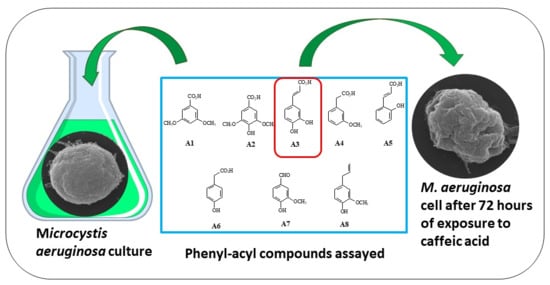
Effect of Phenyl-Acyl Compounds on the Growth, Morphology, and Toxin Production of Microcystis aeruginosa Kützing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Culturing of M. aeruginosa
2.2. Substances
2.3. The Growth Inhibition Test
2.3.1. Cell Counts
2.3.2. The Chl a Measurement
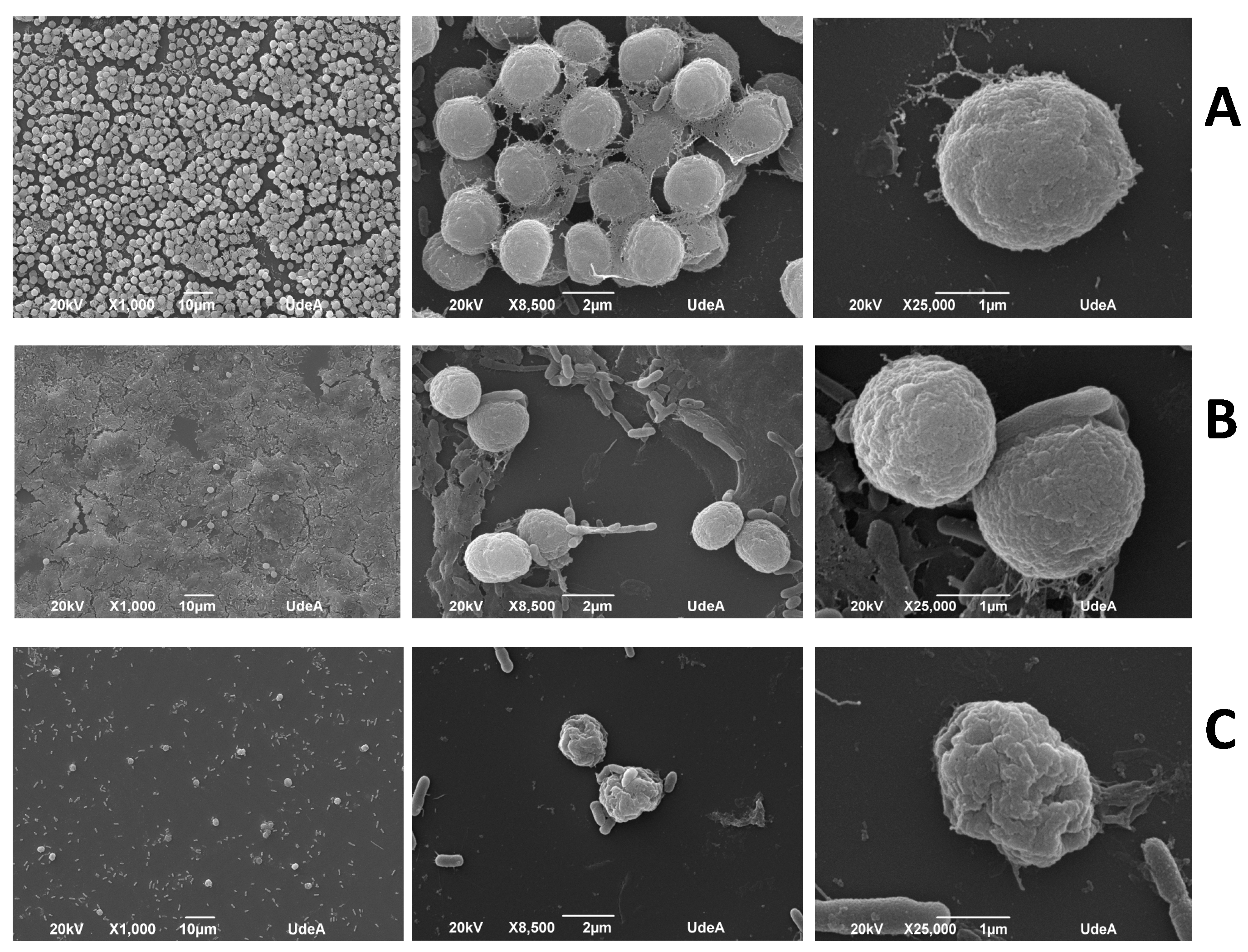
2.4. Morphological Observations under the Optical Microscope and the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.5. The Effect of Phenyl-Acyl Compounds on Toxin Concentration
2.6. The Analysis of the Redox Effect of Caffeic Acid on MC-LR by LC/Q-TOF (Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole-Time of Flight)
2.7. The Acute Toxicity Tests with D. pulex
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
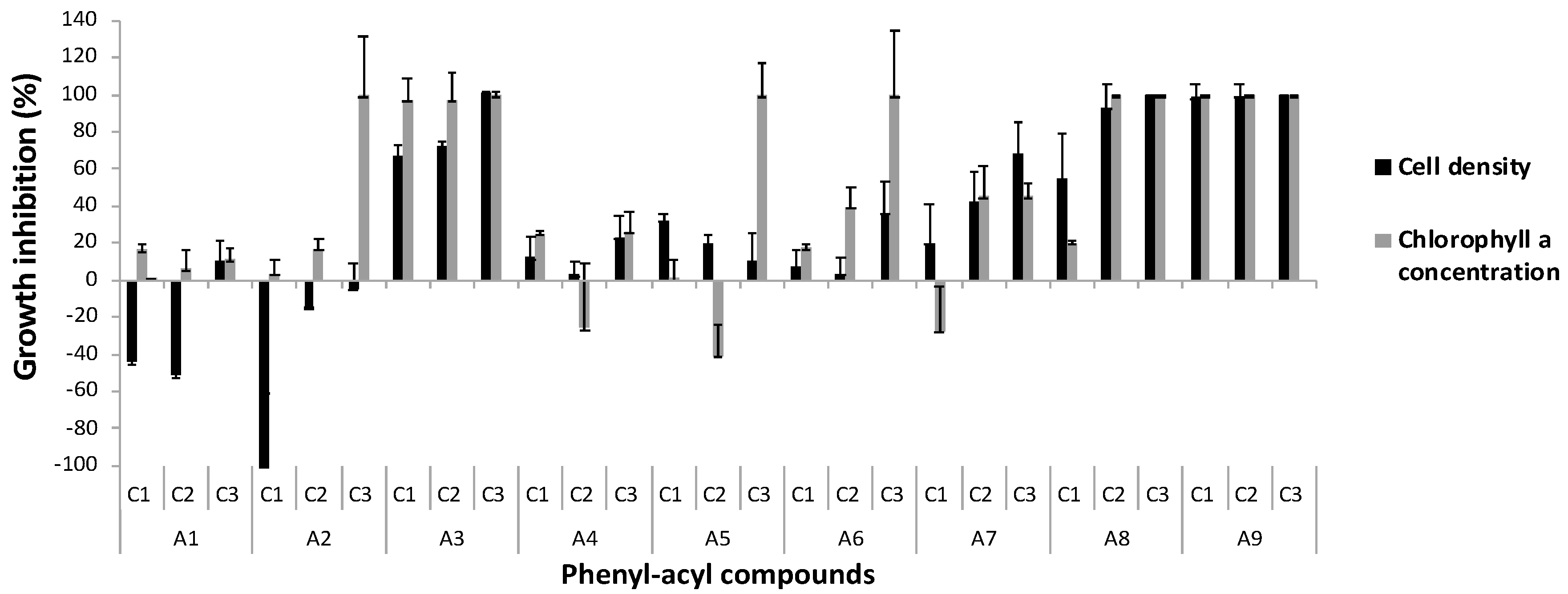
3.1. Growth Inhibition of M. aeruginosa Kützing
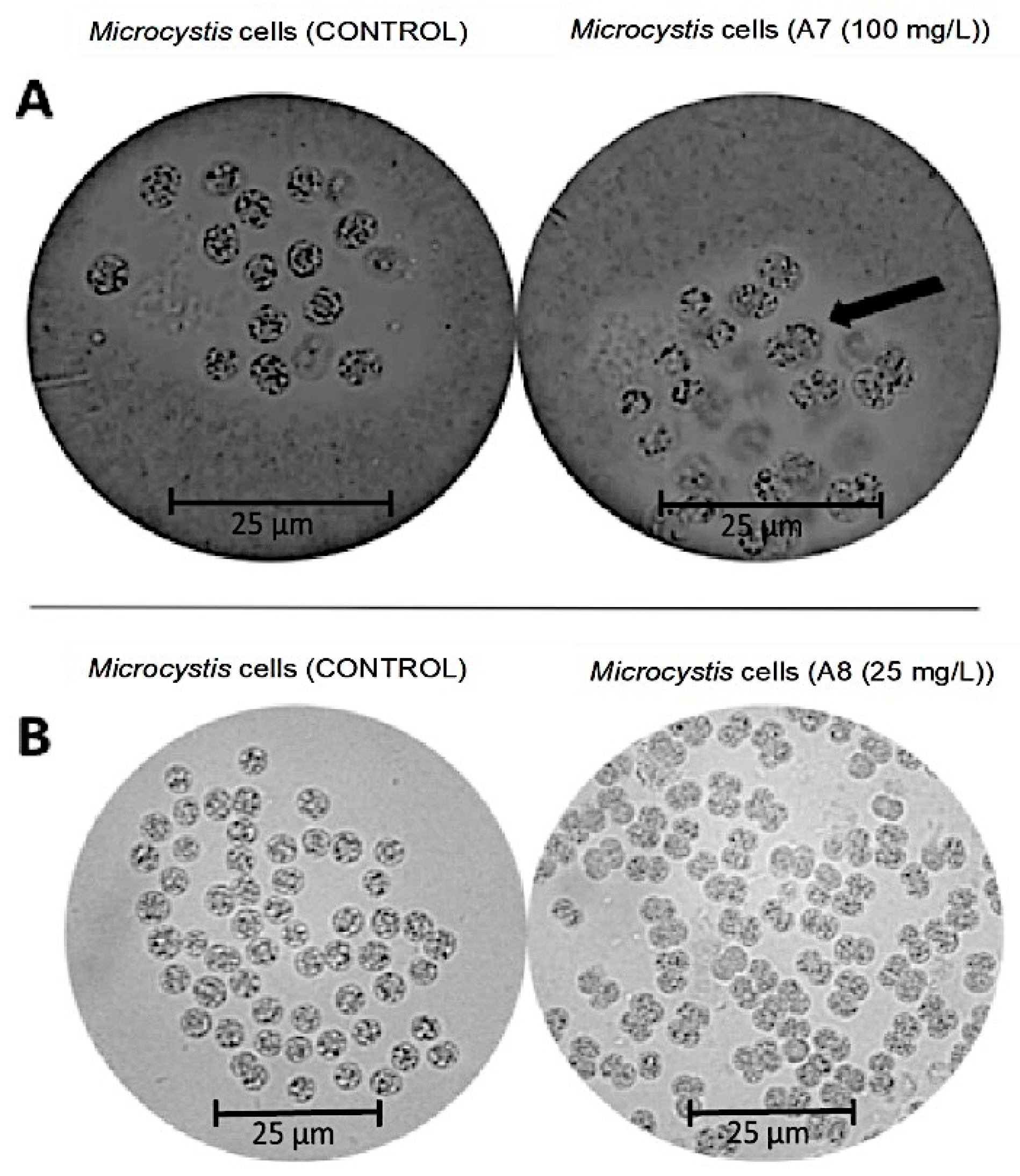
3.2. The Analysis of Morphology of M. aeruginosa Kützing by Microscopy
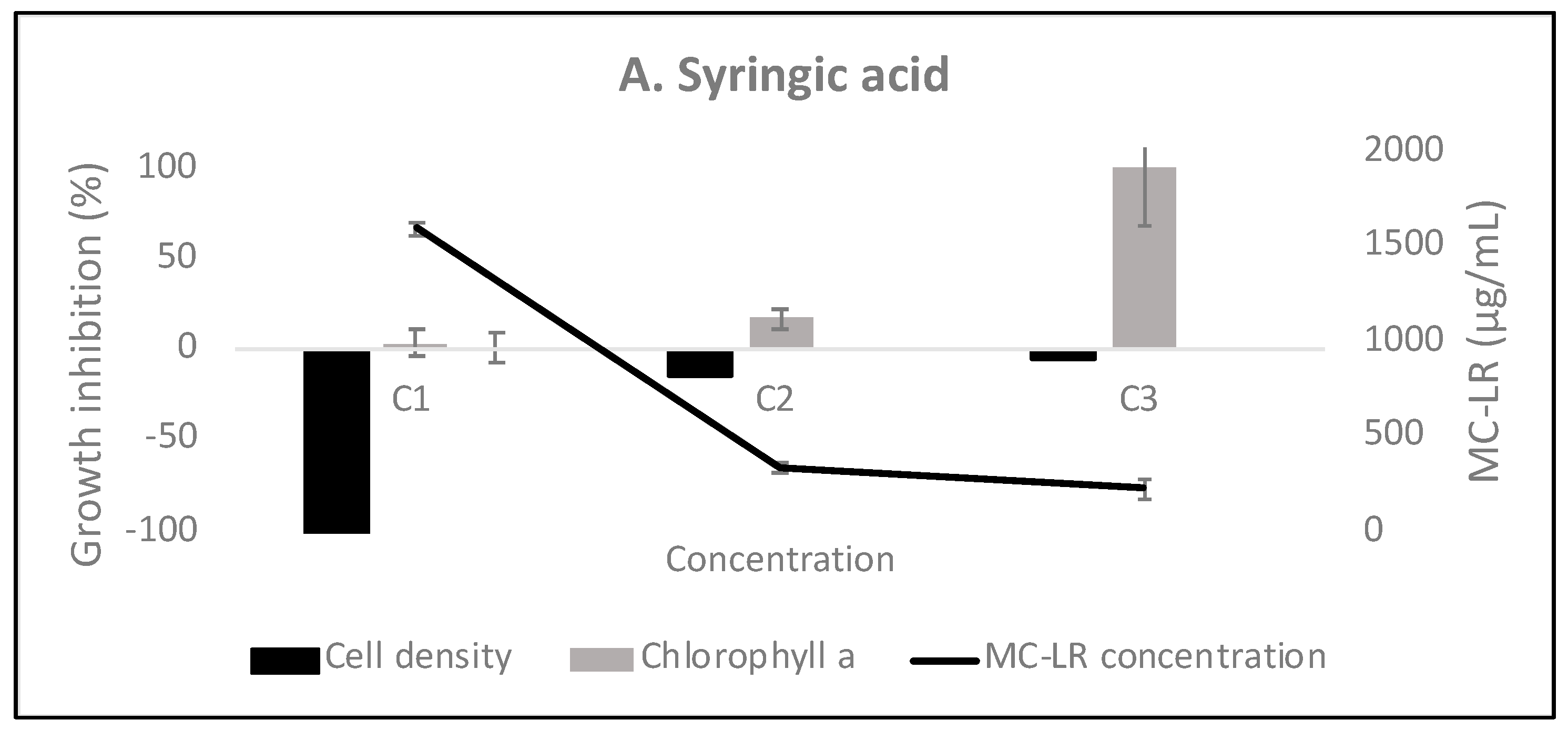
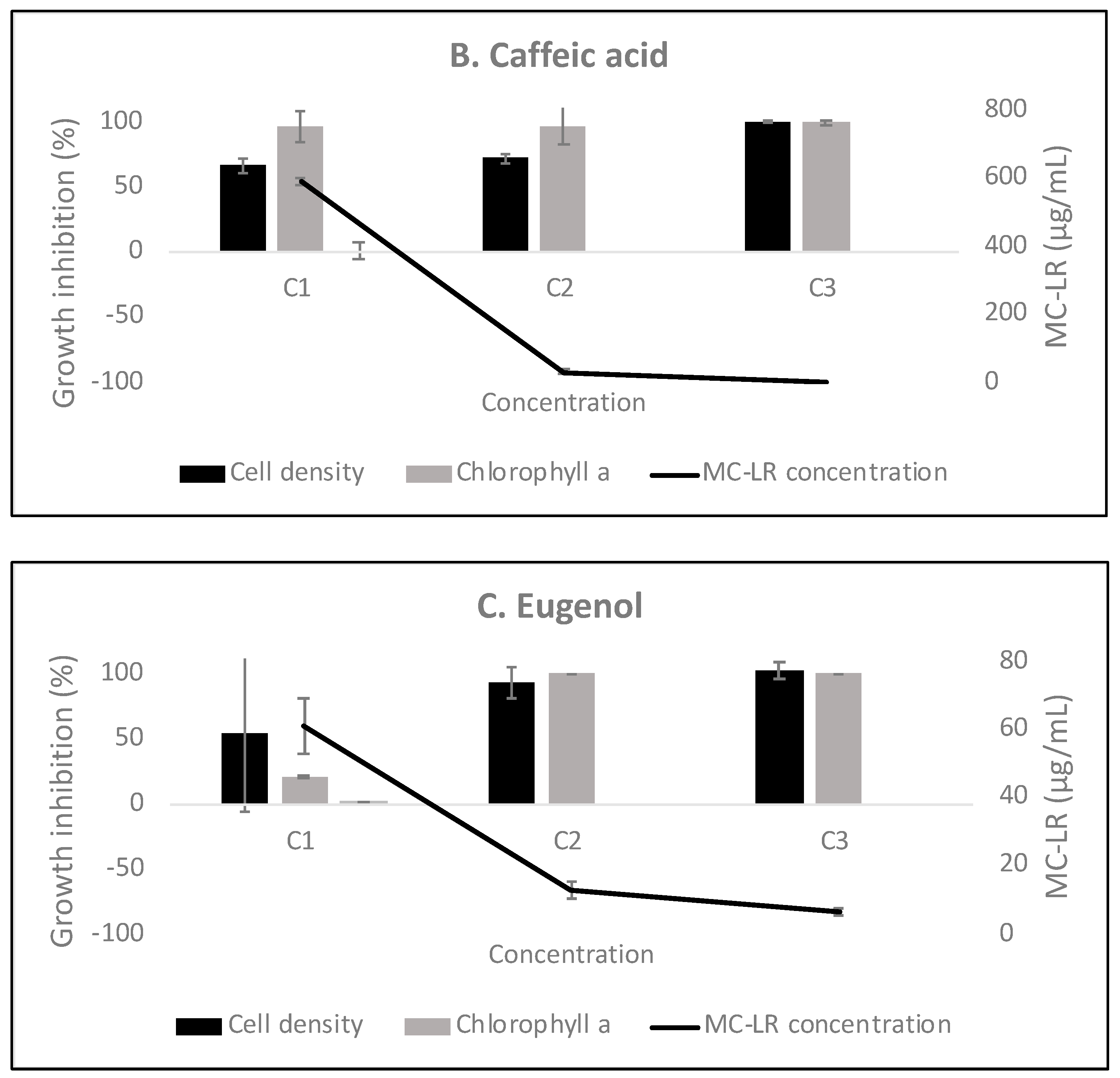
3.3. The Effect of Phenyl-Acyl Compounds on MC-LR Production
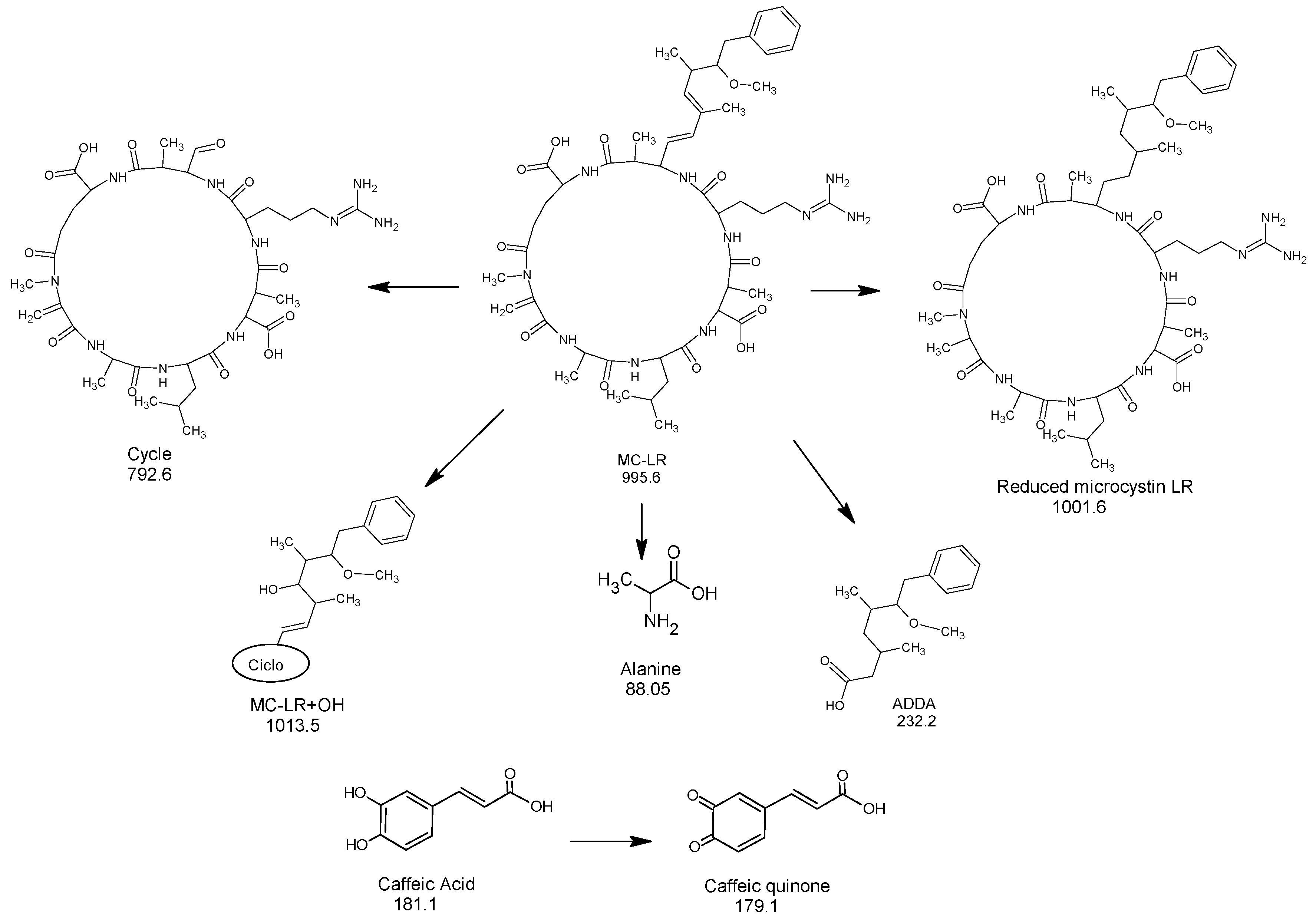
3.4. The Analysis of the Redox Effect of Caffeic Acid on MC-LR by LC/Q-TOF
3.5. Toxicological Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Wert, E.C. Colonial cell disaggregation and intracellular microcystin release following chlorination of naturally occurring Microcystis. Water Res. 2016, 101, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Carmichael, W.W.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Lau, S.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human intoxication by microcystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru — Brazil. Toxicology 2002, 181–182, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, T. Marine bacteria antagonistic to the harmful algal bloom species Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). Biol. Control 2011, 56, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovesi-Fonseca, C.; Philomeno, M.G. Effects of algicide (copper sulfate) application on short-term fluctuations of phytoplankton in Lake Paranoá, central Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2004, 64, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, C. Resilience to Blooms Resilience to Blooms. Science 2015, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, J.; Kawan, A.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Vitamin C modulates Microcystis aeruginosa death and toxin release by induced Fenton reaction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Z.A. Macrophytes-cyanobacteria allelopathic interactions and their implications for water resources management — A review. Limnologica 2017, 63, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.A.; Flórez, M.T.; Echeverri, L.F. Evaluación preliminar de la reducción de microcistina-LR en muestras de florecimientos a través de sistemas sedimentarios. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2015, 31, 405–414. [Google Scholar]
- Mucci, M.; Noyma, N.P.; de Magalhães, L.; Miranda, M.; van Oosterhout, F.; Guedes, I.A.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Marinho, M.M.; Lürling, M. Chitosan as coagulant on cyanobacteria in lake restoration management may cause rapid cell lysis. Water Res. 2017, 118, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.L.; Hua, L.C.; Hung, S.K.; Huang, C. Algal removal from cyanobacteria-rich waters by preoxidation-assisted coagulation–flotation: Effect of algogenic organic matter release on algal removal and trihalomethane formation. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2018, 63, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, A.; Wu, G.; Peng, L.; Xu, Z.; Shao, J. Growth, microcystins synthesis, and cell viability of Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB905 to dissolved organic matter originated from cattle manure. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 118, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanier, R.Y.; Kunisawa, R.; Mandel, M.; Cohen-Bazire, G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (Order Chroococcales). Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 171–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, J.; Geriš, R.; Maršálek, B.; Heteša, J.; Marvan, P. In situ quantification of phytoplankton in reservoirs using a submersible spectrofluorometer. Hydrobiologia 2005, 548, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna, C.L.; Azevedo, M.T.D.P.; Senna, P.A.C.; Komárek, J.; Komárková, J. Planktic Cyanobacteria from São Paulo State, Brazil: Chroococcales. Rev. Bras. Botânica 2004, 27, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguete, E.C.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Leão, J.M.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, J.A.; Menàrd, C.; Lawrence, J.F. HPLC and HPCE analysis of microcystins RR, LR and YR present in cyanobacteria and water by using immunoaffinity extraction. Talanta 2003, 59, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinley, C.M.; Iwinski, K.J.; Hendrikse, M.; Geer, T.D.; Rodgers, J.H. Cell density dependence of Microcystis aeruginosa responses to copper algaecide concentrations: Implications for microcystin-LR release. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, A.B.; Ersan, G.; Tüfekçi, N. Removal of intra- and extracellular microcystin by submerged ultrafiltration (UF) membrane combined with coagulation/flocculation and powdered activated carbon (PAC) adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Rong, S.; Gu, G.; Hu, L.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Yue, F.; Wang, N.; Wu, H.; Li, S. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of linoleic acid sustained-release microspheres on Microcystis aeruginosa at different growth phases. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Xie, P.; Yu, J. Changes in the bacterial community and extracellular compounds associated with the disaggregation of Microcystis colonies. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 61, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; Liu, W.; Fan, Y.; Miao, W. The allelopathic effect and safety evaluation of 3,4-Dihydroxybenzalacetone on Microcystis aeruginosa. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Huang, J.C.; Liu, F.; He, S.; Zhou, W. Effects of selenite on Microcystis aeruginosa: Growth, microcystin production and its relationship to toxicity under hypersalinity and copper sulfate stresses. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecina, G.F.; Dokkedal, A.L.; Saldanha, L.L.; Chia, M.A.; Cordeiro-Araújo, M.K.; do Carmo Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.; da Silva, R.M.G. Response of Microcystis aeruginosa BCCUSP 232 to barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) straw degradation extract and fractions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ling, F.; Yi, Y.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, G.X. Algicidal activity and potential mechanisms of ginkgolic acids isolated from Ginkgo biloba exocarp on Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, S.; Inoue, Y.; Hosomi, M. Algal growth inhibition effects and inducement modes by plant-producing phenols. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Liu, Y.-G.; Yan, Z.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Liu, S.-B.; Wang, W.-J.; Tan, X.-F.; Deng, J.-Q.; Tang, X.; Wang, Q.-P. Allelopathic effect of the rice straw aqueous extract on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehr, J.-C.; Dittmann, E. Biosynthesis and Function of Extracellular Glycans in Cyanobacteria. Life 2015, 5, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.; Zille, A.; Micheletti, E.; Moradas-Ferreira, P.; De Philippis, R.; Tamagnini, P. Complexity of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: Composition, structures, inducing factors and putative genes involved in their biosynthesis and assembly. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 917–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas, E.; Lopez-Rodas, V. Copper sulphate and DCMU-herbicide treatments increase asymmetry between sister cells in the toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa: Implications for detecting environmental stress. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2447–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Sanan, T.; De La Cruz, A.; He, X.; Kong, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Susceptibility of the Algal Toxin Microcystin-LR to UV/Chlorine Process: Comparison with Chlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8252–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


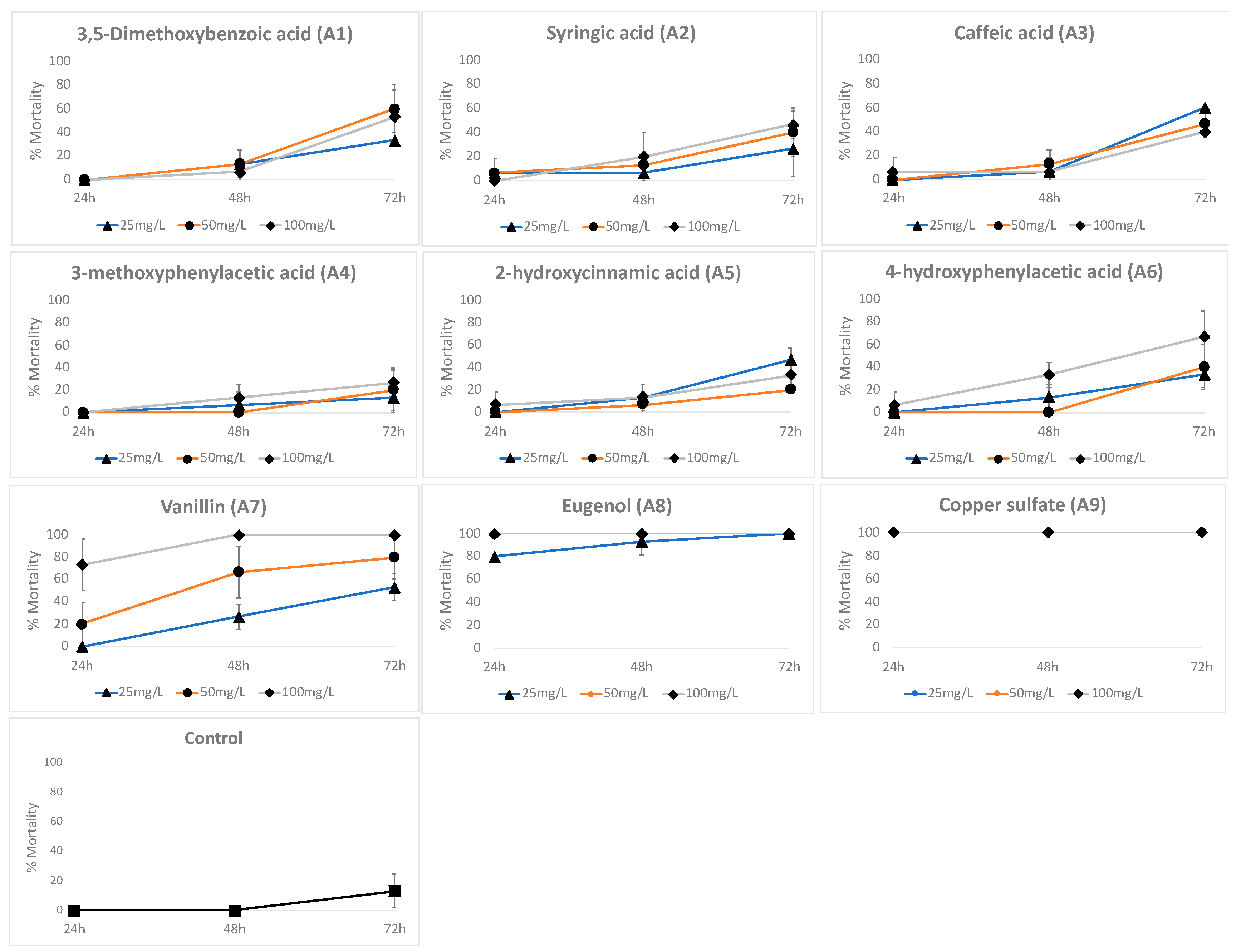
| Phenyl-Acyl | LC50 24 h | LC50 48 h | LC50 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | NE | 251.854 | 71.8 (52.98–108.68) |
| A2 | 760.41 (NE) | 146.26 (101.15–436.72) | 87.49 (66,86–132.07) |
| A3 | 131.62 (NE) | 228.62 (NE) | 84.30 (53.52–241.42) |
| A4 | NE | 179.88 (112.21–7471.96) | 125.42 (88.37–261.20) |
| A5 | 131.62 (NE) | 177.83 (112.21–7471.96) | 125.63 (79.01–554.19) |
| A6 | 131.62 (NE) | 126.25 (93.90–242.85) | 69.37 (52.58–99.22) |
| A7 | 80.42 (67.26–98.41) | 40.43 (32.73–51.42) | 26.62 (22.,41–39.5) |
| A8 | 20.885 (NE) | 13.23 (9.05–19.26) | 7.1 |
| A9 | NE | NE | NE |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera, N.; Florez, M.T.; Velasquez, J.P.; Echeverri, F. Effect of Phenyl-Acyl Compounds on the Growth, Morphology, and Toxin Production of Microcystis aeruginosa Kützing. Water 2019, 11, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020236
Herrera N, Florez MT, Velasquez JP, Echeverri F. Effect of Phenyl-Acyl Compounds on the Growth, Morphology, and Toxin Production of Microcystis aeruginosa Kützing. Water. 2019; 11(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera, Natalia, Maria Teresa Florez, Juan Pablo Velasquez, and Fernando Echeverri. 2019. "Effect of Phenyl-Acyl Compounds on the Growth, Morphology, and Toxin Production of Microcystis aeruginosa Kützing" Water 11, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020236
APA StyleHerrera, N., Florez, M. T., Velasquez, J. P., & Echeverri, F. (2019). Effect of Phenyl-Acyl Compounds on the Growth, Morphology, and Toxin Production of Microcystis aeruginosa Kützing. Water, 11(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020236