Evaluation of Minimum Karst Spring Discharge Using a Simple Rainfall-Input Model: The Case Study of Capodacqua di Spigno Spring (Central Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological and Hydrogeological Setting of the Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
- Q0 is the spring flow rate referred to the specific month taken into account (L/s);
- k is an amplifying or reducing factor from rainfall to discharge values and is representative of each spring and its hydrogeological basin;
- Pi is the rainfall data (in mm) of the rainfall station representative of the hydrogeological basin related to the specific month, with i varying from the n-th preceding month up to the reference month (i = 0);
- is the incidence coefficient between and the rainfall data series and the spring flow data series at different lag times (for i varying from n to 0) and ranges from 0 to 1;
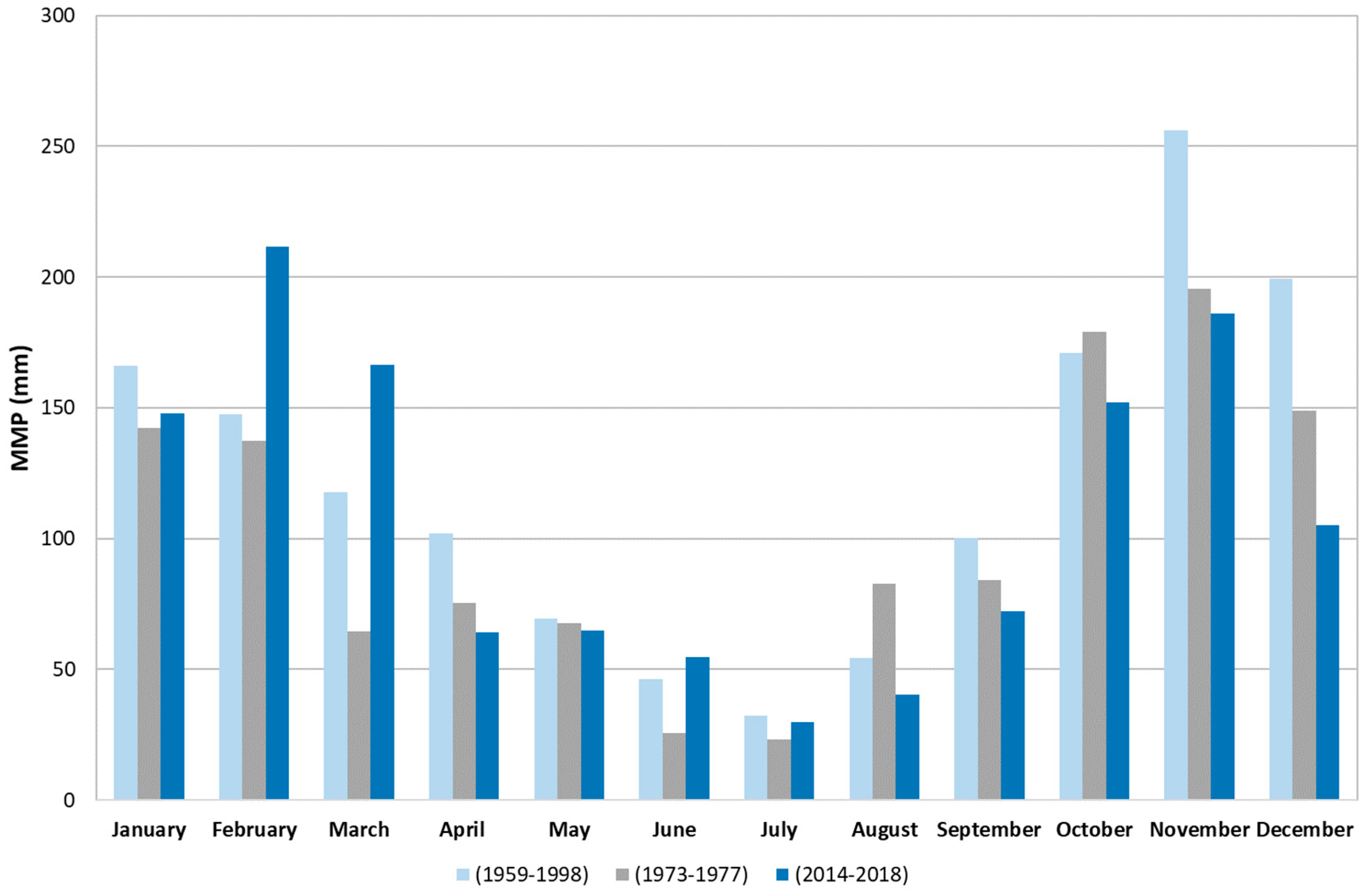
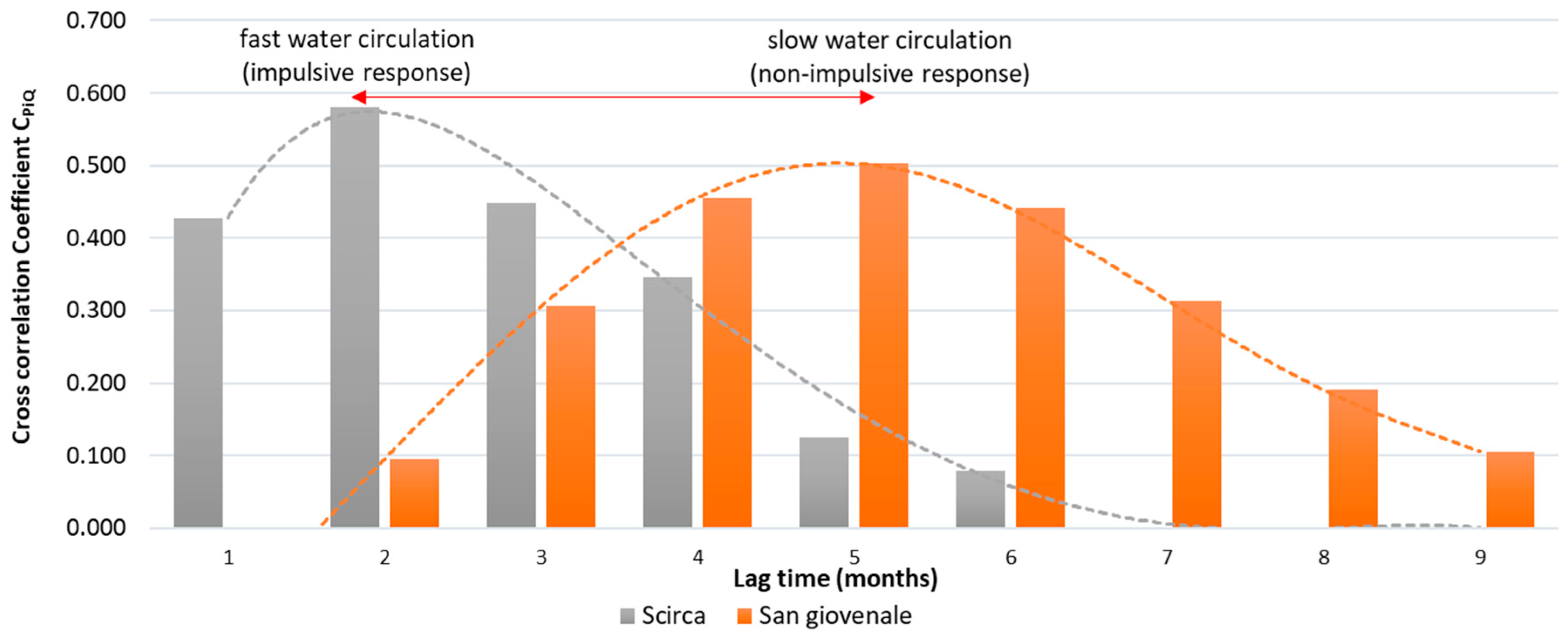
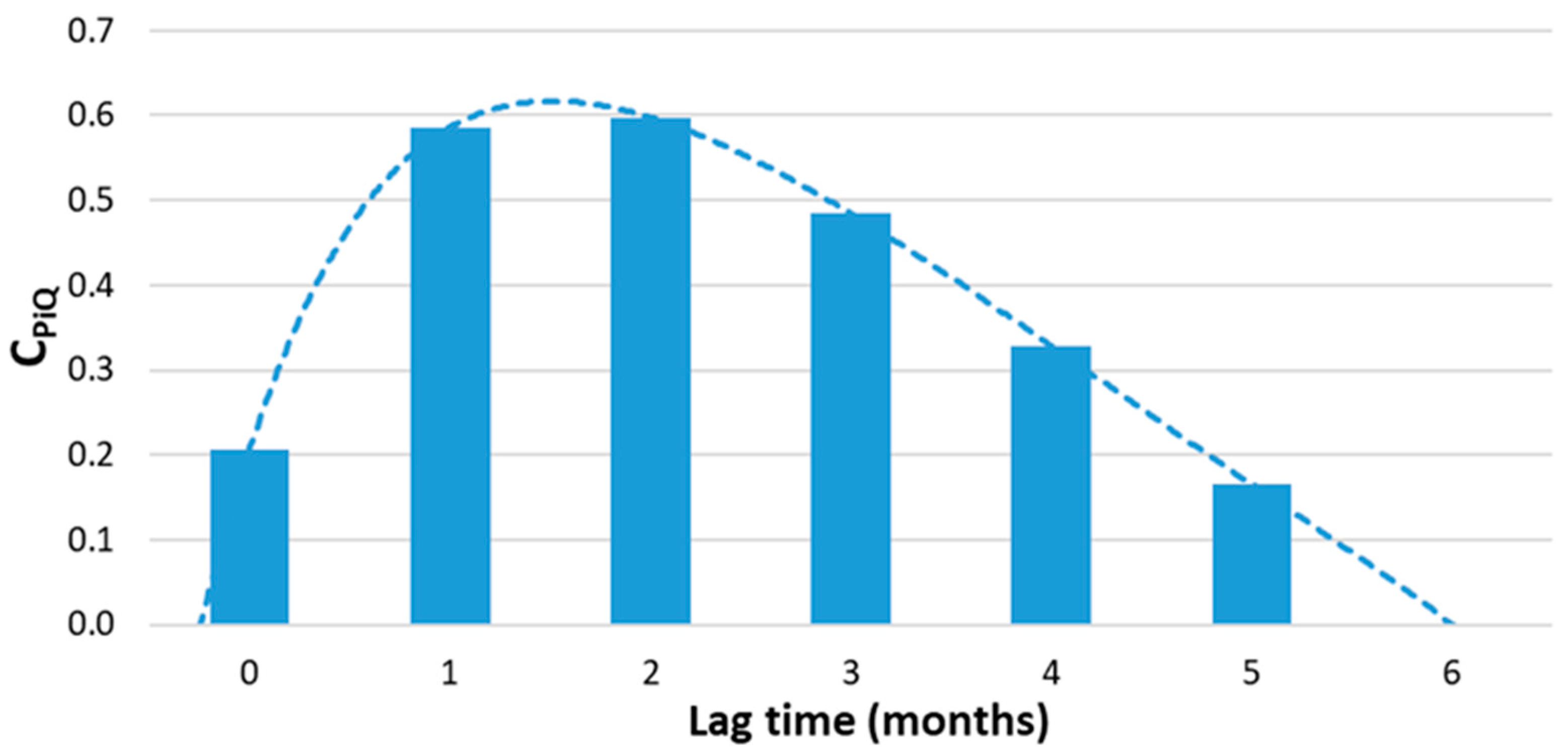
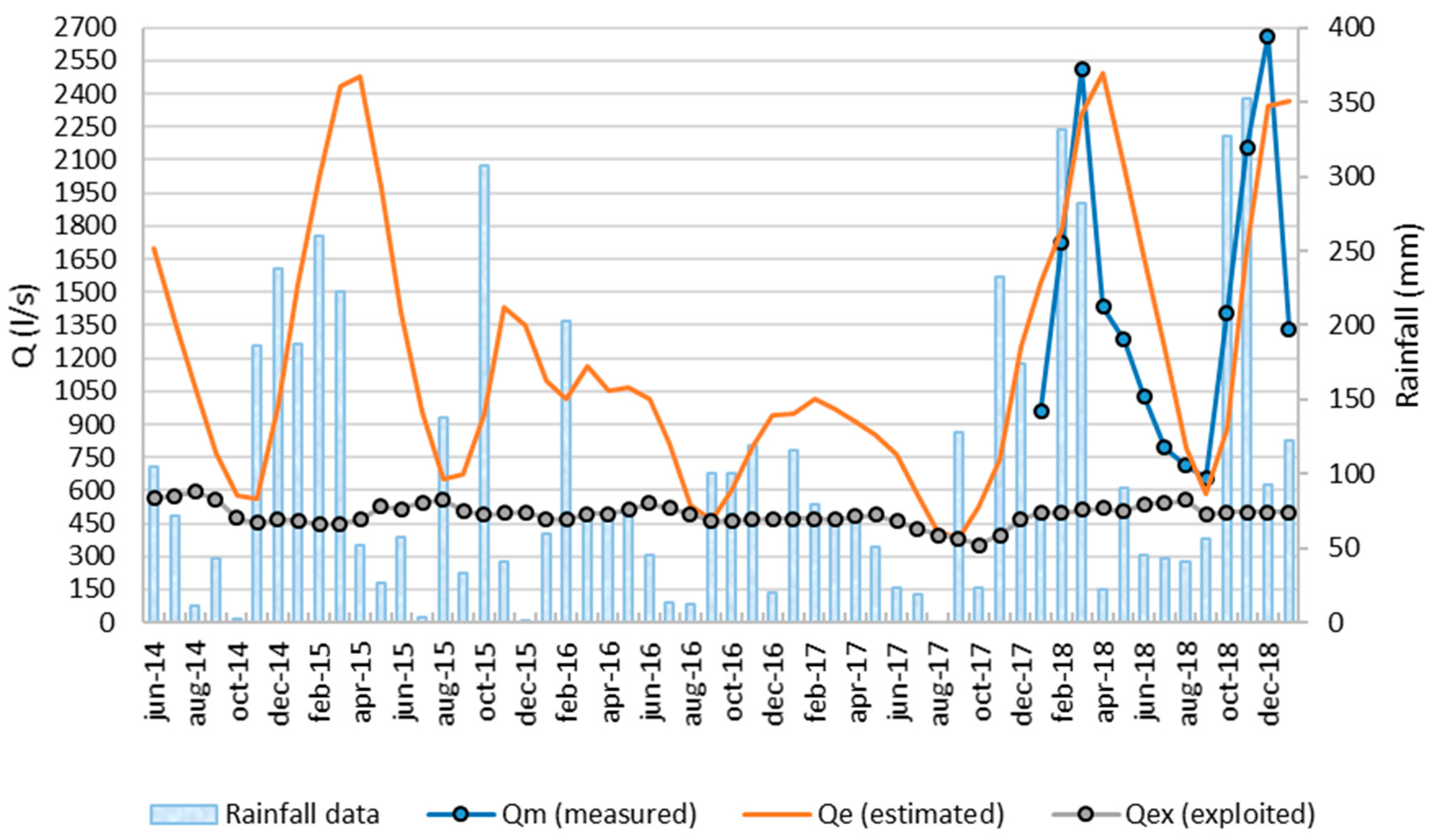
4. Results and Discussion
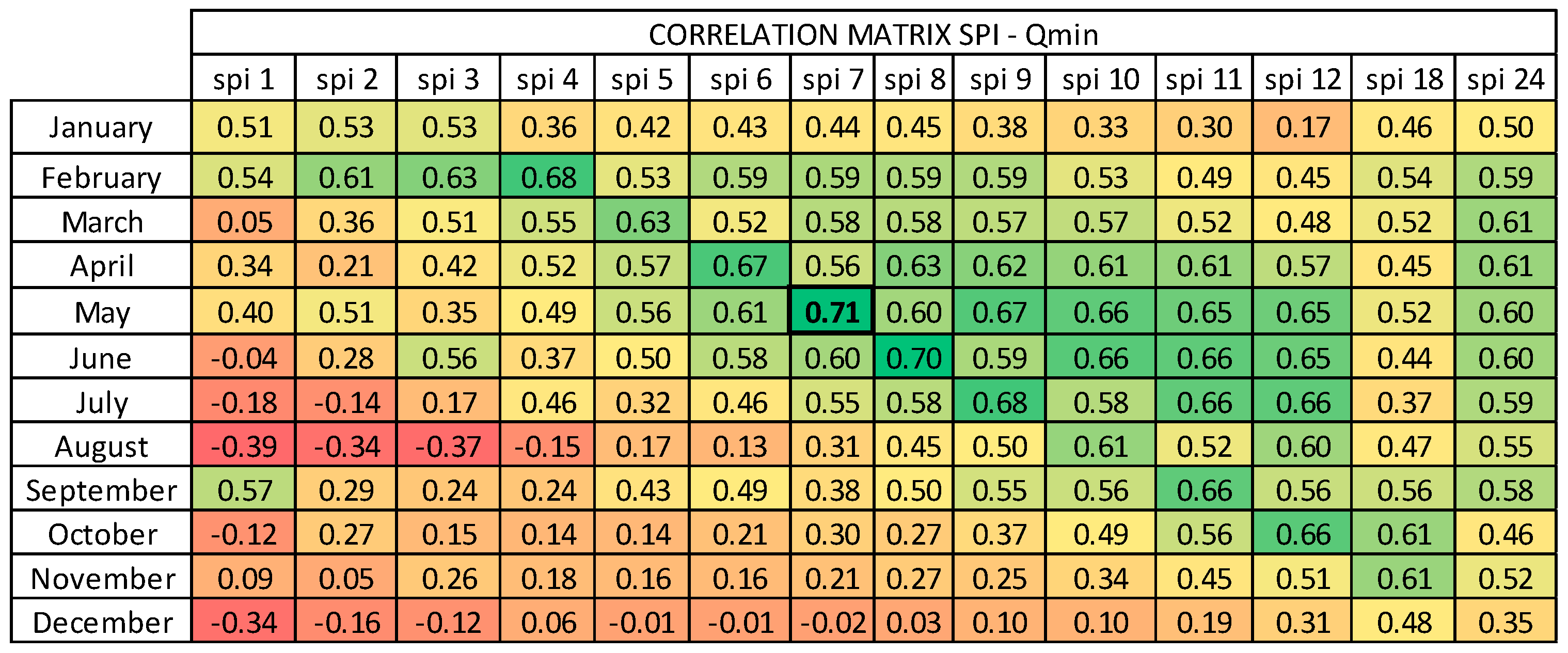
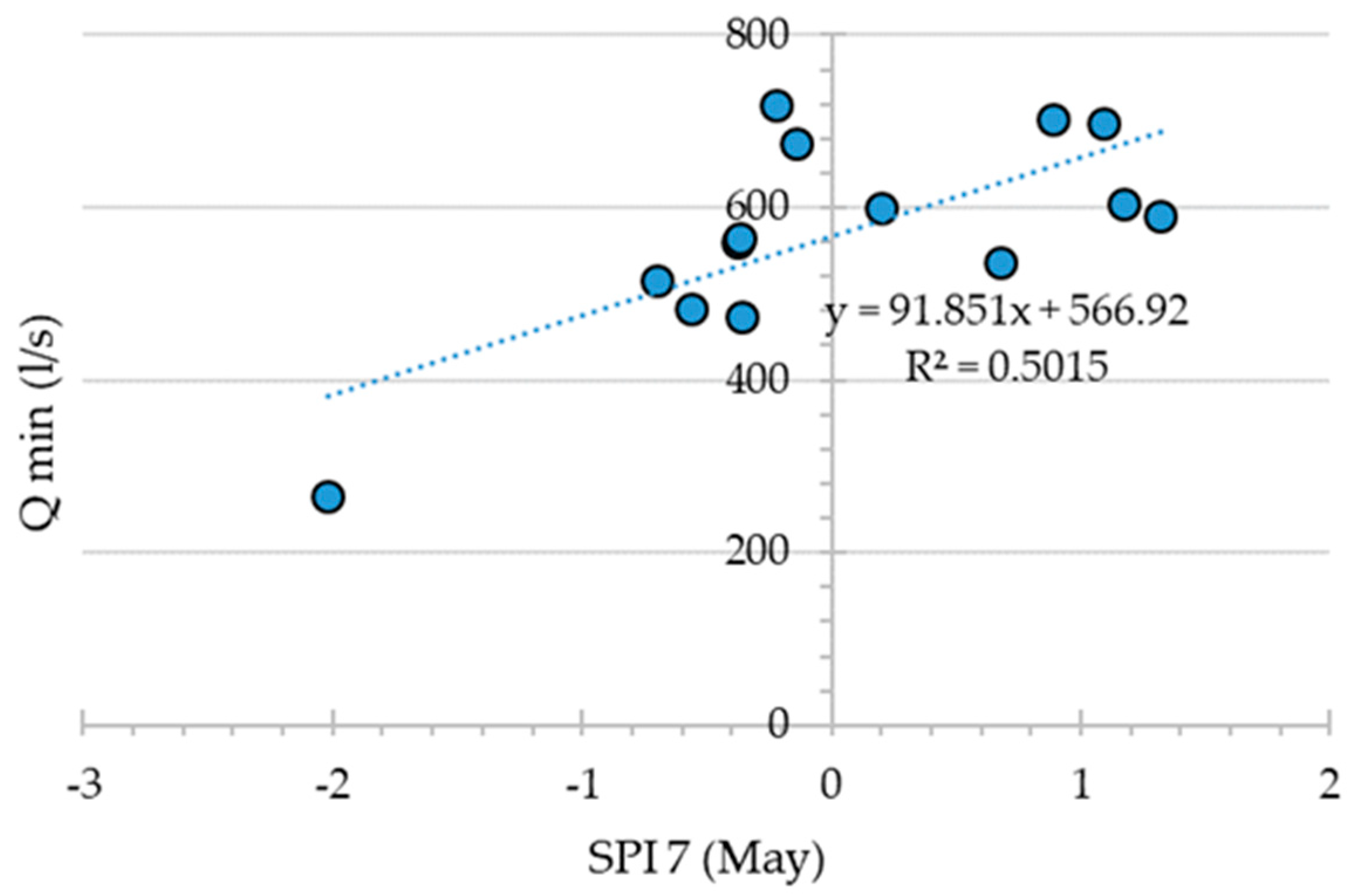
Evaluation of Minimum Spring Discharges Using the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
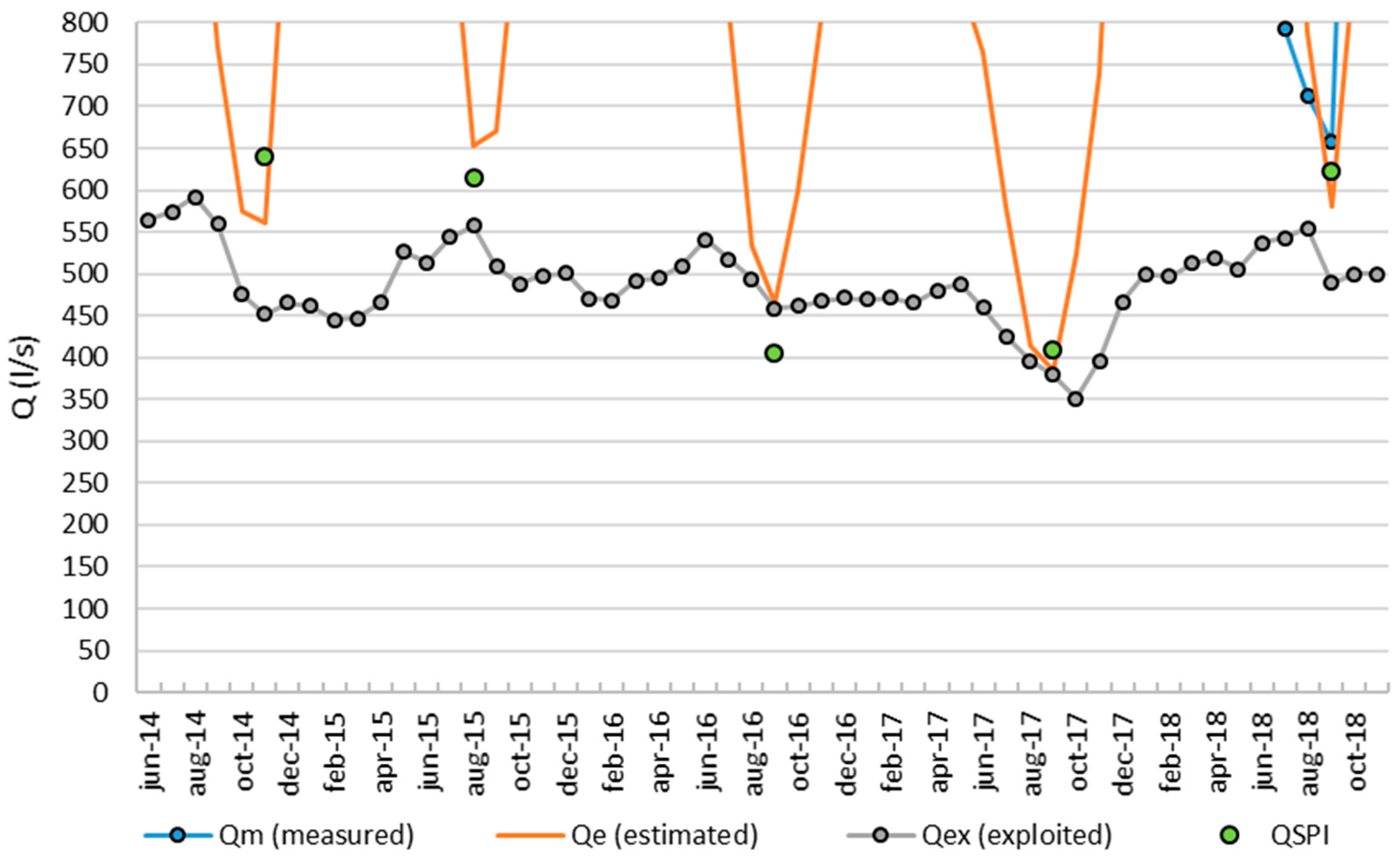
- Qex = exploited discharge;
- Qe = estimated minimum discharge;
- QSPI = estimated minimum discharge with SPI index.
- Qe = estimated minimum discharge;
- QSPI = estimated minimum discharge with the SPI index;
- Qt = total spring minimum discharge.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sappa, G.; Ferranti, F.; Iacurto, S.; De Filippi, F.M. Effects of climate change on groundwater feeding the Mazzoccolo and Capodacqua di Spigno springs (Central Italy): First quantitative assessments. In Proceedings of the 18th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geo Conference Surveing Geology and Mining Ecology Management SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 30 June–9 July 2018; Volume 18, pp. 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Hernàndez-Bedolla, J.; Solera, A.; Paredes-Arquiola, J.; Perdo-Monzonìs, M.; Andreu, J.; Sànchez-Quispe, S.T. The assessment of Sustainability Indexes and Climate Change Impacts on Integrated Water Resource Management. Water 2017, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicalho, C.C.; Batiot-Guilhe, C.; Seidel, J.L.; Van Exter, S.; Jourde, H. Geochemical evidence of water source characterization and hydrodynamic responses in a karst aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2012, 450–451, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappa, G.; Iacurto, S.; Ferranti, F.; De Filippi, F.M. Groundwater quality assessment in a karst coastal region of the West Aurunci Mountains (Central Italy). Geofluids 2019, 2019, 3261713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, E.; Del Bon, A.; Petrangeli, E.; Preziosi, E. Generating synthetic time series of springs discharge in relation to standardized precipitation indices. Case study in Central Italy. J. Hydrol. 2013, 507, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, F.; Tartari, G. A coupled approach of surface hydrological modelling and Wavelet Analysis for understanding the baseflow components of river discharge in karst environments. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.J.; Tombul, M. Monthly streamflow forecasting using continuous wavelet and multi-genegenetic programming combination. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Doglioni, A. The Relation between Karst Spring Discharge and Rainfall by the Cross-Correlation Analysis. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaudani, A.; Di Curzio, D.; Palmucci, W.; Pasculli, A.; Polemio, M.; Rusi, S. Statistical and Fractal Approaches on Long Time-Series to Surface-Water/Groundwater Relationship Assessment: A Central Italy Alluvial Plain Case Study. Water 2017, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Guerriero, L.; Fiorillo, F.; Esposito, L.; Revellino, P.; Grelle, G.; Guadagno, F.M. Predicting Monthly Spring Discharges Using a Simple Statistical Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, F.; Saroli, M.; De Marinis, G.; Gardano, R. Machine learning Models for Spring Discharge Forecasting. Geofluids 2018, 2018, 8328167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, S.; Cristino, G.; Doglioni, A.; Summa, G.; Simeone, V. Data-Driven Analysis of Discharge Variations at Mercure Spring South Italy. Eng. Geol. Soc. Territ. 2015, 5, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Cai, C.; Quingquing, H.; Zhicai, Z.; Peng, S. Simulation of rainfall-underground outflow responses of a karstic watershed in Southwest China with an artificial neural network. Water Sci. Eng. 2008, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.; Chen, X. Monthly Rainfall-Runoff Modeling at Watershed Scale: A Comparative Study of Data-Driven and Theory-Driven Approches. Water 2018, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Wood, A.W. Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandu, A.W.; Silva, R.F.; Martins, E.S. Drought identification in Cearà state using the standardized precipitation index (SPI). In Proceedings of the VI Simpòsio Internacional de Climatologia, Natal, Brazil, 13–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield, J.P.; Marchant, B.P. Analysis of groundwater drought building on the standardised precipitation index approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. 2013, 17, 4769–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, A.Z.; Bassam, K. Investigation of hydrological drought using Cumulative Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI 30) in the eastern Mediterranean region (Damascus, Syria). J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 125, 969–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Guadagno, F.M. Karst Spring Discharges Analysis in Relation to Drought Periods, Using the SPI. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, M.; Hayes, M.; Wood, M. Standardized Precipitation Index User Guide; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, C.; Bono, P. Carta Idrogeologica del Territorio della Regione Lazio—Scala 1:250.000, Regione Lazio, Assessorato alla Programmazione, Ufficio Parchi e Riserve; Università degli Studi di Roma “La Sapienza”: Roma, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, D.; Bigi, S.; Del Castello, M. The structure of the Aurunci Mountains (southern Lazio): A balanced cross-section and its restoration. Ital. J. Geosci. 2002, 1, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Celico, P. Schema Idrogeologico dell’Appennino Carbonatico Centro-Meridionale. Memorie e Note dell’Istituto di Geologia Applicata 1978, 14, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Accordi, B.; Biasini, A.; Caputo, C.; Devoto, G.; Funiciello, R.; La Monica, G.B.; Lupia Palmieri, E.; Matteucci, R.; Pieruccini, U. Geologia e Dissesti del Territorio Montano della Regione Lazio. Carta della Montagna 1976, 2, 55–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ialongo, N. Studio Idrogeologico Sorgente Mazzoccolo; Relazione Idrogeologica; Technical Report (Unpublished); Amministrazione Comunale di Formia: Formia, Italy, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi, A.M.; Marzocchi, A.; Ricci, A.; Mencarini, S.; Vecellio, L.; Graziosi, A.; Di Mauro, G. La torbidità alle captazioni idropotabili dei monti Aurunci, Aquifer Vulnerability and Risk. In Proceedings of the 4th Congress on the Protectionand Management of Groundwater, Parma, Italy, 21–23 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, S.; Braca, G.; Romano, E.; Lastoria, B.; Bussettini, M. Linee Guida Sugli Indicatori di Siccità e Scarsità Idrica da Utilizzare Nelle Attività Degli Osservatori Permanenti per gli Utilizzi Idrici—Stato Attuale e Prospettive Future; Thecnical Report; 2018. Available online: http://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files2018/notizie/LineeGuidaPubblicazioneFinaleL6WP1_concopertina.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- National Drought Mitigation Center—UNL. SPI Generator free software, Version release date: 6 September 2018. Available online: https://drought.unl.edu/droughtmonitoring/SPI/SPIProgram.aspx (accessed on 18 April 2019).




| 1973 | 1974 | 1975 | 1976 | 1977 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | P (mm) | Qm (L/s) | P (mm) | Qm (L/s) | P (mm) | Qm (L/s) | P (mm) | Qm (L/s) | P (mm) | Qm (L/s) |
| January | 370.6 | 1495 | 122.6 | 1525 | 14.8 | 955 | 27.2 | 1015 | 176.4 | 4170 |
| February | 187.6 | 2245 | 294.2 | 1665 | 18.4 | 825 | 111.8 | 1015 | 74.4 | 3270 |
| March | 57.2 | 1925 | 42.4 | 1705 | 78.6 | 945 | 109.2 | 1130 | 35.6 | 1850 |
| April | 70.8 | 1975 | 171 | 1595 | 57.4 | 1095 | 57.2 | 1265 | 20 | 1800 |
| May | 1.6 | 1865 | 158.4 | 2085 | 55.2 | 945 | 83.6 | 1115 | 40.4 | 1744 |
| June | 8.8 | 1235 | 6.2 | 2025 | 15.2 | 795 | 52.2 | 1115 | 45.8 | 1230 |
| July | 26.2 | 865 | 4.4 | 905 | 30.6 | 535 | 33.6 | 965 | 21.2 | 960 |
| August | 73.6 | 725 | 110.6 | 785 | 108.4 | 400 | 35 | 535 | 85.8 | 645 |
| September | 133 | 595 | 92.6 | 765 | 40.4 | 370 | 73.2 | 525 | 81.2 | 643 |
| October | 30.6 | 525 | 368.9 | 675 | 145 | 265 | 288 | 515 | 62.6 | 878 |
| November | 54.6 | 475 | 187.6 | 1215 | 242.4 | 310 | 406 | 1925 | 86.8 | 600 |
| December | 127.4 | 475 | 84.8 | 815 | 143 | 515 | 308 | 3815 | 81.4 | 926 |
| September 2017 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qex (L/s) | Qe (L/s) | εe(2017) (%) | QSPI (L/s) | εSPI(2017) (%) |
| 379.6 | 384.7 | 1.3 | 408.9 | 7.7 |
| September 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qt (L/s) | Qe (L/s) | εe(2017) (%) | QSPI (L/s) | εSPI(2017) (%) |
| 657.44 | 580.41 | 11.72 | 622.03 | 5.69 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sappa, G.; De Filippi, F.M.; Iacurto, S.; Grelle, G. Evaluation of Minimum Karst Spring Discharge Using a Simple Rainfall-Input Model: The Case Study of Capodacqua di Spigno Spring (Central Italy). Water 2019, 11, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040807
Sappa G, De Filippi FM, Iacurto S, Grelle G. Evaluation of Minimum Karst Spring Discharge Using a Simple Rainfall-Input Model: The Case Study of Capodacqua di Spigno Spring (Central Italy). Water. 2019; 11(4):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040807
Chicago/Turabian StyleSappa, Giuseppe, Francesco Maria De Filippi, Silvia Iacurto, and Gerardo Grelle. 2019. "Evaluation of Minimum Karst Spring Discharge Using a Simple Rainfall-Input Model: The Case Study of Capodacqua di Spigno Spring (Central Italy)" Water 11, no. 4: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040807
APA StyleSappa, G., De Filippi, F. M., Iacurto, S., & Grelle, G. (2019). Evaluation of Minimum Karst Spring Discharge Using a Simple Rainfall-Input Model: The Case Study of Capodacqua di Spigno Spring (Central Italy). Water, 11(4), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040807







