Stranded Assets as a Key Concept to Guide Investment Strategies for Sustainable Development Goal 6
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
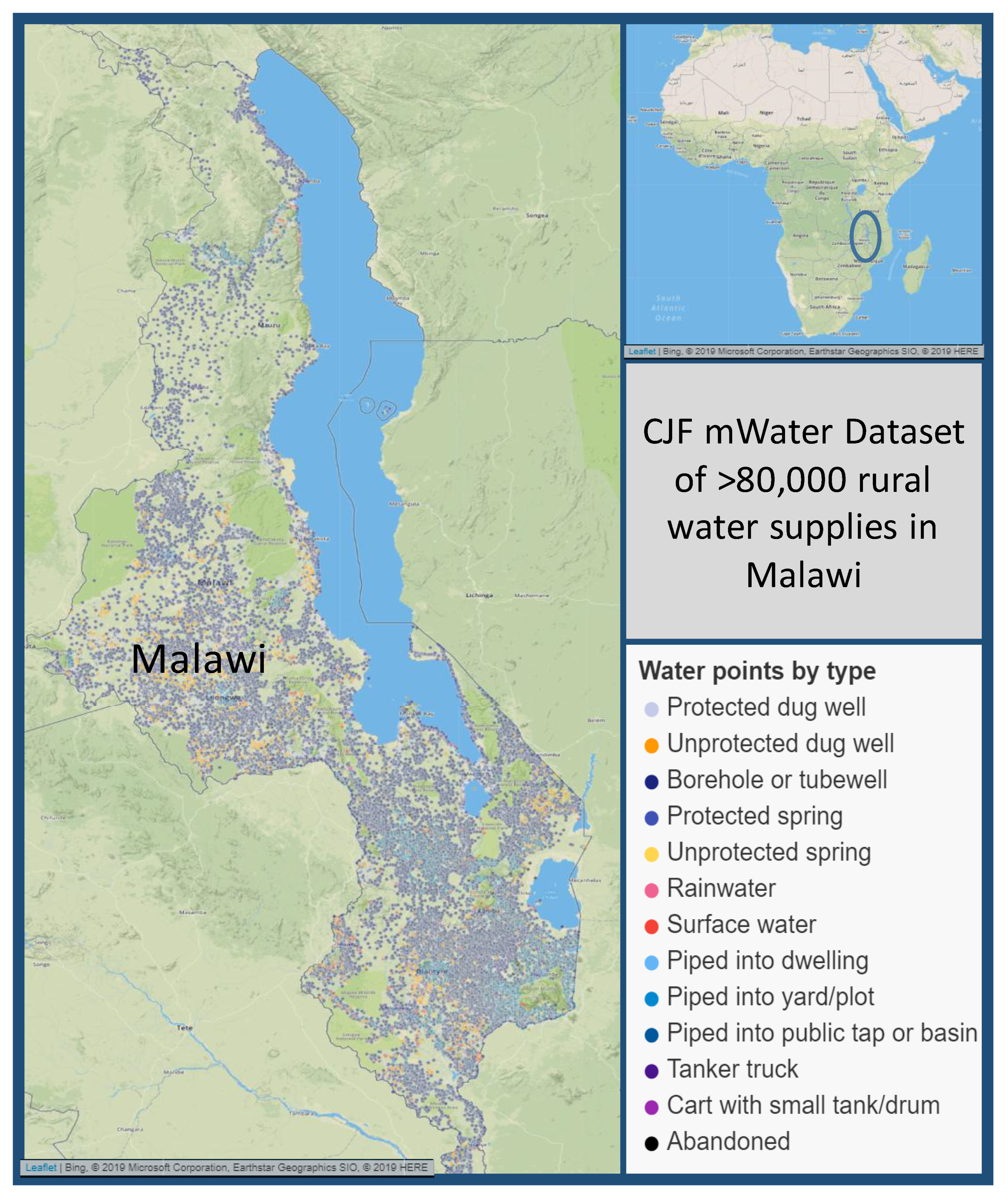
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Climate Justice Fund Water Future Programme Approach
3. Results and Discussion
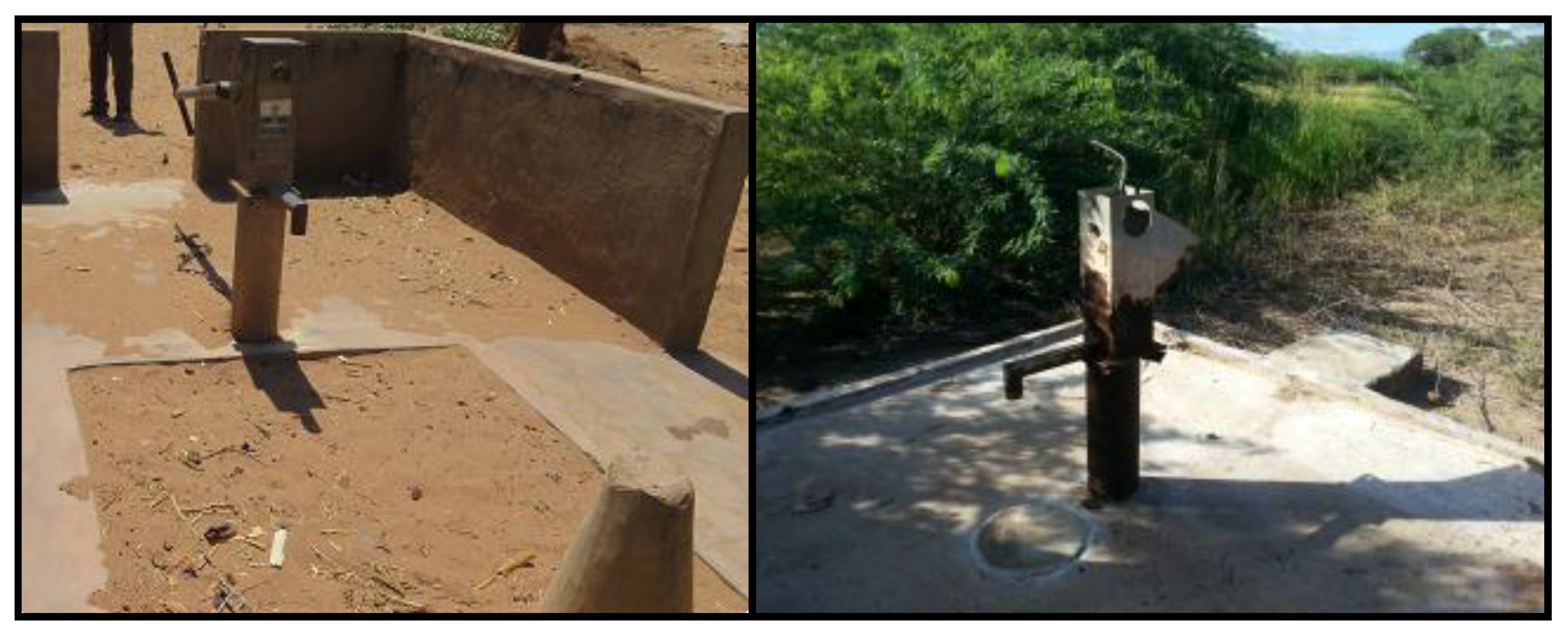
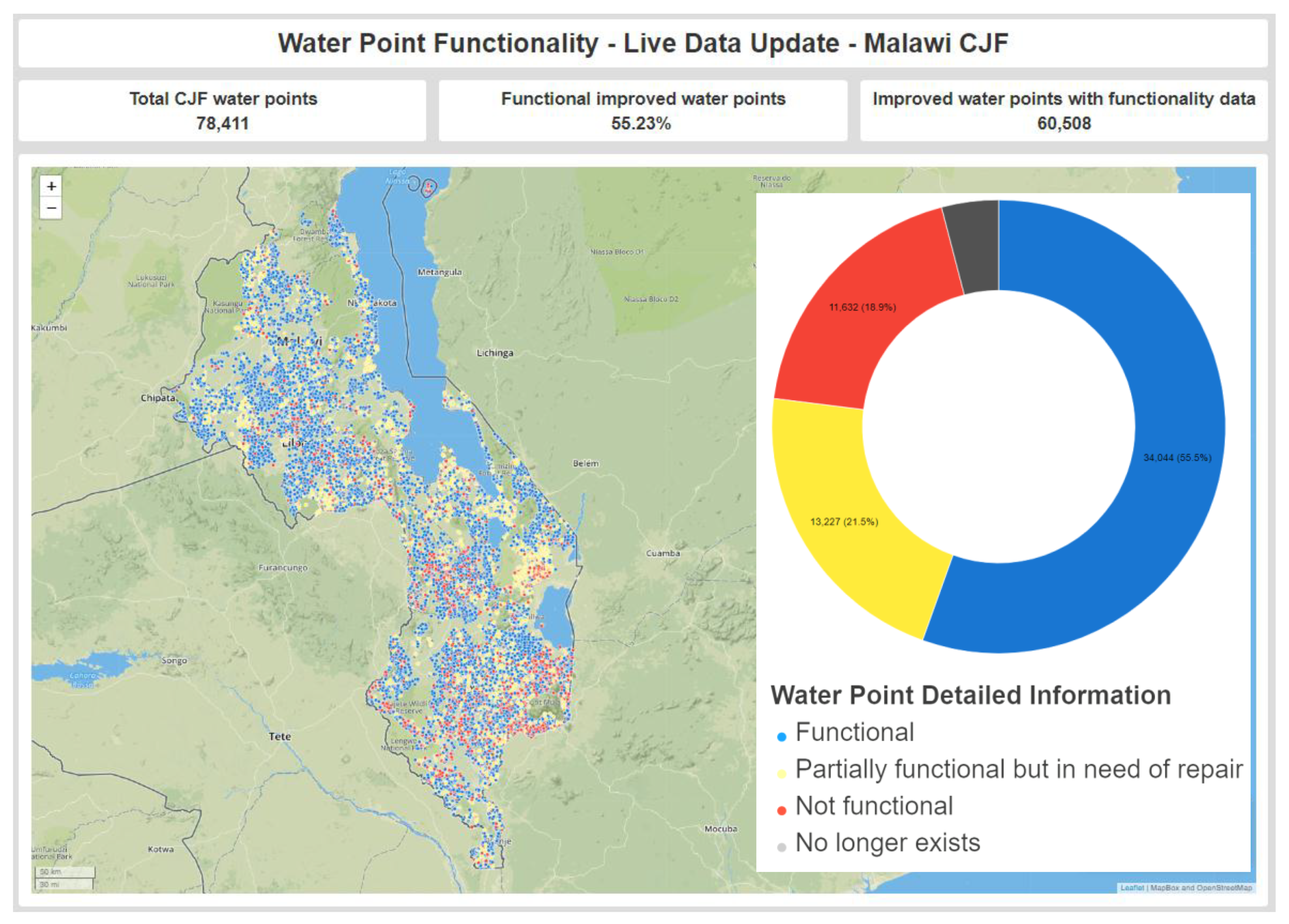
3.1. Assessing Stranded Assets at a National Level
- Functional (52.9%)—where the water resource asset is functioning as designed and providing improved water service to the community as designed;
- Partially Functional, i.e., functional but with problems (21.6%)—where the water resource asset provides water intermittently as a result of a range of issues such as:
- Poorly installed water point affected by decline in groundwater table resulting in a dry water point during some months (Stranded Asset),
- Poorly installed water point or low aquifer yield resulting in a water point running dry on a daily basis (Stranded Asset),
- Poorly maintained water point or water system resulting in limited access to water throughout the year (Stranded Asset),
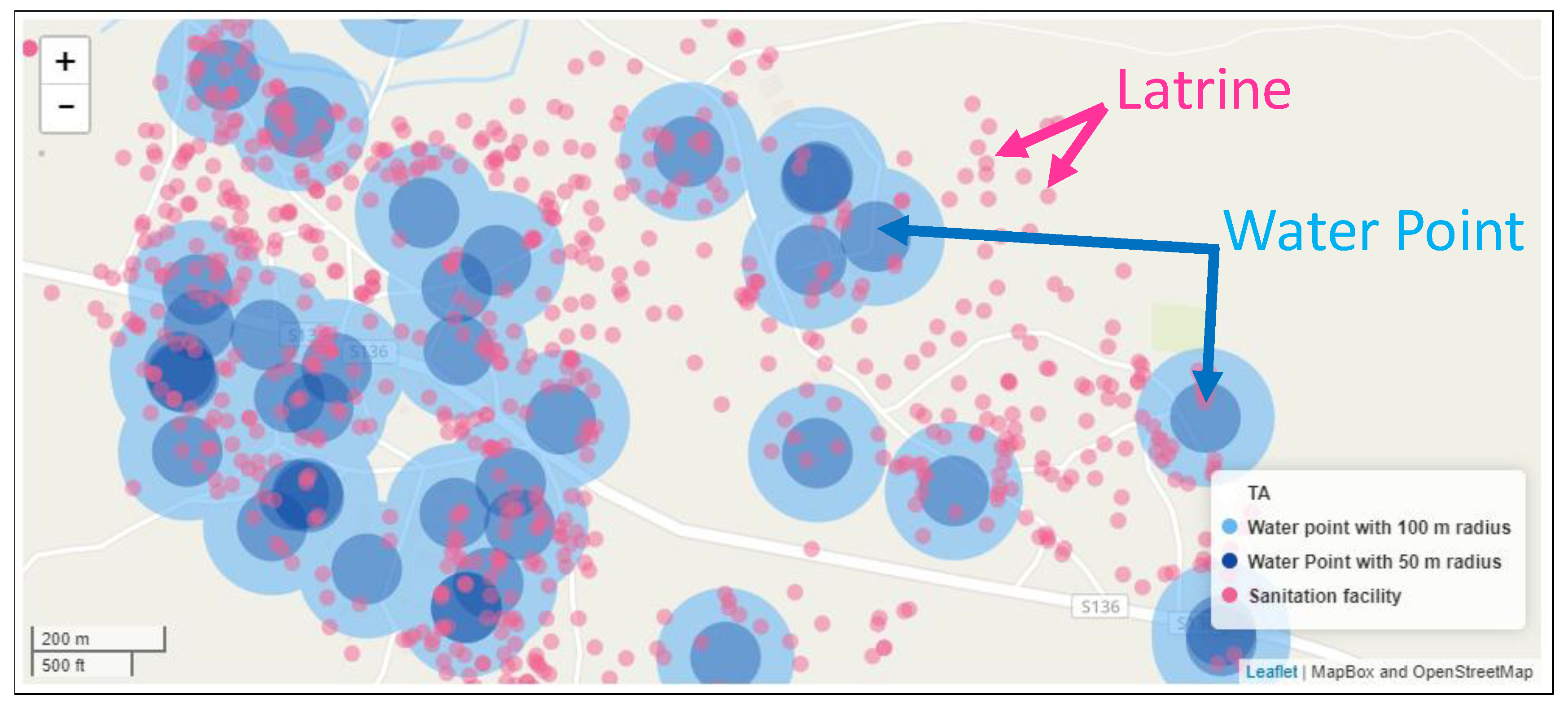
- Poorly installed water point into a water resource that is contaminated or has been contaminated (e.g., salinity and co-location of pit latrines and waste) (Stranded Asset),
- Poorly managed water point (issues with tariff setting/collection, non-professional management, mis-management of resources, lack of capacity) (Stranded Asset);
- Non-Functional (22.3%)—where the water resource asset does not supply water (Stranded Asset);
- No Longer Exists or Abandoned (3.2%)—where the water resource asset has been fully abandoned (Stranded Asset).
3.2. Stranded Assets and SDG6
3.3. Information Supporting Sustainability Targets
3.4. External Risks Contributing to Stranded Assets
4. Recommendations
- There must be a robust method to identify the physical and financial nature of Stranded Assets.
- There is a need for a robust decision support tool appropriate to lower income countries that can be used to guide point by point assessment of water supply assets.
- In terms of a decision support around identified Stranded Assets, this decision needs to be taken based on physical and financial return and clearly indicate if it is worthwhile to ‘fix’ these or decommission them fully and invest instead in new services.
- Inherent within this decision should be considerations of current value in use and financial return on investments alongside considerations of local social circumstances and social values.
- SDG6 investment planning of new assets will need to be much more focused on whole of life value linked to long-term returns on investments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CJF (Climate Justice Fund: Water Futures Programme). Preliminary Survey on the Groundwater Development Plan; Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Water Development, Government of Malawi: Lilongwe, Malawi, 2018.
- Wanda, E.M.; Gulula, L.C.; Phiri, A. Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater used for irrigation in Rumphi and Karonga districts, Northern Malawi. Phys. Chem. Earth Pt. A/B/C 2013, 66, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsor, H.C.; Oates, N.; Chilton, P.J.; Carter, R.C.; Casey, V.; MacDonald, A.M.; Calow, R.; Alowo, R.; Wilson, P.; Tumutungire, M.; et al. A Hidden Crisis: Strengthening the Evidence Base on the Sustainability of Rural Groundwater Supplies—Results from a Pilot Study in Uganda; OR/15/019; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2015; Available online: http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/511071/ (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Burney, J.A.; Naylor, R.L.; Postel, S.L. The case for distributed irrigation as a development priority in sub-Saharan Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12513–12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdinur, A.J.; Khaldoon, A.M. Water Services Sustainability: Institutional Arrangements and Shared Responsibilities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, Á.; Luis Molina, L.; Llop, A.; MacDonald, A.M. Impact of irrigated agriculture on groundwater-recharge salinity: A major sustainability concern in semi-arid regions. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.; Calow, R.; MacDonald, A.; Bartram, J. Climate change and water and sanitation: Likely impacts and emerging trends for action. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Utility Commission of Texas. Report to the 75th Legislature Volume 111 Potentially Strandable Investment (ECOM) Report; Public Utility Commission of Texas: Austin, TX, USA, 1997.
- Caldecott, B. Introduction to Special Issue: Stranded Assets and the Environment. J. Sustain. Financ. Invest. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, H.; Sayers, C.; Smith, A. Stranded Irrigation Assets; Productivity Commission Staff Working Paper; The Productivity Commission: Melbourne, Australia, June 2006. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/6756706.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Wheeler, S.; Loch, A.; Zuo, A.; Bjornlund, H. Reviewing the adoption and impacts of water markets in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2014, 518, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhr, B. Assessing the sources of stranded asset risk: A proposed framework. J. Sustain. Financ. Investig. 2017, 7, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldecott, B.; Howarth, N.; McSharry, P. Stranded Assets in Agriculture: Protecting Value from Environment-Related Risks; Smith School of Enterprise and the Environment, University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2013; Available online: https://www.smithschool.ox.ac.uk/publications/reports/stranded-assets-agriculture-report-final.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines; WHO and UNICEF: Geneva, Switzerland; New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Financing Water: Investing in Sustainable Growth—Policy Perspectives. OECD Environment Policy Perspective Paper No. 11. 2018. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/water/Policy-Paper-Financing-Water-Investing-in-Sustainable-Growth.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Back, J.O.; Rivett, M.O.; Hinz, L.B.; Mackay, N.; Wanangwa, G.J.; Phiri, O.L.; Songolo, C.E.; Thomas, M.A.S.; Kumwenda, S.; Nhlema, M.; et al. Risk assessment to groundwater of pit latrine rural sanitation policy in developing country settings. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613C–614C, 592–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Halcrow, A.H.; Schmalfuss, J.; Stark, J.A.; Truslove, J.P.; Kumwenda, S.; Harawa, K.A.; Nhlema, M.; Songola, C.; Wanangwa, G.J.; et al. Local scale water-food nexus: Use of borehole-garden permaculture to realise the full potential of rural water supplies in Malawi. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 209, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, C.M.; Kalin, R.M.; Rivett, M.O.; Nkhata, M.; Kanjaye, M. A national approach to systematic trans-boundary aquifer assessment and conceptualisation at relevant scales: A Malawi case study. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 20, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannix, N.; Norrie, J.; Paterson, F.; Nhlema, M.; Mleta, P.; Nkhata, M.; Wanangwa, G.; Kumwenda, S.; Clarke, D.; Kalin, R.M. Making the case for improved planning, construction and testing of water supply infrastructure in Malawi. In Transformation towards Sustainable and Resilient WASH Services, Proceedings of the 41st WEDC International Conference, Nakuru, Kenya, 9–13 July 2018; Egerton University: Nakuru, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rivett, M.O.; Miller, A.V.M.; MacAllister, D.J.; Fallas, A.; Wanangwa, G.J.; Mleta, P.; Phiri, P.; Mannix, N.; Monjerezi, M.; Kalin, R.M. A conceptual model based framework for pragmatic groundwater-quality monitoring network design in the developing world: Application to the Chikwawa District, Malawi. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 6, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Nhlema, M.; Kumwenda, S.; Mbalame, E.; Uka, Z.; Feighery, J.; Kalin, R. Evolving water-point mapping to strategic decision making in rural Malawi. In Transformation towards Sustainable and Resilient WASH Services, Proceedings to the 41st WEDC International Conference, Nakuru, Kenya, 9–13 July 2018; Egerton University: Nakuru, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rivett, M.O.; Robinson, H.L.; Wild, L.M.; Melville, J.; McGrath, L.; Phiri, P.; Flink, J.; Wanangwa, G.J.; Mleta, P.; MacLeod, S.S.P.; et al. Arsenic occurrence in Malawi groundwater. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2018, 22, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Truslove, J.P.; Miller, A.V.M.; Mannix, N.; Nhlema, M.; Rivett, M.O.; Coulson, A.B.; Mleta, P.; Kalin, R.M. Understanding the functionality and burden on decentralised rural water supply: Influence of Millennium Development Goal 7c coverage targets. Water 2019, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Budimir, L.; Mannix, N.; Miller, A.V.M.; Addison, M.J.; Moyo, P.; Wanangwa, G.J.; Phiri, O.L.; Songola, C.E.; Nhlema, M.; et al. Responding to salinity in a rural African alluvial valley aquifer system: To boldly go beyond the world of hand-pumped groundwater supply? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1005–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulson, A.B.; Adams, C.A.; Nugent, M.; Haynes, K. Exploring metaphors of capitals and the framing of multiple capitals: Challenges and opportunities for <R>. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2015, 6, 290–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.; Coulson, A.B.; Emmelkamp, T.; Greveling, R.; Klüth, G.; Nugent, M. Multiple Capitals Background Paper for <R>. IRC. ISSN 2052–1723. March 2013. Available online: https://eprint.ncl.ac.uk/file_store/production/215176/53ED3751-3884-4130-9F10-247E6E6C26E9.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Mapoma, H.W.T.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Kawaye, F.P.; Kayira, T.M. Hydrochemistry and quality of groundwater in alluvial aquifer of Karonga, Malawi. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapoma, H.W.T.; Xie, X. Basement and alluvial aquifers of Malawi: An overview of groundwater quality and policies. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoAIWD (Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Water Development). National Water Resources Master Plan, Main Report—Existing Situation; MoAIWD: Lilongwe, Malawi, 2017.
- Monjerezi, M.; Ngongondo, C. Quality of groundwater resources in Chikhwawa, Lower Shire Valley, Malawi. Water Qual. Exp. Health 2012, 4, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, I. An Assessment of Contracts and Drilling Practices for the Future Development of Sustainable Groundwater in Chikwawa, Malawi. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization and UNICEF. JMP (Joint Monitoring Programme) Report 2014: Progress on Drinking Water and Sanitation. JMP Report 14. 2014. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/jmp-report-2014/en/ (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Upton, K.Ó.; Dochartaigh, B.É.; Chunga, B. Africa Groundwater Atlas: Hydrogeology of Malawi. British Geological Survey, 2016. Available online: http://earthwise.bgs.ac.uk/index.php/Hydrogeology_of_Malawi (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Robins, N.; Davis, J.; Farr, D. Groundwater supply and demand from southern Africa’s crystalline basement aquifer: Evidence from Malawi. Hydrolgeol. J. 2013, 21, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, J.Y.; Mbow, C.; Sileshi, G.W.; Beedy, T.; Kundhlande, G.; Musau, J. Mapping vulnerability to climate change in malawi: Spatial and social differentiation in the Shire River Basin. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2015, 4, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, M.K.; Ngongondo, C.; Monjerezi, M.; Chipungu, F.; Liwenga, E.; Majule, A.E.; Stathers, T.; Lamboll, R. Climate change in semi-arid Malawi: Perceptions, adaptation strategies and water governance. Jàmbá 2016, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambombe, O.; Odongo, V.; Mutua, B.; Wambua, R. Impact of climate variability and land use change on streamflow in lake Chilwa basin, Malawi. Int. J. Hydrol. 2018, 2, 364–370. [Google Scholar]

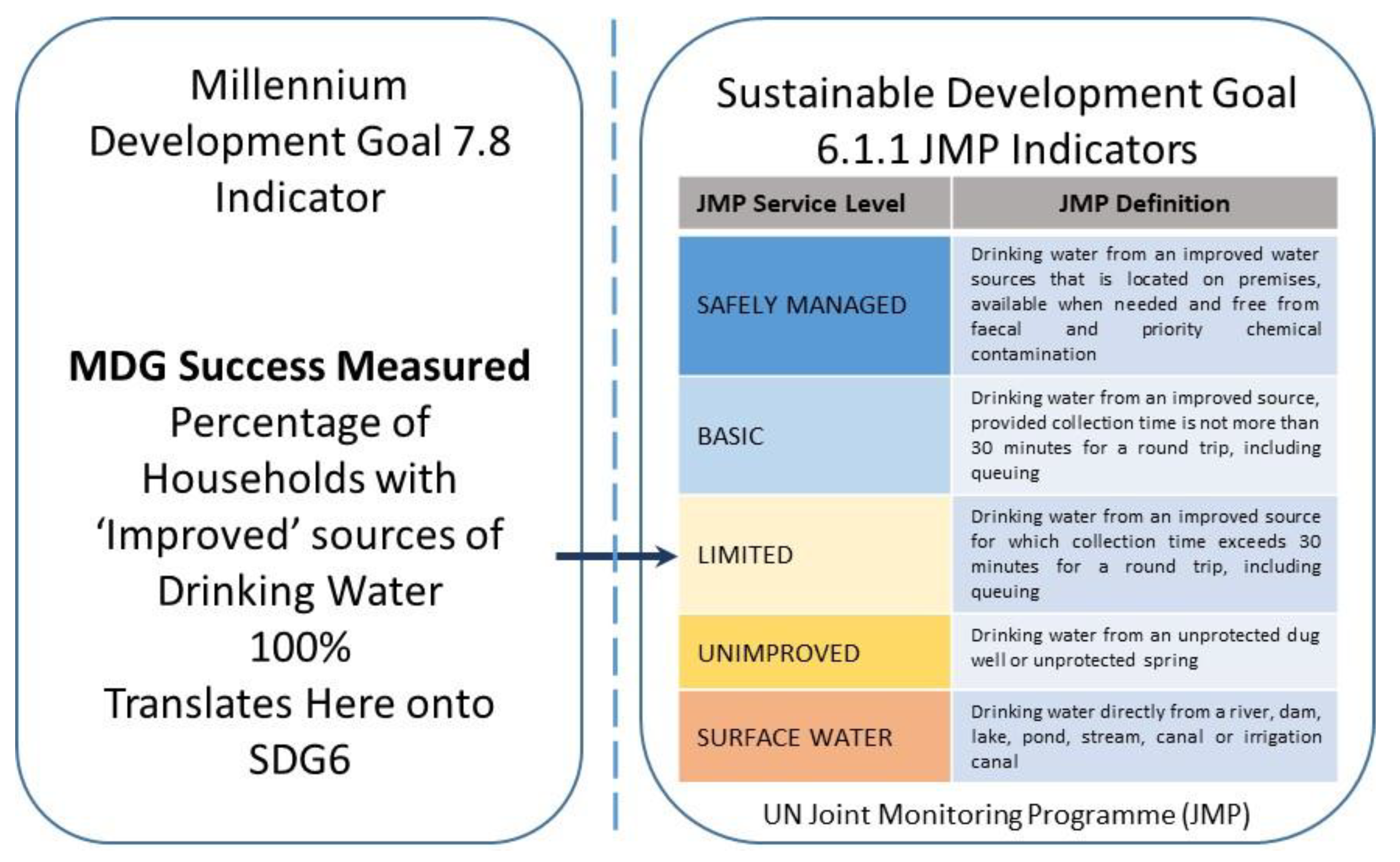
| MDGs | SDGs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | Indicators | Targets | Indicators |
| 7C: Halve the proportion of people without sustainable access to safe drinking water and basic sanitation by 2015 | 7.8: Proportion of population using an improved drinking water source | 6.1 By 2030 achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all | 6.1.1 Proportion of population using safely managed drinking water services |
| Proportion of population using an improved sanitation facility | 6.2 By 2030 achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all, and end open defecation paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations | 6.2.1 Proportion of population using safely managed sanitation services, include a hand-washing facility with soap and water | |
| SDG6.1 Household Survey Group Village Community in Chiradzulu District, Malawi | Insufficient Data from Household to determine Service Level SDG6.1 Indicator | Number of Households with Unimproved or Limited Service Level SDG6.1 Indicator | Number of Households with Basic Service Level SDG6.1 Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Rehabilitation of Stranded Assets | 28 (22%) | 89 (70%) | 10 (8%) |
| After Rehabilitation of Stranded Assets | 16 (13%) | 33 (26%) | 78 (61%) |
| Percentage of Water Supplies (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (m) | 0–10 | 10–20 | 20–30 | 30–40 | 40–50 | 50–60 | >60 |
| Water available year-round | 63.4 | 66.0 | 83.9 | 90.8 | 93.4 | 93.7 | 94.7 |
| Water available only seasonally | 34.5 | 32.4 | 15.0 | 8.8 | 5.8 | 5.5 | 4.1 |
| No information available | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| n = | 1311 | 2288 | 1396 | 4139 | 10,380 | 1745 | 1026 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalin, R.M.; Mwanamveka, J.; Coulson, A.B.; Robertson, D.J.C.; Clark, H.; Rathjen, J.; Rivett, M.O. Stranded Assets as a Key Concept to Guide Investment Strategies for Sustainable Development Goal 6. Water 2019, 11, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040702
Kalin RM, Mwanamveka J, Coulson AB, Robertson DJC, Clark H, Rathjen J, Rivett MO. Stranded Assets as a Key Concept to Guide Investment Strategies for Sustainable Development Goal 6. Water. 2019; 11(4):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040702
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalin, Robert M., Joseph Mwanamveka, Andrea B. Coulson, Donald J. C. Robertson, Holly Clark, Jon Rathjen, and Michael O. Rivett. 2019. "Stranded Assets as a Key Concept to Guide Investment Strategies for Sustainable Development Goal 6" Water 11, no. 4: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040702
APA StyleKalin, R. M., Mwanamveka, J., Coulson, A. B., Robertson, D. J. C., Clark, H., Rathjen, J., & Rivett, M. O. (2019). Stranded Assets as a Key Concept to Guide Investment Strategies for Sustainable Development Goal 6. Water, 11(4), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040702







