Abstract
Among several components of watershed prioritization, morphometric parameters are considered to be essential elements for appropriate water resource planning and management. In the current study, nine hilly sub-watersheds are prioritized using novel hybrid model based on morphometric variables analysis at Bino Watershed (BW) located in the upper Ramganga basin, India. The proposed model is based on the hybridization of principal component analysis (PCA) with weighted-sum approach (WSA), presenting a single-frame methodology (PCWSA) for sub-watershed prioritization. The prioritization process was conducted based on several morphometric parameters including linear, areal, and shape. The PCA was performed to identify the significant correlated factor-loading matrix whereas WSA was established to provide the weights for the morphometric parameters and fix their priority ranking (PR) to be categorized based on compound factor value. The findings showed that 37.81% of total area is under highly susceptible zone sub-watersheds (SW-6 and SW-7). This is verifying the necessity for appropriate soil and water conservation measures for the area. The proposed hybrid methodology demonstrated a reliable approach for water resource planning and management, agriculture, and irrigation activities in the study region.
1. Introduction
For proper identification and prioritization of areas prone to erosion in any catchment, the morphometric variables of the area are very important [1]. As per Youssef et al. [2], hydrological investigations in a watershed are mainly performed using the morphometric variables of the watershed (linear, areal, and shape); they are also important for studies on the conservation and management of water resources. Furthermore, Bagherzadeh [3] highlighted the importance of soil erosion information when formulating appropriate programs for land and water management to ensure sustainable agricultural development. Thus, policy formulation and decision-making for sustaining an environment improving land productivity must be based on accurate erosion assessment information. It is, therefore, essential to check soil erosion risk in the regions.
Over recent years various researchers have used morphometric variables (i.e., linear, areal, and shape) to prioritize watersheds using the application of remote sensing (RS) and geographical information system (GIS) by ordinary methods [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. For instance, Shrimali et al. [4] applied the feasibility of RS and GIS techniques to contextually investigate the Sukhana lake catchment in the Shiwalik hills to prioritize the soil erosion zones. Morphometric characteristics are the feasible entity to understand the hydrological behavior of the watershed. Balasubramanian et al. [8] prioritized 29 sub-watersheds (SW) of lower Bhavani basin, located in Tamil Nadu, India, based on morphometric (linear, areal, shape, and relief) parameters. The morphometric were computed in ArcGIS environment using IRS-LISS III, and Cartosat digital elevation model (DEM) data. They found that the 8 SW were highly prone to soil erosion. Sahu et al. [10] prioritized three sub-basins of the Asna river, located in the Marathwada region of Maharashtra, India, based on geomorphometric parameters computed using geospatial tools. They found sub-basin-1 under high category of soil erosion, sub-basin-2 under low category, and sub-basin-3 under moderate category. Mangan et al. [13] studied the morphometry of the Nanganji River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India, using RS and GIS. The inter-relationship between the morphometric parameters was done using a correlation matrix. Pandey et al. [14] studied the Karso watershed in Hazaribagh, Jharkhand for morphological characteristics and recommended the use of GIS for watershed management. The authors suggested different thematic maps integrated with morphometric variables to determine the suitable areas for citing water and soil conservation measures. In India, several studies on watershed prioritization have been performed based on morphometric analysis using the potential of RS and GIS techniques [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
The motivation to explore new reliable methodologies for watershed prioritization has been always the preserve of a hydrologist. A few works have been recently reported on watershed prioritization using principal component analysis (PCA) and weighted-sum approach (WSA) [23,24,25]. For instance, the use of weighted-sum approach for SWs prioritization was conducted within the Pimpalgaon Ujjaini watershed, India [1]. The authors used a quantitative analysis of morphometric variables based on RS and GIS techniques. PCA was applied based on linear, areal, and shape variables of 8 SW at the Kanhiya Nala watershed, a tributary of Tons River, Madhya Pradesh, India [26], to categorize the used parameters under various components using correlation analysis. The results revealed that some parameters have strong correlation with the components; however, hypsometric integral and texture ratio did not indicate any correlation with the components. PCA-based RS and GIS techniques were used by [23], for morphometric analysis of SW prioritization in the Shakkar River Catchment, India. Meshram and Sharma [27] reduced the dimensionality of data by identifying the significant correlations between the linear, areal, and shape variables based on PCA for SW prioritization in the Mohgaon River catchment, India. Singh and Singh [28] used WSA for prioritization of the Suketi watershed located in the lower Himachal Himalayan region. They reported the WSA to be a more dynamic and effective method in comparison to the traditional methods of watershed prioritization. Malik et al. [22] prioritized 14 hilly SWs of the Naula watershed situated in the upper Ramganga river basin, Uttarakhand State, India, using WSA based on linear, areal, and shape morphometric variables.
Past studies reported that the SW prioritization was carried out based on compound factor values, which are calculated by taking a simple arithmetic average of preliminary priority ranks for final prioritization of SW. In previously used methods, equal importance was given to all the morphometric parameters, which may not be true in reality [1]. In identification of highly susceptible areas for risk assessment and management, the importance of all the input constraints may not be equal as each SW has its own characteristics. In recent years, a few separate studies have been conducted using weighted-sum analysis for watershed prioritization based on morphometric parameters [1,22,28,29,30], as well as principal component analysis for watershed prioritization [23,25,26,27]. The recent implementation of the hybridization between the PCA and WSA demonstrated an optimistic strategy for SW prioritization. Therefore, the current study is devoted to prioritize nine hilly SW of the BW based on morphometric parameters. The modeling procedure is established using morphometric parameters including: (i) linear: mean stream length, basin area and perimeter, stream length, basin length, bifurcation ratio, and stream order; (ii) areal: texture ratio, drainage density, mean length of overland flow, and stream frequency; and (iii) shape: compactness coefficient, form factor, circularity ratio, and elongation ratio. The main objective of doing this research was to provide a reliable methodology for SW prioritization at the BW, contributing to multiple water resource engineering disciplines. This is highly essential for such a region where the reliable watershed management and sustainability is very much needed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study and Data Collection
The study was conducted on the Bino watershed (BW) in the Ramganga river basin, Uttarakhand State, India which was located between 29°47′06″ to 30°02′06″ N latitudes and 79°6′14.4″ to 79°17′16.8″ E longitudes (Figure 1). Figure 1 shows six land use and land cover (LULC) classes as dense forest (26.24%), open forest (69.49%), rainfed-agriculture land (27.29%), irrigated agriculture land (2.19%), waste land (19.76%) and water body (1.17%), respectively. The Bino watershed has a total surface area of 295 km2 with altitude ranging from 798 m to 2911 m above mean sea level. The area has a mean annual rainfall of 931.3 mm; a significant portion of rainfall in the area comes from the South-West monsoon which commences around mid-June and runs to September. The maximum daily mean temperature is experienced from May to June and the lowest daily mean temperature is experienced from December to January. The geological structure of BW consists of mica, schist, quarzitic sandstone, granitic-gneiss, and some calcareous dolomite rocks. The soil in these watersheds is mainly formed from coarse-textured quartzite although shale and silty-phyllites contribute to the process of pedogenesis in some areas of watershed at middle elevation. The lower surfaces of the watershed are mostly composed of colluvial deposits with fined-grained mica sand; however, the upper surfaces are mainly composed of boulders of metamorphic rocks and well-rounded pebbles. The soil texture varies from gravelly loamy sand to silt loam.
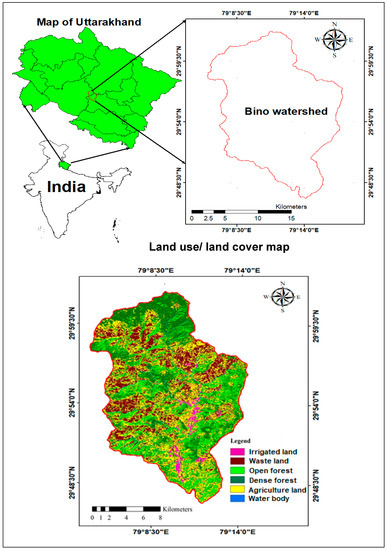
Figure 1.
Location and LULC map of Bino watershed in Uttarakhand State.
The boundary of BW was marked by using Topo-sheet Nos. 53-N/4, 53-N/8, 53-O/1 and 53-O/5 of Survey of India (SOI) on a scale of 1:50,000 for delineation of watershed. Topo-sheets were scanned (tiff format) and geo-referenced to frame complete image of the region using mosaic operation. The mosaicked image was imported in QGIS and the BW boundary was digitized by monitoring the ridge points from the contours. The outlet position was set at the confluence point of BW with the Ramganga river. The DEM of BW and its SW with drainage network pattern created in ArcGIS 10.2 environment is depicted in Figure 2. The DEM was downloaded from https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov; it is Advanced Space-borne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) resolution is 30 m × 30 m. The BW was divided into nine SW, and codification was done in increasing order from the outlet at BW to the furthest distant sub-watershed as SW-1 to SW-9. The stream order of nine SW of BW is depicted in Figure 3.
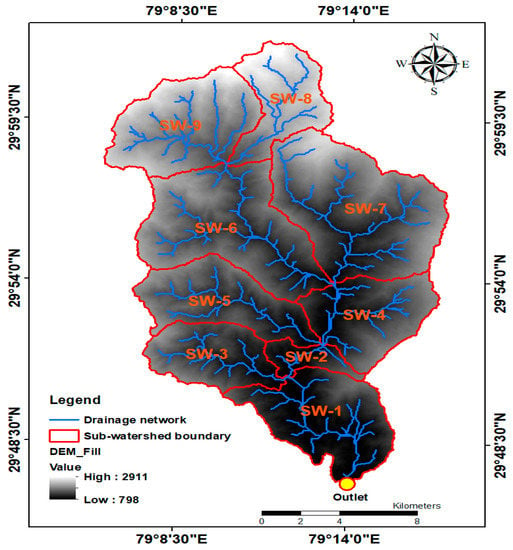
Figure 2.
DEM and drainage network pattern of nine sub-watersheds of BW.
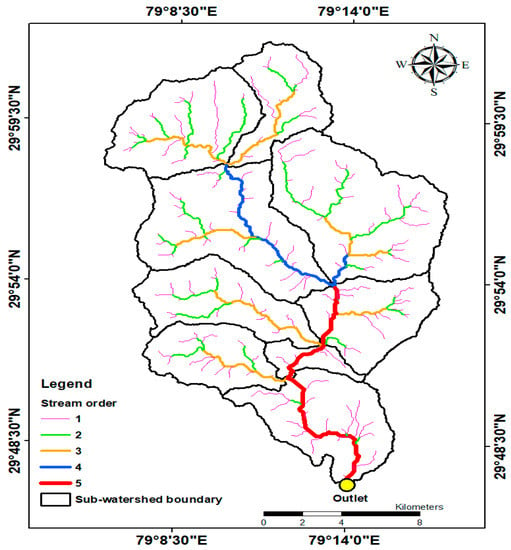
Figure 3.
Stream order map of the nine sub-watersheds of BW.
2.2. Morphometric Analysis and Assign Preliminary Priority Rank to the SWs
In this study, prioritization of nine SW of BW was done based on linear, areal, and morphometric variables. Linear parameters include basin area (A), basin perimeter (P), stream order (u), stream length (), mean stream length (), basin length (), and bifurcation ratio and their computational formulae are given in Table 1 [31,32,33]. Areal parameters include drainage density (), stream frequency (), texture ratio (), mean length of overland flow () their computational formulae are given in Table 2 [31,34]. Shape parameters include form factor , circularity ratio , compactness coefficient and elongation ratio their computational formulae are given in Table 3 [32,33,34,35]. The more value of , more will be the soil erosion [33]. Rai et al. [36] suggested that the value of > 0.7854 indicates that basin is circular, while lower value indicates elongated basin. The smaller value of drainage density indicates that overland flow predominates in the basin, while higher value of indicates that channel flow predominates in the basin. 37. Suresh [37] stated that a lower value of indicates highly permeable sub-surface material and land covered with dense vegetation of low relief, while a higher value of drainage density indicates impermeable sub-surface material with spare vegetation and high relief. Kumar et al. [38] stated that the drainage density indicates channel development and closeness of the channel spacing in the watershed. The value of generally ranges from 0.2 to 0.8. A high value (>0.5) indicates more circularity and more homogeneity in the geological material, while a low value (<0.5) indicates elongated shape of the watershed. In general, the value of is always ≥1. The value of ranges from 0.4 to 1.0 or ≤1.0 for a wide range of climatic and geologic conditions. The value of approximately 1.0 indicates a region of very low relief, while that of 0.4 to 0.8 indicates a region of very high relief and steep ground slope. The , also called drainage texture, is defined as total number of stream segments of all orders to the perimeter of the basin (Horton, 1945). Smith [39] classified the into five different classes of textures: (i) very coarse (<2); (ii) coarse (2 to 4); (iii) moderate (4 to 6); (d) fine (6 to 8); and (e) very fine (>8).

Table 1.
Linear morphometric variables computation formulae with references.

Table 2.
Areal morphometric variables computation formulae with references.

Table 3.
Shape morphometric variables computation formulae with references.
The assignment of the preliminary priority rank (PPR) of 9 SW was performed using a liner , areal (), and shape () morphometric variables. The linear and areal morphometric parameters have direct relationship to the soil erodibility; higher value of these parameters indicates more erodibility potential. Thus, the largest value of linear and areal parameters was assigned rank 1 (highest priority), the next highest value was assigned rank = 2, and so on for all the SW [5,16]. The shape morphometric parameters have inverse relationship to the soil erodibility; lower value indicates more erodibility potential. Thus, the lowest value of shape parameters was assigned rank 1, and the next-lowest was assigned rank 2, and so on for all the SW [5,16]. When the linear, areal, and shape morphometric parameters of two sub-watersheds have a similar value, an equal rank was assigned to such SW [22,40].
2.3. Principal Component Analysis and Weighted-Sum Approach
A hybrid approach combining the PCA and the WSA is suggested in this study as described below.
2.3.1. Principal Component Analysis
Principal component (PC) is a multivariate method used to reduce the dimensionality in a data set and calculates new orthogonal variables with the descending order of effectiveness [41,42]. In this study, eigenvalues and eigenvectors are estimated using a characteristic equation. Correlation or covariance matrix of the available inputs (variables) was calculated and used for this aim.
Firstly, PC was applied on linear, areal, and shape morphometric variables to compute the correlation matrix and to obtain PCs and to get the most important variables. Here, first factor-loading (FL) and the rotated FL matrices were used [23,27]. Let us assume variables X where each has n observed values, and p number of PCs may be represented in the matrix notation as:
where Z and X are the n × p matrices and A indicates coefficient matrix with p × p dimension, jth PC is generally expressed as:
where is an n × 1 (column) vector; and is an p × 1 (column) vector of coefficients. The total variance of X is expressed by the sum of the variances of the p individual X variables. The matrix of variance-covariance X can be represented by Ʃ, a p × p coefficient matrix . In practical applications, the Ʃ is calculated by the sample covariance matrix C:
where is the transpose of the standardized X variables. The value of each element of covariance matrix C is:
The procedure starts with maximizing the variance of all the PCs (starting with first PC onwards). Extending the results from first PC to all PCs, the s are computed from the roots of;
where s are the eigenvalues (characteristics roots) of the matrix C; and I is the identity matrix (p × p). The PCA is principally related to the eigenvalues of the sample matrix of covariance or correlation. Finally, the results from principal component analysis can be generalized as;
where D is the diagonal matrix with elements of eigenvalues of covariance matrix C. The correlation between the ith row of X variables and jth PC is provided as
where r is the correlation coefficient; is the correlation of X variables in ith row and jth PCss; is the covariance of X variables in ith row and jth PCs; is the variance of jth PCs; is the vector coefficient of ith row and jth PCs; is the eigenvalues of jth PCs or covariance matrix (C); i = 1, 2, …, n; and j = 1, 2, …, p (number of observations). Value of r greater than 0.90 indicates strong correlation, r between 0.75 and 0.90 indicates good correlation, and r between 0.60 and 0.75 indicates moderate correlation [26]. To reduce the dimensionality of various PCs and identify physically significant variables, factor analysis is proposed as follows.
ATCA = D
Factor analysis is used to find out the components (or factors) which are profoundly identified with at least one of the X variables; however, not to the others and thus a set of factors (smaller in number compared to the original variables) are discovered by considering most of the variation in the data array. The basic relationship in factor analysis is:
where is the ith variables standardized with zero mean and unity variance; the FLs are , j = 1, 2, …, m (−1 < < 1); is the mutually uncorrelated common factors with unit variance and zero mean; and is a component particular to the ith variable, which has zero mean and is uncorrelated with the other components. It pursues that:
The sum of the squares of FLs and the second term on the right-hand side with no relationship with the common factors, are expressed as communality and specificity (uniqueness), individually, of the variables. Additionally, it can be effortlessly checked by:
In this manner, the relationship between the variables is identified by comparing FLs. If the last term in Equation (8) is ignored as it is related to the particular or special factors, and just the common factors are considered, the connection between the factors or components and X variables is written as:
where F is factor score matrix with n × p dimension; X is an observation matrix with n × p dimension and it is standardized for every p variable (as in PCA); and H includes the coefficients of factor scores (p × p matrix). For F to be orthogonal, it can be written as:
where A is characterized by Equation (1); and indicates the diagonal matrix in which the non-zero components are the reciprocals of the square roots of the eigenvalues of the C matrix expressed by Equation (3). Hence, from Equations (11) and (12):
Hence, using Equations (3) and (6), this simplifies to:
Consequently, demonstrating the orthogonality of F. The PCs are incorporated using Equations (1) and (11) as follows:
As a result of this relationship, which essentially includes a set of p constants, the correlations between the X variables and the F factors are the equivalent as those between the X variables and the Z PCs. It pursues Equation (7) and this correlation matrix can be written as:
where is the diagonal matrix in which the non-zero elements are the square roots of the eigenvalues of the C matrix. The R matrix provides the correlations between the PCs (columns) and the standardized X variables (rows) is occasionally defined by the FL matrix.
Considering the correspondence between the F factors and the Z PCs (Equation (15)), the orthogonal rotation has an impact on the PCs (with changing the relationships with the X variables) and the corresponding factors are the equivalent. We may accordingly explore changes to the PCs. Thus, a comparison is possible with the unrotated components. The rotation ought to be such that getting important physical information from the subsequent components are possible. Thus, using Equations (1) and (12) and expression , the original PCs can be composed as:
The orthogonal rotation will change R to RP (where P is orthogonal, i.e., PTP = I). Thus, the rotated components are given as:
In the PC FL matrix, eigenvalues indicate how well each of the identified factors fit the data from all the morphometric variables on all the principal components. Eigenvalues greater than one indicates significant PC loading. In this study, principal component analysis was performed using SPSS 22.0 software. More details about the PCA can be found from [43].
2.3.2. Weighted-Sum Approach
The weighted-sum analysis was applied to significant morphometric variables which were identification using PCA, and compound factor (CF) value was calculated for final priority ranking and their related category. The mathematical expression for CF computation is written as [1,22,28,29,30]:
where CF = compound factor; PPRMP = preliminary priority rank of significant morphometric parameter identified using PCA; and WSMP = weight of significant morphometric parameter obtained using cross-correlation analysis, and computed as:
CF = PPRSMP × WSMP
In this research, the final priority rank to the nine SW of BW was assigned based on CF value in such a way that the lowest-value CF was assigned priority rank 1, next-lowest value was assigned priority rank 2, and so on for all the SWs. In this study, weighted-sum approach was performed with Microsoft Excel. Figure 4 demonstrates the flowchart of applied methodology used in this study for SW prioritization of the BW.
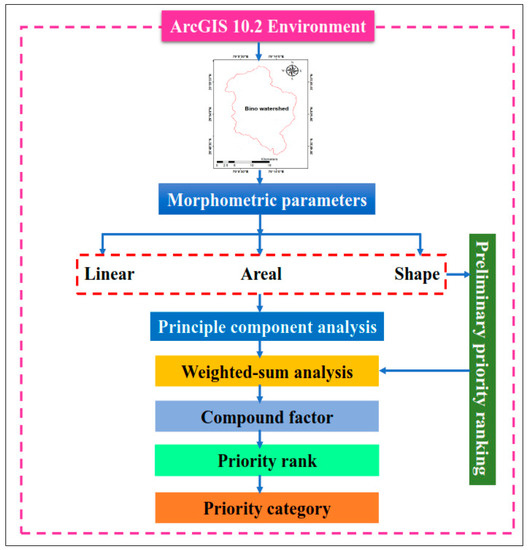
Figure 4.
Working flow chart of nine sub-watershed prioritization of BW.
3. Application Results and Analysis
The morphometric analysis was conducted using RS and GIS for 9 SW of BW to assess the characteristics and properties of the drainage basins. In this study, first linear (A, P, u, Lu, , Lb and Rb), areal (Dd, Fs, Rt and Lom), and shape (Ff, Rc, Cc and Re) morphometric parameters of nine SW of BW was computed in the ArcGIS environment and their quantitative values are given in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively. After morphometric analysis, the PPR were assigned (based on direct and inverse relationship concept) to nine SW as given in Table 6. After PPR, the PCA was applied for reducing the dimensionality of data (i.e., linear, areal, and shape morphometric variables) by identifying the significant morphometric variables based on correlations and FL matrix for reducing. After PCA, the weighted-sum analysis was performed on significant morphometric variables for CF valve computation, and finally assigned priority rank and category to the nine SWs based on CF value.

Table 4.
Linear morphometric variables of nine sub-watersheds of BW.

Table 5.
Linear, areal, and shape variables of nine sub-watersheds of BW.

Table 6.
PPR of nine sub-watersheds based on linear, areal, and shape variables.
Table 5 reveals that the bifurcation ratio varies from 1.619 (SW-5) to 3.476 (SW-1). The value of drainage density of SW (Table 5) varies from 0.695 km/km2 (SW-7) to 1.759 km/km2 (SW-2). The low value of drainage density for SW-7 indicates highly permeable sub-surface under vegetative cover with low relief, whereas a higher value of drainage density for SW-2 indicates a well-developed efficient drainage network with impermeable sub-surface materials with less vegetative cover and high relief. The value of stream frequency of sub-watersheds varies from 0.421 km−2 (SW-2) to 0.617 km−2 (SW-6). A low value of stream frequency indicates low runoff and a higher value indicates more runoff. The value of texture ratio varies from 0.176 km−1 (SW-2) to 0.854 km−1 (SW-7). Accordingly, all SW fall in the very coarse category of drainage texture. The value of mean length of overland flow of 9 SW varies from 0.284 km to 0.719 km in the watershed. Table 5 reveals that the form factor varies from 0.164 to 0.524 indicating elongated shape with lower peak flow for longer duration. The value of circularity ratio for sub-watersheds varies from 0.311 to 0.534 indicating that SW-4, SW-7, and SW-9 have circular shape, while SW-1, SW-2, SW-3, SW-5, SW-6, and SW-8 have elongated shape. The compactness coefficient ranges from 1.358 to 1.778. A high value (>1) of compactness coefficient indicates more compact SWs. The elongation ratio ranges from 0.457 to 0.817, which indicates that all the SWs are of high relief and steep ground slope. Preliminary priority ranking of SWs based on linear, areal and shape parameters of SWs is given in Table 6.
3.1. Principal Component Analysis of Morphometric Variables
The PCA was used to get inter-correlation matrix, first FL, and rotated FL matrices through orthogonal transformation. The results of inter-correlation analysis among linear, areal, and shape morphometric variables are given in Table 7. It is observed from the table that a strong correlation (r > 0.9) exists between and ; between and ; between and ; between and ; between and ; and between and . Though good correlation (r > 0.75) does not exist between the variables, a moderate correlation (r > 0.60) exists between and ; between and ; between and ; between and ; and between and . It was observed from Table 8 that the first three components have eigenvalue greater than 1 and together account for about 93.414% of the total variance in the BW. At this stage, it is too difficult to categorize the variables into components and add physical significance. Therefore, the unrotated and rotated first FL matrices of correlation matrix were then obtained using principal component analysis.

Table 7.
Correlation matrix between linear, areal, and shape morphometric variables of nine sub-watersheds of BW.

Table 8.
Total variance explained for BW.
The first FL (unrotated) matrix of linear, areal, and shape morphometric variables are given in Table 9, which indicates that the first component (PC-1) was strongly correlated with , , , and , and in good correlation with , , and . The second component (PC-2) has no strong, good, and moderate correlation with the morphometric variables. The third component (PC-3) is moderately correlated with and . It was observed from the analysis that some components (PC-1 and PC-3) are strongly, well, and moderately correlated with the morphometric variables, whereas some components (PC-2) do not have any correlation with other morphometric variables. Hence, in this case, it is hard to obtain a physically important component. Therefore, the first FL (unrotated) matrix should be rotated to achieve better correlation.

Table 9.
Unrotated factor-loading matrix of morphometric variables.
The rotated FL matrix of first FL (rotated) matrix is given in Table 10, which reveals that the first component (PC-1) is strongly correlated with , , and , and it has a good correlation with which could be named as a stage-form component. The second component (PC-2) is strongly correlated with , well correlated with , and moderately correlated with , and it could be named as a relief-density component. The third component (PC-3) has a good correlation with , and it is moderately correlated with , and might be named as organization-process component. It was observed from the rotated FL matrix analysis that the most important morphometric variables are stream frequency (), mean length of overland flow (), and form factor (). Finally, these morphometric variables are taken for WSA and prioritization of SW.

Table 10.
Rotated factor-loading matrix of morphometric variables.
3.2. Weighted-Sum Analysis of Significant Morphometric Variables
To prioritize nine SW of BW, 3 significant morphometric variables (, and ) were considered. The cross-correlation between the 3 variables was performed as shown in Table 11 while CF was used as a factor to determine the priority rank (PR) of the 9 SW using Equation (19) as presented in Table 12. The calculation of the weight values assigned to each morphometric parameter was done by using the grand total of correlations to divide each variables’ sum of correlation coefficient (Table 11). A model for the assessment of the final priority ranking was built by assigning weights to different variables. The CF computation for SW prioritization was done thus:

Table 11.
Cross-correlation matrix of , and variables of nine sub-watersheds of BW.

Table 12.
Final priority rank of nine sub-watersheds based on CF value.
3.3. Prioritization of SW Using PCWSA
For the final priority ranking, it was ensured that the lower CF value was assigned rank 1 while the next lower got rank 2, and so on for the rest of the nine SW (Table 12). As Table 12 clearly shows, the SW-6 assigned PR as 1, SW-7 assigned PR as 2, SW-4 assigned PR as 3, SW-3 assigned PR as 4, SW-5 assigned PR as 5, SW-1 assigned PR as 6, SW-8 assigned PR as 7, SW-9 assigned PR as 8, and SW-2 assigned PR as 9. Also, Figure 5 illustrates the final priority rank map of nine SW of BW under observation. Table 13 shows the priority category of nine SW of BW based on CF value. The nine SW have been grouped into the five-priority category [1,22]: (i) very high (1.918 to ≤ 3.161); (ii) high (3.161 to ≤ 4.403); (iii) medium (4.403 to ≤ 5.646); (iv) low (5.646 to ≤ 6.888); and (v) very low >> 6.888 (Table 13). Table 13 clearly shows the sub-watersheds SW-6 and SW-7 under very high category, SW-4 under high category, SW-3 and SW-5 under medium, SW-1, SW-8, and SW-9 under low category, and SW-2 under very low category. Figure 6 is the final priority map of nine SW, which demonstrates the percentage area under very high (37.81%), high (9.53%), medium (17.73%), low (32.52%), and very low (2.41%) categories, respectively.
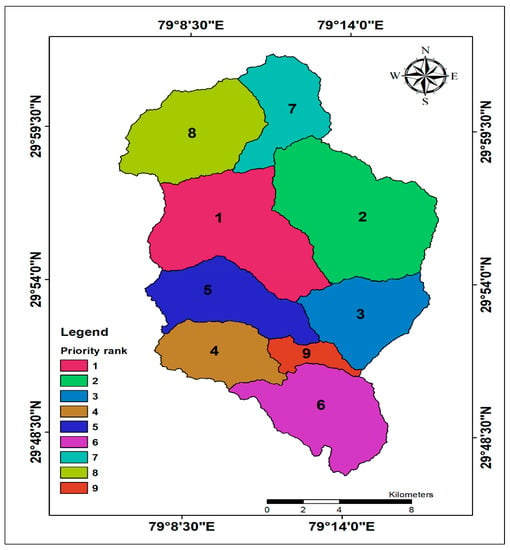
Figure 5.
Map of final priority rank of nine sub-watersheds of BW.

Table 13.
Priority category of nine sub-watersheds based on CF value [1,22].
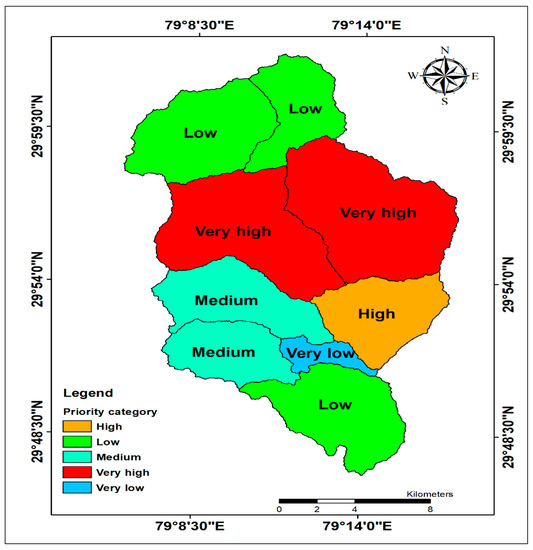
Figure 6.
Map of final priority category of nine sub-watersheds of BW.
4. Discussion
Watershed prioritization is a procedure of positioning diverse watersheds in a way in which they will be taken up for treatment through soil and water conservation measures. In organizing watershed parts, the principal goal is to examine the intensity of the issue in each SW on similar principles to the extent. In this research, the feasibility of a hybrid approach i.e., principal component analysis and weighted-sum approach (PCWSA), was evaluated for prioritization of the nine SW of BW located in the Upper Ramganga River catchment, Uttarakhand, India. The PCWSA approach has been formulated by integrating morphometric parameters with PCA and WSA in a single frame. The morphometric parameters (linear, areal, and shape) of nine SW was calculated using RS and GIS, and PPR was assigned. The dimensionality of data was reduced using PCA, and the significant morphometric parameters were identified based on PCA analysis. After the identification of significant morphometric parameters, the WSA was applied for computation of CF value, and a final priority and category was assigned to these nine SW.
Over the past decade, throughout the world, a number of studies have been conducted by researchers on watershed prioritization based on morphometric parameters using a simple average method [5,18], principal component analysis [25,26,27], and weighted-sum approach [1,22,28,29,30]. Gajbhiye et al. [5] used simple average method for prioritizing erosion-prone area of 14 SWs of the Manot River catchment, Madhya Pradesh, India, based on morphometric (linear, areal, and shape) parameters. They found SW 13 was more prone to soil erosion and required immediate adaptation of soil conservation measures. Sharma et al. [26] applied PCA on 13 dimensionless geomorphic parameters of 8 SWs of the Kanhiya Nala watershed, Madhya Pradesh, India, to group the parameters under different components based on significant correlations. They found that the texture ratio and hypsometric integral do not show correlation with any of the components. Kadam [29] used WSA for morphometric analysis of four SWs of the Shivganga watershed, Maharashtra, India, for determining the plant growth potential, and they found that 13.64% to 45.40% of total area fall under good potential growth zone. In general, the morphological parameters-based prioritization of a watershed is in good agreement with the geological field investigations carried out during the field work. Thus, the proposed methodology for watershed prioritization is a feasible approach to identify the susceptibility or risk assessment priority zones for better decision-making in the study area. However, there is still room for future research where other ecology and socio-economic perspectives could be cooperative for producing more reliable modeling strategies that give more insightful visions on watershed prioritization.
5. Conclusions
Prioritization of SW is an essential task for the development and management of watersheds on a sustainable basis. In this research, RS and GIS were used for morphometric (linear, areal, and shape) parameter characterization. The combination of PCWSA was successfully applied for watershed prioritization of nine SW of BW. The study revealed that the sub-watersheds SW-6 and SW-7 fall into very high vulnerability or susceptible zones. Hence, the top priority is assigned to these, followed by SW-4, SW-3, SW-5, SW-1, SW-8, SW-9, and SW-2, respectively. Such studies assist decision-makers in recognizing priority SW which require fast adaptation of appropriate soil and water conservation practices in the study region. Integration of geospatial tools with statistical methods in single topology resulted in PCWSA as one of the viable and significant techniques, particularly over the data hungry prioritization approaches. Also, the proposed hybrid approach offers dynamic, efficacious, and sustainable results over the traditional or ordinary watershed prioritization methods by considering the equal worth of several morphometric parameters in complex way. This information can be used in development, implementation, and adaptation of the best planning and management practices at micro-level to conserve the available natural resources in which to assist the water resource managers and policymakers in better decision-making in the data-scarce area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.; Formal analysis, A.M. and Z.M.Y.; Investigation, O.K. and Z.M.Y.; Software, O.K.; Supervision, A.K.; Validation, Z.M.Y.; Writing—original draft, A.M.; Writing–review & editing, D.P.K., O.K., S.Q.S., N.A.-A. and Z.M.Y.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aher, P.; Adinarayana, J.; Gorantiwar, S. Quantification of morphometric characterization and prioritization for management planning in semi-arid tropics of India: A remote sensing and GIS approach. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Hassan, A.M. Flash flood risk estimation along the St. Katherine road, southern Sinai, Egypt using GIS based morphometry and satellite imagery. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, A. Estimation of soil losses by USLE model using GIS at Mashhad plain, Northeast of Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrimali, S.S.; Aggarwal, S.P.; Samra, J.S. Prioritizing erosion-prone areas in hills using remote sensing and GIS — a case study of the Sukhna Lake catchment, Northern India. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2001, 3, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Pandey, A. Prioritizing erosion-prone area through morphometric analysis: An RS and GIS perspective. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 4, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, R.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, M.; Yadav, K.K.; Mittal, H.K. Catchment delineation and morphometric analysis using geographical information system. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhan, Y.; Anaba, O. A Remote Sensing and GIS Approach for Prioritization of Wadi Shueib Mini-Watersheds (Central Jordan) Based on Morphometric and Soil Erosion Susceptibility Analysis. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, A.; Duraisamy, K.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Krishnaraj, S.; Yatheendradasan, R.K. Prioritization of subwatersheds based on quantitative morphometric analysis in lower Bhavani basin, Tamil Nadu, India using DEM and GIS techniques. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, P.P.; Nigam, G.K.; Singh, S.K.; Thakur, S. Morphometric based prioritization of watershed for groundwater potential of Mula river basin, Maharashtra, India. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2018, 2, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, U.; Panaskar, D.; Wagh, V.; Mukate, S. An extraction, analysis, and prioritization of Asna river sub-basins, based on geomorphometric parameters using geospatial tools. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Sajjad, H.; Husain, I. Morphometric Parameters-Based Prioritization of Sub-watersheds Using Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process: A Case Study of Lower Barpani Watershed, India. Nat. Resour. Res. 2018, 27, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pardeshi, S.D. Morphometric analysis of Vaitarna and Ulhas river basins, Maharashtra, India: Using geospatial techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, P.; Haq, M.A.; Baral, P. Morphometric analysis of watershed using remote sensing and GIS—a case study of Nanganji River Basin in Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Chowdary, V.M.; Mal, B.C. Morphological analysis and watershed management using geographic information system. Hydrol. J. 2004, 24, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Gupta, V.P.; Moharana, P.C. Watershed prioritization using remote sensing and geographical information system: A case study from Guhiya, India. J. Arid Environ. 2001, 49, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, A.K.; Dhiman, S.D. Morphometric analysis and prioritization of miniwatersheds in Mohr watershed, Gujarat using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2007, 35, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D. Identification of Erosion Prone Areas by Morphometric Analysis Using GIS. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 2014, 95, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, H.; Kumar, A.; Reddy, C.P.; Malik, A. Geomorphologic parameters based prioritization of hilly sub-watersheds using remote sensing and geographical information system. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 17, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, A.; Raj, N.J. Drainage morphometric analysis for assessing form and processes of the watersheds of Pachamalai hills and its adjoinings, Central Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Rajeev, R.; Chandel, S.; Narayan, V.; Prafull, M. Hydrological inferences through morphometric analysis of lower Kosi river basin of India for water resource management based on remote sensing data. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, R.; Bhagat, V. Multi-Criteria Watershed Prioritization of Kas Basin in Maharashtra India: AHP and Influence Approaches. Hydrospatial Anal. 2018, 1, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Kumar, A.; Kandpal, H. Morphometric analysis and prioritization of sub-watersheds in a hilly watershed using weighted sum approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.G.; Sharma, S.K. Prioritization of watershed through morphometric parameters: A PCA-based approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 7, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, M.; Sadeghi, S.H. Sub-watershed prioritization based on sediment yield using game theory. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, Y.; Anbar, A.; Al-Shaikh, N.; Mousa, R. Prioritization of Semi-Arid Agricultural Watershed Using Morphometric and Principal Component Analysis, Remote Sensing, and GIS Techniques, the Zerqa River Watershed, Northern Jordan. Agric. Sci. 2017, 8, 113–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Gajbhiye, S.; Tignath, S. Application of principal component analysis in grouping geomorphic parameters of a watershed for hydrological modeling. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.G.; Sharma, S.K. Application of Principal Component Analysis for Grouping of Morphometric Parameters and Prioritization of Watershed. In Hydrologic Modeling; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 447–458. ISBN 9789811058011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, O.; Singh, J. Soil Erosion Susceptibility Assessment of the Lower Himachal Himalayan Watershed. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.K.; Jaweed, T.H.; Umrikar, B.N.; Hussain, K.; Sankhua, R.N. Morphometric prioritization of semi-arid watershed for plant growth potential using GIS technique. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.K.; Jaweed, T.H.; Kale, S.S.; Umrikar, B.N.; Sankhua, R.N. Identification of erosion-prone areas using modified morphometric prioritization method and sediment production rate: A remote sensing and GIS approach. Geomatics Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 986–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; Hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1945, 56, 275–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basin and channel networks. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A. Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1956, 67, 597–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. Drainage basin characteristics. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1932, 13, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.C. A Quantitative Geomorphic Study of Drainage Basin Characteristics in the Clinch Mountain area, Virginia and Tennessee; Department of Geology, Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, P.K.; Mohan, K.; Mishra, S.; Ahmad, A.; Mishra, V.N. A GIS-based approach in drainage morphometric analysis of Kanhar River Basin, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, R. Soil and water conservation engineering. Stand. Publ. Distrib. Delhi 2007, 799–812. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Darmora, A.; Sharma, S. Comparative Assessment of Hydrologic Behaviour of Two Mountainous Watersheds Using Morphometric Analysis. Hydrol. J. 2012, 35, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. Standards for grading textures of erosional topography. Am. J. Sci. 1950, 248, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, H.; Kumar, A.; Reddy, C.P.; Malik, A. Watershed prioritization based on morphometric parameters using remote sensing and geographical information system. Indian J. Ecol. 2017, 44, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. London, Edinburgh, Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1933, 24, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottegoda, N.T.; Rosso, R. Applied Statistics for Civil and Environmental Engineers; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 392–402. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).