Using an ETWatch (RS)-UZF-MODFLOW Coupled Model to Optimize Joint Use of Transferred Water and Local Water Sources in a Saline Water Area of the North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Model Description
2.2.1. ETWatch
2.2.2. UZF Package and Pedo Transfer Functions Parameters
2.2.3. MODFLOW-NWT
2.3. Data
2.4. Numerical Hydrological Model, Calibration and Validation
2.4.1. Initial Conditions and Lateral Boundary
2.4.2. Sinks and Sources
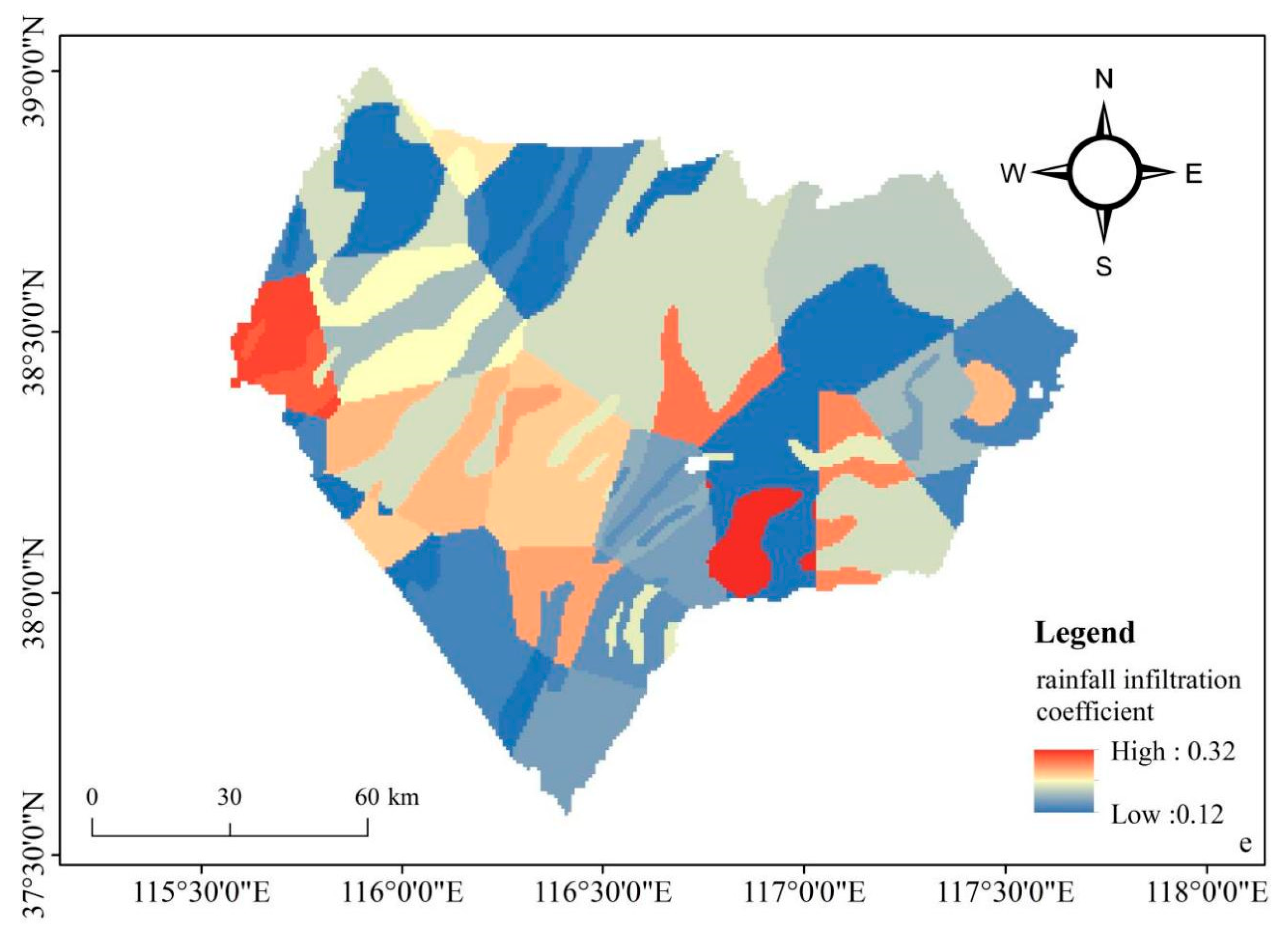
Recharge from Rainfall
Recharge from the Leakage of Reservoir, Lake and River
Groundwater Pumping Data
2.4.3. Calibration and Validation
2.5. Scenarios Setting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Calibration and Validation
3.2. Prediction of Groundwater Dynamics and Simulation with Different Irrigation Scenarios
3.3. Evapotranspiration Lost from Unsaturated Zone and Groundwater
3.4. Optimal Agricultural Irrigation Ways Based on Analysis of Groundwater Balance
3.5. The Strengths and Limitations of the Coupled Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, J.Y.; Guan, H.D.; Huo, Z.L.; Wang, F.X.; Huang, G.H.; Boll, J. Water saving practices enhance regional efficiency of water consumption and water productivity in an arid agricultural area with shallow groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijsberman, F.R. Water scarcity: Factor fiction? Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 80, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R. Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, S. Long-term groundwater variations in Northwest India from satellite gravity measurements. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 116, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M.; Tweed, S.; Van Dijk, A.; Timbal, B. A review of historic and future hydrological changes in the Murray–Darling Basin. Glob。 Planet. Chang. 2012, 80–81, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Faunt, C.C.; Longuevergne, L.; Reedy, R.C.; Alley, W.M.; McGuire, V.L.; McMahon, P.B. Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Nonsustainable groundwater sustaining irrigation: A global assessment. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; van Beek, L.P.H.; van Kempen, C.M.; Reckman, J.W.T.M.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño, S.; Sanz, D.; Gómez-Alday, J.J. Methodology for quantifying groundwater abstractions for agriculture via remote sensing and GIS. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 795–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidoro, D.; Quılez, D.; Aragüés, R. Water balance and irrigation performance analysis: LaViolada irrigation district (Spain) as a case study. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 64, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriam, J.L.; Burt, C.; Clemmens, A.; Solomon, K.; Howell, T.; Strelkoff, T. Irrigation performance measures: Efficiency and uniformity. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1999, 125, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Z.; Hao, X.M.; Du, T.S.; Tong, L.; Su, X.L.; Lu, H.N.; Li, X.L.; Huo, Z.L.; Li, S.E.; Ding, R.S. Improving agricultural water productivity to ensure food security in China under changing environment: From research to practice. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubczynski, M.W. The hydrogeological role of trees in water-limited environments. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balugani, E.; Lubczynski, M.W.; Reyes-Acosta, L.; Van Der, T.C.; Francés, A.P.; Metselaar, K. Groundwater and unsaturated zone evaporation and transpiration in a semi-arid open wood land. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubczynski, M.W.; Gurwin, J. Integration of various data sources for transient groundwater modeling with spatio-temporally variable fluxes—Sardon study case, Spain. J. Hydrol. 2005, 306, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doble, R.C.; Crosbie, R.S. Review: Current and emerging methods for catchment-scale modelling of recharge and evapotranspiration from shallow groundwater. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doble, R.C.; Pickett, T.; Crosbie, R.S.; Morgan, L.; Turnadge, C.; Davies, P. Emulation of recharge and evapotranspiration processes in shallow groundwater systems. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, M.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Lenters, J.; Wang, T. Quantifying the impact of groundwater depth on evapotranspiration in a semi-arid grassland region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 787–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, K.M.; Cihan, A.; Sakaki, T.; Illangasekare, T.H. Evaporation from soils under thermal boundary conditions: Experimental and modeling investigation to compare equilibrium-and none quilibrium-based approaches. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W05540.1–W05540.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Su, Z.; Wan, L.; Wen, J. A simulation analysis of the advective effect on evaporation using a two-phase heat and mass flow model. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, W.; Zhan, H.; Qiu, F.; An, L. New judgement on the source of soil water in extremely dry zone. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balugani, E.; Lubczynski, M.W.; Metselaar, K. A framework for sourcing of evaporation between saturated and unsaturated zone in bare soil condition. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 61, 1981–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babajimopoulos, C.; Panoras, A.; Georgoussis, H.; Arampatzis, G.; Hatzigiannakis, E.; Papamichail, D. Contribution to irrigation from shallow water table under field conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 92, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.J.F.; Famiglietti, J.S. Regional groundwater evapotranspiration in illinois. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmens, A.J.; Allen, R.G. Impact of Agricultural Water Conservation on Water Availability; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2005; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, E.X.; Li, X.W. Dialectical analysis of the relation between water resources shortage and ecosystem environment problem in Heihe River Basin. Inner Mong. Petrochem. Ind. 2005, 3, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jhorar, R.K.; Smit, A.A.M.F.R.; Roest, C.W.J. Assessment of alternative water management options for irrigated agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huo, Z.; Feng, S.; Guo, P.; Guan, H. Estimating groundwater evapotranspiration from irrigated cropland in corp orating root zone soil texture and moisture dynamics. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockstrom, J. Water for food and nature in drought-pron etropics: Vapour shift in rain-fed agriculture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 358, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Doody, T.M.; Guerschman, J.P.; Huete, A.R.; King, E.A.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.; Van Niel, T.G.; Yebra, M.; Zhang, Y.Q. Actual evapotranspiration estimation by ground and remote sensing methods: The Australian experience. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4103–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; McVicar, T.R.; McCabe, M.F. Estimating land surface evaporation: A review of methods using remotely sensed surface temperature data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra, M.; Van Dijk, A.; Leuning, R.; Huete, A.; Guerschman, J.P. Evaluation of optical remote sensing to estimate actual evapotranspiration and canopy conductance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Nachabe, M.; Ross, M. Extinction depth and evapotranspiration from groundwater under selected land covers. Groundwater 2007, 45, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran, M.; Carrera, J.; Massana, J.; Saaltink, M.W.; Olivella, S.; Ayora, C.; Lloret, A. Dynamics of water vapor flux and water separation processes during evaporation from a salty dry soil. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, V.H.R.; Montenegro, S.; Almeida, C.N.; Silva, B.B.; Oliveira, L.M.; Gusmao, A.C.V.; Freitas, E.S.; Montenegro, A.A.A. Alluvial groundwater recharge estimation in semi-arid environment using remotely sensed data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.J.; Kustas, W.P.; Ritchie, J.C.; Jackson, T.J.; Rango, A. Remote sensing in hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1367–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekula, M.; Lubczynski, M.W. Use of remote sensing and long-term in-situ time-series data in an integrated hydrological model of the Central Kalahari Basin, Southern Africa. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1541–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, X.J.; Hu, C.S. Scientific basis for constructing the“BohaiSeaGranary”—Demands, potential and approaches. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2011, 26, 371–374. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.Y.; Li, K.J.; Ma, J.Y.; Zheng, C.L. Utilization status and development potential of shallow salt water in Hebei low Plain. Anhui Agron. Bull. 2007, 13, 66–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.F.; Xiong, J.; Yan, N. ETWatch: Models and methods. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 15, 224–239. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.F.; Yan, N.N.; Xiong, J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Zhu, W.W.; Stein, A. Validation of ETWatch using field measurements at diversel and scapes: A ca se study in Hai Basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436–437, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswonger, R.G.; Prudic, D.E.; Regan, R.S. Documentation of the Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF1) Package for Modeling Unsaturated Flow between the Land Surface and the Water Table with MODFLOW-2005; U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 6-A19; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2006.
- Xu, L.J.; Li, H.C. Analysis of evaporation change characteristics of Cangzhou in recent 40years. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 9032–9034. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Jia, Y.H. Investigation and Evaluation of the Sustainable Use of Groundwater in the North China Plain; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.F. Study on the Analysis and Prediction and Evaluation of Influencing Factors of Ground Settlement in Cangzhou, China; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.L.; Wang, S.Q.; Liu, B.X.; Sun, H.Y.; Sheng, Z.P. Impact of water transfer on interaction between surface water and groundwater in the low land area of North China Plain. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2044–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.P.; Li, G.X.; Liu, F.G.; Wu, X.F.; Kondoh, A.; Shen, Y.J. Using remote sensing to determine spatio-temporal variations in winter wheat growing area in the North China Plain. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 494–505. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Marcal, G.S. A High-Resolution Global Map of Soil Hydraulic Properties Produced by a Hierarchical Parameterization of a Physically-Based Water Retention Model. Harv. Dataverse V1 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.F.; Xiong, J.; Yan, N.; Yang, L.; Du, X. ETWatch for monitoring regional evapotranspiration with remote sensing. Adv. Water Sci. 2008, 19, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.F.; Xiong, J.; Yan, N.; Yang, L. ETWatch: An Operational ET Monitoring System with Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2008ISPRS Workshop on Geo-information and Decision Support Systems, Tehran, Iran, 6–7 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Niswonger, R.G.; Prudic, D.E.; Pohll, G.; Constantz, J. Incorporating seepage losses into the unsteady streamflow equations for simulating intermittent flow along mountain front streams. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W06006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morway, E.D.; Gates, T.K.; Niswonger, R.G. Appraising options to reduce shallow groundwater tables and enhance flow conditions over regional scales in an irrigated alluvial aquifer system. J. Hydrol. 2013, 495, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbaugh, A.W. MODFLOW-2005, the U.S. Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model—The Ground-Water Flow Process; U.S. Geological Survey, Techniques and Methods6-A16; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2005.
- Niswonger, R.G.; Prudic, D.E. Modeling variably saturated flow using kinematic waves in MODFLOW. In Groundwater Recharge in a Desert Environment; Water Science and Application Series; Hogan, J.F., Phillips, F.M., Scanlon, B.R., Eds.; The South Western United States, American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume 9, pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Q.Z.; Huo, Z.L.; Huang, G.H. Long-term groundwater dynamics affected by intense agricultural activities in oasis areas of arid in land river basins. Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, G.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, C.L. Land use and land cover changes in Haihe river basin of China. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2012, 43, 136–141. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.L.; Li, H.M.; Xie, X.M.; Dong, W.Q.; Ge, Y.C.; Wang, Y. Study on the controlled management water level of shallow groundwater in Cangxian area based on GMS. South-To-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 15, 108–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.S.; Luo, Z.S. Study on permissible groundwater extraction in Cangzhou, China. Eng. Surv. 2015, 43, 49–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Basak, N.; Chaudhari, S.K.; Sharma, D.K. Impact of varying Ca/Mg waters on ionic balance, dispersion, and clay flocculation of salt affected soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Pagliai, M.; Vignozzi, N. Effect of reclamation on the structure of silty-clay soils irrigated with saline-sodic waters. Int. Agrophys. 2015, 29, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, S.; Flowers, T.; Doyle, R.; Lane, P.; Haros, G.; Shabala, S. Growth responses of Atriplexlentiformis and Medicagoarborea in three soilty pest reated with saline water irrigation. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 128, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani, U.; Dudley, L.M. Field studies of crop response to water and salts tress. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, B. Effects of saline water irrigation and fertilization regimes on soil microbial metabolic activity. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Guo, H.; Min, W.; Li, Q.; Liao, N.; Hou, Z. Effects of saline water irrigation and N application rate on NH3 volatilization and N use efficiency in a drip-irrigated cotton field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Wan, S.; Xu, J.; Li, N. Response of daylily (Hemerocallishybridus cv.‘ Stelladeoro’) to saline water irrigation in two coastal saline soils. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 205, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Kang, Y.; Wan, S.; Hu, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, T. Soil salinity management with dripirrigation and its effects on soil hydraulic properties in North China coastal saline soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Shao, L.W.; Sun, H.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.F. Effect of brackish water irrigation on soil salt balance and yield of both winter wheat and summer maize. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016, 24, 1049–1058. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


















| Subarea | Vadose Zone Lithology | The Depth of Groundwater Table (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 | 2–4 | 4–6 | 6–8 | >8 | ||
| Alluvial plain | Medium and coarse sand | 0.28–0.3 | 0.35–0.45 | 0.30–0.35 | ||
| Fine sand and silt | 0.26–0.28 | 0.28–0.32 | 0.28–0.30 | |||
| Silt | 0.14–0.23 | 0.23–0.33 | 0.33–0.28 | 0.28–0.25 | 0.25–0.23 | |
| Silt clay | 0.11–0.16 | 0.16–0.24 | 0.22–0.18 | 0.18–0.16 | 0.16–0.14 | |
| Clay | 0.09–0.13 | 0.14–0.18 | 0.16–0.12 | 0.14–0.10 | 0.12–0.10 | |
| Marine plain | Fine sand and silt | 0.25–0.36 | 0.36–0.40 | 0.40–0.28 | 0.28–0.24 | 0.24–0.22 |
| Silt | 0.14–0.24 | 0.17–0.28 | 0.29–0.19 | 0.26–0.20 | 0.18–0.16 | |
| Silt clay | 0.09–0.20 | 0.14–0.26 | 0.26–0.17 | 0.18–0.14 | 0.14–0.12 | |
| Clay | 0.07–0.15 | 0.12–0.19 | 0.10–0.16 | 0.13–0.12 | 0.12–0.11 | |
| Scenario | Shallow Aquifer | Deep Aquifer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Water/(108 m3·a−1) | Agricultural Water/(108 m3·a−1) | Urban Water/(108 m3·a−1) | Agricultural Water/(108 m3·a−1) | ||
| Scenario 1 (current pumping method) | In 2013–2030 | 0.455 | 2.83 | 2.519 | 4.467 |
| Scenario 2 (use saline water) | In 2013–2014 | 0.455 | 2.83 | 2.519 | 4.467 |
| In 2015–2030 | 0.455 | 4.35 | 2.519 | 2.94 | |
| Scenario 3 (surface waterdiversion) | In 2013–2014 | 0.455 | 2.83 | 2.519 | 4.467 |
| In 2015–2030 | 0.455 | 2.78 | 2.519 | 3.25 | |
| Scenario 4 (saline water + surface water) | In 2013–2014 | 0.455 | 2.83 | 2.519 | 4.467 |
| In 2015 | 0.455 | 4.333 | 2.519 | 2.436 | |
| In 2016–2020 | 0.455 | 4.333 | 0.789 | 2.436 | |
| In 2021–2030 | 0.304 | 4.333 | 0 | 2.436 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Li, M.; Lv, M.; Feng, W. Using an ETWatch (RS)-UZF-MODFLOW Coupled Model to Optimize Joint Use of Transferred Water and Local Water Sources in a Saline Water Area of the North China Plain. Water 2020, 12, 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123361
Hou X, Wang S, Jin X, Li M, Lv M, Feng W. Using an ETWatch (RS)-UZF-MODFLOW Coupled Model to Optimize Joint Use of Transferred Water and Local Water Sources in a Saline Water Area of the North China Plain. Water. 2020; 12(12):3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123361
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Xianglong, Shiqin Wang, Xiaorui Jin, Mingliang Li, Mengyu Lv, and Wenzhao Feng. 2020. "Using an ETWatch (RS)-UZF-MODFLOW Coupled Model to Optimize Joint Use of Transferred Water and Local Water Sources in a Saline Water Area of the North China Plain" Water 12, no. 12: 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123361
APA StyleHou, X., Wang, S., Jin, X., Li, M., Lv, M., & Feng, W. (2020). Using an ETWatch (RS)-UZF-MODFLOW Coupled Model to Optimize Joint Use of Transferred Water and Local Water Sources in a Saline Water Area of the North China Plain. Water, 12(12), 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123361





