Water Footprint and Water Pinch Analysis in Ethanol Industrial Production for Water Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
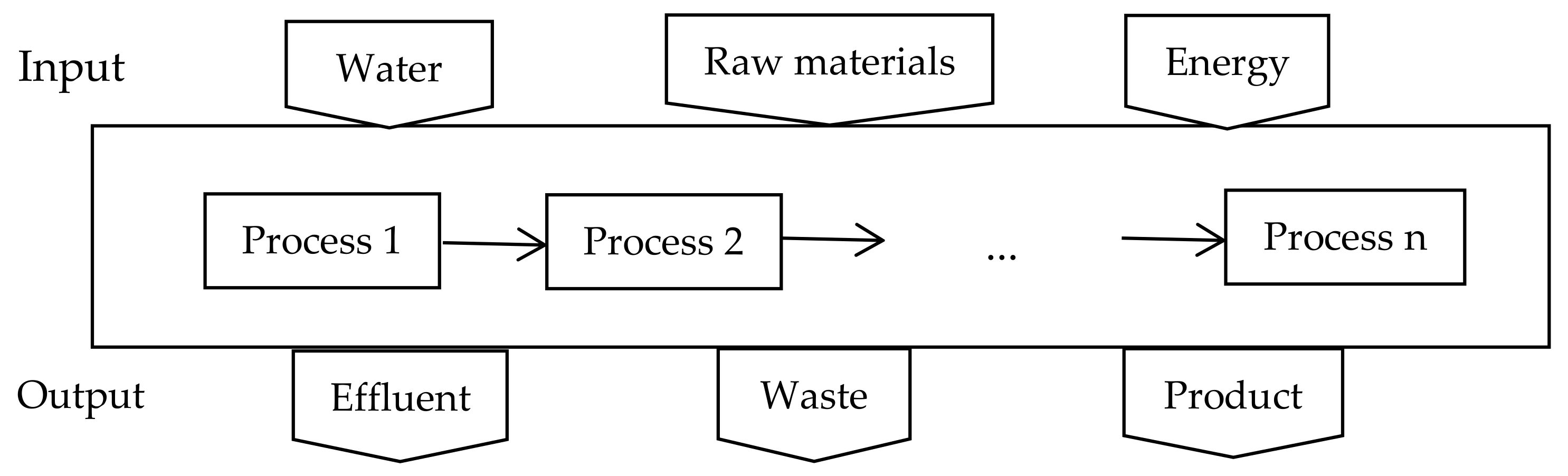
2.1. Industrial Water Footprint Assessment
2.2. Optimization of The Water Network
- The inlet and outlet concentrations of all units were arranged from small to large to form concentration intervals.
- For a given concentration interval k, the pollution mass transfer load mi,k for each water operation in the interval was calculated and the total mass load mk within interval k was obtained.
- The cumulative mass load at the end of each interval was calculated in ascending order of intervals, and the mass transfer load at each interval was summed.
- The flow rate at each interval boundary was calculated according to the accumulated mass load and the interval boundary concentration.
3. Case Study
4. Water Footprint Analysis
4.1. System Boundary and Calculation Method
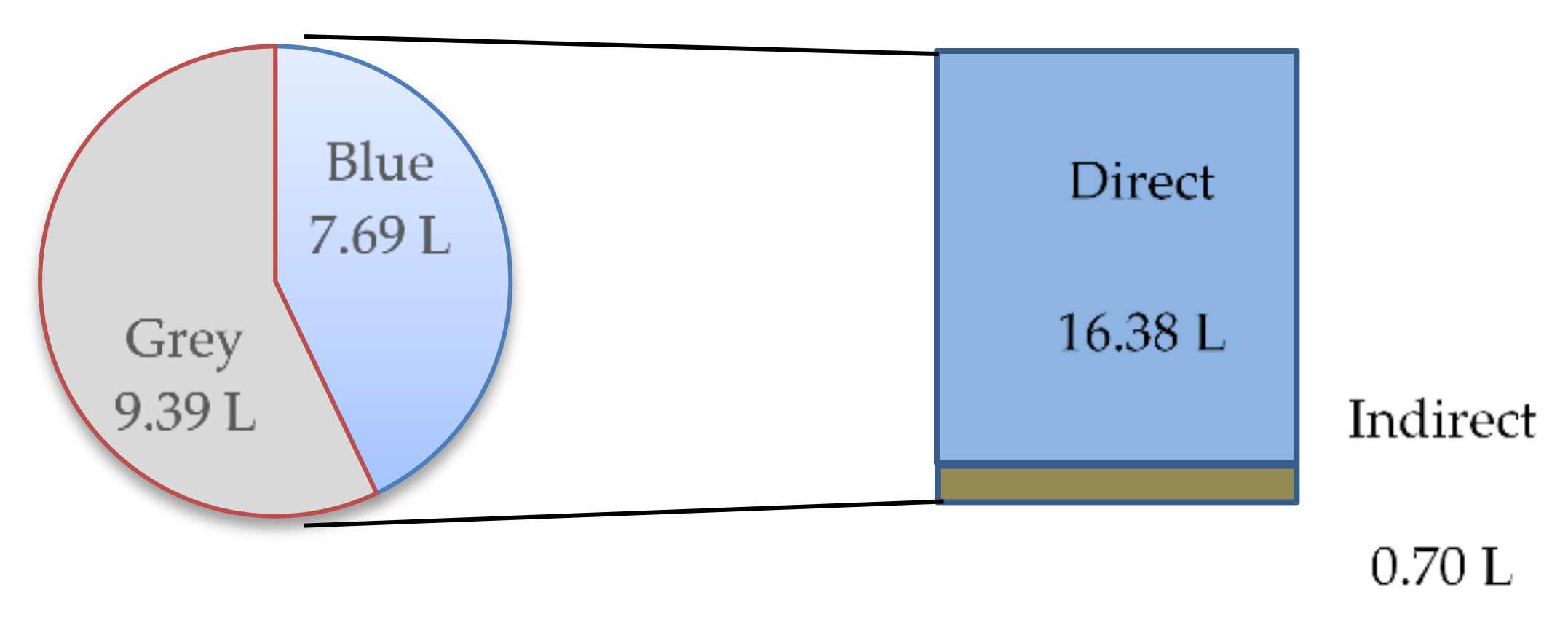
4.2. Results and Analysis of Water Footprint Calculation
5. Water Pinch Analysis
5.1. Analysis of Operations Using Water
5.2. Determining the Pinch Concentration
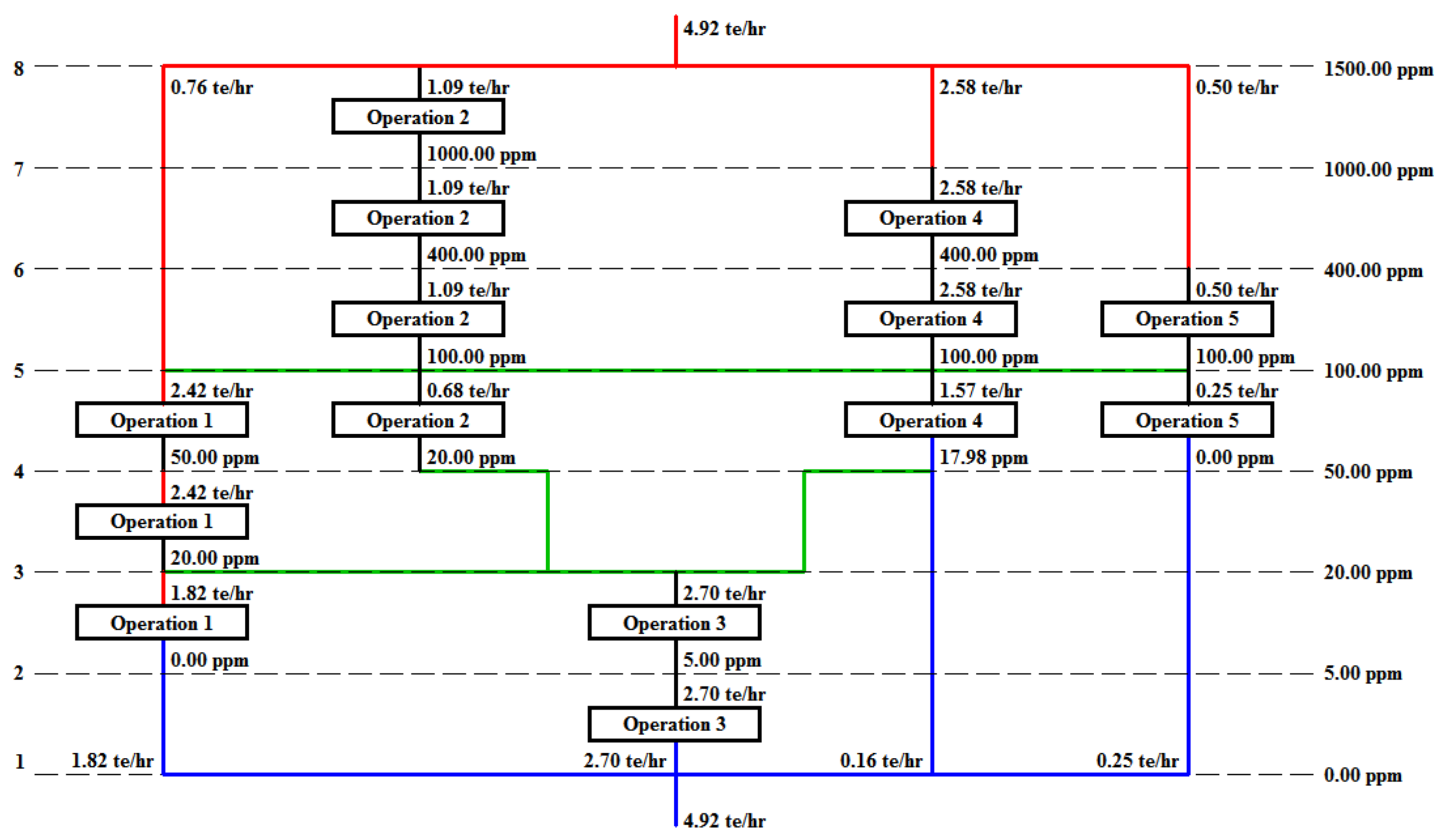
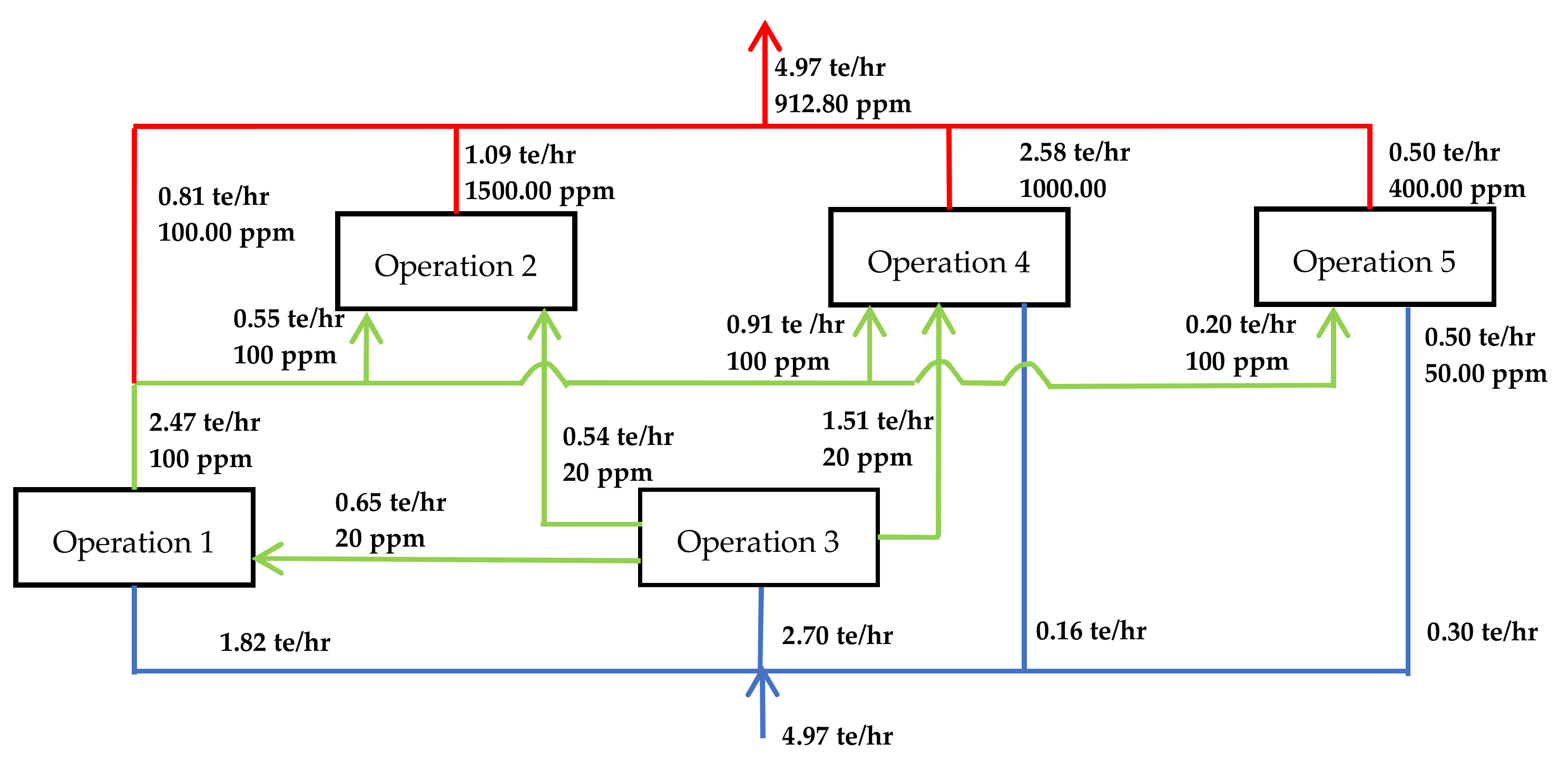
5.3. Optimizing the Water Network
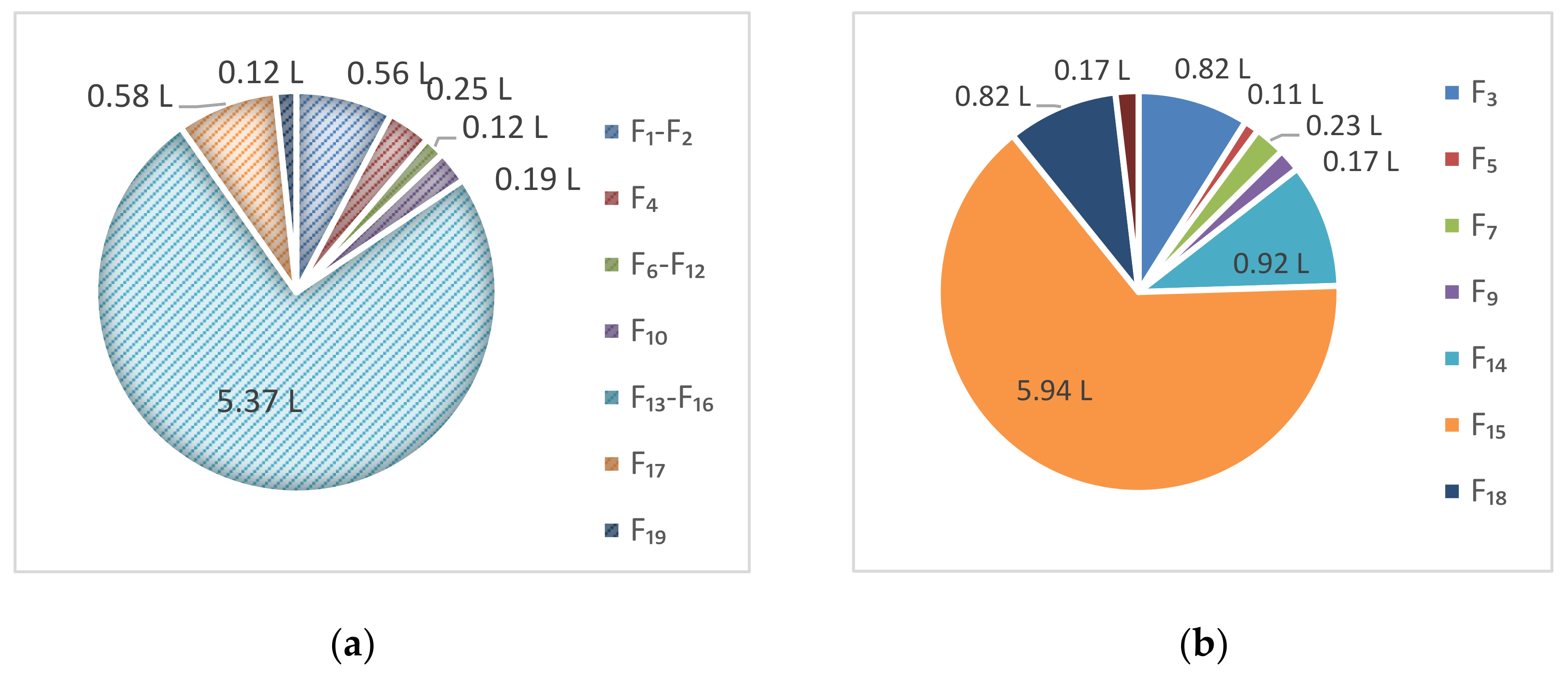
6. Water Footprint Reduction on Water Pinch Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balat, M.; Balat, H. Recent trends in global production and utilization of bio-ethanol fuel. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, P. Focus on bioenergy industry development and energy security in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Fang, C.; Lv, J. Spatial inequality of water footprint in China: A detailed decomposition of inequality from water use types and drivers. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, R.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Dai, D.; Pu, G. Life cycle inventory and energy analysis of cassava-based Fuel ethanol in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Tao, J. Economic, energy and environmental evaluations of biomass-based fuel ethanol projects based on life cycle assessment and simulation. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, S178–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J. Energy balance and GHG emissions of cassava-based fuel ethanol using different planting modes in China. Energy Policy 2013, 56, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silalertruksa, T.; Gheewala, S.H. Environmental sustainability assessment of bio-ethanol production in Thailand. Energy 2009, 34, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papong, S.; Malakul, P. Life-cycle energy and environmental analysis of bioethanol production from cassava in Thailand. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101 (Suppl. 1), S112–S1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Dale, B. Ethanol Fuels: E10 or E85–Life Cycle Perspectives (5 pp). Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2005, 11, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishola, M.M.; Brandberg, T.; Sanni, S.A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Biofuels in Nigeria: A critical and strategic evaluation. Renew. Energy 2013, 55, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglietta, P.P.; Giove, S.; Toma, P. An optimization framework for supporting decision making in biodiesel feedstock imports: Water footprint vs. import costs. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglietta, P.; Morrone, D.; De Leo, F. The Water Footprint Assessment of Electricity Production: An Overview of the Economic-Water-Energy Nexus in Italy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xie, X.; Huang, Z. The policy recommendations on cassava ethanol in China: Analyzed from the perspective of life cycle “2E&W”. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, D.; Adholeya, A. Biological approaches for treatment of distillery wastewater: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, P.K.; Batra, V.S.; Balakrishnan, M. Water management initiatives in sugarcane molasses based distilleries in India. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 52, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelsman, T.; Kavanagh, J.; Coster, H.; Barton, G. Zero discharge fermentation plant design. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 34, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Faus, R.; Powers, S.E.; Burken, J.G.; Alvarez, P.J. The Water Footprint of Biofuels: A Drink or Drive Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K. Water footprints of nations: Water use by people as a function of their consumption pattern. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 21, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbens-Leenes, W.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The water footprint of sweeteners and bio-ethanol. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chooyok, P.; Pumijumnog, N.; Ussawarujikulchai, A. The Water Footprint Assessment of Ethanol Production from Molasses in Kanchanaburi and Supanburi Province of Thailand. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandes, T.A.D.; Bufon, V.B.; Seabra, J.E.A. Water footprint of biofuels in Brazil: Assessing regional differences. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2014, 8, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathioudakis, V.; Gerbens-Leenes, P.W.; Van der Meer, T.H.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The water footprint of second-generation bioenergy: A comparison of biomass feedstocks and conversion techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z. Regional water footprints of potential biofuel production in China. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.P.; Smith, R. Wastewater minimisation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1994, 49, 981–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Smith, R. Design of distributed effluent treatment systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1994, 48, 3127–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Feng, X.; Qian, F.; Cao, D. Water system integration of a chemical plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva-Argáez, A.; Kokossis, A.C.; Smith, R. The design of water-using systems in petroleum refining using a water-pinch decomposition. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 128, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnejad, S.; Bidhendi, G.R.N.; Mehrdadi, N. Water pinch analysis in oil refinery using regeneration reuse and recycling consideration. Desalination 2011, 265, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.R.; Zhou, P.J.; Lv, B. A process integration approach to industrial water conservation: A case study for a Chinese steel plant. J. Environ. Manage. 2008, 86, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K.; Aldaya, M.M.; Mekonnen, M.M. The Water Footprint Assessment Manual; Earthscan: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Jia, J.; Wang, L.H.; Du, C.; Liu, X.L.; Fu, X.; Wu, G. The industrial water footprint of several typical cotton textiles in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 7119–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, V.; Shenoy, U.V. Unified conceptual approach to targeting and design of water and hydrogen networks. AIChE J. 2006, 52, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Matos, H.; Fernandes, M.C.; Nunes, C.P. Improvements for mass-exchange networks design. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 1649–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Tao, J. Simulation-based life cycle assessment of energy efficiency of biomass-based ethanol fuel from different feedstocks in China. Energy 2009, 34, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, A.; Kumar, D.; Murthy, G.S. Economic feasibility and environmental life cycle assessment of ethanol production from lignocellulosic feedstock in Pacific Northwest U.S. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.; Gadd, A.; Kavanagh, J.; Barton, G.W. Integrated biorefinery wastewater design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Du, C. The estimation and application of the water footprint in industrial processes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 6558–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangmeechai, A.; Pavasant, P. Water Footprints of Cassava- and Molasses-Based Ethanol Production in Thailand. Nat. Resour. Res. 2013, 22, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuess, L.T.; Garcia, M.L. Anaerobic digestion of stillage to produce bioenergy in the sugarcane-to-ethanol industry. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojovic, L.; Pejin, D.; Grujić, O.; Markov, S.; Pejin, J.; Rakin, M.; Vukašinović, M.; Nikolić, S.; Savić, D. Progress in the production of bioethanol on starch-based feedstocks. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2009, 15, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 : Water loss by evaporation and drift.
: Water loss by evaporation and drift.
 : Water loss by evaporation and drift.
: Water loss by evaporation and drift.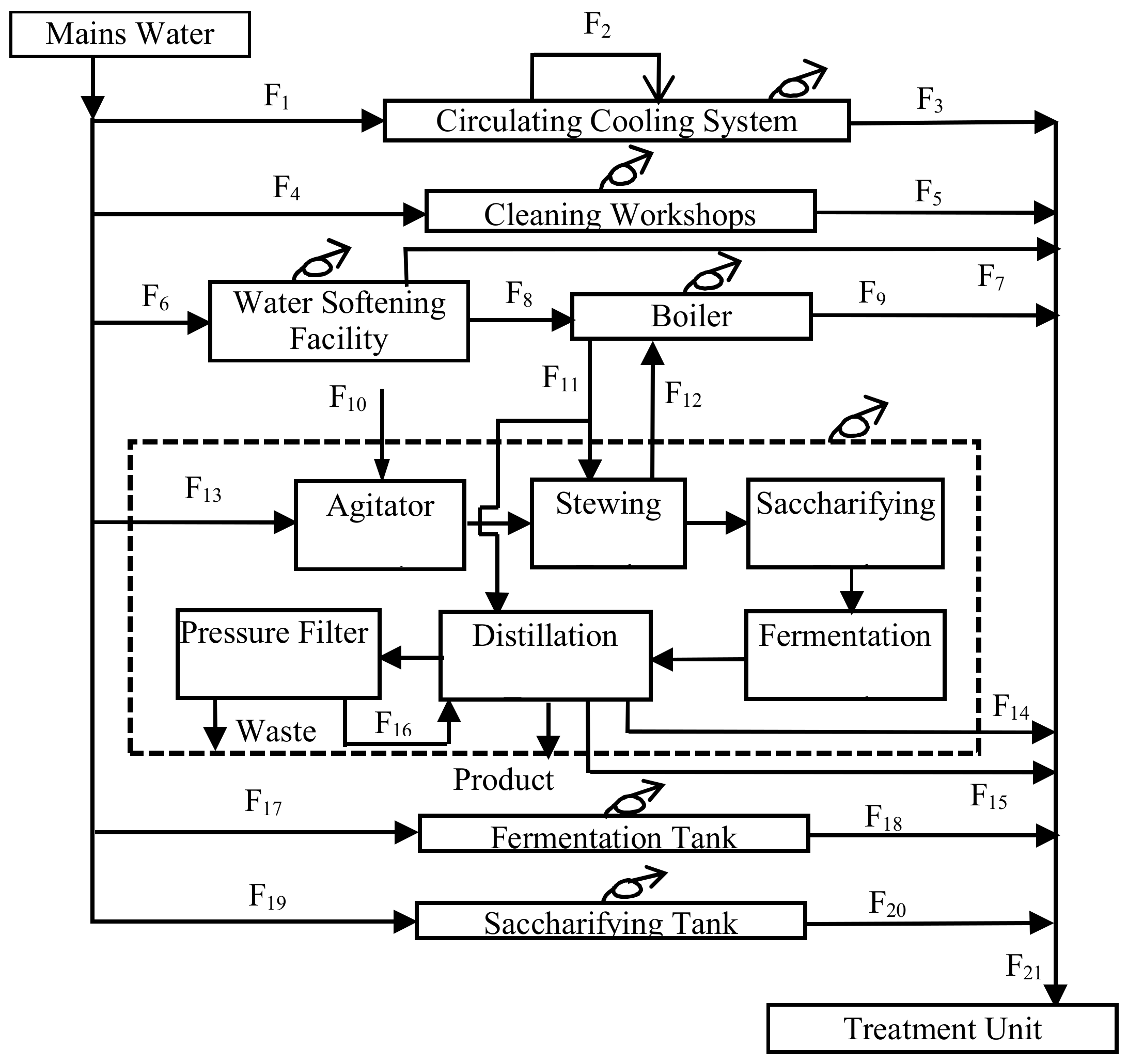
| Number | Description | Flow Rate (t/d) |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | Mains water used to circulate cooling water | 229.18 |
| F2 | Recirculating cooling water | 170.22 |
| F3 | Circulating cooling water blowdown | 58.19 |
| F4 | Mains water used to clean workshops | 26.22 |
| F5 | Waste water after cleaning workshops | 8.13 |
| F6 | Mains water used to prepare soft water | 85.90 |
| F7 | Concentrated water | 15.93 |
| F8 | Boiler feed water | 68.92 |
| F9 | Boiler sewage | 11.84 |
| F10 | Moisture content of cassava | 20.57 |
| F11 | Steam for production process | 130.16 |
| F12 | Steam condensate returns to the boiler | 72.88 |
| F13 | Mains water for ethanol conversion process | 809.67 |
| F14 | Steam condensate | 64.95 |
| F15 | Ethanol stillage | 419.86 |
| F16 | Recycling filtrate of stillage | 239.82 |
| F17 | Mains water used to clean the facilities | 61.83 |
| F18 | Waste water from cleaning the facilities | 58.13 |
| F19 | Mains water to sterilize the saccharifying tank | 12.94 |
| F20 | Waste water after sterilization of the saccharifying tank | 12.11 |
| F21 | Discharged treated water | 649.14 |
| Operation Number | Description | Flow Rate (te/hr) | Limiting Inlet Concentration (COD; ppm) | Limiting Outlet Concentration (COD; ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation 1 | Circulating cooling | 2.42 | 5.00 | 100.00 |
| Operation 2 | Workshops cleaning | 1.09 | 60.00 | 1500.00 |
| Operation 3 | Steam condensate | 2.70 | 0.00 | 20.00 |
| Operation 4 | Facilities cleaning | 2.58 | 50.00 | 1000.00 |
| Operation 5 | Sterilization | 0.50 | 50.00 | 400.00 |
| Concentration (ppm) | Operation 1 2.42 te/hr | Operation 2 1.09 te/hr | Operation 3 2.70 te/hr | Operation 4 2.58 te/hr | Operation 5 0.50 te/hr | Mass Load (kg/hr) | Cumulative Mass Load (kg/hr) | Flowrate (te/hr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |  | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||||
| 0.01 | ||||||||
| 5.00 |  | 0.01 | 2.70 | |||||
| 0.08 | ||||||||
| 20.00 | 0.09 | 4.52 | ||||||
| 0.07 | ||||||||
| 50.00 |  |  | 0.16 | 3.26 | ||||
| 0.05 | ||||||||
| 60.00 |  | 0.22 | 3.63 | |||||
| 0.26 | ||||||||
| 100.00 | 0.48 | 4.92 | ||||||
| 1.25 | ||||||||
| 400.00 | 1.73 | 4.33 | ||||||
| 2.20 | ||||||||
| 1000.00 | 3.93 | 3.93 | ||||||
| 0.55 | ||||||||
| 1500.00 | 4.48 | 2.99 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Ren, L.; Zhuo, H.; Fu, S. Water Footprint and Water Pinch Analysis in Ethanol Industrial Production for Water Management. Water 2019, 11, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030518
Liu H, Ren L, Zhuo H, Fu S. Water Footprint and Water Pinch Analysis in Ethanol Industrial Production for Water Management. Water. 2019; 11(3):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030518
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Heng, Lijun Ren, Huimin Zhuo, and Sanze Fu. 2019. "Water Footprint and Water Pinch Analysis in Ethanol Industrial Production for Water Management" Water 11, no. 3: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030518
APA StyleLiu, H., Ren, L., Zhuo, H., & Fu, S. (2019). Water Footprint and Water Pinch Analysis in Ethanol Industrial Production for Water Management. Water, 11(3), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030518





