Comparisons of Two Types of Particle Tracking Models Including the Effects of Vertical Velocity Shear
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Descriptions
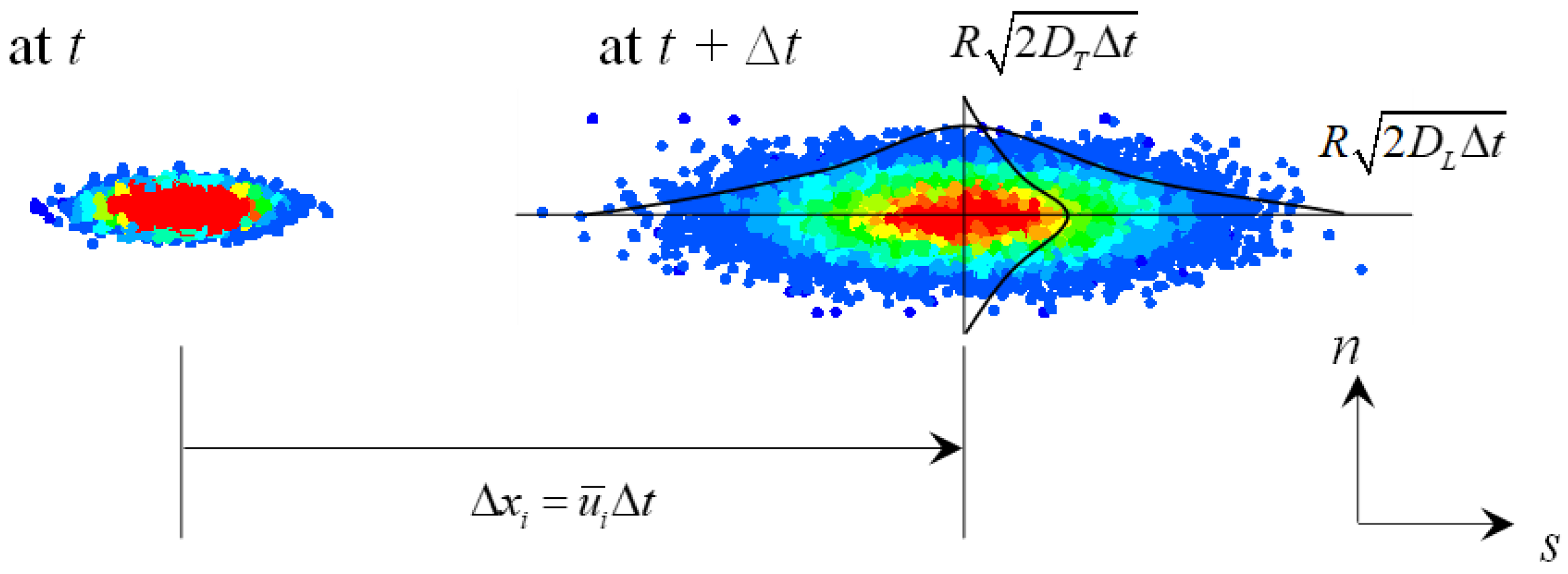
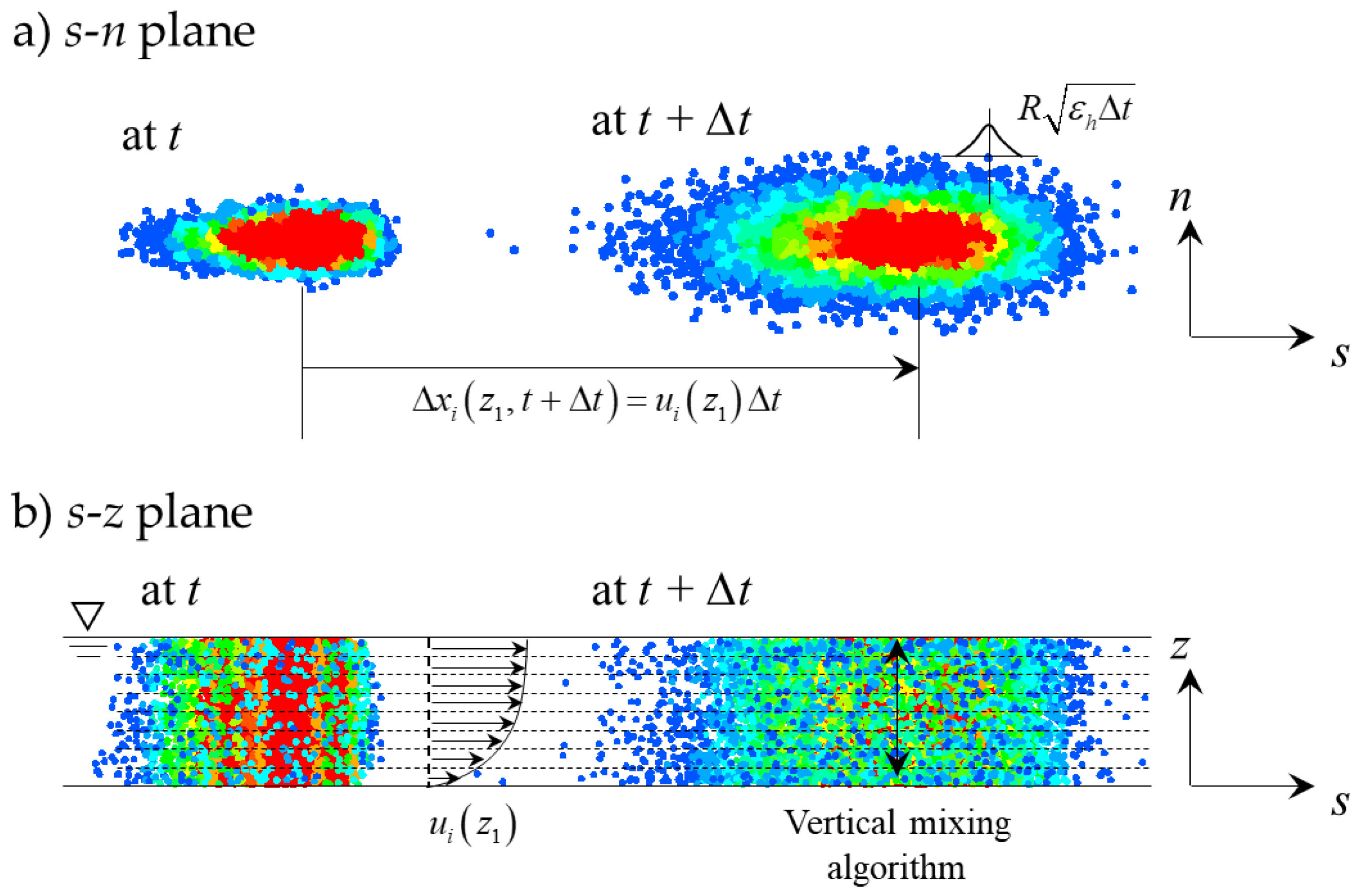
2.1. Particle Tracking Model (PTM)
2.2. Particle Dispersion Model (PDM)
3. 2D Solute Mixing Simulation Results
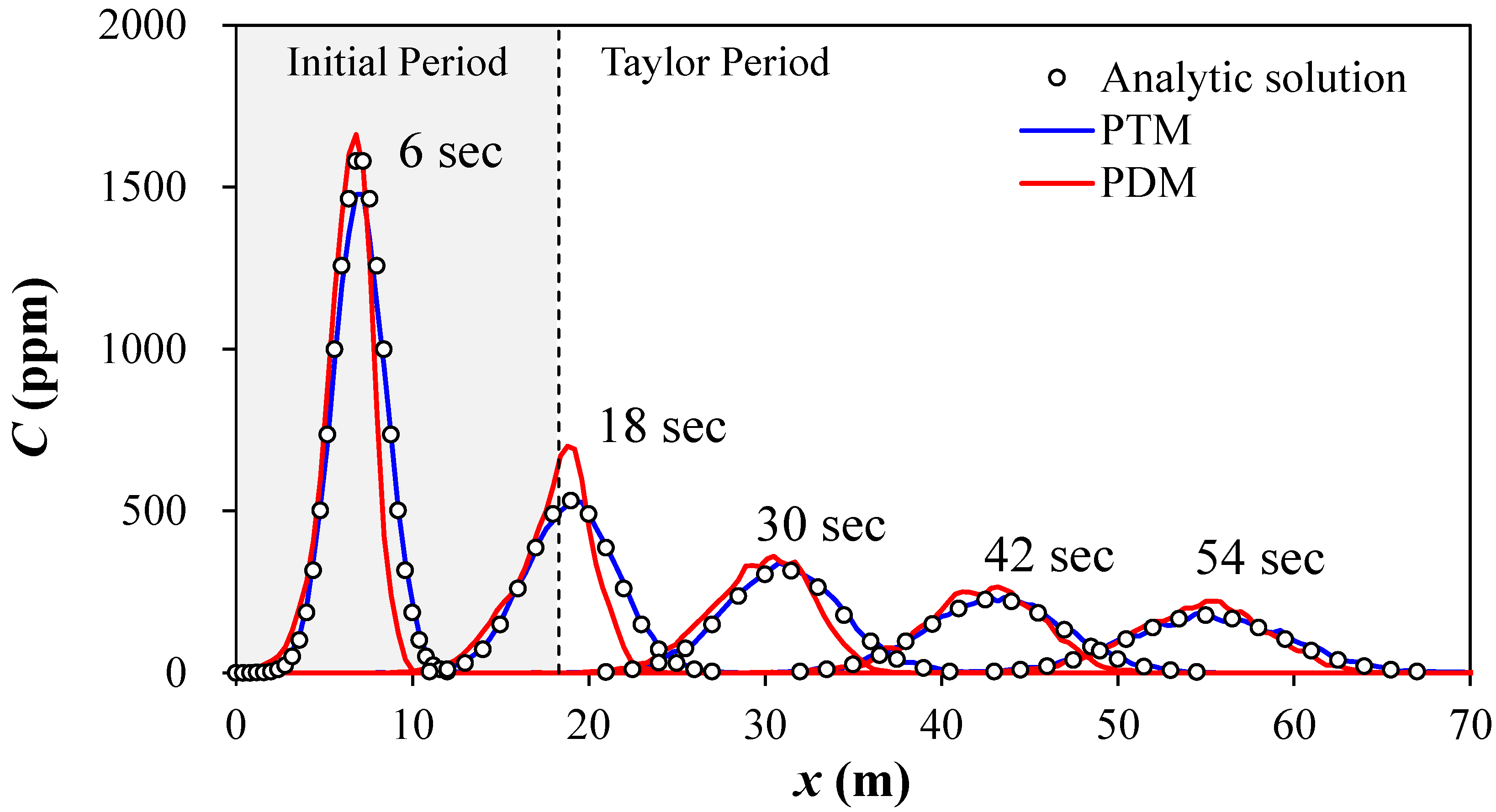
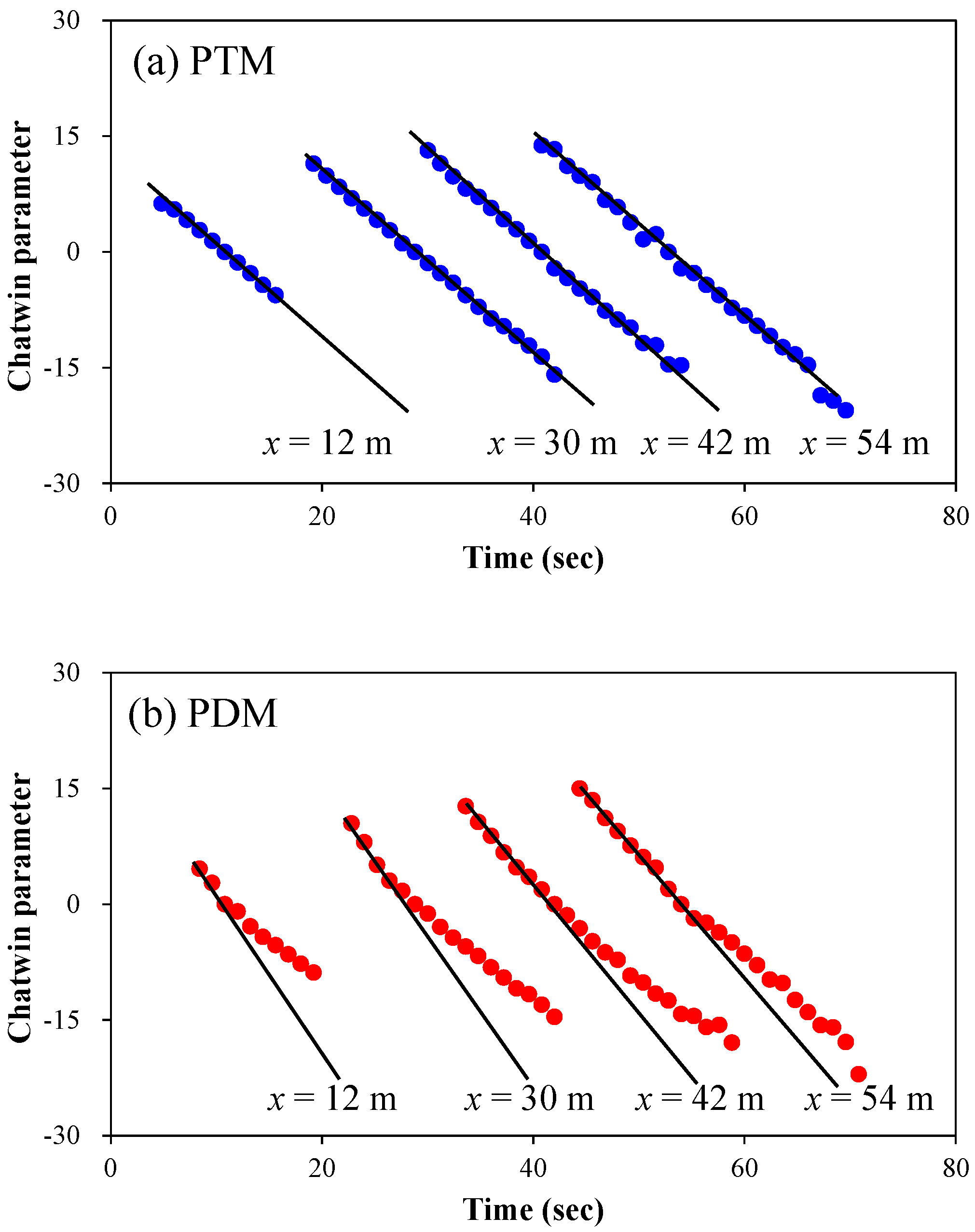
3.1. Model Validations
3.2. 2D Solute Mixing in the Meandering Channel
3.2.1. Temporal Variations of Concentration
3.2.2. Statistical Properties of Concentration Curves in Channel Bends
3.3. Model Applications in the Hongcheon River
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piasecki, M.; Katopodes, N.D. Identification of stream dispersion coefficients by adjoint sensitivity method. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I.W.; Lee, M.E.; Baek, K.O. 2D modeling of heterogeneous dispersion in meandering channels. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, C.; Steffler, P. Estimating transverse mixing in open channels due to secondary current-induced shear dispersion. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. The dispersion of matter in turbulent flow through a pipe. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1954, 223, 446–468. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, H.B.; List, J.E.; Koh, R.C.Y.; Imberger, J.; Brooks, N.H. Mixing in Inland and Coastal Waters, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1979; pp. 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.E.; Seo, I.W. 2D finite element pollutant transport model for accidental mass release in rivers. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 14, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilechi, A.; Mohammadian, A.; Rennie, C.D.; Zhu, D.Z. Efficient method for coupling field data and numerical modeling for the estimation of transverse mixing coefficients in meandering rivers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Song, C.G. Analysis of two-dimensional flow and pollutant transport induced by tidal currents in the Han River. J. Hydroinf. 2018, 20, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.L.; Krishnappan, B.G. Transverse dispersion in rectangular channels. J. Hydraul. Div. 1977, 103, 1173–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, J.C. River Mixing; John Wiley and Sons: London, UK, 1994; pp. 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Boxall, J.B.; Guymer, I. Analysis and prediction of transverse mixing coefficients in natural channels. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2003, 129, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, D.Z. Transverse mixing in an unregulated Northern River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 1426–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.O.; Seo, I.W. Empirical equation for transverse dispersion coefficient based on theoretical background in river bends. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2013, 13, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I.W.; Baek, K.O.; Jeon, T.M. Analysis of transverse mixing in natural streams under slug tests. J. Hydraul. Res. 2006, 44, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, J.W. The dispersion of marked fluid in turbulent shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1959, 5, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.E.; Seo, I.W. Analysis of pollutant transport in the Han River with tidal current using a 2D finite element model. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2007, 1, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.O.; Seo, I.W.; Jung, S.J. Evaluation of dispersion coefficients in meandering channels from transient tracer tests. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I.W.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, Y.D.; Han, E.J. Analysis of two-dimensional mixing in natural streams based on transient tracer tests. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Seo, I.W.; Baek, D. Longitudinal and transverse dispersion coefficients of 2D contaminant transport model for mixing analysis in open channels. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. Assessment of longitudinal dispersion coefficients using Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers in large river. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Seo, I.W.; Shin, J.; Song, C.G. Experimental and numerical investigations of spatially-varying dispersion tensors based on vertical velocity profile and depth-averaged flow field. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 142, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.M.; Lee, J.H.W.; Choi, K.W. A deterministic Lagrangian particle separation-based method for advective-diffusion problems. Commun. Nonlinear. Sci. 2008, 13, 2071–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, K.N.; Adams, E.E. A random-walk, particle tracking model for well-mixed estuaries and coastal waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1993, 37, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitbrecht, V.; Uijttewaal, W.; Jirka, G.H. 2-D particle tracking to determine transport characteristics on shallow flows. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Shallow Flows (IAHR), Delft, The Netherlands, 6–8 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Gesteira, M.; Montero, P.; Prego, R.; Taboada, J.J.; Leitao, P.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Neves, R.; Perez-Villar, V. A two-dimensional particle tracking model for pollution dispersion in A Coruna and Vigo Rias (NW Spain). Oceanol. Acta 1999, 22, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, S.W. A hybrid approach to particle tracking and Eulerian-Lagrangian models in the simulation of coastal dispersion. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomson, A.F.B.; Gelhar, L.W. Numerical simulation of solute transport in three-dimensional, randomly heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2541–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Day, T.J. Longitudinal dispersion in natural channels. Water Resour. Res. 1975, 11, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernuszenko, W.; Rowiński, P.M.; Sukhodolov, A. Experimental and numerical validation of the dead-zone model for longitudinal dispersion in rivers. J. Hydraul. Res. 1998, 36, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazijk, A.; Veling, E.J.M. Tracer experiments in the Rhine Basin: Evaluation of the skewness of observed concentration distributions. J. Hydrol. 2005, 307, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Seo, I.W. Modeling non-Fickian pollutant mixing in open channel flows using two-dimensional particle dispersion model. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatwin, P.C. On the interpretation of some longitudinal dispersion experiments. J. Fluid Mech. 1971, 48, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itō, K.; Nisio, M. On stationary solutions of a stochastic differential equation. J. Math. Kyoto Univ. 1964, 4, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.G.; Seo, I.W.; Kim, Y.D. Analysis of secondary current effect in the modeling of shallow flow in open channels. Adv. Water Res. 2012, 41, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Muller, M.E. A note on the generation of random normal deviates. Ann. Math. Stat. 1958, 29, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huai, W. Estimating the longitudinal dispersion coefficient in straight natural rivers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozovskii, I.L. Flow of Water in Bends of Open Channels; Academy of Science of Ukrainian SSR: Moscow, Russia, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Odgaard, A.J. Meander flow model. I: Development. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1986, 112, 1117–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.B. Methods for Predicting Dispersion Coefficients in Natural Streams, with Applications to Lower Reaches of the Green and Duwamish Rivers Washington; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1968; pp. A22–A25.
- Guymer, I. Longitudinal dispersion in sinuous channel with changes in shape. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, A.; Zaramella, M. Effects of velocity gradients and secondary flow on the dispersion of solutes in a meandering channel. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I.W.; Park, S.W. Effect of velocity structures on tracer mixing in a meandering channel. J. Korean Soc. Civil. Eng. 2009, 29, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Baek, D.; Park, I. Evaluating the impact of turbulence closure models on solute transport simulations in meandering open channels. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickin, E.J. Mean flow structure in meanders of the Squamish River, British Columbia. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1978, 15, 1833–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmid, B.H. On the transient storage equations for longitudinal solute transport in open channels: Temporal moments accounting for the effects of first-order decay. J. Hydraul. Res. 1995, 33, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatwin, P.C. Presentation of longitudinal dispersion data. J. Hydraul. Div. 1980, 106, 71–83. [Google Scholar]

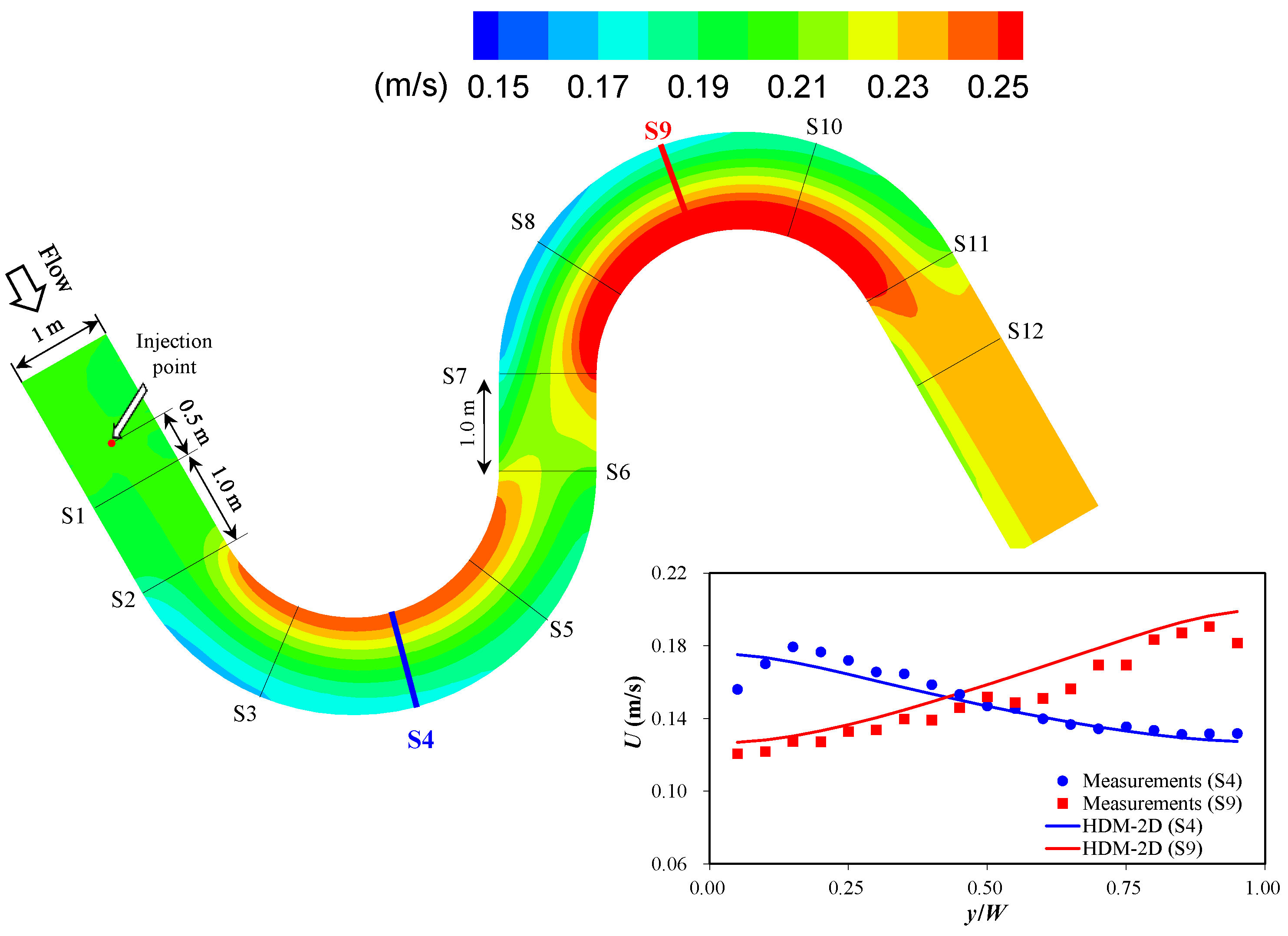
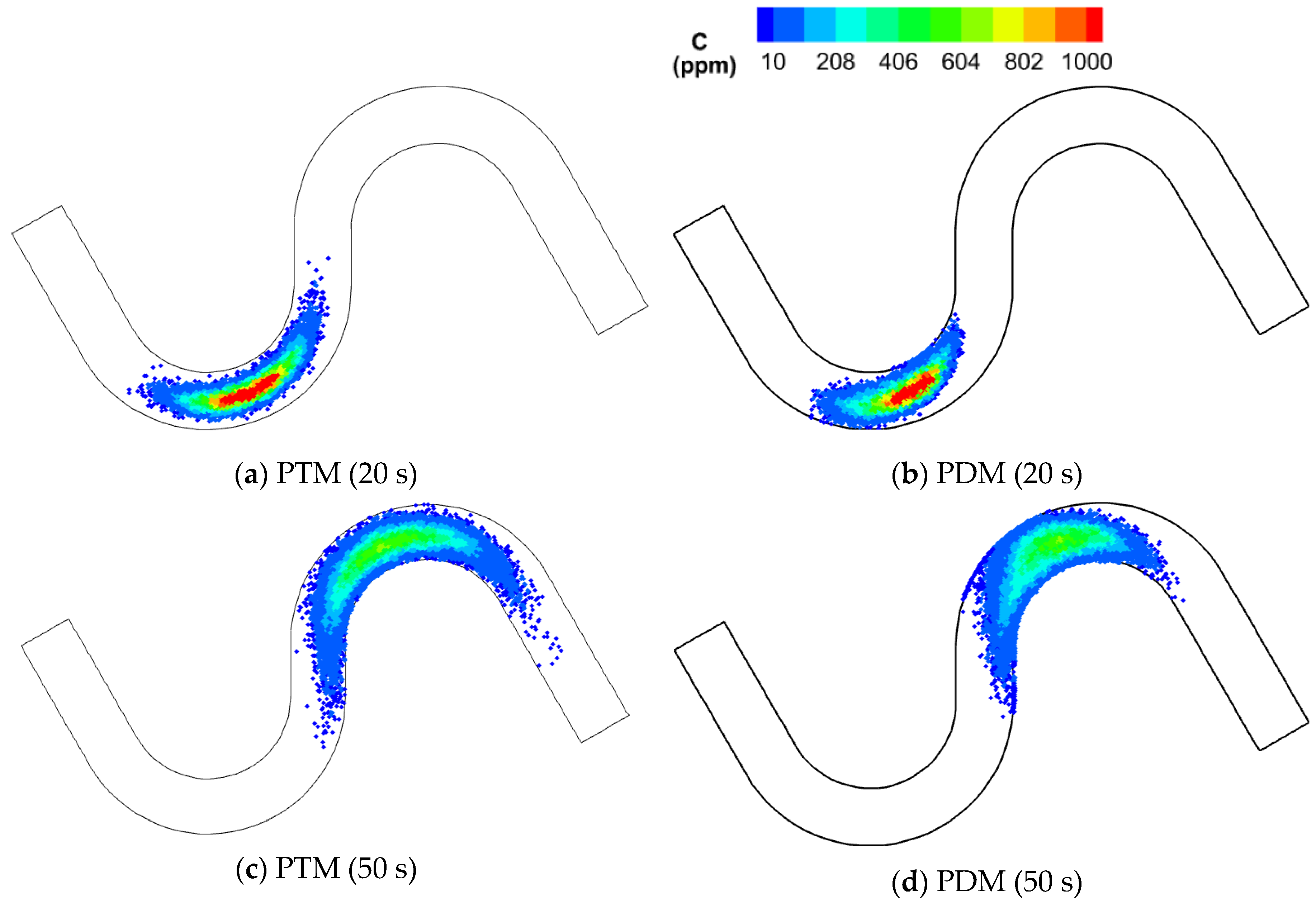
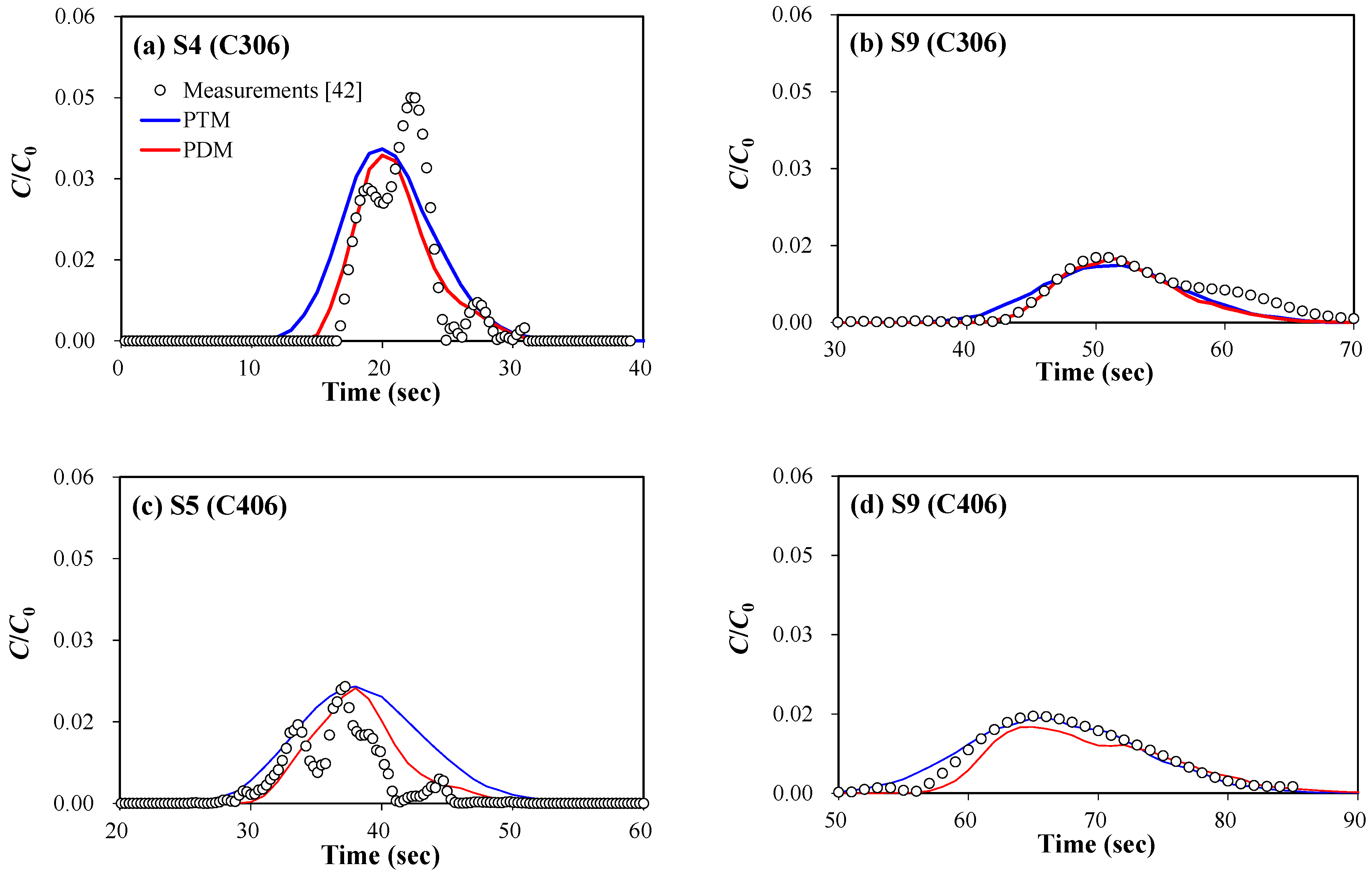


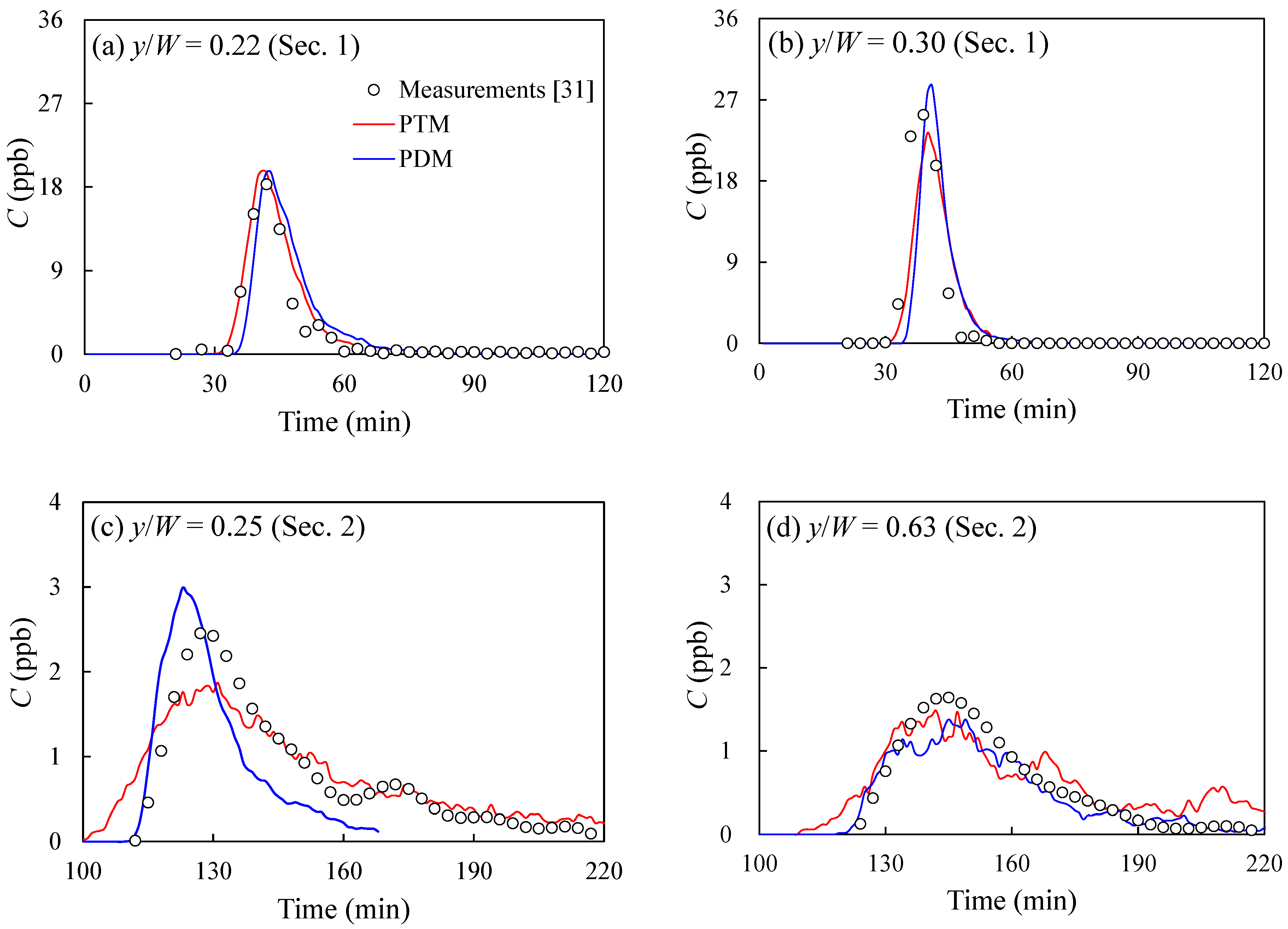
| Case | Q (m3/s) | h (m) | rc (m) | Manning’s nf | L | np |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C306 | 0.06 | 0.3 | 85 | 0.013 | 300 | 30,000 |
| C406 | 0.06 | 0.4 | 90 | 0.015 | 300 | 30,000 |
| Case | Conc. Curve | 1st Bend (S4 or S5) | 2nd Bend (S9) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements [42] | PTM | PDM | Measurements [42] | PTM | PDM | ||
| C306 | Rising part | −1.42 | −0.72 | −1.53 | −1.28 | −0.87 | −1.30 |
| Falling part | −1.13 | −0.71 | −1.06 | −0.68 | −0.72 | −1.13 | |
| C406 | Rising part | −1.24 | −0.92 | −1.59 | −1.60 | −0.87 | −1.74 |
| Falling part | −1.04 | −0.90 | −1.21 | −0.81 | −0.82 | −0.78 | |
| Case | Statistical Values | 1st Bend (S4 or S5) | 2nd Bend (S9) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements [42] | PTM | PDM | Measurements [42] | PTM | PDM | ||
| C306 | 0.045 | 0.035 | 0.034 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.012 | |
| (s) | 21.5 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 50.5 | 52.0 | 52.0 | |
| (s) | 22.3 | 20.7 | 21.1 | 54.2 | 51.5 | 52.2 | |
| 6.4 | 12.0 | 8.9 | 35.5 | 28.8 | 21.4 | ||
| 0.74 | 0.34 | 0.71 | 0.52 | 0.18 | 0.55 | ||
| C406 | 0.022 | 0.021 | 0.021 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.013 | |
| (s) | 36.5 | 38.0 | 38.0 | 65.3 | 66.0 | 65.0 | |
| (s) | 37.1 | 38.6 | 38.3 | 68.2 | 66.9 | 69.3 | |
| 17.2 | 23.7 | 13.0 | 43.1 | 44.02 | 40.7 | ||
| 0.61 | 0.33 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.62 | ||
| Q (m3/s) | h (m) | U (m/s) | rc (m) | Manning’s nf | L | np |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.15 | 0.91 | 0.05 | 148 | 0.036 | 200 | 20,000 |
| Statistical Values | Sec. 1 (y/W = 0.30) | Sec. 2 (y/W = 0.25) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements [31] | PTM | PDM | Measurements [31] | PTM | PDM | |
| (ppb) | 25.4 | 23.3 | 28.6 | 2.50 | 1.9 | 3.0 |
| (min) | 36.4 | 40.0 | 41.0 | 127.0 | 131.0 | 123.0 |
| (min) | 39.2 | 41.6 | 42.5 | 138.5 | 146.5 | 147.9 |
| 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.70 | 1.06 | 0.82 | 1.02 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, I.; Shin, J.; Seong, H.; Rhee, D.S. Comparisons of Two Types of Particle Tracking Models Including the Effects of Vertical Velocity Shear. Water 2020, 12, 3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123535
Park I, Shin J, Seong H, Rhee DS. Comparisons of Two Types of Particle Tracking Models Including the Effects of Vertical Velocity Shear. Water. 2020; 12(12):3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123535
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Inhwan, Jaehyun Shin, Hoje Seong, and Dong Sop Rhee. 2020. "Comparisons of Two Types of Particle Tracking Models Including the Effects of Vertical Velocity Shear" Water 12, no. 12: 3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123535
APA StylePark, I., Shin, J., Seong, H., & Rhee, D. S. (2020). Comparisons of Two Types of Particle Tracking Models Including the Effects of Vertical Velocity Shear. Water, 12(12), 3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123535





