B., J.S. and J.P.; resources, Z.S., C.A.T. and J.S.; data curation, S.S., B.B. and T.T.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.S., S.S., J.S., C.A.T. and B.B.; visualization, Z.S., B.B. and S.S.; supervision, S.S. and J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the European Union and the State of Hungary, co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund in the project of GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00009 ‘ICER’. Z. Szabo was supported by the ÚNKP-18-3 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lewin, J. Floodplain geomorphology. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1978, 2, 408–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, R. Fundamentals of Fluvial Geomorphology; Charlton, R., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2007; ISBN 9780203371084. [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, J.; Demicco, R. Earth Surface Processes, Landforms and Sediment Deposits; Bridge, J.S., Demicco, R.V., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-0-511-45522-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bertalan, L.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Surian, N.; Šulc Michalková, M.; Kovács, Z.; Szabó, S.; Szabó, G.; Hooke, J. Detailed assessment of spatial and temporal variations in river channel changes and meander evolution as a preliminary work for effective floodplain management. The example of Sajó River, Hungary. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scown, M.W.; Thoms, M.C.; De Jager, N.R. Measuring floodplain spatial patterns using continuous surface metrics at multiple scales. Geomorphology 2015, 245, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.Y.; Zhou, W.B.; Wu, D.S.; Zeng, F.P. Heavy metal contamination in sediments and floodplain topsoils of the Lean River catchment, China. Soil Sediment Contam. 2011, 20, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matys Grygar, T.; Elznicová, J.; Kiss, T.; Smith, H.G. Using sedimentary archives to reconstruct pollution history and sediment provenance: The Ohře River, Czech Republic. Catena 2016, 144, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, L.R.; Hengl, T.; Reuter, H.I. Heavy metals in European soils: A geostatistical analysis of the FOREGS Geochemical database. Geoderma 2008, 148, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Braun, M.; Szaloki, I.; Baeyens, W.; Van Grieken, R.; Leermakers, M. Tracing the metal pollution history of the Tisza River through the analysis of a sediment depth profile. Water. Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 200, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovníková, J.; Pálka, B.; Širáň, M.; Kizeková, M.; Kanianska, R. The potential of regulating ecosystem service–Filtering potential foinorganic pollutants–Supplied by soils of Slovakia. Hungarian Geogr. Bull. 2019, 68, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, F.; Meissner, R.; Gröngröft, A.; Grunewald, K. Flood induced heavy metal and arsenic contamination of Elbe river floodplain soils. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2005, 33, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Kooistra, L.; Salas, E.A.L. Study of heavy metal contamination in river floodplains using the red-edge position in spectroscopic data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 3883–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamás, M.; Farsang, A. Determination of heavy metal fractions in the sediments of oxbow lakes to detect the human impact on the fluvial system (Tisza River, SE Hungary). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River. The Danube River Basin District Management Plan; ICPDR: Vienna, Austria, 2015; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz, A.J. A primer on trace metal-sediment chemistry. Water Supply Pap. 1986, 2277, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Salomons, W.; de Rooij, N.M.; Kerdijk, H.; Bril, J. Sediments as a source for contaminants? Hydrobiologia 1987, 149, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, S.; Gosztonyi, G.; Babka, B.; Dócs, N.; Braun, M.; Csorba, P.; Türk, G.; Molnár, L.S.; Bakos, B.; Szabó, G.; et al. Gis database of heavy metals in the floodplain of the Tisza river. Stud. Univ. Vasile Goldis Arad Ser. Stiint. Vietii 2010, 20, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lakatos, G.; Fleit, E.; Mészáros, I. Ecotoxicological studies and risk assessment on the cyanide contamination in Tisza river. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 140–141, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osán, J.; Török, S.; Alföldy, B.; Alsecz, A.; Falkenberg, G.; Baik, S.Y.; Van Grieken, R. Comparison of sediment pollution in the rivers of the Hungarian Upper Tisza Region using non-destructive analytical techniques. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosztonyi, G.; Szabó, S. Examination of heavy metal accumulation in the sediments and plants of an active floodplain near the River Tisza. Stud. Univ. Vasile Goldis Arad Ser. Stiint. Vietii 2011, 21, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Hamar, J.; Sárkány-Kiss, A. (Eds.) The Upper Tisa Valley; Tisza Klub & Liga Pro Europa: Szeged, Hungary, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sárkány-Kiss, I.; Fodorpataki, L.; Macalik, K.; Telcean, I.; Bálint, M.; Braun, M.; Papp, J.; Hamar, J. The ecological state of the Upper Tisa and the Transylvanian tributaries of the Tisa River-based on characteristics of the physico-chemical parameters, the flora and the fauna. Acta Biol. Debrecina Oecologica Hungarica 2012, 27, 147–168. [Google Scholar]
- Dezső, Z.; Szabó, S.; Bihari, Á. Investigation of the sedimentation of the active floodplain of Tisza based on gamma-spectrostropic analysis of 137Cs-isotopes. In Proceedings of the V. Kárpát-medencei Környezettudományi Konferencia, Sapientia-Erdélyi Magyar Tudományegyetem, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 26–29 March 2009; Mócsy, I., Szacsvai, K., Urák, I., Zsigmond, A.R., Eds.; Ábel: Kolozsvár, Romania, 2009; pp. 438–443. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, T.; Sándor, A. Land-use changes and their effect on floodplain aggradation along the Middle-Tisza River, Hungary. AGD Landsc. Environ. 2009, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, T.; Oroszi, V.G.; Sipos, G.; Fiala, K.; Benyhe, B. Accelerated overbank accumulation after nineteenth century river regulation works: A case study on the Maros River, Hungary. Geomorphology 2011, 135, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Balogh, M. Characteristics of Point-Bar Development under the Influence of a Dam: Case Study on the Dráva River at Sigetec, Croatia. J. Environ. Geogr. 2015, 8, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, R. Ártérfejlődési Vizsgálatok Felső-Tiszai Mintaterületeken (Examination of Fluvial Development on Study Areas of Upper Tisza Region); Tóth könyvkereskedés és Kiadó Kft.: Nyíregyháza, Hungary, 2018; ISBN 978-615-00-1833-1. [Google Scholar]
- Piégay, H.; Hupp, C.R.; Citterio, A.; Dufour, S.; Moulin, B.; Walling, D.E. Spatial and temporal variability in sedimentation rates associated with cutoff channel infill deposits: Ain River, France. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, S.; Gosztonyi, G.; Juhos, K. Statistical analysis of heavy metal content of sediment samples from the floodland of Tisza River. Hidrológiai Közlöny 2009, 89, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Crosato, A.; Saleh, M.S. Numerical study on the effects of floodplain vegetation on river planform style. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietz, G.J.; Rutherfurd, I.D.; Stewardson, M.J.; Finlayson, B.L. Hydrodynamics and sedimentology of concave benches in a lowland river. Geomorphology 2012, 147–148, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, A.P. Modelling the continuum of river channel patterns. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregun, C.Z. Ecohydrological and morphological relationships of a regulated lowland river; based on field studies and hydrological modeling. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahilan, S.; Guan, M.; Sleigh, A.; Wright, N.; Chang, H. The influence of floodplain restoration on flow and sediment dynamics in an urban river. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S986–S1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsoer, K.M.; Rhoads, B. Analysis of shallow turbulent flows using the Hilbert-Huang transform: A tool for exploring the characteristics of turbulence and coherent flow structures. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2018, 67, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenden, P.J.; Lewin, J. Distribution of metal pollutants in active stream sediments. Catena 1978, 5, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, J.; Macklin, M.G. Metal mining and floodplain sedimentation in Britain. In International Geomorphology 1986, Proceedings of the First International Conference on Geomorphology (Part I), Manchester, UK, 15–21 September 1985; Gardiner, V., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987; pp. 1009–1027. ISBN 978-0471914716. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, S.; Cox, J. The significance of the floodplain to the cycling of metals in the River Derwent catchment, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 97, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Macklin, M.G.; Taylor, M.P. 2000 years of sediment-borne heavy metal storage in the Yorkshire Ouse basin, NE England, UK. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, S.A.; Brewer, P.A.; Macklin, M.G.; Haresign, W.; Betson, R.E.; Rassner, S.M.E. Flood-related contamination in catchments affected by historical metal mining: An unexpected and emerging hazard of climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, J.; Davies, B.E.; Wolfenden, P.J. Interactions between channel change and historic mining sediments. In River Channel Changes; Gregory, K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1977; pp. 353–369. ISBN 0-471-99524-X-77-4342. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, J.C. Historical valley floor sedimentation in the Upper Mississippi Valley. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1987, 77, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecce, S.A.; Pavlowsky, R.T. Use of mining-contaminated sediment tracers to investigate the timing and rates of historical flood plain sedimentation. Geomorphology 2001, 38, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlowsky, R.T.; Lecce, S.A.; Owen, M.R.; Martin, D.J. Legacy sediment, lead, and zinc storage in channel and floodplain deposits of the Big River, Old Lead Belt Mining District, Missouri, USA. Geomorphology 2017, 299, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.W. Heavy metal concentrations in floodplain surface soils, Lahn River, Germany. Environ. Geol. 1997, 30, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R. The role of fluvial geomorphic processes in the dispersal of heavy metals from mine sites. J. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 58, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, Z. Trace metal pollution and microtopography in a floodplain, the Haros Island (Budapest). Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 1998, 21, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Szalai, Z.; Baloghnné Di Gléria, M.; Jakab, G.; Csuták, M.; Bádonyi, K.; Tóth, A. Physical speciation of sediment associated heavy metals in active floodplains of the Danube and Tisza rivers, Hungary. Födrajzi Értesítő 2005, 54, 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kotková, K.; Nováková, T.; Tůmová, S.; Kiss, T.; Popelka, J.; Faměra, M. Migration of risk elements within the floodplain of the Litavka River, the Czech Republic. Geomorphology 2019, 329, 46–57. [Google Scholar]
- Babcsányi, I.; Tamás, M.; Szatmári, J.; Hambek-Oláh, B.; Farsang, A. Assessing the impacts of the main river and anthropogenic use on the degree of metal contamination of oxbow lake sediments (Tisza River Valley, Hungary). J. Soils Sediments 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, S.C.; Marcus, W.A.; Cherry, S. Differences in trace metal concentrations among fluvial morphologic units and implications for sampling. Environ. Geol. 1998, 36, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Orbock Miller, S.M. Floodplains. In Contaminated Rivers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 177–234. ISBN 978-1-4020-5602-4. [Google Scholar]
- Van Metre, P.; Horowitz, A.J. An 80-year record of sediment quality in the lower Mississippi River. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 27, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Grygar, T.M. A Review of flood-related Storage and remobilization of heavy metal pollutants in river systems. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, J.; Vass, R.; Tóth, C. Examination of fluvial development on study areas of Upper-Tisza region. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2012, 7, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Babka, B.; Futó, I.; Szabó, S. Seasonal evaporation cycle in oxbow lakes formed along the Tisza River in Hungary for flood control. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Braun, M.; Dévai, G.; Nagy, S. A Nagy-morotva rakamazi szakaszának üledékminősége (The quality of the sediments of Nagy-mortotva, Rakamaz). Hidrológiai Közlöny 1998, 78, 375–376. [Google Scholar]
- Dévai, G.; Miskolczi, M.; Jakab, T. Adatok a Nagy-morotva (Rakamaz és Tiszanagyfalu) szitakötő-faunájához (Odonata). (Data for Odonata specias of Nagy-morotva (Rakamaz and Tiszanagyfalu)). Stud. Odonatol. Hung. 2012, 14, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Szabó, Z.; Szabó, S.; Szabó, J.; Tomor, T.; Hunyadi, G. Felszínfejlődési szakaszok és formák vizsgálata LiDAR felmérés alapján a Tisza hullámterén (Examination of the development of land and landforms using LiDAR data in a floodplain of the Tisza River). In Proceedings of the Az Elmélet és Gyakorlat Találkozása a térinformatikában VI, Debrecen, Hungary, 28–29 May 2015; Boda, J., Ed.; Kapitális Nyomdaipari Kft.: Debrecen, Hungary, 2015; pp. 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Szabó, Z.; Tóth, C.A.; Tomor, T.; Szabó, S. Airborne LiDAR point cloud in mapping of fluvial forms: A case study of a Hungarian floodplain. GIScience Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 862–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vari, A.; Linnerooth-Bayer, J.; Ferencz, Z. Stakeholder views on flood risk management in Hungary’s Upper Tisza Basin. Risk Anal. 2003, 23, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Győri, Z.; Boros, N.; Sipos, P.; Szabó, E.B.; Kovács, K.; Horváth, M.; Takács, A.; Heltai, G. Evaluation of the heavy metal content of the Upper Tisza River floodplain soils over the last decade. Hung. J. Ind. Chem. 2015, 43, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Angelova, V.; Akova, V.I.; Ivanov, K.I.; Licheva, P.A. Comparative study of titrimetric and gravimetric methods for the determination of organic carbon in soils. J. Int. Sci. Publ. Ecol. Saf. 2014, 8, 430–440. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G. Soil pH and Soil Acidity. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3—Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 475–489. ISBN 0-89118-825-8. [Google Scholar]
- Particle Size Analysis. In Handbook of Soil Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 15–63. ISBN 978-3-540-31211-6.
- Centeri, C.; Jakab, G.; Szabó, S.; Farsang, A.; Barta, K.; Szalai, Z.; Bíró, Z. Comparison of particle-size analyzing laboratory methods. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.S.A.; Amaral Sobrinho, N.M.B.D.; Pérez, D.V.; Coutinho, I.B. Comparing methods for extracting heavy metals from Histosols for establishing quality reference values. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2016, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vysetti, B.; Vummiti, D.; Roy, P.; Taylor, C.; Kamala, C.T.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Kar, P.; Subramanyam, K.S.V.; Raju, A.K.; Abburi, K. Analysis of geochemical samples by microwave plasma-AES. At. Spectrosc. 2014, 35, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, S. What is a “Heavy Metal”? J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, S.; Vass, R.; Szabó, J.; Szabó, G.; Posta, J. A hullámtéri feltöltődés mennyiségi és minőségi vizsgálata a Beregi-síkon (The examination of the quality and the quantity of the floodplain aggradation on Bereg plain). In Természetföldrajzi Kutatások Magyarországon a XXI, Század Elején: Tiszteletkötet Gábris Gyula Professzor úr 70, Születésnapjára; Horváth, E., Mari, L., Eds.; ELTE TTK Földrajz- és Földtudományi Intézet Természetföldrajzi Tanszék: Budapest, Hungary, 2012; pp. 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- SH/2/6-Swiss-Hungarian Programme. Updating the flood protection plans for sections of the river Tisza under the management of the Environmental and Water Management Directorate of the Tiszántúl Region and the North Hungarian Environment and Water Directorate. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/43668713.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- ESRI. Arcgis Desktop: Release 10.5; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R. Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability 57, An Introdaction to the Bootstrap; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; ISBN 0-412-04231-2. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics, 4th ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Fair Lawn, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-9351500827. [Google Scholar]
- Albers, C.; Lakens, D. When power analyses based on pilot data are biased: Inaccurate effect size estimators and follow-up bias. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2018, 74, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R 3.53 Statistical Software 2019. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Kassambara, A. Package ‘ggcorrplot’. R package version 0.1.3. Visualization of a Correlation Matrix Using “ggplot2”. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggcorrplot (accessed on 19 May 2019).
- Mair, P.; Wilcox, R. Robust statistical methods in R using the WRS2 package. Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project Jamovi 1.1.7. 2019. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Kolozsvári, I.; Molnár, J.; Dévai, G. Recent river channel change detections in the section of the River Tisza above Tiszaújlak (Bилок). Landsc. Environ. 2016, 10, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Nagy, Z.; Balogh, M. Floodplain level development induced by human activity-case study in the lower maros/mures river, Romania and Hungary. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 12, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Marriott, S.B. Dispersion and remobilisation of heavy metals in the River Severn System, UK. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanson, G.C. Point bar and floodplain formation of the meandering Beatton River, northeastern British Columbia, Canada. Sedimentology 1980, 27, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantelon, D.; Pelletier, M.; Michot, L.J.; Barres, O.; Thomas, F. Fe, Mg and Al distribution in the octahedral sheet of montmorillonites. An infrared study in the OH- bending region. Clay Miner. 2001, 36, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinay, G.; Black, V.J.; Planty-Tabacchi, A.M.; Gumiero, B.; Décamps, H. Geomorphic control of denitrification in large river floodplain soils. Biogeochemistry 2000, 50, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Qin, S.; Yang, G.; Fang, K.; Zhu, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y. Regulation of priming effect by soil organic matter stability over a broad geographic scale. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetta, B.; Zaccone, C.; Plaza, C.; Siebecker, M.G.; Rovira, P.; Vischetti, C.; Sparks, D.L. The role of Fe(III) in soil organic matter stabilization in two size fractions having opposite features. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borůvka, L.; Drábek, O. Heavy metal distribution between fractions of humic substances in heavily polluted soils. Plant. Soil Environ. 2004, 50, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Nagy, J.; Fehérváry, I.; Vaszkó, C. (Mis) management of floodplain vegetation: The effect of invasive species on vegetation roughness and flood levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapi, K.; Győri, Z. Investigations on mud on heavy metal contaminated flood-plain of Tisza. Acta Agraric. Debr. 2003, 3, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).