Abstract
The success or failure of river closure is directly related to the construction period and project benefit. Therefore, it is very necessary to study the river closure by an appropriate method. In this paper, a 1D–2D coupled river closure model is established to optimize the closure flow rate, closure period, and layout of a real closure project. The 1D transition model between open channel flow and pressurized flow is established by a finite volume scheme. For the 2D model, 2D shallow water equations are solved using an unstructured finite volume scheme. The 1D model and 2D model are coupled by considering the mass and momentum conservation. To validate the model, a physical experiment of a real river closure project is set up according to the gravity similarity criterion with a scale of 1:80. Then, the experimental data obtained by the calibrated physical experiment is compared with the numerical results. Good agreements are achieved in terms of surface elevation, velocity, and flow rate. Finally, the real river closure project is further investigated by the model. The layout, closure flow rate and closure period of this project is analyzed and optimized. The original design of the berm is more suitable to discharge the flow. Moreover, the first stage cofferdam should be removed to floor elevation upstream and downstream of the dam. The river closure flow rate should not exceed 2380 m3/s.
1. Introduction
In the river channel, it is usually necessary to cut off the flow and divert the flow to discharge structures before constructing the hydraulic structures. The process of cutting off river flow can be named as river closure which is the first and critical step in hydraulic engineering. Successful river closure is also the foundation of ensuring safety, timeliness, and cost of the construction. Therefore, river closure is one of the key and control projects that affects the progress of the whole project in hydraulic engineering.
Hydraulic parameters of the closure gap, as the main factor deciding the success or failure of the closure, are always changing during the river closure. If hydraulic parameters of the closure gap can be obtained (e.g., the section form and the size of the closure gap can be adequately investigated and rationally optimized) by some methods before the closure, the whole process of river closure can be effectively controlled, and the emergency preplan for the possible adverse situation can be made. Obtaining of the hydraulic parameters also can avoid the failure and the unnecessary loss during the river closure. Accordingly, the related study on hydraulic parameters of river closure has significant theoretical and practical meaning.
Both physical experiment and numerical simulation are important methods for researchers to investigate the river closure. With the popularization and development of computer technology, more and more researchers adopt numerical models to simulate river closure. Most of them establish a 2D river closure model to predict open channel flows. However, in the situation where the flow is discharged through the low holes built in the dam and pressurized flows may appear in the low holes, 2D models are questionable to solve pressurized flows. Therefore, the 1D–2D coupled model has been adopted increasingly by researchers [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Li et al. [1] developed a coupling 1D and 2D model, which considered rainfall, runoff, drainage system, and surface flood simultaneously. For the coupling scheme, the Thiessen proximal method was used to subdivide the computational domain into different units firstly. Then Thiessen units in which contained a special adjacent point were defined based on terrain information from a digital elevation model (DEM). The connection between 1D and 2D model was established through the discharge at the special adjacent point within these units during the rainfall-runoff process. Marin et al. [2] proposed joint assimilation coupling (JAC) algorithms to connect the 1D and 2D model for river–floodplain flows. Domain superposition scheme was adopted instead of the decomposition scheme. Chen et al. [3] summarized three main schemes for 1D–2D coupling and introduced the applications of these three coupling modes. In addition, Chen presented a water stage prediction-correction (WSPC) method that coupled the 1D model with the 2D model in a boundary-connected way used the theory of characteristics. Morales-Hernández et al. [4] presented a coupled model based on the finite volume (FV) scheme with a conservative upwind format. To couple the 1D model with the 2D model, a new discrete element which always contained one 1D cell and several adjacent 2D cells was defined. Then the coupling model was established through conservation of mass only (OMC) or conservation of mass and momentum (MMC) in the new discrete element. Finally, OMC or MMC method was selected according to the flow regime to obtain physical results. Timbadiya et al. [5] established a 1D–2D coupled model which used the MIKE11 and MIKE21 to simulate the river and coastal urban floodplain, respectively. After the validation, this model could predict the water surface in the river and urban area accurately. Martins et al. [6] tested two drainage system models based on the full hydrodynamic equations (SIPSON, SWMM) and coupled a 2D surface flow model (GWM) with them to simulate urban stormwater. The connection between the two models was established by assuming that the manholes were the linkage. Vozinaki et al. [7] combined the GIS with a 1D–2D coupled model to estimate the flood hazard region accurately.
1D–2D coupled models are a very powerful tool for numerical simulation. Compared with the pure 2D model, the coupled model not only maintains accuracy, but also dramatically decreases the computational time [8,9,10]. Most of coupled models use the 1D model in the river channel and 2D model in the floodplain to solve the river flood problem [2,3,4,5,11,12,13,14]. The other coupled models simulate urban drainage pipe network and river by 1D model and urban area by 2D model to solve the urban rain-flood problem [1,6,15,16]. To our knowledge, there is no precedent for applying the 1D–2D coupled model for the study of river closure in hydraulic engineering.
In this paper, a 1D–2D coupled model is established to optimize the closure flow rate, closure period and layout of a real closure project. In the 1D model, the staggered grids and semi-implicit discretization scheme are used to discretize the motion equation at the element and continuity equation at the node. In the 2D model, the 2D shallow water equations are solved by vertex-centered finite volume method, and the 2D computational domain is discretized by unstructured grids. The connection between the 1D model and 2D model is implemented by considering the mass and momentum conservation. To validate the 1D–2D coupled model, a physical experiment of a real river closure project is established. Then, the coupling model is validated by comparing numerical water level, velocity and flow rate with the physical experimental data. The transition flow in discharge structure is investigated to avoid the possible damage to the structure. Finally, the closure parameters and flow filed under different flow rate and design layout conditions are analyzed by applying this model to the study of a real river closure project. According to the simulation and analysis, best layout, closure flow rate, and closure period are obtained.
2. Numerical Method
2.1. Saint-Venant Equations
1D unsteady open channel flow can be described by Saint-Venant equations. According to the Preissmann slot method [17,18,19,20,21], pressurized flow can also be calculated through the Saint-Venant equations by adding a conceptual narrow slot on the top of a closed pipe. The Preissmann slot approach assumes that the narrow slot is open to the atmosphere, so the shallow water equations can be applied including this slot. The width of the narrow slot is ideally chosen equaling the speed of gravity waves in the slot to the water hammer wavespeed, so the water level in the slot is equal to the pressure head level. Finally, the governing equations of 1D transition model which includes local head loss are
where represents the cross-sectional area; is the discharge; is the space coordinate; is the time variable; represents the gravitational constant; is the cross-sectional water level; is the friction slope; is the velocity; and is the local head loss.
Governing equations of 1D transition flow are nonlinear partial differential equation system. This system can only be solved by a discrete scheme since the existing mathematical methods cannot gain an analytical solution. In this paper, staggered grid and semi-implicit discretization are used to discretize the equation of motion on the river section (pipe section) and continuity equation on the node. This discrete scheme not only ensures the conservation and stability of the scheme but also facilitates the input of computational data. The detail of discretization can be found in Ref. [22].
2.2. Shallow Water Equations
For large-scale free surface flow on the plane, the vertical scale is generally much smaller than plane scale. In this case, shallow water hypothesis can be introduced to simplify basic governing equations. Vertical pressure can be approximated by the hydrostatic pressure distribution. Meanwhile, the basic governing equations of mass and momentum integrate along the water depth to get the average equations. After a series of derivations, following general form of shallow water equations can be obtained:
where is the water depth; is the gravitational acceleration; is the velocity in direction, respectively; is the inflow discharge; are the source items of slope in direction, respectively, which can obtained by , ; , are the bed slope in and direction; and, ,, is the Manning’s roughness coefficient.
The discretization of the continuity equation is established using the finite volume method to ensure the conservation of the discrete scheme. Meanwhile, the equation of motion is discretized in the local coordinate system formed by the edge of the cell and its normal (the center of the cell) due to the rotation invariance of the 2D shallow water equations. The grid adopts unstructured mesh because of the better fits to boundary, good adaptability to complex geometry, and greater flexibility for local refinement. The detail of discretization can be found in Ref. [23].
3. Model Coupling
Due to the characteristics of the real river closure project (which needs to discharge through the first stage low holes during the second stage closure), it is incapable to simulate river channel and low hole simultaneously only by solving 2D shallow water equations. For this purpose, a 1D–2D coupled model needs to be established to simulate the flow in the river and overflow surface hole on the dam by 2D cells, and to simulate the flow through discharge low hole by 1D cells. The 1D and 2D model are solved in a coupled way by nodes coupling. Then, the coupled 1D–2D model is obtained which can simulate the flow in the river channel and low hole simultaneously. The coupling of 1D and 2D model is a connection in length direction. 1D area and 2D area is connected by 1D nodes and 2D nodes that are around the 1D nodes (Figure 1).
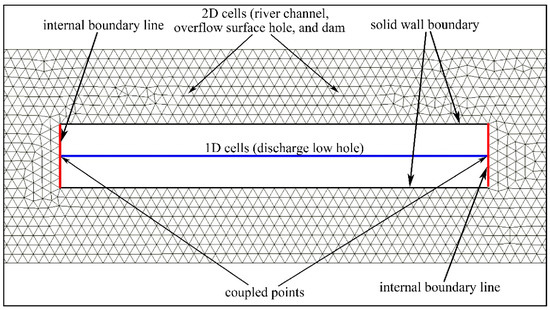
Figure 1.
Schematic of model coupling.
The interaction between the 1D model and 2D model is achieved by treating the coupled points as the internal boundary of 1D and 2D model, respectively. Consequently, the flow information exchanges between 1D nodes and 2D nodes using the Mass and Momentum Conservation (MMC) methods [4]. In this way, the same water level is imposed at internal boundary lines. The total water volume in the coupling zone can be expressed by the equation
where is the water volume in 1D cell, is the length of the 1D cell; represents the water volume in N 2D cells, is the size of the 2D cell; is the volume crossed the internal boundary line, which separates the 1D and 2D model, from 1D to 2D. calculates the water volume of N 2D cells exchanging from 2D to 1D, where , is the outward normal direction and is the side length at the direction of inlet boundary of each 2D cells which coupled with the 1D cell. After the is calculated, the new water level at the coupling point can be obtained by correctly distributing water volume in the 1D and 2D domains. The equation is
where
For the momentum conservation, an angle is introduced to express the flow rate in 1D as a vector.
Similar to mass conservation, the magnitude of momentum in and direction can be expressed as
where and represent the momentum in 1D cell; and are the momentum in 2D cells; , , and are the fluxes that cross the boundary line shared by the 1D and 2D models.
Then, the average velocity in and direction, and , can be determined according to the total water volume in the coupling zone .
Finally, the conserved variables are updated as
4. Physical Experiment Setup
4.1. Project Overview
The hydro-junction project locates on the beach at the outlet of a gorge on the mainstream of a river. It is about 6.6 km away from a bridge and is the last cascade in a river cascade planning. This project is a comprehensive utilization project for flood control, navigation, power generation, water supply, and irrigation. The key structures mainly include water discharge, navigation, power generation, water retaining, irrigation intake, fish passing, and other buildings. The checking flood level of the reservoir is 64.10 m once in 10,000 years, and the corresponding reservoir capacity is 34.79 108 m3. The total installed capacity of the power station is 1600 MW. The construction diversion is divided into two stages according to the topography and layout of the hydro-junction. The first stage is to construct the left side buildings and discharge through narrowed right side river channel. For the second stage, buildings on the right bank are constructed while the flow is discharged through the 20 low holes and 1 surface hole built during the first stage. The river closure of the second stage cofferdam begins from the right bank using the end-dump closure with single berm through economic and technological comparison.
4.2. Experimental Set-Up and Instrumentation
The physical experiment is designed according to the gravity similarity criterion with a scale of 1:80 (Figure 2 and Figure 3). 5.8 km river channel is simulated with 3 km length upstream of the dam and 2.8 km length downstream of the dam. The plane lofting adopts the plane wire control system to ensure that the natural terrain can be accurately reproduced. The error is within ±10 mm. The section method is used to construct the topography with a no more than ±2 mm error. Angle error of the sluice, cofferdam, and berm axis are controlled within ±0.01°. For the complex local topography of the river—such as beaches, islands, and stone beams—some local section and topography are added to improve the accuracy of the topography. The first stage cofferdam and terrain of the experiment are plastered with cement mortar. Hydraulic structures are scaled down to the corresponding size. Longitudinal concrete cofferdams and drainage structures are made of plexiglass and cement mortar.
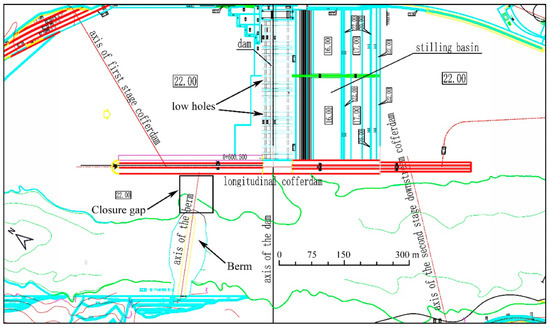
Figure 2.
Local layout of physical experiment.

Figure 3.
Field photo of physical experiment.
A triangular weir is placed at the end of channel to measure the flow rate. The water level is measured by NA2 Level Instrument and Needle Water Level Gauge at the right bank stable flow region upstream and downstream of the berm, respectively. The velocity and flow direction are measured by NKY02-1 Rotary Oars Velocimetry, VDMS Real-Time Flow Field Measurement System and Acoustic Doppler Velocimetry at the closure gap. The flow rate through closure gap is calculated by the average water depth and the average velocity measured at the closure gap. Then the flow rate through low holes can be obtained by subtracting the flow rate through closure gap from the total flow rate.
4.3. Experimental Calibration
The verification of the water surface along the river channel is mainly based on body resistance due to the complex topography of the experimental reach. The roughness of the experiment model is calibrated to make the flow resistance of the experiment coincident to the natural river. The calibrated model has gained a basically consistent free surface to the natural river. The calibration of the roughness is carried out based on the results of the free surface under natural river flow rate (Table 1). In Table 1, is the inflow rate. The comparison between experiment and natural free surface are shown in Figure 4. The maximum difference between the experiment and prototype free surface is 0.12, 0.09, and 0.05 m under flood, middle and dry season flow rate, respectively. The maximum error is 0.12 m with a relative error of 0.3%. The results show that the errors of the measured data are quite small. The experiment can accurately reproduce the real channel flow.

Table 1.
Cases of experimental calibration
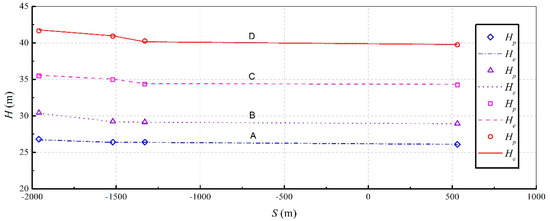
Figure 4.
Comparison of the free surface between experiment and prototype.
Three groups of physical experiment with different widths of the closure gap and different conditions of first stage cofferdam are conducted to validate the 1D–2D coupled numerical model. The results of the experiment are given below.
5. Model Validation
To test the 1D–2D coupled river closure model, the real river closure project, which is a second stage river closure project, is simulated with a model area of 10.8 km2. The river channel and overflow surface hole are simulated by the 2D model and divided by unstructured meshes while the discharge low holes are simulated by the 1D model. The narrowest channel width is about 300 m in the calculation domain, so the mesh size of the 2D model sets 30 m. The sizes of the longitudinal concrete cofferdam, berm, surface hole, and lock approach channel are too small to approximate with the 30 m mesh. Therefore, the mesh should be refined at the local position. Mesh sizes are set to 5 m around the berm and 10 m around the dam, longitudinal cofferdam and lock approach channel. A total of 28,581 2D nodes and 56,382 2D cells are generated. 20 low holes are simulated by 20 lines that are divided by 1D cells with mesh size of 2 m. Figure 5 shows the layout of the model. The initial water level is 30 m for both of the 1D and 2D model. The roughness of the channel adopts = 0.025. The initial flow rate is set to 0 m3/s for the 1D model. The upstream boundary condition is specified by the inflow rate boundary. The downstream boundary of the model is about 5 km away from the axis of the dam, so the stage–discharge relationship at 5 km below the dam is adopted as the downstream boundary condition. Time step is taken to 0.0005 h.
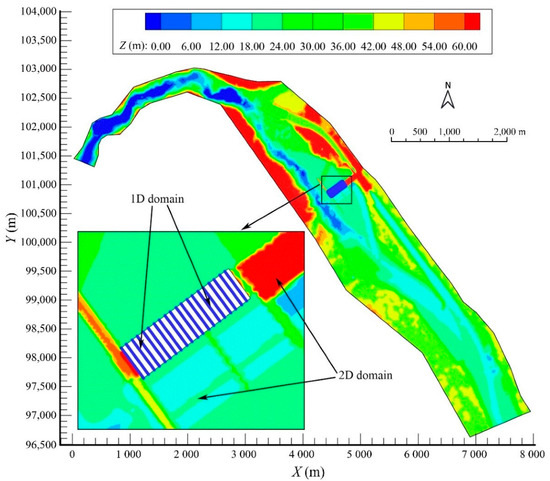
Figure 5.
Layout of the 1D–2D coupled river closure model.
According to the layout of the second stage diversion, the berm locates on the right bank with a 1:2 slope. Top elevation of the berm is 29.87 m. Minimum elevation of the channel is 5.00 m, so the height of the berm exceeds 20 m. The terrain of the berm is dynamically modified by the program. The initial length of the berm and the range of terrain modification are given by four points, respectively. The advance of the berm is obtained by interpolating in the bottom boundary of the berm according to the parameters of the berm. Different widths of the closure gap are considered. Experimental data are obtained from the above-mentioned physical experiment.
The numerical model is validated through three groups of physical experimental data with different widths of the closure gap and different conditions of first stage cofferdam. The first working condition is pre-advancement (Figure 6), in which the flow rate is = 4350 m3/s. The first stage cofferdam near longitudinal cofferdam is removed to 25.00 m in elevation while it is 40.05 m for 100 m length cofferdam near the right bank. The second working condition is river closure with 1050 m3/s flow rate. The advancing process of the berm with a more than 100 m width of the closure gap is called pre-advancement while the advancing process of the berm with a less than 100 m width of the closure gap is called river closure. The height of the first stage cofferdam is 3 m that is removed to 25 m elevation. Parameters of the berm are the same as the first working condition. The third working condition is also the river closure condition with = 1050 m3/s. 23 m is the elevation of the first stage cofferdam after being removed. Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 compare the numerical results with the experimental data under three working conditions, respectively. In these figures, is the width of the closure gap. (m3/s) and (m3/s) represent the flow rate discharged by the closure gap and 20 low holes, respectively. is the split flow rate. Besides, the water levels upstream and downstream of the berm are represented by (m) and (m). The water level difference between and is represented by (m). (m/s) refers to the maximum velocity around the closure gap. The measuring points of water level locate in the stable area upstream and downstream of the berm on the right bank.
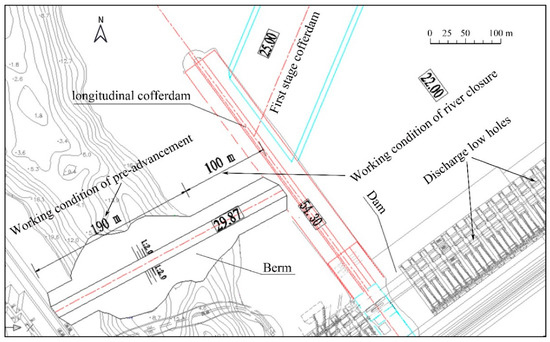
Figure 6.
Description of working condition.
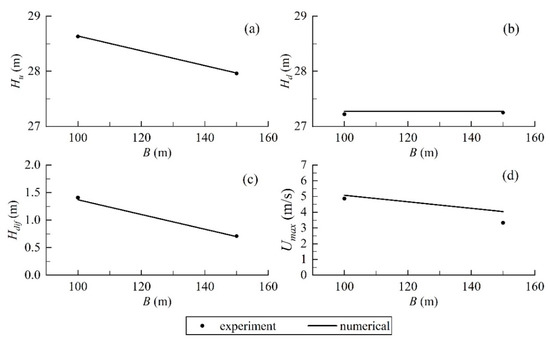
Figure 7.
Comparison between numerical results and experimental data under working condition 1: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) maximum velocity.
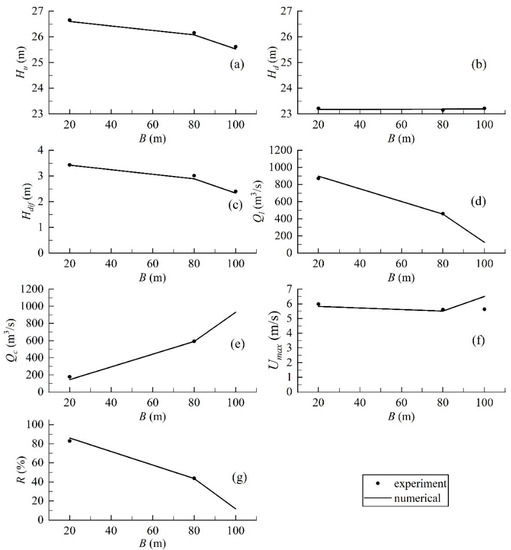
Figure 8.
Comparison between numerical results and experimental data under working condition 2: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) flow rate of low holes; (e) flow rate of closure gap; (f) maximum velocity; (g) split flow rate.
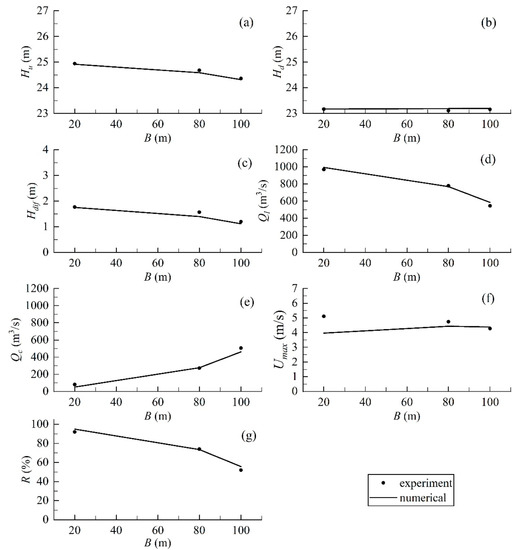
Figure 9.
Comparison between numerical results and experimental data under working condition 3: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) flow rate of low holes; (e) flow rate of closure gap; (f) maximum velocity; (g) split flow rate.
In Figure 7, the numerical results show a good agreement with the experimental data under pre-advancement condition. It can be seen that the numerical water levels are basically consistent with the experimental data with a maximum error of 0.05 m. Meanwhile, the maximum relative error of the water level difference between the upstream and downstream of the berm is 2.8%. The numerical velocity shows a discrepancy at = 100 m while it matches well with the experimental data for the rest width of the closure gap.
Figure 8 and Figure 9 compare the numerical water level, water level difference, flow rate, split flow rate, and velocity with experimental data under river closure condition. All results agree well with the experimental data. The maximum relative error of the water level and water level difference are 0.4% and 10.8%, respectively. The errors of the maximum velocity around the closure gap are a little except for 20 m width of the closure gap in working condition 3, for which the maximum relative error is 22.3%.
In summary, all the numerical results under the pre-advancement condition and river closure condition match well with the experimental data, demonstrating the capability of the 1D–2D coupled model to simulate the river closure.
6. Application to the Real River Closure Project
This real river closure project is the prototype of the physical experiment presented in Section 4. The characteristics of the second stage river closure project are the large discharge, deep riverbed in closure gap section, large quantities of throw fill, high intensity of throw fill, and short construction period. In addition, it is impossible to advance from both sides of the river channel because of the restriction of traffic conditions. These conditions increase the difficulty of the closure. To ensure the implementation of the river closure and solve the related technical issues, the numerical model is applied to investigate the process of the river closure and find the various adverse conditions during the closure. Meanwhile, the layout and advance plan of the river closure are investigated and optimized.
6.1. Transition Flow Rate
The inflow discharge of transition flow is significant to take engineering measures or control the operation model to avoid the air–water interaction and intense pressure fluctuation. Therefore, the inflow discharge of transition flow before the closure is investigated based on the 1D–2D coupled model. The results are shown in Figure 10 in which is the top wall of the discharge low hole, and is the water head. Besides, represents the cumulative distance.
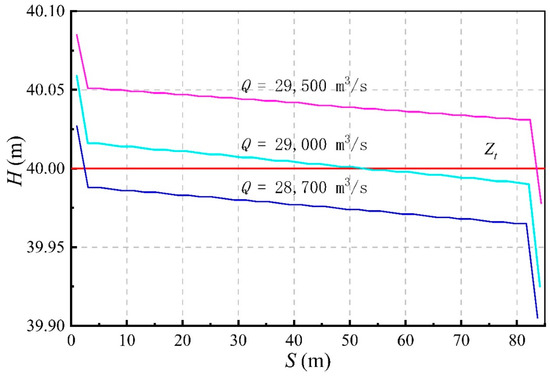
Figure 10.
Water head of discharge low hole for transition flow.
From Figure 10, the transition flow appears when the flow rate is 28,700 m3/s. Then, the transition flow develops gradually and disappears when the flow rate is higher than 29,500 m3/s. Subsequently, the flow pattern in the entire low hole develops into the pressurized flow. The transition feature of the flow is not obvious because of the short length of the low hole.
6.2. Numerical Results Under Different Working Conditions
To analyze and optimize the layout, closure flow rate and closure period of the second stage river closure project, we simulate the flow field of the river closure under different working conditions by the 1D–2D coupled model. The berm is located in the second stage upstream cofferdam because the works for upstream cofferdam are huge, and the time is shorter to construct it. This design can make the cut-off wall of the second stage upstream cofferdam constructed as soon as possible. Therefore, the berm is arranged on the downstream side of the upstream cofferdam and used as the drainage system. To reduce the water level difference between upstream and downstream of the berm and the velocity of the closure gap, the width of the closure chooses 100 m. Therefore, the advancing process is called working condition of pre-advancement when the width of the closure gap is greater than 100 m while it is called working condition of river closure when the width of the closure gap is less than 100 m.
The experimental flow rate is 4350 m3/s for the pre-advancement working condition. The flood standard of the river closure experiment adopts a 5-year recurrence period flood in late November, and the corresponding designed flow rate is 2380 m3/s. Given the possibility of earlier closure, the flood standard needs to add the 5-year recurrence period flood in late October, for which the corresponding designed flow rate is 3870 m3/s. In addition, a small discharge of 1050 m3/s should be considered in order to investigate the influence of incomplete removal of the first stage cofferdam on the split rate.
There are two axes designs for the berm (Figure 11). To select a better design, it is necessary to compare the flow field for the two cases of the closure. Meanwhile, the first stage cofferdam could not be completely removed. Therefore, we establish several models with different discharges and removed conditions of the first stage cofferdam. Numerical simulations are carried out for 250, 200, 150, and 100 m width of the closure gap in order to investigate the split flow rate, upstream and downstream water level of the berm, drop of the water level at the berm, split flow rate, and maximum velocity during the pre-advancement while 100, 80, 60, 40, 30, 20, and 0 m width of the closure gap are selected in closure condition. In addition, varies of inlet flow rate are needed to consider for analyzing the flow field, maximum velocity, upstream and downstream water level, drop of the water level, and split flow rate at the closure gap. Different models and working conditions are summarized in Table 2 in which and is the inlet flow rate and width of the closure gap, respectively. is the elevation of the first stage cofferdam after removal.
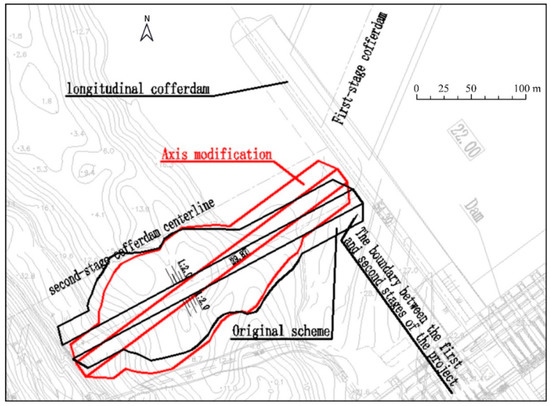
Figure 11.
Layout of the berm.

Table 2.
List of working conditions
The upstream and downstream water levels can be obtained from the water level measuring points. The flow rate and velocity of the closure gap are measured at the axis of the berm while the total flow rate of low holes is calculated by summing up the flow rates through from each low hole.
Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15 show the numerical results of original scheme 1, 2, 3, 4, and axis modified scheme. The upstream water level rises with the reduce of while the downstream water level changes a little. Correspondingly, the water level difference also rises with the reduce of . In addition, the flow rate through 20 low holes increases with the decrease in while the flow rate through the closure gap decreases resulting in raised split flow rate. The maximum velocity raises first and then reduces to 0 with the decrease in . The peak of the maximum velocity reaches at = 30–40 m.
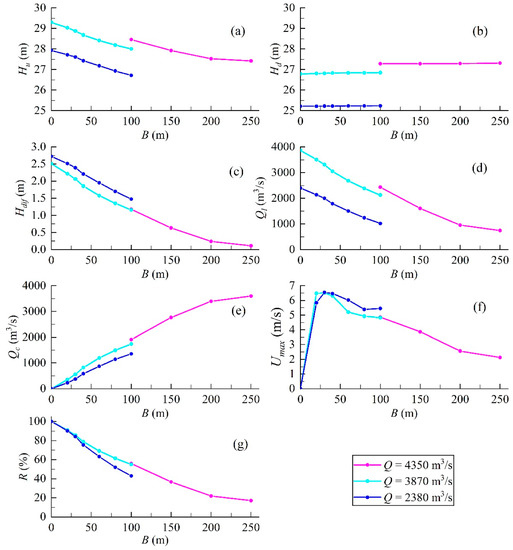
Figure 12.
Numerical results of original scheme 1: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) flow rate of low holes; (e) flow rate of closure gap; (f) maximum velocity; (g) split flow rate.
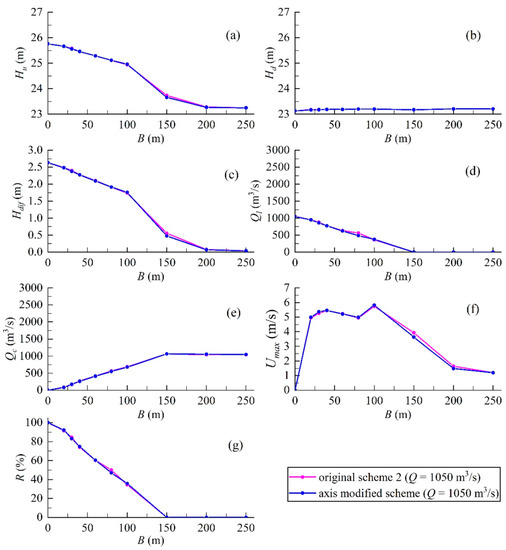
Figure 13.
Comparison between the numerical results of original scheme 2 and axis modified scheme: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) flow rate of low holes; (e) flow rate of closure gap; (f) maximum velocity; (g) split flow rate.
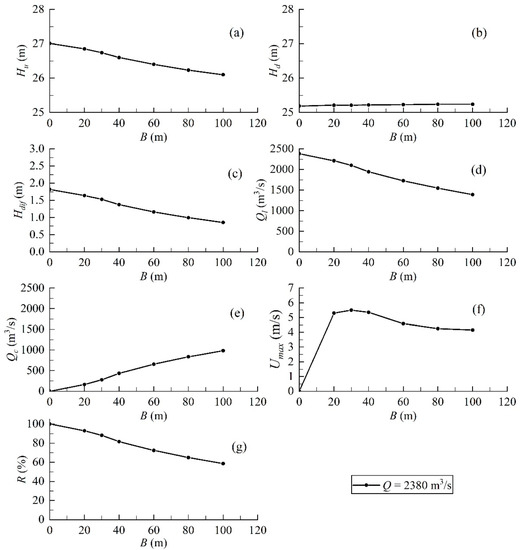
Figure 14.
Numerical results of original scheme 3: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) flow rate of low holes; (e) flow rate of closure gap; (f) maximum velocity; (g) split flow rate.
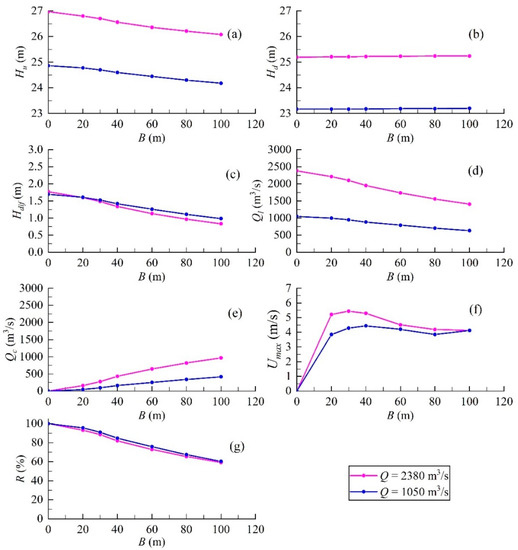
Figure 15.
Numerical results of original scheme 4: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) flow rate of low holes; (e) flow rate of closure gap; (f) maximum velocity; (g) split flow rate.
Comparing Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15, the flow rate through the closure gap reduces with the decreases in the elevation of the first stage cofferdam. Therefore, the split flow rate increases with the decrease in the elevation of the first stage cofferdam. The change in water level difference and maximum velocity are consistence with the flow rate through the closure gap. To maintain the safety of hydraulic engineering, the water level difference and maximum velocity should be as small as possible while the opposite is true for the split flow rate. Therefore, the elevation of the first cofferdam should be as low as possible. The optimum removal elevation of the first stage cofferdam is the floor elevation upstream and downstream of the dam (22 m).
Figure 13 compares the numerical results of the original scheme 2 with the axis modified scheme. A basically consistence results between the original scheme 2 and axis modified scheme can be observed. The calculated upstream and downstream water levels of the two schemes are no big difference except for the 150 m width of the closure gap. The water level differences for the axis modified scheme are smaller than the original scheme 2 except that the 100 m width of the closure gap is the opposite. For pre-advancement working condition, the maximum velocity of the closure gap for axis modified scheme is less than the original scheme 2 while the opposite is true for the working condition of river closure. The peak of the maximum velocity obtains at 40 m and 100 m width of the closure gap. The peak value of the original scheme 2 is 5.74 m/s which is 0.08 m/s less than the axis modified scheme. The maximum velocity of the closure gap decreases firstly, then increases, and decreases again until to 0 when the width of the closure gap is smaller than 100 m. The change of the position, where the maximum velocity locates, is the main reason for this phenomenon. Location of the maximum velocity is at the upstream front toe of berm head when the width of the closure gap is greater than or equal to 100 m. As for less than 100 m width, the position of the maximum velocity locates at the center of the closure gap slightly downstream from the axis of the berm. The split flow rate changes a little for the two schemes. The split flow rates for original scheme 2 are larger than the axis modified scheme at 30 and 80 m width of the closure gap while there is basically no difference for the rest points. In general, the original scheme is more reasonable than the axis modified scheme due to the lower maximum velocity and larger split flow rate for the working condition of river closure.
The numerical results of different flow rate for original scheme 1 are plotted in Figure 16. Both the upstream and downstream water levels rise with the increase in flow rate. The water level difference is minimum (2.062 m) at the flow rate of 3870 m3/s with a constant elevation of the first stage cofferdam. The water level difference raises with the increase or decrease in the flow rate away from 3870 m3/s. The maximum velocity reaches and maintains a large value when the flow rate is greater than or equal to 2380 m3/s. In addition, the split flow rate rises with the raise of the flow rate, and maintains a relatively large value at the flow rate larger than or equal to 2380 m3/s. Therefore, the closure flow rate should not exceed 2380–3870 m3/s.
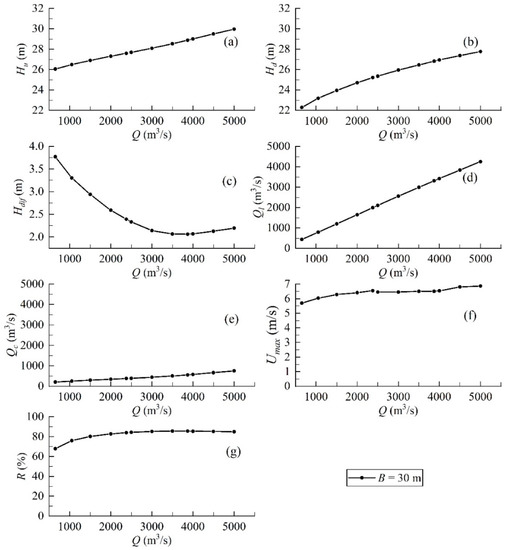
Figure 16.
Numerical results of different flow rates for original scheme 1: (a) upstream water level; (b) downstream water level; (c) water level difference; (d) flow rate of low holes; (e) flow rate of closure gap; (f) maximum velocity; (g) split flow rate.
In summary, the flow pattern of the original scheme is better due to the larger flow rate and smaller maximum velocity at the closure gap. Hence, the original design of berm axis is recommended. Although the water level difference reaches trough at 3870 m3/s flow rate, the upstream water level is 29.297 m after the closure which is only 0.573 m height from the top of the berm. Therefore, the river closure should not be executed with the flow rate greater than or equal to 3870 m3/s for safety reason. The water level difference increases gradually while the maximum velocity of the closure gap changes little and maintains a high value with 2380 m3/s to 3870 m3/s flow rate. When the flow rate is smaller than 2380 m3/s, the water level difference increases gradually while the maximum velocity decreases. Moreover, the upstream water level after the closure is less than 27.929 m which is low enough. In short, it is suggested that the river closure should be performed when the flow rate is less than 2380 m3/s due to the smaller velocity and lower upstream water level.
6.3. Process of River Closure
To show the unsteady flow field, a dynamic river closure is simulated by the 1D–2D coupled model for 2380 m3/s flow rate. The berm moves forward gradually from the 100 m width of the closure gap and begins to affect the flow field. Hence, it is necessary to calculate the long durative flow field which makes the time consuming very large due to the slow advance speed of the berm in reality. To speed up the calculation, the advance speed of the berm sets to 10 m/s. Time step is 0.0005 h. Initial stable time adopts 20 h because the stable time is about 15 h according to the above steady flow simulation. The length of the berm remains unchanged during the initial 20 h. The berm begins to move forward at = 20 h. A physical time of 50 h is simulated. The flow field at different time instants are given in Figure 17.
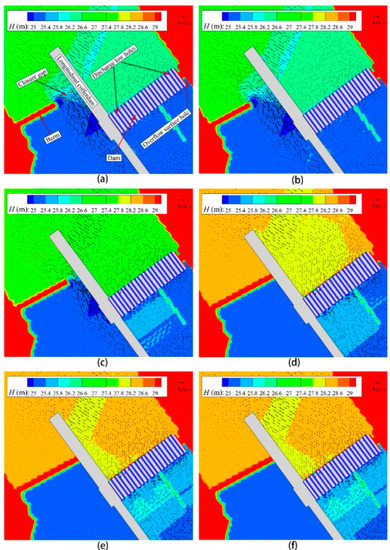
Figure 17.
The flow field at different times: (a) = 15 h; (b) = 20 h; (c) = 25 h; (d) = 30 h; (e) = 35 h; (f) = 50 h. The color represents water level or terrain elevation at nodes. The vector is velocity.
It can be seen that the flow field stabilizes at = 15 h. The flow field is unchanged until = 20 h. After = 20 h, the berm progressively pushes forward. The closure gap is completely closed at = 30 h. The flow field stabilizes again at = 35 h. Then, the flow field remains stable until = 50 h. The upstream water level of the berm increases while the downstream water level of the berm decreases with the advance of the berm. Correspondingly, the water level difference enlarges. On the contrary, the downstream water level of the first stage dam raises with the reduce of the closure gap. The upstream water level of first stage dam rises gradually with the reduce of the closure gap. The water level at the first stage cofferdam is slightly lower than the upstream and downstream of the cofferdam due to higher elevation of the cofferdam. However, the difference reduces gradually with the decrease in the closure gap width.
The velocity around the berm is greater than 4 m/s with a maximum value of 5.45 m/s in Figure 17a,b. For the first stage cofferdam, the maximum velocity, which is 3.3 m/s, locates on the left side downstream of the cofferdam. During the whole process of the river closure, the maximum velocity of the closure gap reaches at 30 m width of the closure gap. The maximum value is about 6.55 m/s located on the slightly downstream channel of the berm. The maximum velocity upstream of the dam appears after the closure. The position of the maximum velocity is at the left bank. Meanwhile, the maximum velocity of the first stage cofferdam is about 4.2 m/s located on the left side downstream of the cofferdam.
7. Conclusions
The 1D–2D coupled model is established by considering the mass and momentum conservation. The model simulates the open channel by the 2D model and discharge low holes by the 1D model. To validate the 1D–2D coupled model, a 1:80 indoor physical experiment of a real river closure project is set up. Three groups of physical experimental data with varying widths of the closure gap and conditions of the first stage cofferdam are compared with the numerical results. Good agreements are achieved in terms of surface elevation, velocity, and flow rate. Then, the coupled model is applied to the real river closure project. The pre-advancement and closure of the berm under different working conditions are numerically studied. Finally, the layout, closure flow rate, and closure period of this project are analyzed and optimized.
By analyzing the numerical results and the flow field, it can be known that maintaining the original axis of the berm is more conducive to improve the flow pattern at the closure gap. The height that the first stage cofferdam is removed should be as large as possible. It is best to remove the cofferdam to 22 m floor elevation upstream and downstream of the dam. In addition, the river closure should be executed when the discharge is smaller than 2380 m3/s.
Author Contributions
J.L. developed models, analyzed data, validated models, and wrote the original manuscript. S.J. developed models and supervised the research. C.A. reviewed results, edited the manuscript, and supervised the research. W.D. reviewed results and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agree to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number [No. 51739011]; and the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number [No. 2016YFC0402707].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, W.; Chen, Q.; Mao, J. Development of 1D and 2D coupled model to simulate urban inundation: An application to Beijing Olympic Village. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Monnier, J. Superposition of local zoom models and simultaneous calibration for 1D–2D shallow water flows. Math. Comput. Simul. 2009, 80, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, D. 1D–2D Coupled Numerical Model for Shallow-Water Flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 138, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Hernández, M.; García-Navarro, P.; Burguete, J.; Brufau, P. A conservative strategy to couple 1D and 2D models for shallow water flow simulation. Comput. Fluids 2013, 81, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timbadiya, P.V.; Patel, P.L.; Porey, P.D. A 1D–2D Coupled Hydrodynamic Model for River Flood Prediction in a Coastal Urban Floodplain. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 20, 05014017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Leandro, J.; Djordjević, S. Influence of sewer network models on urban flood damage assessment based on coupled 1D/2D models. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S717–S728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozinaki, A.E.K.; Morianou, G.G.; Alexakis, D.D.; Tsanis, I.K. Comparing 1D and combined 1D/2D hydraulic simulations using high-resolution topographic data: a case study of the Koiliaris basin. Greece. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Fang, H.W.; Bai, J.; He, G.J. A coupled 1-D and 2-D channel network mathematical model used for flow calculations in the middle reaches of the yangtze river. J. Hydrodyn. 2011, 23, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finaud-Guyot, P.; Delenne, C.; Guinot, V.; Llovel, C. 1D–2D coupling for river flow modeling. Comptes Rendus Mec. 2011, 339, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladé, E.; Gómez-Valentín, M.; Dolz, J.; Aragón-Hernández, J.L.; Corestein, G.; Sánchez-Juny, M. Integration of 1D and 2D finite volume schemes for computations of water flow in natural channels. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 42, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiry, S.N.; Sen, D.; Bates, P.D. Coupled 1D–Quasi-2D Flood Inundation Model with Unstructured Grids. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 136, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Nieto, E.D.; Marin, J.; Monnier, J. Coupling superposed 1D and 2D shallow-water models: Source terms in finite volume schemes. Comput. Fluids 2010, 39, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. A coupled 1D–2D hydrodynamic model for flood simulation in flood detention basin. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1303–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Hernández, M.; Petaccia, G.; Brufau, P.; García-Navarro, P. Conservative 1D–2D coupled numerical strategies applied to river flooding: The Tiber (Rome). Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 2087–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinovic, Z.; Tutulic, D. On the use of 1d and coupled 1D–2D modelling approaches for assessment of flood damage in urban areas. Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ao, T.; Yu, H.; Huang, G.; Li, X. A coupled 1D–2D hydrodynamic model for urban flood inundation. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 2819308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerger, F.; Archambeau, P.; Erpicum, S.; Dewals, B.J.; Pirotton, M. An exact Riemann solver and a Godunov scheme for simulating highly transient mixed flows. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 235, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerger, F.; Archambeau, P.; Erpicum, S.; Dewals, B.J.; Pirotton, M. A fast universal solver for 1D continuous and discontinuous steady flows in rivers and pipes. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2011, 66, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferńdez-Pato, J.; García-Navarro, P. A pipe network simulation model with dynamic transition between free surface and pressurized flow. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pato, J.; García-Navarro, P. Finite volume simulation of unsteady water pipe flow. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2014, 7, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, A.; Karney, B.W. Spurious Numerical Oscillations in the Preissmann Slot Method: Origin and Suppression. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 142, 04015060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z. General hydrodynamic model for sewer/channel network systems. lournal Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Geng, Y. An unstructured finite volume algorithm for nonlinear two dimensional shallow water equation. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. 2005, 17, 306–312. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).