Spatial–Temporal Matching Characteristics between Agricultural Water and Land Resources in Ningxia, Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
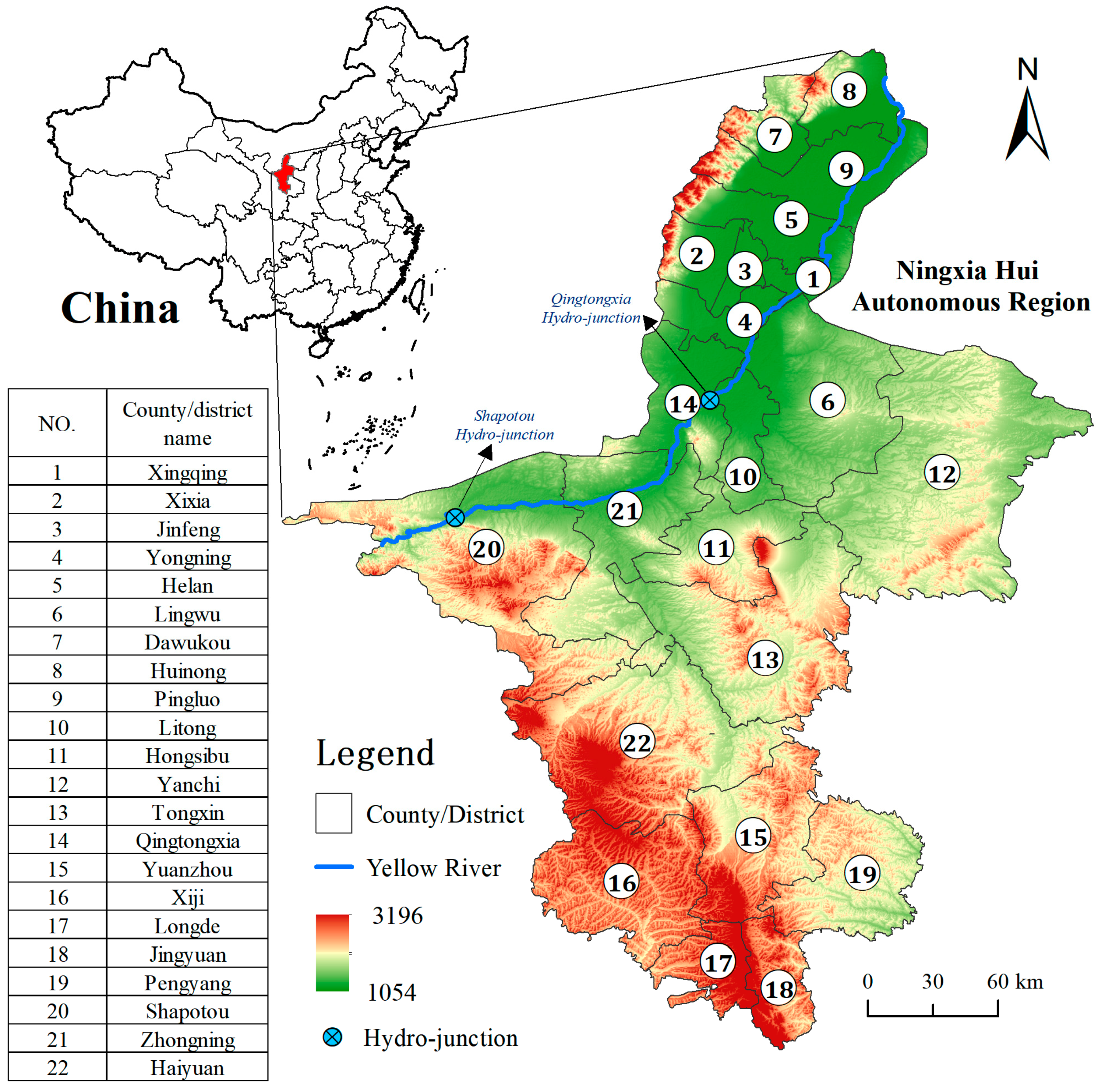
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Gravity Center Model
3.3. Theory of Matching and Mismatching
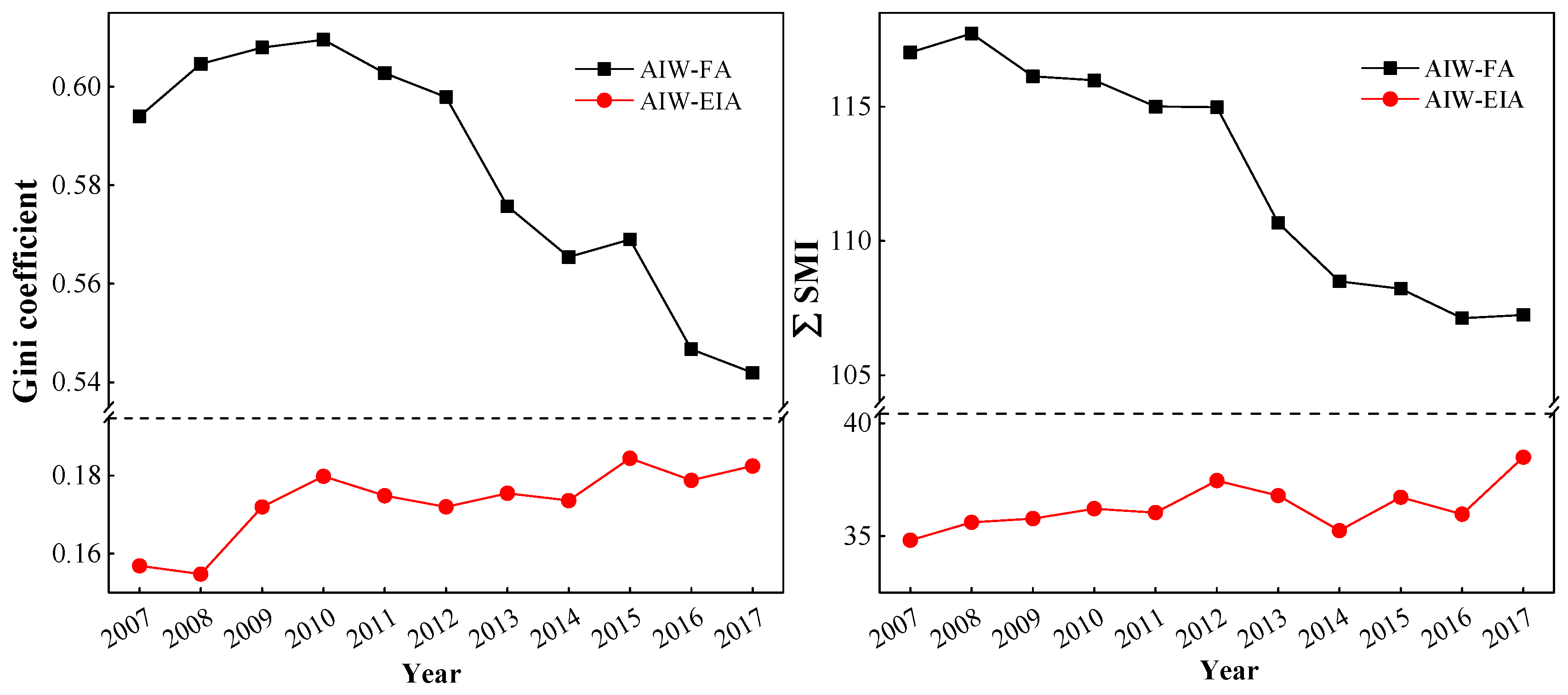
3.3.1. Gini Coefficient
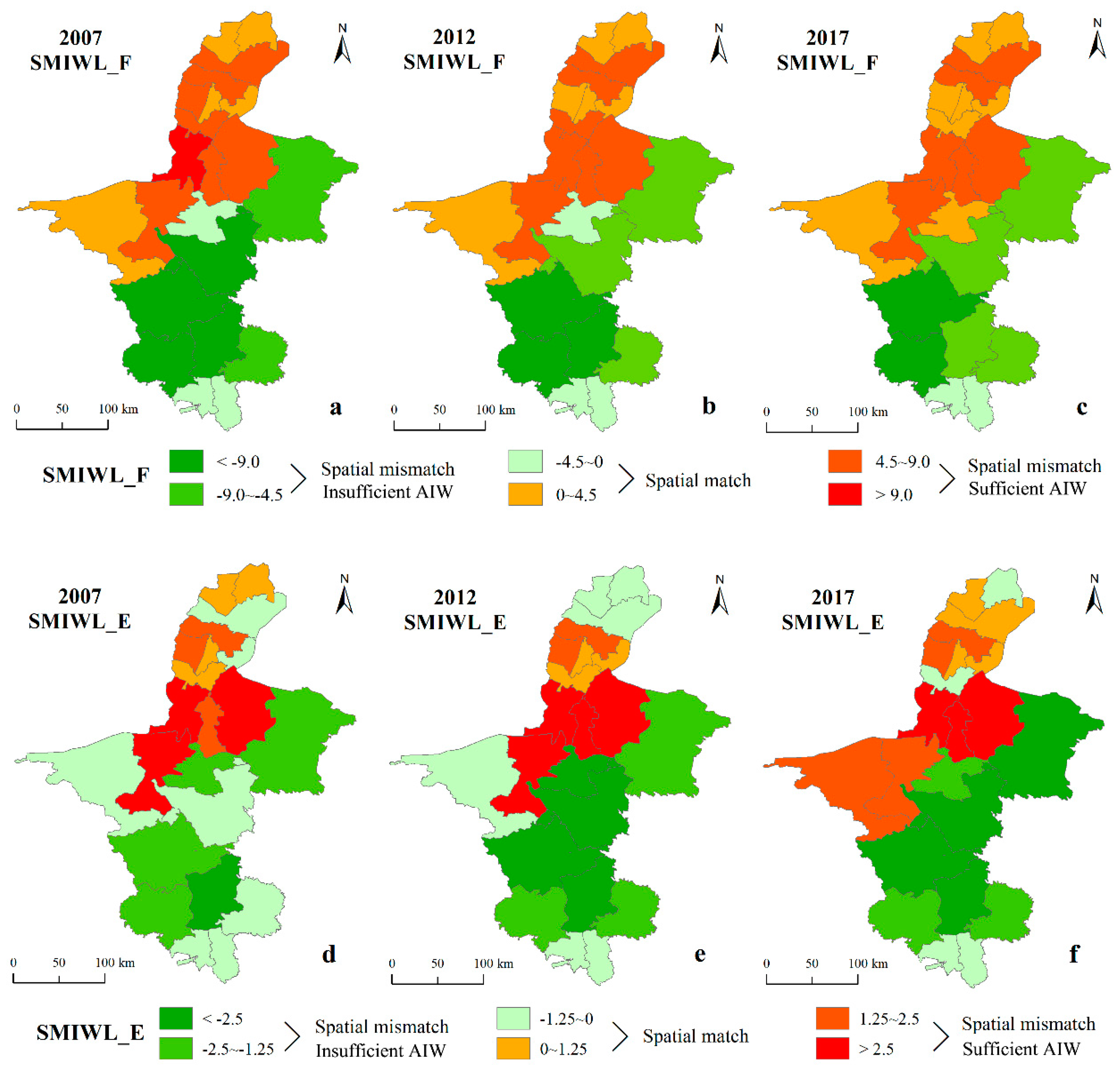
3.3.2. Spatial Mismatch Index
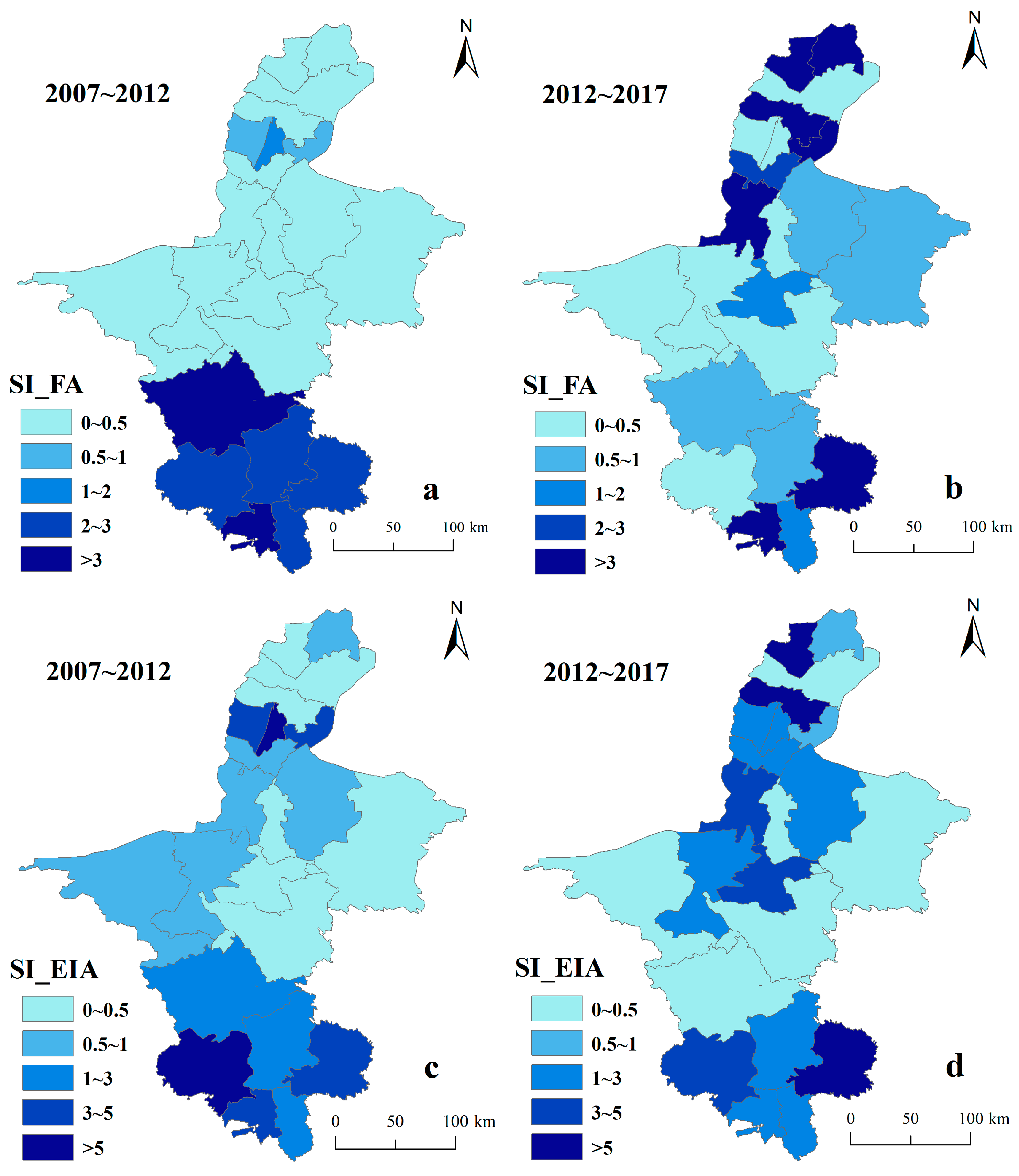
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Results
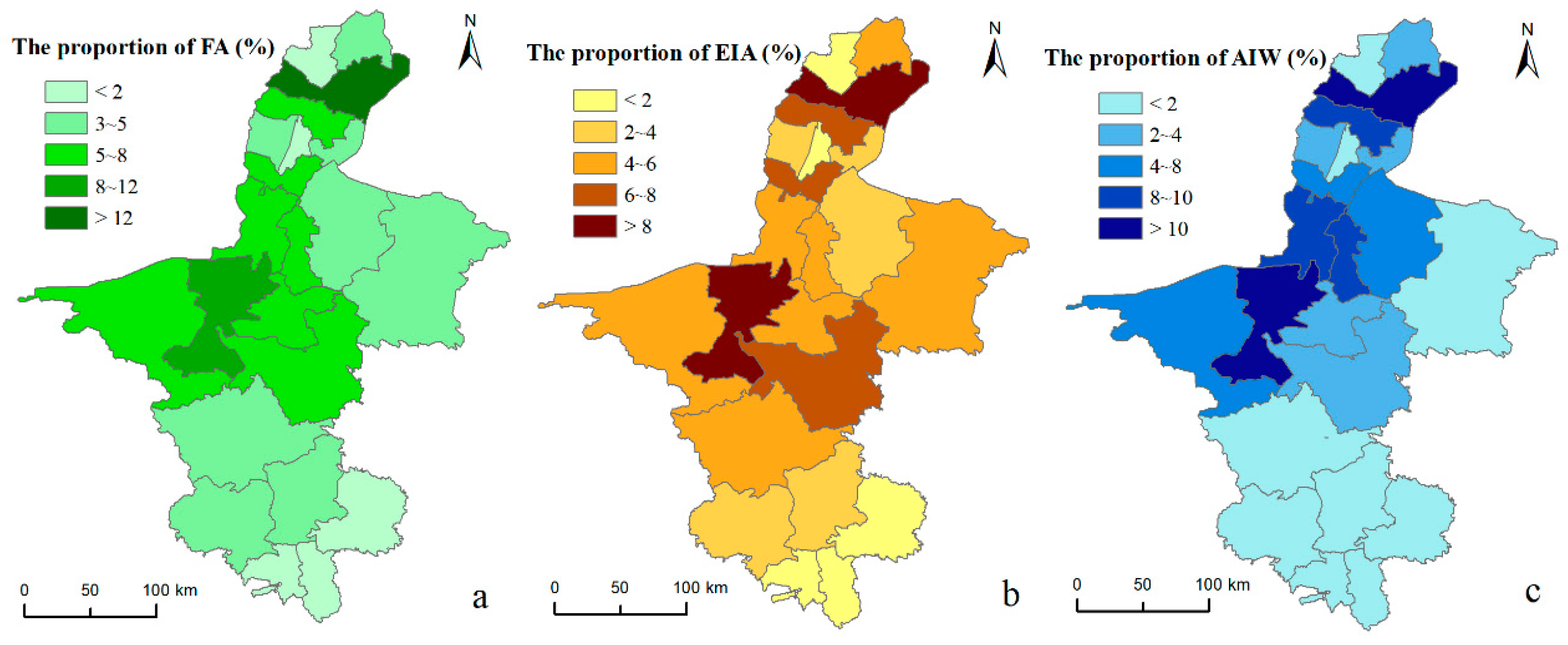
4.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Gravity Center Change of Water and Land Resources
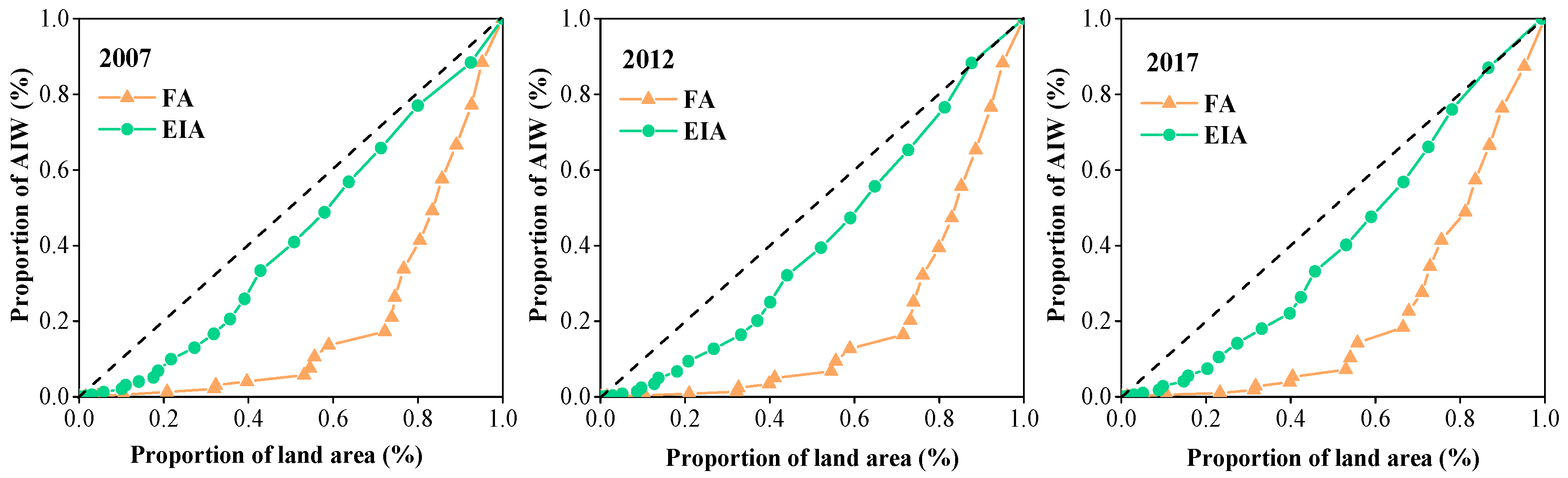
4.2. Spatial Matching Pattern between Water and Land Resources Based on the Gini Coefficient and Spatial Mismatch Index
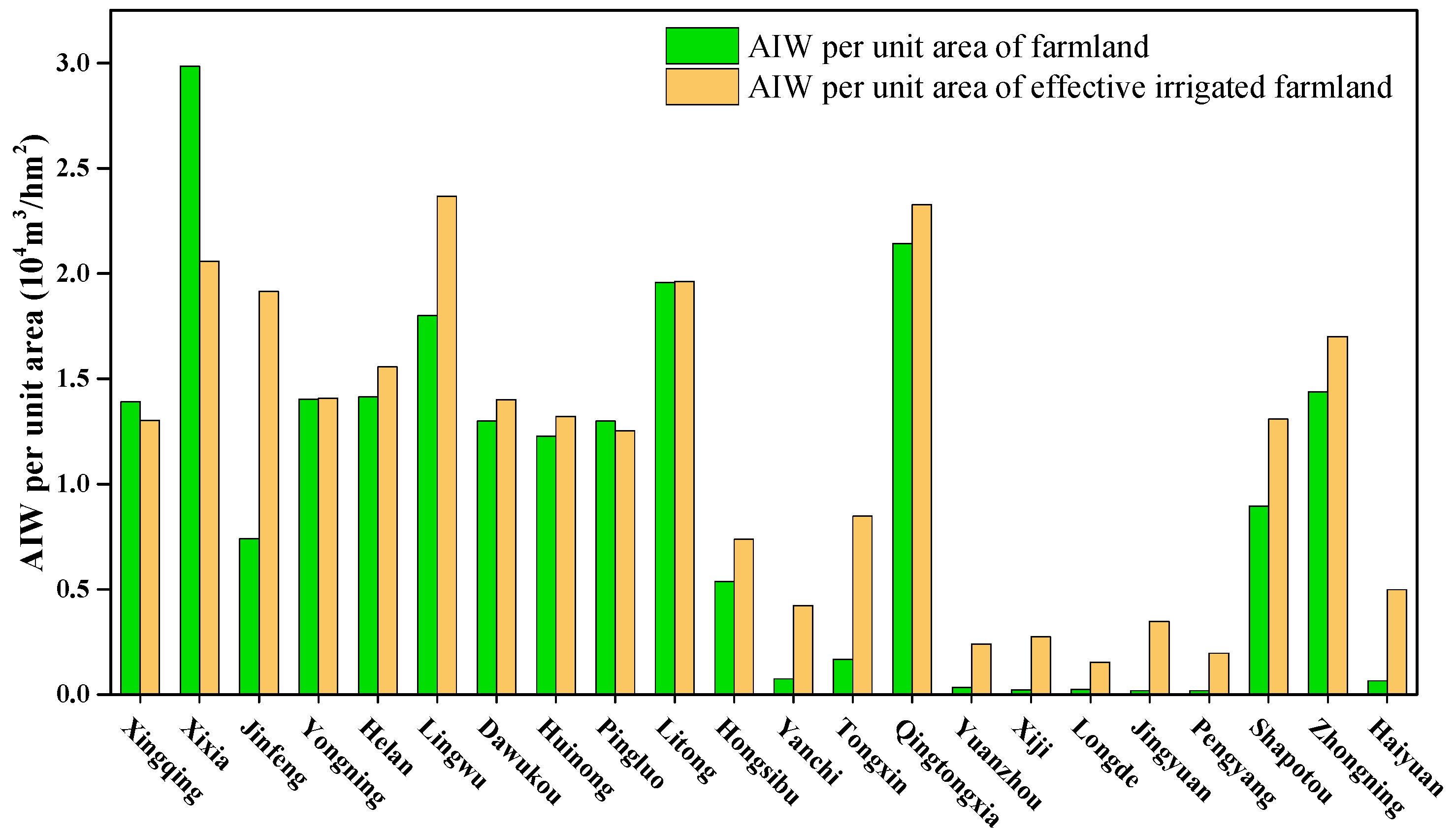
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Agricultural Irrigation Water to Land Resource
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Methods for Matching Characteristics between Water and Land Resources
5.2. Analysis and Suggestions of Spatial Matching Pattern between Water and Land Resources in Ningxia
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Land Use, Irrigation and Agricultural Practices. Available online: http://www.fao.org/economic/ess/environment/data/land-use/en/ (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Schultz, B.; Thatte, C.D.; Labhsetwar, V.K. Irrigation and drainage. Main contributors to global food production. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hejazi, M.; Tang, Q.; Vernon, C.R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Calvin, K. Global agricultural green and blue water consumption under future climate and land use changes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Groundwater resources management through the applications of simulation modeling: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taye, M.; Dyer, E.; Hirpa, F.; Charles, K. Climate Change Impact on Water Resources in the Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture: Managing Systems at Risk; Earthscan: Abingdon, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Du, X.; Castillo, C.S.Z. How does urbanization affect farmland protection? Evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2019, 145, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.Q. Study on the evaluation and management of irrigation water use efficiency for different scales in countrywide. Ph.D. Thesis, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing, China, June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yao, L.; Wei, C.; Li, C. Optimal allocation of regional water resources: From a perspective of equity–efficiency tradeoff. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2016, 109, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Domestic Water Consumption under Intermittent and Continuous Modes of Water Supply. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wu, C.J. Situation of land-water resources and analysis of sustainable food security in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 3, 270–275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, L.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The effect of inter-annual variability of consumption, production, trade and climate on crop-related green and blue water footprints and inter-regional virtual water trade: A study for China (1978–2008). Water Res. 2016, 94, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulli, M.C.; Saviori, A.; D’Odorico, P. Global land and water grabbing. PNAS 2013, 110, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, K.A.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Lo, M.; de Linage, C.; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S.C. Groundwater depletion in the Middle East from GRACE with implications for transboundary water management in the Tigris-Euphrates-Western Iran region. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Young, W. Water use in agriculture in China: Importance, challenges, and implications for policy. Water Policy 2001, 3, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.M.; Yang, Y.Z. Study on the balance of agricultural water and land resources in Ningxia Plain. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2007, 21, 60–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bekchanov, M.; Karimov, A.; Lamers, J.P.A. Impact of Water Availability on Land and Water Productivity: A Temporal and Spatial Analysis of the Case Study Region Khorezm, Uzbekistan. Water 2010, 2, 668–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Bao, H.J. Regional Gini coefficient and tis used in analyzing to balance between water and soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 17, 123–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Gan, H.; Zhang, F.G. Analysis of the Matching patterns of land and water resources in Northeast China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2006, 61, 847–854. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Jia, S.F.; Yan, J.B.; Zhu, W.B.; Liang, Y. Study on the matching pattern of water and potential arable land resources in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 2057–2066. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Fu, Q.; Li, M.; Faiz, M.A.; Khan, M.I.; Li, T.; Cui, S. Construction and application of a refined index for measuring the regional matching characteristics between water and land resources. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.Y.; Jia, L.; Yao, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.T. Agricultural water resources in China and strategic measures for its efficient utilization. Engin. Sci. 2018, 20, 9–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L. Grey Logistic Model to Predict the Effective Irrigation Area in Liaoning Province. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 641–642, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Yang, J.; Li, M. Temporal-Spatial Variation of Drought Indicated by SPI and SPEI in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1399–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, C.; Xiong, L.; Chang, Y. How can agricultural water use efficiency be promoted in China? A spatial–temporal analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2019, 145, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Song, J.; Sun, S. Utilization Characteristics and Sustainability Evaluation of Water Resources in China. Water 2018, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, L.; Salvatore, D. Shift in the world economic center of gravity from G7 to G20. J. Policy Model. 2013, 35, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Analysis of the distribution and evolution of energy supply and demand centers of gravity in China. Energy Policy 2012, 49, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, H. Variation of global fossil-energy carbon footprints based on regional net primary productivity and the gravity model. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 213, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ren, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, F. Spatial mismatch between pollutant emission and environmental quality in China—A case study of NOx. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, H.Q.; Guo, S.L. The Dynamic Evolution Track and the Coupling Mode Analysis for Economic Gravity Center and Population Gravity Center in the Contiguous Areas of Sichuan, Yunnan and Guizhou Province. Energy Procedia 2011, 13, 10052–10060. [Google Scholar]
- Gini, C. Measurement of Inequality of Income. J. Econ. Theory Econom. 1921, 31, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Allen, R.; Sun, T. Spatial mismatch in Beijing, China: Implications of job accessibility for Chinese low-wage workers. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Analysis for spatial–temporal changes of grain production and farmland resource: Evidence from Hubei Province, central China. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 207, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, S.; Ge, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, B. Analysis of the spatial mismatch of grain production and farmland resources in China based on the potential crop rotation system. Land Use Policy 2017, 60, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho-yam Lau, J. Spatial mismatch and the affordability of public transport for the poor in Singapore’s new towns. Cities 2011, 28, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.A.; Moghaddam, D.D.; Kalantar, B.; Pradhan, B.; Kisi, O. A comparative assessment of GIS-based data mining models and a novel ensemble model in groundwater well potential mapping. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Song, W.; Deng, X. Responses of Ecosystem Service to Land Use Change in Qinghai Province. Energies 2016, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehan, S.; Gitau, M.; Flanagan, D. Reliable Future Climatic Projections for Sustainable Hydro-Meteorological Assessments in the Western Lake Erie Basin. Water 2019, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.X.; Chen, Y.H.; Lei, T.J. Study on variation of cultivated land and matching of cultivated land with water resources. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2019, 50, 69–78. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, G.F.; Jiang, Z.H.; Qin, L.J. Analysis of balance between water and land resources in Tonghua region using Gini coefficient. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2012, 33, 67–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Q.L. Research on Zoning of Agricultural Water and Land Resources Utilization and Their Matching Characteristics in Arid Areas of Northwest of China Research Center for Eco-environments and Soil and Water Conservation. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Sciences & Ministry of Education, Yangling, China, June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M. Mismatch between crop water requirements and irrigation in Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y. Grain-for-green policy and its impacts on grain supply in West China. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Cropland Conversion in Response to the “Grain for Green Project” in China’s Loess Hilly Region of Yanchuan County. Remote Sens. 2013, 11, 5642–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.R.; Shang, H.Y.; Wang, C.J. Analysis of dynamic change and driving factors of cultivated land in Ningxia During the past 18 years. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2017, 38, 98–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.S. Efficient utilization of cultivated land resources in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2017, 178–184. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Li, X. China should not massively reclaim new farmland. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Miao, C.; Wu, J.; Duan, Q. Impact assessment of climate change and human activities on net runoff in the Yellow River Basin from 1951 to 2012. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Tang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Water scarcity under various socio-economic pathways and its potential effects on food production in the Yellow River basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
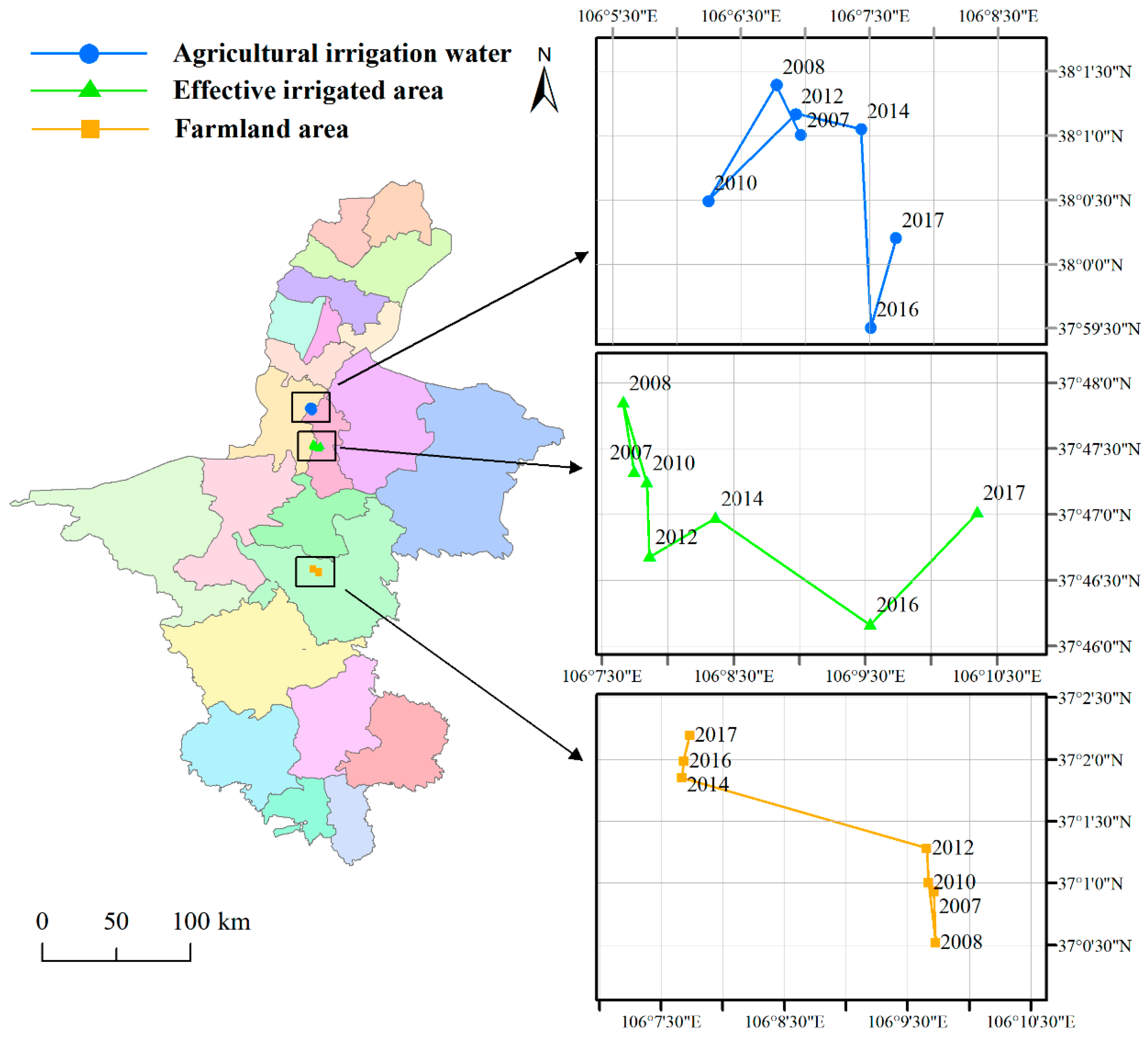
| Period (year) | Gravity Center of FA | Gravity Center of EIA | Gravity Center of AIW | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction (°) | Distance (km) | Direction (°) | Distance (km) | Direction (°) | Distance (km) | |
| 2007~2012 | 99.60 | 0.65 | −79.68 | 1.20 | 104.33 | 0.30 |
| 2012~2014 | 163.99 | 3.83 | 30.07 | 1.07 | −12.72 | 0.96 |
| 2014~2017 | 79.25 | 0.65 | 1.28 | 3.69 | −72.50 | 1.63 |
| 2007~2017 | 147.49 | 4.35 | −6.70 | 4.86 | −47.40 | 1.99 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Li, S. Spatial–Temporal Matching Characteristics between Agricultural Water and Land Resources in Ningxia, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071460
Du J, Yang Z, Wang H, Yang G, Li S. Spatial–Temporal Matching Characteristics between Agricultural Water and Land Resources in Ningxia, Northwest China. Water. 2019; 11(7):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071460
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Jie, Zhaohui Yang, Hao Wang, Guiyu Yang, and Shuoyang Li. 2019. "Spatial–Temporal Matching Characteristics between Agricultural Water and Land Resources in Ningxia, Northwest China" Water 11, no. 7: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071460
APA StyleDu, J., Yang, Z., Wang, H., Yang, G., & Li, S. (2019). Spatial–Temporal Matching Characteristics between Agricultural Water and Land Resources in Ningxia, Northwest China. Water, 11(7), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071460






