Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in the Lancang–Mekong River Using the Modified Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
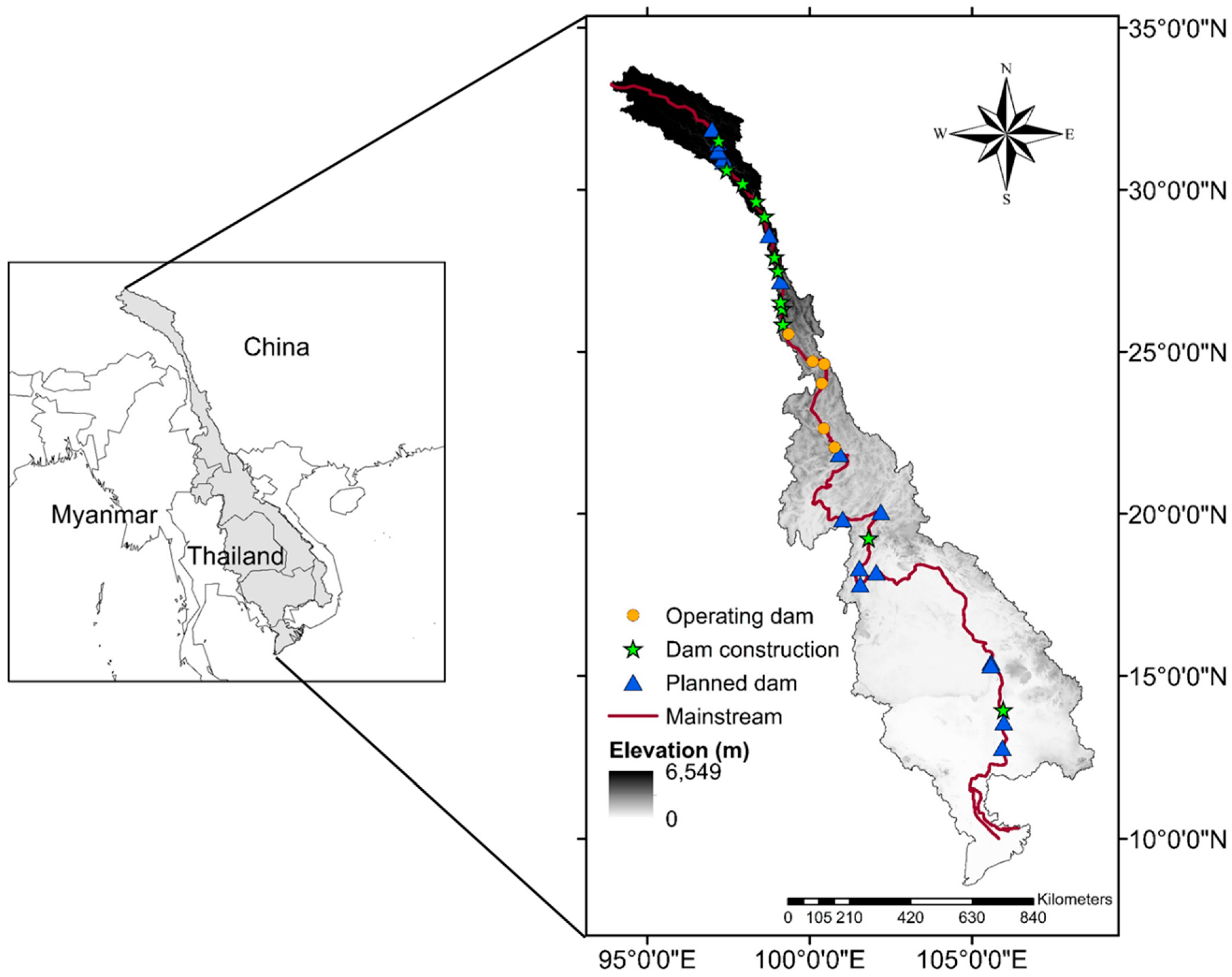
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. RUSLE
3.1.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor
3.1.2. Soil Erodibility Factor
3.1.3. Topographic Factor
3.1.4. Cropping Management Factor
3.1.5. Support Practice Factor
3.1.6. Application of GIS Tools
3.2. Descriptive Statistics in the RUSLE Model
3.3. Technique of Sediment Yield Estimation
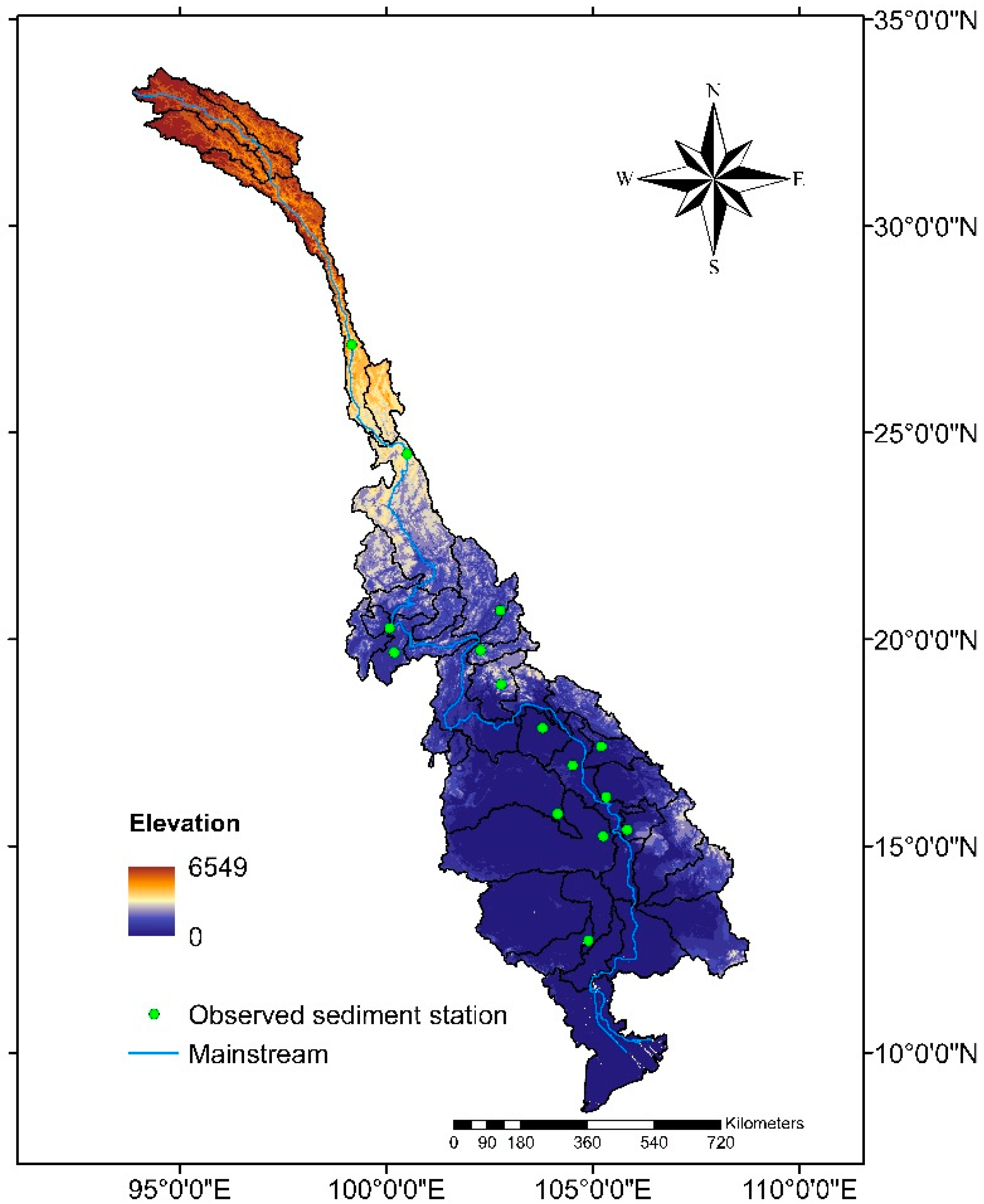
3.4. Observed Sediment Data
4. Results
4.1. Soil Erosion Factors
4.1.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor
4.1.2. Soil Erodibility Factor
4.1.3. Topographic Factor
4.1.4. Cropping Management Factor
4.1.5. Support Practice Factor
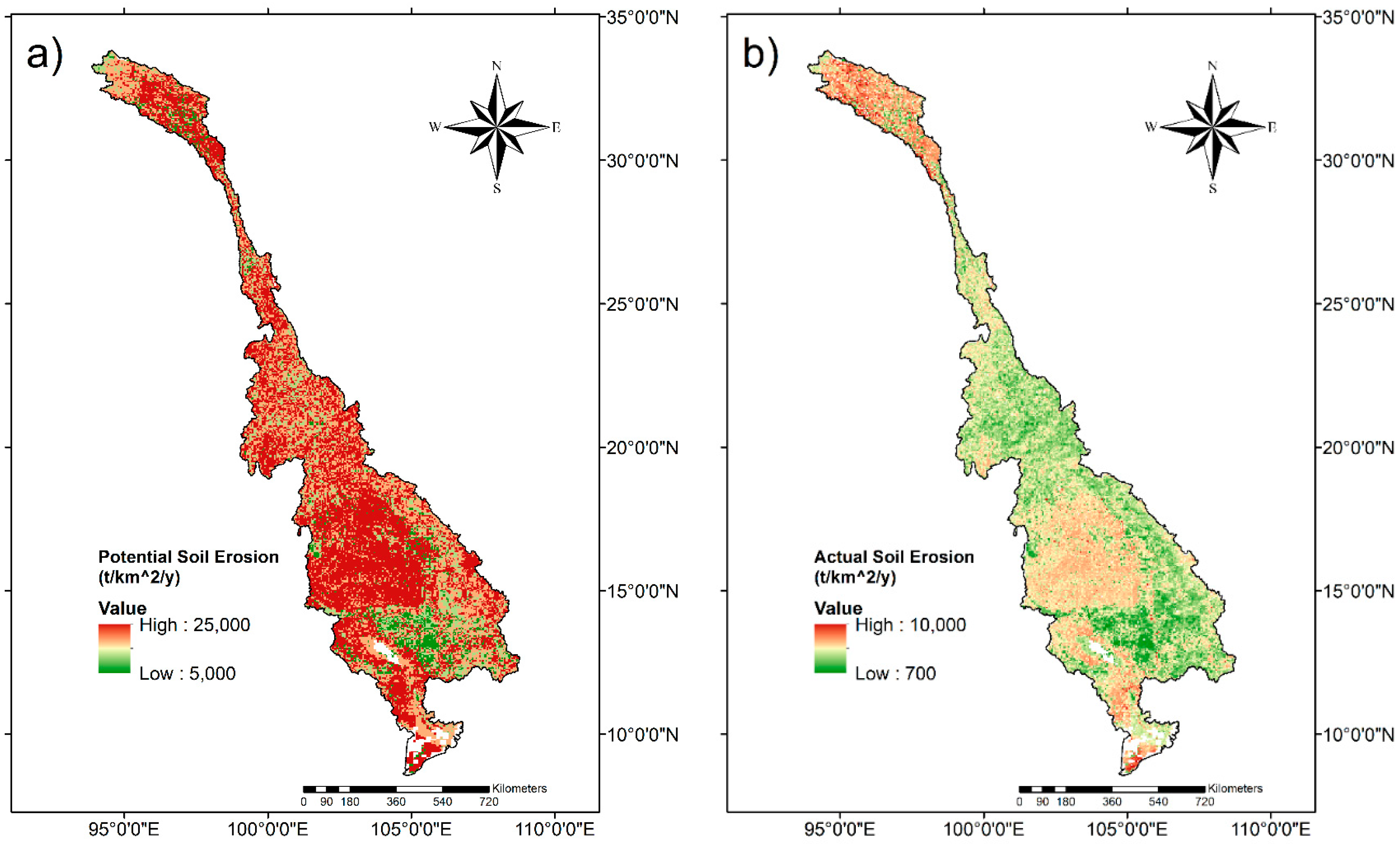
4.2. Potential and Actual Soil Erosion
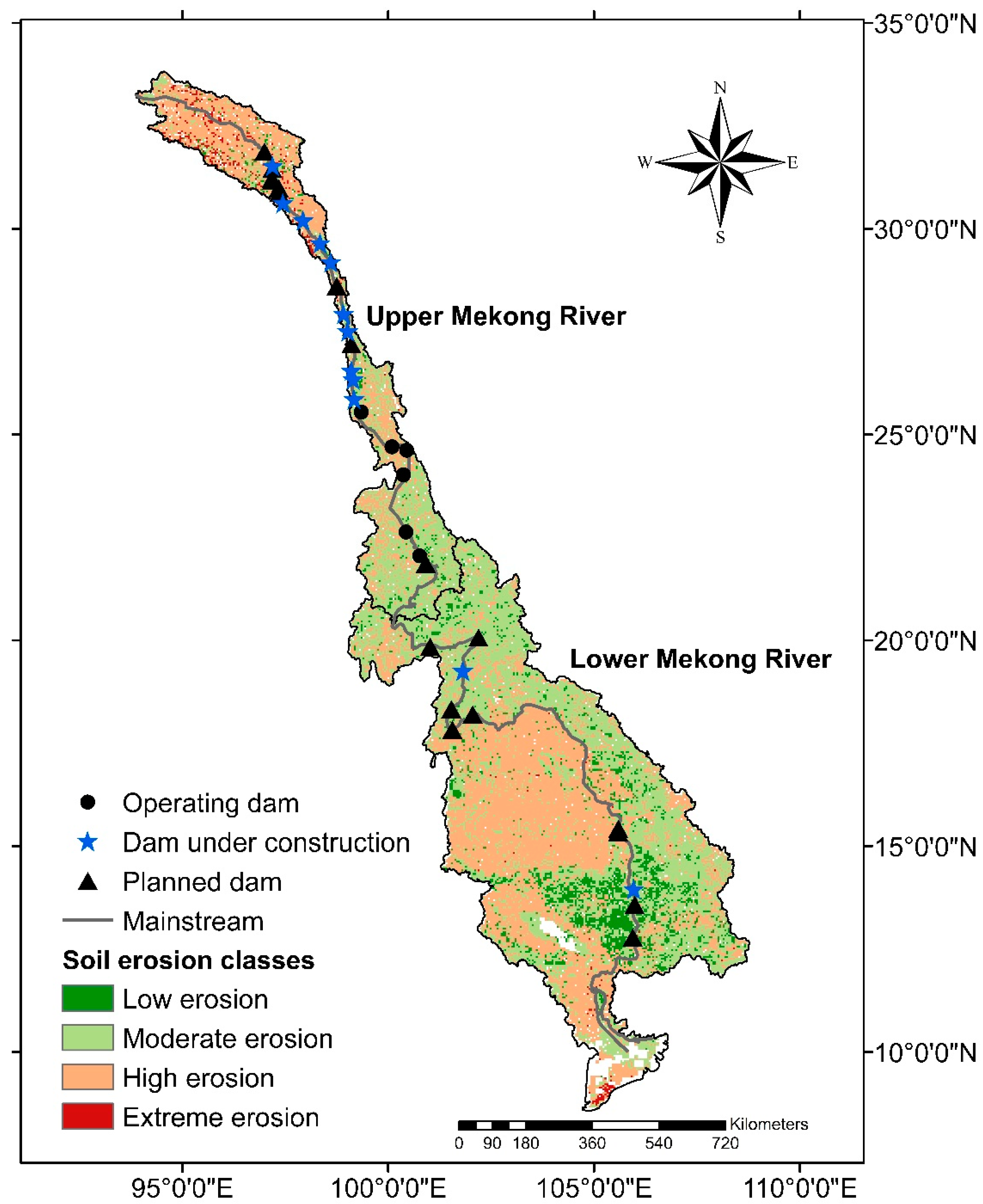
4.3. Soil Erosion Risk Mapping
4.4. Estimation of Sediment Deposition Areas
5. Discussion
5.1. Soil Erosion Rate in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin
5.2. Estimation of Sediment Yield Using the Modified RUSLE Model
5.3. Soil Erosion Impact on Dams
5.4. Delineating Sediment Form
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; Kosmas, C.; Vanacker, V.; Van Oost, K.; Rounsevell, M. Soil erosion as a driver of land-use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schutt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, I.D.; Lategan, F.S.; Yusuf, S.F. The impact of soil erosion on agricultural potential and performance of Sheshegu community farmers in the Eastern Cape of South Africa. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 5, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleboy, M.; Freebairn, D.M.; Hammer, G.L.; Silburn, D.M. Impact of soil-erosion on production in cropping systems. II. Simulation of production and erosion risks for a wheat cropping system. Soil Res. 1992, 30, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Kumar, U. Integrated approach of universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil loss risk assessment in Upper South Koel Basin, Jharkhand. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.G.; Degener, J.; Kappas, M. Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D. Soil erosion: A food and environmental threat. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.Y. Erosion and Sedimentation, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.L.; Fan, J. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 805. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.W.; Yang, S.T.; Zhao, C.S.; Cai, M.Y.; Ya, L. A soil erosion assessment of the Upper Mekong River in Yunnan Province, China. Mt. Res. Dev. 2014, 34, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Principles of Soil Conservation and Management, 1st ed.; Springer: Haarlem, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 617. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Toy, T.J.; Foster, G.R.; Renard, K.G. Soil Erosion: Processes, Prediction, Measurement, and Control; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Soil Change: Impacts and Responses; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oost, K.; Quine, T.A.; Govers, G.; De Gryze, S.; Six, J.; Harden, J.W.; Ritchie, J.C.; McCarty, G.W.; Heckrath, G.; Kosmas, C.; et al. The impact of agricultural soil erosion on the global carbon cycle. Science 2007, 318, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselman, N.E.M.; Middelkoop, H.; Van Dijk, P.M. The impact of changes in climate and land use on soil erosion, transport and deposition of suspended sediment in the River Rhine. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 3225–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouraoui, F.; Grizzetti, B.; Granlund, K.; Rekolainen, S.; Bidoglio, G. Impact of climate change on the water cycle and nutrient losses in a Finnish catchment. Clim. Chang. 2004, 66, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, D.; Rangsiwanichpong, P.; Inoue, N.; Ono, K.; Watanabe, S.; Kazama, S. Distributed probability of slope failure in Thailand under climate change. Clim. Risk Manag. 2018, 20, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, R.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Schneiderman, E.M.; Pierson, D.C.; Anandhi, A.; Zion, M.S.; Matonse, A.H.; Lounsbury, D.G.; Steenhuis, T.S. Suspended sediment source areas and future climate impact on soil erosion and sediment yield in a New York City water supply watershed, USA. Geomorphology 2013, 183, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangsiwanichpong, P.; Kazama, S.; Gunawardhana, L. Assessment of sediment yield in Thailand using revised universal soil loss equation and geographic information system techniques. River Res. Appl. 2018, 34, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Babel, M.S.; Maskey, S.; Van Griensven, A.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Green, A.; Akkharath, I. Impact of climate change on sediment yield in the Mekong River basin: A case study of the Nam Ou basin, Lao PDR. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Peckham, S.D.; Hilberman, R.; Mulder, T. Predicting the terrestrial flux of sediment to the global ocean: A planetary perspective. Sediment. Geol. 2003, 162, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, B.H.; McElroy, B.J. The impact of humans on continental erosion and sedimentation. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2007, 119, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Dong, S.K.; Liu, S.L.; Yang, Z.F.; Peng, M.C.; Zhao, C. Effects of cascading hydropower dams on the composition, biomass and biological integrity of phytoplankton assemblages in the middle Lancang-Mekong River. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Harvey, C.; Resosudarmo, P.; Sinclair, K.; Kurz, D.; Mcnair, M.; Crist, S.; Shpritz, L.; Fitton, L.; Saffouri, R.; et al. Environmental and economic costs of soil erosion and conservation benefits. Science 1995, 267, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Z.; Shan, B.Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, Y.K.; Rong, N.; Zhu, X.L. Heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of representative limnetic ecosystems in Eastern China. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, H.; Cakir, G.; Sivrikaya, F.; Akay, A.E. Using high resolution images and elevation data in classifying erosion risks of bare soil areas in the Hatila Valley Natural Protected Area, Turkey. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2010, 24, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.D.; He, D.M. Analysis and prediction of sediment trapping efficiencies of the reservoirs in the mainstream of the Lancang River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Abbasi, M.; Keesstra, S.; Cerda, A. Assessment of soil particle erodibility and sediment trapping using check dams in small semi-arid catchments. Catena 2017, 157, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Wu, B.S.; Wang, G.Q. Fluvial processes and morphological response in the Yellow and Weihe Rivers to closure and operation of Sanmenxia Dam. Geomorphology 2007, 91, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commission on Dams [WCD]. Dams and Development: A New Framework for Decision-Making; Earth Scan: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Walling, D.E. Human impact on the sediment loads of Asian rivers. In Sediment Problems and Sediment Management in Asian River Basins; IAHS: Wallingford, UK, 2011; Volume 349, pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, E.J.; Brunier, G.; Besset, M.; Goichot, M.; Dussouillez, P.; Nguyen, V.L. Linking rapid erosion of the Mekong River delta to human activities. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.T.; Ouillon, S.; Vinh, G.V. Water and suspended sediment budgets in the lower Mekong from high-frequency measurements (2009–2016). Water 2018, 10, 846. [Google Scholar]
- Manh, N.V.; Dung, N.V.; Hung, N.N.; Kummu, M.; Merz, B.; Apel, H. Future sediment dynamics in the Mekong Delta floodplains: Impacts of hydropower development, climate change and sea level rise. Glob. Planet Chang. 2015, 127, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. The changing sediment load of the Mekong River. AMBIO 2008, 37, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Geomorphic tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean—The importance of small mountainous rivers. J. Geol. 1992, 100, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. State of the Basin Report 2010; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mekong River Commission. The Study on the Sustainable Management and Development of the Mekong River Basin, Including Impacts of Mainstream Hydropower Projects; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Schmitt, R.J.P.; Carling, P.; Darby, S.; Arias, M.; Bizzi, S.; Castelletti, A.; Cochrane, T.A.; Gibson, S.; Kummu, M.; et al. Changing sediment budget of the Mekong: Cumulative threats and management strategies for a large river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of land use changes on soil erosion in a fast developing area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, T.K.O.; Nguyen, V.L.; Tateishi, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Tanabe, S.; Saito, Y. Holocene delta evolution and sediment discharge of the Mekong River southern Vietnam. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehnken, L. Discharge Sediment Monitoring Project (DSMP) 2009–2013: Summary and Analysis of Results Analysis of Results; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2014; pp. 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kummu, M.; Varis, O. Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the Lower Mekong River. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.D.; He, D.M.; Lu, X.X. Sedimentation in the Manwan reservoir in the Upper Mekong and its downstream impacts. Quat. Int. 2008, 186, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, Y.; Des Walling, E.; Wang, J.J. Changes in the sediment load of the Lancang-Mekong River over the period 1965–2003. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Lu, X.X.; Wang, J.J.; Varis, O. Basin-wide sediment trapping efficiency of emerging reservoirs along the Mekong. Geomorphology 2010, 119, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Rubin, Z.K.; Minear, J.T. Dams on the Mekong: Cumulative sediment starvation. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.R.; Yang, Z.F.; Cui, B.S. Soil erosion and its environmental background at Lancang Basin of Yunnan Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 25, 5–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.R.; Yang, Z.F.; Cui, B.S. Spatial analysis on soil erosion of Lancang River Watershed in Yunnan Province under the support of GIS. Geogr. Res. 2006, 25, 421–429. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.Y.; Pan, Y.Z.; Long, Z.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, X. Value evaluation of conserving water and soil for ecosystem supported by remote sensed technique in Yunnan Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 20, 174–178. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Li, D.D.; Zhang, Y.Q. Analysis of spatial characteristics of soil erosion in mountain areas of northwestern Yunnan based on GIS and RUSLE. J. Mt. Sci. 2007, 25, 548–556. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thuy, H.T.; Lee, G. Soil loss vulnerability assessment in the Mekong River Basin. J. Korean Geo Environ. Soc. 2017, 18, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Overview of the Hydrology of the Mekong Basin; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2005; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Mekong River Commission. Assessment of Basin-Wide Development Scenarios—Main Report; Mekong River Commission: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2011; p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- Kummu, M.; Lu, X.X.; Rasphone, A.; Sarkkula, J.; Koponen, J. Riverbank changes along the Mekong River: Remote sensing detection in the Vientiane-Nong Khai area. Quat. Int. 2008, 186, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Centre for Environmental Management. MRC Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) of Hydropower on the Mekong Mainstream: Summary of the Final Report; Mekong River Commission: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2010; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- WLE Graeter Mekong. Dams in the Mekong River Basin: Commissioned, Under Construction, and Planned Dams; WLE Graeter Mekong: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ozcan, A.U.; Erpul, G.; Basaran, M.; Erdogan, H.E. Use of USLE/GIS technology integrated with geostatistics to assess soil erosion risk in different land uses of Indagi Mountain Pass-Cankiri, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhao, W.W.; Chen, L.D.; Zhang, Q.J.; Lu, Y.H.; Gulinck, H.; Poesen, J. Assessment of soil erosion at large watershed scale using RUSLE and GIS: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2005, 16, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaburun, A. Estimating potential erosion risks in Corlu using the GIS-based RUSLE method. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2009, 18, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Lufafa, A.; Tenywa, M.M.; Isabirye, M.; Majaliwa, M.J.G.; Woomer, P.L. Prediction of soil erosion in a Lake Victoria basin catchment using a GIS-based Universal Soil Loss model. Agric. Syst. 2003, 76, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of China. Soil Erosion Rate Standard, Technological Standard of Soil and Water Conservation SD238-87; Water Resources and Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 1988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Lee, J.H.W.; Melching, C.S. River Dynamics and Integrated River Management; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agricultural Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; pp. 285–291.
- Yatagai, A.; Kamiguchi, K.; Arakawa, O.; Hamada, A.; Yasutomi, N.; Kitoh, A. APHRODITE constructing a long-term daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.J.; Chen, M.H.; Lin, F.X.; Huang, Y.H.; Lu, C.L. The rainfall erosivity index in Fujian Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1995, 9, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R. Chapter 25: The epic mode. In Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology; Singh, V.P., Ed.; Water Resource Publications: Woodbridge, VA, USA, 1995; pp. 909–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R.; Renard, K.G.; Dyke, P.T. Epic—A new method for assessing erosions effect on soil productivity. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1983, 38, 381–383. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, G.R.; Mccool, D.K.; Renard, K.G.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Conversion of the universal soil loss equation to SI metric units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1981, 36, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Rammahi, A.A.; Khassaf, S.I. Estimation of soil erodibility factor in RUSLE equation for Euphrates river watershed using GIS. Int. J. Geomate 2018, 14, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawer, R.; Nowocieñ, E.; Podolski, B. Real and calculated K-USLE erodibility factor for selected polish soils. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2005, 14, 655–658. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-Factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Jiang, H.; Xu, Z.X.; Wang, L.J.; Yue, W.F. Evaluating the effect of land use changes on soil erosion and sediment yield using a grid-based distributed modelling approach. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3579–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.H.; Fohrer, N.; Hormann, G.; Kiesel, J. Suitability of S factor algorithms for soil loss estimation at gently sloped landscapes. Catena 2009, 77, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Julien, P.Y. Soil erosion modeling using RUSLE and GIS on the MIHA watershed. Water Eng. J. 2006, 7, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mccool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised slope steepness factor for the universal soil loss equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suif, Z.; Yoshimura, C.; Valeriano, S.; Seingheng, H. Spatially distributed model for soil erosion and sediment transport in the Mekong River Basin. Int. Water Technol. J. 2013, 3, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agriculture Handbook Number 703; USDA: Washington, DC, USA; Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Van Remortel, R.D.; Hamilton, M.E.; Hickey, R. Estimating the LS factor for RUSLE through iterative slope length processing of digital elevation data within Arclnfo grid. Cartography 2001, 30, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Yang, Q.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Gai, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. An improved method for calculating slope length (λ) and the LS parameters of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation for large watersheds. Geoderma 2017, 308, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durigon, V.L.; Carvalho, D.F.; Antunes, M.A.H.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Fernandes, M.M. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuok, K.; Mah, D.; Chiu, P. Evaluation of C and P factors in universal soil loss equation on trapping sediment: Case study of Santubong River. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, T.J.; Foster, G.R. Mined lands, construction sites, and reclaimed lands. In Guidelines for the Use of Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Joe, R.G., Ed.; Version 1.06; Western Regional Coordinating Centre Office of Surface Mining: Denver, CO, USA; The Office of Technology Transfer: Denver, CO, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.W.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Koike, T.; Musiake, K. Global potential soil erosion with reference to land use and climate changes. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2913–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaffas, K.; Hrissanthou, V.; Sevastas, S. Modeling hydromorphological processes in a mountainous basin using a composite mathematical model and ArcSWAT. Catena 2018, 162, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.M.; Hsiang, T.K. Facilitating regional sustainable development through integrated multi-objective utilization, management of water resources in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. J. Chin. Geogr. 1997, 7, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mekong River Commission. Databases of Mekong River Commission; Mekong River Commission (MRC): Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T.; De Jesus, J.M.; MacMillan, R.A.; Batjes, N.H.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Ribeiro, E.; Samuel-Rosa, A.; Kempen, B.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Walsh, M.G.; et al. SoilGrids1km—Global soil information based on automated mapping. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.G.; Hengl, T.; De Jesus, J.M.; Yuan, H.; Dai, Y.J. Mapping the global depth to bedrock for land surface modeling. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 65–88. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Environmental Performance of Agriculture in OECD Countries Since 1990; OECD: Paris, France, 2008; pp. 179–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.X.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Cao, Y.T.; Carling, P.; Fu, K.D.; Guo, Q.C.; et al. Sustainable sediment management in reservoirs and regulated rivers: Experiences from five continents. Earths Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Land Cover of the RUSLE | C Factor | P Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Urban area | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| Bare land | 0.35 | 1.0 |
| Dense forest | 0.001 | 1.0 |
| Sparse forest | 0.01 | 1.0 |
| Mixed forest and cropland | 0.1 | 0.8 |
| Cropland | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Paddy field | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Dense grassland | 0.08 | 1.0 |
| Sparse grassland | 0.2 | 1.0 |
| Mixed grassland and cropland | 0.25 | 0.8 |
| Wetland | 0.05 | 1.0 |
| Water body | 0.01 | 1.0 |
| Permanent ice and snow | 0.001 | 1.0 |
| Level | Soil Loss (t/km2/y) | Area (km2) | Percentage of Total Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal erosion | <500 | - | - |
| Low erosion | 500–2500 | 125,450 | 16 |
| Moderate erosion | 2500–5000 | 335,942 | 45 |
| High erosion | 5000–8000 | 253,342 | 34 |
| Extreme erosion | >8000 | 21,850 | 3 |
| Water | 13,416 | 2 | |
| Total | 750,000 | 100 |
| Independent Variable | Standardized Coefficient (β) | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| ln(R) | 0.168 | 0.000 |
| ln(K) | 0.364 | 0.000 |
| ln(LS) | 0.898 | 0.000 |
| ln(C) | 0.184 | 0.000 |
| ln(P) | 0.246 | 0.000 |
| Sub-Basin | Area (km2) | Observed SSY (t/km2/y) | Estimated SSY from Model (t/km2/y) | Percentage Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingshuilang | 87,205 | 281 | 308 | 10% |
| Weiyuanjiang | 120,000 | 382 | 412 | 8% |
| Nam Pho | 184,845 | 489 | 525 | 7% |
| Nam Chi | 43,100 | 18 | 22 | 22% |
| Nam Kam | 2360 | 35 | 42 | 20% |
| Nam Khan | 5800 | 113 | 122 | 8% |
| Nam Mae Ing | 5700 | 38 | 45 | 18% |
| Nam Mun | 116,000 | 27 | 34 | 26% |
| Nam Ngum | 5220 | 36 | 44 | 22% |
| Nam Ou | 19,700 | 237 | 258 | 9% |
| Nam Songkhram | 4650 | 31 | 40 | 29% |
| Se Bang Fai | 4520 | 80 | 98 | 23% |
| Se Bang Hieng | 19,400 | 163 | 177 | 9% |
| Se Done | 5760 | 206 | 218 | 6% |
| St. Sen | 14,000 | 33 | 40 | 21% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuenchum, P.; Xu, M.; Tang, W. Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in the Lancang–Mekong River Using the Modified Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS Techniques. Water 2020, 12, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010135
Chuenchum P, Xu M, Tang W. Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in the Lancang–Mekong River Using the Modified Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS Techniques. Water. 2020; 12(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuenchum, Pavisorn, Mengzhen Xu, and Wenzhe Tang. 2020. "Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in the Lancang–Mekong River Using the Modified Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS Techniques" Water 12, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010135
APA StyleChuenchum, P., Xu, M., & Tang, W. (2020). Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in the Lancang–Mekong River Using the Modified Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS Techniques. Water, 12(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010135







