An Improved Logistic Model Illustrating Microcystis aeruginosa Growth Under Different Turbulent Mixing Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure
2.2. Sample Analysis and Date Processing
2.3. Test for Hydraulic Parameter Description
3. Experimental Results and Model Constructing
3.1. Effect of Turbulence Mixing on Growth of Microcystis aeruginosa
3.2. Construction of Logistic Model under Water Disturbance
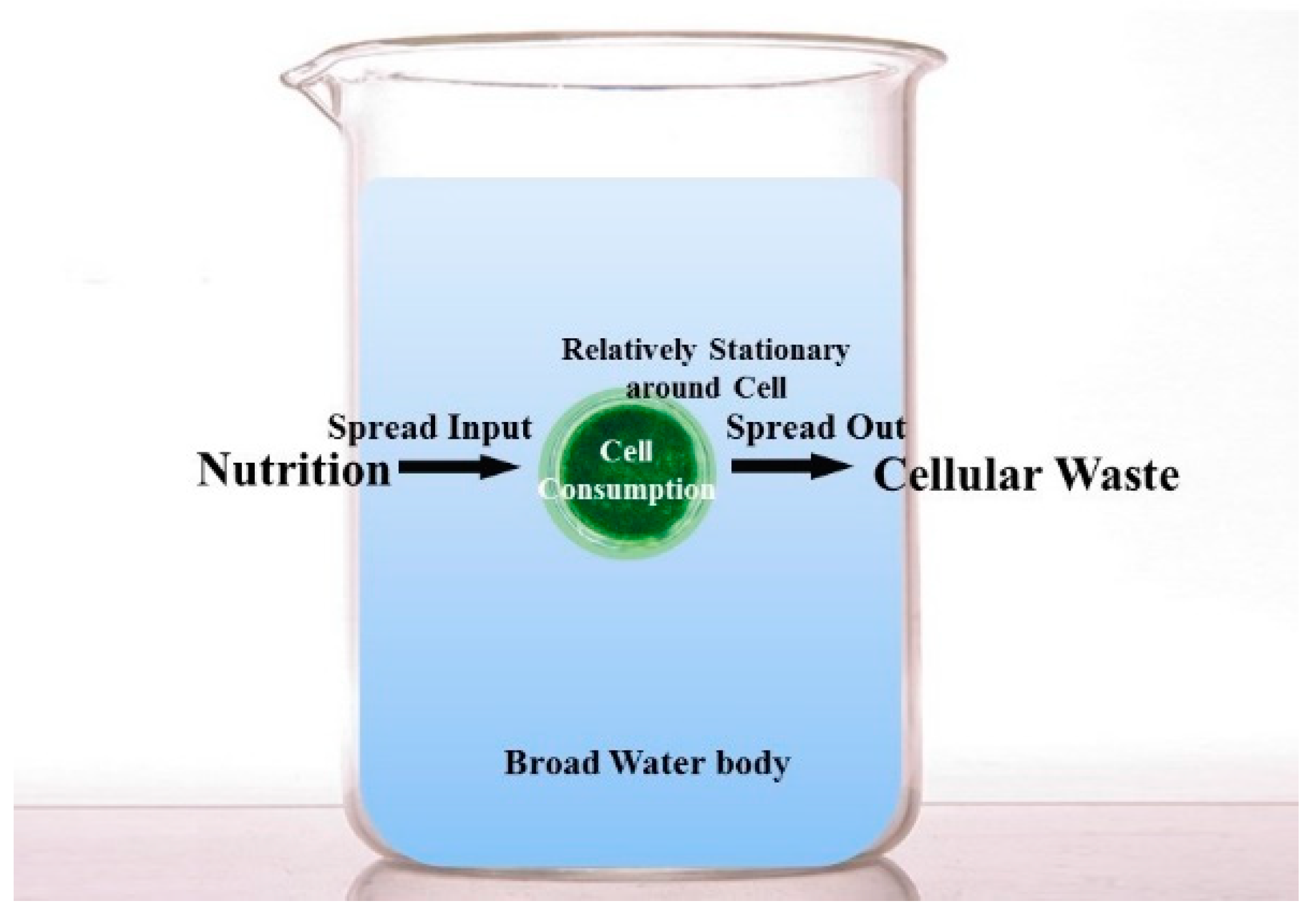
3.2.1. Hypothesis
3.2.2. Modified Equation Deduction Based on Active M
3.2.3. Model Verification
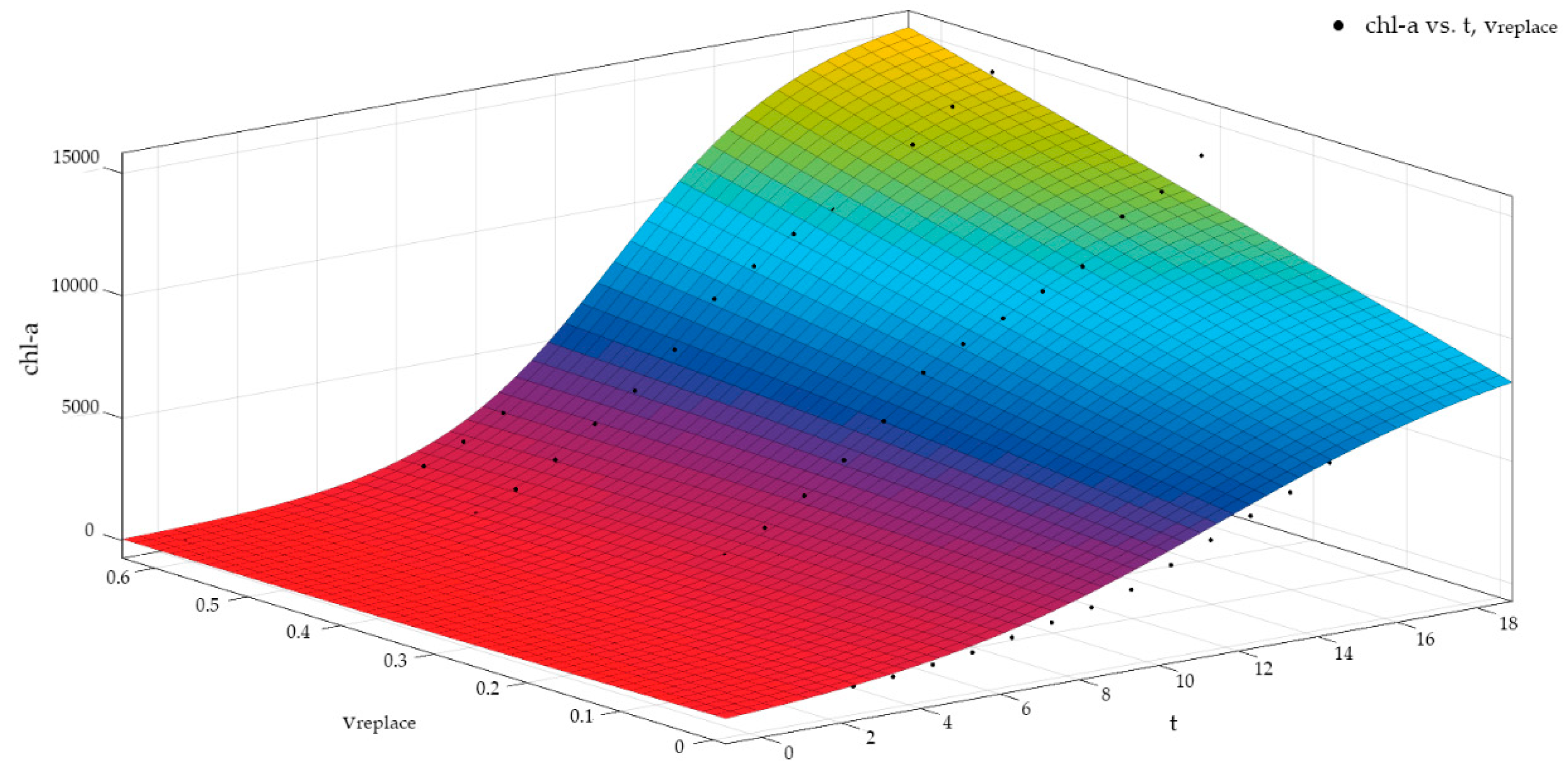
3.2.4. Optimized Parameter Estimation of M
3.2.5. Calculation Fitting Results
3.3. Deduction of Improved Logistic Function Facing Population Competition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mischke, U. Cyanobacteria associations in shallow polytrophic lakes: Influence of environmental factors. Acta Oecol. 2003, 24, S11–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, F.; Straile, D.; Lorke, A.; Ollinger, D. Turbulent mixing and phytoplankton spring bloom development in a deep lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate-Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Bormans, M.; Huisman, J. Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, T.; Shteinman, B. Phytoplankton development and turbulent mixing in Lake Kinneret, 1992–1996. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imteaz, M.A.; Asaeda, T. Artificial mixing of lake water by bubble plume and effects of bubbling operations on algal bloom. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, D.F.; Johnson, D.M.; Yi, Z.Q.; Huang, Y.L. Effects of vertical mixing on phytoplankton blooms in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir: Implications for management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnenmeier, R.; Märkl, H. Hydrodynamic stress capacity of microorganisms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1982, 24, 553–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regel, R.H.; Brookes, J.D.; Ganf, G.G.; Griffiths, R. The influence of experimentally generated turbulence on the Mash01 unicellular Microcystis aeruginosa strain. Hydrobiologia 2004, 517, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Sharples, J.; Stroom, J.M.; Visser, P.M.; Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Sommeijer, B. Changes in turbulent mixing shift competition for light between phytoplankton species. Ecology 2004, 85, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhu, Y.P.; Xiao, Y.H.; Chen, L. Effect of flow velocity on phytoplankton biomass and composition in a freshwater lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.R.; Meyer, D.L.; Waite, A.M.; Ivey, G.N.; Hamilton, D.P. Disaggregation of Microcystis aeruginosa colonies under turbulent mixing: Laboratory experiments in a grid-stirred tank. Hydrobiologia 2004, 519, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Chen, R.H.; Li, F.P.; Chen, L. Effect of flow rate on environmental variables and phytoplankton dynamics: Results from field enclosures. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limn. 2015, 33, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, L.; Long, T.Y.; Liu, C.C.K. Algal bioproductivity in turbulent water: An experimental study. Water 2017, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.Y.; Wu, L.; Meng, G.H.; Guo, W.H. Numerical simulation for impacts of hydrodynamic conditions on algae growth in Chongqing Section of Jialing River, China. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobbelaar, J.U. Turbulence in Mass Algal Cultures and the Role of Light/Dark Fluctuations. J. Appl. Phycol. 1994, 6, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arin, L.; Marrase, C.; Maar, M.; Peters, F.; Sala, M.M.; Alcaraz, M. Combined effects of nutrients and small-scale turbulence in a microcosm experiment. I. Dynamics and size distribution of osmotrophic plankton. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 29, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, K.R.; Primicerio, R.; Larsen, A.; Egge, J.K.; Peters, F.; Guadayol, O.; Jacobsen, A.; Havskum, H.; Marrase, C. Effects of small-scale turbulence on lower trophic levels under different nutrient conditions. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondzo, M.; Warnaars, T.A. Coupled effects of small-scale turbulence and phytoplankton biomass in a small stratified lake. J. Environ. Eng-Asc. 2008, 134, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondzo, M.; Wuest, A. Do Microscopic Organisms Feel Turbulent Flows? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huo, J.S. Effect of small-scale turbulence on the physiology and morphology of two bloom-forming cyanobacteria. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missaghi, S.; Hondzo, M.; Sun, C.; Guala, M. Influence of fluid motion on growth and vertical distribution of cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G.-Tóth, L.; Parpala, L.; Balogh, C.; Tãtrai, I.; Baranyai, E. Zooplankton community response to enhanced turbulence generated by water-level decrease in Lake Balaton, the largest shallow lake in Central Europe. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2211–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Ostos, E.; Cruz-Pizarro, L.; Basanta, A.; George, D. The influence of wind-induced mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant and sinking phytoplankton species. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Luo, L.; Ding, Y.; Bian, G. Dynamics of cyanobacterial bloom formation during short-term hydrodynamic fluctuation in a large shallow, eutrophic, and wind-exposed Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8546–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, H.; Sun, D.Y.; Yu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, L.J. Detection of algal bloom and factors influencing its formation in Taihu Lake from 2000 to 2011 by MODIS. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3705–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, S.; Fastner, J.; Dittmann, E. Microcystin production revisited: Conjugate formation makes a major contribution. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Qin, B.Q.; Han, X.X.; Zhu, L. Turbulence increases the risk of microcystin exposure in a eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu) during cyanobacterial bloom periods. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H. The Effect of Turbulence on Microcystis Aeruginosa and Scenedesmus Quadricauda. Master’s Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bergstedt, M.S.; Hondzo, M.M.; Cotner, J.B. Effects of small scale fluid motion on bacterial growth and respiration. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasto, J.S.; Rusconi, R.; Stocker, R. Fluid mechanics of planktonic microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2012, 44, 373–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prairie, J.C.; Sutherland, K.R.; Nickols, K.J.; Kaltenberg, A.M. Biophysical interactions in the plankton: A cross-scale review. Limnol. Oceanogr Fluids Environ. 2012, 2, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.R.; Ivey, G.N.; Hamilton, D.P.; Waite, A.M. Simple mixing criteria for the growth of negatively buoyant phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KarpBoss, L.; Boss, E.; Jumars, P. Nutrient fluxes to planktonic osmotrophs in the presence of fluid motion. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1996, 34, 71–107. [Google Scholar]
- Warnaars, T.A.; Hondzo, M. Small-scale fluid motion mediates growth and nutrient uptake of Selenastrum capricornutum. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.H.; Gibson, C.H. Effects of small-scale turbulence on microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 1990, 2, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
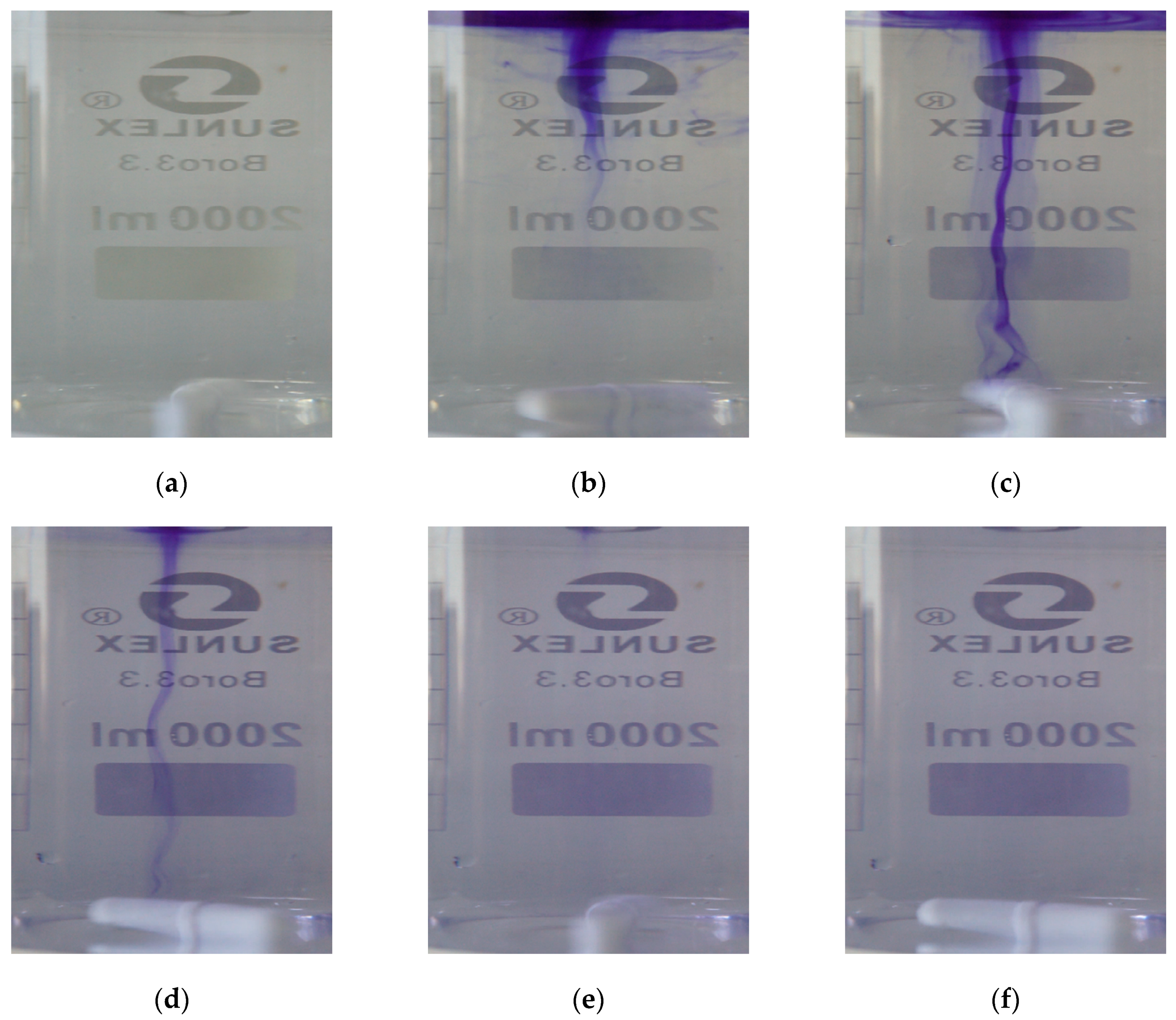
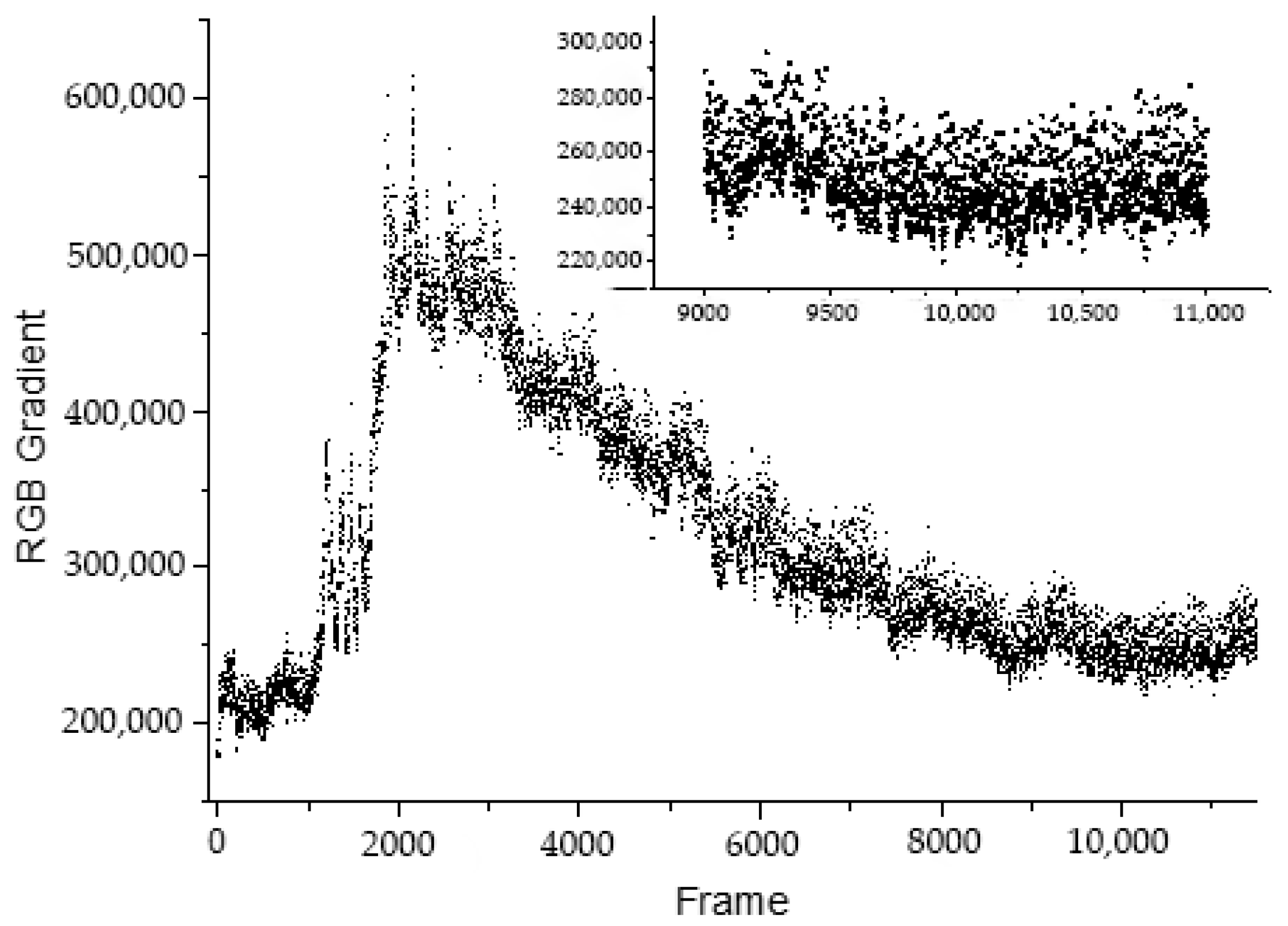
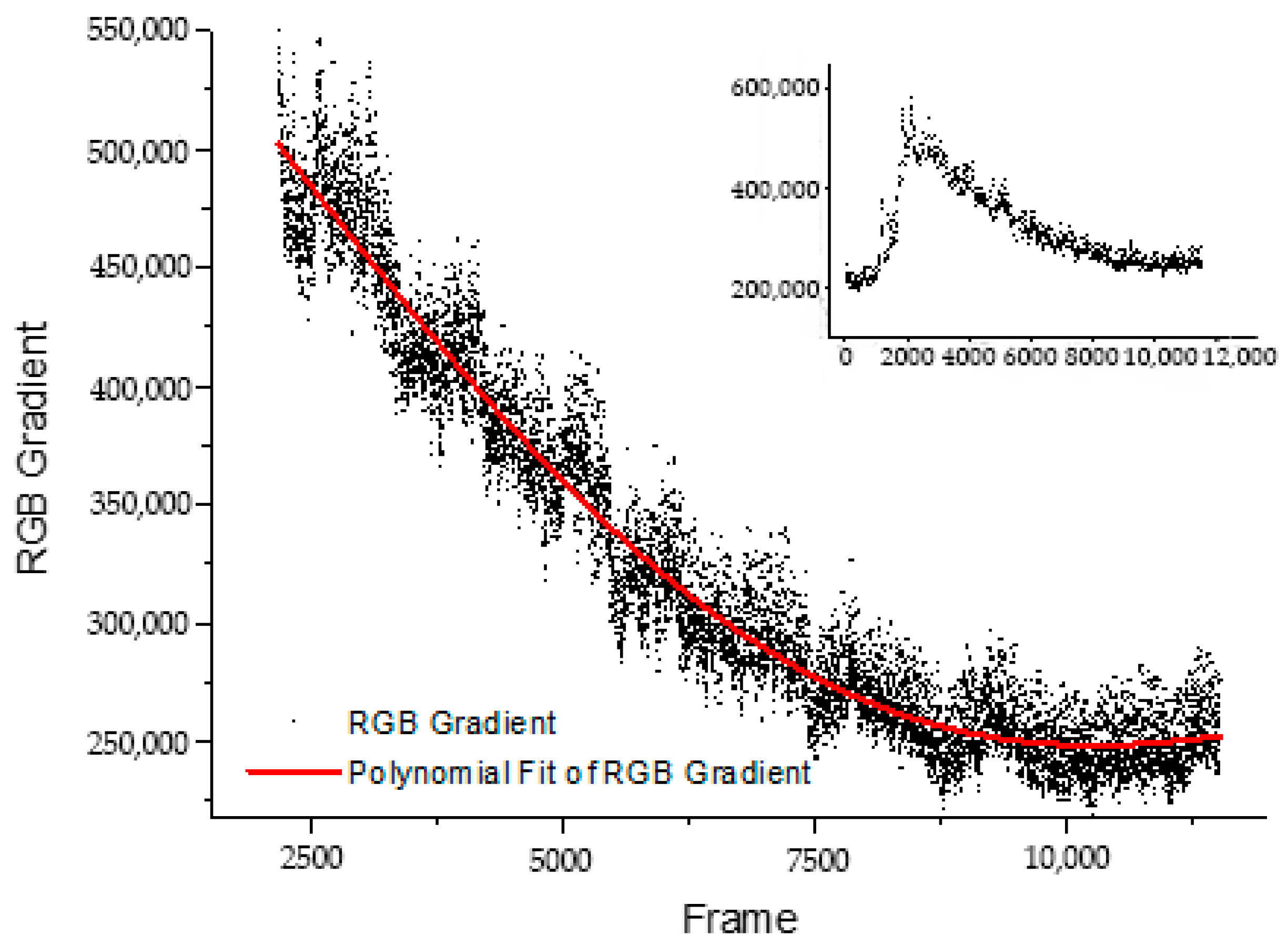
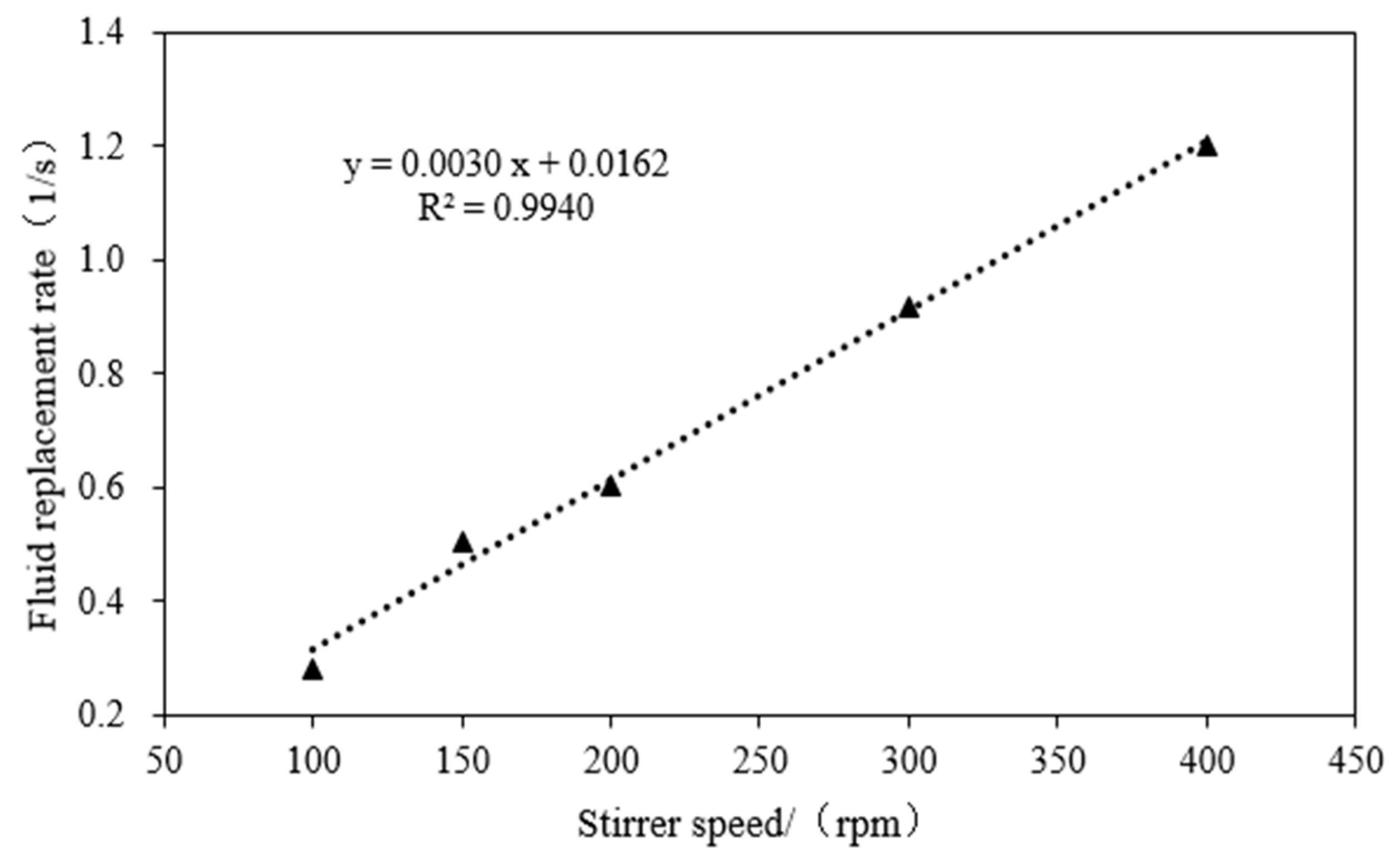

| Parameter | Calculated Value | Estimated Lower Limit | Estimated Higher Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| M0 (μg/mL) | 9471 | 8192 | 1.075 × 104 |
| km | 9779 | 7527 | 1.203 × 104 |
| r | 2.899 × 10−5 | 2.059 × 10−5 | 3.738 × 10−5 |
| t* (d) | 11.53 | 10.72 | 12.33 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| SSE (sum of squares due to error) | 9.682 × 107 |
| R2 | 0.9411 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9386 |
| RMSE (Root mean square error) | 1160 |
| Rotation Rate (rpm) | Maximum Biomass (μg/mL) | Hybrid Effect Coefficient | Biological Plot Ratio (Microcystis aeruginosa Is Unit 1) | Specific Growth Rate | Half-Saturation Time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2620 | –2586 | 0.9205 | 1.025 × 10−4 | 21.21 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Li, F.; Gu, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y. An Improved Logistic Model Illustrating Microcystis aeruginosa Growth Under Different Turbulent Mixing Conditions. Water 2019, 11, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040669
Zhang H, Huang F, Li F, Gu Z, Chen R, Zhang Y. An Improved Logistic Model Illustrating Microcystis aeruginosa Growth Under Different Turbulent Mixing Conditions. Water. 2019; 11(4):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040669
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haiping, Fan Huang, Feipeng Li, Zhujun Gu, Ruihong Chen, and Yuehong Zhang. 2019. "An Improved Logistic Model Illustrating Microcystis aeruginosa Growth Under Different Turbulent Mixing Conditions" Water 11, no. 4: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040669
APA StyleZhang, H., Huang, F., Li, F., Gu, Z., Chen, R., & Zhang, Y. (2019). An Improved Logistic Model Illustrating Microcystis aeruginosa Growth Under Different Turbulent Mixing Conditions. Water, 11(4), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040669





