Fish Rescue during Streamflow Intermittency May Not Be Effective for Conservation of Rio Grande Silvery Minnow
Abstract
1. Introduction
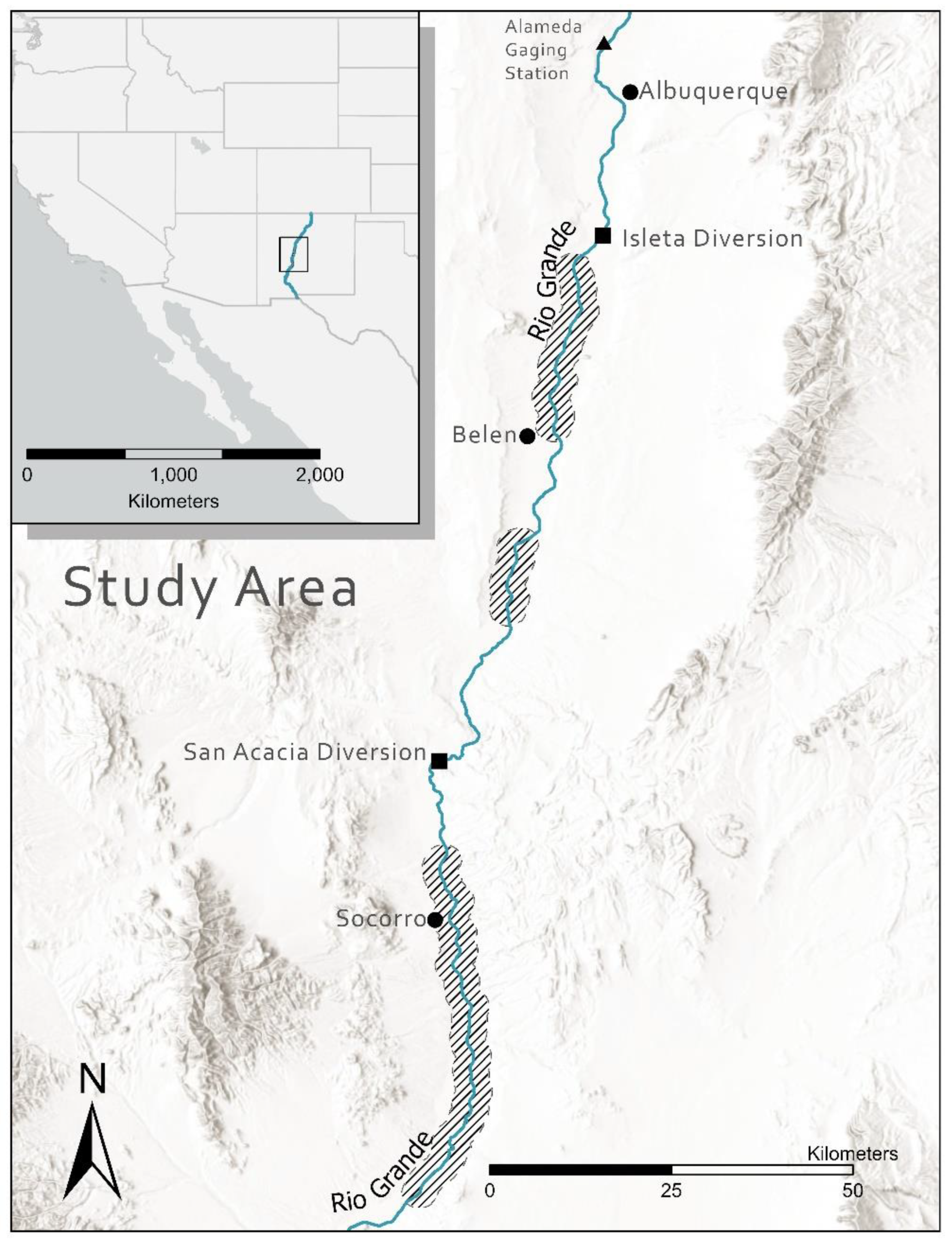
2. Materials and Methods
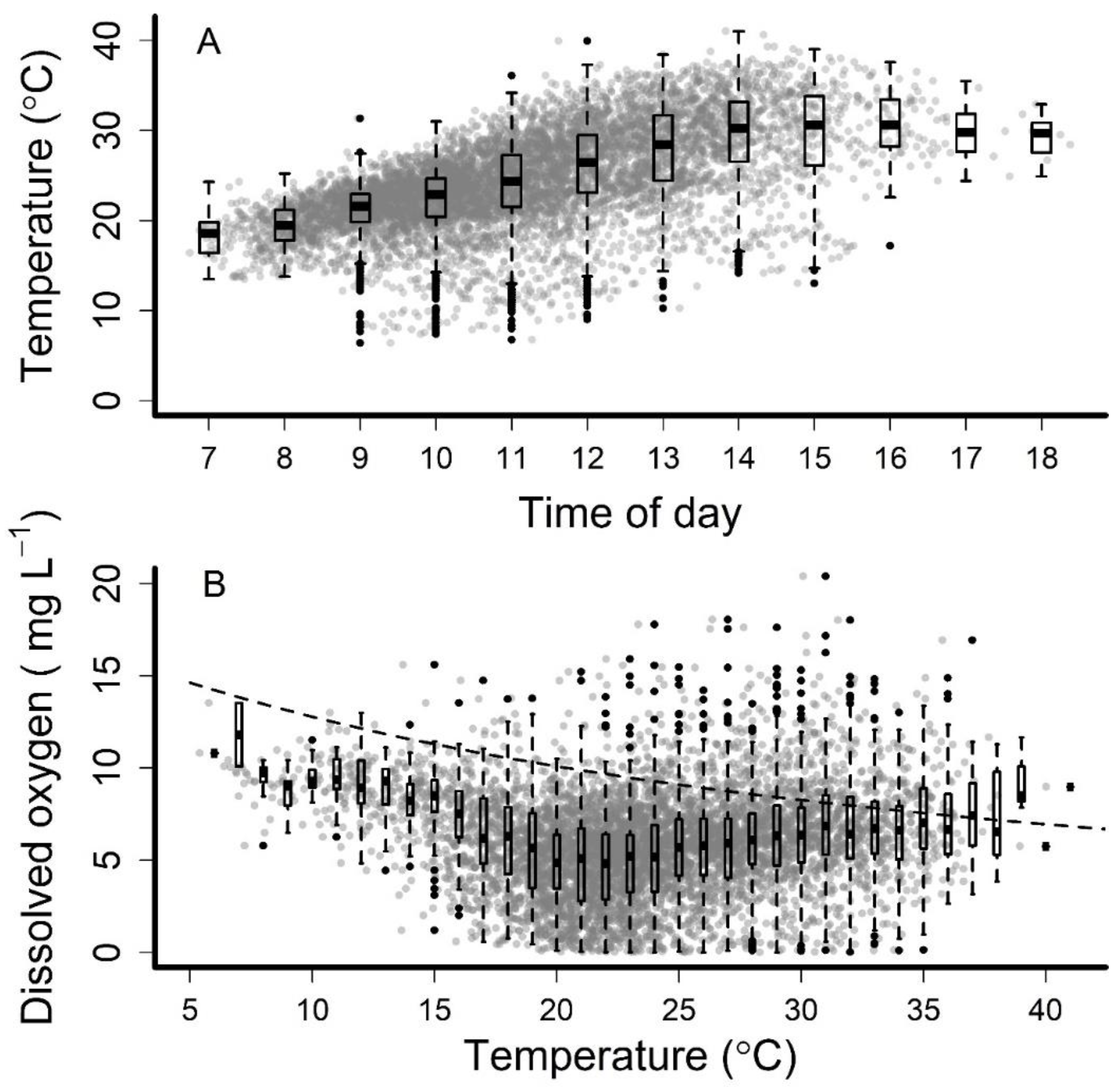
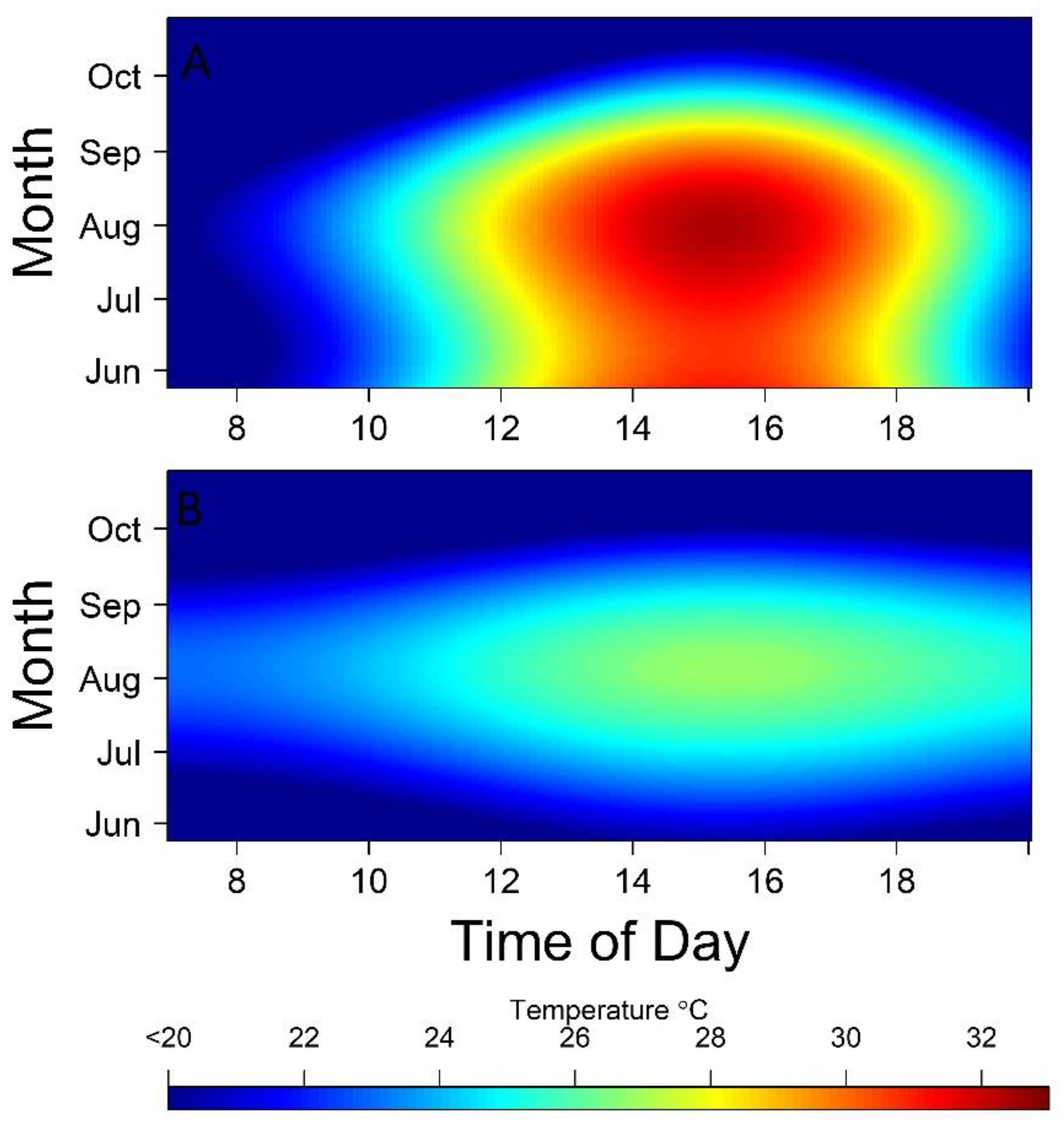
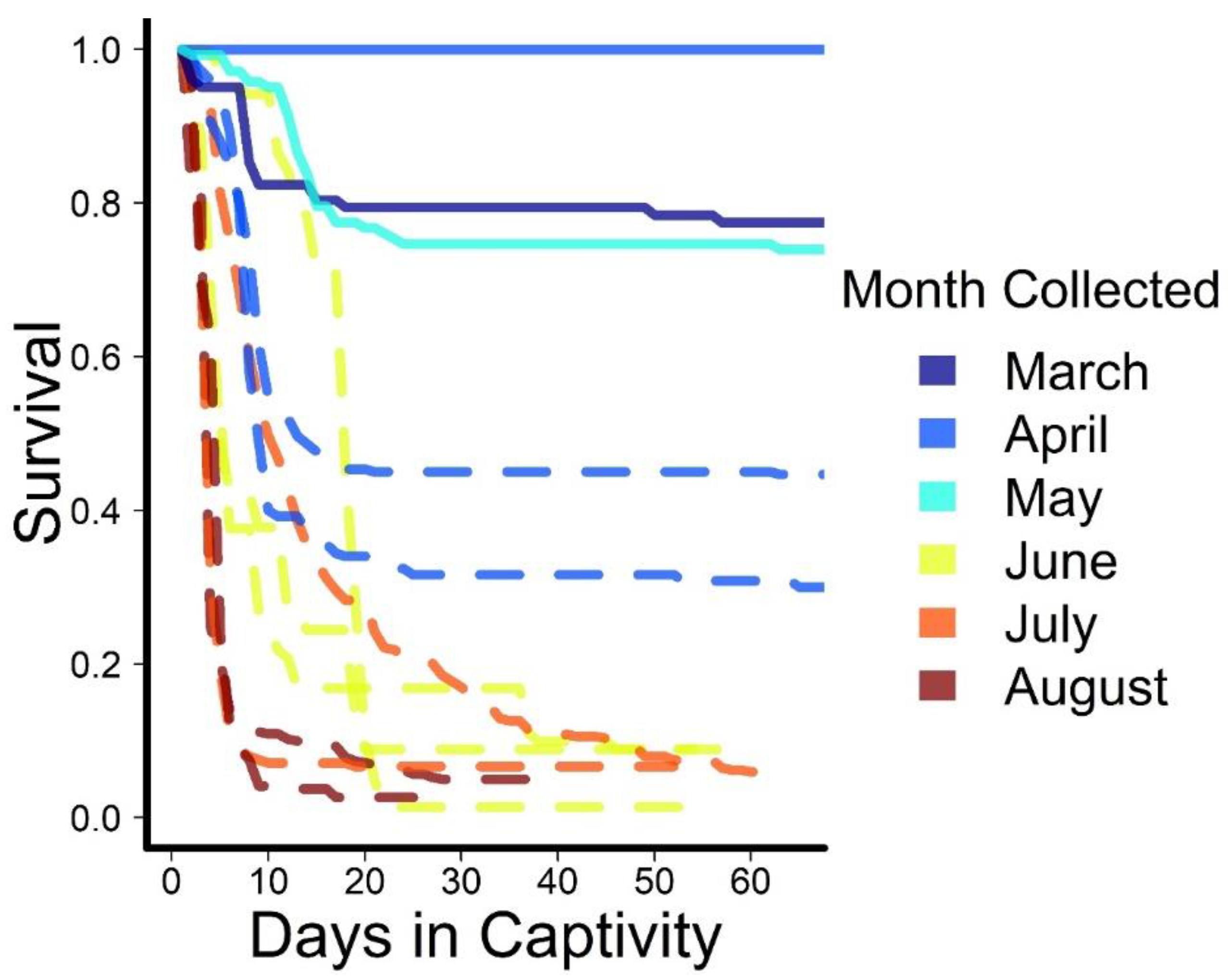
3. Results
4. Discussion
Appendix A
| Model | Parameter | Estimate | SE | t-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate Pools | ||||
| Intercept | 16.9809 | 1.2183 | 13.938 | |
| sine time | −5.1871 | 0.3277 | −15.83 | |
| cosine time | −8.495 | 0.8906 | −9.539 | |
| sine time (2nd harmonic) | 1.2147 | 0.2123 | 5.722 | |
| cosine time (2nd harmonic) | −1.537 | 0.3304 | −4.652 | |
| sine day | 6.1214 | 1.0853 | 5.64 | |
| cosine day | −5.3918 | 1.1174 | −4.825 | |
| sine day (2nd harmonic) | 4.4314 | 0.5364 | 8.262 | |
| cosine day (2nd harmonic) | −1.926 | 0.1974 | −9.758 | |
| Perennial Flow | ||||
| Intercept | 14.17188 | 0.103947 | 136.34 | |
| sine time | −1.55107 | 0.00554 | −279.97 | |
| cosine time | −0.55226 | 0.005598 | −98.65 | |
| sine time (2nd harmonic) | 0.479119 | 0.005553 | 86.29 | |
| cosine time (2nd harmonic) | 0.169554 | 0.005589 | 30.34 | |
| sine day | −3.68166 | 0.005618 | −655.37 | |
| cosine day | −9.53207 | 0.005798 | −1643.96 | |
| sine day (2nd harmonic) | 1.024666 | 0.005507 | 186.05 | |
| cosine day (2nd harmonic) | −0.83944 | 0.005737 | −146.32 | |
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- Acuña, V.; Datry, T.; Marshall, J.; Barceló, D.; Dahm, C.N.; Ginebrada, A.; McGregor, G.; Sabater, S.; Tockner, K.; Palmer, M.A. Why should we care about intermittent waterways? Science 2014, 343, 1080–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milly, P.; Dunne, K.; Vecchia, A. Global pattern of trends in streamflow and water availability in a changing climate. Nature 2005, 438, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falke, J.A.; Fausch, K.D.; Magelky, R.; Aldred, A.; Durnford, D.S.; Riley, L.K.; Oad, R. The role of groundwater pumping and drought in shaping ecological futures for stream fishes in a dryland river basin of the western Great Plains, USA. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.C.; Kopp, D.A.; Costigan, K.H.; Datry, T.; Hugueny, B.; Turner, D.S.; Bodner, G.S.; Flood, T.J. Citizen scientists document long-term streamflow declines in intermittent rivers of the desert southwest, USA. Freshw. Sci. 2019, 38, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.L.; Olden, J.D.; Pelland, N.A. Climate change poised to threaten hydrologic connectivity and endemic fishes in dryland streams. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13894–13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Jaworski, N.A.; Pace, M.L.; Sides, A.M.; Seekell, D.; Belt, K.T.; Secor, D.H.; Wingate, R.L. Rising stream and river temperatures in the United States. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaak, D.J.; Wenger, S.J.; Peterson, E.E.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; Nagel, D.E.; Luce, C.H.; Hostetler, S.W.; Dunham, J.B.; Roper, B.R.; Wollrab, S.P.; et al. The NorWeST summer stream temperature model and scenarios for the western U.S.: A crowd-sourced database and new geospatial tools foster a user community and predict broad climate warming of rivers and streams. Water Resourc. Res. 2017, 53, 9181–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrodski, A.; Raby, G.D.; Hasler, C.T.; Taylor, M.K.; Cooke, S.J. Fish stranding in freshwater systems: Sources, consequences, and mitigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 103, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, M.T.H.; Ludwig, F.; Kabat, P. Global streamflow and thermal habitats of freshwater fishes under climate change. Clim. Chang. 2013, 121, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramer, E.J. Catastrophic mortality of stream fishes trapped in shrinking pools. Am. Midl. Nat. 1977, 97, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundahl, N. Heat death of fish in shrinking stream pools. Am. Midl. Nat. 1990, 123, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevelhimer, M.; Bennett, W. Assessing cumulative thermal stress in fish during chronic intermittent exposure to high temperatures. Environ. Sci. Policy 2000, 3, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrand, K.G.; Wilde, G.R. Temperature, dissolved oxygen, and salinity tolerances of five prairie stream fishes and their role in explaining fish assemblage patterns. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2001, 130, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardakas, L.; Kalogianni, E.; Economou, A.N.; Koutsikos, N.; Skoulikidis, N.T. Mass mortalities and population recovery of an endemic fish assemblage in an intermittent river Reach during drying and rewetting. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2017, 190, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, G.W.; Gido, K.B.; Pennock, C.A.; Hedden, S.C.; Frenette, B.D.; Barts, N.; Hedden, C.K.; Bruckerhoff, L.A. Nowhere to swim: Interspecific responses of prairie stream fishes in isolated pools during severe drought. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficke, A.D.; Myrick, C.A.; Hansen, L.J. Potential impacts of global climate change on freshwater fisheries. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2007, 17, 581–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, R.J.; Crook, D.A.; Moyle, P.B.; Struthers, D.P.; Cooke, S.J. Toward a better understanding of freshwater fish responses to an increasingly drought-stricken world. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish 2019, 29, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archdeacon, T.P. Reduction in spring flow threatens Rio Grande silvery minnow: Trends in abundance during river intermittency. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2016, 145, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurlock, D. From the Rio to the Sierra: An Environmental History of the Middle Rio Grande Basin; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1998. [CrossRef]
- Sublette, J.E.; Hatch, M.D.; Sublette, M. The Fishes of New Mexico; University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Seager, R.; Ting, M.; Held, I.; Kushnir, Y.; Lu, J.; Vecchi, G.; Huang, H.; Harnik, N.; Leetmaa, A.; Lau, N.; et al. Model projections of an imminent transition to a more arid climate in Southwestern North America. Science 2007, 316, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.B.; Miller, G.; Talsma, C.; Jonko, A.; Bruggeman, A.; Atchley, A.; Lavadie-Bulnes, A.; Kwicklis, E.; Middleton, R. Future water resource shifts in the high desert Southwest of Northern New Mexico, USA. J. Hydrol. Regional Stud. 2020, 28, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexstone, G.A.; Penn, C.A.; Liston, G.E.; Gleason, K.E.; Moeser, C.D.; Clow, D.W. Spatial variability in seasonal snowpack trends across the Rio Grande headwaters (1984–2017). J. Hydrometeor. 2020, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, T.L.; Schmidt, J.C. Estimating the natural flow regime of rivers with long-standing development: The northern branch of the Rio Grande. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 1212–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.A.; Clow, D.W.; Sexstone, G.A.; Murphy, S.F. Changes in climate and land cover affect seasonal streamflow forecasts in the Rio Grande headwaters. J. Am. Water Resourc. Assoc. 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestgen, K.R.; Platania, S.P. Status and conservation of the Rio Grande silvery minnow, Hybognathus amarus. Southwest. Nat. 1991, 36, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.E. Biological Monitoring of the Reintroduction Efforts of the Rio Grande Silvery Minnow into the Big Bend Region of Texas and Mexico. (Unpublished). Available online: https://tpwd.texas.gov/business/grants/wildlife/section-6/docs/fish/tx-e-169-r-final-performance-report.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Bestgen, K.R.; Platania, S.P. Extirpation of Notropis simus simus (Cope) and Notropis orca Woolman (Pisces: Cyprinidae) from the Rio Grande in New Mexico, with notes on their life history. Occas. Pap. Mus. Southwest. Biol. 1990, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Treviño-Robinson, D.T. The ichthyofauna of the Lower Rio Grande, Texas and Mexico. Copeia 1959, 1959, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winemiller, K.O.; Rose, K.A. Patterns of life-history diversification in North American fishes: Implications for population regulation. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 2196–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winemiller, K.O. Life history strategies, population regulation, and implications for fisheries management. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, R.J.; Keller, D.H.; Overbeck, P.F.; Platania, S.P.; Dudley, R.K.; Carson, E.W. Age and growth of the Rio Grande silvery minnow, an endangered, short-lived cyprinid of the North American Southwest. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archdeacon, T.P.; Diver-Franssen, T.A.; Bertrand, N.G.; Grant, J.D. Drought results in recruitment failure of Rio Grande silvery minnow (Hybognathus amarus), an imperiled, pelagic broadcast-spawning minnow. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2020, 103, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, C.A.; Falco, H.; Knight, W.; Ulibarri, M.; Gould, W.R. Reproductive potential of captive Rio Grande silvery minnow. N. Am. J. Aquacult. 2019, 8, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platania, S.; Altenbach, C. Reproductive Strategies and Egg Types of Seven Rio Grande Basin Cyprinids. Copeia 1998, 1998, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, T.A.; Echelle, A.A.; Perkin, J.S.; Mollenhauer, R.; Farless, N.; Dyer, J.J.; Logue, D.; Brewer, S.K. The emblematic minnows of the North American Great Plains: A synthesis of threats and conservation opportunities. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 271–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archdeacon, T.P.; Reale, J.K. No quarter: Lack of refuge during flow intermittency results in catastrophic mortality of an imperiled minnow. Freshw. Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, A.A.; Davis, J.J.; Edwards, M.S.; Turner, T.F. Habitat and resource use by larval and juvenile fishes in an arid-land river (Rio Grande, New Mexico). Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, R.A.; Haggerty, G.M.; Richard, K.; Klobucar, D. Managed spring runoff to improve nursery floodplain habitat for endangered Rio Grande silvery minnow. Ecohydrology 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, T.R.; Fausch, K.D. Dynamics of intermittent stream habitat regulate persistence of a threatened fish at multiple scales. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 1774–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.K.; Bunn, S.E.; Thoms, M.C.; Marshall, J.C. Persistence of aquatic refugia between flow pulses in a dryland river system (Cooper Creek, Australia). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.F.; Pires, A.M.; Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Magalhães, M.F. Variation in fish assemblages across dry-season pools in a Mediterranean stream: Effects of pool morphology, physicochemical factors and spatial context. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2010, 19, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogan, M.T.; Leidy, R.A.; Neuhaus, L.; Hernandez, C.J.; Carlson, S.M. Biodiversity value of remnant pools in an intermittent stream during the great California drought. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, T.; Bannister, J.; Bennett, K.; Byrnes, E.; Crook, D.A.; Morgan, D.L.; Gleiss, A.; Beatty, S.J. Influence of discharge regime on the movement and refuge use of a freshwater fish in a drying temperate region. Ecohydrol. 2020, e2253, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Vorste, R.; Obedzinski, M.; Nossaman Pierce, S.; Carlson, S.M.; Grantham, T.E. Refuges and ecological traps: Extreme drought threatens persistence of an endangered fish in intermittent streams. Global Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 3834–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, D.E. Water requirements for native species—Rio Grande silvery minnow (Hybognathus amarus). In There’s no doubt we’re in a drought! In Proceedings of the 47th Annual New Mexico Water Conference, Ruidoso, NM, USA, 9–11 October 2002; New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2003; pp. 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, M.P.; Bice, C.M.; Hall, A.; Frears, A.; Watt, A.; Whiterod, N.S.; Beheregaray, L.B.; Harris, J.O.; Zampatti, B.P. Freshwater fish conservation in the face of critical water shortages in the southern Murray–Darling Basin, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 64, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddlier, S.; Koehn, J.D.; Hammer, M.P. Let’s not forget the small fishes–Conservation of two threatened species of pygmy perch in south-eastern Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 64, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.S.; Bradford, M.J. Evaluation of a large-scale fish salvage to reduce the impacts of controlled flow reduction in a regulated river. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1996, 16, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, B.A. Evaluating Fish Rescue as a Drought Adaptation Strategy for Imperiled Coho Salmon: A Life-Cycle Modeling Approach. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Horn, D.; Reale, J.; Archdeacon, T. Water quality in three potential aquatic refugia in an arid-land river: Assessing suitability to sustain populations of an endangered fish species. Unpublished work.
- Buhl, K. (U.S. Geological Survey, Yankton, SD, USA). Personal communication, 2011.
- Bliss, C.I. The calculation of time-mortality curve. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1937, 24, 815–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, F.E.J. Effects of the environment on animal activity. Univ. Toronto Stud. Biol. 1947, 68, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Beitinger, T.; Bennett, W.; McCauley, R. Temperature tolerances of North American freshwater fishes exposed to dynamic changes in temperature. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2000, 58, 237–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Kunzmann, A.; Thiele, R.; Slater, M.J. Effects of extreme ambient temperature in European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax acclimated at different salinities: Growth performance, metabolic and molecular stress responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 139371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.H.; Gamperl, A.K. Effect of acute and chronic hypoxia on the swimming performance, metabolic capacity and cardiac function of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lau, K.; Lai, K.P.; Zhang, J.; Chung-Kwan, A.; Li, J.; Tong, Y.; Chan, T.; Wong, C.K.; Chiu, J.M.; et al. Hypoxia causes transgenerational impairments in reproduction of fish. Nat Commun. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, P.S. Ecological effects of perturbation by drought in flowing waters. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SWCA Environmental Consultants; Albuquerque, New Mexico. Unpublished work. 2007.
- Farless, N.A.; Brewer, S.L. Thermal tolerances of fishes occupying groundwater and surface-water dominated streams. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 36, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Horn, D.J.; Reale, J.K.; Segura, M.S. Assessing temporal and spatial continuous water quality trends in the Upper Rio Grande, Rio Chama, and Middle Rio Grande (Water Years 2015–2019). Unpublished work.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using {lme4}. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archdeacon, T.P.; Remshardt, W.J.; Knecht, T.L. Comparison of two methods for implanting passive integrated transponders in Rio Grande silvery minnow. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2009, 29, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franssen, N.R.; Gilbert, E.I.; James, A.P.; Davis, J.E. Isotopic tissue turnover and discrimination factors following a laboratory diet switch in Colorado pikeminnow (Ptychocheilus lucius). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, C.A.; Barrows, R.T.; Ulibarri, M.; Gould, W.R. Diet optimization of juvenile Rio Grande silvery minnow. N. Am. J. Aquacult. 2010, 72, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Widmer, A.M.; Carveth, C.J.; Bonar, S.A.; Simms, J.R. Upper temperature tolerance of loach minnow under acute, chronic, and fluctuating thermal regimes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2006, 135, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.S.; Coleman, M.A.; Konowal, A.M.; May, M.K.; Johnson, S.; Vieira, N.K.M.; Saunders, J.R. Development of new water temperature criteria to protect Colorado’s fisheries. Fisheries 2008, 33, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, W.H.; Sweeney, B.W.; Law, J.M. Fish growth, physiological stress, and tissue condition in response to rate of temperature change during cool or warm diel thermal cycles. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahm, C.N.; Candelaria-Ley, R.I.; Reale, C.S.; Reale, J.K.; Van Horn, D.J. Extreme water quality degradation following a catastrophic forest fire. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2584–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, B.R.; Vinyard, G.L. Effects of high chronic temperatures and diel temperature cycles on the survival and growth of Lahontan cutthroat trout. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1999, 128, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, V.; Muñoz, I.; Giorgi, A.; Omella, M.; Sabater, F.; Sabater, S. Drought and postdrought recovery cycles in an intermittent Mediterranean stream: Structural and functional aspects. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, H.T. Primary production in flowing waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 1, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixby, B.; Burdett, A.; University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, USA. Unpublished work. 2011.
- Phillips, F.M.; Mills, S.; Hendrickx, M.H.; Hogan, J. Environmental tracers applied to quantifying causes of salinity in arid-region rivers: Results from the Rio Grande Basin, Southwestern USA. Dev. Water Sci. 2003, 50, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, D.L.; Anderholm, S.K.; Hogan, J.F.; Phillips, F.M.; Hibbs, B.J.; Witcher, J.C.; Matherne, A.M.; Falk, S.E. Knowledge and Understanding of Dissolved Solids in the Rio Grande–San Acacia, New Mexico, to Fort Quitman, Texas, and Plan for Future Studies and Monitoring. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2013–1190. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2013/1190/ (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Moore, S.J.; Bassett, R.L.; Liu, B.; Wolf, C.P.; Doremus, D. Geochemical tracers to evaluate hydrogeologic controls on river salinization. Groundwater 2008, 46, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Tecklenburg, C.; Munz, M.; Naden, E. Streambed nitrogen cycling beyond the hyporheic zone: Flow controls on horizontal patterns and depth distribution of nitrate and dissolved oxygen in the upwelling groundwater of a lowland river. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, C.S.; Valett, M.H.; Dahm, C.N. Whole-stream metabolism in two montane streams: Contribution of the hyporheic zone. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 3, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, J.K.; Van Horn, D.J.; Condon, K.E.; Dahm, C.N. The effects of catastrophic wildfire on water quality along a river continuum. Freshw. Sci. 2015, 34, 1426–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, P.J.; González-Pinzón, R.; Van Horn, D.J.; Reale, J.K.; Nichols, J.; Khandewal, A. Water quality impacts of urban and non-urban arid-land runoff on the Rio Grande. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frus, R.; Crossey, L.J.; Dahm, C.N.; Karlstrom, K.E.; Crowley, L. Influence of desert springs on habitat of endangered Zuni bluehead sucker (Catostomus discobolus yarrowi). Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2020, 26, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P.; Lefrançois, C.; Shingles, A. Hypoxia and the antipredator behaviours of fishes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2007, 362, 2105–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P.; Herbert, N.A.; Lefrançois, C.; Steffensen, J.F.; McKenzie, D.J. The Effect of Hypoxia on Fish Swimming Performance and Behaviour. In Swimming Physiology of Fish; Palastra, A., Planas, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameida, L.Z. Effects of Lake Erie Hypoxia on Fish Habitat Quality and Yellow Perch Behavior and Physiology. Master’s Thesis, Perdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Turko, A.J.; Nolan, C.B.; Balshine, S.; Scott, G.R.; Pitcher, T.E. Thermal tolerance depends on season, age and body condition in imperilled redside dace Clinostomus elongatus. Conserv. Physiol. 2020, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.J.; Caldwell, C.A.; Gould, W.R. Physiological stress responses of Rio Grande silvery minnow: Effects of individual and multiple physical stressors of handling, confinement, and transport. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2009, 29, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, R.K.; Platania, S.P. Flow regulation and fragmentation imperil pelagic-spawning riverine fishes. Ecolog. Appl. 2007, 17, 2074–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkin, J.S.; Gido, K.B.; Costigan, K.H.; Daniels, M.D.; Johnson, E.R. Fragmentation and drying ratchet down Great Plains stream fish diversity. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2015, 25, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, J.A.; Moyle, P.B.; Fangue, N.; Connon, R.E. Is extinction inevitable for Delta Smelt and Longfin Smelt? An opinion and recommendations for recovery. San Francisco Estuary Watershed Sci. 2017, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardador, L.; Brotons, L.; Mougeot, F.; Giralt, D.; Bota, G.; Pomarol, M.; Arroyo, B. Conservation traps and long-term species persistence in human-dominated systems. Conserv. Lett. 2015, 8, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, G.J.; Wolock, D.M. Recent declines in Western, U.S. snowpack in the context of twentieth-century climate variability. Earth Interact. 2009, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seager, R.; Ting, M.; Li, C.; Naik, N.; Cook, B.; Nakamura, J.; Liu, H. Projections of declining surface-water availability for the southwestern United States. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.J. Social, political, and institutional setting: Water management problems of the Rio Grande. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2009, 135, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Hermoso, V.; Linke, S.; Nipperess, D.; Turak, E.; Hughes, L. Freshwater conservation planning under climate change: Demonstrating proactive approaches for Australian Odonata. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruch-Mordo, S.; Evans, J.S.; Severson, J.P.; Naugle, D.E.; Maestas, J.D.; Kiesecker, J.M.; Falkowski, M.J.; Hagen, C.A.; Reese, K.P. Saving sage-grouse from the trees: A proactive solution to reducing a key threat to a candidate species. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 167, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Date | Conditions | Number | Survival |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26 March 2018 | Continuous | 102 | 76.4 |
| 24 April 2018 | Continuous | 67 | 100 |
| 9 May 2018 | Continuous | 142 | 73.9 |
| 3 April 2018 | Intermittent | 250 | 24.4 |
| 10 April 2018 | Intermittent | 300 | 43.7 |
| 8 July 2018 | Intermittent | 226 | 2.6 |
| 4 August 2018 | Intermittent | 267 | 6.6 |
| 11 June 2020 | Intermittent | 45 | 8.9 |
| 12 June 2020 | Intermittent | 290 | 1.4 |
| 14 June 2020 | Intermittent | 101 | 8.9 |
| 14 July 2020 | Intermittent | 389 | 5.4 |
| 7 August 2020 | Intermittent | 421 | 5.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Archdeacon, T.P.; Diver, T.A.; Reale, J.K. Fish Rescue during Streamflow Intermittency May Not Be Effective for Conservation of Rio Grande Silvery Minnow. Water 2020, 12, 3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123371
Archdeacon TP, Diver TA, Reale JK. Fish Rescue during Streamflow Intermittency May Not Be Effective for Conservation of Rio Grande Silvery Minnow. Water. 2020; 12(12):3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123371
Chicago/Turabian StyleArchdeacon, Thomas P., Tracy A. Diver, and Justin K. Reale. 2020. "Fish Rescue during Streamflow Intermittency May Not Be Effective for Conservation of Rio Grande Silvery Minnow" Water 12, no. 12: 3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123371
APA StyleArchdeacon, T. P., Diver, T. A., & Reale, J. K. (2020). Fish Rescue during Streamflow Intermittency May Not Be Effective for Conservation of Rio Grande Silvery Minnow. Water, 12(12), 3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123371





