Abstract
Numerous anthropogenic stressors impact rivers worldwide. Hypoxia, resulting from organic waste releases and eutrophication, occurs very commonly in Mediterranean rivers. Nonetheless, little is known about the effects of deoxygenation on the behavior of Mediterranean freshwater fish. To fill this knowledge gap, we assessed the impact of three different dissolved oxygen levels (normoxia, 48.4%, 16.5% saturation) on kinematics indicators (swimming velocity, acceleration, distance traveled) and shoaling cohesion of adult Iberian barbel, Luciobarbus bocagei, a widespread cyprinid species inhabiting a broad range of lotic and lentic habitats. We conducted flume experiments and video-tracked individual swimming movements of shoals of five fish. Our results reveal significant differences between the treatments regarding kinematics. Swimming velocity, acceleration, and total distance traveled decreased stepwise from the control to each of the two oxygen depletion treatments, whereby the difference between the control and both depletion levels was significant, respectively, but not between the depletion levels themselves. Shoaling cohesion showed dissimilarities between the treatments regarding the maximum distance between fish, as the high depletion treatment differed from each of the other two, indicating that under severe oxygen depletion some individuals move away from the shoal. Overall, our results show how oxygen depletion changes fish behavior, which may entail ecological responses, highlighting the need to maintain an unfragmented river network to ensure movement dispersal among habitats, thus providing conditions for species escapement from hypoxia.
1. Introduction
Mediterranean rivers are characterized by frequent hydrological disturbances, including seasonally predictable drought events, exposing biota to harsh environmental conditions [1]. An extensive period of low summer flows naturally leads to an increase in temperature and primary production, and subsequently to a reduction of oxygen levels [2]. Mediterranean fish populations are adapted to naturally occurring seasonal oxygen fluctuations [1]. However, human activities, such as water abstraction, the discharge of organic wastes, and the diffusion of agricultural fertilizers into aquatic systems, are common problems in Mediterranean rivers, causing further diminishment of oxygen levels of already stressed freshwater systems and possibly leading to hypoxic conditions [3,4] that affect fish and subsequently the entire aquatic community [3,4,5,6].
Hypoxic conditions can cause behavioral and physiological stress in fish [7], which can entail many ecological consequences, including impaired reproduction, feeding, and predator avoidance [8,9]. Regarding swimming activity, fish experience a trade-off between activity increase as they try to find more oxygenated water and activity decrease due to lower oxygen availability [10]. When exposed to hypoxia, fish groups may reduce their school density and size as they tend to increase their horizontal spacing to one another in a tentative manner to counteract the limiting effect of oxygen depletion on schools [5]. However, this may cause disadvantages, such as lower coordination or higher energetic costs of locomotion [11]. Both activity changes, individual fish movements and shoaling cohesion, are, however, species-dependent and are influenced by the degree of hypoxia [5,9]. Too low oxygen saturation will at some point be lethal for fish, whereby the lethal concentration also differs between species [12].
The Mediterranean region has been identified as one of the most prominent hot spots of climate change [13]. According to future predictions of climate change for Southern Europe, precipitation will decrease by up to 20% [14], which will also entail significant changes in seasonal runoff asymmetry [15]. Hence, exacerbated and extended summer low flow conditions, in combination with existing human pressures, will likely increase the frequency and duration of hypoxic events in rivers [1,15,16]. To protect and manage rivers, it is vital to understand the impact of deoxygenation on individual fish movements, schooling behavior, and the implications thereof for fish populations, which are a pivotal component of aquatic ecosystems.
To our knowledge, no study has assessed the effects of oxygen depletion on the movements of Mediterranean freshwater fish. Therefore, this work analyzed the impact of three different dissolved oxygen levels on the behavior of a common fish species of the Iberian Peninsula, the Iberian barbel, Luciobarbus bocagei. We hypothesized that increasing levels of oxygen depletion would (1) reduce fish movement and (2) decrease the cohesion of fish shoals.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted flume experiments in a section (2.0 × 1.0 m) of an artificial channel, set at a slope of 3% and a discharge of 28 L∙s−1, resulting in a water depth of 0.7 m. We caught 75 wild adult Iberian barbel, Luciobarbus bocagei (150–250 mm total length), via electrofishing in the Lizandro River, Portugal (33 m a.s.l.), and brought them to the lab facilities (92 m a.s.l.), where they were held in three 800 L tanks (25 fish per tank) in a controlled environment for 48 h before experimentation. After the trials, fish were returned alive to the river. Further details on fish sampling, holding, and the testing facility are given in Branco et al. [17,18] and Santos et al. [19].
In each experiment, we monitored the movement of a shoal of five fish [20] under three levels of dissolved oxygen (DO) conditions: (1) a control level (normoxic condition with DO saturations >80% [21]), (2) a mild depletion level of 48.4% DO saturation (4.4 ± 0.2 mg∙L−1), and (3) a high depletion level of 16.5% DO saturation (1.4 ± 0.1 mg∙L−1) (Table 1). These levels allowed for testing along a decreasing gradient, whereby the latter represents a level of extreme oxygen depletion that may induce stress or even death in fish [6,22]. We reduced oxygen values by adding sodium sulfite (Na2SO3). This compound is a recognized oxygen scavenger [23] that has been used to create oxygen-deficient conditions in fish research [18,24], as well as in aquatic research more generally [25,26]. Each experiment lasted for eight minutes (six min acclimation [27] plus two min video-tracking) and was replicated five times, whereby a new subset of fish was used for each trial, giving a total of 75 tested fish.

Table 1.
Physiochemical and biological description of the experiments (average values ± SD), and number of analyzed videos and frames per treatment.
The experiments were conducted in strict accordance with ethical provisions on the welfare of experimental animals enforced by the European Union and were coordinated by J.M. Santos, who holds FELASA level C certification (www.felasa.eu) to direct animal experiments. Fish sampling permits were obtained from the Institute for Nature Conservation and Forests (ICNF). Fish experiments and maintenance in the laboratory and experimental facility were authorized by the Department for Health and Animal Protection (Direcção de Serviços de Saúde e Protecção Animal; permit issued on 6 October 2011) in accordance with the recommendations of the “protection of animal use for experimental and scientific work”.
We recorded fish movements with a GoPro Hero 3 Black edition camera mounted above the channel. The camera was set to record at 1280 × 720 pixels. We processed the videos with GoPro Studio to exclude the fisheye effect and then analyzed them at 10 frames per second, resulting in 1200 data points per single fish (Table 1) with the software Tracker (http://physlets.org/tracker/), whereby we calibrated the measurement settings of each video with the size of the channel’s bottom tiles (20 × 20 cm).
We calculated kinematics indicators, i.e., mean swimming velocity (cm∙s−1), acceleration (cm∙s−2), and distance traveled (cm) for every single fish to investigate spontaneous locomotion activity changes between DO treatments [27]. To test for differences in shoaling cohesion between treatments, we measured the horizontal (XY) inter-individual distance between all fish within a shoal, based on center of mass [27,28], whereby we used the average of the minimum, mean, and maximum values as a proxy for the shoal cohesion. In all analyses, we first tested for overall statistical significance between the treatment levels. If this was detected, it was followed by pair-wise post-hoc tests. For most of the tests, data did not fulfill all assumptions required for parametric tests. Therefore, omnibus tests were conducted with the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis H test, followed by Dunn’s pairwise tests (adjusted using the Bonferroni correction) (α = 0.05) using SPSS 24. The dataset to this article can be found online in the Supplementary Material Section (Datasheet S1).
3. Results
3.1. Kinematics
We detected significantly different swimming velocities between the treatments (χ2 = 21.37, p < 0.001, Figure 1a). Pairwise comparison found that fish in the control treatment (T0) swam faster than those in the mild depletion treatment (T1) (χ2 = 18.92, p < 0.01), as well as those in the high depletion treatment (T2) (χ2 = 26.96, p < 0.001), whereas the mild and high depletion treatment (T1 and T2) were not distinct from each other. The average swimming velocity was 10.8 (±0.3 Standard Error (SE)), 8.6 (±0.5 SE), and 7.9 (± 0.4 SE) cm∙s−1 for T0, T1, and T2, respectively.
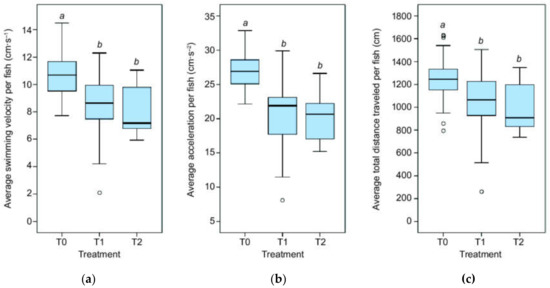
Figure 1.
Fish kinematics. (a) Average swimming velocity, (b) acceleration, and (c) distance traveled per fish in the three treatment levels: T0 = control, T1 = mild depletion, T2 = high depletion; “a” and “b” above the boxplots indicate a significant difference between two treatments, whereby the same letter indicates no statistically significant difference by Kruskal-Wallis test.
For acceleration, we found a similar pattern (χ2 = 34.26, p < 0.001, Figure 1b), whereby the pairwise comparison was highly significant for both T0 and T1 (χ2 = 27.40, p < 0.001), as well as T0 and T2 (χ2 = 32.04, p < 0.001). Average fish acceleration was 27.1 (± 0.6 SE), 20.7 (± 1.0 SE), and 20.3 (± 0.7 SE) cm∙s−2 for T0, T1, and T2, respectively.
We found significant differences in the total distance traveled by each fish among the treatments (χ2 = 13.10, p < 0.001, Figure 1c), though pairwise comparison revealed that fish only traveled longer distances in T0 (1247 cm ± 44.0 cm SE) when compared to T2 (987 cm ± 45.6 cm SE) (χ2 = 21.51, p < 0.001). T0 and T1 (1055 cm ± 57.2 cm SE) were marginally significant (χ2 = 13.76, p = 0.050).
3.2. Shoaling Cohesion
Average minimum distances between fish ranged from 8.5–14.4 cm, mean distances from 46.6–67.8 cm, and maximum distances from 82.2–124.5 cm (Table 2). Regarding the minimum and mean distance between the fish, we did not detect differences between the three treatments. However, for the maximum distance between fish, we found significant dissimilarities between the treatments (Table 2), as the distance between fish was higher in T2 when compared to T0 (χ2 = −15.02, p < 0.05) as well as T1 (χ2 = −16.90, p < 0.05).

Table 2.
Average minimum, mean, and maximum distances (cm ± SE) between fish within a shoal during the three treatments.
4. Discussion
Hypoxic events affect Mediterranean rivers worldwide [2,29], and fish, in particular, are highly sensitive to reduced oxygen concentrations [9,30]. The ecological impact of such events ranges from beneficial to mortality [31], but common responses include behavioral alterations [5,9,18].
4.1. Kinematics
Our results showed that swimming velocity, acceleration, and distance traveled significantly differed between the treatment levels. Pair-wise tests revealed that fish in the control treatment exhibited higher spontaneous activity than those in the mild depletion as well as high depletion treatment, which implies that barbel reduce their activity if DO values are lowered. A similar behavioral response is documented for several other species [9,32]. Such lowered activity can be interpreted as an adaptive energy-saving response [33]. Carassius carassius, e.g., reduces its locomotor activity to 50% of that during normoxia when exposed to prolonged periods of anoxia, thereby saving 35–40% of total energy consumption [34]. Swimming speed of Ammodytes tobianus decreased by 95% after 40 min at the lowest stepwise reduced critical partial pressure of oxygen (3.1 kPa) [32]. Even though the acclimation phase and analysis time in our study were short, fish responded quickly to decreased DO levels by significantly reducing their movement activity.
4.2. Shoaling Cohesion
Under low DO (20%) conditions, school measurements of Clupea harengus significantly increased [35]. We found a similar pattern regarding the maximum distance between individuals at the high depletion treatment in comparison to both the control and the mild one, whereas this was not the case for the minimum and average distance. Nevertheless, this might indicate that at approximately 15% DO, some barbel start to depart from the shoal, while others still seem to prefer the close vicinity of the shoal. In such high oxygen depleted situations, individual movement appears to override shoal movements as individuals risk leaving shoal protection to find more oxygenated areas further away, thus reducing shoal integrity by splitting the shoal into two or more groups [11].
4.3. Ecological Implications
In natural situations, fish might try to escape unfavorable conditions. In a hypoxic environment, Oncorhynchus mykiss selected lower temperature ranges, enhancing their chance of survival [36]. In the confined flume section of the present study, barbel seemed to reduce their swimming activity, possibly adopting a “sit-and-wait” strategy, which has also been described for other species [5]. In connected pool habitat experiments, however, barbel continued to move despite reduced oxygen levels, possibly searching for higher-oxygenated areas. Nevertheless, the number of movements significantly decreased under low (15%) DO concentrations [18]. Under such oxygen-depleted conditions, isolated habitats may, therefore, cause severe threats to stream fish, highlighting the need to maintain an unfragmented river network to ensure movement dispersal among habitats, and thus providing conditions for species escapement from hypoxia.
In our experiments, the addition of sodium sulfite not only reduced DO levels but also led to an increase in water temperature, conductivity, and pH, making it difficult to completely disentangle the effects of lowered DO from the increase of the other parameters. Nevertheless, similar changes in these variables can often occur with the release of organic stressors, such as sewage, into rivers [18,25]. To increase understanding of fish resistance to oxygen-depleted conditions and its implications for aquatic ecosystems, future studies should investigate the effects of long-term DO depletion on riverine fish species.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/11/4/642/s1, Datasheet S1: Fish tracking data (kinematics and shoaling).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.F. and P.B.; methodology, T.F., P.B., and J.M.S.; formal analysis, P.B., J.M.S., and D.S.H.; investigation, D.S.H.; data curation, D.S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S.H.; writing—review and editing, D.S.H., P.B., J.M.S., and T.F.; visualization, D.S.H.; supervision, P.B. and T.F.; project administration, T.F., P.B., and J.M.S.; funding acquisition, T.F.
Funding
This research was financed by the EU FP7 MARS project (contract no. 603378). D.S.H. and P.B. received a grant from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal (FCT) (PD/BD/114440/2016 and SFRH/BPD/94686/2013). J.M.S. was funded by a grant (MARS/BI/2/2014) from the MARS project and is presently the recipient of an FCT researcher contract (IF/00020/2015). CEF is a research unit funded by FCT (UID/AGR/00239/2013).
Acknowledgments
We thank Filipe Romão, Susana Amaral, Inês Marques, and Filipe Vieira for their assistance in the lab, as well as the contributions of the three reviewers. Supported by BOKU Vienna Open Access Publishing Fund.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. Streams in Mediterranean climate regions: Abiotic influences and biotic responses to predictable seasonal events. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1999, 30, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillebø, A.I.; Morais, M.; Guilherme, P.; Fonseca, R.; Serafim, A.; Neves, R. Nutrient dynamics in Mediterranean temporary streams: A case study in Pardiela catchment (Degebe River, Portugal). Limnol. Ecol. Manag. Inl. Waters 2007, 37, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Ian, M.; Mike, M.; Ian, S. Effects of short-term oxygen depletion on fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 2937–2942. [Google Scholar]
- Prat, N.; Munné, A. Water use and quality and stream flow in a Mediterranean stream. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3876–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P.; Herbert, N.A.; Lefrançois, C.; Steffensen, J.F.; McKenzie, D.J. The Effect of Hypoxia on Fish Swimming Performance and Behaviour. In Swimming Physiology of Fish; Palstra, A., Plana, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013; pp. 129–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ekau, W.; Auel, H.; Pörtner, H.O.; Gilbert, D. Impacts of hypoxia on the structure and processes in pelagic communities (zooplankton, macro-invertebrates and fish). Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1669–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, N.A.; Steffensen, J.F. The response of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, to progressive hypoxia: Fish swimming speed and physiological stress. Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.L. Dissolved oxygen and fish behavior. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1987, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.J.; McKenzie, D.J. Behavioral Responses and Ecological Consequences. In Fish Physiology; Richards, J.G., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 25–77. ISBN 978-0-12-374632-0. [Google Scholar]
- Killen, S.S.; Marras, S.; Ryan, M.R.; Domenici, P.; Mckenzie, D.J. A relationship between metabolic rate and risk-taking behaviour is revealed during hypoxia in juvenile European sea bass. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P.; Steffensen, J.F.; Marras, S. The effect of hypoxia on fish schooling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, M.J.; Van Den Heuvel, M.R.; Ling, N. Relative sensitivities of common freshwater fish and invertebrates to acute hypoxia. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 39, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F. Climate change hot-spots. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Impacts of Europe’s Changing Climate–Indicator Based Assessment; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Da Cunha, L.V.; Da Oliveira, R.P.; Nascimento, J.; Ribeiro, L. Impacts of climate change on water resources: A case-study for Portugal. In Water in Celtic Countries: Quantity, Quality and Climate Variability, Proceedings of the Fourth InterCeltic Colloquium on Hydrology and Management of Water Resources; IAHS Publ.: Guimarães, Portugal, 2007; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ficke, A.D.; Myrick, C.A.; Hansen, L.J. Potential impacts of global climate change on freshwater fisheries. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2007, 17, 581–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.; Santos, J.M.; Katopodis, C.; Pinheiro, A.; Ferreira, M.T. Pool-Type Fishways: Two Different Morpho-Ecological Cyprinid Species Facing Plunging and Streaming Flows. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, P.; Santos, J.M.; Amaral, S.; Romão, F.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Ferreira, M.T. Potamodromous fish movements under multiple stressors: Connectivity reduction and oxygen depletion. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.M.; Silva, A.; Katopodis, C.; Pinheiro, P.; Pinheiro, A.; Bochechas, J.; Ferreira, M.T. Ecohydraulics of pool-type fishways: Getting past the barriers. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 48, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Nie, L.; Wu, H.; Kuang, L.; Huang, Q. The effect of group size on school structure in juvenile black carp. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 6062–6067. [Google Scholar]
- Schurmann, H.; Steffensen, J.F. Spontaneous swimming activity of Atlantic Cod Gadus Morhua exposed to graded hypoxia at three temperatures. J. Exp. Biol. 1994, 197, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Small, K.; Kopf, R.K.; Watts, R.J.; Howitt, J. Hypoxia, Blackwater and Fish Kills: Experimental Lethal Oxygen Thresholds in Juvenile Predatory Lowland River Fishes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.M., Jr. Morphological adaptations of cyprinodontoids for inhabiting oxygen deficient waters. Copeia 1970, 2, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampton, W.G.R. Effects of anoxia on the distribution, respiratory strategies and electric signal diversity of gymnotiform fishes. J. Fish Biol. 1998, 53, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calapez, A.R.; Branco, P.; Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, T.; Hein, T.; Brito, A.G.; Feio, M.J. Macroinvertebrate short-term responses to flow variation and oxygen depletion: A mesocosm approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peay, S.; Hiley, P.D.; Collen, P.; Martin, I. Biocide treatment of ponds in Scotland to eradicate signal crayfish. Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic. 2006, 380–381, 1363–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.; Gerlai, R. Automated tracking of zebrafish shoals and the analysis of shoaling behavior. In Zebrafish Protocols for Neurobehavioral Research; Kalueff, A.V., Stewart, A.M., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Delcourt, J.; Poncin, P. Shoals and schools: Back to the heuristic definitions and quantitative references. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2012, 22, 595–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, D.; Sabater, S. Water quality and assessment under scarcity: Prospects and challenges in Mediterranean watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, M.; Regan, M.D. Can variation among hypoxic environments explain why different fish species use different hypoxic survival strategies? J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb161349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Introduction to Environmental and Economic Consequences of Hypoxia. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2011, 27, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, J.W.; Steffensen, J.F. The effect of hypoxia on behavioural and physiological aspects of lesser sandeel, Ammodytes tobianus (Linnaeus, 1785). Mar. Biol. 2007, 150, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Rademacher, K.; Kils, U. In situ investigations on the respiration and behaviour of the eelpout Zoarces viviparus under short-term hypoxia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 88, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, G.E.; Rosen, P.R.; Johansson, D. Anoxic depression of spontaneous locomotor activity in crucian carp quantified by a computerized imaging technique. J. Exp. Biol. 1993, 180, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Domenici, P.; Silvana Ferrari, R.; Steffensen, J.F.; Batty, R.S. The effect of progressive hypoxia on school structure and dynamics in Atlantic herring Clupea harengus. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurmann, H.; Steffensen, J.F.; Lomholt, J.P. The influence of hypoxia on the preferred temperature of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. Exp. Biol. 1991, 157, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).