Production of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Laboratory Cultures of Arctic Sea Ice Algae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture Incubations
2.2. Culture Sampling
2.3. Biological and Chemical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Progressions of Chl a and Bacteria
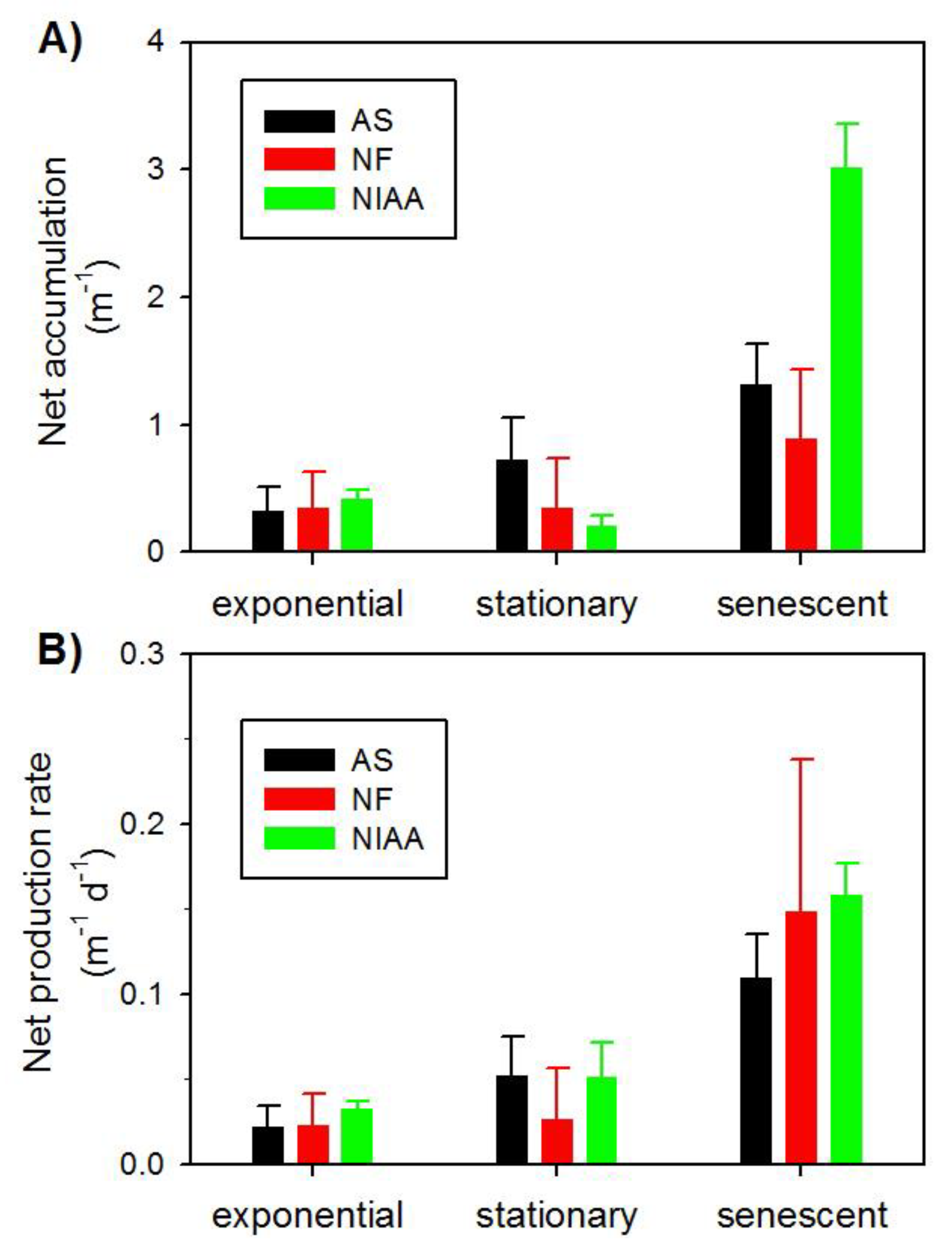
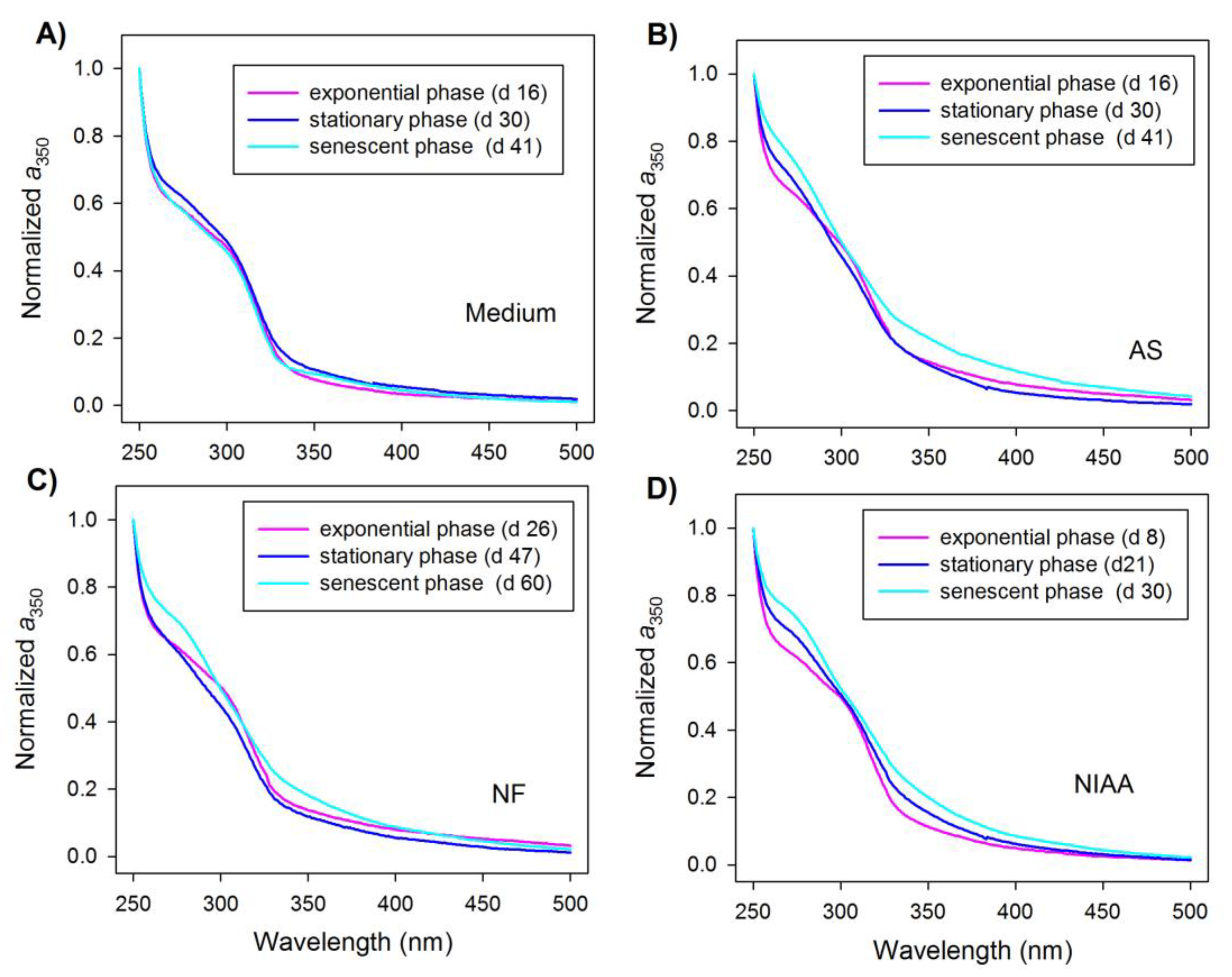
3.2. Temporal Progression of CDOM
4. Discussion
4.1. Possible Mechanisms for CDOM Production
4.2. Production of Short-UV Absorbing Chromophores
4.3. Implications for CDOM Production in Sea Ice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belzile, C.; Johannessen, S.C.; Gosselin, M.; Demers, S.; Miller, W.L. Ultraviolet attenuation by dissolved and particulate constituents of first-year ice during late spring in an Arctic polynya. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, N.M.; Miller, W.L. Spatial and temporal dynamics of colored dissolved organic matter in the North Water polynya. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1009–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Gosselin, M. Photoproduction of carbon monoxide in first-year sea ice in Franklin Bay, southeastern Beaufort Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Aubry, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, G. Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in first-year sea ice in the western Canadian Arctic. Mar. Chem. 2014, 165C, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, V.J.; Zimmerman, R.C. Characteristics of colored dissolved organic material in first year landfast sea ice and the underlying water column in the Canadian Arctic in the early spring. Mar. Chem. 2016, 180, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, P.; Meler, J.; Kauko, H.M.; Pavlov, A.K.; Zabłocka, M.; Peeken, I.; Dybwad, C.; Castellani, G.; Granskog, M.A. Bio-optical properties of Arctic drift ice and surface waters north of Svalbard from winter to spring. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 4634–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, S.R.; Ha, S.Y.; Kim, K.; Derrien, M.; Lee, Y.K.; Hur, J. Optical and molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in the Arctic ice core and the underlying seawater (Cambridge Bay, Canada): Implication for increased autochthonous DOM during ice melting. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perovich, D.K.; Roesler, C.S.; Pegau, W.S. Variability in Arctic sea ice optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, V.J. Impacts of chromophoric dissolved organic material on surface ocean heating in the Chukchi Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C07024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusikivi, J.; Vähätalo, A.V.; Granskog, M.A.; Sommaruga, R. Contribution of mycosporine-like amino acids and colored dissolved and particulate matter to sea ice optical properties and ultraviolet attenuation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granskog, M.A.; Kaartokallio, H.; Kuosa, H. Sea ice in non-polar regions. In Sea Ice; Thomas, D.N., Dieckmann, G.S., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 531–577. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.N.; Papadimitriou, S.; Michel, C. Biogeochemistry of sea ice. In Sea Ice; Thomas, D.N., Dieckmann, G.S., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 425–467. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, L.; Thomas, D.N.; Stedmon, C.A.; Granskog, M.A.; Papadimitriou, S.; Krapp, R.H.; Meiners, K.M.; Lannuzel, D.; van der Merwe, P.; Dieckmann, G.S. The characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Antarctic sea ice. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2011, 58, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, V.; Thomas, D.N.; Haas, C.; Kattner, G.; Kennedy, H.; Dieckmann, G.S. Behaviour of dissolved organic matter and inorganic nutrients during experimental sea-ice formation. Ann. Glaciol. 2001, 33, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.N.; Lara, R.J.; Eicken, H.; Kattner, G.; Skoog, A. Dissolved organic matter in Arctic multi-year sea ice during winter: Major components and relationship to ice characteristics. Polar Biol. 1995, 15, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.N.; Kattner, G.; Engbrodt, R.; Giannelli, V.; Kennedy, H.; Haas, C.; Dieckmann, G.S. Dissolved organic matter in Antarctic sea ice. Ann. Glaciol. 2001, 33, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.; Nielsen, T.G.; Nozais, C.; Gosselin, M. Significance of sedimentation and grazing by ice micro-and meiofauna for carbon cycling in annual sea ice (northern Baffin Bay). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 30, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, M.; Daugbjerg, N.; Gradinger, R.; Ilyash, L.; Ratkova, T.; von Quillfeldt, C. The pan-Arctic biodiversity of marine pelagic and sea–ice unicellular eukaryotes: A first-attempt assessment. Mar. Biodivers. 2011, 41, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Quillfeldt, C.H.; Ambrose, W.G.; Clough, L.M. High number of diatom species in first-year ice from the Chukchi Sea. Polar Biol. 2003, 26, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, A.R.; Krembs, C. Effects of snow removal and algal photoacclimation on growth and export of ice algae. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, V.; Levasseur, M.; Mundy, C.J.; Gosselin, M.; Tremblay, J.-É.; Scarratt, M.; Gratton, Y.; Papakiriakou, T.; Poulin, M.; Lizotte, M. Biological and physical processes influencing sea ice, under-ice algae, and dimethylsulfoniopropionate during spring in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 3746–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, M.; Stramski, D.; Ferrari, G.M.; Claustre, H.; Bricaud, A.; Obolensky, G.; Hoepffner, N. Variations in the light absorption coefficients of phytoplankton, nonalgal particles, and dissolved organic matter in coastal waters around Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2003, 108, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Holm-Hansen, O.; Lorenzen, C.J.; Holmes, R.W.; Strickland, J.D. Fluorometric determination of chlorophyll. J. Cons. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer. 1965, 30, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzile, C.; Brugel, S.; Nozais, C.; Gratton, Y.; Demers, S. Variations of the abundance and nucleic acid content of heterotrophic bacteria in Beaufort Shelf waters during winter and spring. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L.; Zepp, R.G. Photochemical production of dissolved inorganic carbon from terrestrial organic matter: Significance to the oceanic organic carbon cycle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, C.L.; O’Sullivan, D.W.; Boyd, T.J. Increases in the longwave photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, J.; Bolton, J.R. Photochemistry of nitrite and nitrate in aqueous solution: A review. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1999, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Scarratt, M.G.; Moore, R.M. Carbon disulphide production in laboratory cultures of marine phytoplankton. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carder, K.L.; Steward, R.G.; Harvey, G.R.; Ortner, P.B. Marine humic and fulvic acids: Their effects on remote sensing of ocean chlorophyll. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1989, 34, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.B.; Siegel, D.A.; Michaels, A.F. Seasonal dynamics of colored dissolved material in the Sargasso Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I 1998, 45, 931–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle-Newall, E.J.; Fisher, T.R. Production of chromophoric dissolved organic matter fluorescence in marine and estuarine environments: An investigation into the role of phytoplankton. Mar. Chem. 2002, 77, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; van Dijk, M.A.; Liu, M.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B. The contribution of phytoplankton degradation to chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in eutrophic shallow lakes: Field and experimental evidence. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4685–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera-Castillo, C.; Sarmento, H.; Alvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Gasol, J.M.; Marrasé, C. Net production and consumption of fluorescent colored dissolved organic matter by natural bacterial assemblages growing on marine phytoplankton exudates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7490–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romera-Castillo, C.; Sarmento, H.; Alvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Gasol, J.M.; Marraséa, C. Production of chromophoric dissolved organic matter by marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Tanoue, E. Basin scale distribution of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Aubry, C.; Bélanger, S.; Song, G. The dynamics of absorption coefficients of CDOM and particles in the St. Lawrence estuarine system: Biogeochemical and physical implications. Mar. Chem. 2012, 128, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Maranger, R. Respiration and bacterial carbon dynamics in Arctic sea ice. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Xie, H.; Aubry, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gosselin, M.; Mundy, C.J.; Philippe, B.; Papakyriakou, T.N. Spatiotemporal variations of dissolved organic carbon and carbon monoxide in first-year sea ice in the western Canadian Arctic. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C00G05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Not, C.; Brown, K.; Ghaleb, B.; Hillaire-Marcel, C. Conservative behavior of uranium vs. salinity in Arctic sea ice and brine. Mar. Chem. 2012, 130, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, A.; Michel, C.; Gosselin, M.; LeBlanc, B. Winter–spring dynamics in sea-ice carbon cycling in the coastal Arctic Ocean. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rózańska, M.; Gosselin, M.; Poulin, M.; Wiktor, J.M.; Michel, C. Influence of environmental factors on the development of bottom ice protist communities during the winter–spring transition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 386, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, J.N.; Harland, R.C. Bacterial production in the bottom surface of sea ice in the Canadian Sub-Arctic. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottmeier, S.T.; Sullivan, C.W. Late winter primary production and bacterial production in sea ice and seawater west of the Antarctic Peninsula. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1987, 36, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, J.L.; Worby, A.; Delille, B.; Brabant, F.; Papadimitriou, S.; Thomas, D.; De Jong, J.; Lannuzel, D.; Haas, C. Temporal evolution of decaying summer first-year sea ice in the Western Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2008, 55, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, V.; Levasseur, M.; Scarratt, M.; Mundy, C.J.; Gosselin, M.; Kiene, R.P.; Gourdal, M.; Lizotte, M. Under-ice microbial dimethylsulfoniopropionate metabolism during the melt period in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 524, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Growth Phase | Duration (Day Range) (d) | Chl a (mg m−3) | BCA (105 cells mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Septentrionalis | |||
| Lag | 6 (0–6) | 21.8 | 12.3 |
| Exponential | 15 (6–21) | 125.2 | 12.9 |
| Stationary | 14 (21–35) | 312.1 | 12.8 |
| Senescent | 12 (35–47) | 107.3 | 53.7 |
| N. Frigida | |||
| Lag | 26 (0–26) | 19.0 | 34.5 |
| Exponential | 15 (26–41) | 104.0 | 42.9 |
| Stationary | 13 (41–54) | 220.7 | 63.0 |
| Senescent | 6 (54–60) 1 | 169.8 1 | 75.9 1 |
| Natural Ice Algal Assemblage (NIAA) | |||
| Lag | 8 (0–8) | 8.95 | 10.7 |
| Exponential | 13 (8–21) | 61.5 | 9.33 |
| Stationary | 4 (21–25) | 130.3 | 5.93 |
| Senescent | 19 (25–44) | 52.6 | 40.2 |
| Ice Algae 1 | Bacteria 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture | μ ± SE (d−1) | R2 | p | μ ± SE (d−1) | R2 | p |
| AS | 0.160 ± 0.008 | 0.996 | 0.0001 | 0.166 ± 0.015 | 0.992 | 0.004 |
| NF | 0.166 ± 0.015 | 0.992 | 0.004 | 0.052 ± 0.010 | 0.924 | 0.01 |
| NIAA | 0.169 ± 0.016 | 0.985 | 0.0008 | 0.342 ± 0.035 | 0.996 | 0.002 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Xie, H.; Song, G.; Gosselin, M. Production of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Laboratory Cultures of Arctic Sea Ice Algae. Water 2019, 11, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050926
Li G, Xie H, Song G, Gosselin M. Production of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Laboratory Cultures of Arctic Sea Ice Algae. Water. 2019; 11(5):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050926
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guiju, Huixiang Xie, Guisheng Song, and Michel Gosselin. 2019. "Production of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Laboratory Cultures of Arctic Sea Ice Algae" Water 11, no. 5: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050926
APA StyleLi, G., Xie, H., Song, G., & Gosselin, M. (2019). Production of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Laboratory Cultures of Arctic Sea Ice Algae. Water, 11(5), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050926





