Identifying the Influence of Land Cover and Human Population on Chlorophyll a Concentrations Using a Pseudo-Watershed Analytical Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
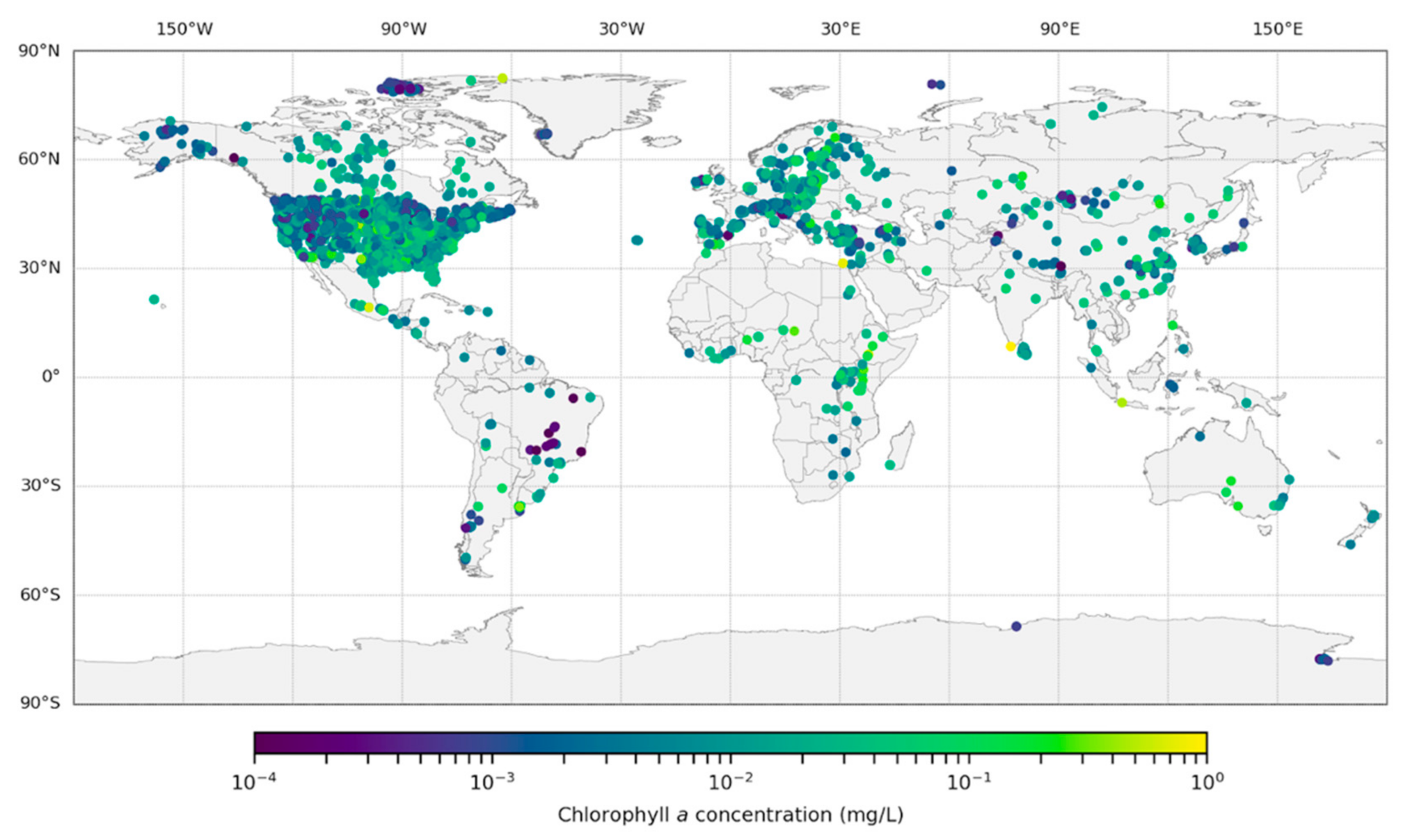
2.1. Data Acquisition
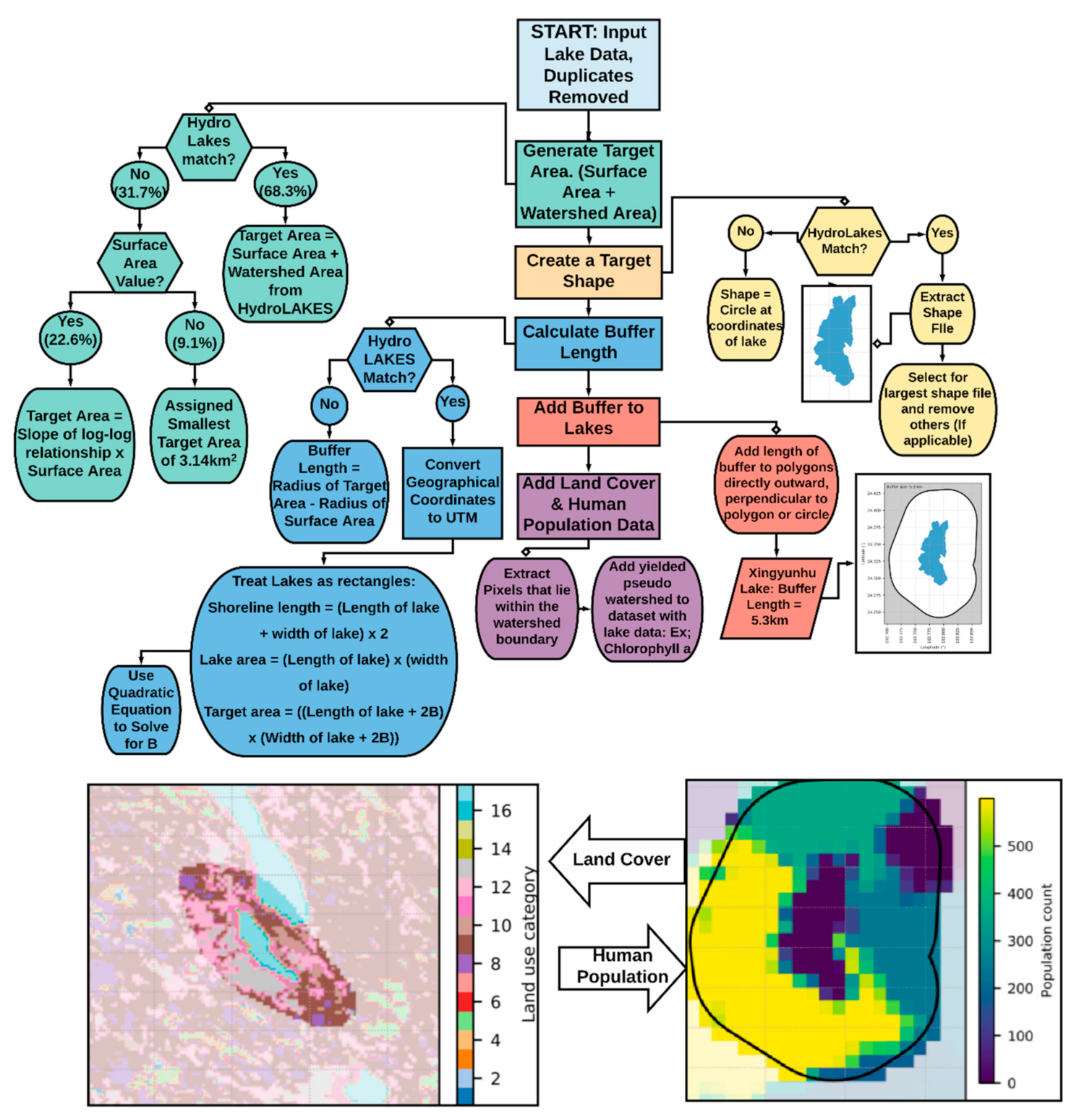
2.2. Development of an Analytical Framework
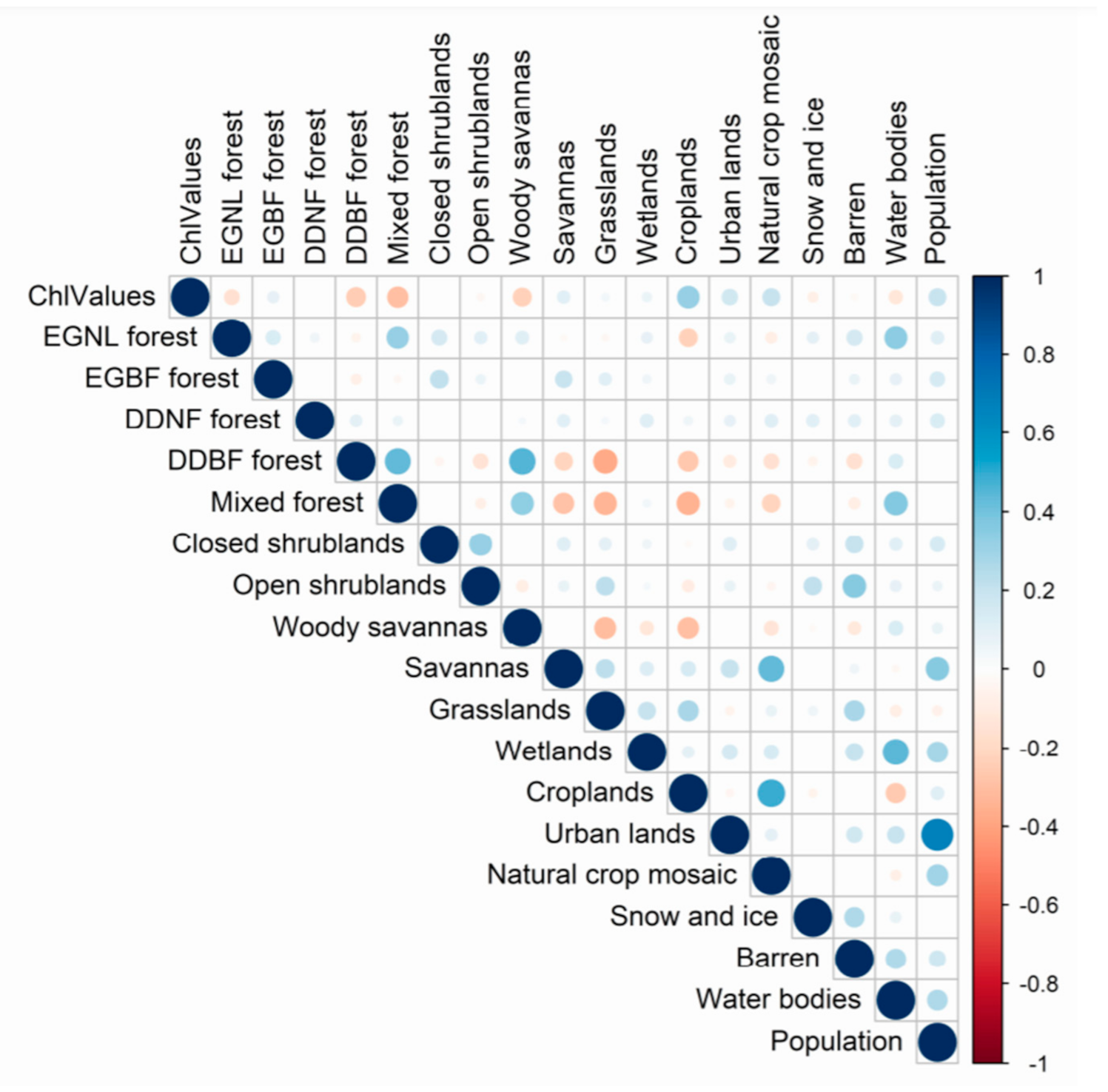
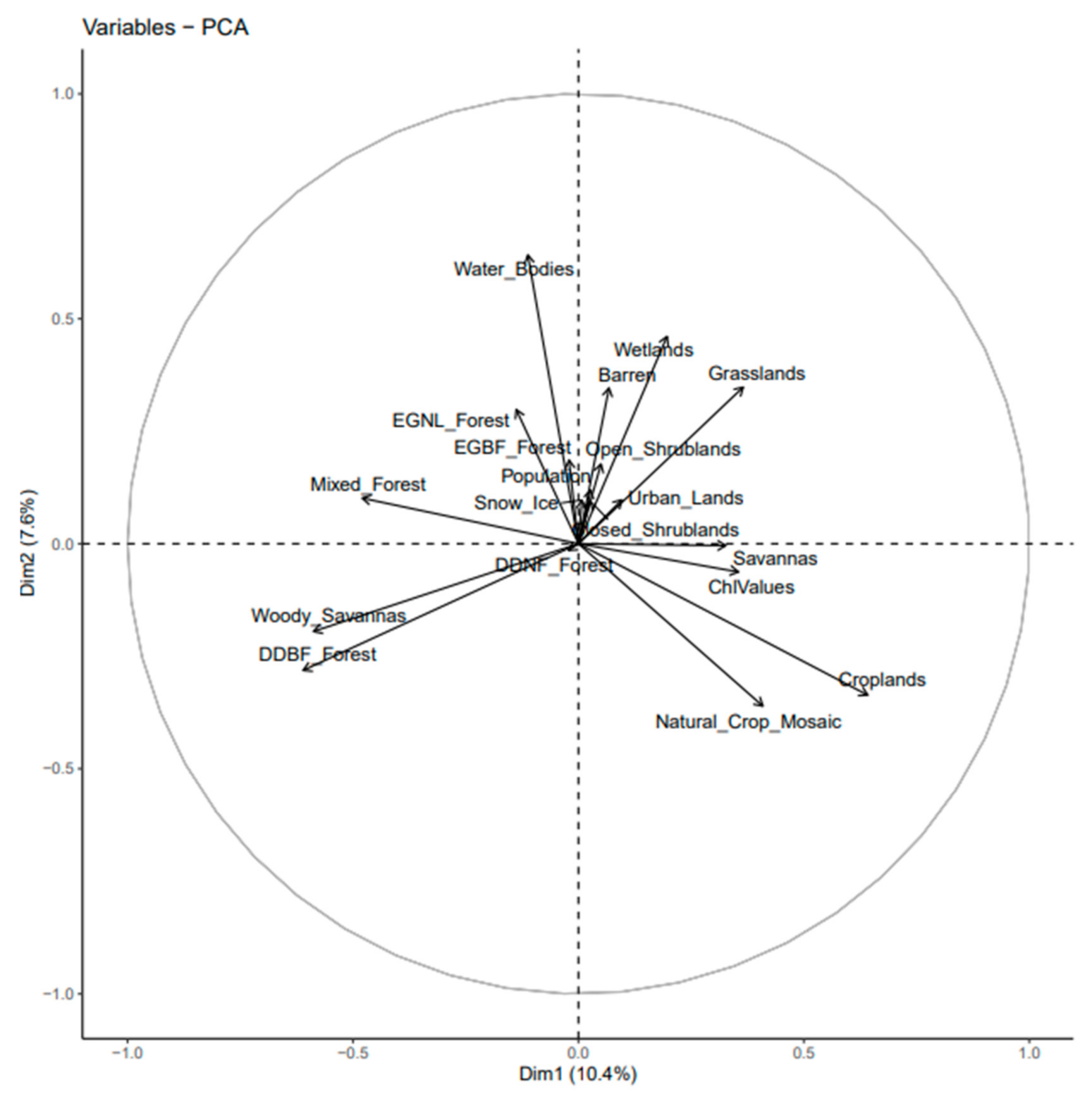
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Framework for the Development of Pseudo-Watersheds
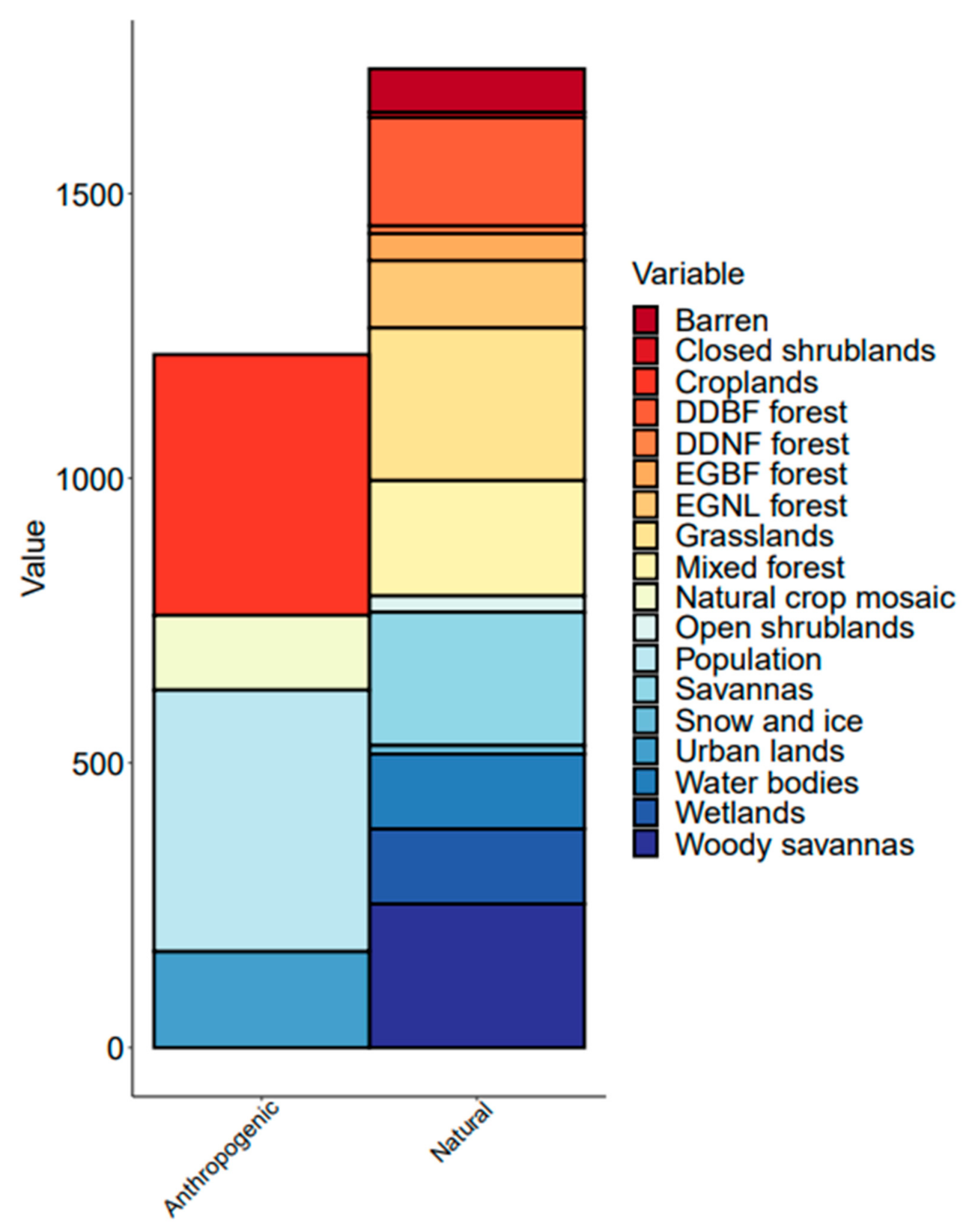
3.2. Quantification of Land Cover and Human Density on Chlorophyll Concentrations
4. Discussion
4.1. Analytical Framework
4.2. Agricultural Influences on Chlorophyll
4.3. Natural and Anthropogenic Land Cover
4.4. Sustainable Water Management
4.5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strayer, D.L.; Dudgeon, D. Freshwater biodiversity conservation: Recent progress and future challenges. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Stanley, E.H.; Vander Zanden, M.J. State of the World’s Freshwater Ecosystems: Physical Chemical and Biological Changes. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2011, 36, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, R.; Filazzola, A.; Mahdiyan, O.; Shuvo, A.; Blagrave, K.; Ewins, C.; Moslenko, L.; Gray, D.K.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Relationship of total phosphorus and chlorophyll in lakes worldwide. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.K.; Steele, B.G.; Weathers, K.C.; Cottingham, K.L.; Ewing, H.A.; Hanson, P.C.; Carey, C.C. Differential Responses of Maximum Versus Median Chlorophyll-a to Air Temperature and Nutrient Loads in an Oligotrophic Lake Over 31 Years. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theissen, K.M.; Hobbs, W.H.; Ramstack, J.M.; Zimmer, K.D.; Domine, L.M.; Cotner, J.B.; Sugita, S. The altered ecology of Lake Christina: A record of regime shifts, land-use change, and management from a temperate shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus and the Eutrophication of Freshwater Lakes. J. Phycol. 1971, 7, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, Z.E.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Quantifying Relationships Among Phosphorus, Agriculture, and Lake Depth at an Inter-Regional Scale. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, B.D.; Finlay, J.C.; Hobbie, S.E.; Baker, L.A.; Sterner, R.W.; Nidzgorski, D.; Wilson, B.N. Contrasting influences of stormflow and baseflow pathways on nitrogen and phosphorus export from an urban watershed. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Colom, W.; Pierson, D.; Pettersson, K. Water column stability and summer phytoplankton dynamics in a temperate lake (Lake Erken, Sweden). Inland Waters 2016, 6, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, X.; Valero, E.; Santos, R.M.B.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Anthropogenic nutrients eutrophication in multiple land use watershed: Best management practices and policies for the protection of water resources. Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Ringler, C.; Zhu, T. Water for Agriculture: Maintaining Food Security under Growing Scarcity. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, T.A.; Katpatal, Y.B.; Vasudeo, A.D. Spatial evaluation of impacts of increase in impervious surface area on SCS-CN and runoff in Nagpur urban watersheds, India. Arab J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.E.; Lazor, R.; Chambers, P.A.; Yates, A.G. Land-use practices influence nutrient concentrations of southwestern Ontario streams. Can. Water Resour. J. 2018, 43, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ma, R.; Xiong, J. Can the watershed non-point phosphorus pollution be interpreted by critical soil properties? A new insight of different soil P states. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Martinez-Casasnovas, J.A. Climate change influence on runoff and soil losses in a rainfed basin with Mediterranean climate. Nat. Hazards. 2015, 78, 1065–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious Surface Coverage; The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Peng, J. Impervious surface impact on water quality in the process of rapid urbanization in Shenzhen, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 2365–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Engel, B.A.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Lim, K.J. Forecasting land use change and its environmental impact at a watershed scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 76, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.P.; Stager, J. Rangeland to cropland conversions as replacement land for prime farmland lost to urban development. Soc. Sci. J. 2001, 38, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burant, A.; Selbig, W.; Furlong, E.T.; Higgins, C.P. Trace organic contaminants in urban runoff; Associations with urban land use. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 248, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Roberts, D.P.; Xie, L.; Maul, J.E.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liao, X. Development of a biologically based fertilizer, incorporating Bacillus megaterium A6, for improved phosphorus nutrition of oilseed rape. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, C.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Wang, X.; Ren, P. Nitrogen and Phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrice, J.A.; Danz, N.P.; Regal, R.R.; Kelly, J.R.; Niemi, G.J.; Reavie, E.D.; Hollenhorst, T.; Axler, R.P.; Trebitz, A.S.; Cotter, A.M.; et al. Human Influence on Water Quality in Great Lakes Coastal Wetlands. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, T.; Soranno, P.A.; Webster, K.E.; Cheruvelil, K.S. Landscape drivers of regional variation in the relationship between total phosphorus and chlorophyll in lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cournane, F.C.; McDowell, R.; Littlejohn, R.; Condron, L. Effects of cattle, sheep and deer grazing on soil physical quality and losses of phosphorus and suspended sediment losses in surface runoff. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, J.J.; Newham, L.T.H.; Greene, R.S.B.; Jakeman, A.J.; Croke, B.F.W. A review of nitrogen and phosphorus export to waterways; context for catchment modelling. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2006, 57, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Mei, Z.P. Effects of human activities on the ecological changes of lakes in China. GeoJournal 1996, 40, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juma, D.W.; Wang, H.; Li, F. Impacts of population growth and economic development on water quality of a lake: Case study of Lake Victoria Kenya water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5737–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.F.; Labou, S.G.; Cramer, A.N.; Brousil, M.R.; Luff, B.T. The global lake area, climate and population dataset. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.W.; Schindler, D.E.; Scheuerell, M.D.; Smith, D.; Frodge, J. Lake Eutrophication at the Urban Fringe, Seattle Region, USA. Ambio A J. Hum. Environ. 2003, 32, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.; Morgenroth, E. Estimating the effect of land-use and catchment characteristics on lake water quality: Irish lakes 2004–2009. J. Stat. Soc. Inq. Soc. Irel. 2013, 42, 64–80. [Google Scholar]
- Whalley, K.; Luo, W. The Pressure of Society on Water Quality: A Land Use Impact Study of Lake Ripley in Oaklan, Wisconsin. Geoscience 2017, 3, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Mahdiyan, O.; Shuvo, A.; Ewins, C.; Moslenko, L.; Sadid, T.; Blagrave, K.; Imrit, M.A.; Gray, D.K.; Quinlan, R.; et al. A database of chlorophyll and water chemistry in freshwater lakes. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for International Earth Science Information Network-CIESIN-Columbia University. Gridded Population of the World, Version 4 (GPWv4): Population Count, Revision 11; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, M.; Sulla-Menashe, D. MCD12Q1 MODIS/Terra + Aqua Land Cover Type Yearly L3 Global 500m SIN Grid V006. Distributed by NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC. 2019. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MCD12Q1.006 (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the volume and age of water stored in global lakes using a geo-statistical approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R foundation of Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Croux, C.; Dehon, C. Influence functions of the Spearman and Kendall correlation measures. Stat. Methods Appl. 2010, 19, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra; Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses; CRAN R package: Version 1.0.7; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L.F. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Coombes, K.R.; Wang, M. PCDimension: Finding the Number of Significant Principal Components; CRAN R Package: Version 1.1.11; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by RandomForest. R News. 2002, 2–3, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larned, S.T.; Moores, J.; Gadd, J.; Ballies, B.; Schallenberg, M. Evidence for the effects of land use on freshwater ecosystems in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 54, 551–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Khan, R.; Ahmad, N.; Mapsood, I. Randon Forests and Decision Trees. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues. 2012, 9, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Tilman, D. Global environmental impacts of agricultural expansion: The need for sustainable and efficient practices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5992–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.R.; Quin, B.F.; Nguyen, M.L. Phosphorus Runoff from Agricultural Land and Direct Fertilizer Effects: A Review. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1954–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Bradley-Silvester, R.; Jones, D.L.; Healey, J.R.; Talboys, P.J. Feed the Crop Not the Soil; Rethinking Phosphorus Management in the Food Chain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6523–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooda, P.S.; Edwards, A.C.; Anderson, H.A.; Miller, A. A review of water quality concerns in livestock farming areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 250, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.; Trolle, D.; Sondergaard, M.; Laurdisen, T.L.; Bjerring, R.; Olesen, J.E.; Jeppesen, E. Watershed land use effects on lake water quality in Denmark. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowrance, R.; Todd, R.; Fail, J.; Hendrickson, O.; Leonard, R.; Asmussen, L. Riparian Forest as Nutrient Filters in Agricultural Watersheds. Bioscience 1984, 34, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Bu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G. Eutrophication in the Yunnan Plateau lakes: The influence of lake morphology, watershed land use, and socioeconomic factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, C.K.; Birk, S.; Eme, D.; Gerisch, M.; Hering, D.; Kernan, M.; Maileht, K.; Mischke, U.; Ott, I.; Pletterbauer, F.; et al. Disentangling the effects of land use and geo-climactic factors on diversity in European freshwater ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; O’Grady, A.P.; Dale, A.; Arthington, A.H.; Gell, P.A.; Driver, P.D.; Bond, N.; Casanova, M.; Finlayson, M.; Watts, R.J.; et al. When trends intersect: The challenge of protecting freshwater ecosystems under multiple land use and hydrological intensification scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 534, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Chen, K.; Pan, M.; Zhou, Z. Dianchi Lake watershed impervious surface area dynamics and their impact on lake water quality from 1988 to 2017. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29643–29653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, A.; Dunnett, N. Amount of water runoff from different vegetation types on extensive green roofs: Effects of plant species, diversity and plant structure. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2012, 104, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Engel, B.A.; Collingsworth, P.D.; Pijanowski, B.C. Optimal implementation of green infrastructure practice to minimize influences of land use change and climate change on hydrology and water quality: Case study in Spy Run Creek watershed, Indiana. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisinger, A.J.; Woytowitz, E.; Majcher, E.; Rosi, E.J.; Belt, K.T.; Duncan, J.M.; Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M. Changes in long-term water quality of Baltimroe streams are associated with both gray and green infrastructure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, S60–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Shrestha, N.; MacIvor, J.S. The contribution of constructed green infrastructure to urban biodiversity: A synthesis and meta-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 2131–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Samuelson, L.; Jagrud, L.; Mattsson, E.; Celander, T.; Malmer, A.; Bengtsson, K.; Johansson, O.; Schaaf, N.; Svending, O.; et al. Water, Forests, People: The Swedish Experience in Building Resilient Landscapes. Environ. Manag. 2018, 62, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humann, M.; Schuler, G.; Muller, C.; Schneider, R.; Johst, M.; Caspari, T. Identification of runoff –The impact of different forest types and soil properties on runoff formation and floods. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, B.X.; Gomi, T.; Miyata, S.; Sidle, R.C. Peak flow responses and recession flow characteristics after thinning of Japanese cypress forest in a headwater catchment. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2012, 6, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.; Alfredo, K.; Fisher, J. Sustainable Water Management in Urban, Agricultural, and Natural Systems. Water 2014, 6, 3934–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Green, P.; Balk, D.; Fekete, B.M.; Revenga, C.; Todd, M.; Montgomery, M. Urban growth, climate change, and freshwater availability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6312–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healthwaite, A.L. Multiple stressors on water availability at global to catchment scales; understanding human impact on nutrient cycles to protect water quality and water availability in the long term. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L., II; Lambin, E.F.; Reenberg, A. The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20666–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, G.S.; Buerkert, A.; Hoffman, E.M.; Schlecht, E.; von Cramon-Taubadel, S.; Tscharntke, T. Implications of agricultural transitions and urbanization for ecosystem services. Nature 2014, 515, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, M.Y.; Liang, S.; Lee, J. Toxin-Producing Cyanobacteria in Freshwater: A review of the problems, impact on drinking water safety, and efforts for protecting public health. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Boyer, G.L. Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraterrigo, J.M.; Downing, J.A. The Infleunce of Land Use and Lake Nutrients Varies with Watershed Transport Capacity. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleifle, A.; Saavedra, O.; Yoshimura, C.; Elzeir, M.; Tawfik, A. Optimization of integrated water waulity management for agricultural efficiency and environmental conservation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8095–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.S. Increasing agricultural water use efficiency to meet future food production. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilderback, T.E. Water management is key in reducing nutrient runoff from Container Nurseries. HortTechnology 2002, 12, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moslenko, L.; Blagrave, K.; Filazzola, A.; Shuvo, A.; Sharma, S. Identifying the Influence of Land Cover and Human Population on Chlorophyll a Concentrations Using a Pseudo-Watershed Analytical Framework. Water 2020, 12, 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113215
Moslenko L, Blagrave K, Filazzola A, Shuvo A, Sharma S. Identifying the Influence of Land Cover and Human Population on Chlorophyll a Concentrations Using a Pseudo-Watershed Analytical Framework. Water. 2020; 12(11):3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113215
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoslenko, Luke, Kevin Blagrave, Alessandro Filazzola, Arnab Shuvo, and Sapna Sharma. 2020. "Identifying the Influence of Land Cover and Human Population on Chlorophyll a Concentrations Using a Pseudo-Watershed Analytical Framework" Water 12, no. 11: 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113215
APA StyleMoslenko, L., Blagrave, K., Filazzola, A., Shuvo, A., & Sharma, S. (2020). Identifying the Influence of Land Cover and Human Population on Chlorophyll a Concentrations Using a Pseudo-Watershed Analytical Framework. Water, 12(11), 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113215




