Estimating the Isotopic Altitude Gradient for Hydrogeological Studies in Mountainous Areas: Are the Low-Yield Springs Suitable? Insights from the Northern Apennines of Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
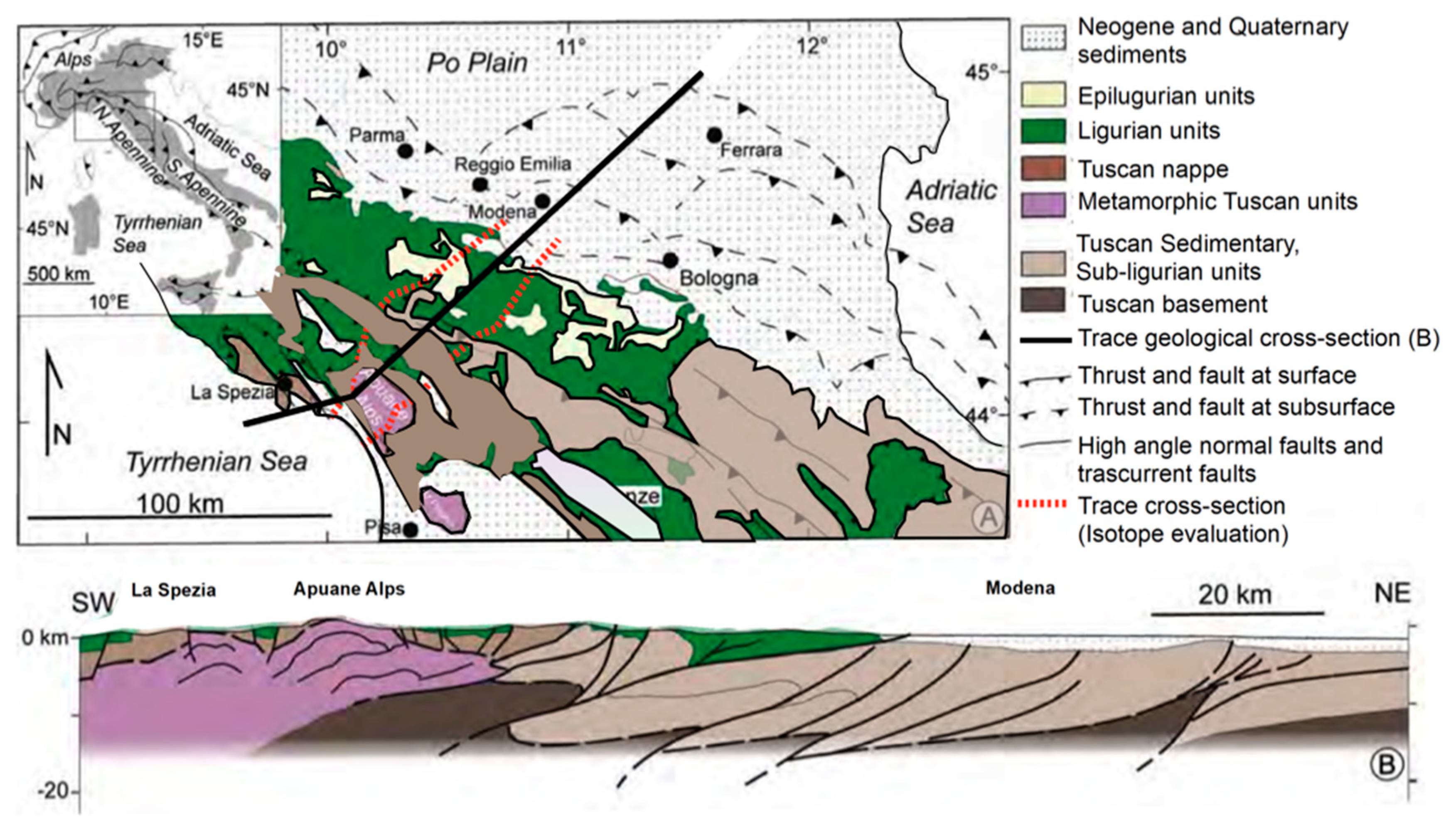
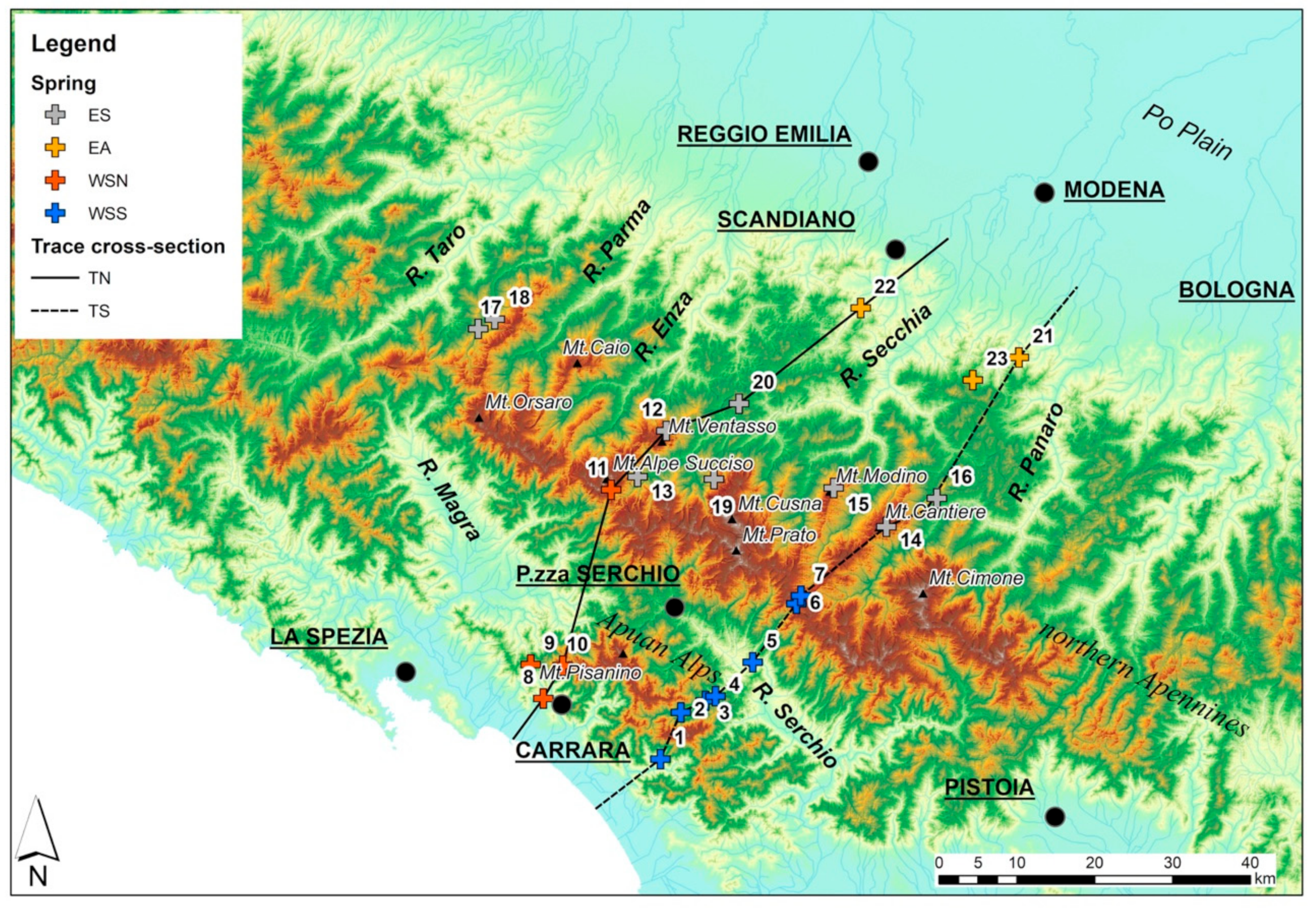
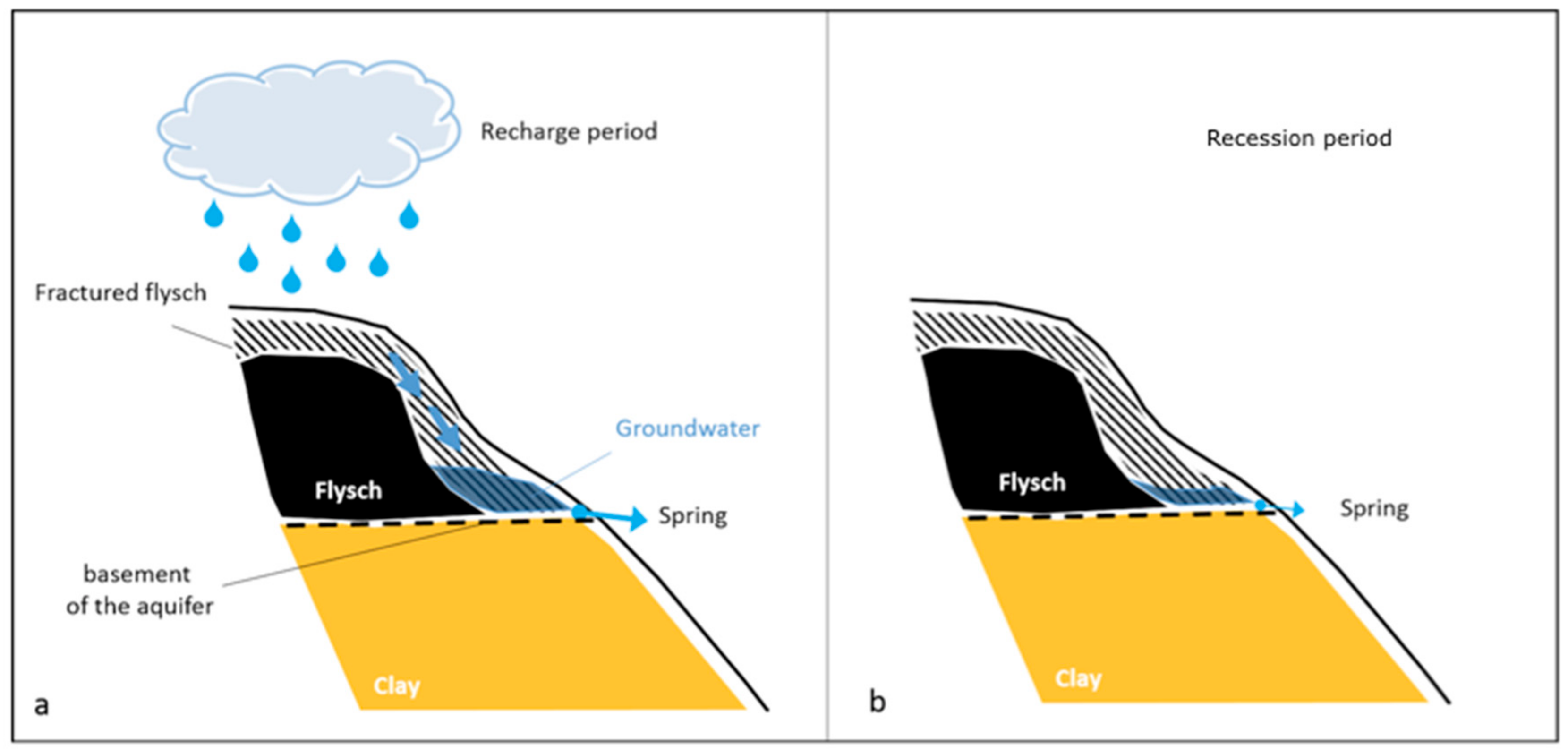
2. Climatic, Geological and Hydrogeological Setting of the Study Area
3. Methods
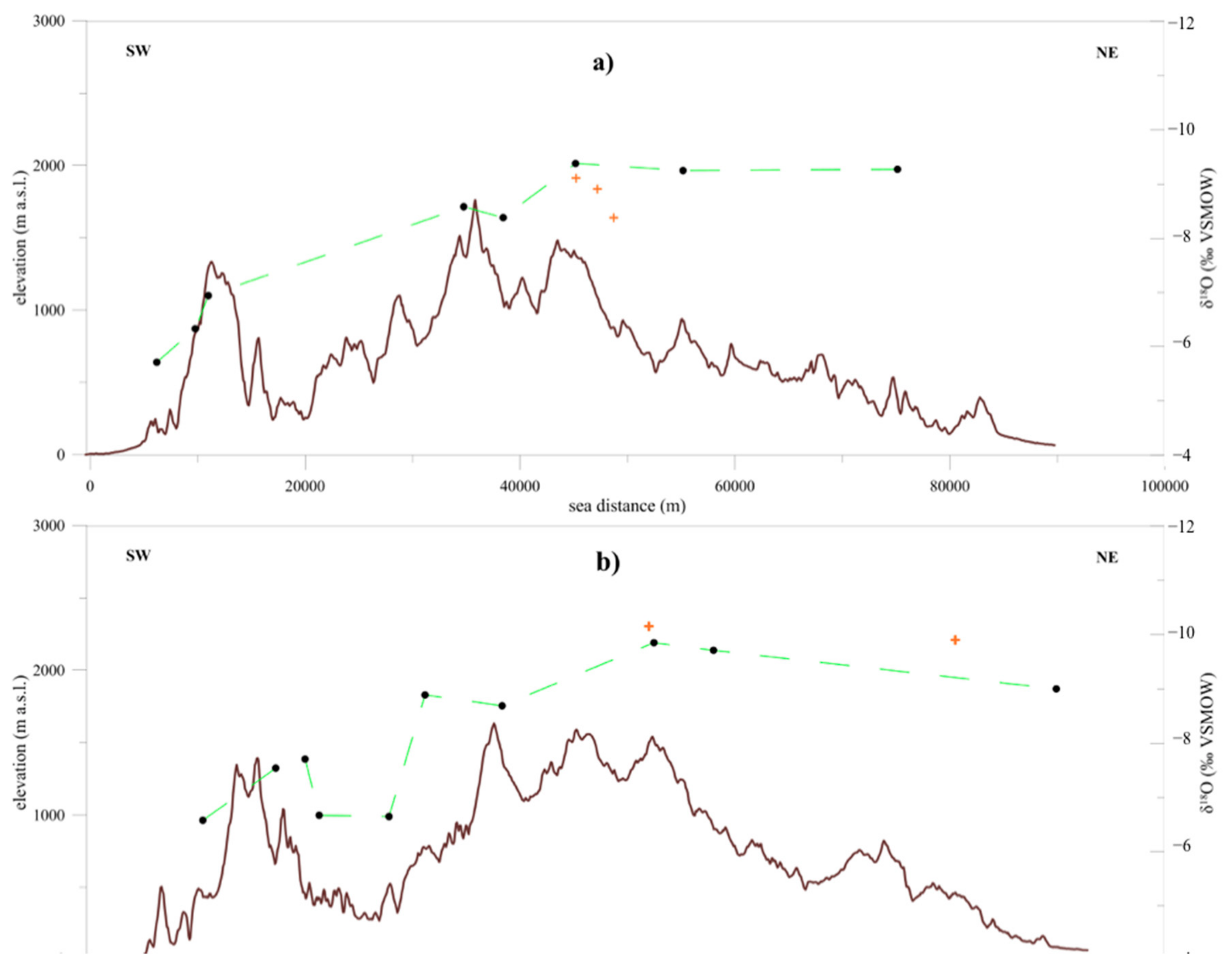
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rozanski, K.; Sonntag, C. Vertical distribution of deuterium in atmospheric water vapour. Tellus 1982, 34, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, T.; Tazioli, A.; Vivalda, P. Problems in the application of environmental isotopes to the hydrogeology of high mountain aquifers. Aqua Mundi 2013, 4, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Schemmel, F.; Mikes, T.; Rojay, B.; Mulch, A. The impact of topography on isotopes in precipitation across the Central Anatolian Plateau (Turkey). Am. J. Sci. 2013, 313, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustini, F.; Brilli, M.; Patera, A. Mapping oxygen stable isotopes of precipitation in Italy. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 8, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duy, N.; Heidbüchel, I.; Meyer, H.; Merz, B.; Apel, H. What controls the stable isotope composition of precipitation in the Mekong Delta? A model-based statistical approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1239–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4822-4291-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R.; Carmi, I. Evolution of the isotopic composition of atmospheric waters in the Mediterranean Sea area. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R. Chapter 3—Environmental isotopes in lake studies. In The Terrestrial Environment, B; Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; Fritz, P., Fontes, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 113–168. ISBN 978-0-444-42225-5. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozanski, K.; Araguás-Araguá, L.; Gonfiantini, R. Isotopic Patterns in Modern Global Precipitation. In Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records; Swart, P.K., Lohmann, K.C., McKenzie, J., Savin, S., Eds.; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 1–36. ISBN 978-1-118-66402-5. [Google Scholar]
- McGuire, K.; Mcdonnell, J. Stable Isotope Tracers in Watershed Hydrology. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 334–374. ISBN 978-0-470-69185-4. [Google Scholar]
- Doveri, M.; Menichini, M.; Cerrina Feroni, A. Gli isotopi stabili dell’acqua come strumento fondamentale nello studio degli acquiferi carsici: Alcuni esempi di applicazione sui complessi carbonatici delle Alpi Apuane (Toscana nw)—Stable water isotope sas fundamental tool in karst aquifer sudies: some results from isotopic applications in the Apuan Alps carbonatic complexes (NW Tuscany, Italy)—IJEGE. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2013, 13, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Doveri, M.; Menichini, M.; Scozzari, A. Protection of Groundwater Resources: Worldwide Regulations and Scientific Approaches. In Threats to the Quality of Groundwater Resources: Prevention and Control (The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry); Scozzari, A., Dotsika, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 13–30. ISBN 978-3-662-48596-5. [Google Scholar]
- Montanari, D.; Minissale, A.; Doveri, M.; Gola, G.; Trumpy, E.; Santilano, A.; Manzella, A. Geothermal resources within carbonate reservoirs in western Sicily (Italy): A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 169, 180–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazioli, A. Does the recharge area of a Spring Vary from year to year? Information from the water isotopes. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 2017, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Hendry, M.J.; Chostner, V.L.; Lis, G.P. High Resolution Pore Water δ2H and δ18O Measurements by H2O(liquid)−H2O(vapor) Equilibration Laser Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9262–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, M.J.; Wassenaar, L.I. Inferring Heterogeneity in Aquitards Using High-Resolution δD and δ18O Profiles. Groundwater 2009, 47, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpp, C.; Hendry, M.J. Spatial and temporal dynamics of water flow and solute transport in a heterogeneous glacial till: The application of high-resolution profiles of δ18O and δ2H in pore waters. J. Hydrol. 2012, 438, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussi, M.; Nanni, T.; Tazioli, A.; Vivalda, P.M. The Mt Conero limestone ridge: The contribution of stable isotopes to the identification of the recharge area of aquifers. Ital. J. Geosci. 2017, 136, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, M.; Mussi, M. Water Isotopes as Environmental Tracers for Conceptual Understanding of Groundwater Flow: An Application for Fractured Aquifer Systems in the “Scansano-Magliano in Toscana” Area (Southern Tuscany, Italy). Water 2014, 6, 2255–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervi, F.; Corsini, A.; Doveri, M.; Mussi, M.; Ronchetti, F.; Tazioli, A. Characterizing the recharge of fractured aquifers: A case study in a flysch rock mass of the northern apennines (italy). In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory—Volume 3: River Basins, Reservoir Sedimentation and Water Resources; Springer, Cham: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Vespasiano, G.; Apollaro, C.; De Rosa, R.; Muto, F.; Larosa, S.; Fiebig, J.; Mulch, A.; Marini, L. The Small Spring Method (SSM) for the definition of stable isotope—Elevation relationships in Northern Calabria (Southern Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, M.; Cervi, F.; Pennisi, M.; Mussi, M.; Bertrand, C.; Tazioli, A.; Corsini, A.; Ronchetti, F. Chemical and isotopic investigations (δ18O, δ2H, 3H, 87Sr/86Sr) to define groundwater processes occurring in a deep-seated landslide in flysch. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2669–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longinelli, A.; Selmo, E. Isotopic composition of precipitation in Italy: A first overall map. J. Hydrol. 2003, 270, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zuppi, G.M.; Fontes, J.C.; Letolle, R. Isotopes du milieu et circolations d’eaux sulfureès dans le Latium. In Proceedings of the Isot. Techn. in Groundwater Hydrology; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1974; Volume 1, pp. 341–361. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, M.; Boschetti, T.; Petitta, M.; Tallini, M. Stable isotope (2H, 18O and 87Sr/86Sr) and hydrochemistry monitoring for groundwater hydrodynamics analysis in a karst aquifer (Gran Sasso, Central Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 2063–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conversini, P.; Tazioli, G.S. Indagini idrogeologiche nella media e alta valle del fiume Menotre, Umbria orientale. Atti Tic. Sci. Terra 1993, 36, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Tazioli, A.; Mosca, M.; Tazioli, G.S. Location of recharge area of Gorgovivo Spring, Central Italy. A contribution from isotope hydrology. In Proceedings of the International Symposium “Advances in Isotope Hydrology and Its Role in Sustainable Water Resources Management (IHS-2007)”; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2007; pp. 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tazioli, A.; Conversini, P.; Peccerillo, A. Hydrogeological and geochemical characterisation of the Rock of Orvieto. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, M.; Mussi, M.; Ronchetti, F. Discharge and environmental isotope behaviours of adjacent fractured and porous aquifers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervi, F.; Ronchetti, F.; Doveri, M.; Mussi, M.; Marcaccio, M.; Tazioli, A. The use of stable water isotopes from rain gauges network to define the recharge areas of springs: Problems and possible solutions from case studies in the northern Apennines. Geoing. Ambient. Min. 2016, 149, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Molli, G. Northern Apennine—Corsica orogenic system: An updated overview. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2008, 298, 413–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civita, M.; Forti, P.; Marini, P.; Meccheri, M.; Micheli, L.; Piccini, L.; Pranzini, G. Note Illustrative Della Carta Della Vulnerabilità All’inquinamento Degli Acquiferi Delle Alpi Apuane—Pollution Vulnerability Map for the Aquifers of the Apuane Alps a Brief Guide; SELCA: Firenze, Italy, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Baldacci, F.; Cecchini, S.; Lopane, G.; Raggi, G. Le risorse idriche del bacino del Fiume Serchio ed il loro contributo all’alimentazione dei bacini idrografici adiacenti. Mem. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1993, 49, 365–391. [Google Scholar]
- Antolini, G.; Pavan, V.; Tomozeiu, R.; Marletto, V. Atlante climatico dell’Emilia-Romagna. Casma Tipolito srl–Bologna, Italy, 1961–2015. Available online: https://www.arpae.it/cms3/documenti/_cerca_doc/meteo/clima/Atlante_climatico_1961-2015.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- Longinelli, A.; Anglesio, E.; Flora, O.; Iacumin, P.; Selmo, E. Isotopic composition of precipitation in Northern Italy: Reverse effect of anomalous climatic events. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuppi, G.M.; Bortolami, G. Hydrogeology: A privileged field for environmental stable isotopes applications. Some Italian examples. Rend. Della Soc. Ital. Mineral. Petrol. 1983, 38, 1197–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Boccaletti, M.; Elter, P.; Guazzone, G. Polarita strutturali delle Alpi e dell’Appennino settentrionale in rapporto all’inversione di una zona di subduzione nord-tirrenica. Mem. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1971, 10, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Carmignani, L.; Kligfield, R. Crustal extension in the Northern Apennines: The transition from compression to extension in the Alpi Apuane Core Complex. Tectonics 1990, 9, 1275–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molli, G.; Cortecci, G.; Vaselli, L.; Ottria, G.; Cortopassi, A.; Dinelli, E.; Mussi, M.; Barbieri, M. Fault zone structure and fluid—Rock interaction of a high angle normal fault in Carrara marble (NW Tuscany, Italy). J. Struct. Geol. 2010, 32, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, A.; Cervi, F.; Ronchetti, F. Weight of evidence and artificial neural networks for potential groundwater spring mapping: An application to the Mt. Modino area (Northern Apennines, Italy). Geomorphology 2009, 111, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargini, A.; De Nardo, M.T.; Piccinini, L.; Segadelli, S.; Vincenzi, V. Spring discharge and groundwater flow systems in sedimentary and ophiolitic hard rock aquifers: Experiences from Northern Apennines (Italy). In Fractured Rock Hydrogeology; IAH—Selected Papers on Hydrogeology; Sharp, J.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 129–145. ISBN 978-1-138-00159-6. [Google Scholar]
- Molli, G.; Doveri, M.; Manzella, A.; Bonini, L.; Botti, F.; Menichini, M.; Montanari, D.; Trumpy, E.; Ungari, A.; Vaselli, L. Surface-subsurface structural architecture and groundwater flow of the Equi Terme hydrothermal area, northern Tuscany Italy. Ital. J. Geosci. 2015, 134, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, M.; Piccini, L.; Menichini, M. Hydrodynamic and Geochemical Features of Metamorphic Carbonate Aquifers and Implications for Water Management: The Apuan Alps (NW Tuscany, Italy) Case Study. In Karst Water Environment; The handbook of environmental chemistry; Younos, T., Schreiber, M., Kosič Ficco, C., Eds.; Springer, Cham: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-319-77368-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi, M.; De Waele, J.; Forti, P. Origin and evolution of a salty gypsum/anhydrite karst spring: The case of Poiano (Northern Apennines, Italy). Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargini, A.; Vincenzi, V.; Piccinini, L.; Zuppi, G.M.; Canuti, P. Groundwater flow systems in turbidites of the Northern Apennines (Italy): Natural discharge and high speed railway tunnel drainage. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1577–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervi, F.; Borgatti, L.; Dreossi, G.; Marcato, G.; Michelini, M.; Stenni, B. Isotopic features of precipitation and groundwater from the Eastern Alps of Italy: Results from the Mt. Tinisa hydrogeological system. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, F.; Borgatti, L.; Cervi, F.; Gorgoni, C.; Piccinini, L.; Vincenzi, V.; Corsini, A. Groundwater processes in a complex landslide, northern Apennines, Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice-Hall: Englewood cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979; ISBN 978-0-13-365312-0. [Google Scholar]
- Cervi, F.; Borgatti, L.; Martinelli, G.; Ronchetti, F. Evidence of deep-water inflow in a tectonic window of the northern Apennines (Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2389–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.; Mayeda, T. Variation of O18 content of waters from natural sources. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1953, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.L.; Shepherd, T.; Durham, J.J.; Rouse, J.E.; Moore, G.R. Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis. Anal. Chem. 1982, 54, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussi, M.; Leone, G.; Nardi, I. Isotopic geochemistry of natural waters from the Alpi Apuane—Garfagnana area, Northern Tuscany, Italy. Mineral. Petrogr. Acta 1998, 41, 163–178. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Simmons, C.T.; Love, A.J. Orographic controls on rain water isotope distribution in the Mount Lofty Ranges of South Australia. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, M.; Stenni, B.; Petrini, R.; Giannecchini, R.; Dreossi, G.; Menichini, M.; Ghezzi, L. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic composition of waters in a past-mining area of southern Apuan Alps (Italy): Hydrogeological characterization and implications on the fate of potentially toxic elements. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 205, 106338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

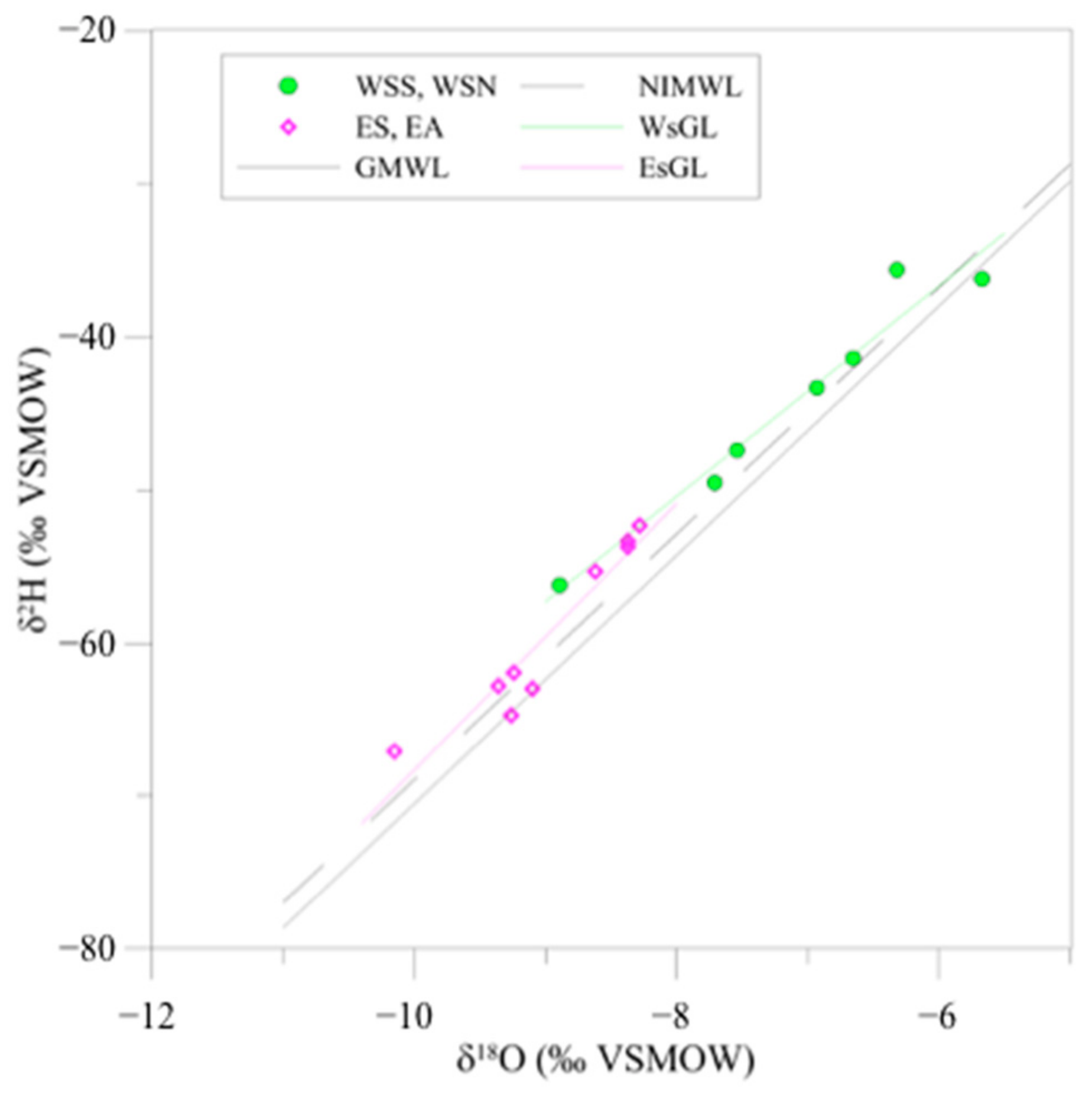
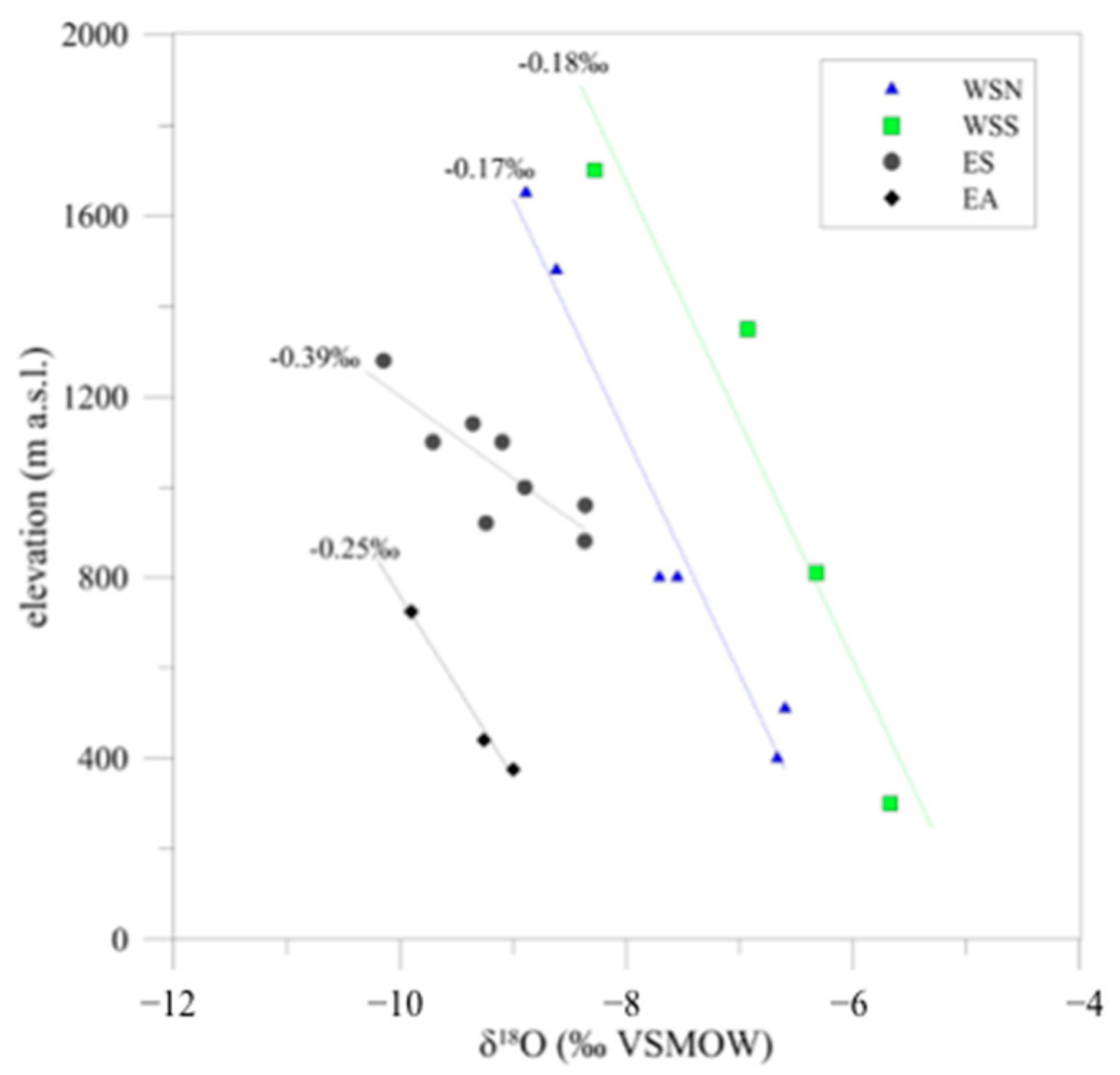
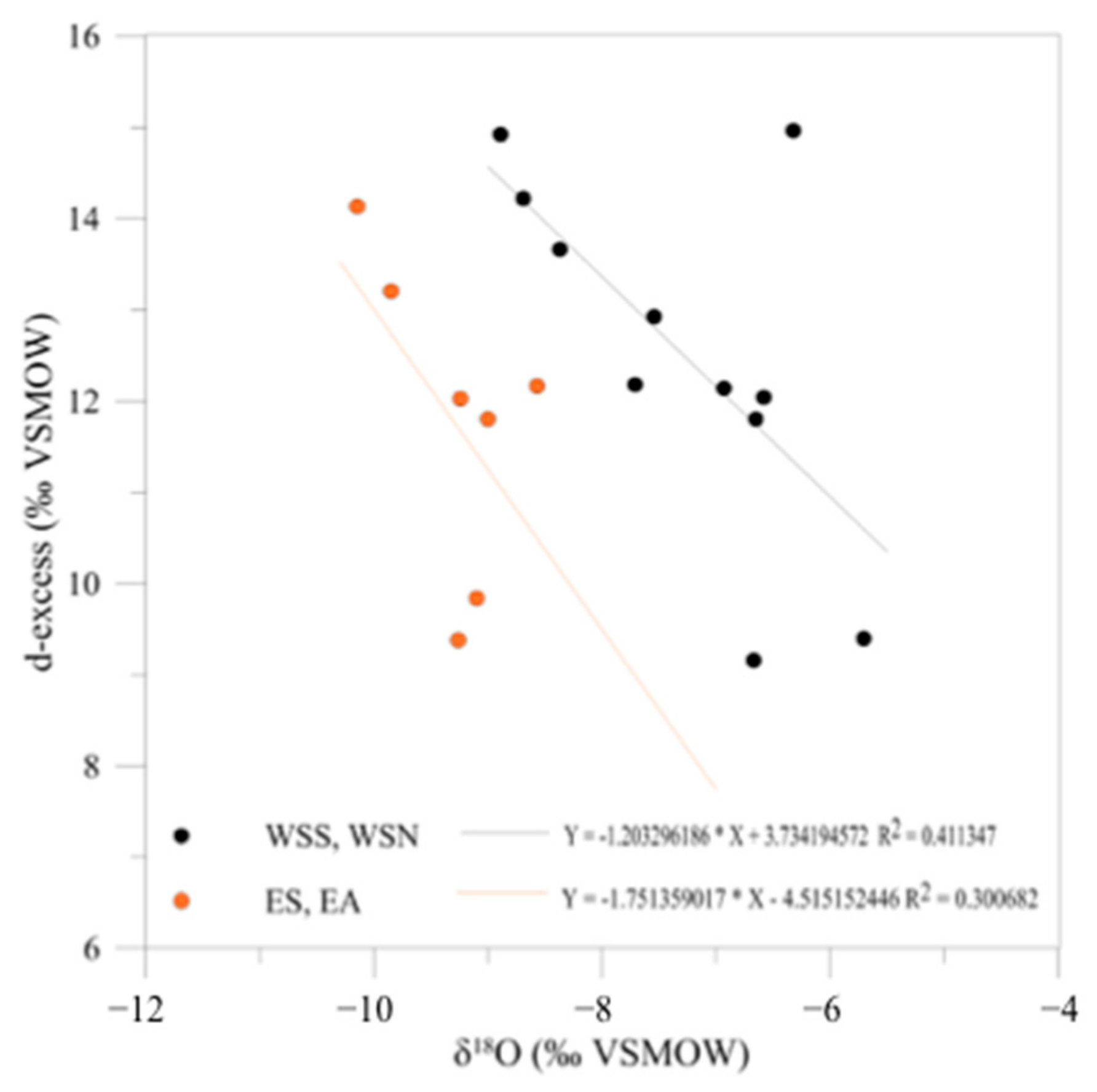
| No. on Map | Name of the Spring | Number of Values | Emerging Altitude | Mean Altitude of the Watershed | Oxygen-18 (Low Flow Value) | +/− | Deuterium (Low Flow Value) | +/− | d-excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | km 14.6 | 8 | 475 | 700 | −6.58 | 0.16 | −40.6 | 12.04 | |
| 2 | km 29.2 | 7 | 600 | 800 | −7.54 | 0.05 | −47.4 | 0.23 | 12.92 |
| 3 | km 32.6 | 6 | 425 | 800 | −7.71 | 0.09 | −49.5 | 0.6 | 12.18 |
| 4 | km 35.4 | 8 | 370 | 400 | −6.67 | 0.11 | −44.2 | 0.5 | 9.16 |
| 5 | S. francesco | 9 | 490 | 510 | −6.65 | 0.05 | −41.4 | 0.3 | 11.8 |
| 6 | La fredda | 9 | 1540 | 1650 | −8.89 | 0.13 | −56.2 | 0.3 | 14.92 |
| 7 | Imbrancamento | 14 | 1350 | 1480 | −8.69 | 0.26 | −55.3 | 0.7 | 14.22 |
| 8 | Fontana fredda | 17 | 150 | 300 | −5.7 | 0.06 | −36.2 | 0.7 | 9.4 |
| 9 | Maestà | 10 | 800 | 810 | −6.32 | 0.29 | −35.6 | 0.5 | 14.96 |
| 10 | Acqua sparta | 10 | 1275 | 1350 | −6.93 | 0.23 | −43.3 | 0.4 | 12.14 |
| 11 | Secchia springs | 2 | 1500 | 1700 | −8.57 | 0.11 | −56.4 | 0.2 | 12.16 |
| 12 | Cadoniche | 1 | 1325 | 1350 | −9.37 | ||||
| 13 | Collagna | 7 | 850 | 960 | −8.37 | 0.13 | −53.7 | 1.6 | 13.26 |
| 14 | Mt Cantiere | 8 | 1170 | 1450 | −9.85 | 0.08 | −65.6 | 0.8 | 13.2 |
| 15 | Venano | 7 | 1180 | 1280 | −10.15 | 0.1 | −67.07 | 1.5 | 14.13 |
| 16 | Borra | 1 | 900 | 1100 | −9.71 | ||||
| 17 | Fugazzolo | 1 | 1017 | 1000 | −8.9 | ||||
| 18 | Berceto | 13 | 825 | 880 | −8.37 | 0.21 | −53.3 | 0.3 | 13.66 |
| 19 | Montecagno | 22 | 1050 | 1100 | −9.10 | 0.05 | −62.96 | 0.3 | 9.84 |
| 20 | Bismantova | 14 | 800 | 920 | −9.24 | 0.38 | −61.9 | 0.6 | 12.02 |
| 21 | M. di Puianello | 2 | 350 | 375 | −9.00 | 0.18 | −60.2 | 0.4 | 11.8 |
| 22 | Lusino | 7 | 325 | 440 | −9.26 | 0.11 | −64.7 | 0.5 | 9.38 |
| 23 | La fontanina | 1 | 650 | 725 | −9.9 | 0.12 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tazioli, A.; Cervi, F.; Doveri, M.; Mussi, M.; Deiana, M.; Ronchetti, F. Estimating the Isotopic Altitude Gradient for Hydrogeological Studies in Mountainous Areas: Are the Low-Yield Springs Suitable? Insights from the Northern Apennines of Italy. Water 2019, 11, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091764
Tazioli A, Cervi F, Doveri M, Mussi M, Deiana M, Ronchetti F. Estimating the Isotopic Altitude Gradient for Hydrogeological Studies in Mountainous Areas: Are the Low-Yield Springs Suitable? Insights from the Northern Apennines of Italy. Water. 2019; 11(9):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091764
Chicago/Turabian StyleTazioli, Alberto, Federico Cervi, Marco Doveri, Mario Mussi, Manuela Deiana, and Francesco Ronchetti. 2019. "Estimating the Isotopic Altitude Gradient for Hydrogeological Studies in Mountainous Areas: Are the Low-Yield Springs Suitable? Insights from the Northern Apennines of Italy" Water 11, no. 9: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091764
APA StyleTazioli, A., Cervi, F., Doveri, M., Mussi, M., Deiana, M., & Ronchetti, F. (2019). Estimating the Isotopic Altitude Gradient for Hydrogeological Studies in Mountainous Areas: Are the Low-Yield Springs Suitable? Insights from the Northern Apennines of Italy. Water, 11(9), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091764








