Natural and Anthropogenic Groundwater Contamination in a Coastal Volcanic-Sedimentary Aquifer: The Case of the Archaeological Site of Cumae (Phlegraean Fields, Southern Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
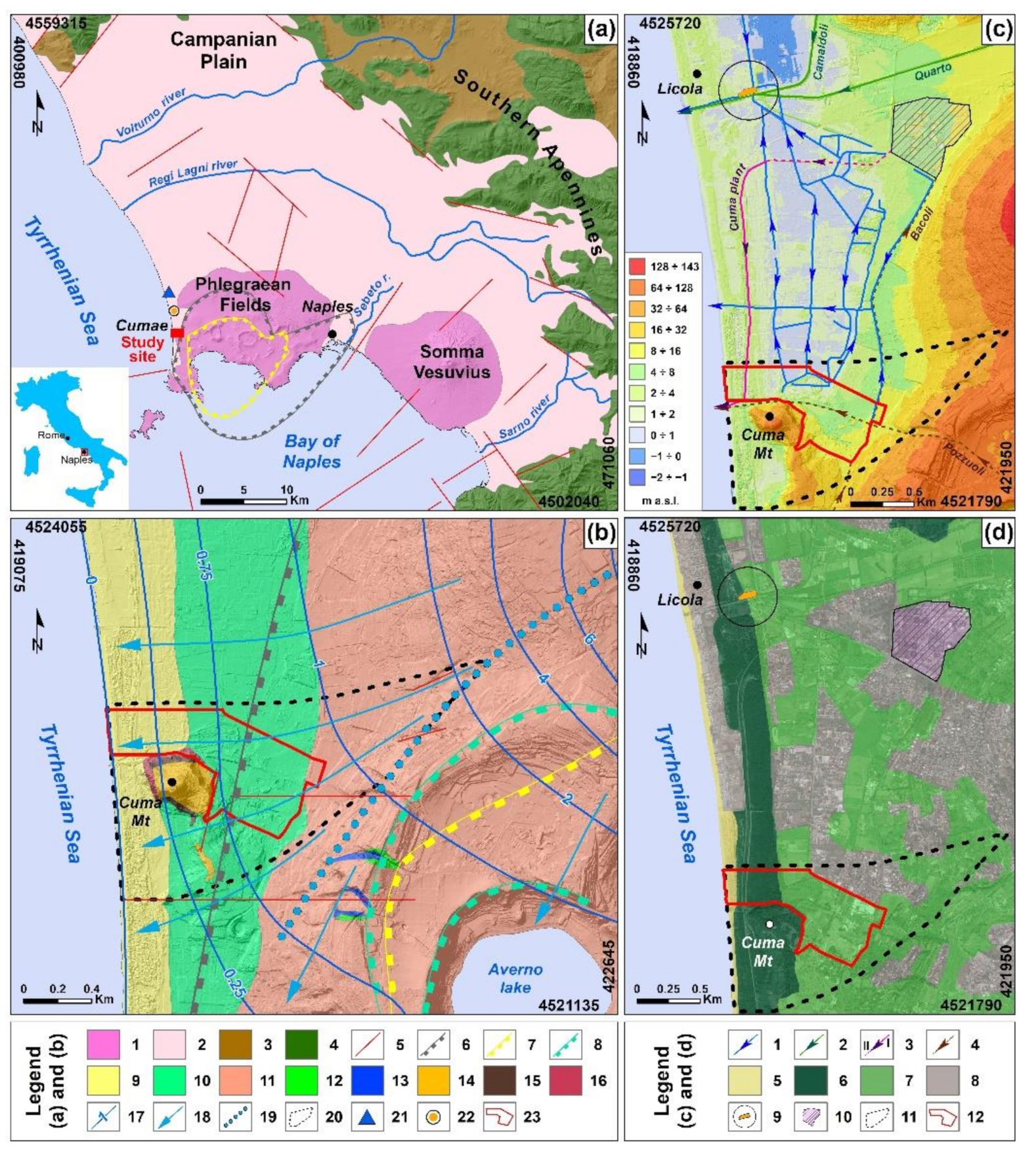
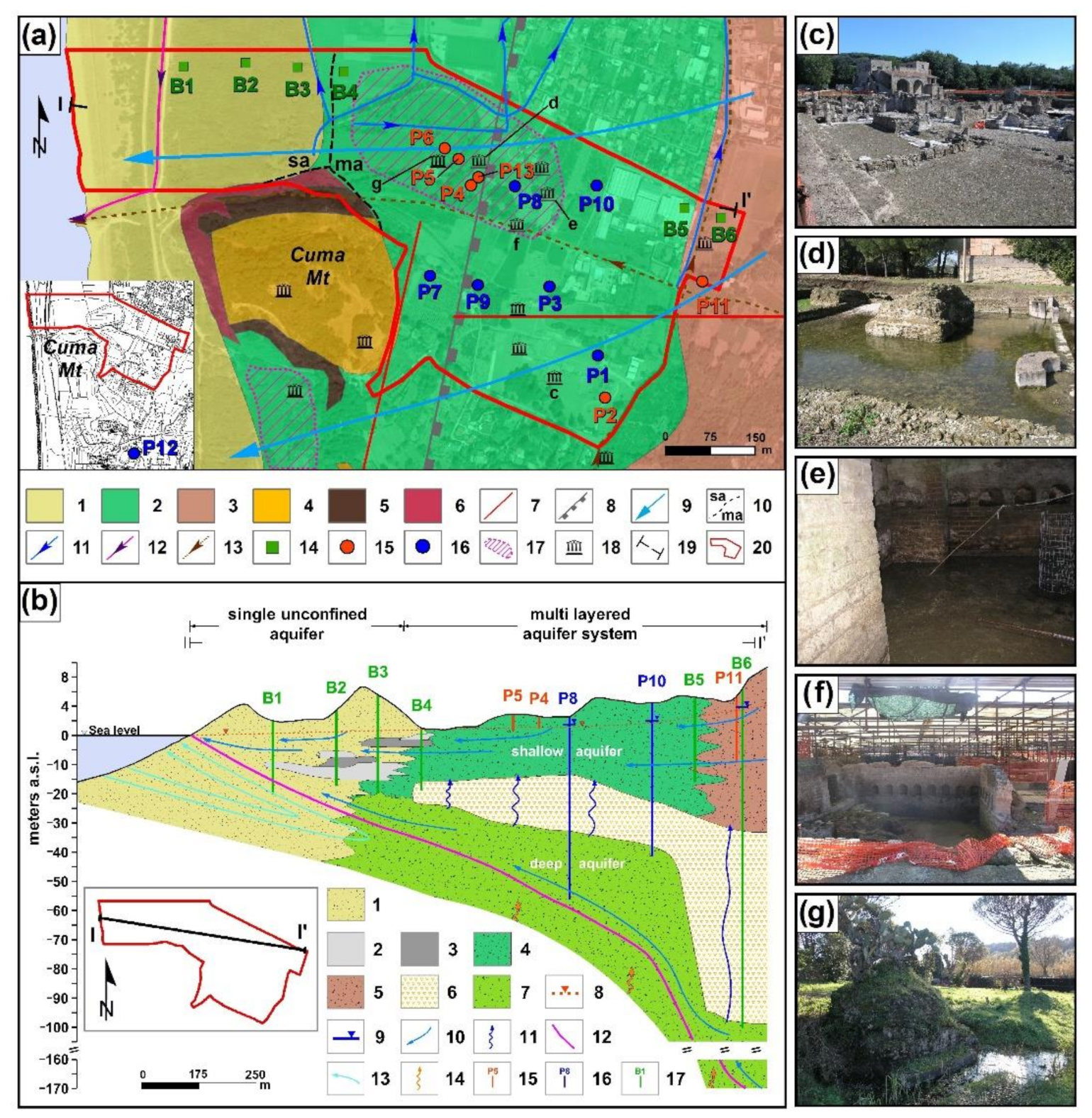
2. Description of the Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hydrogeological Survey
3.2. Hydrochemical Sampling and Analysis
3.3. Isotopic Monitoring
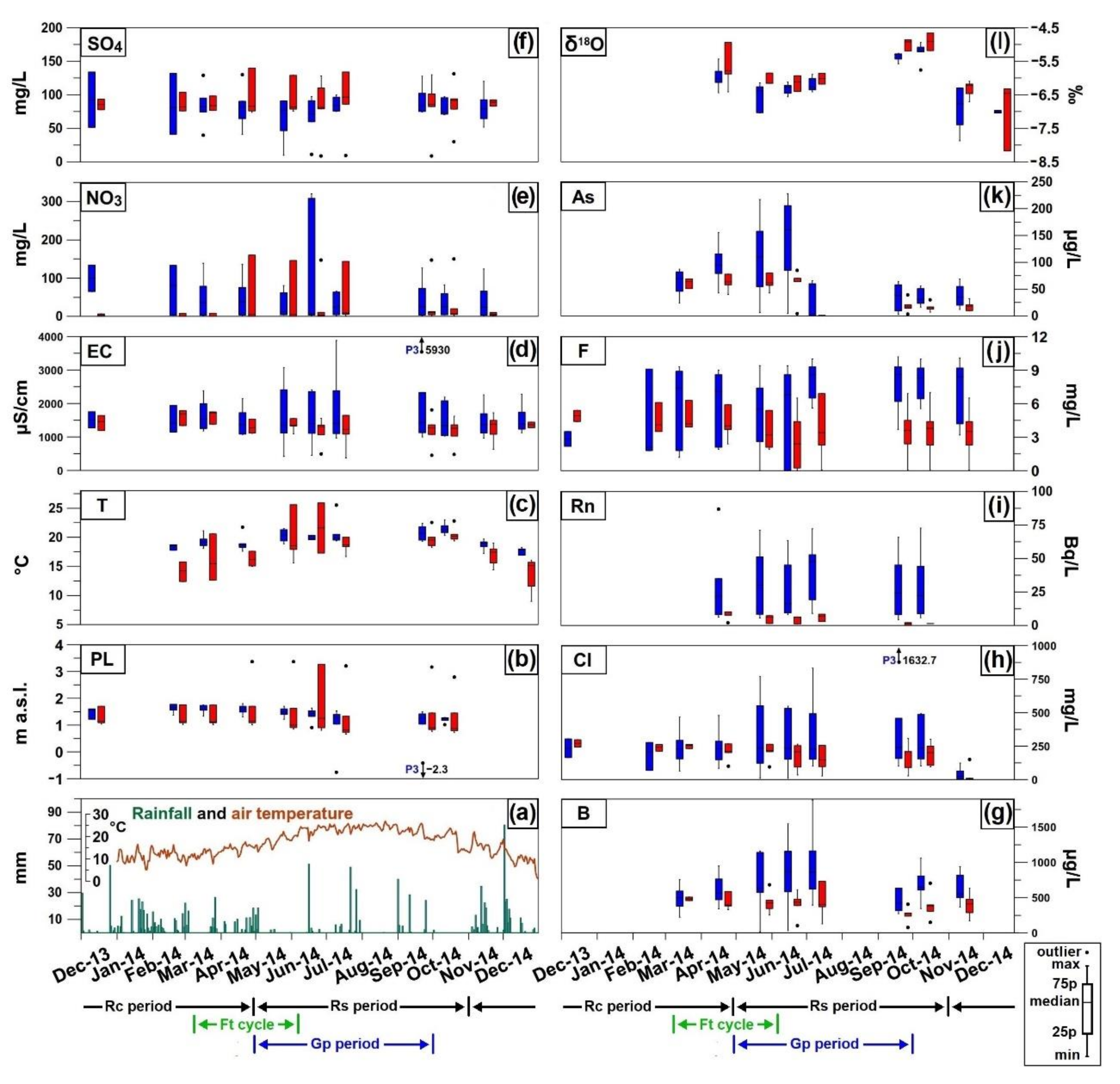
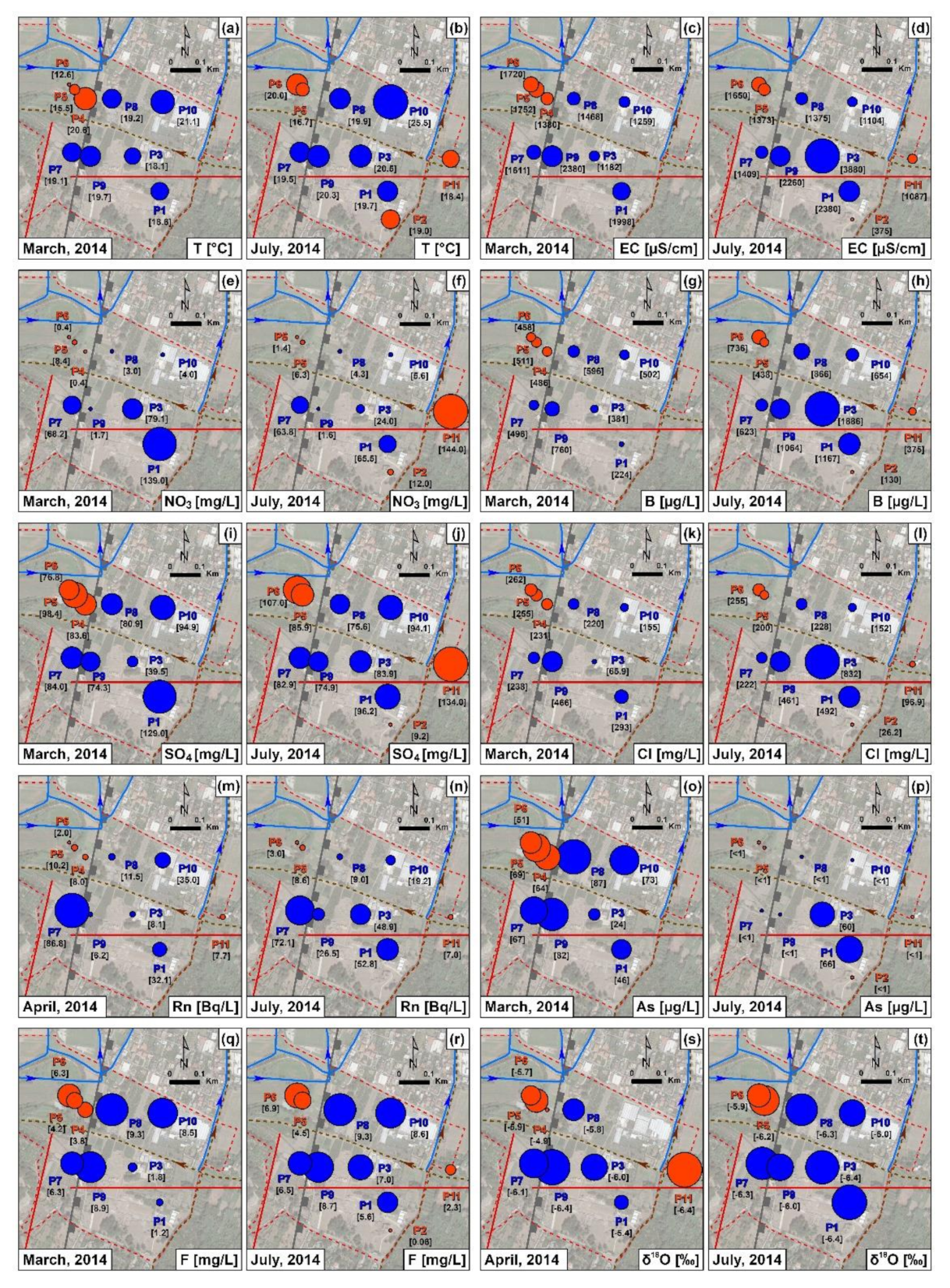
4. Results
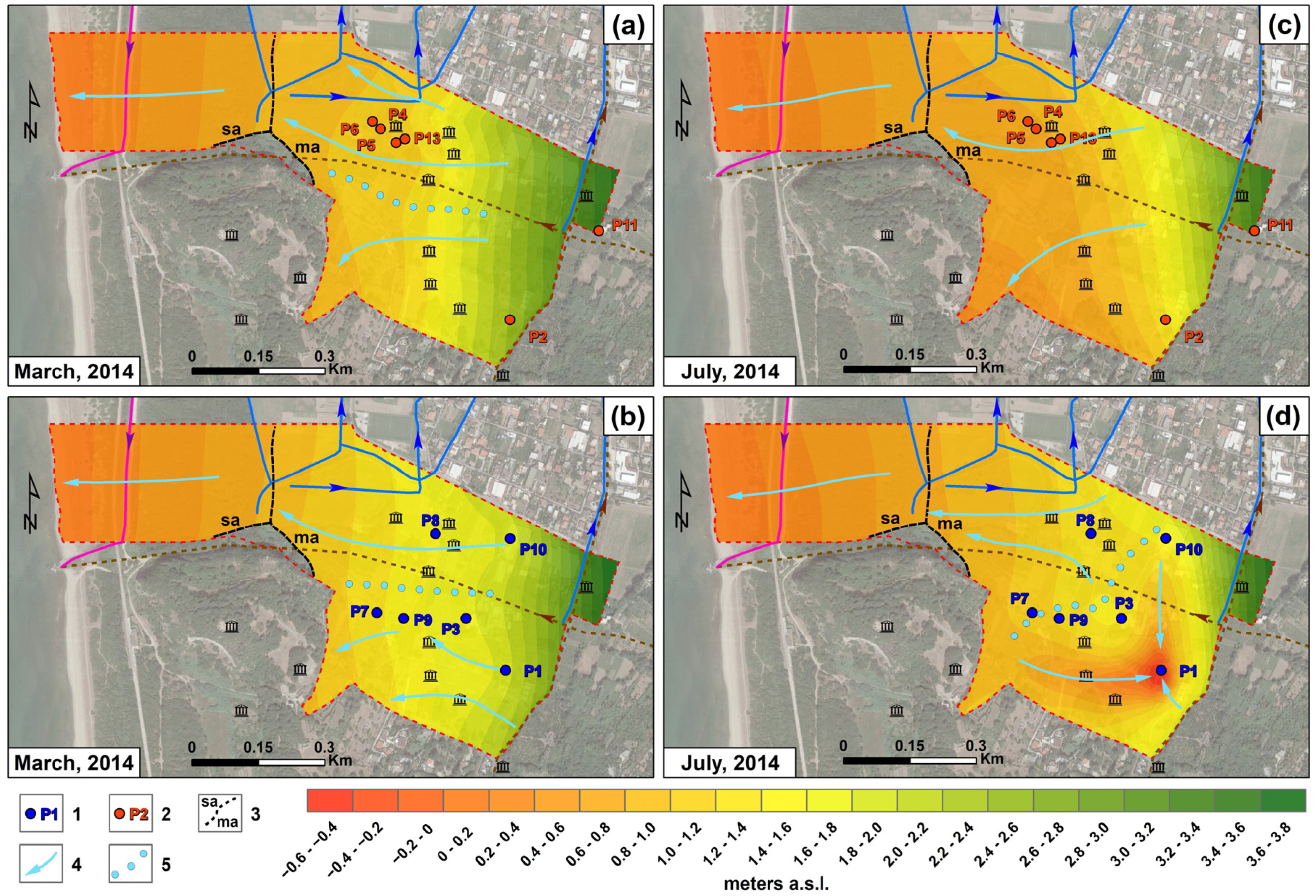
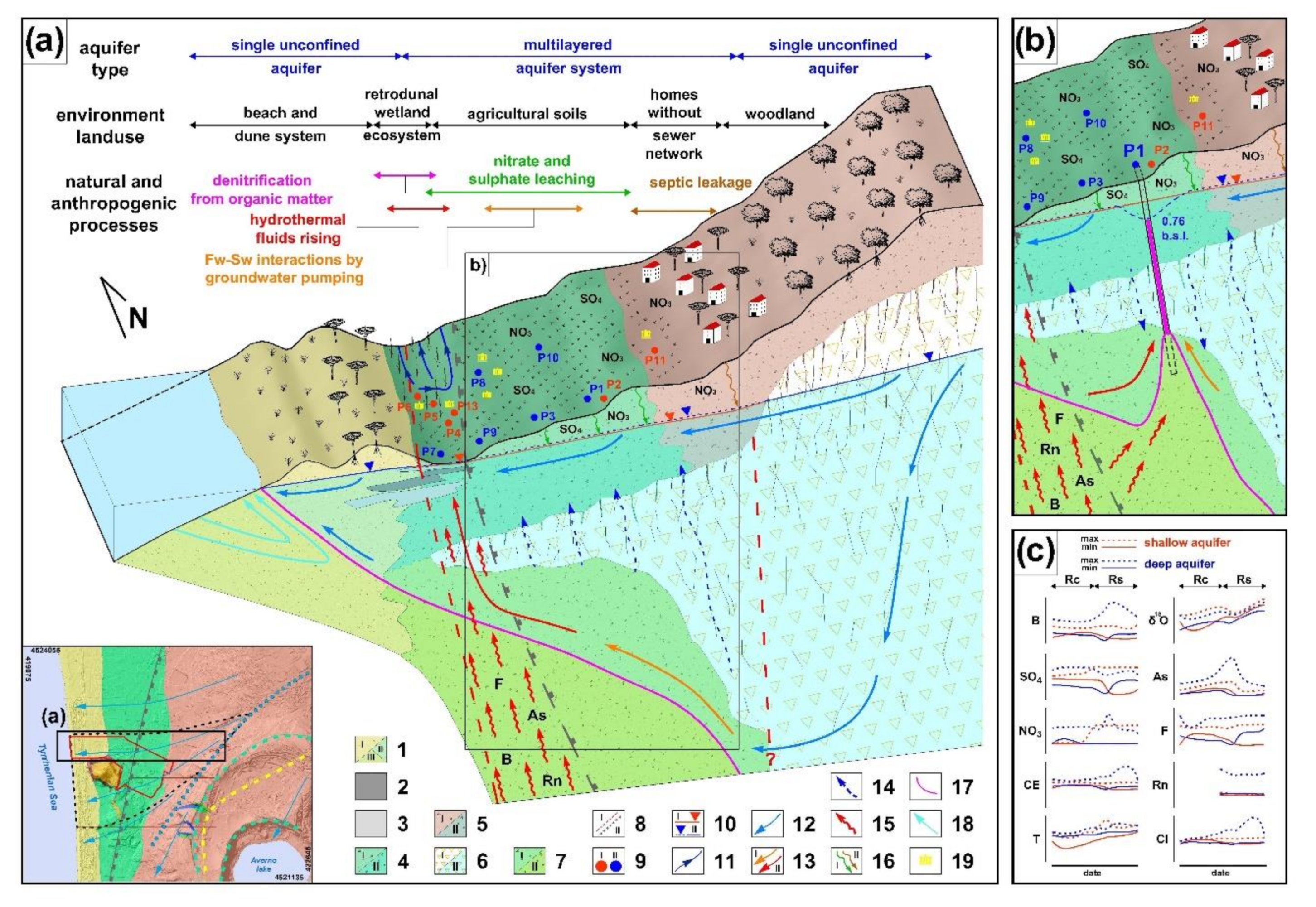
4.1. Hydrogeology
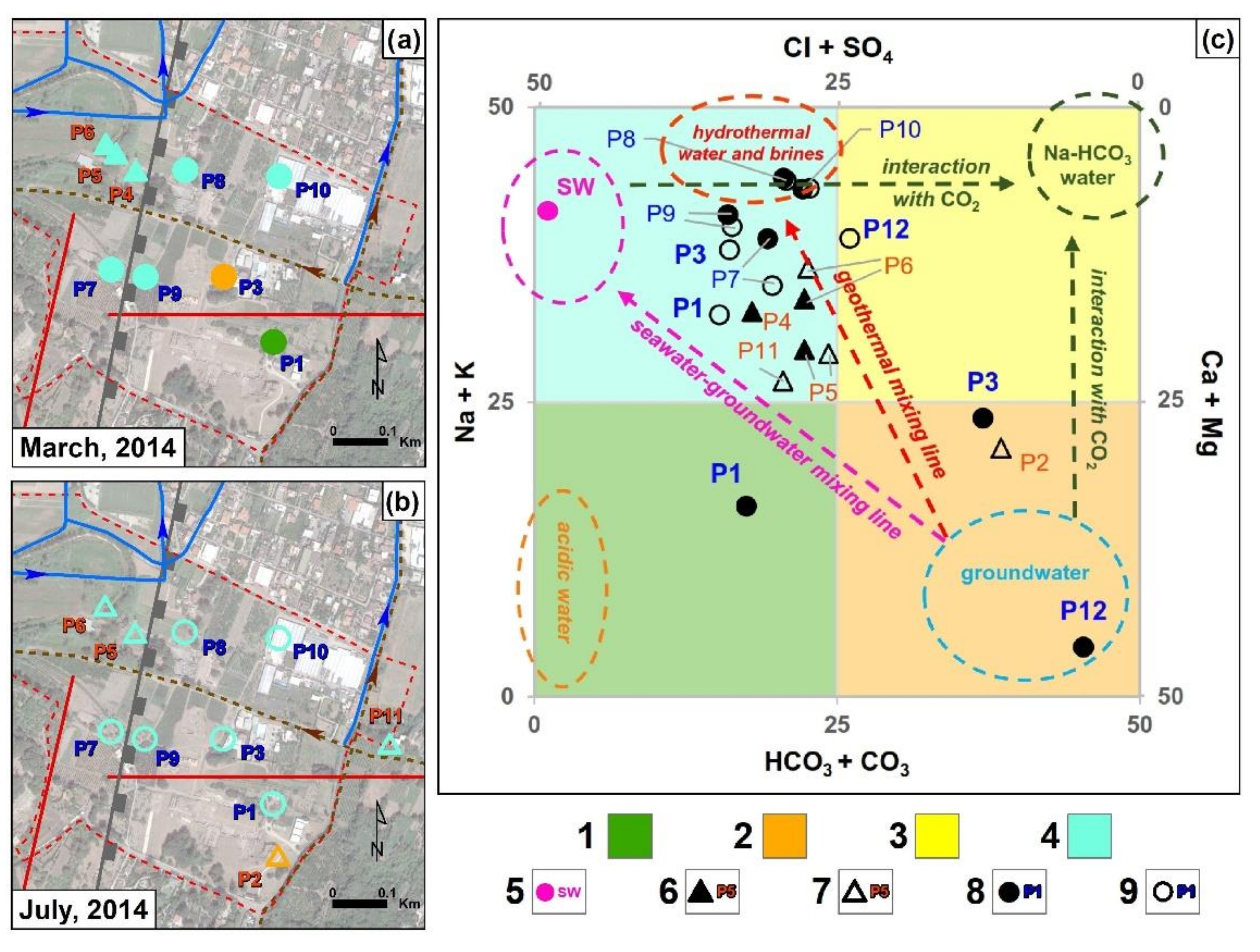
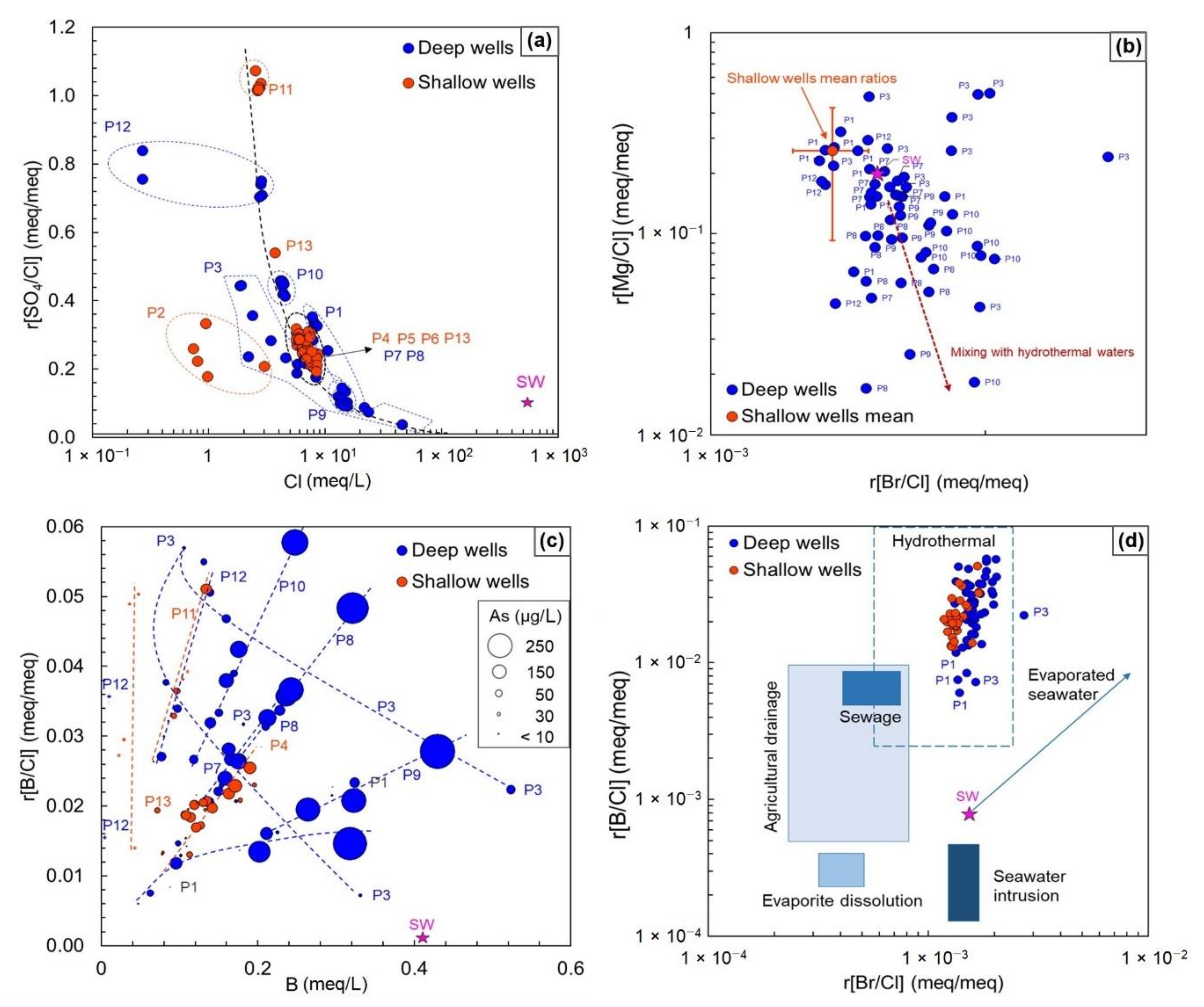
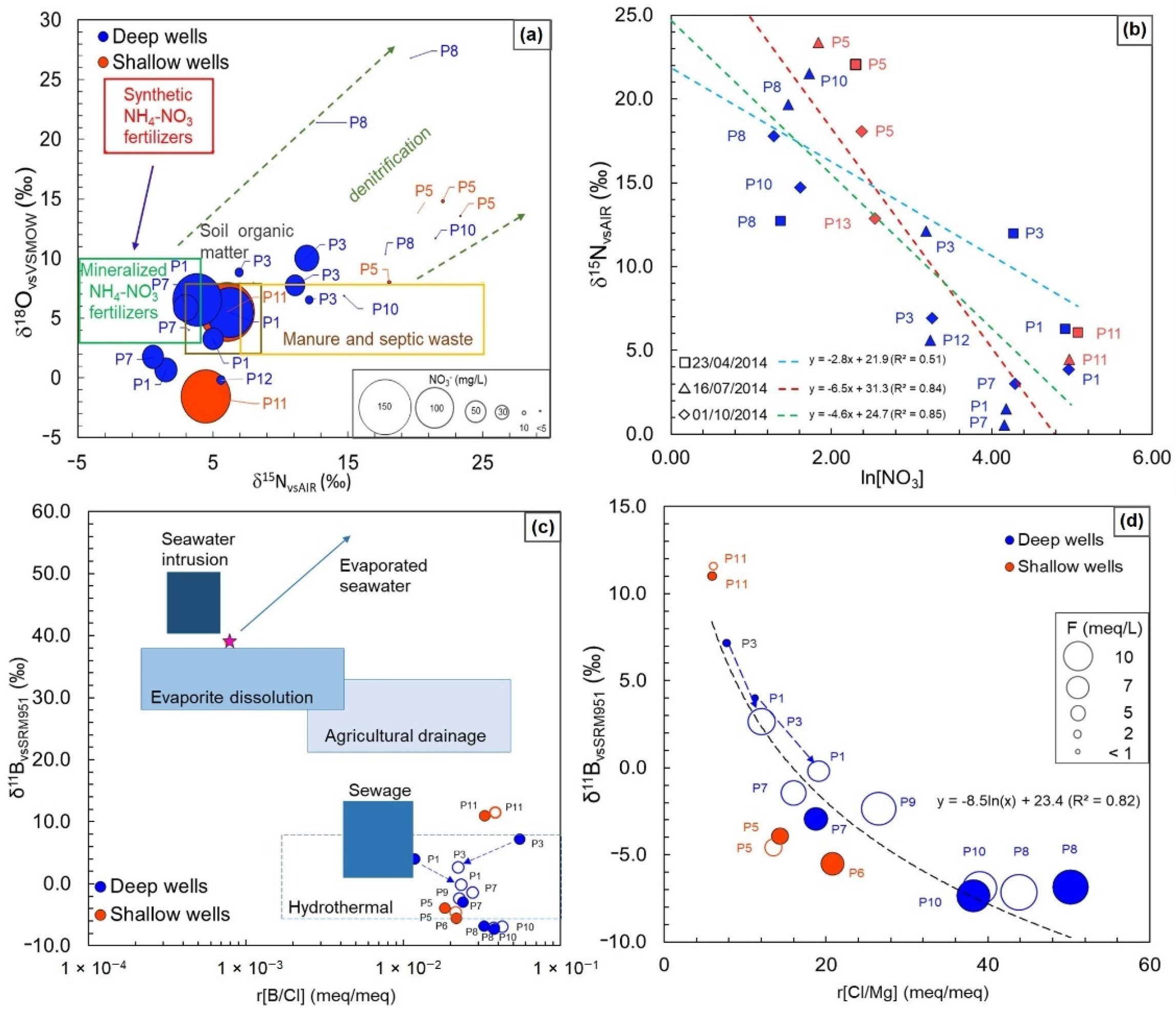
4.2. Hydrochemistry
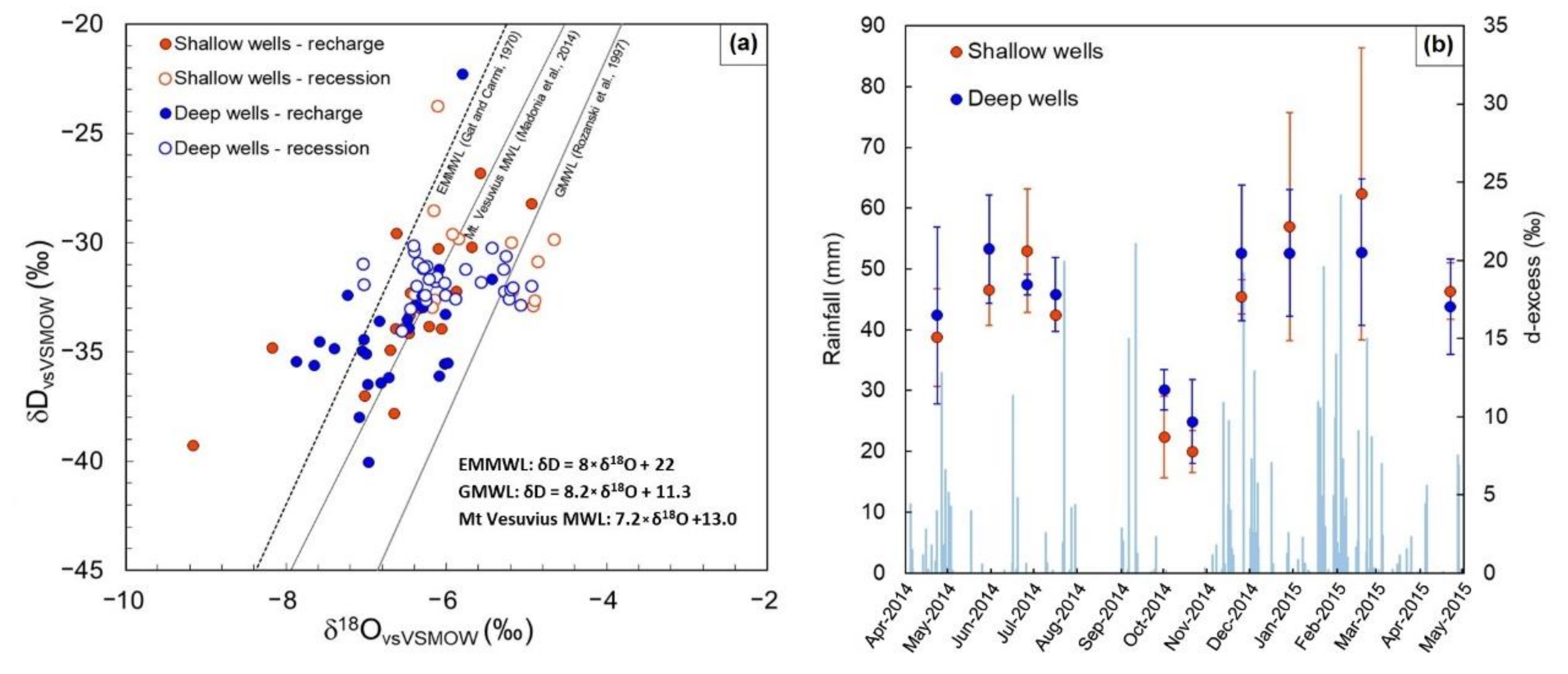
4.3. Isotopic Survey
5. Discussion
6. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zepeda Quintana, D.S.; Loeza Rentería, C.M.; Munguía Vega, N.E.; Peralta, J.E.; Velazquez Contreras, L.E. Sustainability strategies for coastal aquifers: A case study of the Hermosillo Coast aquifer. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, B.; Yagbasan, O.; Yazicigil, H. Assessing the impacts of climate change on sustainable management of coastal aquifers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, E.; Aquilina, L.; Pételet-Giraud, E.; Cary, L.; Bertrand, G.; Labasque, T.; Hirata, R.; Martins, V.; Montenegro, S.; Vergnaud, V.; et al. Glacial recharge, salinisation and anthropogenic contamination in the coastal aquifers of Recife (Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T. Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renau-Pruñonosa, A.; Morell, I.; Pulido-Velazquez, D. A Methodology to Analyse and Assess Pumping Management Strategies in Coastal Aquifers to Avoid Degradation Due to Seawater Intrusion Problems. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4823–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. 2007: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-521-88009-1. [Google Scholar]
- Russak, A.; Sivan, O. Hydrogeochemical Tool to Identify Salinization or Freshening of Coastal Aquifers Determined from Combined Field Work, Experiments, and Modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombani, N.; Osti, A.; Volta, G.; Mastrocicco, M. Impact of Climate Change on Salinization of Coastal Water Resources. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A. Salinization and Saline Environments. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 1–35. ISBN 978-0-08-043751-4. [Google Scholar]
- Custodio, E. Coastal aquifers of Europe: An overview. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, K.-S.; Koh, D.-C.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, S.-G.; Park, W.-B.; Koh, G.-W.; Woo, N.-C. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer: A case study in Jeju volcanic island, Korea. J. Hydrol. 2003, 270, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, P.M.; Marques, J.M.; Nunes, D. Source of groundwater salinity in coastline aquifers based on environmental isotopes (Portugal): Natural vs. human interference. A review and reinterpretation. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 41, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastén-Zapata, E.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R.; Harter, T.; Ramírez, A.I.; Mahlknecht, J. Assessment of sources and fate of nitrate in shallow groundwater of an agricultural area by using a multi-tracer approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.K. Nitrosamines as potential environmental carcinogens in man. Clin. Biochem. 1990, 23, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricker, A.R.; Preussmann, R. Carcinogenic N-nitrosamines in the diet: Occurrence, formation, mechanisms and carcinogenic potential. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. 1991, 259, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena, R.; Evans, M.L.; Cherry, J.A. Stable Isotopes of Oxygen and Nitrogen in Source Identification of Nitrate from Septic Systems. Groundwater 1993, 31, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Tracing nitrate pollution sources and transformations in the over-exploited groundwater region of north China using stable isotopes. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 218, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsiou, D.; Karydis, M. Coastal marine eutrophication assessment: A review on data analysis. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 778–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, X. Eutrophication control strategies for highly anthropogenic influenced coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, E.; UNEP; The Woods Hole Research Centre. Reactive Nitrogen in the Environment: Too Much or Too Little of a Good Thing; UNEP/Earthprint: Paris, France, 2007; ISBN 978-92-807-2783-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nord, A.G.; Tronner, K.; Mattsson, E.; Borg, G.C.; Ullén, I. Environmental Threats to Buried Archaeological Remains. Ambio 2005, 34, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beer, H.; Matthiesen, H. Groundwater monitoring and modelling from an archaeological perspective: Possibilities and challenges. In Geology for Society; Slagstad, T., Ed.; Geological Survey of Norway Special Publication; Geological Survey of Norway: Trondheim, Norway, 2008; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kreyns, P.; Geng, X.; Michael, H.A. The influence of connected heterogeneity on groundwater flow and salinity distributions in coastal volcanic aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C. Tracing Nitrogen Sources and Cycling in Catchments. In Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Kendall, C., McDonnell, J.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 519–576. ISBN 978-0-444-81546-0. [Google Scholar]
- Custodio, E. Effects of human activities on salt–fresh water relationships in coastal aquifers. In Groundwater Problems in Coastal Areas; Custodio, E., Bruggeman, G.A., Eds.; Studies and Reports in Hydrology; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Petelet-Giraud, E.; Négrel, P.; Aunay, B.; Ladouche, B.; Bailly-Comte, V.; Guerrot, C.; Flehoc, C.; Pezard, P.; Lofi, J.; Dörfliger, N. Coastal groundwater salinization: Focus on the vertical variability in a multi-layered aquifer through a multi-isotope fingerprinting (Roussillon Basin, France). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Su, X.; Kang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, M. A hydrogeochemistry and multi-isotope (Sr, O, H, and C) study of groundwater salinity origin and hydrogeochemcial processes in the shallow confined aquifer of northern Yangtze River downstream coastal plain, China. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 86, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Al Naeem, M.F.; Yusoff, I.; Ng, T.F.; Maity, J.P.; Alias, Y.; May, R.; Alborsh, H. A study on the impact of anthropogenic and geogenic factors on groundwater salinization and seawater intrusion in Gaza coastal aquifer, Palestine: An integrated multi-techniques approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 156, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Spivack, A.J.; Artzi, Y.; Ayalon, A. Geochemical and boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean Coast of Israel. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1877–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellato, L. Isotopic Methodologies: A Valuable Tool to Study Stream Water-Groundwater Interactions. In Horizons in Earth Science Research; Veress, B., Szigethy, J., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 239–260. ISBN 978-1-60741-221-2. [Google Scholar]
- De Giorgio, G.; Chieco, M.; Zuffianò, L.E.; Limoni, P.P.; Sottani, A.; Pedron, R.; Vettorello, L.; Stellato, L.; Di Rienzo, B.; Polemio, M. The Compatibility of Geothermal Power Plants with Groundwater Dependent Ecosystems: The Case of the Cesine Wetland (Southern Italy). Sustainability 2018, 10, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinelli, G.; Dadomo, A.; De Luca, D.A.; Mazzola, M.; Lasagna, M.; Pennisi, M.; Pilla, G.; Sacchi, E.; Saccon, P. Nitrate sources, accumulation and reduction in groundwater from Northern Italy: Insights provided by a nitrate and boron isotopic database. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 91, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducci, D.; Del Gaudio, E.; Sellerino, M.; Stellato, L.; Corniello, A. Hydrochemical and isotopic analyses to identify groundwater nitrate contamination. The alluvial-pyroclastic aquifer of the Campanian plain (southern Italy). Geoing. Ambient. Min. 2019, 156, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.W.; Sanford, W.E. Chemical and isotopic methods for quantifying ground-water recharge in a regional, semiarid environment. Ground Water 1995, 33, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R.; Fröhlich, K.; Araguás-Araguás, L.; Rozanski, K. Isotopes in Groundwater Hydrology. In Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Kendall, C., McDonnell, J.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 203–246. ISBN 978-0-444-81546-0. [Google Scholar]
- Thyne, G.D.; Gillespie, J.M.; Ostdick, J.R. Evidence for interbasin flow through bedrock in the southeastern Sierra Nevada. GSA Bull. 1999, 111, 1600–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Herczeg, A.L.; Barnes, C. Isotope Engineering—Using Stable Isotopes of the Water Molecule to Solve Practical Problems. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Cook, P.G., Herczeg, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 79–110. ISBN 978-1-4615-4557-6. [Google Scholar]
- Herczeg, A.L.; Edmunds, W.M. Inorganic Ions as Tracers. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Cook, P.G., Herczeg, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 31–77. ISBN 978-1-4615-4557-6. [Google Scholar]
- Genereux, D.P.; Wood, S.J.; Pringle, C.M. Chemical tracing of interbasin groundwater transfer in the lowland rainforest of Costa Rica. J. Hydrol. 2002, 258, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.C.; Kreitler, C.W. Geochemical Techniques for Identifying Sources of Ground-Water Salinization; Smoley, C.K., Ed.; CRC Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-1-56670-000-9. [Google Scholar]
- Stellato, L.; Petrella, E.; Terrasi, F.; Belloni, P.; Belli, M.; Sansone, U.; Celico, F. Some limitations in using 222Rn to assess river–groundwater interactions: The case of Castel di Sangro alluvial plain (central Italy). Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellato, L.; Terrasi, F.; Marzaioli, F.; Belli, M.; Sansone, U.; Celico, F. Is 222Rn a suitable tracer of stream–groundwater interactions? A case study in central Italy. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 32, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-F.; You, C.-F.; Lin, Y.-P.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Baltatzis, E. New boron isotopic evidence for sedimentary and magmatic fluid influence in the shallow hydrothermal vent system of Milos Island (Aegean Sea, Greece). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 310, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, Q.; Wu, G.; Guo, W.; She, W.; Yan, W. Boron geochemistry of the geothermal waters from two typical hydrothermal systems in Southern Tibet (China): Daggyai and Quzhuomu. Geothermics 2019, 82, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Heumann, K.G.; Juraske, S.; Kasher, R. Boron Isotope Application for Tracing Sources of Contamination in Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Kloppmann, W.; Chery, L.; Bonnin, J.; Rochdi, H.; Guinamant, J.-L. Nitrate in groundwater: An isotopic multi-tracer approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 72, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Botte, J.; De Baets, B.; Accoe, F.; Nestler, A.; Taylor, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Berglund, M.; Boeckx, P. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca, V.; Celico, P. Scenari idrodinamici nella piana ad Oriente di Napoli (Italia) nell’ultimo secolo: Cause e problematiche idrogeologiche connesse. G. Di Geol. Appl. 2008, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca, V.; Coda, S.; De Vita, P.; Iorio, A.; Viola, R. Rising groundwater levels and impacts in urban and semirural are around Naples (southern Italy). Rend. Soc. Geol. It. 2016, 41, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coda, S.; Tessitore, S.; Di Martire, D.; De Vita, P.; Allocca, V. Environmental effects of the groundwater rebound in the eastern plain of Naples (Italy). Rend. Soc. Geol. It. 2019, 48, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, I.M.; Abd El-Tawab, N.A. Effects of the groundwater on deterioration of the catacombs of Kom El-Shoqafa, Alexandria, Egypt. E Conserv. 2013, 168–181. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, P.; Morichi, R.; Paone, R. Cuma e il Suo Parco Archeologico. Un Territorio E le Sue Testimonianze; Scienze e Lettere; Bardi Ed.: Rome, Italy, 2010; ISBN 978-88-88620-87-9. [Google Scholar]
- Capano, M.; Rescigno, C.; Sirleto, R.; Passariello, I.; Marzaioli, F.; D’Onofrio, A.; Terrasi, F. AMS 14C dating at CIRCE: The Major Temple in Cumae (NA–Italy). Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2015, 361, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; West, L.J.; Howard, A.J.; Maxfield, E.; Panter, I.; Oxley, J. Hydrological controls of in situ preservation of waterlogged archaeological deposits. Earth Sci. Rev. 2006, 78, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Noort, R. Assessment and management of sites in wetland landscapes: Four case studies from the Humber wetlands. In Preserving Archaeological Remains in Situ; Corfield, M., Hinton, P., Nixon, T., Pollard, M., Eds.; Museum of London Archaeology Service: London, UK, 1996; pp. 133–143. ISBN 1-56670-000-0. [Google Scholar]
- Van De Noort, R.; Chapman, H.P.; Cheetham, J.L. In situ preservation as a dynamic process: The example of Sutton Common, UK. Antiquity 2001, 75, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Molisso, F.; Pacifico, A.; Vigliotti, M.; Sabbarese, C.; Ruberti, D. Late-Holocene to recent evolution of Lake Patria, South Italy: An example of a coastal lagoon within a Mediterranean delta system. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 117, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivo, B.; Rolandi, G.; Gans, P.B.; Calvert, A.; Bohrson, W.A.; Spera, F.J.; Belkin, H.E. New constraints on the pyroclastic eruptive history of the Campanian volcanic Plain (Italy). Mineral. Petrol. 2001, 73, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravi, S.; Fuscaldo, M.; Guarino, P.M.; Schiattarella, M. Evoluzione sedimentaria olocenica dell’area dell’antico porto di Cumae (Campi Flegrei). In Variazioni Climatico-Ambientali ed Impatto Sull’uomo Nell’area Circum-Mediterranea Durante L’olocene. Territorio Storico ed Ambiente; EdiPuglia: Bari, Italy, 1996; pp. 23–64. [Google Scholar]
- ISPRA. Note Illustrative Della Carta Geologica d‘Italia Alla Scala 1: 50.000, Foglio 446-447 Napoli; Litografia Artistica Cartografica; APAT, Dipartimento Difesa del Suolo, Servizio Geologico d‘Italia: Firenze, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Celico, P.; Dall’Aglio, M.; Ghiara, M.R.; Stanzione, D.; Brondi, M.; Prosperi, M. Geochemical monitoring of the thermal fluids in the Phlegraean Fields from 1970 to 1990. Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1992, 111, 409–422. [Google Scholar]
- De Vita, P.; Allocca, V.; Celico, F.; Fabbrocino, S.; Mattia, C.; Monacelli, G.; Musilli, I.; Piscopo, V.; Scalise, A.R.; Summa, G.; et al. Hydrogeology of continental southern Italy. J. Maps 2018, 14, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tufano, R.; Allocca, V.; Coda, S.; Cusano, D.; Fusco, F.; Nicodemo, F.; Pizzolante, A.; De Vita, P. Groundwater vulnerability of principal aquifers of the Campania region (southern Italy). J. Maps 2020, 16, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca, V.; Coda, S.; De Vita, P.; Di Rienzo, B.; Ferrara, L.; Giarra, A.; Mangoni, O.; Stellato, L.; Trifuoggi, M.; Arienzo, M. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical study of a volcanic-sedimentary coastal aquifer in the archaeological site of Cumae (Phlegraean Fields, southern Italy). J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 185, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocca, V.; Manna, F.; De Vita, P. Estimating annual groundwater recharge coefficient for karst aquifers of the southern Apennines (Italy). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coda, S.; Tessitore, S.; Di Martire, D.; Calcaterra, D.; De Vita, P.; Allocca, V. Coupled ground uplift and groundwater rebound in the metropolitan city of Naples (southern Italy). J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coda, S.; Confuorto, P.; De Vita, P.; Di Martire, D.; Allocca, V. Uplift Evidences Related to the Recession of Groundwater Abstraction in a Pyroclastic-Alluvial Aquifer of Southern Italy. Geosciences 2019, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambeck, K.; Anzidei, M.; Antonioli, F.; Benini, A.; Esposito, A. Sea level in Roman time in the Central Mediterranean and implications for recent change. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 224, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todesco, M.; Costa, A.; Comastri, A.; Colleoni, F.; Spada, G.; Quareni, F. Vertical ground displacement at Campi Flegrei (Italy) in the fifth century: Rapid subsidence driven by pore pressure drop. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Città Metropolitana di Napoli—Telerilevamento Mediante Lidar. Available online: http://sit.cittametropolitana.na.it/lidar.html (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Radon in Water Sampling Program; EPA/EERF Manual 78-1; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; p. 11.
- Belloni, P.; Cavaioli, M.; Ingrao, G.; Mancini, C.; Notaro, M.; Santaroni, P.; Torri, G.; Vasselli, R. Optimization and comparison of three different methods for the determination of Rn-222 in water. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 173–174, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-1-56670-249-2. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.R.; Kendall, C.; Wilkison, D.H.; Ziegler, A.C.; Chang, C.C.Y.; Avanzino, R.J. A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppich, G.R.; Wimpenny, J.B.; Yin, Q.-Y.; Esser, B.K. California GAMA Special Study: Stable Isotopic Composition of Boron in Groundwater—Analytical Method Development—Tech. Rep. LLNL-TR-498360; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 2011; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Ying-Kai, X.; Bu-Yong, L.; Wei-Guo, L.; Yun, X.; George, H.S. Ion Exchange Extraction of Boron from Aqueous Fluids by Amber-lite IRA 743 Resin. Chin. J. Chem. 2003, 21, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.-W.; Song, S.-H.; Kang, S.-H.; Rhee, Y.-W.; Lee, C.-S.; Lee, B.-J.; Hudson, S.; Hwang, T.-S. Adsorption Kinetics of Boron by Anion Exchange Resin in Packed Column Bed. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2007, 13, 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Langelier, W.F.; Ludwig, H.F. Graphical Methods for Indicating the Mineral Character of Natural Waters. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1942, 34, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.E.; Thomas, D.M. Cl/Mg ratio of Hawaiian groundwaters as a regional geothermal indicator. Geotherm. Resour. Counc. Trans. 1979, 3, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Aiuppa, A.; Avino, R.; Brusca, L.; Caliro, S.; Chiodini, G.; D’Alessandro, W.; Favara, R.; Federico, C.; Ginevra, W.; Inguaggiato, S.; et al. Mineral control of arsenic content in thermal waters from volcano-hosted hydrothermal systems: Insights from island of Ischia and Phlegrean Fields (Campanian Volcanic Province, Italy). Chem. Geol. 2006, 229, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonia, P.; Federico, C.; Favara, R. Isotopic composition of rain- and groundwater at Mt. Vesuvius: Environmental and volcanological implications. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanski, K.; Araguas-Araguas, L.; Gonfiantini, R. Isotope patterns in modern global precipitation. Am. Geophys. Union Monogr. 1993, 78, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R.; Carmi, I. Evolution of the isotopic composition of atmospheric waters in the Mediterranean Sea area. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amore, F.; Fancelli, R.; Panichi, C. Stable isotope study of reinjection processes in the Larderello geothermal field. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, H.; Gaus, I.; le Nindre, Y.M.; Pearce, J.; Czernichowski-Lauriol, I. Chemistry of fluids from a natural analogue for a geological CO2 storage site (Montmiral, France): Lessons for CO2–water–rock interaction assessment and monitoring. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 2817–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, I.; Weaver, T.; Tweed, S.; Ahearne, D.; Cooper, M.; Czapnik, C.; Tranter, J. O, H, C isotope geochemistry of carbonated mineral springs in central Victoria, Australia: Sources of gas and water–rock interaction during dying basaltic volcanism. J. Geochem. Explor. 2000, 69–70, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliro, S.; Chiodini, G.; Avino, R.; Minopoli, C.; Bocchino, B. Long time-series of chemical and isotopic compositions of Vesuvius fumaroles: Evidence for deep and shallow processes. Ann. Geophys. 2011, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolytė, R.; Serno, S.; Johnson, G.; Gilfillan, S.M.V. The influence of oxygen isotope exchange between CO2 and H2O in natural CO2-rich spring waters: Implications for geothermometry. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 84, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlivat, L.; Jouzel, J. Global climatic interpretation of the deuterium-oxygen 18 relationship for precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1979, 84, 5029–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, K.; Gibson, J.J.; Aggarwal, P.K. Deuterium excess in precipitation and its climatological significance. In Study of Environmental Change Using Isotope Techniques; C&S Paper Series; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2002; pp. 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl, S.; Sodemann, H. What controls deuterium excess in global precipitation? Clim. Past 2014, 10, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariotti, A.; Landreau, A.; Simon, B. 15N isotope biogeochemistry and natural denitrification process in groundwater: Application to the chalk aquifer of northern France. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, T.; Hiscock, K.M.; Dennis, P.F.; Grischek, T. A dual isotope approach to identify denitrification in groundwater at a river-bank infiltration site. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3070–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stellato, L.; Coda, S.; Arienzo, M.; De Vita, P.; Di Rienzo, B.; D’Onofrio, A.; Ferrara, L.; Marzaioli, F.; Trifuoggi, M.; Allocca, V. Natural and Anthropogenic Groundwater Contamination in a Coastal Volcanic-Sedimentary Aquifer: The Case of the Archaeological Site of Cumae (Phlegraean Fields, Southern Italy). Water 2020, 12, 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123463
Stellato L, Coda S, Arienzo M, De Vita P, Di Rienzo B, D’Onofrio A, Ferrara L, Marzaioli F, Trifuoggi M, Allocca V. Natural and Anthropogenic Groundwater Contamination in a Coastal Volcanic-Sedimentary Aquifer: The Case of the Archaeological Site of Cumae (Phlegraean Fields, Southern Italy). Water. 2020; 12(12):3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123463
Chicago/Turabian StyleStellato, Luisa, Silvio Coda, Michele Arienzo, Pantaleone De Vita, Brunella Di Rienzo, Antonio D’Onofrio, Luciano Ferrara, Fabio Marzaioli, Marco Trifuoggi, and Vincenzo Allocca. 2020. "Natural and Anthropogenic Groundwater Contamination in a Coastal Volcanic-Sedimentary Aquifer: The Case of the Archaeological Site of Cumae (Phlegraean Fields, Southern Italy)" Water 12, no. 12: 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123463
APA StyleStellato, L., Coda, S., Arienzo, M., De Vita, P., Di Rienzo, B., D’Onofrio, A., Ferrara, L., Marzaioli, F., Trifuoggi, M., & Allocca, V. (2020). Natural and Anthropogenic Groundwater Contamination in a Coastal Volcanic-Sedimentary Aquifer: The Case of the Archaeological Site of Cumae (Phlegraean Fields, Southern Italy). Water, 12(12), 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123463











