Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment for the Upper Reaches of Syr Darya River in Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
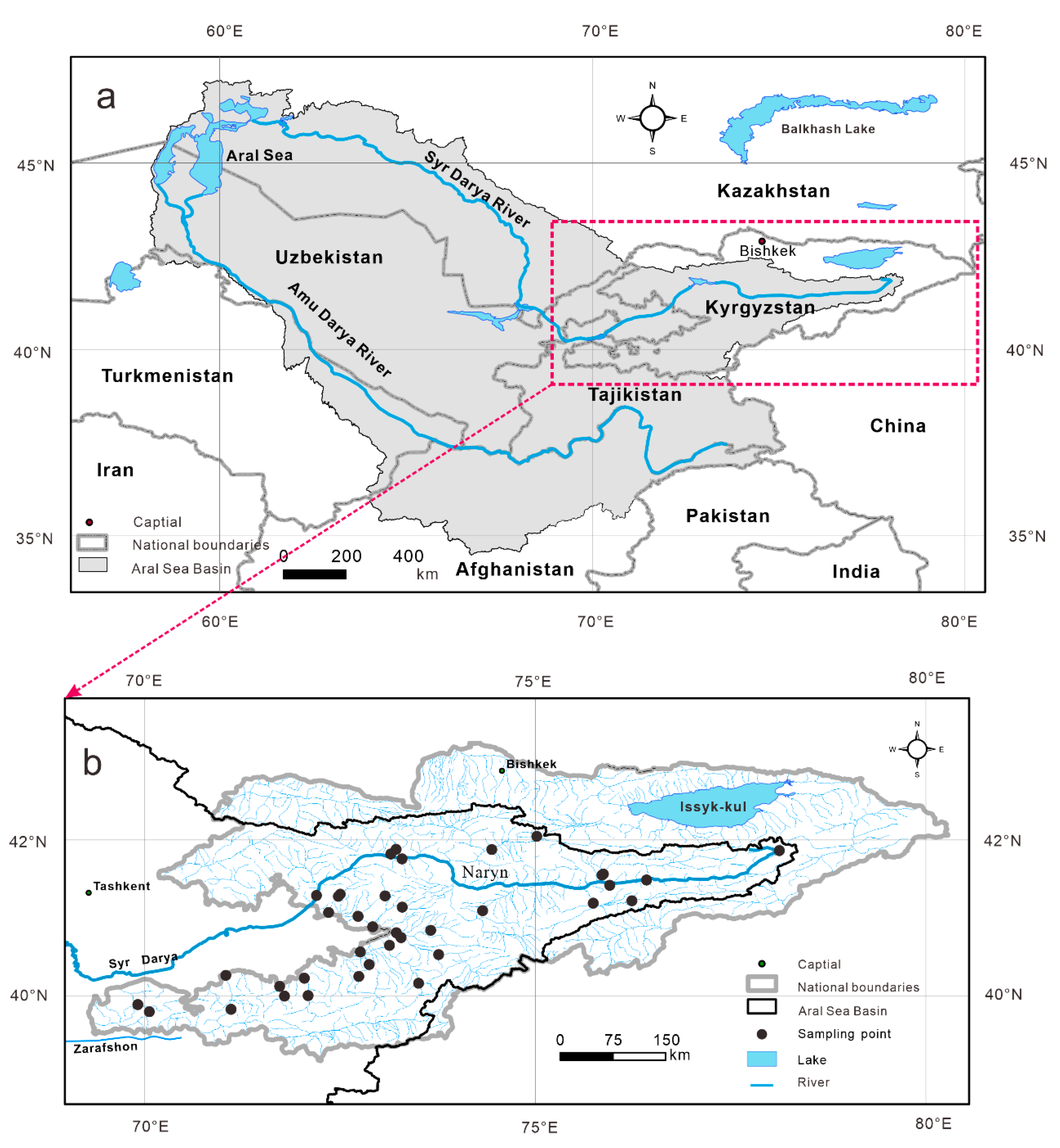
2. Geographic Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Hydrochemistry Analyses
3.2. Data Processing Methods
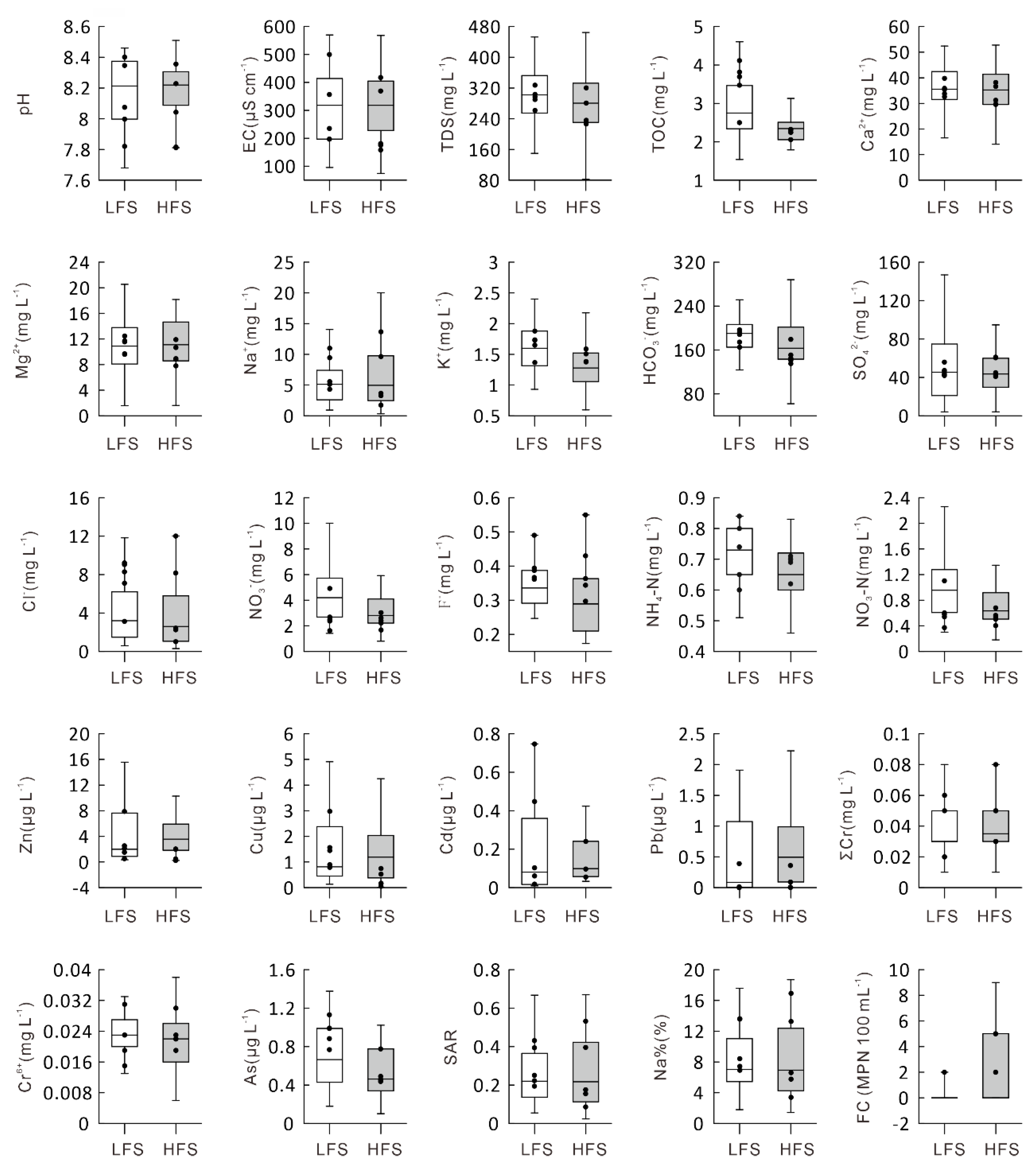
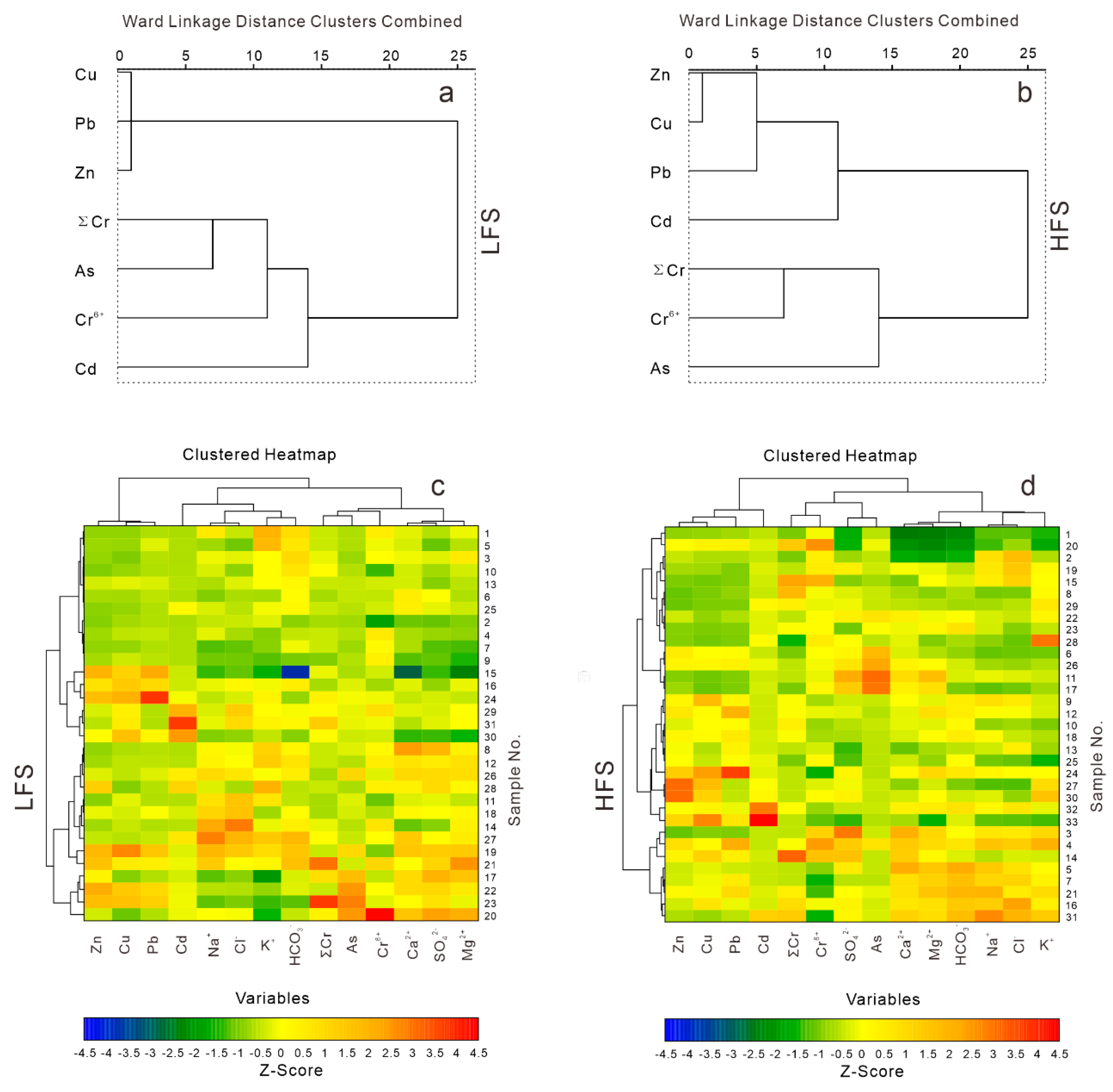
4. Results
5. Discussion
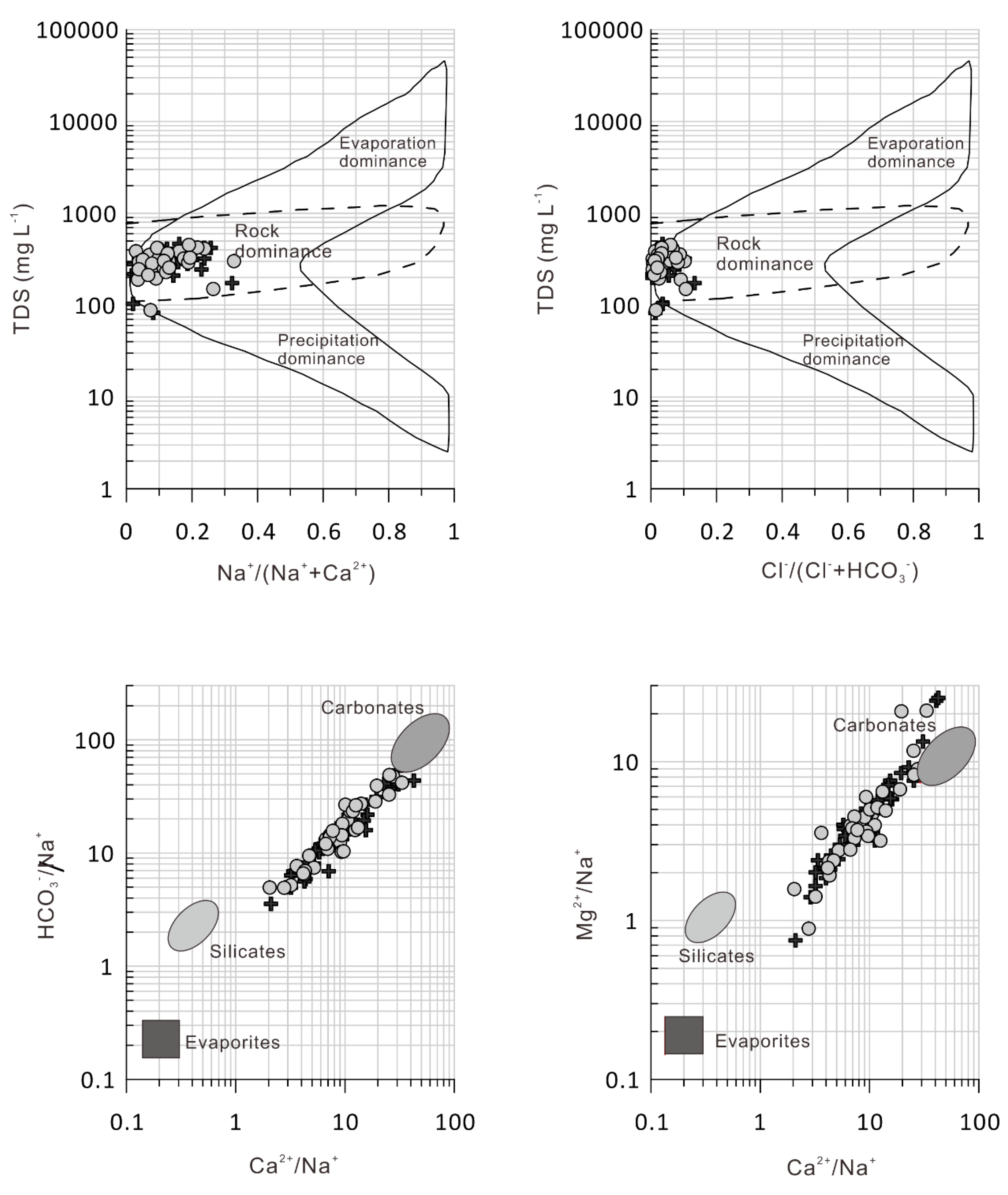
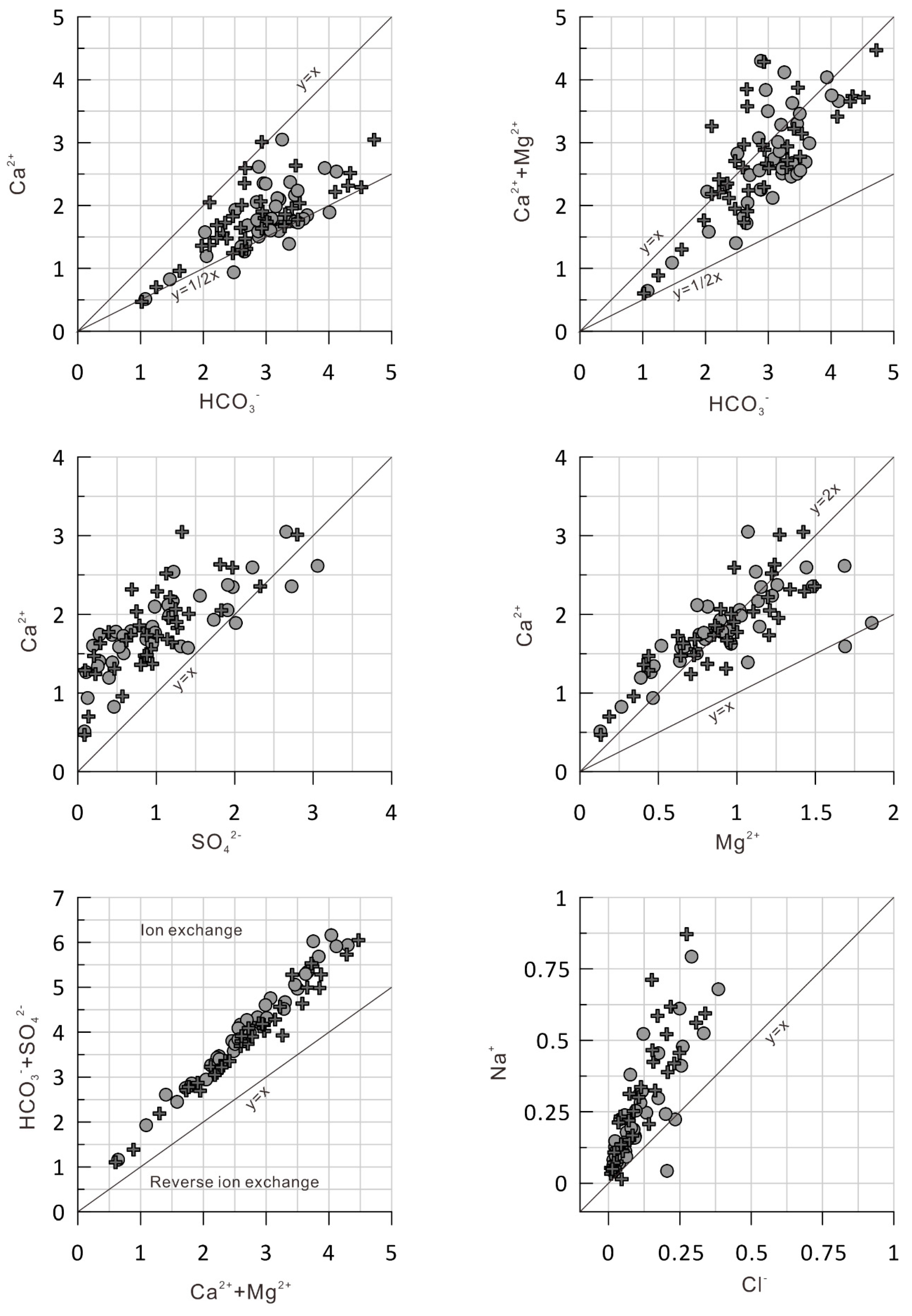
5.1. Sources and Influencing Factors for the Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements
5.2. Evaluation of the Irrigation Suitability
6. Conclusions
- There are some differences in ion concentration between the LFS and HFS periods, but the hydrochemical classification reflected that all water samples fall in the calcium bicarbonate category, except that only three samples fall in the not dominant category during the LFS.
- The analysis shows that the main ions in the water from the upper reaches of Syr Darya River and its tributaries in Kyrgyzstan, come from the bedrock, and the intensity of carbonate dissolution is higher than that of silicate weathering.
- Human activities have had an impact on the water body, which is especially inferred from the indicators of the NH4-N concentration, FC contamination, and levels of potentially toxic elements. FC bacteria were detected in four river samples from the main channel of Syr Darya River (Naryn) and its tributaries during the LFS. However, FC bacteria were detected in 16 river samples from the main channel of Syr Darya River (Naryn) and its tributaries during the HFS. There may be anthropogenic intrusions of Cu, Pb, and Zn during the LFS period and of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd during the HFS period.
- The contents of potentially toxic elements in the water from the parts of the Aral Sea Basin in Kyrgyzstan are lower than international drinking water standards, but there are clustering differences between the LFS and HFS periods. The water quality classification shows that the water samples fall in the excellent to good categories for irrigation use.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Micklin, P. The Aral Sea Disaster. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2007, 35, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, C.; Reager, J.T.; Yao, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Brun, F.; Schmied, H.M.; Marston, R.A.; et al. Recent global decline in endorheic basin water storages. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkaveev, P.N.; Gordeev, V.V.; Zav’yalov, P.O.; Polukhin, A.A.; Khlebopashev, P.V.; Kochenkova, A.I. Hydrochemical Characteristics of the Aral Sea in 2012–2013. Water Resour. 2018, 45, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.E.; Sloan, L.C.; Nychka, D. Changes in surface air temperature caused by desiccation of the Aral Sea. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.B.; Smith, M.; Morris, L.; Orlovsky, N.; Khalilov, A. Impact of the desiccation of the Aral Sea on summertime surface air temperatures. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 110, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakov, R.M.; Kosnazarov, K.A. Dust and salt transfer from the exposed bed of the Aral Sea and measures to decrease its environmental impact. In The Aral Sea Basin; Springer-Verlag: Berlin and Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, S.L.; Wiggs, G.F.S.; Mamedov, B.; Davidson, G.; Hubbard, R.B. Exposure to airborne dust contaminated with pesticide in the Aral Sea region. Lancet 2000, 355, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J.; Galayeva, O.; Semenov, O.; Bazarbayeva, T. Aeolian transportation of sand and dust in the Aral Sea region. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, R.; Glazirina, M.G.; Schär, C. On the relationship between the Indian summer monsoon and river flow in the Aral Sea basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L05706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullaev, I.; Molden, D. Spatial and temporal variability of water productivity in the Syr Darya Basin, central Asia. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W08S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezlin, N.P.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Lebedev, S.A. Interannual variations of the discharge of Amu Darya and Syr Darya estimated from global atmospheric precipitation. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 47, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaiylov, G.K.; Fedorov, V.M.; Nezhad, S.D.S. Assessment of possible anthropogenic changes in the runoff of the Syr Darya River on the basis of a mathematical model. Water Resour. 2007, 34, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, F.; Berthier, E.; Wagnon, P.; Kääb, A.; Treichler, D. A spatially resolved estimate of High Mountain Asia glacier mass balances from 2000 to 2016. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, D.; Mayer, C.; Hagg, W.; Vorogushyn, S.; Duethmann, D.; Gafurov, A.; Farinotti, D. Changes in glacierisation, climate and runoff in the second half of the 20th century in the Naryn basin, Central Asia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 110, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, A.; Mosello, B.; Shalpykova, G.; Allan, A.; Hill Clarvis, M.; Stoffel, M. Coping with changing water resources: The case of the Syr Darya river basin in Central Asia. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 43, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, T.; Bernauer, T. Estimating the performance of international regulatory regimes: Methodology and empirical application to international water management in the Naryn/Syr Darya basin. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Q.; Chen, Y.N. Trend analysis of temperature and precipitation in the Syr Darya Basin in Central Asia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 120, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, V.B.; Aizen, E.M.; Melack, J.M.; Dozier, J. Climatic and hydrologic changes in the Tien Shan, central Asia. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, A.; Bolch, T.; Stoffel, M.; Solomina, O.; Beniston, M. Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Kozhoridze, G.; Batyrbaeva, M.; Vitkovskaya, I.; Orlovsky, N.; Blumberg, D.; Orlovsky, L. Dust emission and environmental changes in the dried bottom of the Aral Sea. Aeolian Res. 2015, 17, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L.; Wu, N.; Liu, D. Potential transport pathways of dust emanating from the playa of Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, in arid northwest China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.H.; Ensher, J.R.; Matthews, M.R.; Wieman, C.E.; Cornell, E.A. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry: Evaporation-Crystallization Process. Science 1971, 172, 870–872. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.L.; Raiber, M.; Cox, M.E. Assessment of groundwater–surface water interaction using long-term hydrochemical data and isotope hydrology: Headwaters of the Condamine River, Southeast Queensland, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, R.R.; Zhang, F.; Rehman, F.U.; Wang, G.; Ye, M.; Zeng, C.; Tang, H. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.F.; Minbaeva, C.K.; Wilson, A.M.; Satylkanov, R. Hydrologic Controls and Water Vulnerabilities in the Naryn River Basin, Kyrgyzstan: A Socio-Hydro Case Study of Water Stressors in Central Asia. Water 2017, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadyrzhanov, K.K.; Barber, D.S.; Solodukhin, V.P.; Poznyak, V.L.; Kazachevskiy, I.V.; Knyazev, B.B.; Lukashenko, S.N.; Khazhekber, S.; Betsill, J.D.; Passell, H.D. Radionuclide contamination in the Syrdarya river basin of Kazakhstan—Results of the Navruz Project. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2005, 263, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Balsiger, B.; Röllin, S.; Jakob, A.; Burger, M. Radioactive and chemical contamination of the water resources in the former uranium mining and milling sites of Mailuu Suu (Kyrgyzstan). J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 138, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The Aral Sea Transboundaryriver Basin. 2012. Available online: www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/basins/aral-sea/aral.sea-CP_eng.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- FAO. Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan: Expanding Finance in Rural Areas. 2006. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/aj276r/aj276r00.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- Hartmann, J.; Moosdorf, N. The new global lithological map database GLiM: A representation of rock properties at the Earth surface. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13, Q12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Harmonized World Soil Database, version 1.2.; FAO: Rome, Italy; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Akimaliev, D.A.; Zaurov, D.E.; Eisenman, S.W. The Geography, Climate and Vegetation of Kyrgyzstan. In Medicinal Plants of Central Asia: Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan; Eisenman, S.W., Zaurov, D.E., Struwe, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seim, A.; Omurova, G.; Azisov, E.; Musuraliev, K.; Aliev, K.; Tulyaganov, T.; Nikolyai, L.; Botman, E.; Helle, G.; Dorado Liñan, I.; et al. Climate Change Increases Drought Stress of Juniper Trees in the Mountains of Central Asia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, W.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal precipitation variations in the arid Central Asia in the context of global warming. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, R.; Lüthi, D.; Vidale, P.L.; Schär, C. The precipitation climate of Central Asia—Intercomparison of observational and numerical data sources in a remote semiarid region. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 28, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, S.; Zondervan, I.; Riebesell, U. Effect of CO2 concentration on C:N:P ratio in marine phytoplankton: A species comparison. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talling, J.F. The Depletion of Carbon Dioxide from Lake Water by Phytoplankton. J. Ecol. 1976, 64, 79–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Adeloju, S.B. Nitrate biosensors and biological methods for nitrate determination. Talanta 2016, 153, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.L.; Zitomer, F. Differential Colorimetric Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate lons. Anal. Chem. 1960, 32, 1684–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, C.; Zhu, G. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yidana, S.M.; Bawoyobie, P.; Sakyi, P.; Fynn, O.F. Evolutionary analysis of groundwater flow: Application of multivariate statistical analysis to hydrochemical data in the Densu Basin, Ghana. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 138, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchemin, D.; Berman, S. Determination of trace metals in reference water standards by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with on-line preconcentration. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.T.; Lin, C.; Shern, C.-C.; Yeh, G.; Le, V.G.; Tran, H.T. Contamination, ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and water of a contaminated river in Taiwan. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; USDA Circular No. 969.; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955; p. 19.
- Wang, X.; Ozdemir, O.; Hampton, M.A.; Nguyen, A.V.; Do, D.D. The effect of zeolite treatment by acids on sodium adsorption ratio of coal seam gas water. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5247–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Tang, C.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, C.; Aquilina, L.; Boisson, A.; Vergnaud-Ayraud, V.; Labasque, T.; Longuevergne, L.; Laurencelle, M.; Dufresne, A.; de Dreuzy, J.R.; Pauwels, H.; et al. Autotrophic denitrification supported by biotite dissolution in crystalline aquifers: (2) transient mixing and denitrification dynamic during long-term pumping. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamier, J.; Wicht, M.; Cyster, L.; Ndindi, N.P. Aluminium (Al) fractionation and speciation; getting closer to describing the factors influencing Al3+ in water impacted by acid mine drainage. Chemosphere 2015, 130, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Q. Characteristics and driving factors of drainage water in irrigation districts in arid areas. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 5323–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhillips, L.E.; Creamer, A.E.; Rahm, B.G.; Walter, M.T. Assessing dissolved methane patterns in central New York groundwater. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2014, 1, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Kawamura, A.; Tong, T.N.; Nakagawa, N.; Amaguchi, H.; Gilbuena, R. Clustering spatio-seasonal hydrogeochemical data using self-organizing maps for groundwater quality assessment in the Red River Delta, Vietnam. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xia, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X. Chemical balance of the Yellow River source region, the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Insights about critical zone reactivity. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Sillanpää, M. Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in rivers of the “Water Tower of Asia”. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajigholizadeh, M.; Melesse, A.M. Assortment and spatiotemporal analysis of surface water quality using cluster and discriminant analyses. Catena 2017, 151, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Khan, S.M.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmad, H. A novel approach to phytosociological classification of weeds flora of an agro-ecological system through Cluster, Two Way Cluster and Indicator Species Analyses. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.C. Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 456–463. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Niu, F.; Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Yin, G. Hydrochemistry and controlling mechanism of lakes in permafrost regions along the Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor, China. Geomorphology 2017, 297, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geldern, R.; Schulte, P.; Mader, M.; Baier, A.; Barth, J.A.C.; Juhlke, T.R.; Lee, K. Insights into agricultural influences and weathering processes from major ion patterns. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, R. Hydrochemical characteristics and multivariate statistical analysis of natural water system: A case study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water (Switzerland) 2018, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, F.; Deng, G.; Tang, Y.; Li, P. Hydrogeochemistry of Shallow Groundwater in a Karst Aquifer System of Bijie City, Guizhou Province. Water 2017, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Chesnaux, R.; Cloutier, V.; Gaboury, D. The influence of water/rock-water/clay interactions and mixing in the salinization processes of groundwater. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 13, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, G.; Elango, L. Hydrogeochemical processes and impact of tanning industries on groundwater quality in Ambur, Vellore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24364–24383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Pu, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, D.; Li, L. Stable isotope and aquatic geochemistry of a typical subtropical karst subterranean stream in southwest China. Carbonates Evaporites 2017, 32, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallon, P.; Magajna, B.; Lofranco, C.; Leung, K.T. Microbial Indicators of Faecal Contamination in Water: A Current Perspective. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 166, 139–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, Fourth Editon. 2011. Available online: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241548151_eng.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- EU. Council Directive 98/83/EC on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. 1998. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:31998L0083 (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- USEPA. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. China National Standards for Drinking Water Quality; GB5749-2006; Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wegerich, K.; Van Rooijen, D.; Soliev, I.; Mukhamedova, N. Water Security in the Syr Darya Basin. Water 2015, 7, 4657–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikanorova, A.; Dronin, N. Optimal Future for the Irrigation Agriculture Under Climate Change in the Fergana Valley, Central Asia. Res. Artic. 2017, 3, 555607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichsel, C. Conflict Transformation in Central Asia: Irrigation Disputes in the Ferghana Valley; Routledge: London, UK, 2009; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Hao, Q.; Liu, H.; Hao, Z.; Meng, G.; Pei, Q.; Yan, H. Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in a Long-Term Reclaimed Water Irrigation Area, North China Plain. Water 2018, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Potentially Toxic Elements | Maximum of Concentrations | Standards for Drinking Water Quality from Different Countries and Organizations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFS (mg L−1) | HFS (mg L−1) | World Health Organization (mg L−1) | European Union (mg L−1) | United States (mg L−1) | China (mg L−1) | |
| Zn | 0.016 | 0.010 | 3.0 | / | 5.0 | 1.0 |
| Cu | 0.0049 | 0.0043 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 1.3 | 1.0 |
| Pb | 0.0019 | 0.0022 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.015 | 0.01 |
| Cd | 0.00075 | 0.00042 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| As | 0.0014 | 0.0010 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Cr6+ | 0.033 | 0.038 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J.; Li, Y.; Abdyzhapar uulu, S.; Mu, S. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment for the Upper Reaches of Syr Darya River in Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia. Water 2019, 11, 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091893
Ma L, Abuduwaili J, Li Y, Abdyzhapar uulu S, Mu S. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment for the Upper Reaches of Syr Darya River in Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia. Water. 2019; 11(9):1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091893
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Long, Jilili Abuduwaili, Yaoming Li, Salamat Abdyzhapar uulu, and Shuyong Mu. 2019. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment for the Upper Reaches of Syr Darya River in Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia" Water 11, no. 9: 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091893
APA StyleMa, L., Abuduwaili, J., Li, Y., Abdyzhapar uulu, S., & Mu, S. (2019). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment for the Upper Reaches of Syr Darya River in Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia. Water, 11(9), 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091893





