Downscaling Regional Hydrological Forecast for Operational Use in Local Early Warning: HYPE Models in the Sirba River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
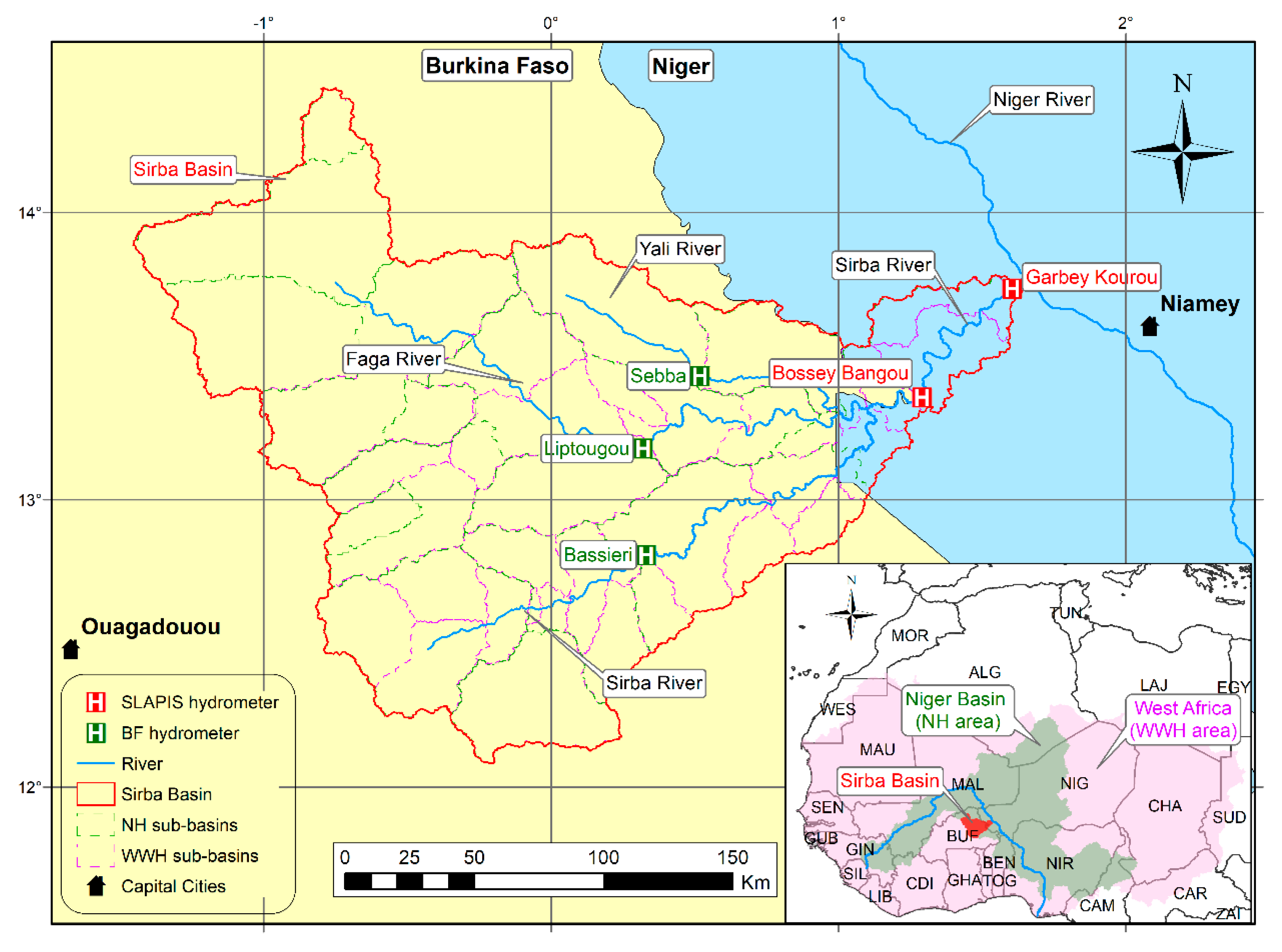
2.1. Study Area
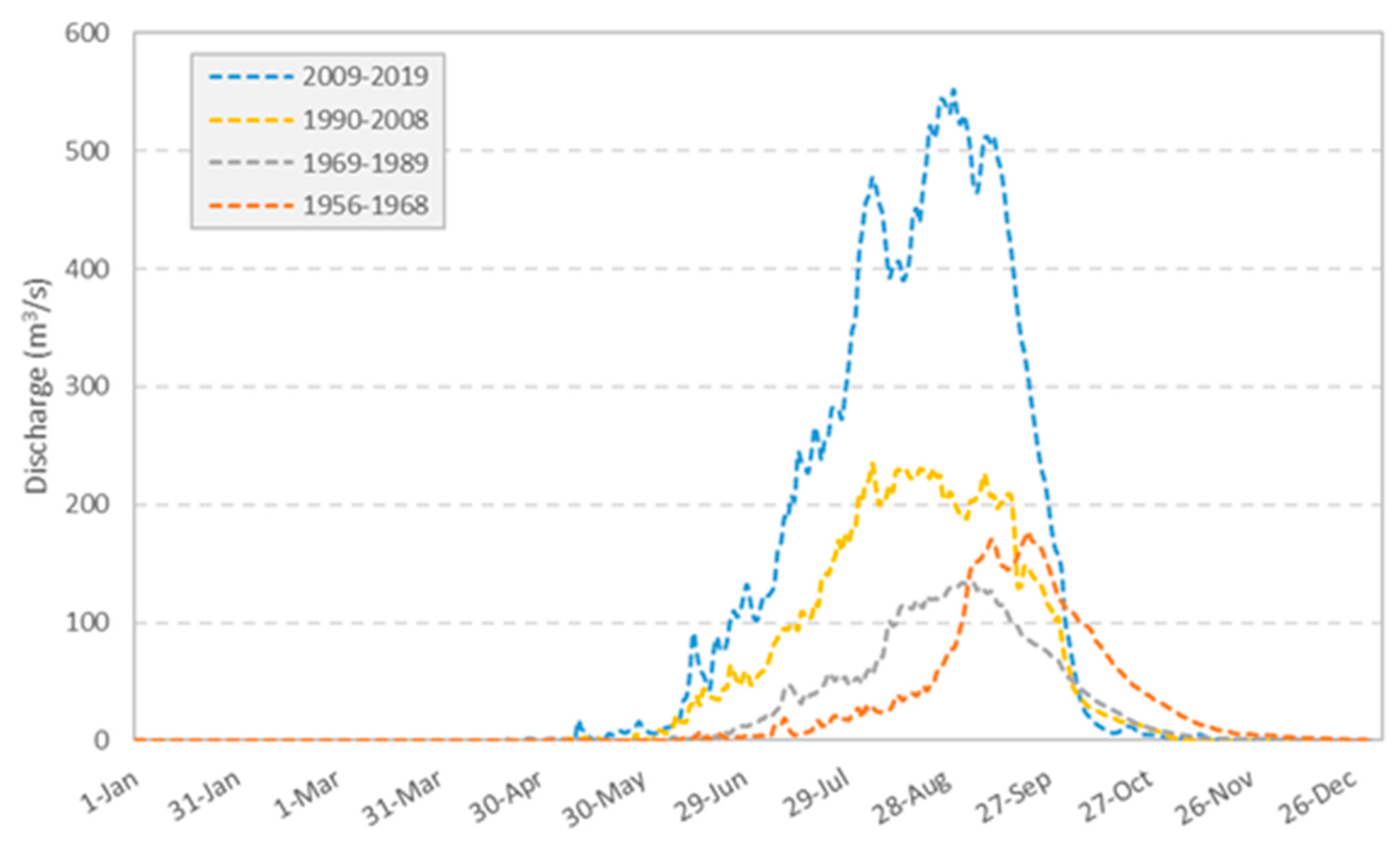
2.2. Sirba Hydrology and Observed Flow Series
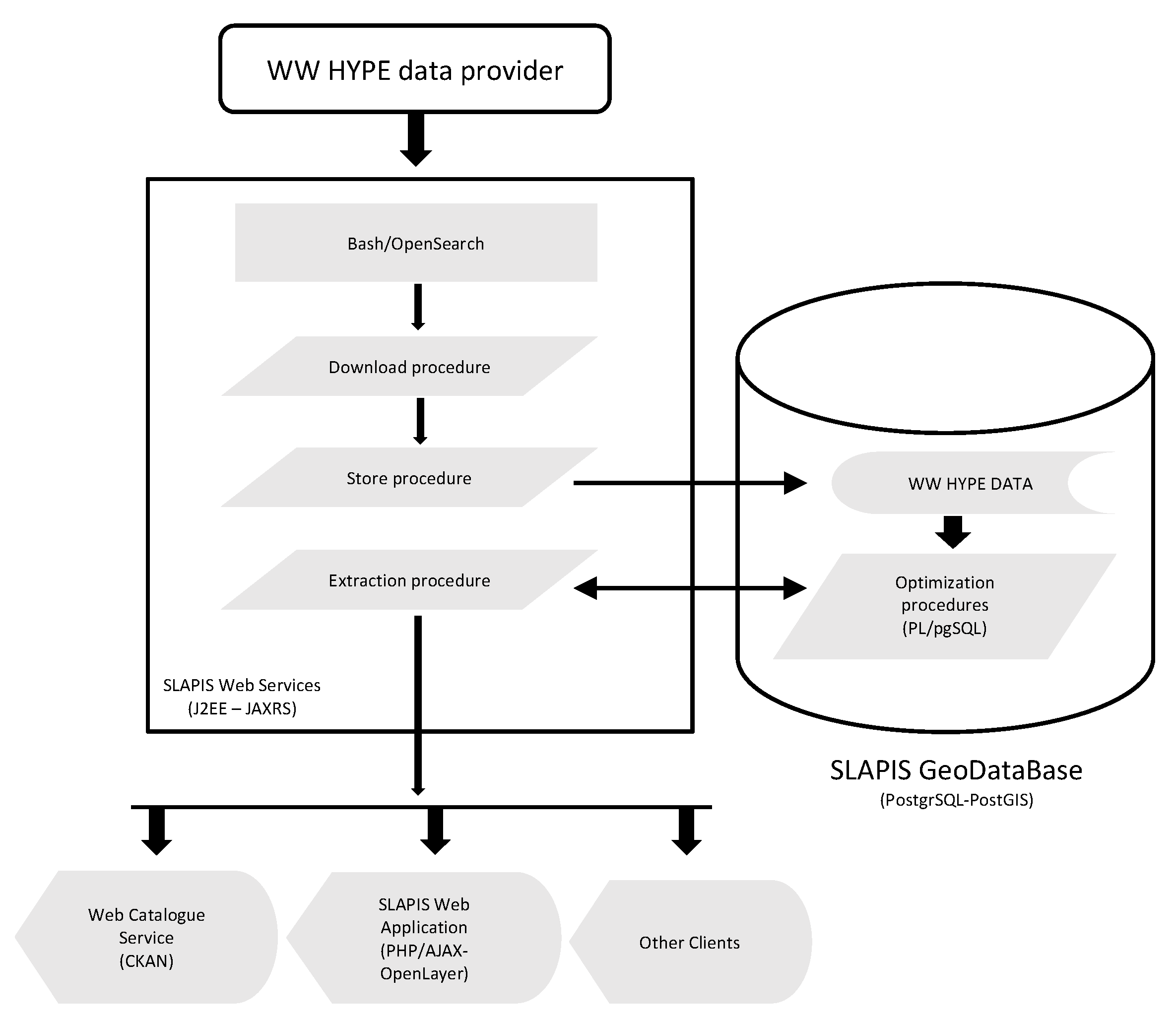
2.3. SLAPIS: the Sirba EWS
2.4. The FANFAR System, HYPE Models and Forecasted Streamflow
2.5. Hazard Thresholds
3. Methods
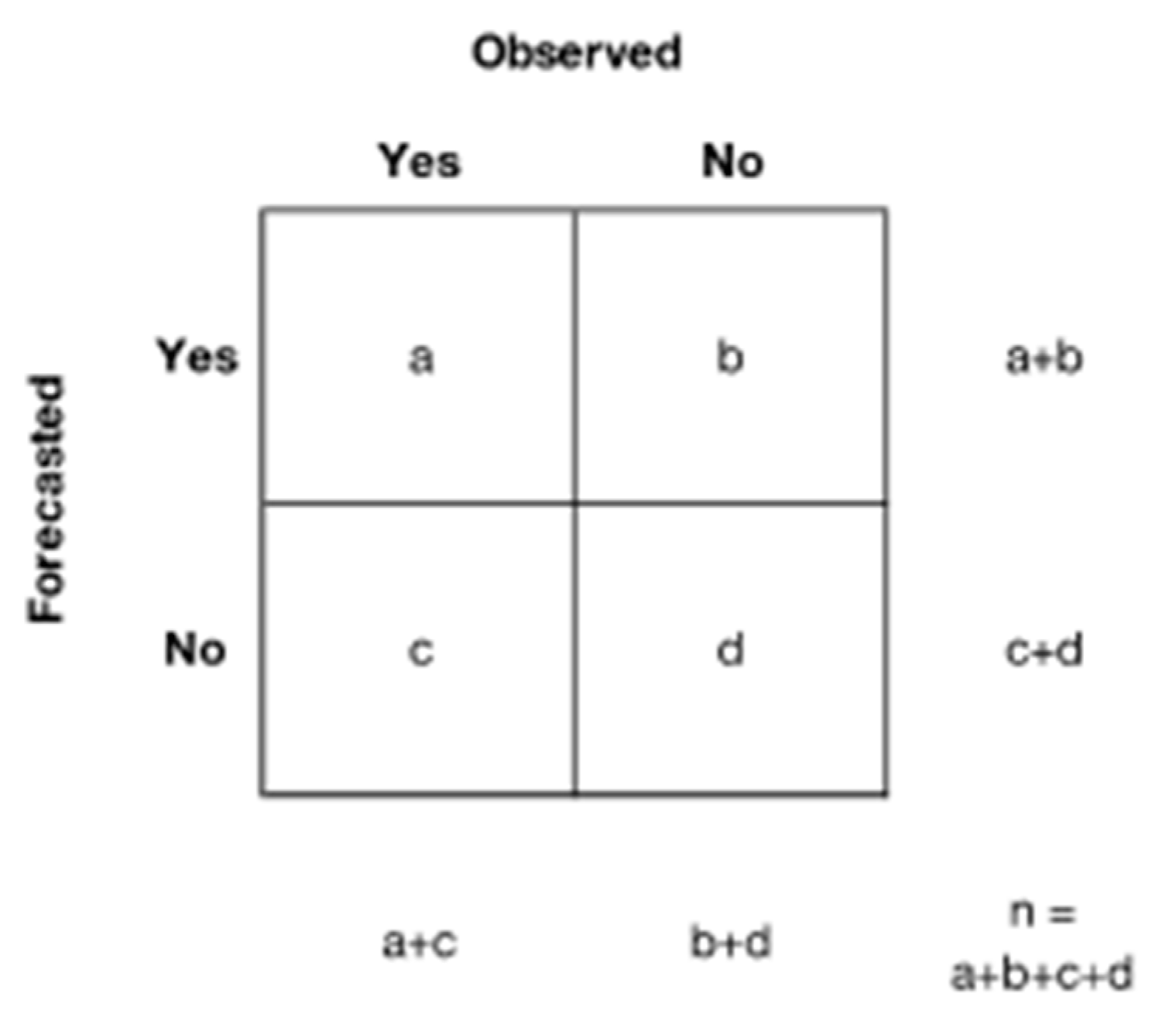
3.1. Model Evaluation
3.2. Model Optimization
4. Results
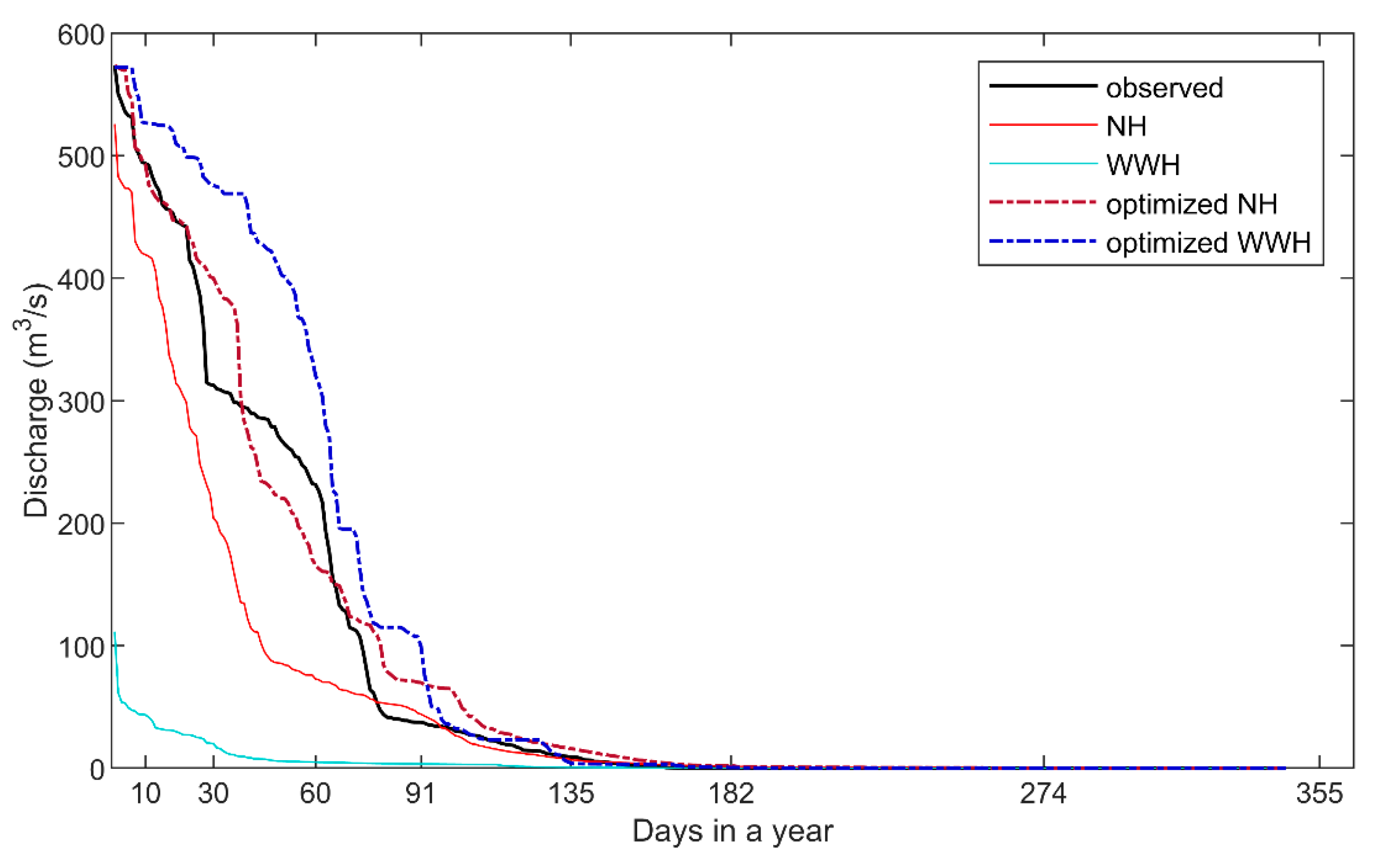
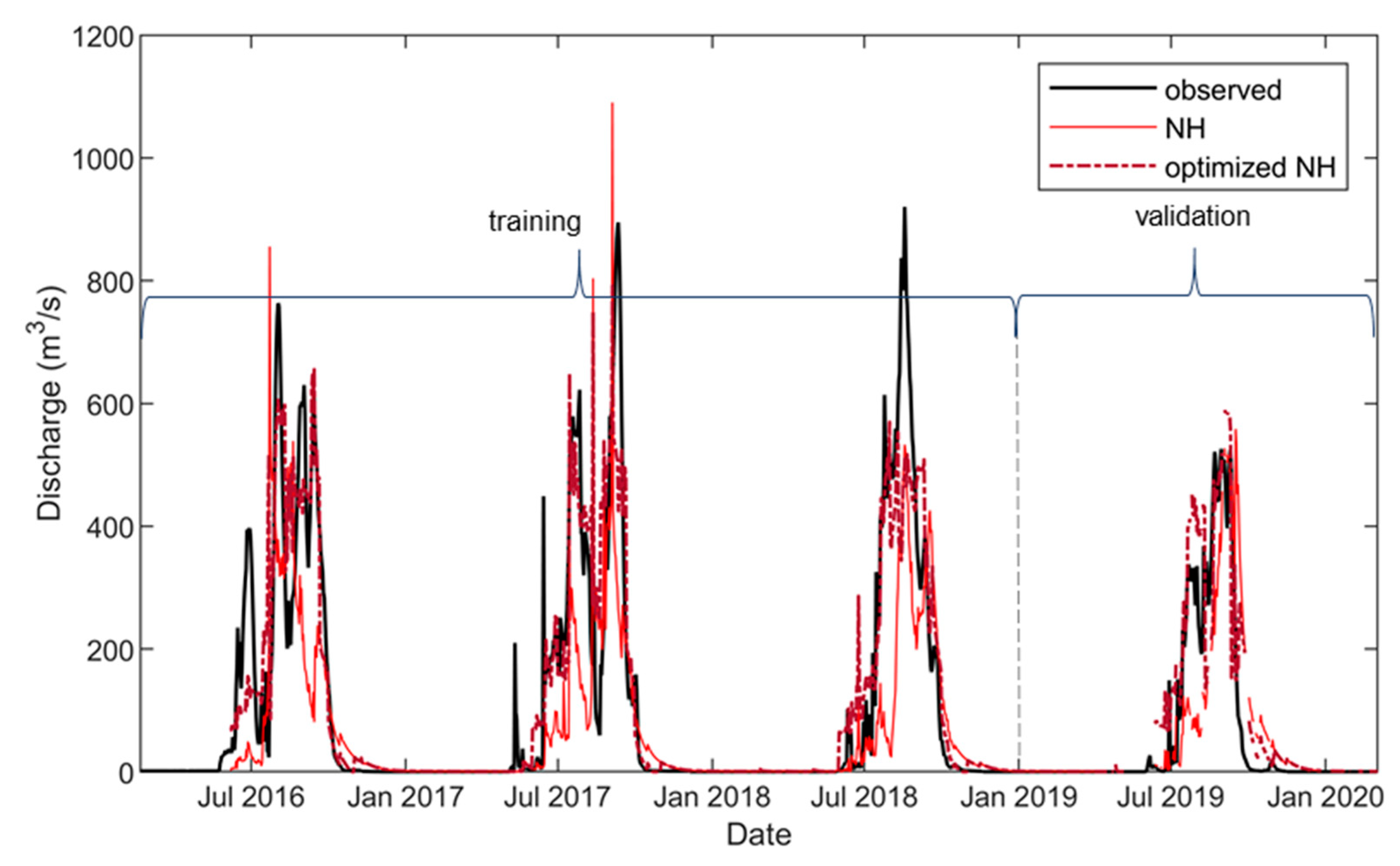
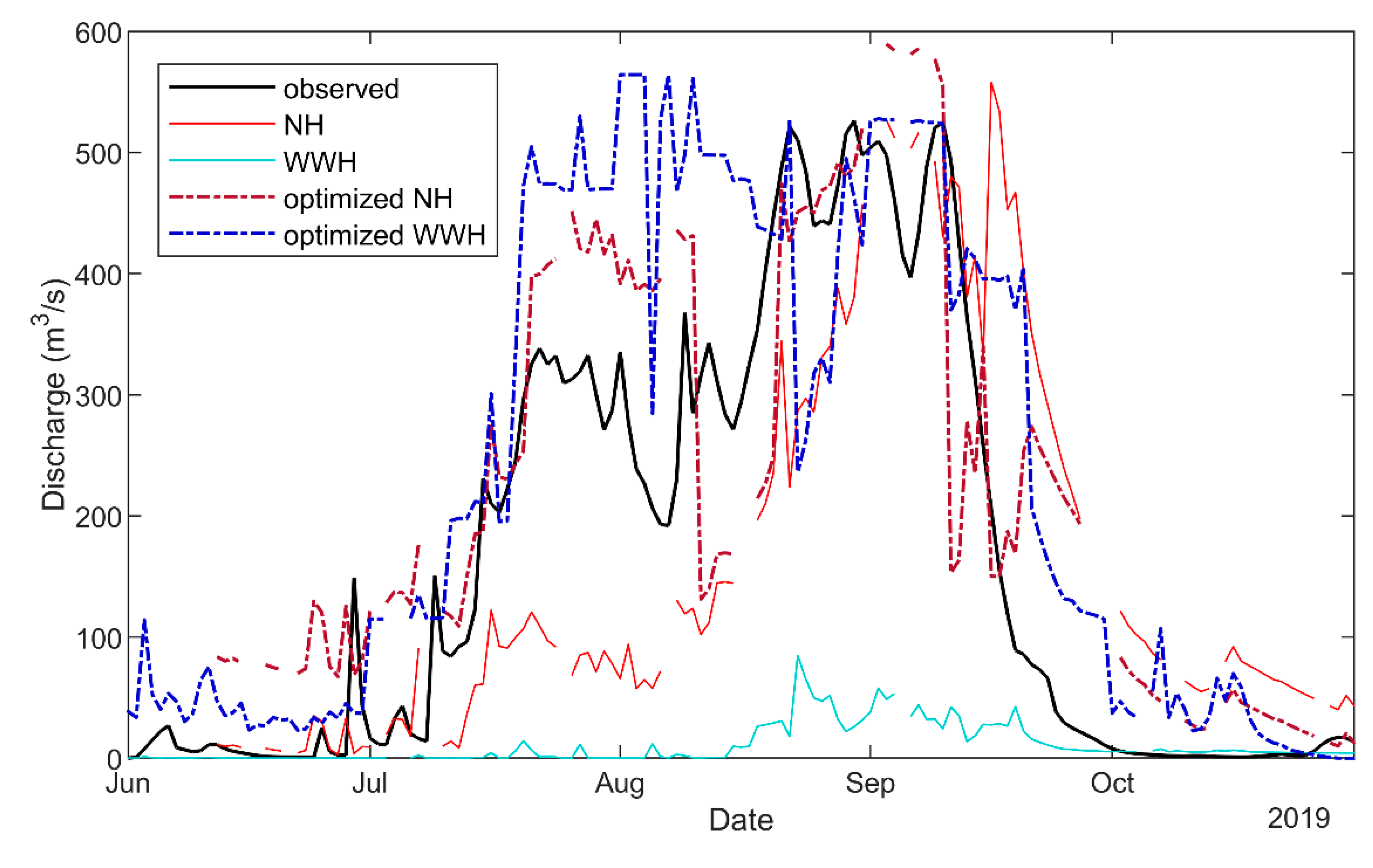
4.1. Forecast Performances
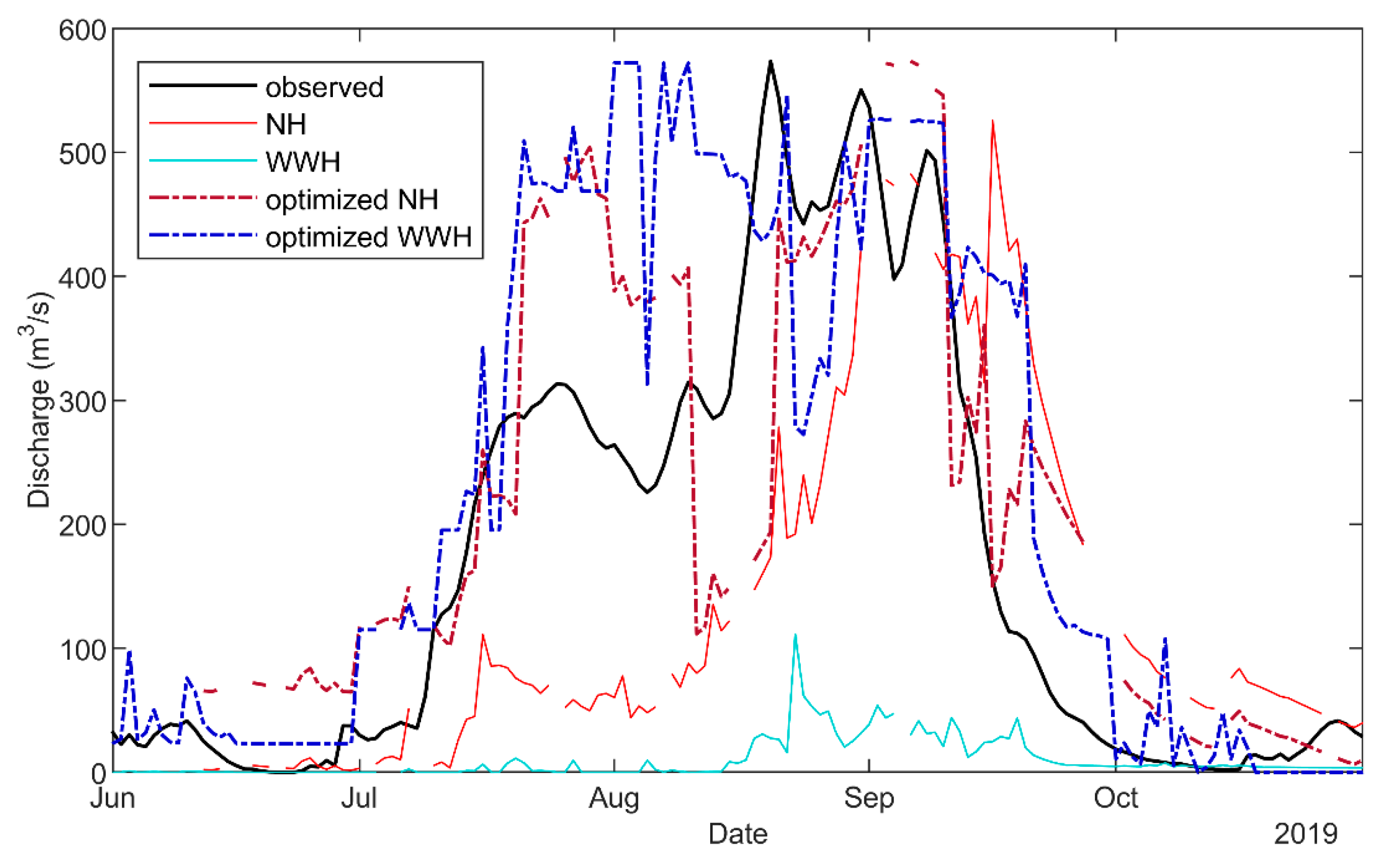
4.2. SLAPIS Operational Application
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Index | Observed | NH | WWH | Optimized NH | Optimized WWH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum (m3/s) | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Mean (m3/s) | 75.1 | 66.6 | 5.3 | 107.0 | 114.0 |
| Maximum (m3/s) | 573.5 | 525.8 | 111.4 | 573.7 | 572.0 |
| Model | RMSE | RSR | NSE | BIAS | POD | FAR | PC | TS | HSS | Operational Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH | 102.6 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.92 | 0.38 | 0.58 | 94.2 | 0.25 | 0.37 | 81% |
| WWH | 161.3 | 1.04 | −0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | / | 94.7 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 92% |
| NHOTT | 74.1 | 0.44 | 0.80 | 1.31 | 0.85 | 0.35 | 96.9 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 81% |
| WWHOTT | 87.1 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 2.50 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 88.1 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 92% |
| Model | RMSE | RSR | NSE | BIAS | POD | FAR | PC | TS | HSS | Operational Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH | 112.7 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 81% |
| WWH | 161.8 | 1.05 | −0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | / | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 92% |
| NHOTT | 78.3 | 0.47 | 0.78 | 1.13 | 0.40 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 81% |
| WWHOTT | 86.80 | 0.57 | 0.68 | 2.22 | 0.50 | 0.78 | 0.87 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 92% |
References
- Aich, V.; Koné, B.; Hattermann, F.F.; Paton, E.N. Time series analysis of floods across the Niger River Basin. Water 2016, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Descroix, L.; Genthon, P.; Amogu, O.; Rajot, J.L.; Sighomnou, D.; Vauclin, M. Change in Sahelian Rivers hydrograph: The case of recent red floods of the Niger River in the Niamey region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 98, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descroix, L.; Guichard, F.; Grippa, M.; Lambert, L.A.; Panthou, G.; Mahé, G.; Gal, L.; Dardel, C.; Quantin, G.; Kergoat, L.; et al. Evolution of Surface Hydrology in the Sahelo-Sudanian Strip: An Updated Review. Water 2018, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Descroix, L.; Bouzou, I.; Genthon, P.; Sighomnou, D.; Mahe, G.; Mamadou, I.; Vandervaere, J.P.; Gautier, E.; Faran, O.; Rajot, J.L.; et al. Impact of Drought and Land—Use Changes on Surface—Water Quality and Quantity: The Sahelian Paradox. In Current Perspectives in Contaminant Hydrology and Water Resources Sustainability; Bradley, P., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1046-0. [Google Scholar]
- Descroix, L. Processus et Enjeux D’eau en Afrique de L’ouest Soudano-Sahélienne; Editions des archives contemporaines: Paris, France, 2018; ISBN 978-2-8130-0314-0. [Google Scholar]
- Descroix, L.; Mahé, G.; Lebel, T.; Favreau, G.; Galle, S.; Gautier, E.; Olivry, J.C.; Albergel, J.; Amogu, O.; Cappelaere, B.; et al. Spatio-temporal variability of hydrological regimes around the boundaries between Sahelian and Sudanian areas of West Africa: A synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahe, G.; Lienou, G.; Descroix, L.; Bamba, F.; Paturel, J.E.; Laraque, A.; Meddi, M.; Habaieb, H.; Adeaga, O.; Dieulin, C.; et al. The rivers of Africa: Witness of climate change and human impact on the environment: How climate and human changes impacted river regimes in Africa. Hydrol. Processes 2013, 27, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, V.; Liersch, S.; Vetter, T.; Andersson, J.C.M.; Müller, E.N.; Hattermann, F.F. Climate or land use? Attribution of changes in river flooding in the Sahel zone. Water 2015, 7, 2796–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthou, G.; Vischel, T.; Lebel, T. Recent trends in the regime of extreme rainfall in the Central Sahel. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3998–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahe, G.; Paturel, J.E.; Servat, E.; Conway, D.; Dezetter, A. The impact of land use change on soil water holding capacity and river flow modelling in the Nakambe River, Burkina-Faso. J. Hydrol. 2005, 300, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, E.; Maselli, F.; Tarchiani, V.; Vignaroli, P. Analysis of land degradation processes on a tiger bush plateau in South West Niger using MODIS and LANDSAT TM/ETM+ data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 62, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amogu, O.; Esteves, M.; Vandervaere, J.P.; Malam Abdou, M.; Panthou, G.; Rajot, J.L.; Souley Yéro, K.; Boubkraoui, S.; Lapetite, J.M.; Dessay, N.; et al. Runoff evolution due to land-use change in a small Sahelian catchment. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagnone, P.; Massazza, G.; Pezzoli, A.; Rosso, M. Hydrology of the Sirba River: Updating and Analysis of Discharge Time Series. Water 2019, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorillo, E.; Crisci, A.; Issa, H.; Maracchi, G.; Morabito, M.; Tarchiani, V. Recent Changes of Floods and Related Impacts in Niger Based on the ANADIA Niger Flood Database. Climate 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V.; Shirshov, G.S.; Melnikova, N.B.; Belleman, R.G.; Rusadi, F.I.; Broekhuijsen, B.J.; Gouldby, B.P.; Lhomme, J.; Balis, B.; Bubak, M.; et al. Flood early warning system: Design, implementation and computational modules. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 4, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, D.K.; Phaiju, A.G. Community Based Approach to Flood Early Warning in West Rapti River Basin of Nepal. J. Integr. Disaster Risk Manag. 2013, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Practical Action and Mercy Corps. Community Based Early Warning Systems in South and South East Asia; Practical Action and Mercy Corps: Rugby, UK, 2012; Available online: http://flagship4.nrrc.org.np/sites/default/files/documents/best-practice-learning-in-community-based-EWS.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Shukla, Y.; Mall, B. Enhancing Frontline Resilience: Transborder Community-Based Flood Early Warning System in India and Nepal. In Technologies for Development, Proceedings of the UNESCO Chair Conference on Technologies for Development, Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–6 May 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 201–212. ISBN 978-3-319-91067-3. [Google Scholar]
- Community Early Warning Systems: Guiding Principles; International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Alfieri, L.; Burek, P.; Dutra, E.; Krzeminski, B.; Muraro, D.; Thielen, J.; Pappenberger, F. GloFAS—Global ensemble streamflow forecasting and flood early warning. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 9, 12293–12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, S.; Zsoter, E.; Alfieri, L.; Prudhomme, C.; Salamon, P.; Wetterhall, F.; Barnard, C.; Cloke, H.; Pappenberger, F. GloFAS-ERA5 Operational Global River Discharge Reanalysis 1979-Present. Hydrol. Soil Sci. Hydrol. 2020, 12, 2043–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arheimer, B.; Pimentel, R.; Isberg, K.; Crochemore, L.; Andersson, J.C.M.; Hasan, A.; Pineda, L. Global catchment modelling using World-Wide HYPE (WWH), open data, and stepwise parameter estimation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartholmes, J.C.; Thielen, J.; Ramos, M.H.; Gentilini, S. The european flood alert system EFAS—Part 2: Statistical skill assessment of probabilistic and deterministic operational forecasts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pechlivanidis, I.G.; Crochemore, L.; Rosberg, J.; Bosshard, T. What are the key drivers controlling the quality of seasonal streamflow forecasts? Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.C.M.; Ali, A.; Arheimer, B.; Gustafsson, D.; Minoungou, B. Providing peak river flow statistics and forecasting in the Niger River basin. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2017, 100, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massazza, G.; Tamagnone, P.; Wilcox, C.; Belcore, E.; Pezzoli, A.; Vischel, T.; Panthou, G.; Housseini Ibrahim, M.; Tiepolo, M.; Tarchiani, V.; et al. Flood Hazard Scenarios of the Sirba River (Niger): Evaluation of the Hazard Thresholds and Flooding Areas. Water 2019, 11, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karen, M.; Kanmani, V.; Kanchan, M.D.; Shobha, Y.; Sumit, D.; Rajani, M. Urgent Case for Recovery: What We Can Learn from the August 2014 Karnali River Floods in Nepal; Zurich Insurance Group Ltd: Zürich, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tarchiani, V.; Massazza, G.; Rosso, M.; Tiepolo, M.; Pezzoli, A.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Katiellou, G.L.; Tamagnone, P.; Filippis, T.D.; Rocchi, L.; et al. Community and Impact Based Early Warning System for Flood Risk Preparedness: The Experience of the Sirba River in Niger. Sustainability 2020, 24, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiepolo, M.; Rosso, M.; Massazza, G.; Belcore, E.; Issa, S.; Braccio, S. Flood Assessment for Risk-Informed Planning along the Sirba River, Niger. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passerotti, G.; Massazza, G.; Pezzoli, A.; Bigi, V.; Zsótér, E.; Rosso, M. Hydrological Model Application in the Sirba River: Early Warning System and GloFAS Improvements. Water 2020, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, J.; Ali, A.; Arheimer, B.; Crochemore, L.; Gbobaniyi, B.; Gustafsson, D.; Hamatan, M.; Kuller, M.; Lienert, J.; Machefer, M.; et al. Flood forecasting and alerts in West Africa—Experiences from co-developing a pre-operational system at regional scale. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2020, Online, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiepolo, M.; Tarchiani, V. Risque et Adaptation Climatique Dans la Région Tillabéri, Niger; l’Harmattan Paris: Paris, France, 2016; ISBN 978-2-343-08493-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bigi, V.; Pezzoli, A.; Rosso, M. Past and Future Precipitation Trend Analysis for the City of Niamey (Niger): An Overview. Climate 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarhule, A. Damaging rainfall and flooding: The other Sahel hazards. Clim. Chang. 2005, 72, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climateservices.it. Available online: https://climateservices.it/anadia_blog/ (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- UNISDR. Developing Early Warning Systems: A Checklist; UNISDR: Bonn, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Système Locale d’Alerte Précoce pour les Inondations de la Sirba. Available online: www.slapis.niger.org (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Lienert, J.; Andersson, J.; Hofmann, D.; Silva Pinto, F.; Kuller, M. Report on the Co-Design Workshops in FANFAR to Create a Flood Forecast and Alert System for West Africa; Eawag and FANFAR Consortium: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://fanfar.eu/resources D2.2 Report on co-design process (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- FANFAR: Reinforced Cooperation to Provide Operational Flood Forecasting and Alerts in West Africa. Available online: https://fanfar.eu/ (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Andersson, J.C.M.; Arheimer, B.; Traoré, F.; Gustafsson, D.; Ali, A. Process refinements improve a hydrological model concept applied to the Niger River basin. Hydrol. Processes 2017, 31, 4540–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, J.; Santos, L.; Isberg, K.; Gustafsson, D.; Musuuza, J.; Minoungou, B.; Crochemore, L. FANFAR Deliverable D3.2—Report Documenting and Explaining the Hydrological Models; FANFAR Consortium: Norrköping, Sweden, 2020; p. 41. Available online: https://fanfar.eu/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2020/05/FANFAR-D3.2-Hydrological-Models.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Berg, P.; Donnelly, C.; Gustafsson, D. Near-real-time adjusted reanalysis forcing data for hydrology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, P.; Almén, F.; Bozhinova, D. HydroGFD3.0: A 25 km global near real-time updated precipitation and temperature data set. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020. Under Review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.; Vischel, T.; Panthou, G.; Bodian, A.; Blanchet, J.; Descroix, L.; Quantin, G.; Cassé, C.; Tanimoun, B.; Kone, S. Trends in hydrological extremes in the Senegal and Niger Rivers. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.; Singla, A.R.; Aggarwal, H. Service Oriented Architecture Adoption Trends: A Critical Survey. In Contemporary Computing. IC3 2012. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Parashar, M., Kaushik, D., Rana, O.F., Samtaney, R., Yang, Y., Zomaya, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical methods in the atmospheric sciences. In International Geophysics Series, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-12-751966-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, K.; Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S. Artificial neural network modeling of the rainfall-runoff process. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2517–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.W.K. Heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent covariance matrix estimation. Econometrica 1991, 59, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.; Santilano, A.; Godio, A. Particle swarm optimization of electromagnetic data with parallel computing in the 2D case. In Proceedings of the 23rd European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Malmo, Sweden, 3–7 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.; Godio, A.; Santilano, A.; Comina, C. Joint optimization of geophysical data using multi-objective swarm intelligence. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 1502–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. An improved multi-cores parallel artificial Bee colony optimization algorithm for parameters calibration of hydrological model. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 81, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, C. Automatic calibration a hydrological model using a master–slave swarms shuffling evolution algorithm based on self-adaptive particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Brubaker, K. Multi-objective model auto-calibration and reduced parameterization: Exploiting gradient-based optimization tool for a hydrologic model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 70, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutner, M.H. Applied Linear Statistical Models; McGraw-Hill International Edition; McGraw-Hill Irwin: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-07-112221-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, R.C.; Griffiths, W.E.; Lim, G.C. Principles of Econometrics, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-470-62673-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bischiniotis, K.; van den Hurk, B.; Zsoter, E.; Coughlan de Perez, E.; Grillakis, M.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Evaluation of a global ensemble flood prediction system in Peru. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1171–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, C.; Ernst, K.; Arheimera, B. A comparison of hydrological climate services at different scales by users and scientists. Clim. Serv. 2018, 11, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, L.G.G.; Orrell, T. Data Interoperability: A Practitioner’s Guide to Joining up Data in the Development Sector; United Nations World Data Forum (UNWDF): Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey, J.; Gasser, U. Interop: The Promise and Perils of Highly Interconnected Systems; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Niger HYPE | World-Wide HYPE |
|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.23 | 1.3.6 |
| Geographic Domain | Niger River Basin | West Africa |
| Area (million km2) | 2.1 | 8.9 |
| Sub-Basins (#) | 803 | 4581 |
| Average Sub-Basin Size (km2) | 2665 | 1870 |
| Sub-basins in Sirba Watershed (#) | 17 (3 in Niger) | 29 (6 in Niger) |
| ID of the Sub-Basins Used | 5004 (Garbey Kourou) 3529 + 3472 + 4786 (upstream Bossey Bangou) | 208596 (Garbey Kourou) 219145 (Bossey Bangou) |
| Forcing Data | HydroGFD v. 1 | HydroGFD v. 2 |
| Forecast Frequency | daily | daily |
| Time of Forecast Production | afternoon (16 h–17 h) | morning (11:30 h–12 h) |
| Analysis Period | 1 June 2016–3 March 2020 | 8 June 2017–3 March 2020 |
| Scenario | SLAPIS | Niger-HYPE | World-Wide HYPE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP (year) | Q (m3/s) | RP (year) | Q (m3/s) | RP (year) | Q (m3/s) | |
| Yellow | 5 | 600 | 2 | 480 | 2 | 96 |
| Orange | 10 | 800 | 5 | 700 | 5 | 163 |
| Red | 30 | 1500 | 30 | 1080 | 30 | 274 |
| Index | Formula | Best Value | Worst Value | UM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 0 | + ∞ | (m3/s) | |
| RSR | 0 | + ∞ (usually within 1) | (-) | |
| NSE | 1 | − ∞ (usually within 0) | (-) |
| Index | Formula | Best Value | Worst Value | UM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIAS | 1 | Major distance from 1 | (-) | |
| POD | 1 | 0 | (-) | |
| FAR | 0 | 1 | (-) | |
| PC | 1 | 0 | (-) | |
| TS | 0 | 1 | (-) | |
| HSS | 0 | 1 | (-) |
| Month | June | July | August | September | Oct. | Nov. May | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days | - | 1–10 | 11–20 | 21–31 | 1–10 | 11–20 | 21–31 | 1–10 | 11–20 | 21–30 | - | - |
| Period | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| QMIN (m3/s) | 0 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 120 | 59 | 157 | 146 | 148 | 51 | 1 | 0 |
| QMEAN (m3/s) | 64 | 125 | 214 | 288 | 480 | 450 | 566 | 540 | 468 | 262 | 31 | 1 |
| QMAX (m3/s) | 449 | 416 | 579 | 701 | 1216 | 1044 | 1403 | 1202 | 965 | 696 | 594 | 66 |
| Flood (#days) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 26 | 36 | 37 | 40 | 31 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| Flood (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 14.1 | 19.6 | 20.1 | 21.7 | 16.8 | 5.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Index | Observed | NH | WWH | Optimized NH | Optimized WWH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum (m3/s) | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Mean (m3/s) | 72.8 | 76.5 | 5.6 | 108.4 | 116.2 |
| Maximum (m3/s) | 526.1 | 557.7 | 84.6 | 589.5 | 564.3 |
| Model | RMSE | RSR | NSE | BIAS | POD | FAR | PC | TS | HSS | Operational Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH | 107.7 | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 0.23 | 0.71 | 0.934 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 81% |
| WWH | 161.5 | 1.05 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | / | 0.944 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 92% |
| NHOTT | 76.2 | 0.46 | 0.79 | 1.22 | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.945 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 81% |
| WWHOTT | 87.0 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 2.36 | 0.56 | 0.76 | 0.875 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 92% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massazza, G.; Tarchiani, V.; Andersson, J.C.M.; Ali, A.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Pezzoli, A.; De Filippis, T.; Rocchi, L.; Minoungou, B.; Gustafsson, D.; et al. Downscaling Regional Hydrological Forecast for Operational Use in Local Early Warning: HYPE Models in the Sirba River. Water 2020, 12, 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123504
Massazza G, Tarchiani V, Andersson JCM, Ali A, Ibrahim MH, Pezzoli A, De Filippis T, Rocchi L, Minoungou B, Gustafsson D, et al. Downscaling Regional Hydrological Forecast for Operational Use in Local Early Warning: HYPE Models in the Sirba River. Water. 2020; 12(12):3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123504
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassazza, Giovanni, Vieri Tarchiani, Jafet C. M. Andersson, Abdou Ali, Mohamed Housseini Ibrahim, Alessandro Pezzoli, Tiziana De Filippis, Leandro Rocchi, Bernard Minoungou, David Gustafsson, and et al. 2020. "Downscaling Regional Hydrological Forecast for Operational Use in Local Early Warning: HYPE Models in the Sirba River" Water 12, no. 12: 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123504
APA StyleMassazza, G., Tarchiani, V., Andersson, J. C. M., Ali, A., Ibrahim, M. H., Pezzoli, A., De Filippis, T., Rocchi, L., Minoungou, B., Gustafsson, D., & Rosso, M. (2020). Downscaling Regional Hydrological Forecast for Operational Use in Local Early Warning: HYPE Models in the Sirba River. Water, 12(12), 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123504








