Filterability of Polysulfone Membrane in a Tilted Panel System for Activated Sludge Filtration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Preparation and Panel Assembly
2.2. Membrane Characterization
2.3. Activated Sludge (Feed)
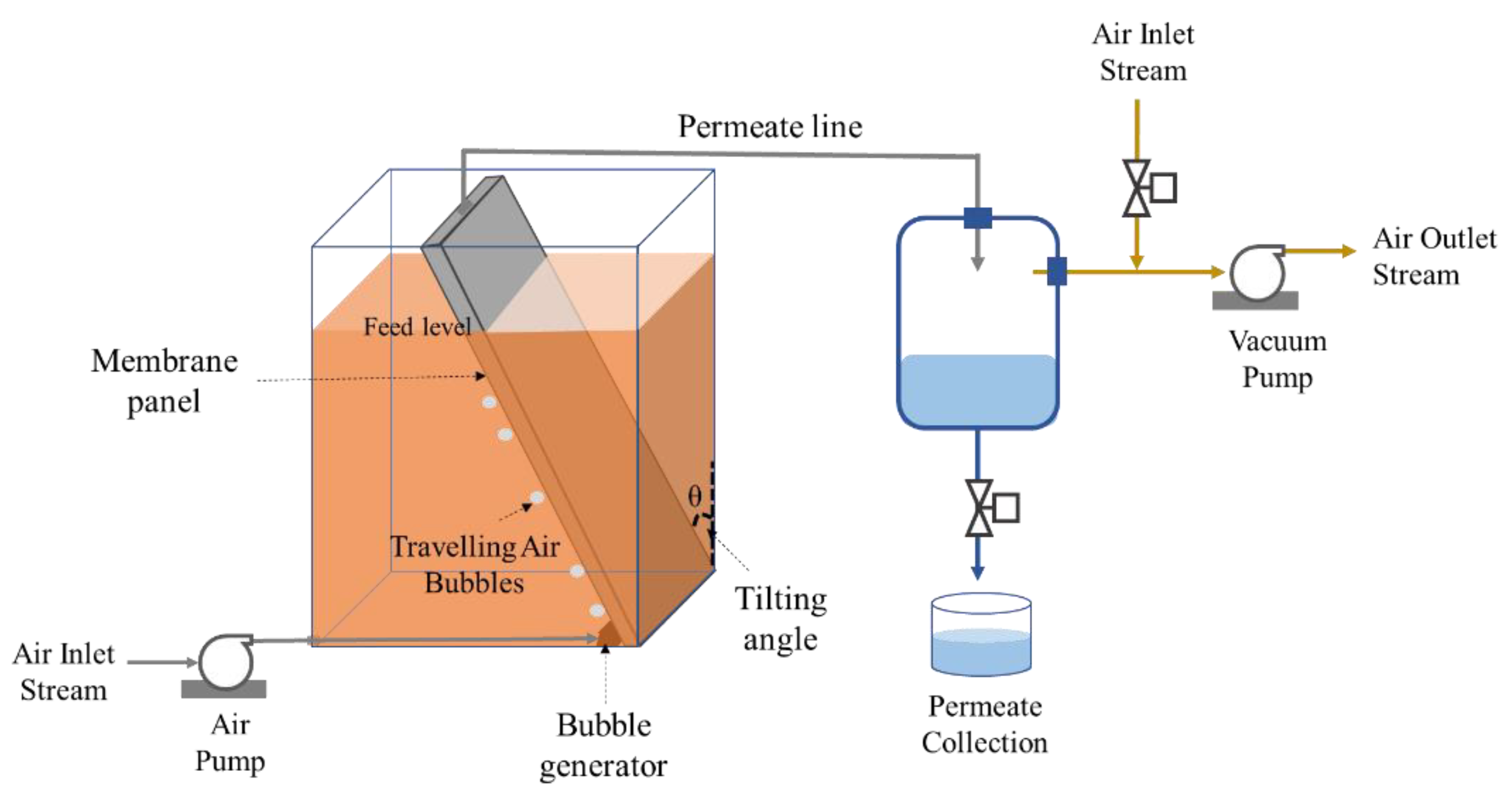
2.4. Filtration Set-Up
2.5. Filterability Test
3. Results and Discussion
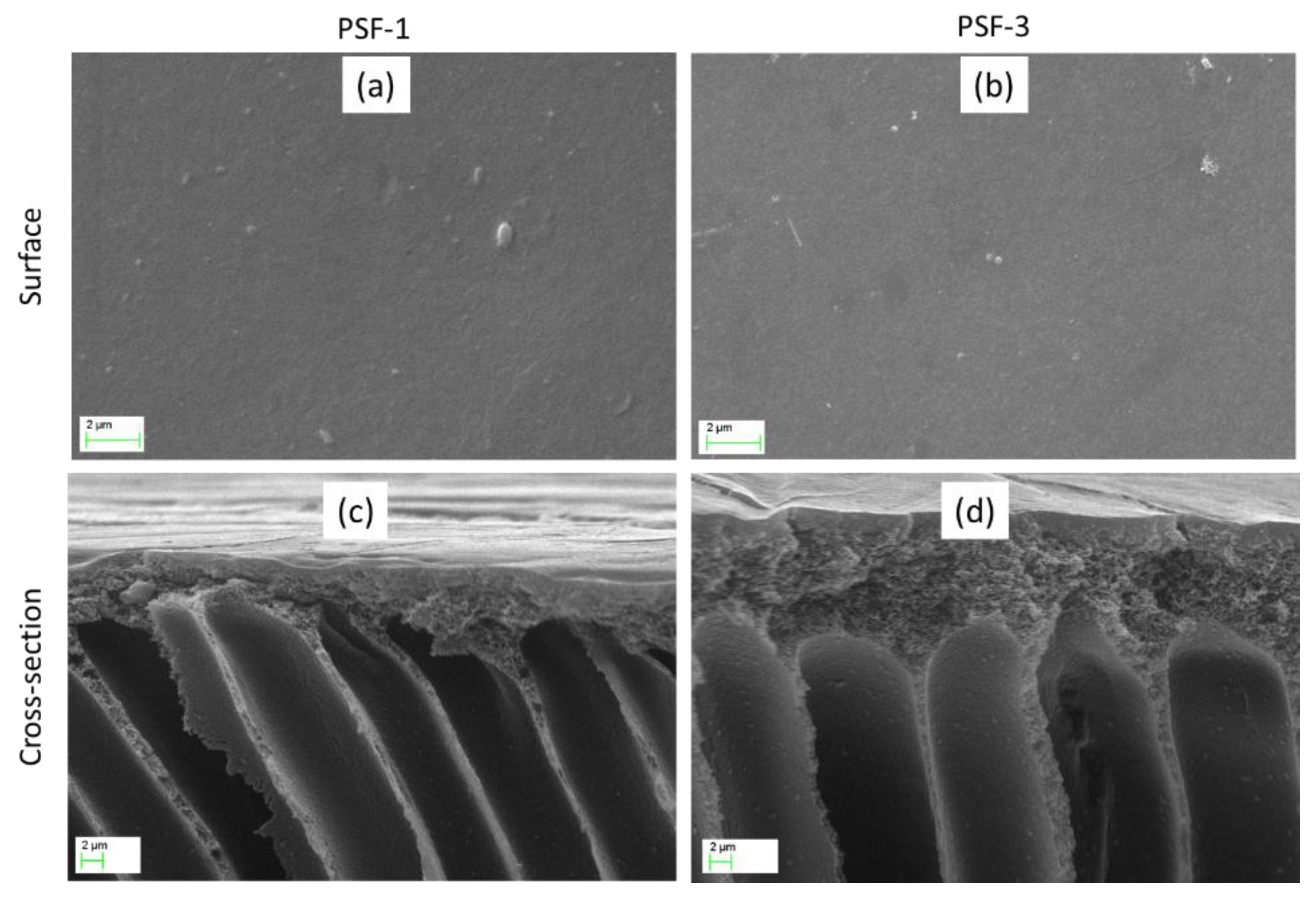
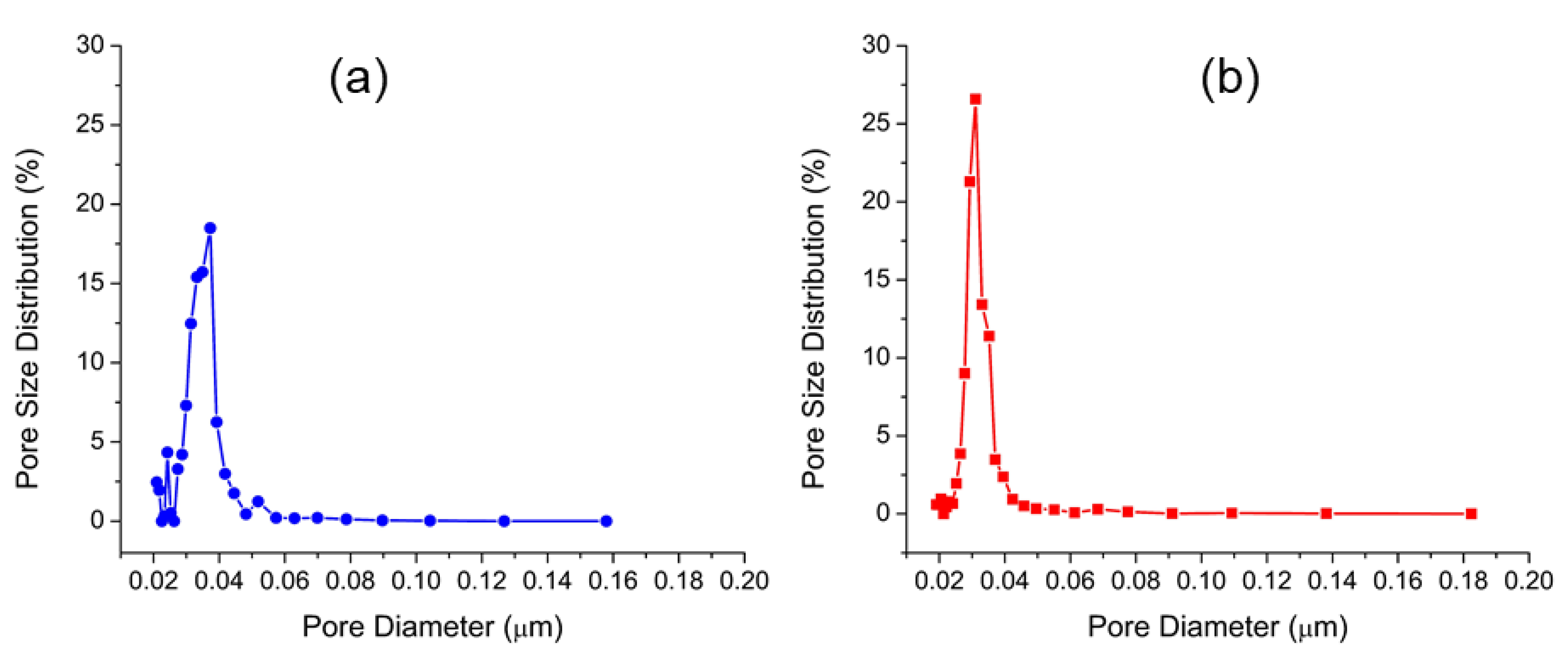
3.1. Membrane Characterization
3.2. Activated Sludge Filtration
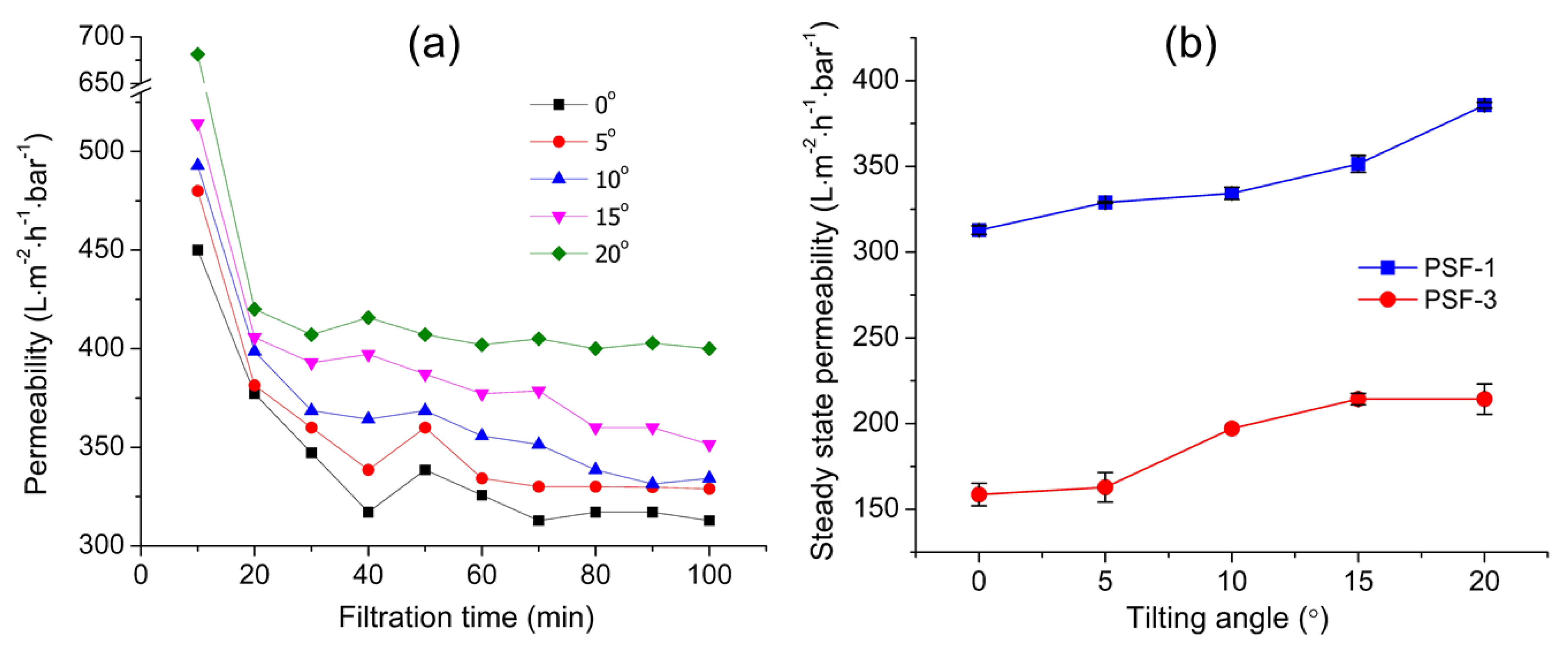
3.2.1. Effect of Tilting Angle
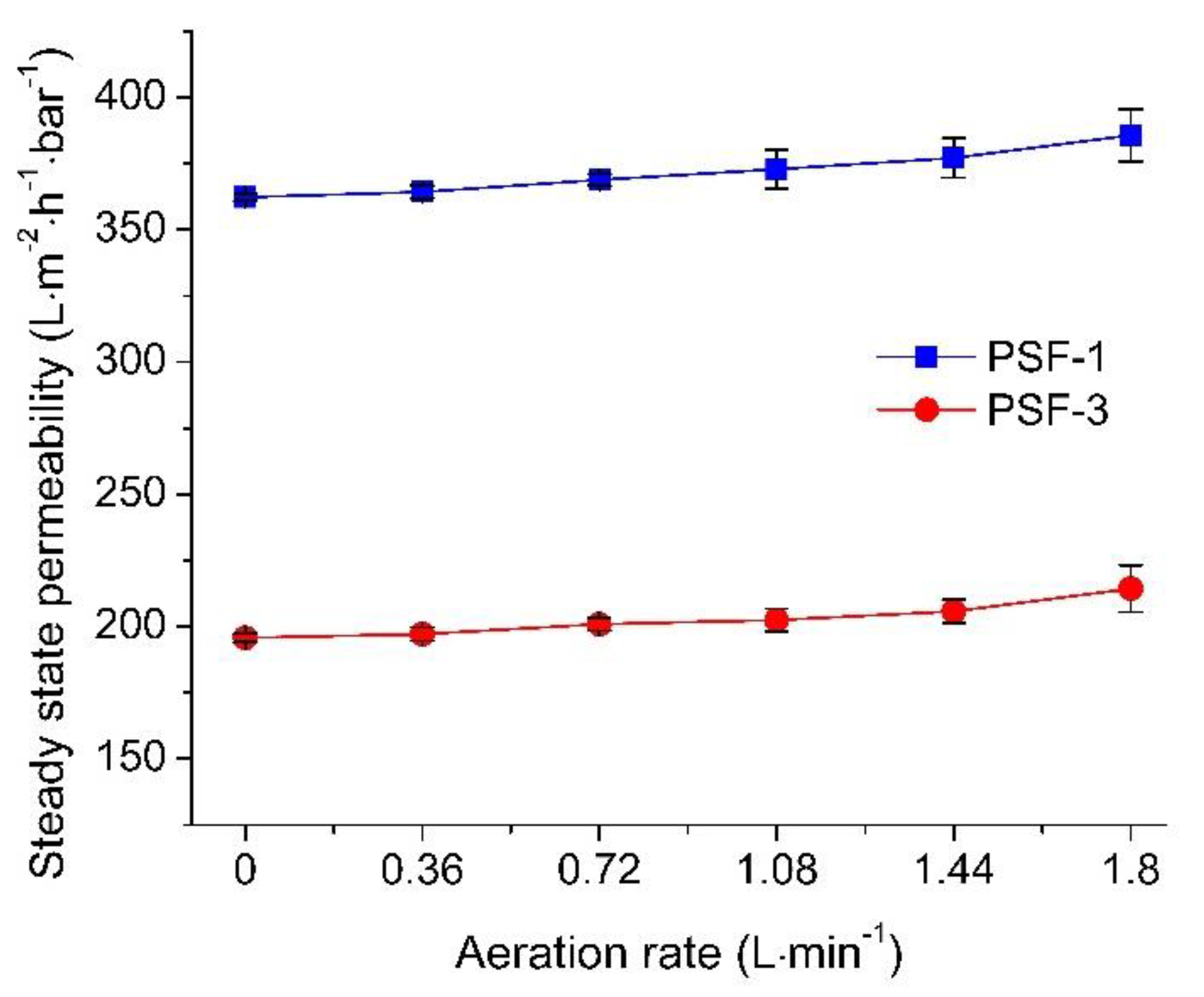
3.2.2. Effect of Aeration Rate
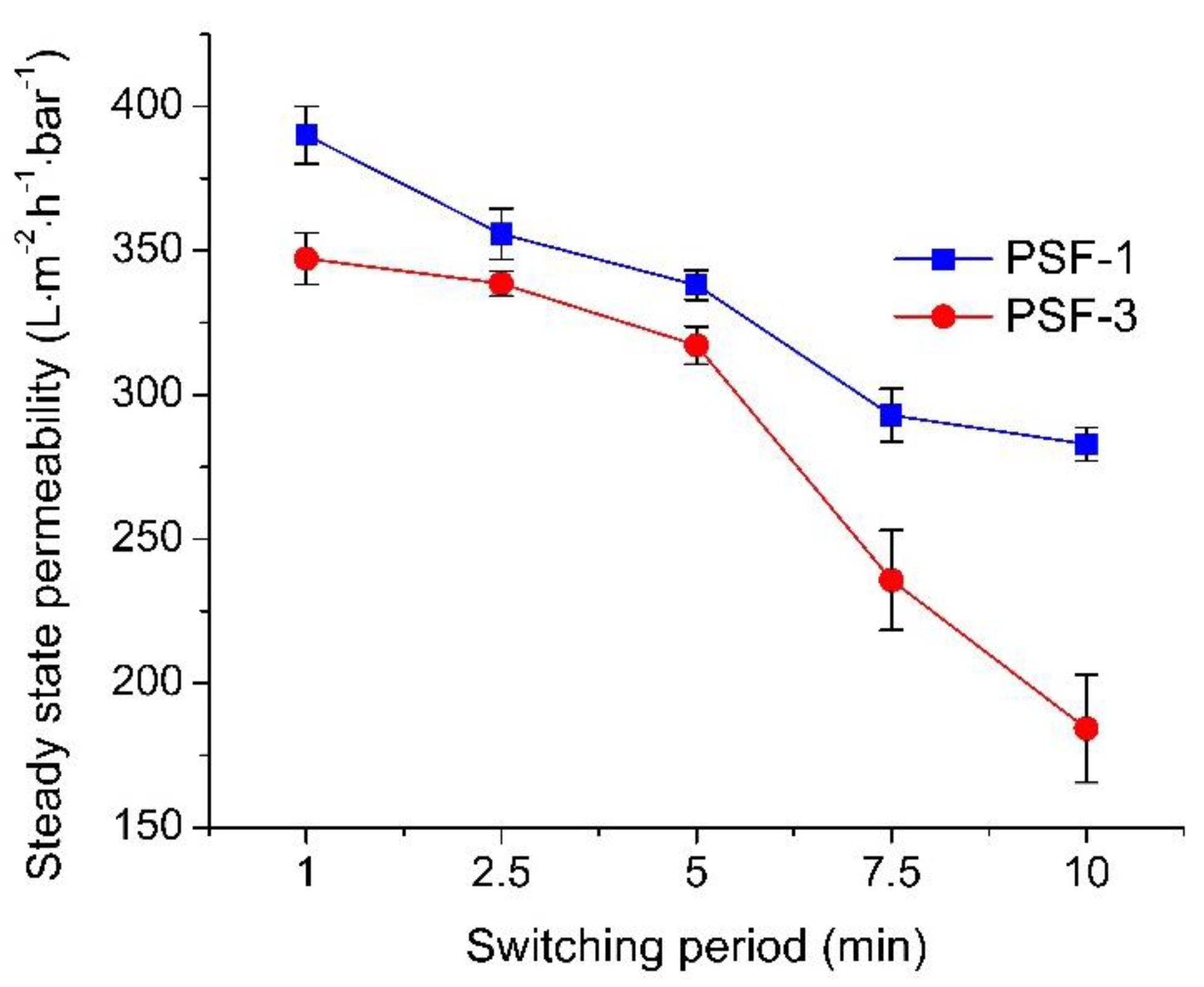
3.2.3. Effect of Switching Period/Intermittent Aeration
3.3. Effect of Membrane Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mutamim, N.S.A.; Noor, Z.Z.; Hassan, M.A.A.; Olsson, G. Application of membrane bioreactor technology in treating high strength industrial wastewater: A performance review. Desalination 2012, 305, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatilake, S. Methods of removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Methods 2015, 1, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, M.; Charfi, A.; Lesage, G.; Heran, M.; Kim, J. Membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: A review of mechanical cleaning by scouring agents to control membrane fouling. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Hamza, R.A.; Tay, J.H. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Membrane fouling. Membranes 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Xu, Y.; Liang, S.; Lei, T.; Sun, J.; Wen, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Engineering application of membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment in China: Current state and future prospect. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrance, L.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Gupta, B.; Paullier, P.; Geaugey, V. Contribution of various constituents of activated sludge to membrane bioreactor fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 73, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Marel, P.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Kemperman, A.; Wessling, M.; Temmink, H.; van der Meer, W. Influence of membrane properties on fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Bae, T.-H.; Tak, T.; Hong, S.; Randall, A. Fouling control in activated sludge submerged hollow fiber membrane bioreactors. Desalination 2002, 143, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.; Oh, Y.-K.; Kim, B.; Han, J.-I. Dramatic improvement of membrane performance for microalgae harvesting with a simple bubble-generator plate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.-S.; Chen, H.-L.; Chen, Y.-S. Membrane fouling and resistance analysis in dead-end ultrafiltration of Bacillus subtilis fermentation broths. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, K.-H. Effect of PEG additive on membrane formation by phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 138, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Khataee, A.; Safarpour, M.; Orooji, Y.; Vatanpour, V. A review on the applications of ultrasonic technology in membrane bioreactors. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, K.A.; Das, C. Effects of solubility parameter differences among PEG, PVP and CA on the preparation of ultrafiltration membranes: Impacts of solvents and additives on morphology, permeability and fouling performances. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Borea, L.; Belgiorno, V. Sonochemical control of fouling formation in membrane ultrafiltration of wastewater: Effect of ultrasonic frequency. J. Water Process. Eng. 2015, 8, e92–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Subramaniam, D.D.; Shamsuddin, N.; Khan, A.L.; Jaafar, J.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D. Low-pressure submerged membrane filtration for potential reuse of detergent and water from laundry wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 36, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseus, A.; Bilad, M.R.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Khan, A.L.; Putra, Z.A.; Wirzal, M.D.H.; Aslam, M.; Aqsha, A.; Jaafar, J. Two-way switch: Maximizing productivity of tilted panel in membrane bioreactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseus, A.; Bilad, M.; Nordin, N.; Putra, Z.; Wirzal, M. Tilted membrane panel: A new module concept to maximize the impact of air bubbles for membrane fouling control in microalgae harvesting. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Nawi, M.; Izati, N.; Samsuri, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Shamsuddin, N.; Khan, A.L.; Jaafar, J.; Nordin, N.A.H. Patterned Membrane in an Energy-Efficient Tilted Panel Filtration System for Fouling Control in Activated Sludge Filtration. Polymers 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Zain, N.M.; Noordin, M. Synthesis, characterization and performance of asymmetric polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membranes with polyethylene glycol of different molecular weights as additives. Desalination 2007, 207, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Okamura, R.; Ishigami, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Kato, N.; Matsuyama, H. The effect of membrane material and surface pore size on the fouling properties of submerged membranes. Water 2016, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Meng, J.; Ye, J.; Yang, B.; Tian, Q.; Deng, C. Surface modification of PES ultrafiltration membrane by polydopamine coating and poly (ethylene glycol) grafting: Morphology, stability, and anti-fouling. Desalination 2014, 344, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.H.; Shi, X. Pore fouling of microfiltration membranes by activated sludge. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 264, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Nawi, N.I.; Chean, H.M.; Shamsuddin, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Khan, A.L. Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ivars, J.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.-I.; Iborra-Clar, M.-I.; Mendoza-Roca, J.-A.; Pastor-Alcañiz, L. Enhancement in hydrophilicity of different polymer phase-inversion ultrafiltration membranes by introducing PEG/Al2O3 nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Purkait, M. Increase in hydrophilicity of polysulfone membrane using polyethylene glycol methyl ether. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-L.; Cheng, W.; Li, C.; Jiang, Z. Preparation of antifouling ultrafiltration membranes with poly (ethylene glycol)-graft-polyacrylonitrile copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 329, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.L.; Qusay, F.A. Effect of polyethylene glycol molecular weights and concentrations on polyethersulfone hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 3398–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunos, M.Z.; Harun, Z.; Basri, H.; Ismail, A.F. Studies on fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) on polysulfone membranes: Effect of polyethylene glycol (PEG). Desalination 2014, 333, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioan, C.; Robescu, D.N. Effect of increased inflow and dilution on the activated sludge properties and viability of microbial community. UPB Sci. Bull 2015, 77, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Eliseus, A.; Putra, Z.; Bilad, M.; Nordin, N.; Wirzal, M.; Jaafar, J.; Khan, A.L. Energy minimization of a tilted panel filtration system for microalgae filtration: Performance modeling and optimization. Algal Res. 2018, 34, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujihara, R.; Mino, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Matsuyama, H. Effects of the ionic strength of sodium hypochlorite solution on membrane cleaning. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, D. Contact angle measurement for the surface characterization of solids. Himal. Phys. 2011, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shi, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C. Effect of PEG additive on the morphology and performance of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2011, 272, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.K.; Bilad, M.; Nordin, N.; Faungnawakij, K.; Narkkun, T.; Wang, D.K.; Mahlia, T.; Jaafar, J. Effect of membrane properties on tilted panel performance of microalgae biomass filtration for biofuel feedstock. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 120, 109666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, M.; Izati, N.; Abd Halim, N.S.; Lee, L.C.; Wirzal, M.D.H.; Bilad, M.R.; Nordin, N.A.H.; Putra, Z.A. Improved Nylon 6, 6 Nanofiber Membrane in A Tilted Panel Filtration System for Fouling Control in Microalgae Harvesting. Polymers 2020, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, N.N.A.N.; Rahmawati, R.; Bilad, M.R.; Pratiwi, A.E.; Elma, M.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Jaafar, J.; Lam, M.K. Finned spacer for enhancing the impact of air bubbles for membrane fouling control in Chlorella vulgaris filtration. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Yuasa, K.; Ishigami, T.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Kamio, E.; Ohmukai, Y.; Saeki, D.; Ni, J.; Matsuyama, H. Effect of membrane polymeric materials on relationship between surface pore size and membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.-H.; Tak, T.-M. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on fouling mitigation of ultrafiltration membranes for activated sludge filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoonfal, M.; Mehrnia, M.R.; Rahmani, S.; Mojtahedi, Y.M. Fabrication of alumina/polysulfone nanocomposite membranes with biofouling mitigation approach in membrane bioreactors. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 22, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Code | PEG Loading (%) | Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pore Morphology | Pore Size (μm) | Membrane Thickness (μm) | Contact Angle (°) | Clean Water Permeability (L·m−2·h−1·bar−1) | ||
| PSF-1 | 1 | Asymmetric | 0.04 | 261 ± 5 | 67.9 ± 1.0 | 923 ± 54 |
| PSF-3 | 3 | Asymmetric | 0.03 | 288 ± 3 | 61.8 ± 1.0 | 817 ± 35 |
| System Configuration | Permeability (L·m−2·h−1·bar−1) | Type of Membrane and Materials | Membrane Properties | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Angle (°) | Pore Size (µm) | CWP (L·m−2·h−1·bar−1) | ||||
| Tilted panel with aeration submerged membrane | 390 | Flat sheet (PSF + PEG) | 67.9 | 0.04 | 817 | This study |
| Crossflow filtration | 226 | Flat sheet (PSF + TiO2) | 73.1 | - | 230 | [38] |
| MBR with air scouring | 200 | Hollow fiber (PSF) | - | 0.10 | - | [8] |
| Crossflow filtration | 4 | Flat sheet (PSF + Al2O3) | 51 | - | 692 | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, A.A.A.; Mulyati, S.; Aprilia, S.; Yusoff, M.H.M.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Ismail, A.F.; Arahman, N. Filterability of Polysulfone Membrane in a Tilted Panel System for Activated Sludge Filtration. Water 2020, 12, 3533. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123533
Ismail AAA, Mulyati S, Aprilia S, Yusoff MHM, Nawi NIM, Bilad MR, Ismail AF, Arahman N. Filterability of Polysulfone Membrane in a Tilted Panel System for Activated Sludge Filtration. Water. 2020; 12(12):3533. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123533
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Ahmad Aliyan Alif, Sri Mulyati, Sri Aprilia, Mohd Hizami Mohd Yusoff, Normi Izati Mat Nawi, Muhammad Roil Bilad, Ahmad Fauzi Ismail, and Nasrul Arahman. 2020. "Filterability of Polysulfone Membrane in a Tilted Panel System for Activated Sludge Filtration" Water 12, no. 12: 3533. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123533
APA StyleIsmail, A. A. A., Mulyati, S., Aprilia, S., Yusoff, M. H. M., Nawi, N. I. M., Bilad, M. R., Ismail, A. F., & Arahman, N. (2020). Filterability of Polysulfone Membrane in a Tilted Panel System for Activated Sludge Filtration. Water, 12(12), 3533. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123533









