Assessment of Field Water Uniformity Distribution in a Microirrigation System Using a SCADA System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
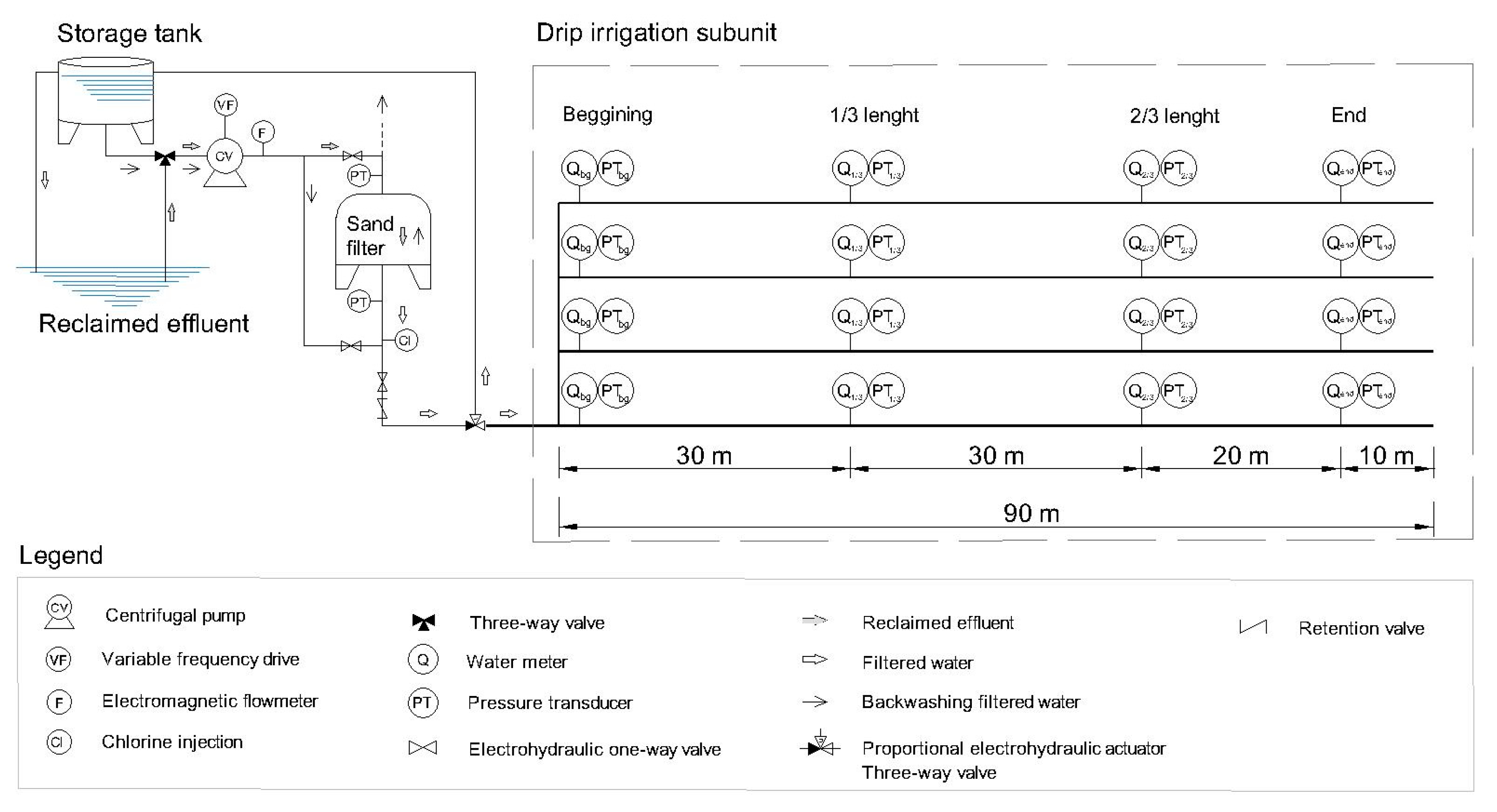
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Monitoring Equipment
2.3. SCADA System and Components
- Two modules 1769-IQ32 (Allen-Bradley, Milwaukee, WI, USA) with 32 digital inputs each having a direct current of 24 V to detect current flow from lateral water meters and pressure transducers.
- One module 1769-OB16 with 16 digital outputs to activate quality panel valves.
- Three modules 1769-IF16C with 16 analogic inputs with a range of measurement from 4 to 20 mA and a 16-bit resolution, connected to lateral water meters and pressure transducers.
- Two modules 1769-IF4I with four analogic inputs with a range of measurement from 4 to 20 mA and a 16-bit resolution, connected to quality panel transmitters.
- Two modules 1734-IB8 with eight digital inputs of direct current of 24 V to detect direct current flow from the four washing triggers of the quality panel, emergency stop, water level sensor of the catch basin, and filtered tank and chlorine tank sensor level.
- Three modules 1734-IEOB8 with eight digital outputs to activate motorized valves and pumping system.
- Three modules 1734-IE8C with eight analogic inputs with a measurable range from 4 to 20 mA and a 16-bit resolution and connected to the headboard flowmeter, quality panel water meters, and to the filter pressure transducers.
- One module 1734-OE4C with four analogic outputs with a measurable range from 4 to 20 mA and a 16-bits resolution connected to the variable frequency drive, headboard centrifugal pump, proportional valve, and the chlorine injection system.
2.4. Quality of the Wastewater
2.5. Operational Procedure and Data Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pressure Distribution across Laterals
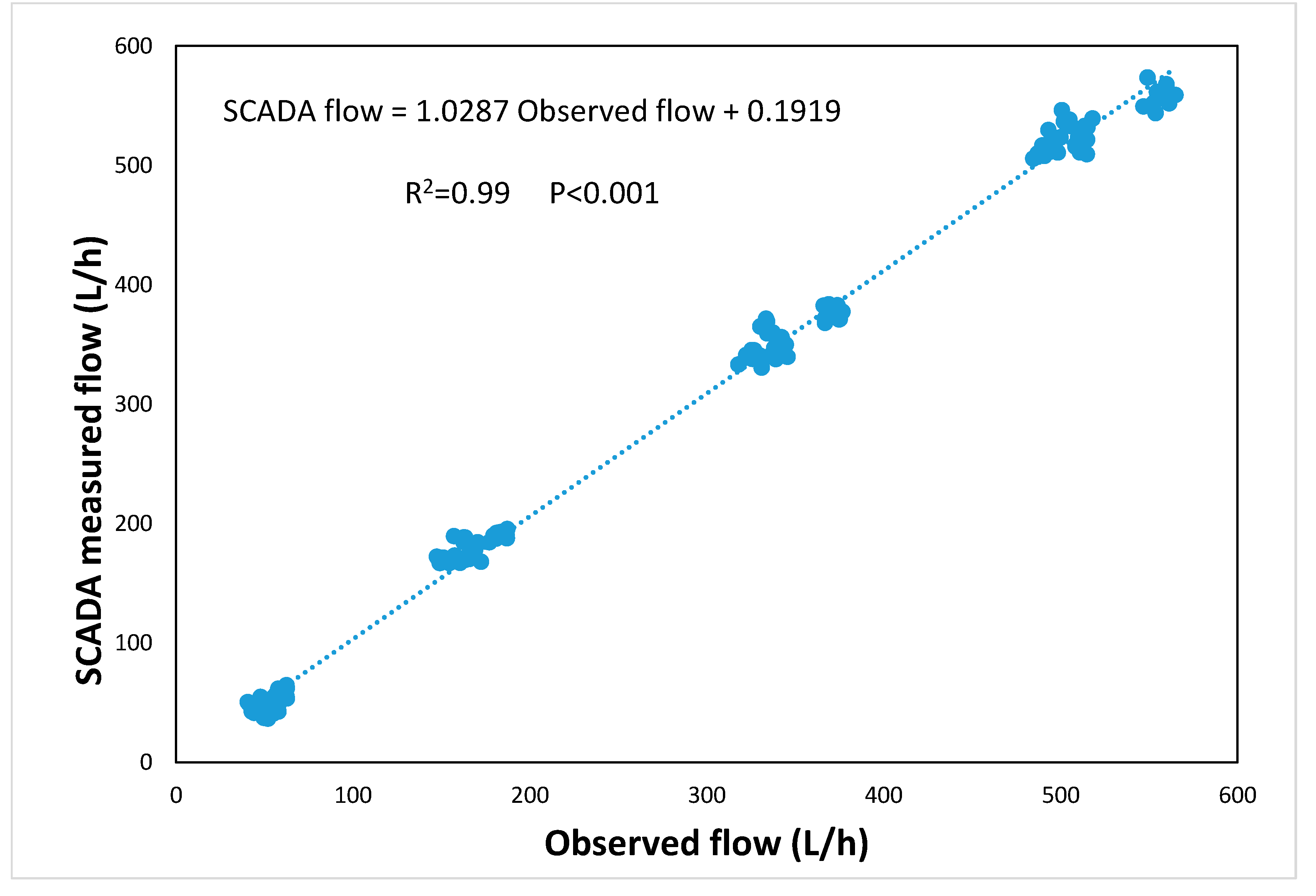
3.2. Measured SCADA Flow Distribution across Laterals
3.3. Dripline Flow Evolution throughout the Experiment
3.4. Comparison of Different Procedures for DUlq Determination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayars, J.E.; Bucks, D.A.; Lamm, F.R.; Nakayama, F.S. Introduction. In Microirrigation for Crop Production. Design, Operation and Management; Lamm, F.R., Ayars, J.E., Nakayama, F.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- ICID 2019. Sprinkler and Micro Irrigated Area. Available online: http://www.icid.org/sprinklerandmircro.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Bucks, D.A.; Nakayama, F.S.; Gilbert, R.G. Trickle irrigation water quality and preventive maintenance. Agric. Water Manag. 1979, 2, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater; World Health Organization Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T.; Burton, F.L.; Leverenz, H.L. Water Reuse: Issues, Technologies and Applications; McGraw Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Barragán, J.; Bralts, V.; Wu, I.P. Assessment of emission uniformity for microirrigation design. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 93, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.P.; Barragán, J.; Bralts, V. Field performance and evaluation. In Microirrigation for Crop Production. Design, Operation and Management; Lamm, F.R., Ayars, J.E., Nakayama, F.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 357–388. [Google Scholar]
- Ravina, I.; Paz, E.; Sofer, Z.; Marcu, A.; Shisha, A.; Sagi, G. Control of emitter clogging in drip irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Irrig. Sci. 1992, 13, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriam, J.L.; Keller, J. Farm Irrigation System Evaluation: A Guide for Management; Department of Agricultural and Irrigation Engineering, USU: Logan, UT, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeiren, L.; Jobling, G.A. Localized Irrigation; Irrigation and Drainage Paper 36; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Juana, L.; Rodríguez-Sinobas, L.; Sánchez, R.; Losada, A. Evaluation of drip irrigation: Selection of emitters and hydraulic characterization of trapezoidal units. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trooien, T.P.; Lamm, F.R.; Stone, L.R.; Alam, M.; Rogers, D.H.; Clark, G.A.; Schlegel, A.J. Subsurface drip irrigation using livestock wastewater: Dripline flow rates. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2000, 16, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Bargués, J.; Arbat, G.; Elbana, M.; Duran-Ros, M.; Barragán, J.; Ramírez de Cartagena, F.; Lamm, F.R. Effect of flushing frequency on emitter clogging in microirrigation with effluents. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madramootoo, C.A.; Morrison, J. Advances and challenges with micro-irrigation. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 62, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhamer, D.A.; Fereres, E. Irrigation scheduling of almond trees with trunk diameter sensors. Irrig. Sci. 2004, 23, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadesús, J.; Mata, M.; Marsal, J.; Girona, J. A general algorithm for automated scheduling of drip irrigation in tree crops. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 83, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Perea, R.; Fernández García, I.; Martín Arroyo, M.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Montesinos, P. Multiplatform application for precision irrigation scheduling in strawberries. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 183, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, J.G.; Martín, M.; Camacho, E.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Montesinos, P. Toward precision irrigation for intensive strawberry cultivation. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 151, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagami, A.; Hareeshvare, U.; Maheshwar, S.; Venkatachalapathy, V.S.K. Automated irrigation system for greenhouse monitoring. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 2018, 99, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Molina-Martínez, J.M.; Jiménez, M.; Pagán, F.J.; Ruiz-Canales, A. SCADA platform for regulated deficit irrigation management of almond trees. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hendricks Franssen, H.-J.; Han, X.; Jiménez-Bello, M.A.; Martínez Alzamora, F.; Vereecken, H. Evaluation of an operational real-time irrigation scheduling scheme for drip irrigated citrus fields in Picassent, Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijo, M. Design and field tuning of an upstream controlled canal network SCADA. Irrig. Drain. 2008, 57, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijo, M.; Arranja, C. Supervision and water depth automatic control of an irrigation canal. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2010, 136, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bové, J.; Puig-Bargués, J.; Arbat, G.; Duran-Ros, M.; Pujol, T.; Pujol, J.; Ramírez de Cartagena, F. Development of a new underdrain for improving the efficiency of microirrigation sand media filters. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, H. Effects of chlorination schemes on clogging in drip emitters during application of sewage effluent. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2010, 26, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Ros, M.; Puig-Bargués, J.; Arbat, G.; Barragán, J.; Ramírez de Cartagena, F. Definition of a SCADA system for a microirrigation network with effluents. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 64, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliesner, R.D. Field evaluation of trickle irrigation efficiency. In Proceedings of the ASCE Irrigation and Drainage Division Specialty Conference on Water Management for Irrigation and Drainage, Reno, NV, USA, 20–22 July 1977; pp. 382–393. [Google Scholar]





| Subunit | Filter Inlet | Filter Outlet | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Temperature | Electrical Conductivity | Dissolved Oxygen | Turbidity | Dissolved Oxygen | Turbidity | |
| (-) | (°C) | (dS/m) | (mg/L) | (FTU) | (mg/L) | (FTU) | |
| A | 7.33 ± 0.20 b | 20.61 ± 3.26 a | 2.64 ± 0.46 a | 3.27 ± 0.83 b | 6.22 ± 2.11 | 3.31 ± 0.82 b | 4.46 ± 1.24 b |
| B | 7.43 ± 0.24 a | 20.12 ± 3.49 ab | 2.46 ± 0.53 b | 3.57 ± 1.02 a | 5.82 ± 3.08 | 3.56 ± 1.04 a | 4.18 ± 1.42 c |
| C | 7.31 ± 0.22 b | 19.68 ± 3.57 b | 2.63 ± 0.44 a | 3.28 ± 1.04 b | 6.42 ± 2.77 | 3.25 ± 0.65 b | 4.89 ± 1.13 a |
| Irrigation Time | 0 h | 500 h | 1000 h | Mean ± Standard Deviation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subunit | A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| Merriam and Keller (M&K) | 98.75 | 98.66 | 98.80 | 98.77 | 98.27 | 99.12 | 99.03 | 99.04 | 98.92 | 98.82 ± 0.26 |
| SCADA | 98.94 | 98.88 | 98.70 | 99.00 | 98.31 | 99.13 | 99.13 | 98.88 | 98.90 | 98.88 ± 0.25 |
| Irrigation Subunit | Irrigation Time (h) | qr | Δqr | DUlq | ΔDUlq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 1.00 | - | 95.41 | - |
| 500 | 0.92 | 8.02 | 92.83 | 2.70 | |
| 1000 | 0.91 | 8.58 | 89.18 | 6.53 | |
| B | 0 | 1.00 | - | 93.97 | - |
| 500 | 0.94 | 5.93 | 93.07 | 0.96 | |
| 1000 | 0.92 | 8.26 | 87.88 | 6.48 | |
| C | 0 | 1.00 | - | 96.31 | - |
| 500 | 0.93 | 7.40 | 94.84 | 1.53 | |
| 1000 | 0.94 | 6.37 | 91.44 | 5.06 |
| DUlq (%) | p-Value of Regression with SCADA Procedure | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 0 h | 500 h | 1000 h | |||||||
| Subunit | A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| M&K1/2 | 95.15 | 96.28 | 97.82 | 41.37 | 82.55 | 94.74 | 28.61 | 0.00 | 33.86 | <0.05 |
| M&K2/3 | 94.85 | 96.06 | 97.67 | 66.36 | 82.13 | 95.74 | 46.57 | 33.55 | 60.89 | <0.01 |
| M&K5/6 | 96.49 | 93.60 | 97.75 | 95.02 | 93.14 | 95.08 | 85.29 | 84.81 | 92.98 | <0.01 |
| M&K20/21 | 95.57 | 95.47 | 96.76 | 92.62 | 94.40 | 96.27 | 90.23 | 90.46 | 95.96 | <0.001 |
| Observed | 95.41 | 93.97 | 96.31 | 92.83 | 93.07 | 94.84 | 89.18 | 87.88 | 91.44 | <0.01 |
| SCADA | 90.54 | 91.71 | 95.50 | 85.35 | 88.93 | 96.03 | 79.26 | 76.92 | 94.66 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solé-Torres, C.; Duran-Ros, M.; Arbat, G.; Pujol, J.; Ramírez de Cartagena, F.; Puig-Bargués, J. Assessment of Field Water Uniformity Distribution in a Microirrigation System Using a SCADA System. Water 2019, 11, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071346
Solé-Torres C, Duran-Ros M, Arbat G, Pujol J, Ramírez de Cartagena F, Puig-Bargués J. Assessment of Field Water Uniformity Distribution in a Microirrigation System Using a SCADA System. Water. 2019; 11(7):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071346
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolé-Torres, Carles, Miquel Duran-Ros, Gerard Arbat, Joan Pujol, Francisco Ramírez de Cartagena, and Jaume Puig-Bargués. 2019. "Assessment of Field Water Uniformity Distribution in a Microirrigation System Using a SCADA System" Water 11, no. 7: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071346
APA StyleSolé-Torres, C., Duran-Ros, M., Arbat, G., Pujol, J., Ramírez de Cartagena, F., & Puig-Bargués, J. (2019). Assessment of Field Water Uniformity Distribution in a Microirrigation System Using a SCADA System. Water, 11(7), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071346







