Impact of Pressure-Driven Demand on Background Leakage Estimation in Water Supply Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
Overview of Pressure-Dependent Demand Functions
2. Methods
Integrating a PDD Function and Pressure-Dependent Leakage Modeling in the WSN Hydraulic Model Formulation
3. Results and Analysis
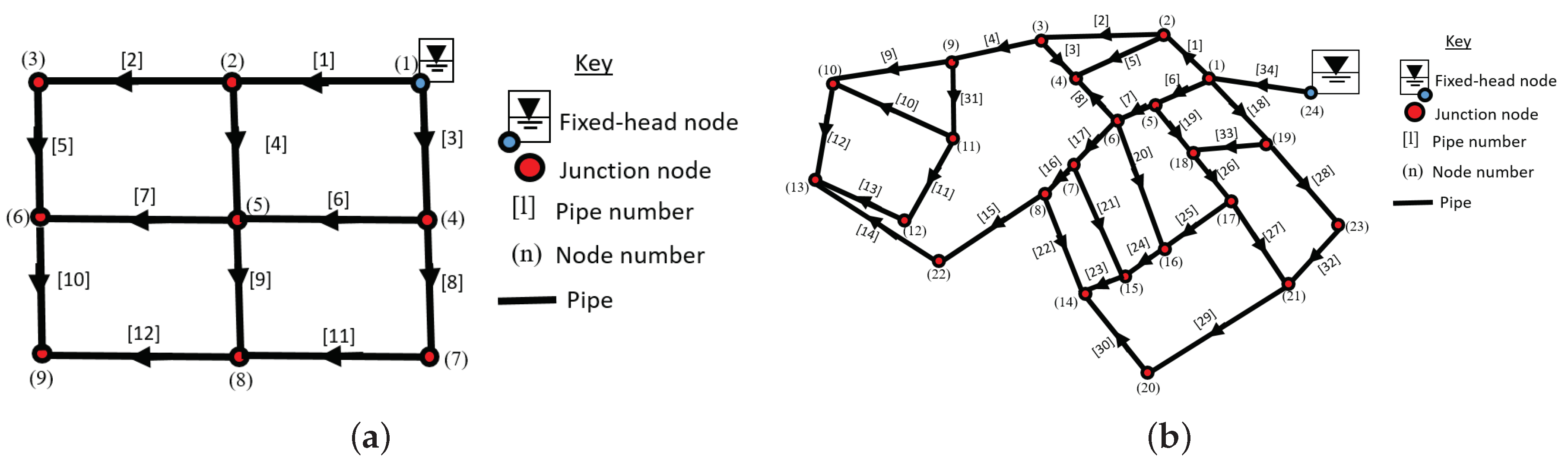
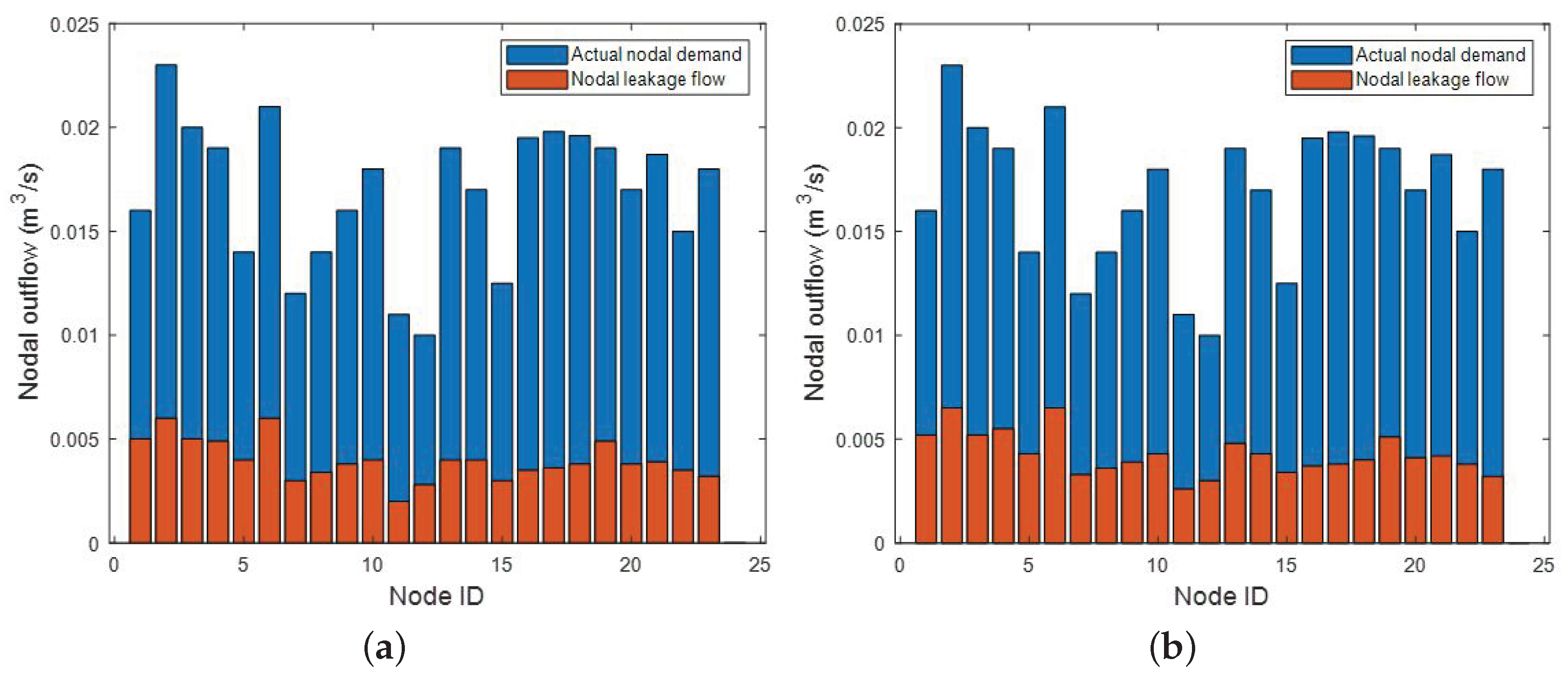
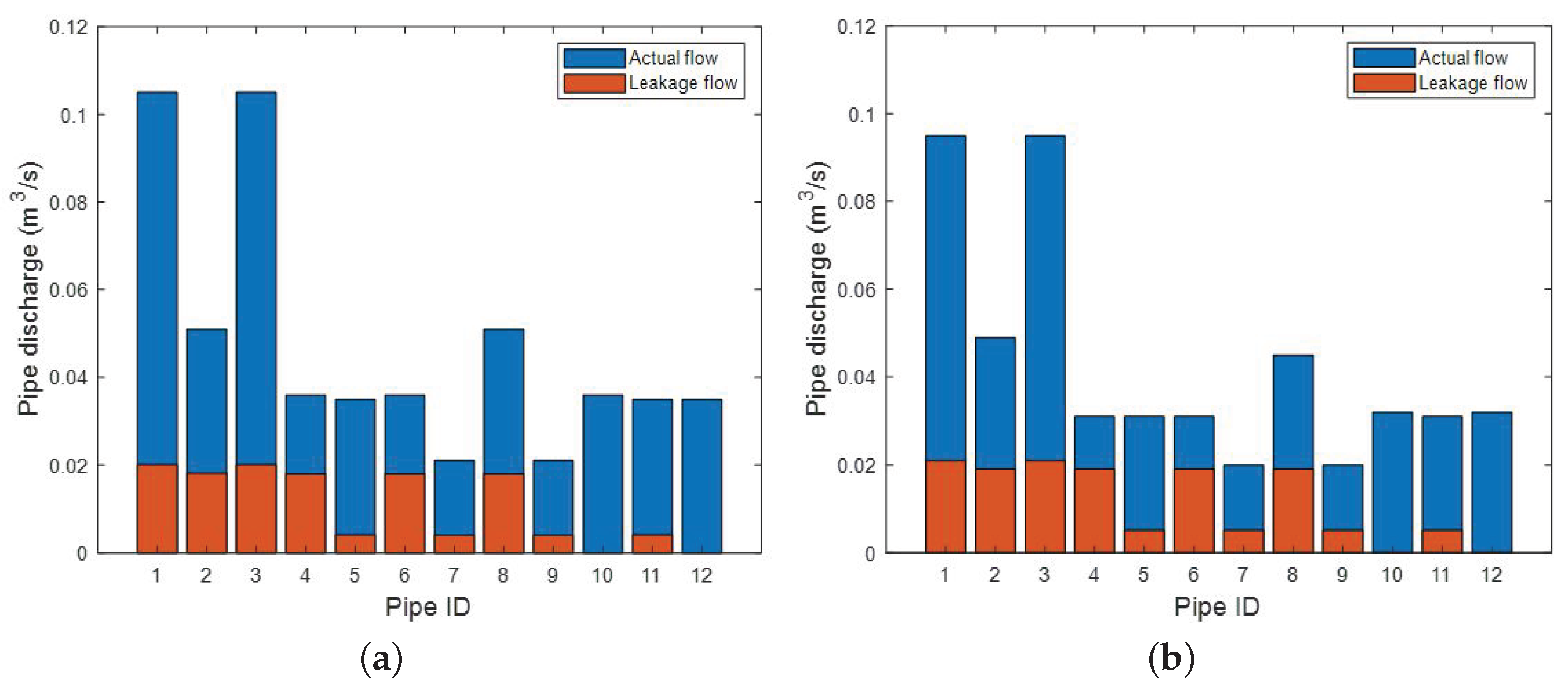
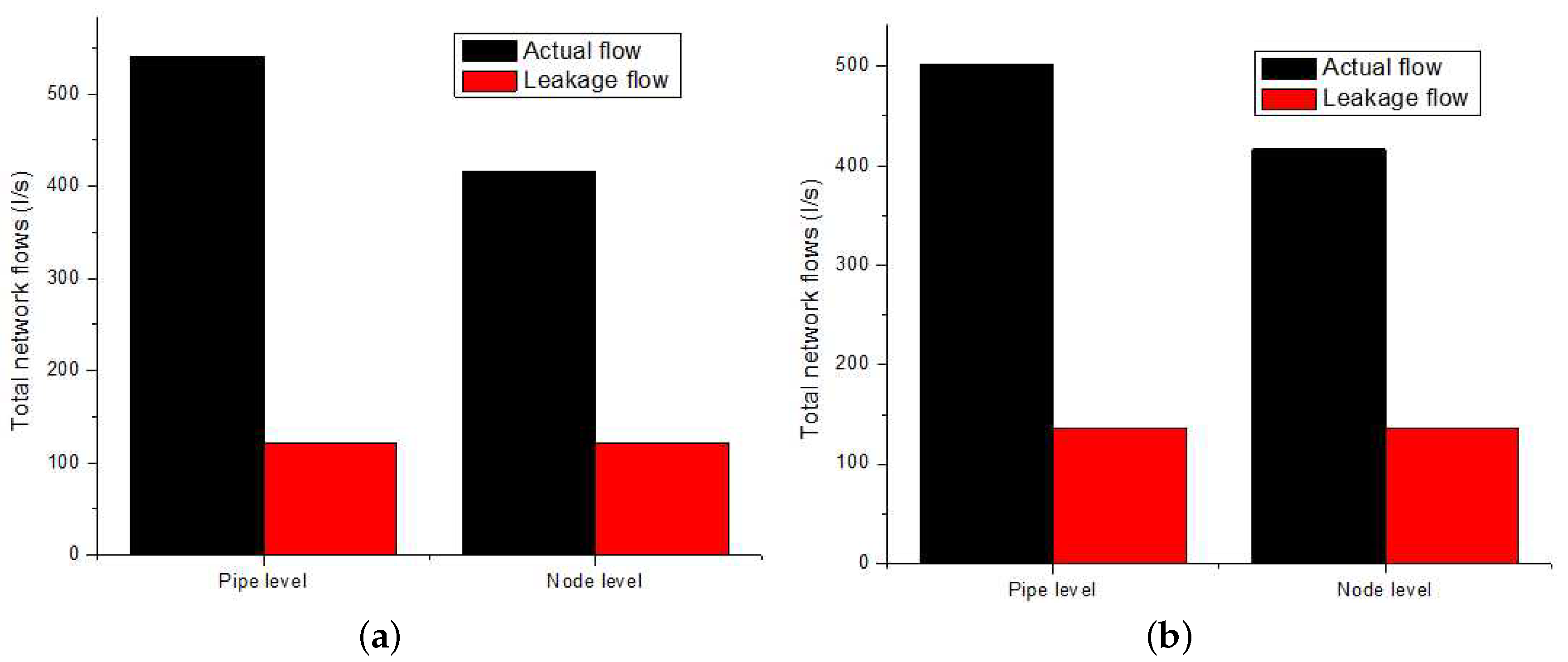
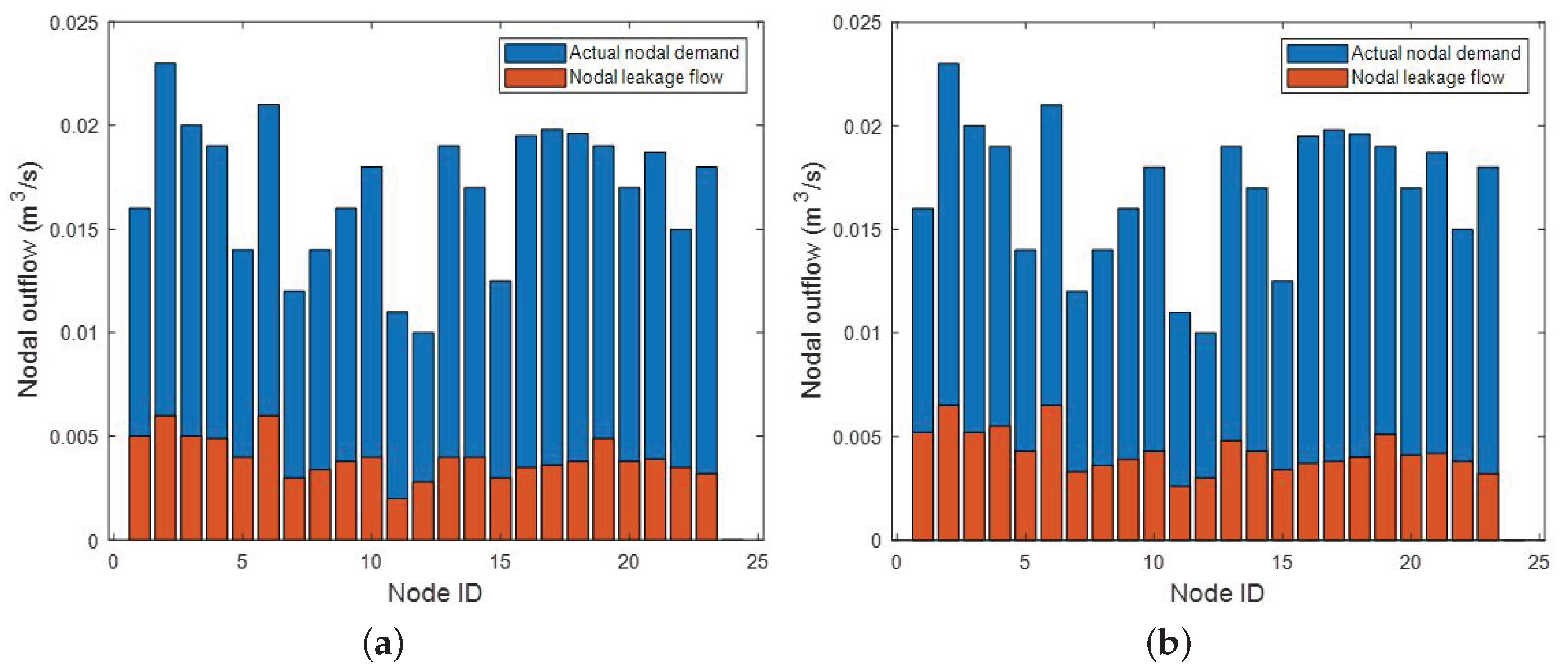
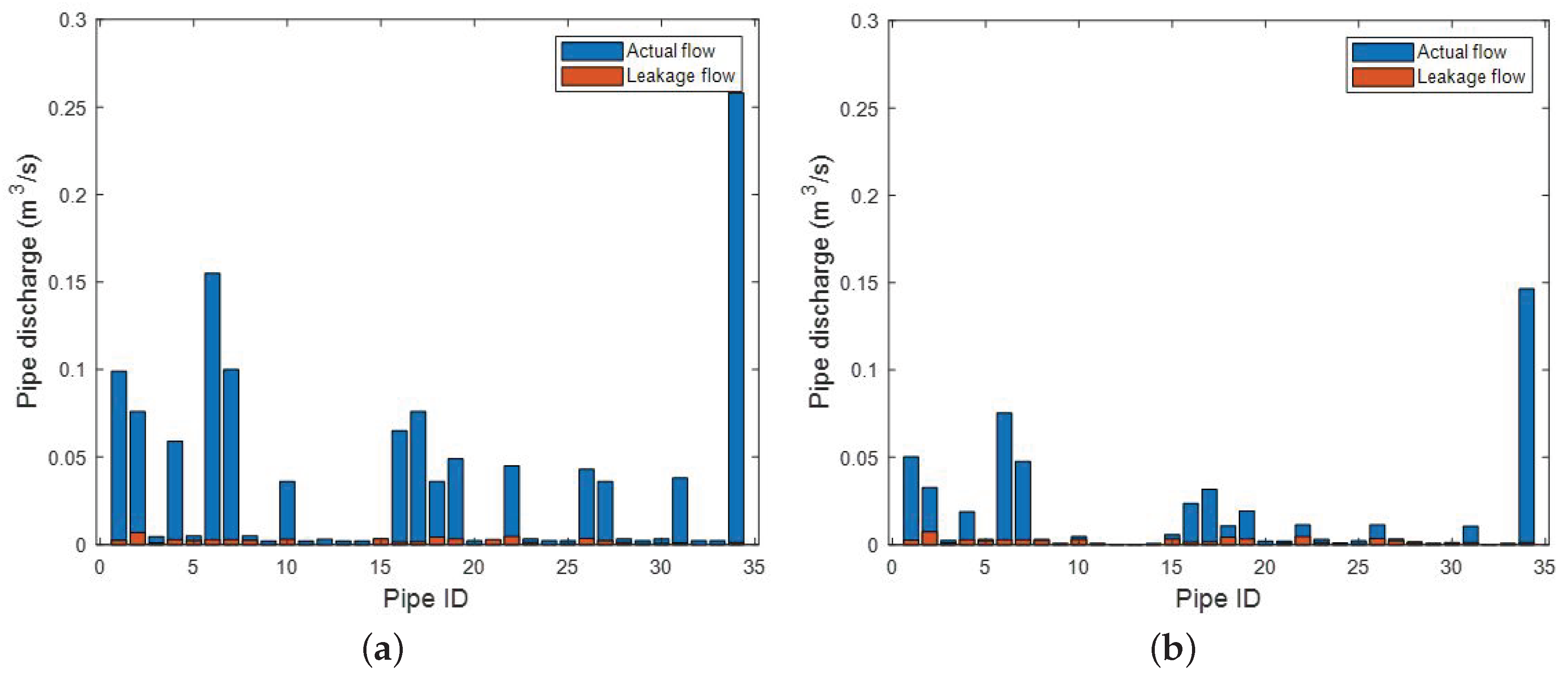
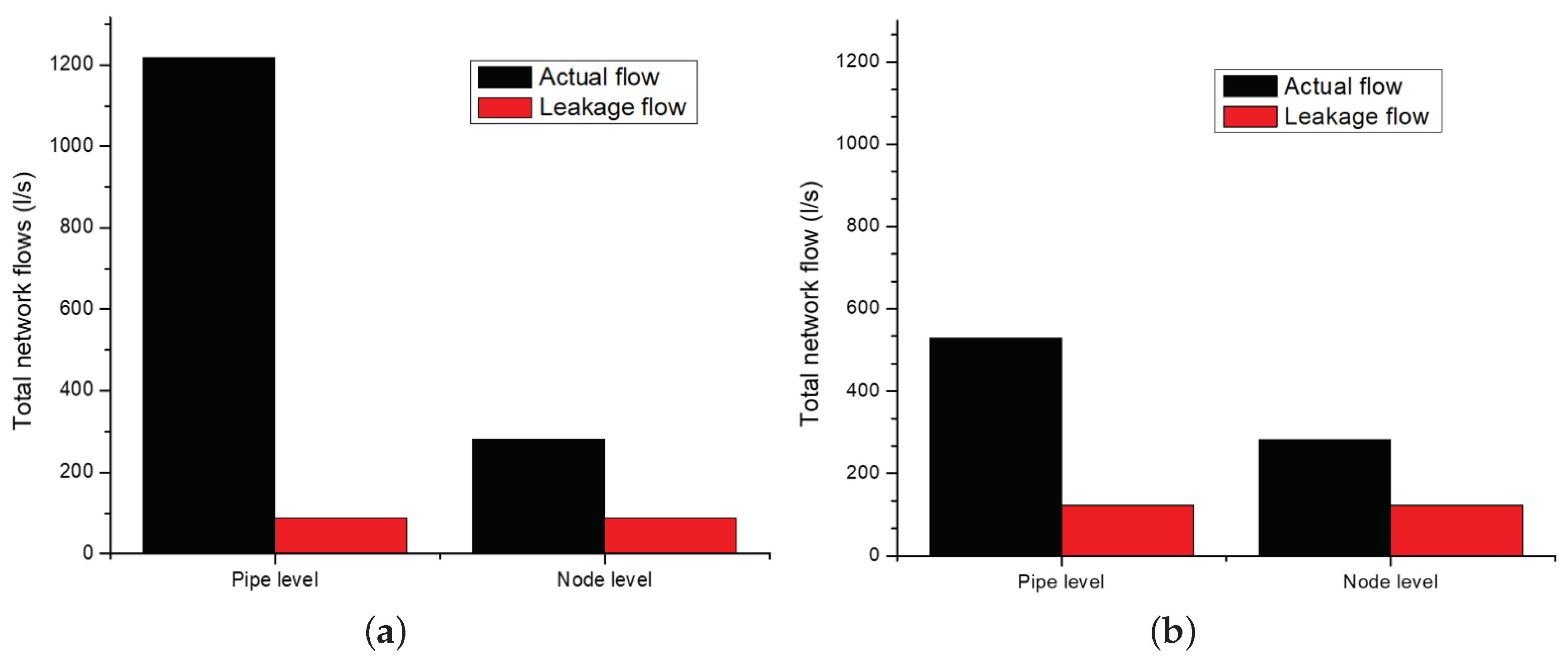
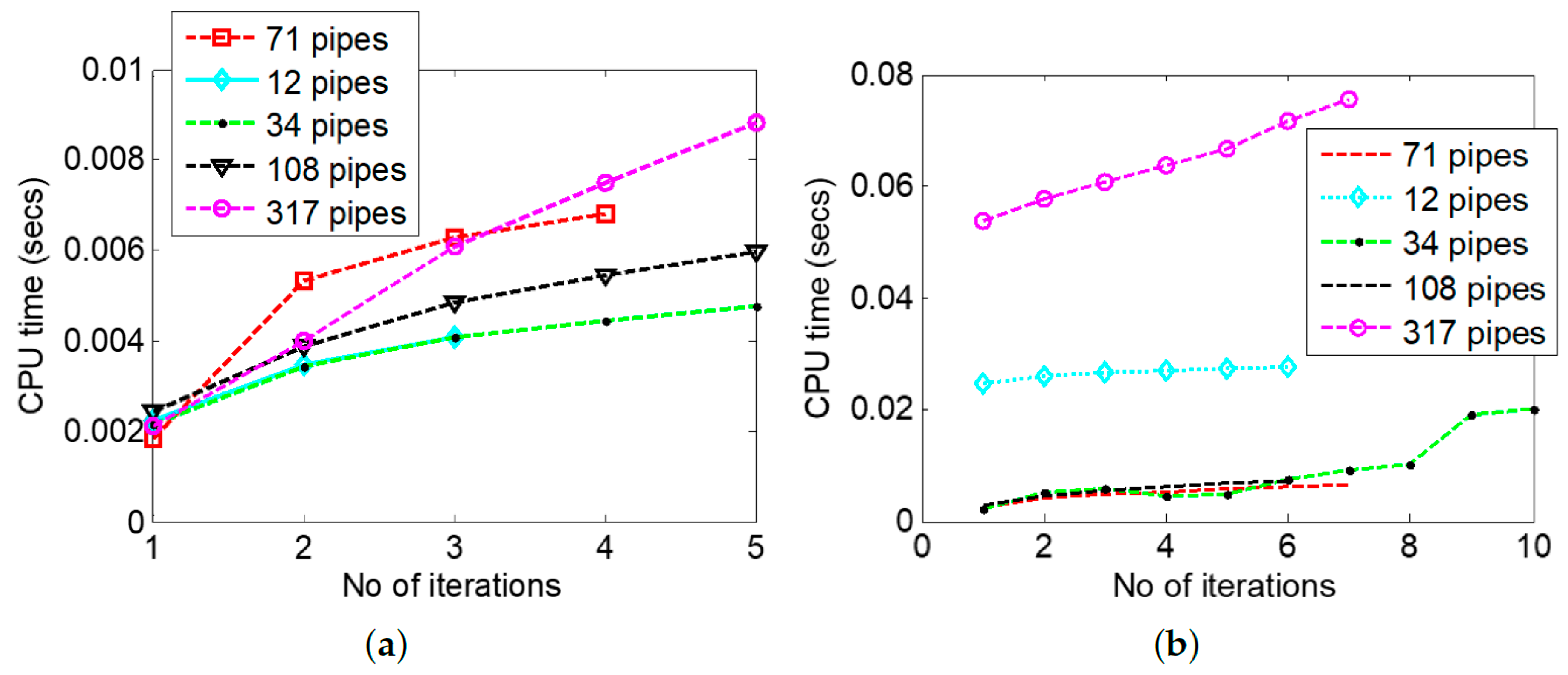
Numerical Examples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Continuation of the PDM with Background Leakage Model Derivation
References
- Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abe, B.T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Towards achieving a reliable leakage detection and localization algorithm for application in water piping networks: An overview. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 20272–20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Farley, M.; Turtle, D.; Kapelan, Z.; Boxall, J.; Mounce, S.; Dahasahasra, S.; Mulay, M.; Kleiner, Y. Water Loss Reduction, 1st ed.; Bentley Institute Press: Exton, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hindi, K.S.; Hamam, Y. Locating pressure control elements for leakage minimisation in water supply network: An optimisation model. Eng. Optim. 1991, 17, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindi, K.S.; Hamam, Y. Pressure control for leakage minimisation, in water distribution networks, Part 1, Single period models. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1991, 22, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindi, K.S.; Hamam, Y. Pressure control for leakage minimisation, in water distribution networks, Part 2, Multi-period models. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1991, 22, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.R.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Yoyo, S. Real-time adjustment of pressure to demand in water distribution systems: Parameter-less P-controller algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.R.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Yoyo, S. Parameter-less remote real-time control for the adjustment of pressure in water distribution systems. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.R.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Mothetha, M.L. Pressure management of water distribution systems via the remote real-time control of variable speed pumps. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abe, B.T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Pressure management strategies for water loss reduction in large-scale water piping networks: A review. In Advances in Hydroinformatics; Gourbesville, P., Cunge, J., Caignaert, G., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 465–480. [Google Scholar]
- Sechi, G.M.; Zucca, R. A cost-simulation approach to finding economic optimality in leakage reduction for complex supply systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4601–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, B.B.; Saurin, T.A. Losses in water distribution systems: A complexity theory perspective. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, L.S.; Ramos, H.; Coelho, S.T. Pressure control for leakage minimisation in water distribution systems management. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, E.; Shahrour, I. Leakage detection using smart water system: Combination of water balance and automated minimum night flow. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4821–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, S.S.; Bui, Q.N. Leak prediction model for water distribution networks created using a Bayesian network learning approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2719–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.R.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Piller, O.; Mothetha, M.; Osman, M.S. Robustness of parameter-less remote real-time pressure control in water distribution systems. In Advances in Hydroinformatics; Gourbesville, P., Cunge, J., Caignaert, G., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 449–463. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hamam, Y.; Page, P.R.; Adedeji, K.B.; Anele, A.O.; Todini, E. Real-time dynamic hydraulic model of water distribution networks. Water 2019, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, E. A more realistic approach to the extended period simulation of water distribution networks. In Advances in Water Supply Management; Swets and Zeitlinger Publishers: Lisse, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, M.; Piller, O.; Deuerlein, J.; Mortazavi, I. Limitations of demand-and pressure-driven modelling for large deficient networks. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2017, 10, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustolisi, O.; Berardi, L.; Laucelli, D.; Savic, D.; Walski, T.; Brunone, B. Battle of back- ground leakage assessment for water networks at WDSA conference 2014. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, C.; Cimorelli, L.; Cozzolino, L.; Della Morte, R.; Pianese, D. Reduction in water losses in water distribution systems using pressure reduction valves. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abe, B.T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Leakage detection and estimation algorithm for loss reduction in water piping networks. Water 2017, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, P.R. Node flow analysis distribution systems. Transp. Eng. J. ASCE 1981, 107, 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.M.; Shamir, U.; Marks, D.H. Water distribution reliability: Simulation methods. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 1988, 114, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandapillai, J. Realistic simulation of water distribution system. J. Transp. Eng. 1991, 117, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, R.H.; Walski, T.M.; Yang, S.Y.; Bowdler, D.; Baggett, C.C. Extended global-gradient algorithm for pressure-dependent water distribution analysis. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2009, 135, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germanopoulos, G. A technical note in the inclusion of pressure dependent demand and leakage terms in water supply network models. Civ. Eng. Syst. 1985, 2, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, L.S.; Elango, K. Analysis of water distribution networks with head-dependent outlets. Civ. Eng. Syst. 1989, 6, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.; Templeman, A. A new nodal outflow function for water distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Engineering Computational Technology, Lisbon, Portugal, 7–9 September 2004; Civil Comp Press: Stirling, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tabesh, M.; Shirzad, A.; Arefkhani, V.; Mani, A. A comparative study between the modified and available demand driven based models for head driven analysis of water distribution networks. Urban Water J. 2014, 11, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Fire Suppression Rating Schedule, 6th ed.; Insurance Services Office: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Twort, A.; Law, F.; Crowley, F.; Ratnayaka, D. Water Supply, 4th ed.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Adedeji, K.B. Development of a Leakage Detection and Localisation Technique for Real-Time Applications in Water Distribution Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, Tshwane University of Technology, Pretoria, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hamam, Y.; Brameller, A. Hybrid method for the solution of piping network. Proc. IEE 1971, 118, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustolisi, O.; Todini, E. Pipe hydraulic resistance correction in WDN analysis. Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Network ID | Head-Loss Model Used | (m) | (m) | Total Required Demand (L/s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 1 | HW | 0 | 10 | 208.1 |
| N2 | 34 | 24 | 23 | 1 | HW | 10 | 30 | 282 |
| N3 | 71 | 46 | 45 | 1 | HW | 5 | 20 | 88.82 |
| N4 | 108 | 70 | 67 | 3 | HW | 5 | 90 | 535 |
| N5 | 317 | 272 | 268 | 4 | HW | 5 | 80 | 406.94 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Impact of Pressure-Driven Demand on Background Leakage Estimation in Water Supply Networks. Water 2019, 11, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081600
Adedeji KB, Hamam Y, Abu-Mahfouz AM. Impact of Pressure-Driven Demand on Background Leakage Estimation in Water Supply Networks. Water. 2019; 11(8):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081600
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdedeji, Kazeem B., Yskandar Hamam, and Adnan M. Abu-Mahfouz. 2019. "Impact of Pressure-Driven Demand on Background Leakage Estimation in Water Supply Networks" Water 11, no. 8: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081600
APA StyleAdedeji, K. B., Hamam, Y., & Abu-Mahfouz, A. M. (2019). Impact of Pressure-Driven Demand on Background Leakage Estimation in Water Supply Networks. Water, 11(8), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081600






