Cost–Benefit Analysis of Leakage Reduction Methods in Water Supply Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
Water Supply in Finland
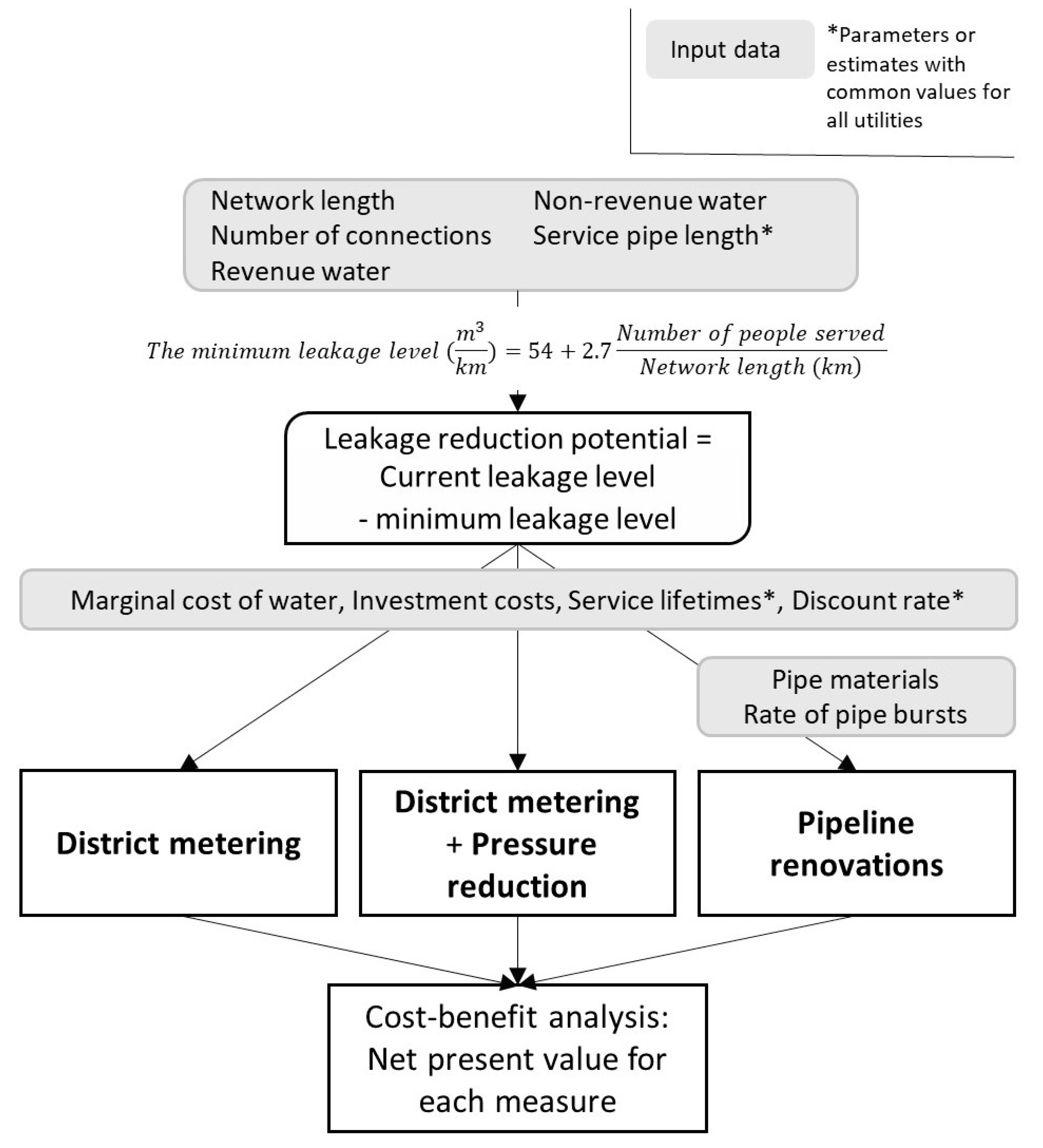
2.2. Estimating the Leakage Reduction Potential
2.3. The Leakage Reduction Methods
2.3.1. District Metering
2.3.2. Pressure Reduction
2.3.3. Renovations
2.4. The Economic Level of Leakage
2.5. Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. Limitations of the Method
3. Results
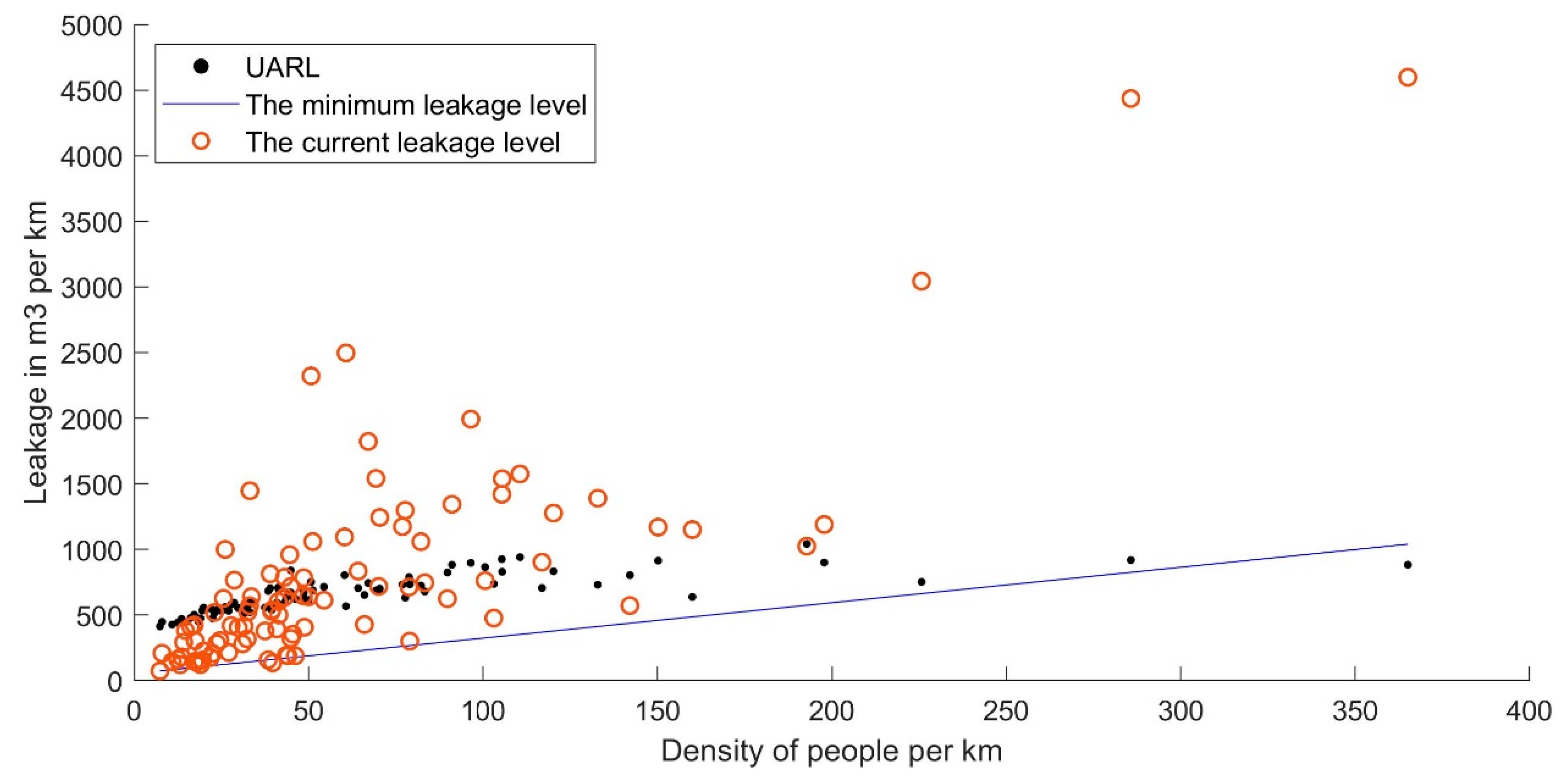
3.1. Current Leakage Levels and Leakage Reduction Potential in Finland
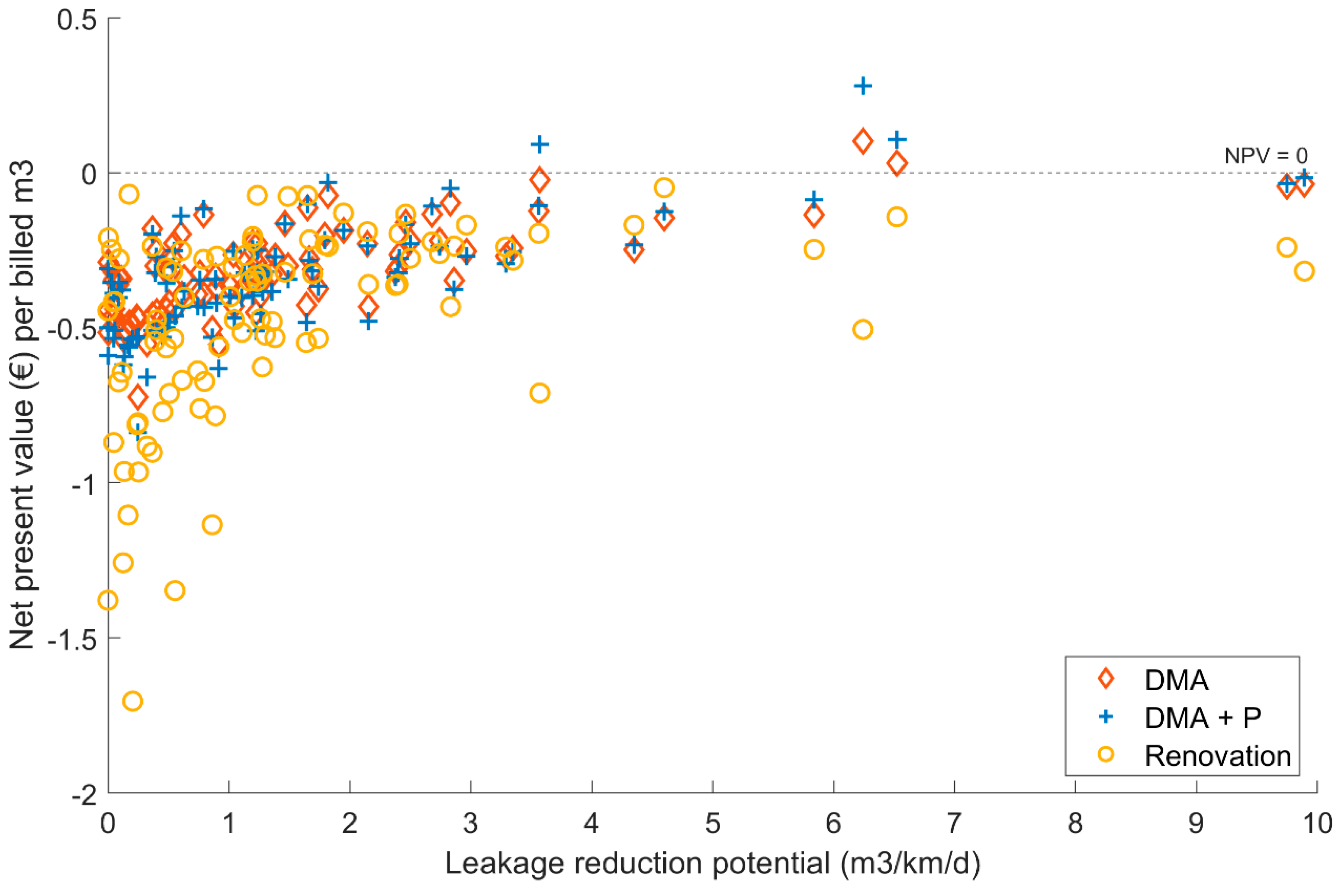
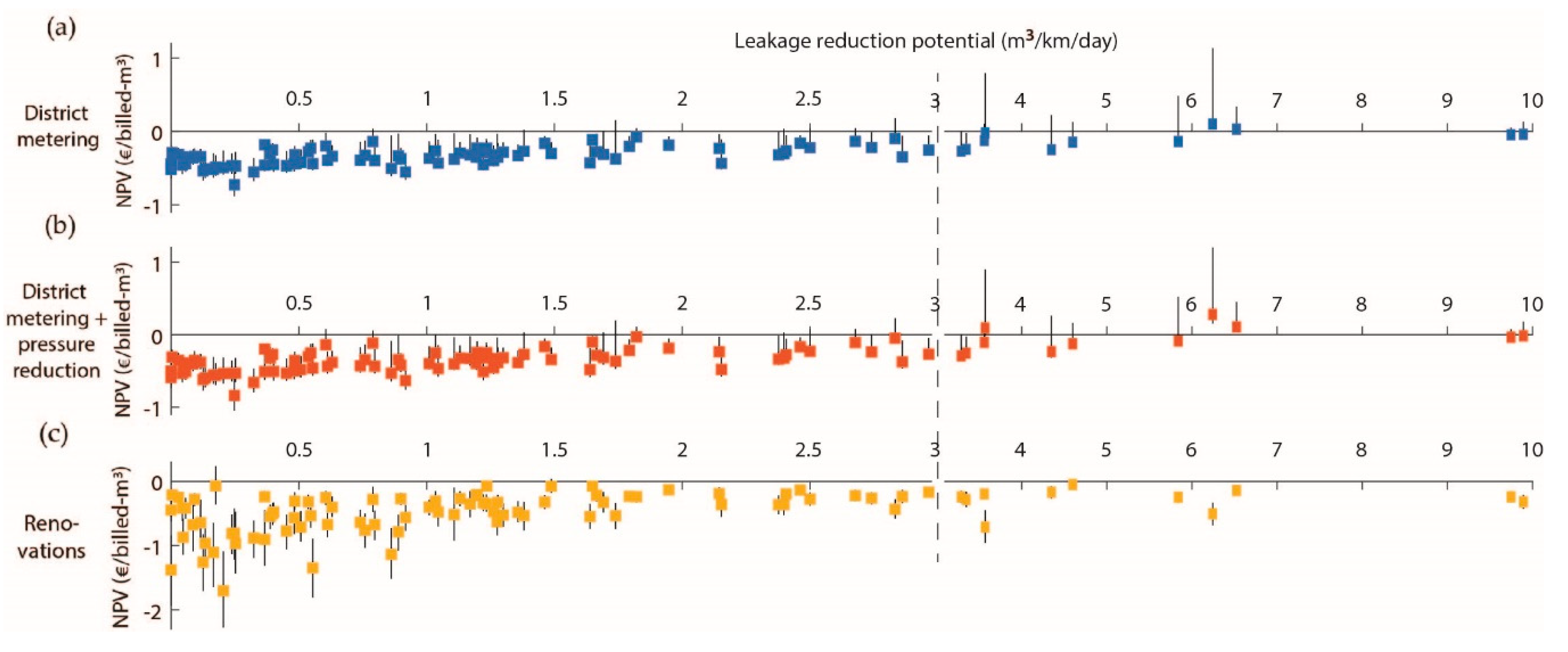
3.2. The Cost–Benefit Analysis of Leakage Reduction Measures
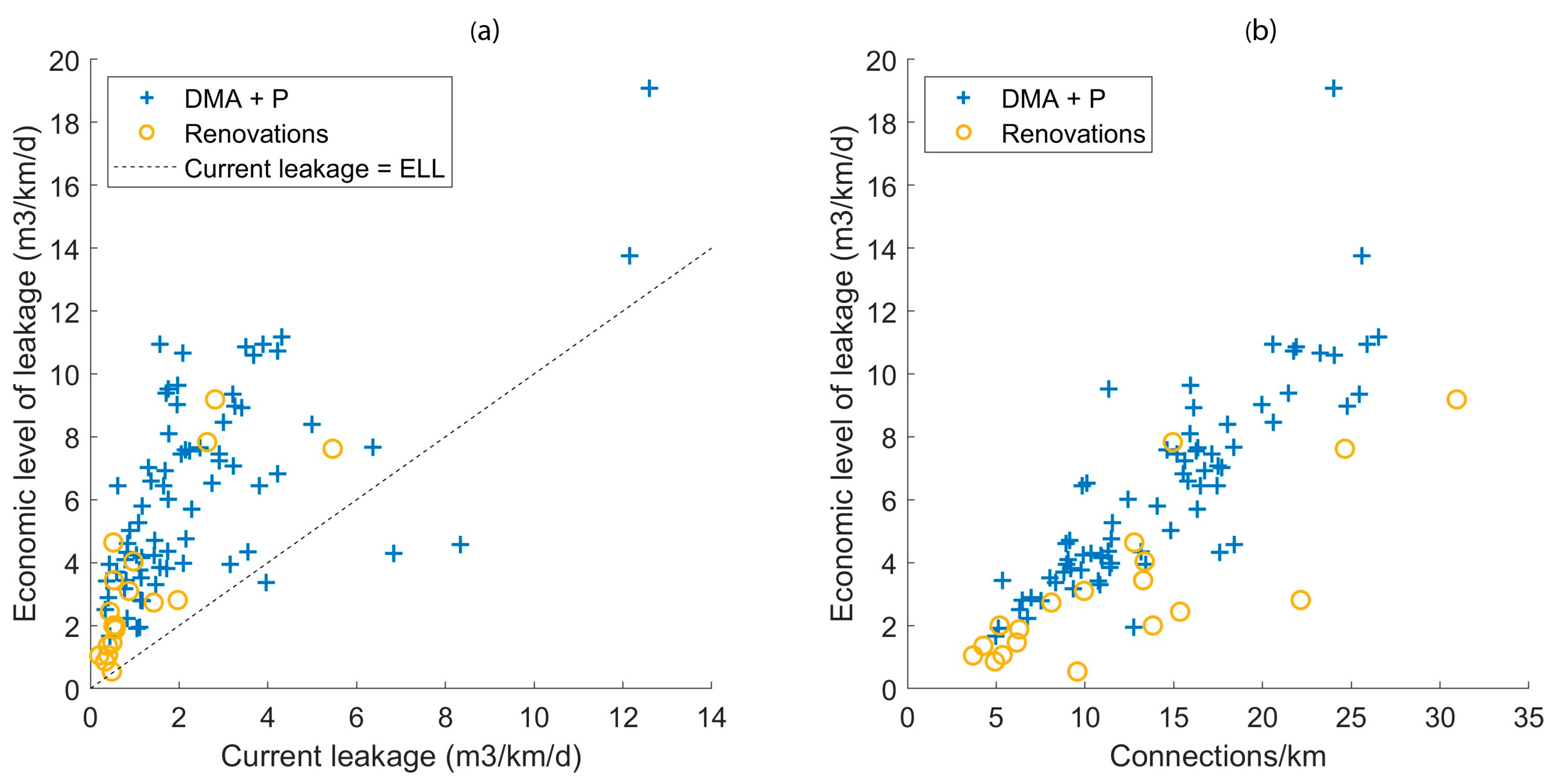
3.3. The Economic Level of Leakage (ELL)
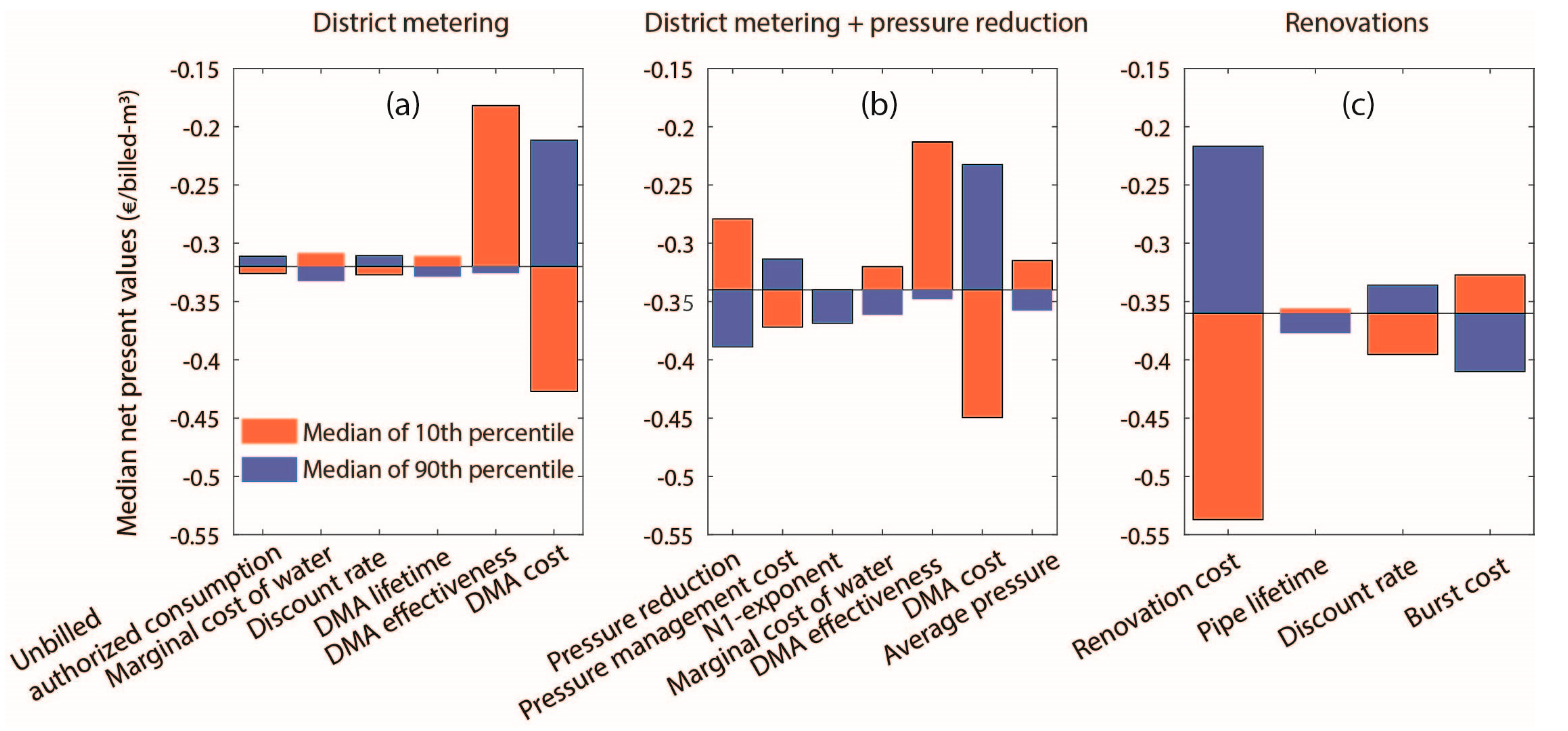
3.4. Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Context-Specific Findings: Mostly Low Water Loss Levels in Finland
4.2. Leakage Reduction Methods
4.3. Leakage Indicators and Policies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liemberger, R.; Wyatt, A. Quantifying the global non-revenue water problem. Water Supply 2019, 19, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puust, R.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.A.; Koppel, T. A review of methods for leakage management in pipe networks. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.; Charalambous, B. Leak Detection: Technology and Implementation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-78040-471-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, R.; Sá Marques, A.; Sousa, J. Identification of the optimal entry points at District Metered Areas and implementation of pressure management. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, D.J.; Garrote, L.; Sánchez, R.; Santillán, D. Pressure Management in Water Distribution Systems: Current Status, Proposals, and Future Trends. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04015061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Agency; Ofwat; Defra. Review of the Calculation of Sustainable Economic Level of Leakage and Its Integration with Water Resource Management Planning; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2012.
- Venkatesh, G. Cost-benefit analysis—leakage reduction by rehabilitating old water pipelines: Case study of Oslo (Norway). Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, A.; Moberg, F.; Rosén, L.; Pettersson, T.J.R. Cost-Benefit Analysis and Uncertainty Analysis of Water Loss Reduction Measures: Case Study of the Gothenburg Drinking Water Distribution System. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 5451–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Coelho, F.; Fortunato, A. Water losses and hydrographical regions influence on the cost structure of the Portuguese water industry. J. Product. Anal. 2012, 38, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferro, G.; Mercadier, A.C. Technical efficiency in Chile’s water and sanitation providers. Util. Policy 2016, 43, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Mocholí-Arce, M.; Sala-Garrido, R. Estimating the environmental and resource costs of leakage in water distribution systems: A shadow price approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 568, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Babel, M.S. Economic Analysis of Leakage in the Bangkok Water Distribution System. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.A. Uses, Abuses, and Alternatives to the Net-Present-Value Rule. Financ. Manag. 1995, 24, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finland’s Environmental Administration. Vesihuoltolaitosten Raportteja [Several Data Files]. Available online: http://www.ymparisto.fi/fi-FI/Kartat_ja_tilastot/Vesihuoltoraportit/Vesihuoltolaitosten_raportit/ (accessed on 10 April 2018). (In Finnish)
- Energy Authority. Sähkön Hintatilastot. Available online: https://www.energiavirasto.fi/sahkon-hintatilastot (accessed on 10 March 2017). (In Finnish).
- Ojala, M. Kiinteistöjen Tonttivesijohtojen ja -Viemäreiden Saneeraus, KTVVS-Tutkimus 2001; VVY:n monistesarja 9: Helsinki, Finland, 2002. (In Finnish) [Google Scholar]
- Lapinlampi, T.; Raassina, S. Water Supply and Sewer Systems 1998—2000. Waterworks (In Finnish); The Finnish Environment 541: Helsinki, Finland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ahopelto, L.; Veijalainen, N.; Guillaume, J.; Keskinen, M.; Marttunen, M.; Varis, O. Can There be Water Scarcity with Abundance of Water? Analyzing Water Stress during a Severe Drought in Finland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, O.; Takala, A.; Katko, T. Challenges to Finnish water and wastewater services in the next 20–30 years. E-WAter 2011, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä, O. IWA Yearbook 2013—Finland. Available online: http://www.vesiyhdistys.fi/english.html (accessed on 28 March 2017).
- Rajala, R.P.; Hukka, J.J. Asset life cycle management in Finnish water utilities. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2018, 10, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alegre, H.; Baptista, J.F.d.M.; Cabrera, E.; Cubillo, F.; Duarte, P.; Hirner, W.; Merkel, W.; Parena, R. Performance Indicators for Water Supply Services, 2nd ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-1-78040-633-6. [Google Scholar]
- van Zyl, J.E.; Lambert, A.O.; Collins, R. Realistic Modeling of Leakage and Intrusion Flows through Leak Openings in Pipes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A. What do we know about pressure/leakage relationships in distribution systems? In Proceedings of the IWA Specialised Conference, System Approach to Leakage Control and Water Distribution Systems Management, Brno, Czech Republic, 16–18 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.O.; Fantozzi, M. Recent developments in pressure management. In Proceedings of the Water Loss 2010 Conference, Sao Paolo, Brazil, 6–9 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tuhovcak, L.; Suchacek, T.; Rucka, J. The Dependence of Water Consumption on the Pressure Conditions and Sensitivity Analysis of the Input Parameters. Proceedings 2018, 2, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, K.; Laakso, T.; Paatela, H.; Virta, S.; Rautiainen, J.; Virtanen, R.; Tynkkynen, O.; Piila, N.; Dubovik, M.; Vahala, R. Sustainable Water Services for the Future—Direction, Steering and Organisation; Prime Minister’s Office: Helsinki, Finland, 2018. (In Finnish)
- Järvenpään Vesi. Järvenpään Vesihuoltoverkostojen Saneerausohjelma. Available online: https://www.jarvenpaa.fi/jarvenpaa/attachments/text_editor/774.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2017). (In Finnish).
- Pöyry. Verkostosaneerausten Vaikuttavuuden Arviointi, Raportti 67090591.BBP. Available online: https://docplayer.fi/360892-Verkostosaneerausten-vaikuttavuuden-arviointi.html (accessed on 2 October 2019). (In Finnish).
- Pietarila, V. Evaluation of Renovation Debt in Water Supply Network in Oulu. Bachelor’s Thesis, Oulu University of Applied Sciences, Oulu, Finland, 2012. (In Finnish). [Google Scholar]
- Polvinen, H.-L. Vesiputkien Taloudellisesti Optimaalinen Saneerausajankohta. Master’s Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2015. (In Finnish). [Google Scholar]
- ELY Centre. Vesihuoltoverkoston Saneeraustarpeen Selvittäminen: Työkaluja Varojen Kohdentamiseen; Reports 10/2017; The Southeast Finland Centre for Economic Development, Transport and the Environment: Turku, Finland, 2017. (In Finnish) [Google Scholar]
- Pianosi, F.; Sarrazin, F.; Wagener, T. A Matlab toolbox for Global Sensitivity Analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 70, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianosi, F.; Beven, K.; Freer, J.; Hall, J.W.; Rougier, J.; Stephenson, D.B.; Wagener, T. Sensitivity analysis of environmental models: A systematic review with practical workflow. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 79, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.L.; Kenway, S.J.; Lant, P.A. City-scale analysis of water-related energy identifies more cost-effective solutions. Water Res. 2017, 109, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, D.; Dias, A.C.; Gabarrell, X.; Arroja, L. Environmental assessment of an urban water system. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, J.; Catel, L.; Renaud, E.; Augeard, B.; Roux, P. Up to what point is loss reduction environmentally friendly? The LCA of loss reduction scenarios in drinking water networks. Water Res. 2016, 104, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LNEC; ERSAR. Water and Waste Services Quality Assessment Guide. 2nd Generation of the Assessment System; Water and Waste Services Regulation Authority (ERSAR), National Laboratory for Civil Engineering (LNEC): Lissabon, Portugal, 2013; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Svenskt Vatten. Hållbarhetsindex för Kommunernas VA-Verksamhet, Beskrivning av Verktygets Syfte och Konstruktion inför Undersökningen 2017; Svenskt Vatten AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017; p. 34. (In Swedish) [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Resource and Economic Efficiency of Water Distribution Networks in the EU; Final Report (ENV.D.1/SER/2010/0029); European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Creaco, E.; Walski, T. Economic Analysis of Pressure Control for Leakage and Pipe Burst Reduction. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A. Ten Years’ Experience in Using the UARL Formula to Calculate Infrastructure Leakage Index. In Proceedings of the Water Loss 2009 Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 26–30 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
| Age Category | Pipe Failure Rate (Failures/100 km/year) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal | Plastic | Other/Unknown | |
| Old (≥50 or ≥40 years old) | 16 | 10 | 6 |
| New (≤15 years old) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Average of all ages | 9 | 1 | 3.3 |
| Ratio of old to average pipe failure rate | 1.8 | 7.1 | 1.8 |
| Leakage rate compared to metal pipes (based on the average pipe failure rates) | 1 | 0.15 | 0.36 |
| Variable | Unit | Distribution | Estimated Mean (µ) | Standard Deviation (σ) | Uniform Dist. Bounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The total length of service lines | m | normal | 22.5 | 5 | - |
| Unbilled authorized consumption | % of network input | uniform | 2 | - | [0.5, 3.5] |
| Average pressure | m | uniform | 50 | - | [35, 65] |
| Discount rate | % per year | normal | 3.5 | 0.8 | - |
| Marginal cost of water | euros/m3 | truncated normal | varies by utility (median 0.11) | 0.1 µ (min. value 0.04) | - |
| DMA effectiveness | % of the total leakage reduction potential | uniform | 30 | - | [20, 100] |
| DMA cost | euros/DMA area | normal | 48,000 | 10,000 | - |
| DMA lifetime | years | normal | 20 | 2 | - |
| N1 (leakage–pressure exponent) | - | uniform | varies by utility | - | [0.5, 1.5] |
| Average pressure reduction | m | uniform | 5 | [1, 10] | |
| Cost of pressure management | euros/station | normal | 9000 | 2000 | - |
| Burst repair cost | euros | truncated normal | 5500–14,500 (varies by utility size) | 0.25 µ (min. value 2000) | - |
| Renovation cost | euros/metre | truncated normal | 94–628 (varies by utility size) | 0.25 µ (min. value 50) | - |
| Pipe lifetime | years | normal | 70 | 15 | - |
| Utility Size (Sample Size) | Figure | Service Conn/km | No. of People/km | Leakage % 2 | Leakage m3/km/d | ILI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small (n = 43), | ||||||
| 3000–10,000 pop., | Median | J | F | J | J | J |
| 900–3700 conn. | Min–Max | 4–21 | 7–67 | 4–49 | 0.2–7 | 0.2–4.4 |
| Medium (n = 39), | ||||||
| 10,000–60,000 pop., | Median | J | M | J | J | J |
| 2000–16,000 conn. | Min–Max | 5–31 | 17–198 | 6–28 | 0.4–5 | 0.3–2.2 |
| Large (n = 10), | ||||||
| 60,000–1200,000 pop., | Median | J | M | J | J | J |
| 11,000–73,000 conn. | Min–Max | 13–27 | 70–365 | 6–20 | 1–13 | 0.6–5.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahopelto, S.; Vahala, R. Cost–Benefit Analysis of Leakage Reduction Methods in Water Supply Networks. Water 2020, 12, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010195
Ahopelto S, Vahala R. Cost–Benefit Analysis of Leakage Reduction Methods in Water Supply Networks. Water. 2020; 12(1):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010195
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhopelto, Suvi, and Riku Vahala. 2020. "Cost–Benefit Analysis of Leakage Reduction Methods in Water Supply Networks" Water 12, no. 1: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010195
APA StyleAhopelto, S., & Vahala, R. (2020). Cost–Benefit Analysis of Leakage Reduction Methods in Water Supply Networks. Water, 12(1), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010195




