Abstract
Seagrass meadows and coral reefs along the coast of Saipan, a US commonwealth in the Northern Pacific, have been declining since the 1940s, possibly due to nutrient loading. This study investigated whether submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) contributes to nutrient loading and supports primary production on Saipan’s coast. SGD can be an important source of freshwater, nutrients, and other pollutants to coastal waters, especially in oceanic islands without well-developed stream systems. Ra and Rn isotopes were used as natural tracers of SGD. Nitrate, phosphate, and ammonium concentrations, ancillary water quality parameters, δ15N and δ18O of dissolved nitrate, and δ15N of primary producer tissue were measured. Our results pointed to discharge of low-salinity groundwater containing elevated concentrations of sewage-derived N at specific locations along Saipan’s coast. High SGD areas had lower salinity and pH, higher dissolved inorganic nitrogen concentrations, and elevated primary producer δ15N, indicative of sewage nitrogen inputs. We estimated that SGD could support 730–6400 and 3000–15,000 mol C d−1 of primary production in Tanapag and Garapan Lagoons, respectively, or up to approximately 60% of primary production in Garapan Lagoon. Efforts to improve water quality, reduce nutrient loading, and preserve coastal ecosystems must account for groundwater, since our results demonstrate that it is an important pathway of nitrogen delivery.
1. Introduction
1.1. Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD)
Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) is the flow of groundwater across the land-ocean interface into the ocean [1]. It includes groundwater originating from confined or unconfined aquifers and recirculated sea water. The mixing of saline ocean water and fresh groundwater can occur on tidal or seasonal scales [2], and SGD can occur either at the shoreline or offshore.
Over the past 30 years, SGD has gained recognition as an important source of freshwater and nutrients into the coastal ocean, and Burnett et al. [1] state that “almost all coastal zones are subject to such flow”. Numerous studies have demonstrated that SGD can provide subsidies of freshwater [3,4,5] and nutrients [3,6,7] that are comparable to or greater than those from river discharge or other sources. On oceanic islands with fractured geology and minimal overland flow, SGD can be especially important [8,9].
Measuring SGD can be challenging. Unlike a river, submarine groundwater discharge is invisible. Flow can also be patchy and diffuse, which can make it difficult to identify locations where SGD is occurring [1]. Natural tracers, such as radium (Ra) and radon (Rn), can be especially useful in areas with heterogeneous SGD because of their ability to provide spatially integrated estimates. Ra and Rn are part of the uranium and thorium decay series, and their concentrations are naturally elevated in groundwater as a result of rock-water interactions [1,10]. Ra has four naturally occurring isotopes (223Ra, 224Ra, 226Ra, and 228Ra) with half-lives of 11.4 days, 3.6 days, 1600 years, and 5.7 years, respectively. Rn has three naturally occurring isotopes, but only 222Rn has a sufficient half-life (3.8 days) to allow for quantification of SGD. Rastrongly sorbs to aquifer substrates under freshwater conditions and desorbs due to the saline nature of subterranean estuaries; thus, it isa tracer of brackish or saline SGD. In contrast, Rn concentrations are not greatly affected by salinity, so it is a tracer of total SGD. These two tracers can sometimes be used in combination to distinguish different groundwater inputs to subterranean estuaries, where groundwater salinity can range from fresh to saline [1]. Ra and Rn are often incorporated into mass-balance or box models to calculate SGD flux [3,5,11].
SGD-borne nutrient inputs can affect coastal ecosystems by increasing overall primary productivity or altering the relative competitiveness of different primary producer species. Nutrient inputs, whether entering coastal ecosystems via overland flow or SGD, can strain coral reefs and contribute to phase shifts and macroalgal overgrowth [12,13,14,15,16]. The same is true of seagrass meadows; eutrophication has been identified as a primary cause of their worldwide decline [17,18,19,20]. Anthropogenic nitrogen sources include sewage, manure, and synthetic fertilizer. Stable isotopes (δ15N and δ18O of dissolved nitrate and δ15N of primary producer tissue) can be used to differentiate between the sources of N supporting primary production [21,22,23].
1.2. Study Area: Saipan
Saipan is the largest of the 14 islands that comprise the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), an insular area and commonwealth of the United States in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. Saipan’s geology consists of a volcanic basement overlaid with terraced limestone shelves. Despite abundant rainfall, little fresh surface water exists, and the majority of available freshwater occurs in aquifers due to the high permeability of fragmented limestone [24]. Although some perennial streams exist on the eastern side of the island, those on the western coast (Figure 1) are few in number, widely spaced, and have low flows.
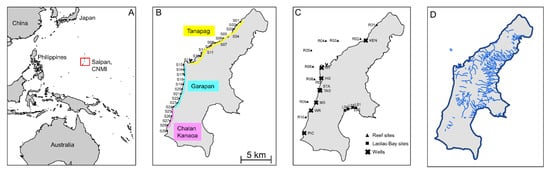
Figure 1.
Map of study site. (A) Location of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), of which Saipan is part, in the Pacific. (B) Location of shoreline sampling sites S01–S29 on the western shore of Saipan, with the three lagoons highlighted in yellow (Tanapag), cyan (Garapan), and pink (Chalan Kanaoa). (C) Well, reef, and Laolao Bay sampling sites. (D) Hydrologic network with streams shown in blue.
Various potential sources of nutrients and other contaminants to coastal aquifers and surface waters exist in Saipan. These include groundwater infiltration from septic leach fields, golf courses, some small-scale agriculture, and small industries [24]. Point sources to the coastal ocean include the outfalls from two wastewater treatment plants and brackish effluent from reverse osmosis (RO) water treatment surface impoundments [25]. Additional contamination may be present in leachate from a shuttered unlined solid waste facility in the coastal village of Puerto Rico [24]. Agricultural practices that would generate or use manure are not very prevalent in the area [26]. However, Saipan does have the highest human population in CNMI (~48,000) [27] and failing wastewater infrastructure is a recognized problem, leading to elevated levels of fecal indicator bacteria in both beach surface water and groundwater [28].
Saipan is bordered by a fringing reef off the western coast. The extensive lagoon system (13 km2) is hydrodynamically separated into three distinct lagoons [29]: Tanapag, Garapan, and Chalan Kanaoa (Figure 1). Tanapag Lagoon is the largest, northernmost lagoon and contains Mañagaha Marine Conservation Area, a 5 km2 no-take marine protected area [30]. Tanapag Lagoon has been subject to orthophosphate pollution, with exceedances of regulatory limits in all samples taken in 2016 [31]. Garapan Lagoon borders the populous middle region of the coastal plain. To accommodate urban development, the Garapan area has numerous stormwater drains, and concern exists about outdated sewage infrastructure leaking and releasing nutrient pollution into the aquifer. In addition, remnants of historic munitions from World War II have been associated with heavy metal pollution on the island [32].
Since the 1940s, the Saipan Lagoon system has lost about 20% of its seagrass and coral cover [30]. One driver of this ecosystem damage may be excess inputs of nitrogen and other nutrients from human activities on land. Environmental managers from Saipan suspect that SGD may serve as a conduit of nitrogen pollution, but SGD has not been previously quantified in this region. This study presents the first published data about SGD, SGD-derived nutrient inputs, and nitrogen source tracking in Saipan. Specifically, we (1) characterize spatial and temporal variability in SGD and associated nutrient fluxes along the western coast of Saipan, (2) estimate SGD and SGD-derived nutrient fluxes, and (3) use isotopic methods to determine what N sources support seagrass primary productivity.
2. Methods
2.1. Sampling Locations and Strategy
Samples were collected during two field campaigns to Saipan in March and August 2018, to capture the variation between the dry and wet seasons, respectively. Surface water and algal tissue samples were collected and in situ water quality parameters were measured at 29 locations spaced approximately 750 m apart along the western shore (S01–S29; Figure 1). An additional four sites (L01-L04) were sampled in Laolao Bay on the eastern shore of the island. Corresponding groundwater samples were collected approximately 1 m inland of each shoreline sampling point using a 24 (60-cm) push point sampler (MHE Products, East Tawas, MI, USA) connected to a 60-mL syringe. We attempted to collect groundwater samples at each site, but in some cases rocky substrate, a low water table, or impermeable sediments prevented sampling. To characterize water quality offshore of the seagrass beds, we sampled nine reef locations 0.5–2 km offshore and spaced approximately 2 km apart (R01-R09, Figure 1). Groundwater further inland was characterized by sampling 8 wells at the following locations: the Hyatt Regency in Garapan (HY), Kensington Hotel in San Roque (KEN), Pacific Islands Club in San Antonio (PIC), and Saipan World Resort in Susupe (WR) in March, and Modern Stationary in Oleai (MS), S.T.a.R. Water (STA), Tasi Tours and Transportation (TAS), and Horiguchi Building in Garapan (HG) in August.
2.2. In Situ Water Quality Measurements
Salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and pH were measured using a YSI Professional Plus handheld probe (Yellow Springs, OH, USA). Due to equipment malfunction in March, the YSI probe could not be used in the field; thus, salinity and pH were measured on grab samples brought back to the lab within 6 h of collection, and temperature and dissolved oxygen data were not recorded. Because salinity was determined based on conductivity measurements using the Practical Salinity Scale, salinity measurements are reported without units [33]. Uncertainties associated with YSI measurements were as follows: the greater of ±1% of reading or ±1 units for salinity, ±0.2 °C for temperature, the greater of ±2% of the reading or 2% of air saturation for dissolved oxygen, and ±0.2 units for pH.
2.3. Radon (Rn)
Rn sampling aimed to characterize (1) spatial variability in surface water Rn along the shoreline, (2) Rn elevation in shoreline samples relative to “background” levels further offshore, (3) Rn in discharging groundwater at the beach face and in inland groundwater, and (4) tidal variability in surface water Rn at the shoreline. To this end, Rn activities were measured at all nearshore and well locations in both March and August and at 4 of the reef locations in August. Tidal variability was characterized by collecting high and low tide samples at S4, S11, S18, S19, and S23 on both sampling trips, and S21 was sampled every ~2 h for one tidal cycle in March. Surface water and well water samples for Rn analysis were collected in 2-L polyethylene terephthalate (PET) soda bottles and analyzed using a RAD7 with Big Bottle RAD H2O accessory following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, air was bubbled through the samples in a closed loop for 45 min to remove the gas and Rn was counted for 10 15-min counting cycles (total count time of 3.5 h). Sample temperature, which was equivalent to room temperature, was measured concurrently and recorded to determine the air-water partition coefficient. Beach groundwater samples were collected into 250-mL glass vials and analyzed on the RAD7 using the RAD H2O accessory following the recommended protocol. The smaller volume was used for beach groundwater because it was generally not possible to extract 2 L of water using the PushPoint sampler and because sample Rn activity was expected to be higher. Rn analyses were completed within two days of collection.
2.4. Radium (Ra) Isotopes
Dissolved Ra in surface water samples was measured along transects at three sites (S18, S19, and S21) at distances of 0, 50, and 100 m from the shore during both the March and August campaigns. Groundwater Ra was measured in all well samples from both campaigns and in one beach pit sample per transect in August. Beach pits were excavated to a depth of approximately 0.3–0.6 m to access the water table. Sample volumes were as follows: 100 L for surface water, 20 L for wells, and 13–17.2 L for beach pits. Samples were filtered immediately after collection through a cartridge containing ~10 g of Mn-coated acrylic fiber supplied by Scientific Computing Instruments (West Columbia, South Carolina, USA). Fibers were rinsed with fresh tap water to remove salt and sediment and air-dried to a moisture content of 40–110% dry fiber mass before analysis. Initial measurements of 224Ra and 223Ra activities (dpm [100 L]−1) were carried out on a Radium Delayed Coincidence Counter (RaDeCC) system following the recommendations of Moore [10] within nine days of sampling. Samples were run again 3–5 weeks later to correct for 228Th supported 224Ra activity. Due to radioactive decay, by that time the 224Ra activity had decreased to <1% of its original value. Thus, 224Ra measured in the second run corresponds to 228Th in the original measurement [10]. Errors were calculated following the methods described by Garcia-Solsona et al. [34], and the mean relative errors were 23% and 32% of sample activity for 223Ra and 224Ra, respectively.
Briefly, 226Ra activity was quantified based on a slight modification of the procedure described by Dimova et al. [35]. Instead of using MnO2 resin, the same Mn fibers used for short-lived Ra isotope analysis were placed in glass cartridges specially manufactured by Lillie Glassblowers (Smyrna, GA, USA). Fibers were placed in the air-tight cartridges, flushed with He, incubated for at least three weeks to allow for ingrowth of 222Rn, and then analyzed on a RAD7 radon detector with the instrument configuration described in Figure 3a of Dimova et al. [35]. The average relative uncertainty was 20% of sample activity.
Further, 228Ra activity was measured on the same fibers on the RaDeCC following the procedure described by Young et al. [36]. The fibers were aged for at least six months to allow for partial decay of 228Th and ingrowth of new 228Th from the 228Ra captured on the fibers. Sample 228Ra activity was calculated by measuring 220Rn after aging, subtracting the 228Th-supported 220Rn, and correcting for the percentage of secular equilibrium and the decay of 228Ra since the sample was collected. The average relative uncertainty was 32% of sample activity.
2.5. Nutrients
Groundwater and surface water samples were filtered into amber high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles using 0.2 μm syringe filters. Samples were kept on ice and frozen later that day; they remained frozen until analysis. Nutrient analyses were performed using standard colorimetric analysis on an EasyChem Plus autoanalyzer (Systea, Anagni, Italy), following the recommended protocols supplied by the instrument manufacturer, which were based on United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) methods [37]. Combined NO3− and NO2− (N + N) was determined by reducing to NO2− with vanadium chloride, followed by diazotizing with sulfanilamide and adding N-1-naphthylenediamine dihydrochloride to form a colored complex. The same procedure, without the vanadium chloride step, was used to measure NO2−. NO2− concentrations were very low and almost always below the detection limit. Thus, combined NO3− and NO2− (N + N) is reported and can be considered equivalent to NO3−. Measurement of ammonium (NH4+) required adaptation and optimization of the indophenol blue method, as the salinity of the samples caused precipitation of calcium and magnesium. The method was adapted to include stoichiometrically equivalent quantities of phenol and sodium citrate [38], which prevented precipitation and allowed for optical measurement. Dissolved orthophosphate (PO43−) was determined using USEPA Methods 365.1 and 365.3 [39]. Briefly, samples were mixed with sulfuric acid, ammonium molybdate and antimony potassium tartrate to form antimony-1, 2-phosphorous molybdenum acid. This complex was then reduced by ascorbic acid, producing a blue color with an intensity proportional to the PO43− concentration. Samples were not digested, so reported PO43− concentrations represent dissolved ortho-phosphate, not total phosphorus.
2.6. Nitrogen Isotopes
Tissue samples from five primary producer species or genera, including seagrasses and macroalgae (Padina, Halimeda macroloba, Halimeda opuntia, Caulerpa, Turbinaria and Enhalus), were collected at each shoreline site (S1–S29) for N isotope analysis. Halimeda opuntia was only collected in August because Halimeda macroloba was present at all sites in March, but it was absent at some sites in August. Thus, we collected H. opuntia in August because it was present at all sites. We took care to sample only plants that were attached to the bottom and to ensure that each of the five replicates came from a different plant, rather than a different part of the same plant. Samples were rinsed with seawater to remove sediment, frozen, and shipped to the University of Hong Kong for analysis.
The algae and seagrass samples were screened for foreign material such as invertebrate eggs, algal fouling or silt. Subsequently, they were rinsed in deionized water and dried for at least 24 h at 60 °C. The dried samples were ground to a fine powder with a porcelain mortar and pestle and weighed in tin (Caulerpa, Turbinaria, and Enhalus) or silver capsules (Padina, Halimeda sp.). The samples in the silver capsules were acidified with Pierce 6N ultra-pure constant-boiling HCl to remove inorganic carbon, while the species in the tin capsules did not react with the acid, so no additional treatment was required. Primary producer tissue samples were analyzed on an EA-IRMS (Thermo EA-isolink + ConFlo IV + Delta V Advantage for the March samples and EuroVector, EA3028 + Nu Instruments, Perspective series IRMS for the August samples). Isotope values are reported as δ15N relative to atmospheric N2 (δ15N = [(Rsample/RAIR) − 1] × 1000). Two in-house standards, acetanilide and caffeine (iACET, δ15N = 1.18‰, caffeine δ15N = 20.05‰) were used for the calibration and determination of precision, which was 0.2 ‰.
At every odd numbered site, surface water and groundwater samples for dual isotope analysis of nitrate were collected and filtered following the same protocols as for nutrient samples. If groundwater could not be extracted at a given odd-numbered site, we attempted to collect groundwater at the next (even-numbered) site instead. Samples were stored frozen until analysis.
δ15N and δ18O of dissolved nitrate were determined using the denitrifier method [40,41]. Briefly, P. aureofaciens, a denitrifying bacterium lacking N2O reductase, was added to sealed vials which were then flushed with He for 3 h. An aliquot of sample water was then added such that each vial contained 20 nmol N, which the bacteria converted to N2O in ≤12 h. The gas generated in the headspace was injected through a Thermo Gasbench with a dual cold trap to the IRMS (Thermo Delta V Advantage) for isotopic analysis. Isotope measurements are reported in delta notation (‰) relative to atmospheric N2 for δ15N and V-SMOW for δ18O. Two international standards, USGS34 and USGS35, were used for calibration. Multiple measurements of the standard resulted in standard deviations of 0.7‰ and 2.3‰ for δ15N and δ18O, respectively.
2.7. SGD Calculations
SGD was calculated based on Ra isotope activity at each site where Ra was measured (S18, S19 and S21). Following the method of Su et al. [42], the flux of each short-lived Ra isotope (223Ra and 224Ra; dpm day−1) was calculated as follows:
where I (dpm) is the Ra inventory in the control volume and Tf is the tidal flushing time (days).
The inventory for each control volume was calculated by multiplying the average Ra activity (dpm m−3) by the volume (m3). The control volume for each site had a shore-parallel length of 750 m, a shore-perpendicular width of 100 m (the furthest offshore point where Ra was measured), and an average depth of 1 m, based on bathymetry maps [43]. We assumed that Ra activities would decline in a log-linear fashion to negligible levels by 100 m offshore and verified this assumption by linear regression of log-transformed Ra activity (Equation (2)), where x is the distance from shore (m) and a and b are the coefficients of the linear model.
Solving for Rax yields the following:
The fitted model for each site was then used to find the average Ra activity over 100 m by integration:
This yields:
The measured Ra inventory (I, dpm) was then calculated from:
where Ve (m3) is the volume of the enriched zone and Āsite is expressed in dpm m−3. We also compared Ra activities at 100 m to those measured further offshore on the reef to ascertain that Ra enrichment did not extend beyond 100 m.
We attempted to quantify the flushing time (Tf; h) in two ways: the tidal prism method [44] and the Ra age method based on Ra isotope ratios [45]. The tidal prism method was applied to each lagoon (Tanapag, Garapan, and Chalan Kanaoa):
where V (m3) is the mean volume of the water body, T (h) is the tidal period, b is the return flow factor, P (m3) is the tidal prism or domain volume, dm is the average depth, and R is the tidal range (mean high tide minus mean low tide; m). The return flow factor was set at b = 0.5 for a conservative estimate of tidal flushing [44]. For a reasonable estimate of the lower bound of flushing time, b = 0. Mean depth of each of the three lagoons was determined in ArcMap using the bathymetric map from the CNMI Bureau of Environmental and Coastal Quality open data portal. Since these data were based on mean low water, they were corrected to mean tide. All other required quantities were available from NOAA tides and currents, Saipan station (https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/datums.html?id=1633227).
The Ra isotope activity ratio (AR) method [45] assumes a linear, shore-parallel Ra source, generally SGD, at the shoreline. Assuming the Ra source has a consistent ratio between a short-lived and a longer-lived Ra isotope, the decline in AR with time after water is disconnected from the geologic Ra source can be used to estimate the water age:
Once the Ra flux (FRa; dpm day−1) had been calculated, SGD (m3 day−1) was calculated based on it and the groundwater endmember Ra activity (Ragw; dpm m−3):
Since Ra was sampled at only three sites, SGD at other sites was estimated based on the assumption that Ra, Rn, and SGD all followed the same spatial distribution along Saipan’s western coast. First, we calculated the proportion of total Rn activity (pi) in each segment of the shoreline. Segments were defined as 750-m shore parallel lengths centered on each shoreline sampling point (S1–S29):
where Rni is the Rn activity (Bq m−3) at shoreline sampling point i and ∑Rni is the sum of Rni for all shoreline sampling points.
The total shoreline SGD was extrapolated from Ra-quantified SGD as the sum of SGD calculated at sites with Ra transects (SGD18,19,21) divided by the sum of pi for those sites (p18,19,21). This was then multiplied by the proportion of total shoreline Rn at segment i (pi) to estimate SGD for all other shoreline segments:
Nutrient (N+N, NH4+, PO43−) fluxes (mol day−1) were estimated by multiplying the nutrient concentration of the discharging groundwater endmember (mol m−3) by the SGD (m3day−1).
3. Results
3.1. Salinity
Salinities measured in all groundwater samples (wells and beach groundwater collected from pits and with the PushPoint sampler) were consistently lower than in the adjacent coastal ocean (Figure 2). Coastal ocean and beach groundwater salinities ranged from 34.9–37.9 and 2.4–37.8 in March, respectively, and 20.7–34.4 and 1.6–33.6 in August (Table 1). Well salinities ranged from 4.3–37.3. To compare the salinity of beach groundwater to that of coastal seawater, we calculated the salinity difference (coastal seawater salinity–beach groundwater salinity) for each site and sampling event. A positive difference indicates that beach groundwater is fresher than adjacent seawater and thus a potential source of fresh water to the coastal ocean. In March, the salinity difference was negligible from S4 to S11 and from S24 to S27. In other parts of the coastline, the salinity difference was positive, indicating potential fresh SGD. The greatest salinity difference, possibly corresponding to a larger volume and/or a lower salinity of SGD, was observed in the vicinity of Garapan Lagoon, between S12 and S24. The spatial pattern was similar in August, although beach groundwater could not be sampled at many of the northern sites. In Laolao Bay samples, surface water and beach groundwater salinities ranged from 32.2 to 37.0 and 36.4 to 37.2, respectively, and positive salinity differences were not observed.
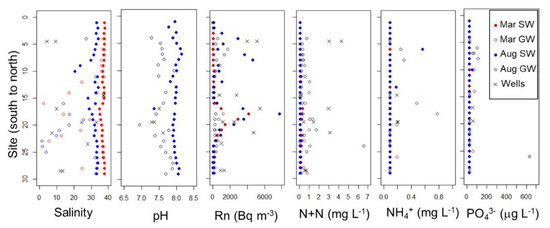
Figure 2.
Variation in salinity, pH, Rn, combined nitrate + nitrite (N+N), ammonium (NH4+), and phosphate (PO43−) in surface water (SW), groundwater collected from push point sampler (GW), and wells along the western shore of Saipan.

Table 1.
Mean (range) of water quality data from the western shoreline of Saipan, Laolao Bay, and wells in March and August 2018.
At sites that were resampled at high and low tide (S4, S11, S18, S19, S21, and S23), lower salinities were observed at low tide (Figure 3). The mean difference between high and low tide salinity was 0.3, and the range was −1.6 to +2.0. This tidal variation was much less than the observed spatial variation among different shoreline sites.
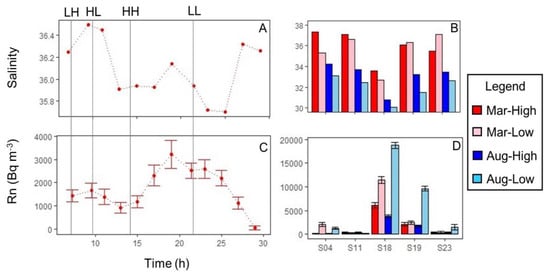
Figure 3.
Tidal variability in surface water salinity (A,B) and Rn (C,D). Abbreviations for different parts of Saipan’s mixed semidiurnal tidal cycle: LH = low high tide, HL=high low tide, HH = high high tide, LL = low low tide. Panels A and C show data from S21, where samples were collected every 2 h for 24 h in March 2018. Panels B and D show data from 5 other sites sampled at high and low tide during both trips. Error bars indicate analytical uncertainty of Rn measurements.
3.2. Temperature and pH
Temperature and pH were only recorded in August due to an equipment malfunction in the field in March. Coastal ocean and beach groundwater temperatures ranged from 28 to 30.8 and 27.4 to 30.7 °C, respectively. Beach groundwater was not consistently warmer or cooler than adjacent surface water. Groundwater pH (6.94–7.93) was consistently more acidic than that of surface water (7.78–8.25). At every site where groundwater pH could be measured, it was lower than the corresponding surface water pH (Figure 2). The magnitude of this difference ranged from 0.10–0.96. The largest differences occurred at S20, and differences generally decreased to both the north and south.
3.3. Radon
In areas where Rn-enriched SGD is occurring, Rn activities are generally highest in groundwater, intermediate in coastal waters receiving SGD, and lowest in offshore seawater. This pattern was observed to some extent on the western coast of Saipan. On average, wells had the highest Rn activities, followed by shoreline surface water samples and offshore reef samples (Table 1). However, groundwater samples collected from the beach face were often lower in Rn than adjacent shoreline surface water samples (Figure 2), suggesting that shallow groundwater flow through the beach face is not the source of Rn enrichment at the shoreline.
Both spatial and temporal variation in Rn activity were observed. A peak in shoreline Rn activities, centered around S18, was apparent during both sampling events (Figure 2). In August, a second area of elevated Rn occurred between S03 and S08. Other areas of the shoreline had low Rn activity indistinguishable from that of reef water further offshore (Figure 2). Rn tended to be higher at low tide than at high tide (Figure 3). This effect was most apparent at sites within the Rn peak area (S18 and S19) and did not occur at S11, where Rn was low all the time. Rn also tended to be higher across all sites in August than in March (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
In shoreline surface water samples and wells, salinity and radon concentrations showed a strong inverse correlation within each sampling campaign (Figure 4). In surface water at all sites, salinity was notably lower during the August sampling campaign, which took place during the rainy season (Figure 2). Maximum groundwater salinity values were also lower in August, but minimum groundwater salinity values were similar (Figure 2). Additionally, samples with comparable Rn activities between the two sampling campaigns had lower salinity in August compared to March (Figure 4).
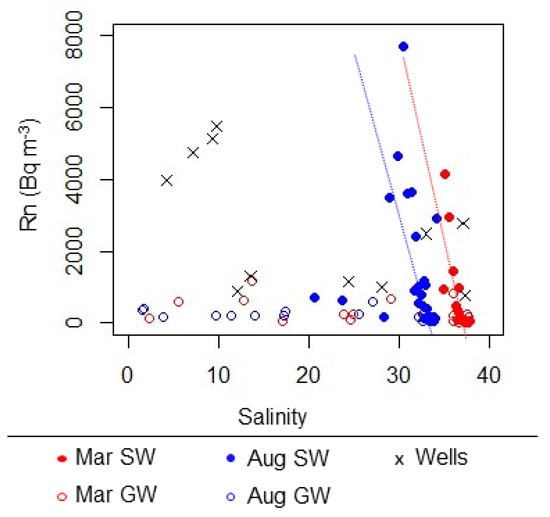
Figure 4.
Relationship between salinity and Rn in surface water (SW), beach groundwater sampled with a push-point sampler (GW) and well samples from the western shoreline of Saipan in March and August 2018.
3.4. Radium (Ra)
Ra isotope activities followed a log-linear, decreasing trend with distance from shore (Figure 5). This shore-perpendicular decreasing trend was consistent among all sites, isotopes, and sampling campaigns except 226Ra in August. No consistent differences in Ra isotope activity or the slope of the shore-perpendicular decrease were observed between the March and August sampling events or among the three Ra transect sites.
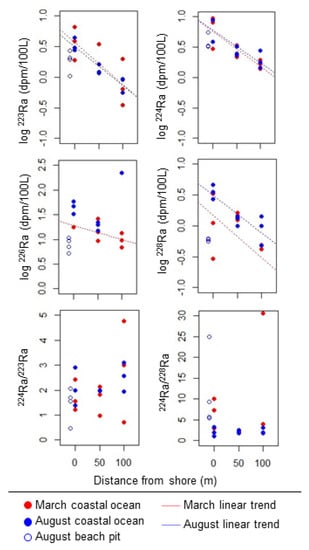
Figure 5.
Variation in Ra isotope activities and activity ratios along 100 m shore-perpendicular transects during both trips. No linear trend is shown when there was no significant relationship with distance from shore.
Ra isotope activities measured in groundwater from four beach pits (Table 2) were similar to or lower than those measured in coastal ocean water at the same sites (Table 2, Figure 5). However, groundwater samples from wells (located 100–300 m inland) had considerably and significantly higher Ra isotope activities than groundwater from beach pits and coastal ocean water samples (Table 2).

Table 2.
Mean (range) Ra isotope activities from S18, S19 and S21 and wells in March and August 2018.
To use the Ra activity ratio (AR) method of estimating water age (Moore 2000), the AR of a short-lived Ra isotope to a longer-lived one should have a uniform, higher value in the groundwater endmember and a lower value in the receiving seawater. The mean 224Ra/223Ra AR was the same in wells (2.1) and coastal ocean samples (2.2) and was lowest in beach pits (1.2). The mean 224Ra/228Ra AR was higher in wells (51) than in coastal ocean samples (29) or beach pits (13), but the very high level of variability in well AR (range = 6.4–233) indicated that we did not have enough data about the discharging groundwater endmember to accurately characterize its AR. Thus, the tidal prism method of estimating flushing time was used in all SGD calculations.
3.5. Nutrients
Combined nitrate and nitrite (N + N) concentrations were generally lower in shoreline and reef locations than in groundwater. Ammonium (NH4+) concentrations were low and similar across all sample types (Table 1). Because the form of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) can change from N + N to NH4+ in the environment in response to dissolved oxygen concentration, redox state, and other factors, we also calculated DIN by summing N+N and NH4+. DIN was generally higher in groundwater (below detection–6.9 mg N L−1) than in surface water at the shoreline (below detection–0.65 mg N L−1) or reef (below detection at all sites).
DIN concentrations in both surface water and groundwater were generally higher in March than in August at the same site. Within each sampling campaign and location, groundwater DIN tended to be higher than adjacent surface water. Two beach groundwater samples in August had much higher DIN concentrations (7.5 and 6.6 mg N L−1 at S05 and S24, respectively) than any other groundwater samples collected on either trip (below detection–1.44 mg N L−1 in March and below detection–1.72 mg N L−1 in August). Surface water DIN generally increased from north to south along the coast to a maximum near S18 and then decreased again toward the southeast. Wells exhibited a high degree of variability, with half under 0.6 mg N L−1 and the rest ranging from 1.5 to 18.8 mg N L−1 DIN.
Surface water PO43− concentrations were low: of 57 samples, only nine were above the detection limit of ~54 µg P L−1. For those sites above the detection limit, PO43− was typically higher in March, but there were some isolated sites (S10 and S20) where August PO43− concentrations were greater than those measured in March (Figure 2). Groundwater PO43− concentrations were similar and low during both campaigns between S18 and S29. There was a region from S09 to S14 with elevated PO43− concentrations in March and a region from S06 to S08 with elevated PO43− concentrations in August. Beach groundwater PO43− concentrations tended to be higher than those in surface water. Very few well sites had measurable concentrations of PO43− (Table 1).
3.6. Nitrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
In surface and groundwater samples, δ15N and δ18O values were consistent with a manure or septic NO3− source, as well as some mixing with marine and/or atmospheric NO3− (Figure 6). Samples generally fell along a 1:1 line, although considerable scatter occurred. δ15N values in surface and groundwater fell between 1.4 and 24.3. They were lower in August than in March in both surface and groundwater, although the ranges overlapped. No distinct spatial variability in δ15N of dissolved NO3− was observed (Figure 7A).
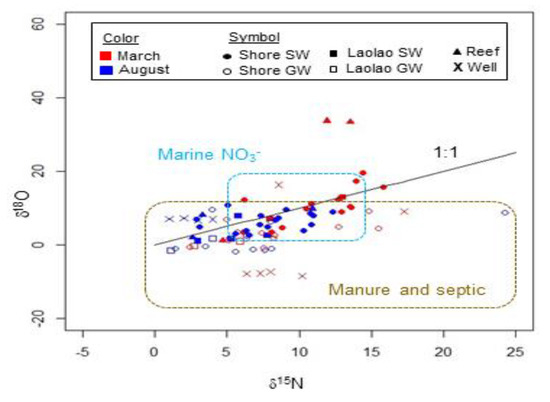
Figure 6.
Nitrogen and oxygen isotope signature of dissolved nitrate in surface and groundwater samples, with ranges typical of selected N sources shown. Ranges are reproduced from Kendall et al. (2007). The δ18O of atmospheric nitrate measured with the denitrifier method (60–100) was too high to show in the figure.
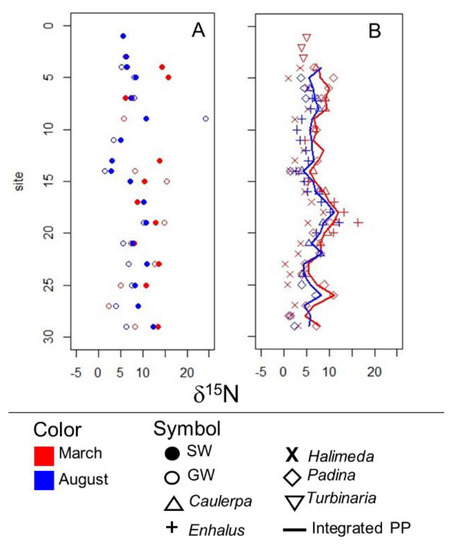
Figure 7.
Variation in (A) the nitrogen isotope signature of dissolved nitrate in surface and groundwater and (B) primary producer (PP) tissue along the western shoreline of Saipan.
Primary producers collected for δ15N analysis included Caulerpa, Enhalus, Halimeda, Padina, and Turbinaria. None of the primary producers occurred across all the sites, although Caulerpa, Enhalus, and Halimeda were widespread along the western coastline. δ15N values in primary producers ranged from −2.2 to +16.4. It was not fully possible to separate variability in δ15N related to primary producer species or genus from that related to location. However, when species or genera co-occurred at the same site, Caulerpa, Enhalus and Padina appeared to generally have higher δ15N than Halimeda (Table 3, Figure 7B).

Table 3.
Mean (range) of primary producer δ15N by genus and location in March and August 2018. If no range is given, only one sample was collected. “N/a” indicates that no sample was collected.
To simplify the primary producer δ15N data and facilitate correlations with water quality measurements, we calculated an integrated primary producer δ15N. We observed that: (1) Caulerpa frequently co-occurred with Padina, Halimeda macroloba, or Enhalus and (2) δ15N values in Caulerpa showed strong, positive correlations with δ15N in each of these three other species. We determined the line of best fit for each of these correlations and used it to estimate the Caulerpa δ15N from the measured δ15N of other species. Finally, the integrated primary producer δ15N was calculated as the mean of all measured and estimated Caulerpa δ15N values for a given site and sampling campaign. Halimeda opuntia and Turbinaria were not included in the integrated value because they did not co-occur with Caulerpa.
Integrated primary producer δ15N showed a pattern of spatial variability that was remarkably consistent between March and August (Figure 7B), although August values were slightly lower. The pattern included an area of elevated primary producer δ15N centered around S18 and a smaller peak centered around S26. The difference between March and August primary producer δ15N was largest between S4 and S7.
3.7. Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Associated Nutrient Fluxes
SGD was quantified based on 223Ra activity because 223Ra consistently decreased in a log-linear fashion with distance from shore, and the zone of 223Ra enrichment did not appear to extend further than 100 m offshore (Figure 5). Further, 224Ra enrichment did not decrease to offshore levels by 100 m offshore (Figure 5). Because the activity of 223Ra and other Ra isotopes was lower in groundwater from beach pits than in coastal ocean samples collected near the shoreline (Figure 5), groundwater in beach pits could not be the discharging groundwater endmember causing Ra enrichment in coastal waters. Instead, the average 223Ra activity of wells located inland of the control volume (MS, TAS, STA, and HG; average 223Ra = 14 dpm [100 L]−1) was used as the endmember value.
In the region where Ra was sampled (S18, S19, S21), SGD calculated from 223Ra fluxes ranged from 1200–9000 m3m−1day−1 in March and 1600–4400 m3m−1day−1 in August. SGD estimates at sites 18 and 19 were similar between sampling campaigns, but rainy season (August) SGD was slightly higher. In contrast, SGD for S21 was significantly higher in March.
SGD extrapolated from the Rn distribution was highest in Garapan Lagoon, with estimated discharge at individual sites ranging from 0.06–10.9 m3m−1day−1 in March and 0.07–10.4 m3m−1day−1 in August (Table 4, Figure 8). Total SGD into Garapan Lagoon was 1.1 × 104–2.3 × 104 m3day−1 in March and 1.0 × 104–2.0 × 104 m3day−1 in August, implying consistent year-round SGD to this lagoon. Tanapag Lagoon exhibited evidence of seasonal SGD in August, during the rainy season (3.5 × 103–7.1 × 103 m3day−1). The discharge in March was approximately an order of magnitude less, ranging from 3.3 × 102–6.6 × 102 m3day−1. Site specific discharge in Tanapag Lagoon was lower than in Garapan Lagoon. Chalan Kanaoa Lagoon had the lowest SGD, with lagoon-wide discharge ranging from 1.9 × 102 to 3.8 × 102 m3day−1 in March and 2.5 × 102 to 4.9 × 102 m3day−1 in August.

Table 4.
Rn-estimated SGD for the three lagoons in March and August 2018. Both the total SGD into each lagoon and SGD per meter of shoreline are presented.
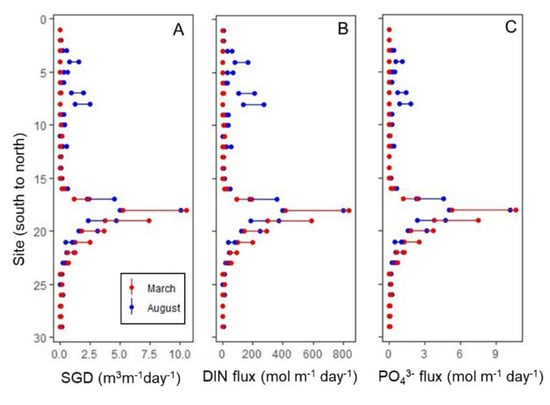
Figure 8.
Variation in Rn-estimated SGD and SGD-associated dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and PO43− fluxes along the western shoreline of Saipan. Ranges, indicated by the length of the bar between the two endpoints, represent sampling error and analytical uncertainty propagated through the calculations.
SGD-associated total DIN flux into the lagoon system was higher in August (1500–3000 mol N day−1) than March (1200–2300 mol N day−1). DIN flux was greatest in Garapan Lagoon (1100–2200 and 1000–2000 mol N day−1 in March and August, respectively). Tanapag Lagoon had a significant but lower SGD-derived DIN input in August (480–960 mol day−1). PO43− followed similar trends (Table 5, Figure 8).

Table 5.
SGD-derived DIN and PO43− fluxes, N:P ratios in well groundwater endmembers and surface water, and estimated SGD-supported primary productivity in Tanapag, Garapan and Chalan Kanaoa lagoons in March and August 2018.
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydrogeology
Beach groundwater and well salinity values indicate an extensive subterranean estuary extending at least 300 m inland from the coast, where the furthest inland well was sampled. PushPoint beach groundwater, pit groundwater, and well water samples were brackish to saline. These observations are consistent with prior work documenting that Saipan’s freshwater lens has a brackish zone near the coast [24]. Beach groundwater showed evidence of a high degree of mixing with coastal ocean water adjacent to Tanapag and Chalan Kanaoa Lagoons during both sampling events, although the salinity in March exhibited more spatial variation than that in August. Beach groundwater salinity adjacent to Garapan Lagoon was highly variable both spatially and temporally, which may imply varying degrees of connectivity to the coastal aquifer, differing responses to precipitation and tidal mixing, or variability in surface runoff. Well salinity showed evidence of spatial variability along the coast, with the highest salinity values occurring near Garapan Lagoon (Figure 2). The 2006 Water Quality Assessment Report indicates that all the sampled wells lie within the Class III groundwater management zone and are subject to both tidal mixing and additional salinization due to overdraws [46].
Rn surveys showed spatially heterogeneous distribution of SGD along the coastline and indicated general differences by lagoon (Tanapag, Garapan, and Chalan Kanaoa). There is strong evidence of consistent SGD into Garapan Lagoon, evidence for seasonal SGD into Tanapag Lagoon, and little evidence of SGD into Chalan Kanaoa Lagoon at any time of year. Variation in Rn and salinity between high and low tide at re-sampled sites (Figure 3) was less than variation among shoreline sites (Figure 2), indicating that the spatial variation observed is not the result of uncharacterized tidal variability. The underlying geology of the adjacent regions may provide some explanation for these trends. While all regions of the coast have underlying formations with low permeability, the northern region of Saipan (immediately inland of Tanapag Lagoon) has an overlying layer of highly permeable Mariana limestone [24]. Since the hydraulic conductivity of the Mariana limestone is higher than that in other regions, the flow of groundwater may exhibit a faster response to precipitation events.
The strong inverse correlations between Rn and salinity within each sampling campaign are consistent with varying amounts of a groundwater endmember with consistent properties (low salinity, high Rn) discharging at different points along the coast. The linear relationships between salinity and Rn in March and August have the same slope, but lower salinities for the same Rn activities, in August. This pattern could be explained by a higher volume of SGD across all sites in August, with the groundwater endmember similar to that in March. Alternatively, there could be a similar volume of lower-salinity, higher Rn SGD. Aquifer recharge caused by increased precipitation during the rainy season may increase the hydraulic head in the aquifer, steepening the coastal hydraulic gradient and increasing SGD. Since the rainy season typically begins in July, this would imply a relatively rapid hydraulic response. Hoffman, Carruth, and Meyer [47] reported horizontal hydraulic conductivity of the Mariana limestone ranging from 88 to 762 m day−1. The maximum distance from the shoreline to the central axis of Saipan inland of Tanapag Lagoon is 1555 m, suggesting a rapid hydraulic response of approximately 2–17 days. Rainfall occurred before and during each sampling trip, and the amount was greater in August than in March [48] (Figure 9).
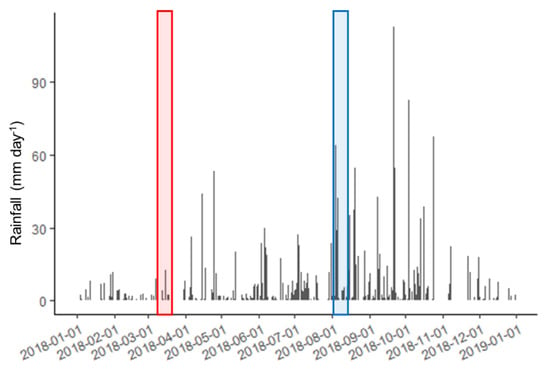
Figure 9.
Daily rainfall measured at the Saipan airport during calendar year 2018. Approximate duration of the March and August sampling campaigns are shown as red and blue boxes, respectively. Dates are given in YYYY-MM-DD format.
In August (rainy season) only, three sites did not conform to the general inverse linear trend between salinity and Rn. These outliers were Sites 9, 10, and 15. Sites 9 and 10 are located near the outlets of intermittent streams (Figure 1) which are more likely to flow during the rainy season. This would contribute fresh water to the lagoon in those regions, thus accounting for the decrease in salinity not accompanied by elevated Rn. Site 15 is near Tanapag Harbor, American Memorial Park, and a constructed wetland discharge channel [25], although it is unknown whether the channel discharges seasonally.
4.2. Quantitative Estimation of SGD and Nutrient Fluxes
Both 223Ra-derived SGD at S18, S19 and S21 and SGD extrapolated from the Rn distribution along the entire coast show good agreement with two studies in Guam [49,50], which quantified SGD in the range of 2.2–100 m3m−1day−1. The estimates of SGD in Saipan are also consistent with other islands with fracture flow such as Luzon (Philippines), Okinawa (Japan), Hainan Island (China), and the US Hawaiian islands of O’ahu, Maui, Moloka’i, and Hawai’i [3,5,9,11,42,51,52,53]. Ranges from these and other islands typically had a higher upper bound. This may be because SGD studies often focus on areas that are known or suspected to have high SGD, whereas this one extended over an entire coastline.
The tidal prism method, used to calculate residence times in the three lagoons, has several limitations as applied here. First, this model does not account for wind-driven mixing, which can substantially decrease flushing time in some circumstances. Second, some hydrologic connectivity has been reported between Tanapag, Garapan, and Chalan Kanaoa lagoons, which may violate some of the assumptions of the tidal prism method. Third, Kruger et al. [29] showed that northern Tanapag lagoon is subject to continual wave action in addition to tidal exchange, since the fringing reef is at 0 m relative to mean low low water (MLLW), and the water level does not drop below 0.1 m at neap tide. Southern Garapan and Chalan Kanaoa lagoons are generally shallow and are also subject to wave-driven circulation that is not accounted for by the tidal prism method [29]. It is likely that the actual residence times are lower than estimated here (and therefore SGD is higher), but there is insufficient information to quantify it at this time.
Additional limitations apply to the method used to extrapolate SGD to the entire shoreline. Several assumptions were based on the best available information, but they may not be accurate. First, we assumed that inventories of 223Ra, Rn, and SGD were proportional. However, at the three sites where Ra was measured, Ra and Rn were not completely proportional. This may be because 223Ra and Rn are not always present in a consistent ratio in discharging groundwater or because Rn loss to the atmosphere via evasion occurs more at some coastal ocean sites than at others, for example because of windier conditions or greater water turbulence. Thus, the spatial distribution of extrapolated SGD is unlikely to be completely representative of the true distribution on a site-by-site basis.
Variability in SGD-derived nutrient loading among lagoons was driven by spatial and temporal variability in the magnitude of SGD rather than by differences in groundwater nutrient concentration. Nutrient fluxes into lagoons with negligible to low estimated SGD (Chalan Kanaoa in both March and August; Tanapag in March) were also very low. To compare these loading rates with those reported for other locations, non-negligible loading rates were normalized to daily loading per meter of shoreline. DIN (mol N m−1day−1) and PO43− (mol P m−1day−1) were both generally consistent with other published results in Guam, O’ahu, Kaua’i, and Hawai’i [3,5,49,53]. We note that this method of estimating nutrient flux retains all the limitations of SGD estimation methods. Additionally, because each well was only sampled once, no temporal variability in the quality of discharging groundwater was incorporated. Groundwater nutrient concentrations may, in fact, vary in time, and there may be additional spatial variability in groundwater nutrient concentrations that is not represented here. Biogeochemical transformations of nutrients also probably occur along groundwater flow paths from wells (approximately 200 m inland, on average) to the point where they leave the aquifer for the coastal ocean. If nutrient concentrations are reduced as a result of biogeochemical transformations, our calculation method may have overestimated nutrient fluxes.
4.3. SGD-Supported Primary Productivity
An estimate of the primary productivity supported by SGD-derived nutrients was made based on the Redfield ratio (C:N:P = 106:16:1). The N:P ratio for wells, which we assumed were representative of the groundwater endmembers discharging into each lagoon, was much greater than 16 for each of the three lagoons (Table 5). Thus, we assumed that SGD-supported primary production to the three lagoons was P limited. We then converted the PO43− fluxes into carbon units using the Redfield C:P ratio of 106:1. We also estimated SGD-supported primary productivity assuming N limitation, since coastal ocean N:P ratios averaged (range) 15.3 (1.3–45) and 6.3 (0.7–15.3) in March and August, respectively. Estimated SGD-derived nutrient fluxes could support up to 3000 mol C day−1 of primary productivity in Garapan Lagoon and 730 mol C day−1 in Tanapag Lagoon under P limitation or 15,000 mol C day−1 in Garapan Lagoon and 6400 mol C day−1 in Tanapag Lagoon under N limitation (Table 4).
To assess whether the rate of supported primary productivity listed here is plausible, we compared it to a recently published study in Saipan. Perez et al. (2018) determined primary productivity at the Pau Pau reef flat, which is near S09 and adjacent to Tanapag Lagoon. In the 7500 m2 study area, composed of 47% algae, 12.5% live coral, and 40.5% turf and rubble, Perez et al. [30] quantified the primary productivity as roughly −20–100 mmol C m2h−1 during the sampling event (May–June 2017). Scaling nutrient fluxes from S09 to the bounds of the study area presented in Perez et al. [30], the estimate of N-limited SGD supported primary productivity ranged from 0.02–0.04 mmol C m2h−1 in March to 0.11–0.23 mmol C m2h−1 in August. If the system is P-limited, SGD-supported primary productivity could range from 0.003–0.006 mmol C m2h−1 in March to 0.02–0.04 mmol C m2h−1 in August. Using Figure 5a from Perez et al. [30], we estimated daily primary production roughly at 1200 mmol C day−1, which would imply that SGD-derived nutrient fluxes at site S09 support, at most, <1% of the growth. However, if we assume a similar magnitude of primary production at Garapan Lagoon, the much higher SGD-derived nutrient fluxes there could support about 60% of it.
The correspondence in spatial distribution of SGD (Figure 8) and integrated δ15N of primary producers (Figure 7) provides additional support for the idea that SGD-borne N subsidies play an important role in supporting primary production. It is especially interesting that the part of the coastline with substantial seasonal variability in SGD (S03–S08) was also the only location where integrated primary producer δ15N varied substantially between the two sampling campaigns.
4.4. Nutrient Sources and Implications for Coastal Ecosystem Management
Several lines of evidence support the idea that an area of persistent high SGD exists in Garapan Lagoon, centered around S18. The groundwater discharging in this area has high Ra and Rn, low salinity, elevated DIN, and an isotopic signature consistent with manure or septic systems. Sewage appears to be a more likely N source than manure because the area has relatively little agriculture that would produce or use manure [26], but a relatively large human population and failing sewage infrastructure. Isotopic data suggest that these SGD-borne inputs of sewage-derived N support a considerable amount of primary production in Garapan Lagoon and may also have a seasonal effect in Tanapag Lagoon.
A companion study that focused on source-tracking of fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) in Saipan’s coastal waters [54] further supports the idea that SGD is carrying sewage pollution into Garapan Lagoon. That study showed higher FIB levels and greater prevalence of human fecal markers in the part of the coastline surrounding S18 than in any other area except a heavily visited tourist area, the Grotto, that was not included in the present study. Microbial evidence of sewage pollution was observed in both surface water and groundwater in the central part of Garapan Lagoon and occurred to a greater extent in August, when our data also indicated greater SGD.
It is interesting that the area of high SGD-borne N inputs corresponds with the part of the coastline where Enhalus seagrasses occur and with elevated δ15N in their tissue. Previous research in Saipan [55] found that Enhalus has responded positively to human disturbance occurring in Saipan since the 1940s, while Halodule seagrass and corals have been negatively affected. Our results corroborate those of Houk and Van Woesik [55], showing that human alteration and sewage N inputs may benefit some coastal primary producers (e.g., Enhalus) to the detriment of others, thus shifting the balance of species and habitat types over time.
The data presented here will help manage Saipan’s coastal ecosystems by providing local managers with data on (1) the location, magnitude, variability, and quality of SGD inputs to coastal waters, and (2) the importance of SGD-borne N inputs in supporting primary production in different parts of Saipan’s western coast. In Garapan Lagoon between S17 and S21, large and consistent N-enriched SGD inputs occur; thus, any attempt to reduce N loading to the coastal ocean must focus on groundwater. In Tanapag Lagoon between S4 and S8, a smaller and less consistent amount of SGD occurs. Further study is needed to determine the frequency and timing of SGD in Tanapag Lagoon. Since sampling occurred during only two campaigns, we cannot make firm conclusions about the drivers of temporal variability in SGD into Tanapag Lagoon. Further research is needed to help local agencies as they develop land use plans for the northern Tanapag area, especially since there have been ongoing concerns about orthophosphate [31]. In parts of the coastline where SGD was low or negligible, most nutrient and other pollutant inputs likely enter the coastal ocean through surface runoff, so attempts to decrease the quantity and/or improve the quality of such runoff would be the most effective.
5. Conclusions
This manuscript presents the first published estimate of SGD in the coastal waters of Saipan. SGD was localized in two parts of Saipan’s western coastline: an area of apparently year-round SGD in Garapan Lagoon and an area of apparently seasonal SGD in Tanapag Lagoon. Estimates of SGD-borne DIN and PO43− inputs to coastal areas suggested that SGD contributes ecologically significant subsidies of these nutrients to Garapan Lagoon, supporting a potentially large fraction of coastal primary production. Nitrogen isotope data, combined with the results of a concurrent microbial source tracking study [54], suggested that SGD-borne DIN inputs are at least partially sewage-derived and that these inputs may favor Enhalus seagrasses over other primary producers. These results underscore the importance of including groundwater and SGD in any efforts to reduce nutrient loading to Saipan’s coastal ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and K.L.K.; methodology, N.G., K.K., K.L.K, and M.A.K.; data analysis, N.G. and M.A.K.; investigation, N.G., K.K., and K.L.K; resources, K.K. and K.L.K; writing—original draft preparation, N.G. and M.A.K.; writing—review and editing, K.L.K.; visualization, N.G., K.L.K and M.A.K.; supervision, K.K. and K.L.K.; project administration, K.K.; funding acquisition, K.K., K.L.K and M.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by NOAA (award #NA17NOS4820082 to K.K. and K.L.K.), NASA DC Space Grant (to M.A.K. and K.L.K.), the Research Grants Council, Hong Kong and the HKU Faculty of Science SIRMS postdoctoral fellowship (T21-602/16-R for N.G.).
Acknowledgments
We thank the wonderful staff of the CNMI Bureau of Coastal and Environmental Quality (BECQ) for logistical help, technical support, lab access, and sharing their local knowledge with us. We are especially grateful to David Benavente (Coastal Resources Management) for his support while in Saipan. Jiana Blaha, Alexandra Morris, Madeeha Froze Mughal, Marissa Thompson and Yvonne Yau helped conduct field and lab work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Burnett, W.C.; Aggarwal, K.; Aureli, A.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Cable, J.E.; Charette, M.A.; Kontar, E.; Krupa, S.; Kulkarni, K.M.; Loveless, A.; et al. Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 498–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knee, K.L.; Paytan, A. Submarine Groundwater Discharge: A Source of Nutrients, Metals, and Pollutants to the Coastal Ocean. In Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science; Elsevier, Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Chapter 4.08; pp. 205–233. [Google Scholar]
- Garrison, G.H.; Glenn, C.R.; McMurtry, M.G. Measurement of submarine groundwater discharge in Kahana Bay, O’ahu, Hawai’i. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Ishitobi, T.; Seaki, K.-I. Evaluation of time-space distributions of submarine ground water discharge. Groundwater 2005, 43, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knee, K.L.; Street, J.H.; Grossman, E.E.; Boehm, A.B.; Paytan, A. Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean from submarine groundwater discharge in a groundwater-dominated system: Relation to land use (Kona coast, Hawaii, USA). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotwell, A.M.; Moore, W.S. Nutrient and Radium Fluxes from Submarine Groundwater Discharge to Port Royal Sound, South Carolina. Aquat. Geochem. 2003, 9, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Watayakorn, G.; Taniguchi, M.; Dulaiova, H.; Sojisuporn, P.; Rungsupa, S.; Ishitobi, T. Groundwater-derived nutrient inputs to the Upper Gulf of Thailand. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kim, J.-S.; Hwang, D.-W. Submarine groundwater discharge from oceanic islands standing in oligotrophic oceans: Implications for global biological production and organic carbon fluxes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knee, K.; Crook, E.; Hench, J.; Leichter, J.; Paytan, A. Assessment of Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) as a Source of Dissolved Radium and Nutrients to Moorea (French Polynesia) Coastal Waters. Estuaries Coasts 2016, 39, 1651–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Fifteen years experience in measuring 224Ra and 223Ra by delayed-coincidence counting. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.C.; Watanabe, A.; Nadaoka, K.; Motooka, S.; Herrera, E.C.; Yamamoto, T. Estimation of nearshore groundwater discharge and its potential effects on a fringing coral reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomascik, T.; Sander, F. Effects of eutrophication on reef-building corals II. Structure of scleractinian coral communities on fringing reefs, Barbados, West Indies. Mar. Biol. 1987, 94, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, P.R.F. Eutrophication and coral reefs—some examples in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Water Res. 1992, 26, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Clark, M.W. Nutrient inputs from the watershed and coastal eutrophication in the Florida keys. Estuaries 1992, 15, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, K.E. Effects of terrestrial runoff on the ecology of corals and coral reefs: Review and synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D′Angelo, C.; Wiedenmann, J. Impacts of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs: New perspectives and implications for coastal management and reef survival. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 7, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, J.M.; Tomasko, D.A.; Touchette, B.W. Seagrasses and eutrophication. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 46–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, P.J.; Tomasko, D.; Seddon, S.; Moore, K.; MacInnis-Ng, C. Human impact on seagrasses: Contamination and eutrophication. In Seagrass Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 567–593. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.L.; Wysmyk, J.K.C.; Craig, S.E.; Lotze, H.K. Regional-scale effects of eutrophication on ecosystem structure and services of seagrass beds. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Go, G.A.; Watanabe, A.; Miyajima, T.; Nakaoka, M.; Uy, W.H.; Nadaoka, K.; Watanabe, S.; Fortes, M.D. 17-year change in species composition of mixed seagrass beds around Santiago Island, Bolinao, the northwestern Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 88, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Elliott, E.M.; Wankel, S.D. Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 2, pp. 375–449. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton, K.; Baker, D.M.; Cuddy, M.R.; Raymundo, L.J.; Meyer, K.A.; Kim, K. Nitrogen dynamics on Guam as revealed by the seagrass Enhalus acoroides. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 528, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botrel, M.; Bristow, L.A.; Altabet, M.A.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Maranger, R. Assimilation and nitrification in pelagic waters: Insights using dual nitrate stable isotopes (δ 15 N, δ 18 O) in a shallow lake. Biogeochemistry 2017, 135, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruth, R.L. Ground-Water Resources of Saipan, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2003.
- Perreault, J.A. Reconnaissance Study of the Hydrology of American Memorial Park, Island of Saipan, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2007.
- Anonymous. 2017 Agricultural Census Northern Mariana Islands (2018) Commonwealth and Island Data. In Geographic Area Series; 2020. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Publications/AgCensus/2017/Full_Report/Outlying_Areas/cnmi.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Anonymous. Understanding the Population of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands; Bureau, U.S.C., Ed.; 2020; p. 1. Available online: https://www.census.gov/history/pdf/sis_2020map_cnmi.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Arriola, J.; Jonathan, A.; Rodney, C.; Derek, C.; Erin, D.; Jose, K.; Ryan, O.; Kathy, Y. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands 303(d), 305(b) and 314 Water Quality Assessment Integrated Report. B. o. E. a. C. Quality Ed.; CNMI: 2016; p. 144. Available online: http://www.deq.gov.mp/resources/files/branches/WQS/Final2016%20305b%20and%20303d%20Integrated%20Report.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Kruger, J.; Kumar, S.; Damlamian, H.; Sharma, A. Oceanographic Survey, Shoreline Mapping and Preliminary Hydrodynamic Modeling Report, Saipan, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. In SOPAC Data Release Report; Pacific Islands Applied Geoscience Commission: Suva, Fiji, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, D.I.; Phinn, S.R.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Shaw, E.; Johnston, L.; Iguel, J. Primary Production and Calcification Rates of Algae-Dominated Reef Flat and Seagrass Communities. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 2362–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, D.; Okano, R. A Preliminary Investigation of Groundwater and Surface Water Impacts on Newarshore Biological Communities in Saipan Lagoon; CNMI Watershed Working Group: 2016; p. 27. Available online: https://dcrm.gov.mp/wp-content/uploads/crm/2016.7.20_WWG-meeting_OkanoOkano_SaipanLagoon.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- GDenton, R.W.; Emborski, C.A.; Habana, N.C.; Starmer, J.A. Influence of urban runoff, inappropriate waste disposal practices and World War II on the heavy metal status of sediments in the southern half of Saipan Lagoon, Saipan, CNMI. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO. The international system of units (SI) in oceanography. In UNESCO Technical Papers; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Solsona, E.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Masqué, P.; Dulaiova, H. Uncertainties associated with 223Ra and 224Ra measurements in water via a Delayed Coincidence Counter (RaDeCC). Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova, N.; Burnett, W.C.; Horwitz, E.P.; Lane-Smith, D. Automated measurement of 224Ra and 226Ra in water. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2007, 65, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.B.; Gonneea, M.E.; Fong, D.A.; Moore, W.S.; Herrera-Silveira, J.; Paytan, A. Characterizing sources of groundwater to a tropical coastal lagoon in a karstic area using radium isotopes and water chemistry. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. EPA 600/4-79-020 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes; Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1983; p. 491. Available online: https://www.wbdg.org/FFC/EPA/EPACRIT/epa600_4_79_020.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Solorzano, L. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenol-hypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 799–801. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. EPA-NERL: 365.1: Phosphorus (All Forms) by Semi-Automated Colorimetry; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1993.
- Sigman, D.M.; Casciotti, K.L.; Andreani, M.; Barford, C.; Galanter, M.; Böhlke, J.K. A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4145–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciotti, K.L.; Sigman, D.M.; Hastings, M.G.; Bohlke, J.K.; Hilkert, A. Measurement of the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate in seawater and freshwater using the denitrifier method. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4905–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Du, J.; Moore, W.S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J. An examination of groundwater discharge and the associated nutrient fluxes into the estuaries of eastern Hainan Island, China using 226Ra. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3909–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.S.; Costa, B.; McKagan, S.; Johnston, L.; Okano, D. Benthic Habitat Maps of Saipan Lagoon; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017; p. 77. Available online: https://coastalscience.noaa.gov/data_reports/benthic-habitat-maps-of-saipan-lagoon-commonwealth-of-the-northern-mariana-islands-ncei-accession-0162517/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Sanford, L.P.; Boicourt, W.C.; Rives, S.R. Model for estimating tidal flushing of small embayments. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1992, 118, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W. Determining coastal mixing rates using radium isotopes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.; Houk, P.; Chambers, D.; Tanaka, C. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands Integrated 305(b) and 303(d) Water Quality Assessment Report; Division of Environmental Quality: 2006. Available online: http://www.deq.gov.mp/resources/files/branches/WQS/305b%202006%20Final.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Hoffman, J.P.; Carruth, R.L.; Meyer, W. Geology, Ground-Water Occurrence, and Estimated Well Yields from the Mariana Limestone, Kagman Area, Saipan, CNMI.; Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1998.
- NOAA. Station Data Inventory, Access & History, Saipan International Airport, US. In National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration National Centers for Environmental Information; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Matson, E.A. Nutrient flux through soils and aquifers to the coastal zone of Guam (Mariana Islands. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.G. A water-budget model and estimates of groundwater recharge for Guam. In U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigation Report; 2012; p. 53. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2012/5028/pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H.; Siringan, F.; Foronda, J.; Wattayakorn, G.; Rungsupa, S.; Kontar, E.A.; Ishitobi, T. Groundwater discharge as an important land-sea pathway into Manila Bay, Philippines. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 24, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, J.H.; Knee, K.L.; Grossman, E.E.; Paytan, A. Submarine groundwater discharge and nutrient addition to the coastal zone and coral reefs of leeward Hawai’i. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knee, K.; Layton, B.; Street, J.; Boehm, A.; Paytan, A. Sources of Nutrients and Fecal Indicator Bacteria to Nearshore Waters on the North Shore of Kaua’i (Hawai’i, USA). Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinigalliano, C.; Yuknavage, K.; Gidley, M.; Palacois, D.; Bautista, C.; Bonacolta, A.; Lee, H.W.; Knee, K.L.; Kim, K.; Maurin, L. Microbial Source Tracking of Fecal Indicating Bacteria in Coral Reef Waters, Recreational Waters, and Groundwater of Saipan by Real-Time Quantitative PCR. Front. Microbiol. 2020. in Review. [Google Scholar]
- Houk, P.; Woesik, R.V. Dynamics of shallow-water assemblages in the Saipan Lagoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 356, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).