Temporal and Vertical Relations between Various Environmental Factors in the Largest Lake of Łęczna-Włodawa Lake District (Eastern Poland)
Abstract
1. Introduction
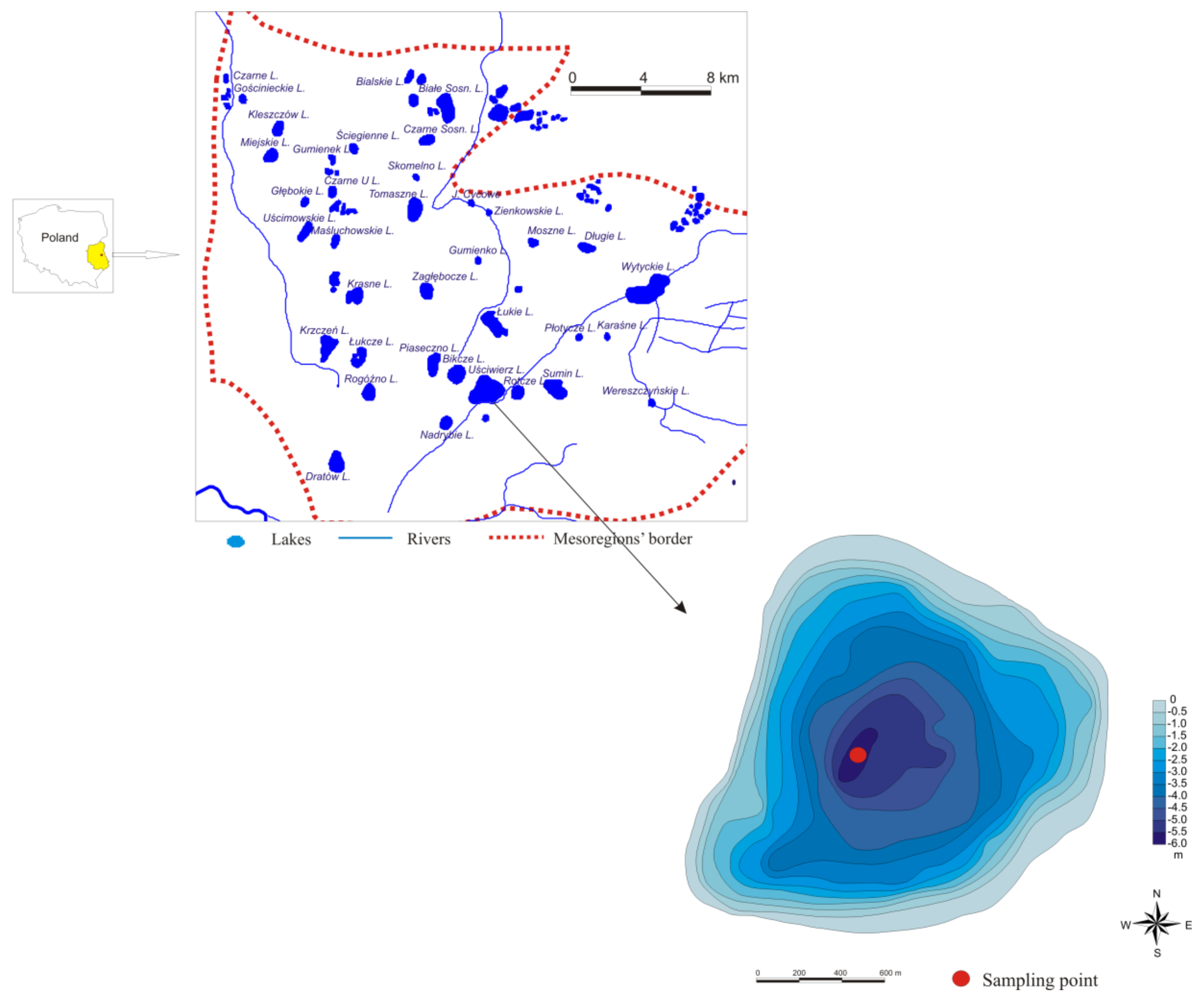
2. Study Area
3. Methods
Statistical Analyses
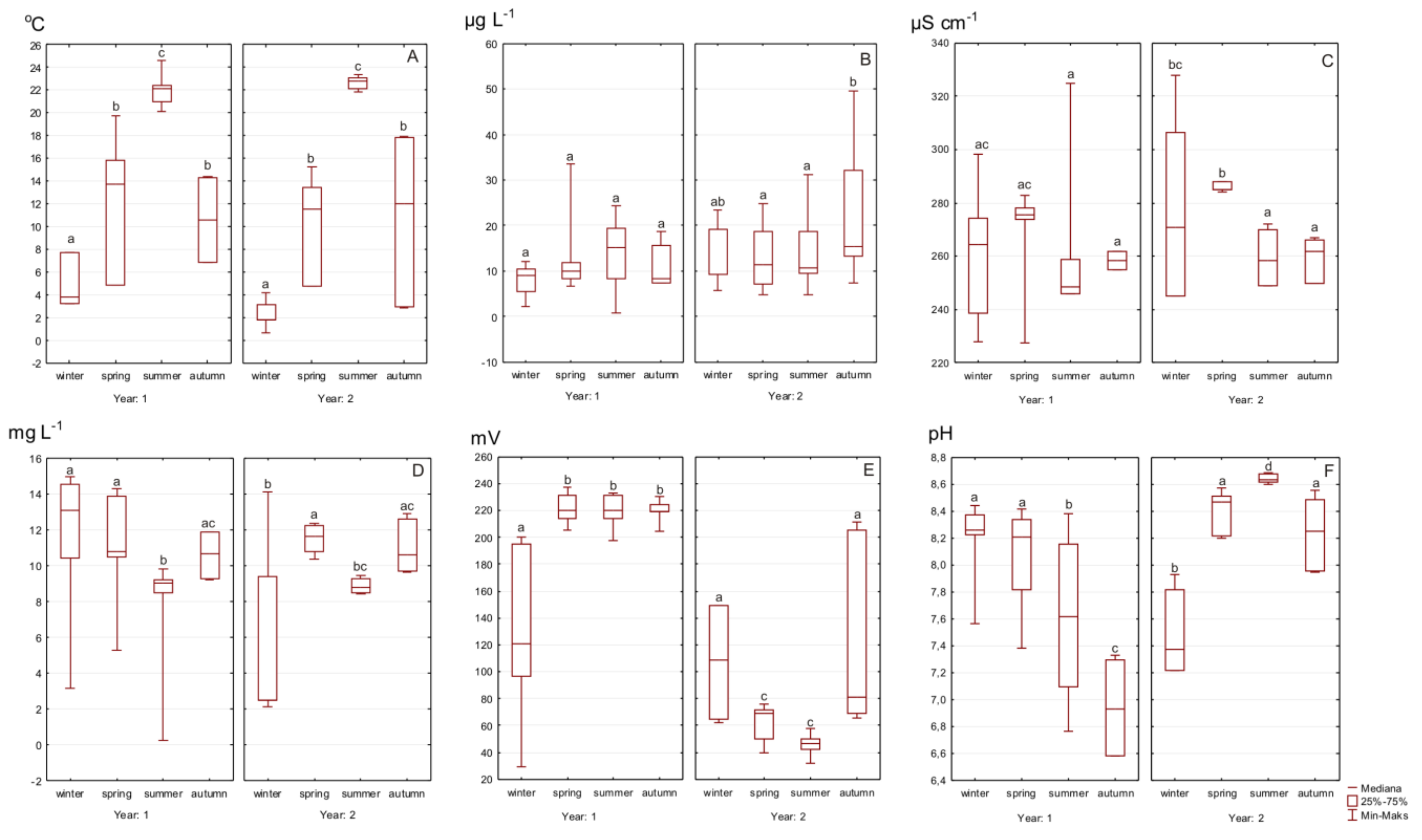
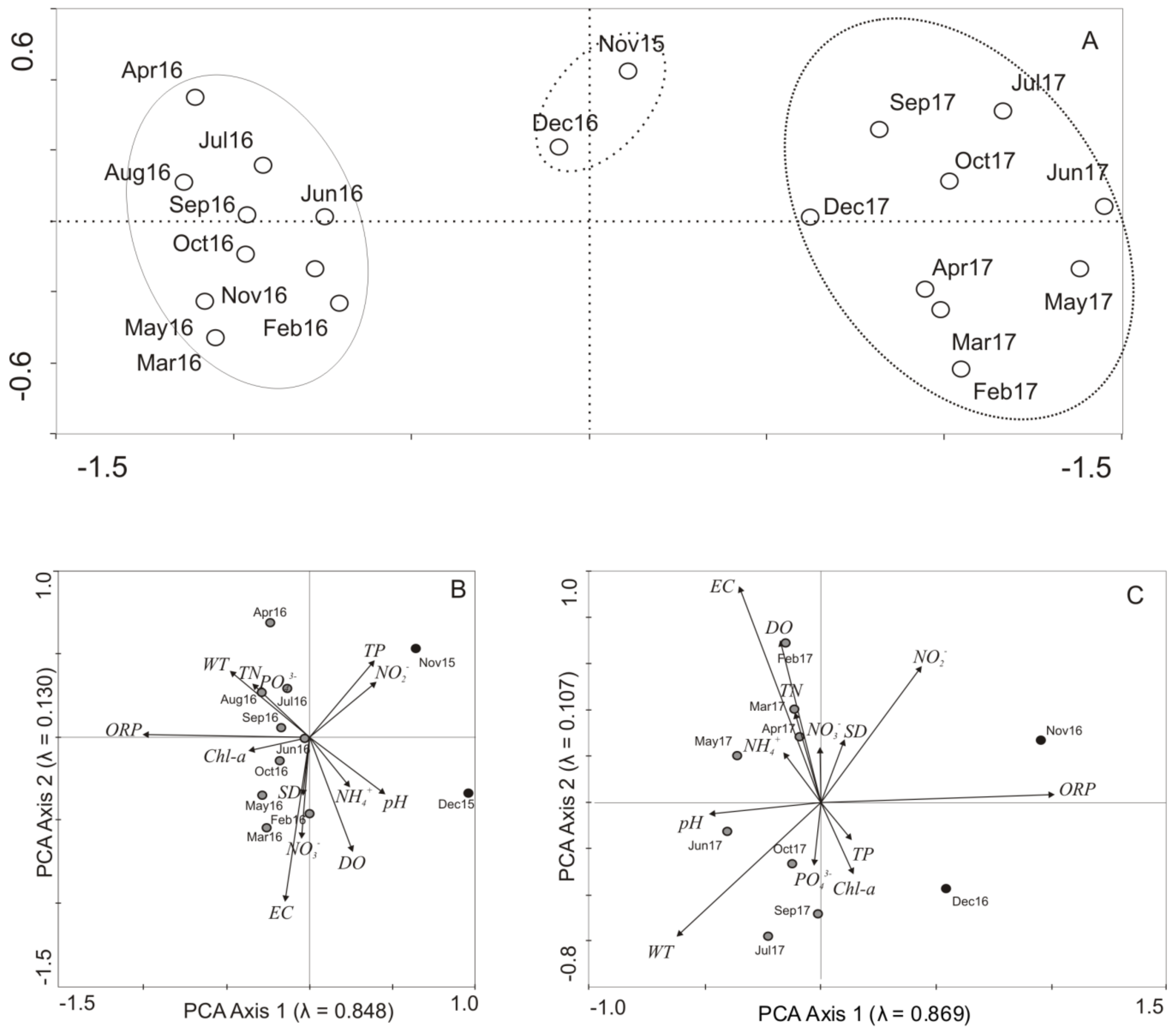
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toporowska, M.; Ferencz, B.; Dawidek, J. Impact of lake—catchment processes on phytoplankton community structure in temperate shallow lakes. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannard, A.; Planas, D.; Beisner, B.E. Macrozooplankton and the persistence of the deep chlorophyll maximum in a stratified lake. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, S.; Domaizon, I.; Anneville, O. The need for ecological monitoring of freshwaters in a changing world: A case study of Lakes Annecy, Bourget, and Geneva. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 186, 3455–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elçi, I.S. Effects of thermal stratification and mixing on reservoir water quality. Limnology 2008, 9, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, W.; Imberger, J.; Saggio, A. Biogeochemical evolution in response to physical forcing in the water column of a warm monomictic lake. Biogeochemistry 2002, 61, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.C.; Weathers, K.C.; Kratz, T.K. Networked lake science: How the global lake ecological observatory network (GLEON) works to understand, predict, and communicate lake ecosystem response to global change. Inl. Waters 2016, 6, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, F.; Korehi, H.; Mollakarami, S.; Skandari, S.; Zaferani, S.G.G.; Shashm, Z.M.C. Phytoplankton diversity and nutrients at the Jajerood River in Iran. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 9, 1787–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.L.; Kong, F.X. The distribution of phytoplankton along trophic gradients and its mediation by available light in the pelagic zone of large eutrophic lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Otify, A.M. Evaluation of the physicochemical and chlorophyll-a conditions of a subtropical aquaculture in Lake Nasser area, Egypt. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasztaleniec, A.; Kutyła, S. The ecological status of lakes in national and landscape parks: Does the location of a lake and its catchment within a protected area matter? Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Janssen, F.; Aleynik, D.; Bange, H.W.; Boltacheva, N.; Çagatay, M.N.; Dale, A.W.; Etiope, G.; Erdem, Z.; Geraga, M.; et al. Investigating hypoxia in aquatic environments: Diverse approaches to addressing a complex phenomenon. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 1215–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehrer, B.; Golmen, L.; Løvik, J.E.; Rahn, K.; Klaveness, D. Thermobaric stratification in very deep Norwegian freshwater lakes. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2013, 39, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jul-Larsen, E.; Kolding, J.; Overa, R.; Nielsen, J.R.; van Zwieten, P. Management, Co-Management or No Management? Major Dilemmas in Southern African Freshwater Fisheries; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2003; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Macuiane, M.; Hecky, R.; Guildford, S. Temporal and spatial changes in water quality in Lake Malawi/Niassa, Africa: Implications for cage aquaculture management. Oceangr. Fish. 2016, 1, 555552. [Google Scholar]
- Halstvedt, C.B.; Rohlack, T.; Andersent, T.; Skulberg, O.; Edvardsen, B. Seasonal dynamics and depth distribution of Planktothrix spp. in Lake Steinsfjorden (Norway) related to environmental factors. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Vertical distribution of cyanobacteria biomass and cyanotoxin production in the polymictic Siemianówka Dam Reservoir (eastern Poland). Arch. Pol. Fish. 2014, 22, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, J.; Wiedner, C.; Zippel, P. Factors controlling the dominance of Planktothrix agardhii and Limnothrix redekei in eutrophic shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 1997, 342, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangur, M.; Puusepp, L.; Buhvestova, O.; Haldna, M.; Kangur, K. Spatio-temporal variability of surface sediment phosphorus fractions and water phosphorus concentration in Lake Peipsi (Estonia/Russia). Est. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 62, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, H.; Mwamburi, J. Spatial variations in nutrients and other physicochemical variables in the topographically closed Lake Baringo freshwater basin (Kenya). Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2014, 19, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.Z.; Creed, I.F.; Bayley, S.E.; Devito, K.J. Interannual variability in trophic status of shallow lakes on the Boreal Plain: Is there a climate signal? Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W08443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferral, A.; Luccini, E.; Solis, V.; Frery, A.C.; Aleksinko, A.; Bernasconi, I.; Scavuzzo, C.M. In-situ and satellite monitoring of water quality of an eutrophic lake with an artificial air diffusion system. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2018, 16, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetraki-Paleolog, A. Planktonic rotifers of four dimictic lakes of Łęczyńsko-Włodawskie Lakeland (Eastern Poland). Teka Arch. Comm. Prot. Form. Nat. Environ. 2008, 5, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mieczan, T. Periphytic ciliates in littoral zone of three lakes of different trophic status. Pol. J. Ecol. 2005, 53, 489–502. [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh, N.; Nordin, R.N.; Pommen, L.W.; Swain, L.G. Guidelines for Designing and Implementing a Water Quality Monitoring Program in British Columbia. Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks; Government Publication No. 7680000554; 1998. Available online: http://www.ilmb.gov.bc.ca/ risc/pubs/aquatic/ (accessed on 27 April 2012).
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Biometris: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thomaz, S.M.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A.; Roberto, M.C.; Esteves, F.A.; Lima, A.F. Seasonal variation of some limnological features of lagoa do Guaraná, a várzea lake of the High Rio Paraná, State of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Rev. Hydrobiol. Trop. 1992, 25, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.G.M.; Menezes, N.A.; Junk, W.J. Adaptation of fish species to oxygen depletion in a central Amazonian floodplain lake. Hydrobiologia 2006, 568, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, S.M.; Takeda, A.M.; Grzybkowska, M.; Monkolski, A. Distribution of ephemeropteran nymphs associated with different stolon sections of Eichhornia azurea (Schwartz) in two floodplain lakes of the upper Paraná River (Brazil). Pol. J. Ecol. 2004, 52, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Masud, M.; Ferdous, B.; Faramarzi, J. Projected changes in hydrological variables in the agricultural region of Alberta, Canada. Water 2018, 10, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xia, J.; Wu, S.; She, D.; Zou, L. Characterizing and explaining spatio-temporal variation of water quality in a highly disturbed river by multistatistical techniques. Springer Plus 2016, 5, 117–134. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Liu, Z. Lake restoration and management in a climate change perspective: An introduction. Water 2017, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencz, B.; Toporowska, M.; Dawidek, J.; Sobolewski, W. Hydro-chemical conditions of shaping the water quality of shallow Łęczna-Włodawa Lakes (Eastern Poland). CLEAN Soil Air Water 2017, 45, 1600152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, D.D.; Lee, T.; Srinivasan, R.; Abbaspour, K.; Jeong, C.Y. Assessment of seasonal and spatial variation of surface water quality, identification of factors associated with water quality variability, and the modeling of critical nonpoint source pollution areas in an agricultural watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.G.; DeSellas, A.M.; Fletcher, R.; Heintsch, L.; Morley, A.; Nakamoto, L.; Utsumi, K. Algal blooms in Ontario, Canada: Increases in reports since 1994. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2011, 27, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.S.; Bais, V.S. Seasonal variation of temperature, alkalinity and dissolved oxygen in the Sagar Lake. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2006, 15, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Sumaiya, K.M. Chlorophyll-a and dissolved oxygen concentration of lake Varhala. Pharm. Chem. 2016, 8, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Nyarko, E.K.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M. Modelling daily water temperature from air temperature for the Missouri River. Peer J. 2018, 6, e4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanescu, G.; Stoleriu, C. The seasonal variation of temperature, pH and dissolved oxygen concentration in Lake Rosu, Romania. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2013, 42, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.R.A.; Thomaz, S.M. Variação temporal de fatores limnológicos em ambientes da planície de inundação do alto rio Paraná (PR/MS-Brasil). Acta Scientiarum. Biol. Sci. 2004, 26, 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Catalan, J.; Donato Rondón, J.C. Perspectives for an integrated understanding of tropical and temperate high-mountain lakes. J. Limnol. 2016, 75, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillin, G.; Lepparanta, M.; Terzhevik, A.; Granin, N.; Bernhardt, J.; Engelhardt, C.; Efremova, T.; Golosov, S.; Palshin, N.; Sherstyankin, P.; et al. Physics of seasonally ice-covered lakes: A review. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 659–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obertegger, U.; Obrador, B.; Flaim, G. Dissolved oxygen dynamics under ice: Three winters of high-frequency data from Lake Tovel, Italy. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 7234–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.M.; Lucas, M.C.; Wilson, R. The effect of high pH on ion balance, nitrogen excretion and behaviour in freshwater fish from an eutrophic lake: A laboratory and field study. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 73, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindasamy, C.; Kannan, L.; Azariah, J. Seasonal variation in physico-chemical properties and primary production in the coastal water biotopes of Coromandel coast, India. J. Environ. Biol. 2000, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Araoye, P.A. The seasonal variation of pH and dissolved oxygen (DO2) concentration in Asa lake IIorin, Nigeria. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2009, 4, 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- Laudon, H.; Westling, O.; Bishop, K. Cause of pH decline in stream water during spring melt runoff in northern Sweden. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 1888–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanescu, G.; Michu-Pintilie, A.; Trifanov, C.; Stoleriu, C.C. The variations of physico-chemical parameters during summer in Lake Eurenciuk from the Danube Delta (Romania). Limnol. Rev. 2018, 18, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heini, A.; Puustinen, I.; Tikka, M.; Jokiniemi, A.; Leppäranta, M.; Arvola, L. Strong dependence between phytoplankton and water chemistry in a large temperate lake: Spatial and temporal perspective. Hydrobiologia 2014, 731, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencz, B.; Dawidek, J.; Toporowska, M. Hydrochemical versus biological conditions of the functioning of three shallow lakes in Łeczna-Włodawa. Water Environ Res. 2014, 86, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudet, V.; Revil, A.; Rizzo, E.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Bégassat, P. Groundwater redox conditions and conductivity in a contaminant plume from geoelectrical investigations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.W.; Ye, X.Y. Relationship between phytoplankton and environment factors in Lake Hongfeng. J. Environ. Biol. 2013, 34, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.M.; Jadhav, M.J.; Ustad, I.R. Physical analysis of Triveni Lake water of Amravati district in [MS] India. Biosci. Discov. 2012, 3, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Robarts, R.D.; Waiser, M.J.; Arts, M.T.; Evans, M.S. Seasonal and diel changes of dissolved oxygen in a hypertrophic prairie lake. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2005, 10, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.R.A.; Thomaz, S.M.; Carvalho, P.; Gomes, L.C. Modeling chlorophyll-a and dissolved oxygen concentration in tropical floodplain lakes (Parana’ River, Brazil). Braz. J. Biol. 2009, 69, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.B.; Lei, K.; Meng, W.; Fu, G.; Yan, W.J. Temporal and spatial changes in nutrients and chlorophyll-a in a shallow lake, Lake Chaohu, China: An 11-year investigation. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| WT (°C) | EC (µS cm−1) | pH | ORP (mV) | Chl-a (µg L−1) | DO (mg L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study period | ||||||
| SL | 2.9–24.6 ± 8.1 | 228–275 ± 13.5 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 92.3–230.2 ± 39.3 | 3.3–33.6 ± 6.3 | 8.8–15.0 ± 2.0 |
| 0.5 | 2.9–24.6 ± 7.9 | 227.7–279.3 ± 16 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 96.8–231.7 ± 40.3 | 3.7–31.5 ± 5.8 | 9.0–14.5 ± 1.9 |
| 1.0 | 2.9–24.5 ± 7.9 | 227.6–275.4 ± 15.4 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 96.4–233.1 ± 41.2 | 3.2–29.1 ± 5.6 | 9–14.8 ± 1.9 |
| 1.5 | 2.9–24.4 ± 7.8 | 227.7–275.4 ± 15.1 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 94.8–232.6 ± 42 | 3.1–32.1 ± 6.1 | 8.8–14.7 ± 1.9 |
| 2.0 | 2.9–24.1 ± 7.8 | 234.8–277.8 ± 12.9 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 96.1–233.7 ± 42.2 | 2.8–41.4 ± 8.0 | 8.8–14.6 ± 1.9 |
| 2.5 | 2.9–23.8 ± 7.7 | 236.6–277.9 ± 12.6 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 96.3–235.5 ± 42.6 | 2.1–40.5 ± 7.9 | 8.5–14.7 ± 1.9 |
| 3.0 | 2.9–22.3 ± 7.3 | 238.1–277.9 ± 12.2 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 96.4–236.8 ± 42.9 | 6.1–43.8 ± 8.4 | 7.5–14.6 ± 2.1 |
| 3.5 | 2.9–22.1 ± 7.1 | 238.9–325.0 ± 21.2 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 96.4–237.6 ± 43.6 | 0.9–49.5 ± 9.7 | 1.5–14.8 ± 3.4 |
| 4.0 | 2.9–21.9 ± 7.0 | 240.1–325.0 ± 22.6 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 28.9–237.6 ± 58.4 | 2.1–41.7 ± 8.7 | 0.3–14.5 ± 3.9 |
| 4.5 | 2.9–21.8 ± 7.0 | 247.0–323.0 ± 21.2 | 6.6–8.4 ± 0.6 | 37.2–231.3 ± 62.0 | 0.9–45.3 ± 10.1 | 0.2–13.0 ± 4.2 |
| 5.0 | 4.0–21.8 ± 6.6 | 247.0–327 ± 30.3 | 7.3–8.2 ± 0.3 | 51.2–231.5 ± 72.9 | 3.9–46.5 ± 25.7 | 0.2–9.1 ± 3.1 |
| Spring | ||||||
| WC | 4.78–19.75 ± 5 | 277.6–288 ± 12.73 | 7.4–8.6 ± 0.3 | 39.7–237.6 ± 80.5 | 4.8–33.6 ± 5.8 | 5.3–14.3 ± 1.6 |
| Summer | ||||||
| WC | 20.1–24.6 ± 1.1 | 246–325 ± 18.8 | 6.8–8.7 ± 0.6 | 31.8–233.5 ± 85.9 | 0.9–31.2 ± 7.1 | 0.2–9.8 ± 2.2 |
| Autumn | ||||||
| WC | 2.9–17.9 ± 5.02 | 228–267 ± 10.5 | 6.6–8.6 ± 0.7 | 65.4–230.9 ± 65.8 | 2.1–49.5 ± 11.7 | 9.2–12.9 ± 1.2 |
| Winter | ||||||
| WC | 0.6–4.21 ± 0.93 | 245–328 ± 24.5 | 7.2–8.4 ± 0.5 | 28.9–200.6 ± 53.9 | 5.7–23.4 ± 4.9 | 2.1–15 ± 5.3 |
| Water Year 2016 | Water Year 2017 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | EC | pH | ORP | DO | Chl-a | WT | EC | pH | ORP | DO | Chl-a | |
| WT | 1.00 | −0.15 | −0.18 | 0.53 | −0.64 | 0.36 | 1.00 | −0.33 | 0.75 | −0.63 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| EC | 1.00 | 0.28 | 0.05 | −0.17 | −0.11 | 1.00 | 0.02 | −0.30 | 0.36 | −0.22 | ||
| pH | 1.00 | −0.35 | 0.23 | −0.22 | 1.00 | −0.44 | 0.61 | −0.24 | ||||
| ORP | 1.00 | −0.09 | 0.34 | 1.00 | −0.09 | 0.00 | ||||||
| DO | 1.00 | −0.25 | 1.00 | −0.10 | ||||||||
| Chl-a | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferencz, B.; Toporowska, M.; Dawidek, J. Temporal and Vertical Relations between Various Environmental Factors in the Largest Lake of Łęczna-Włodawa Lake District (Eastern Poland). Water 2019, 11, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061263
Ferencz B, Toporowska M, Dawidek J. Temporal and Vertical Relations between Various Environmental Factors in the Largest Lake of Łęczna-Włodawa Lake District (Eastern Poland). Water. 2019; 11(6):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061263
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerencz, Beata, Magdalena Toporowska, and Jarosław Dawidek. 2019. "Temporal and Vertical Relations between Various Environmental Factors in the Largest Lake of Łęczna-Włodawa Lake District (Eastern Poland)" Water 11, no. 6: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061263
APA StyleFerencz, B., Toporowska, M., & Dawidek, J. (2019). Temporal and Vertical Relations between Various Environmental Factors in the Largest Lake of Łęczna-Włodawa Lake District (Eastern Poland). Water, 11(6), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061263







