Interactions between Lake-Level Fluctuations and Waterlogging Disasters around a Large-Scale Shallow Lake: An Empirical Analysis from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
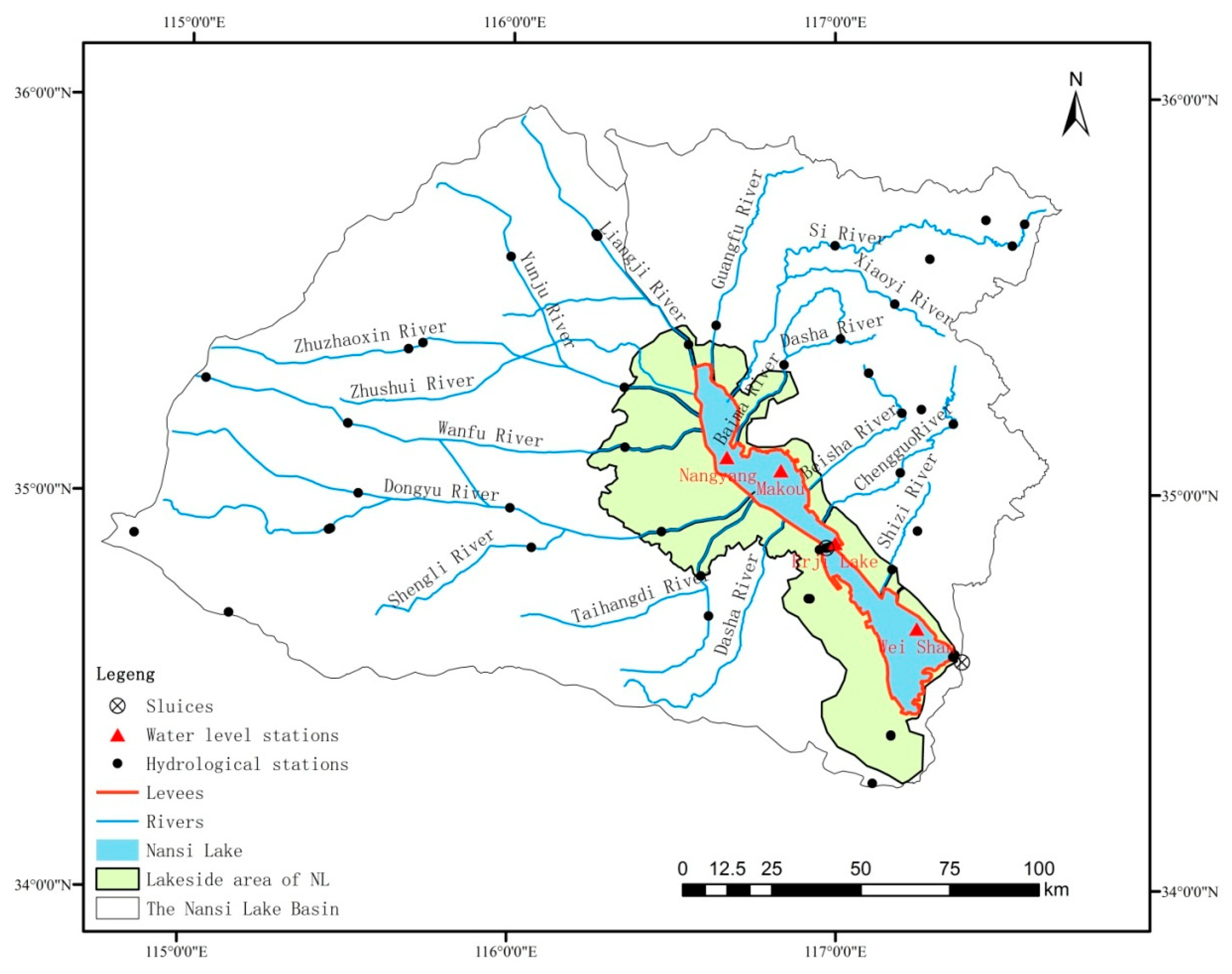
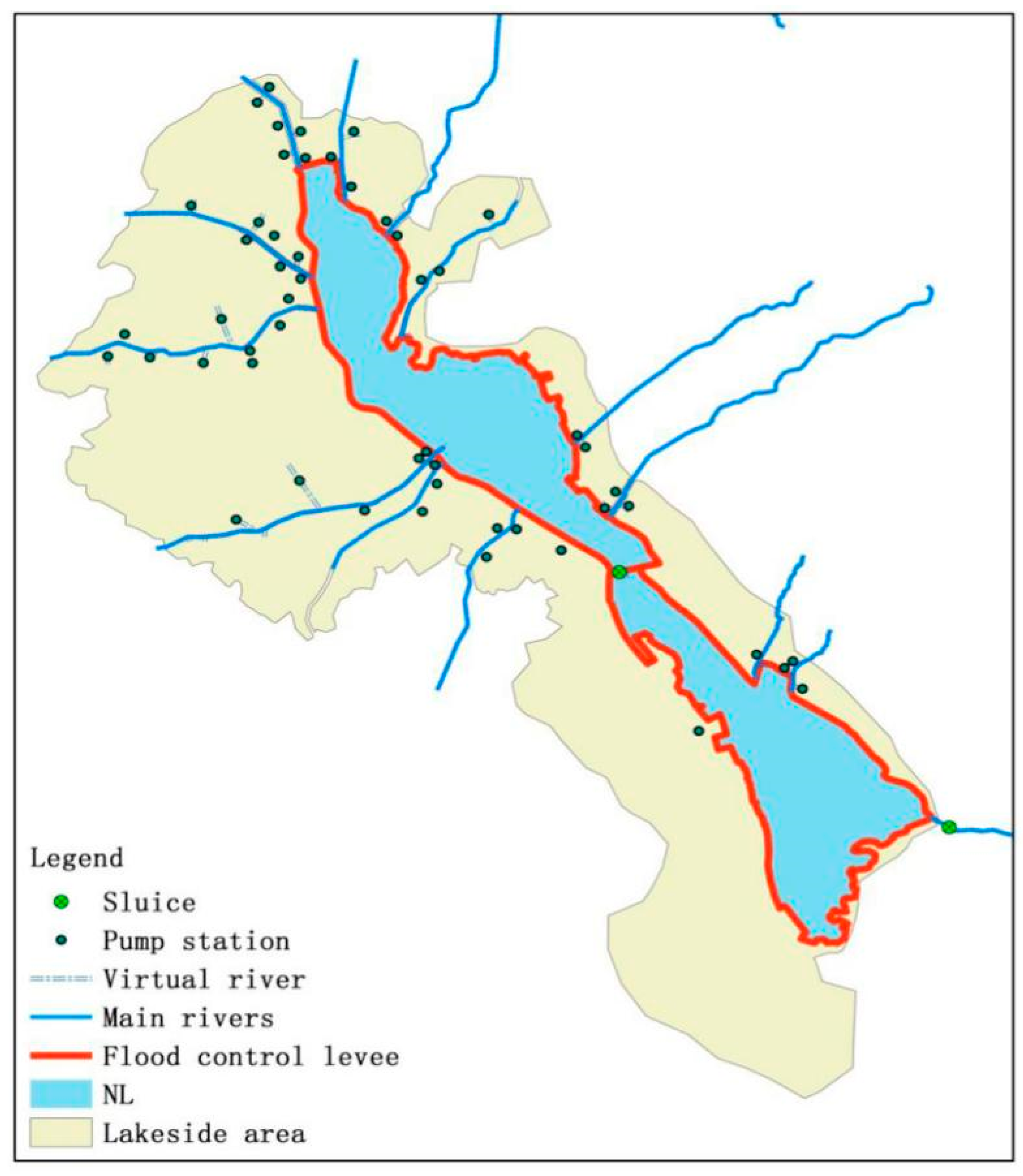
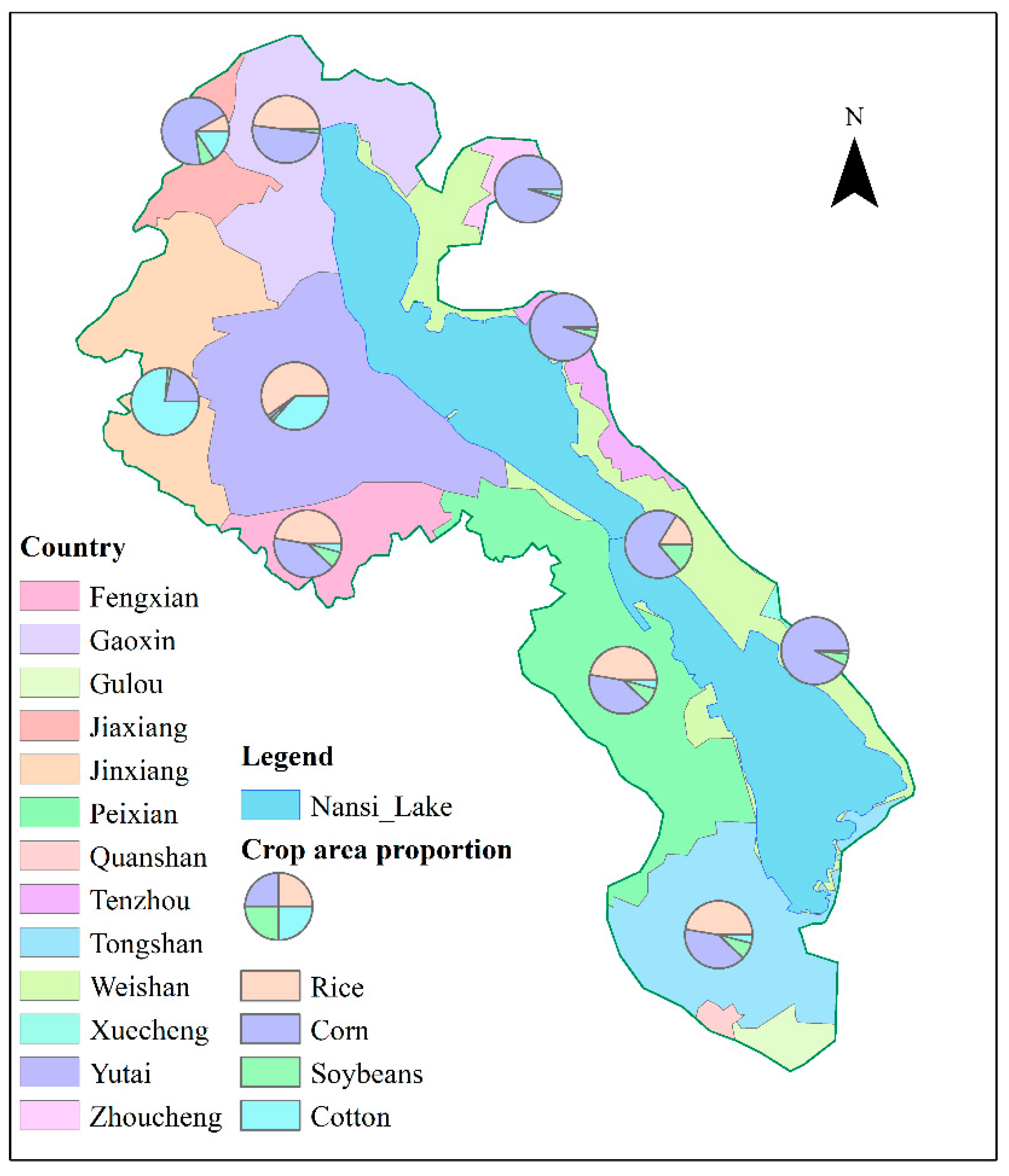
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
3. Methodology: Establishment of NLFWSM
3.1. Model Structure
3.2. 1D River Channel Model Set Up
3.3. 2D Waterlogging Inundation Model Set Up
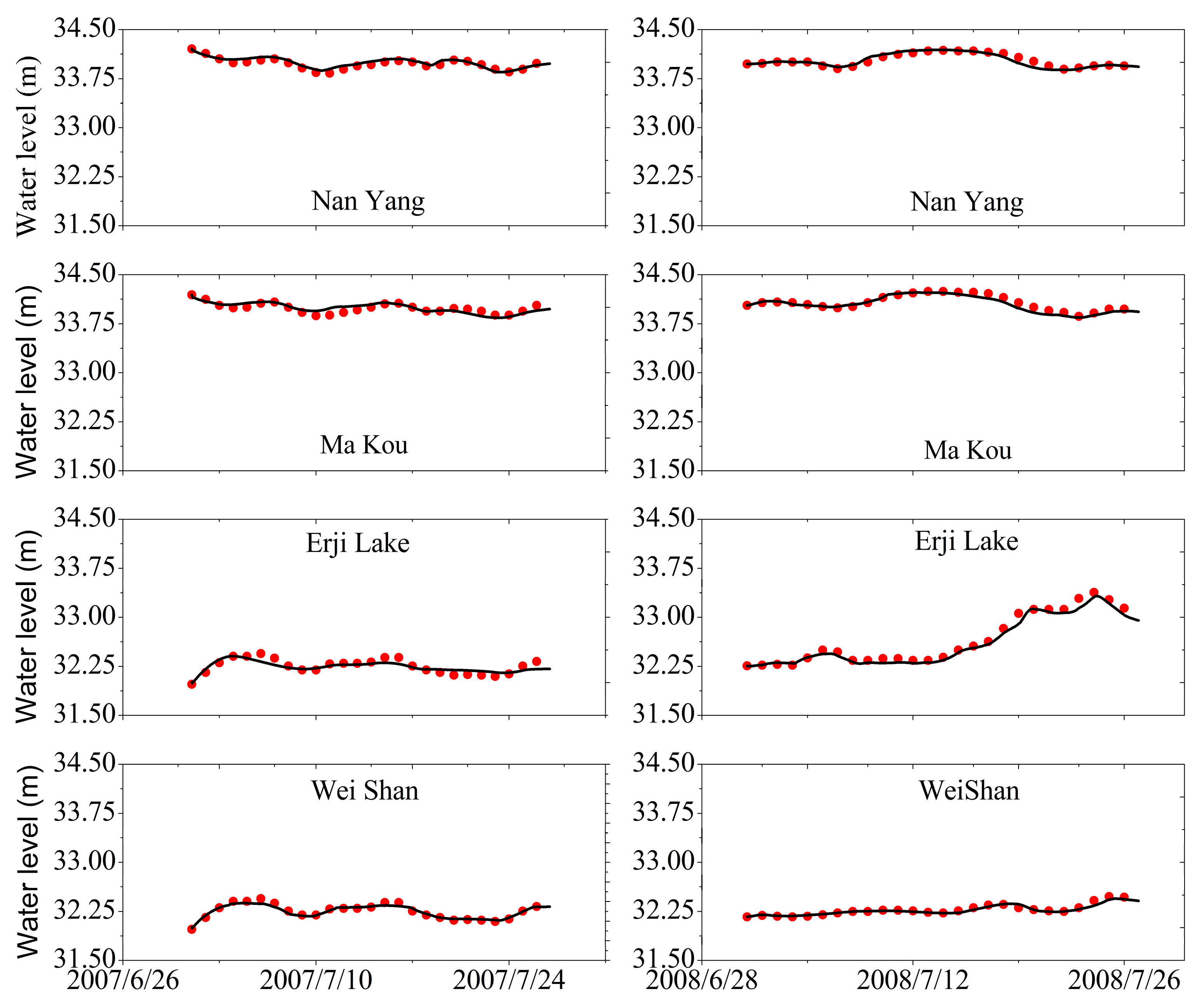
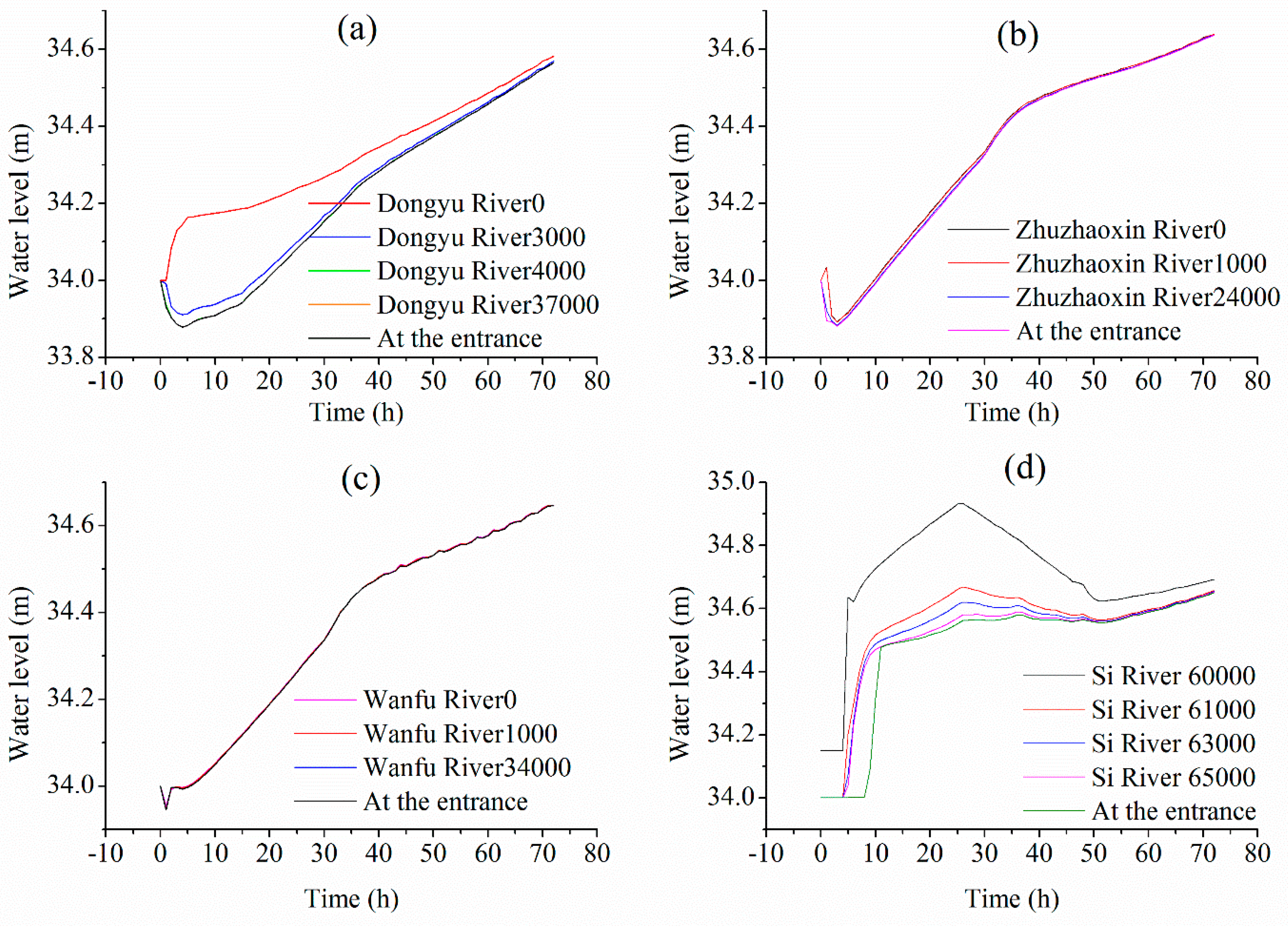
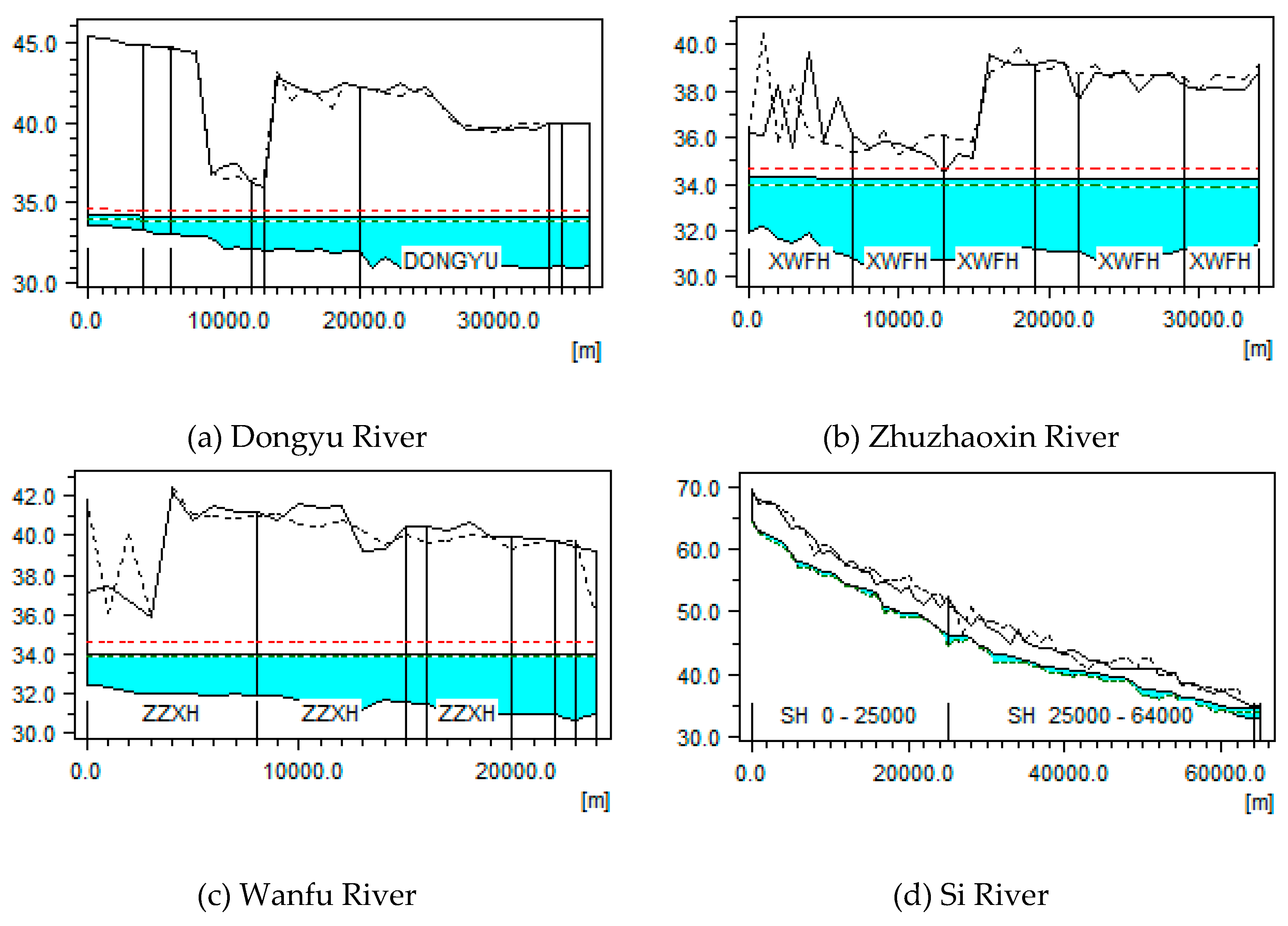
3.4. Calibration and Validation of the Nansi Lake Flooding and Waterlogging Simulation Model
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Scenario Design
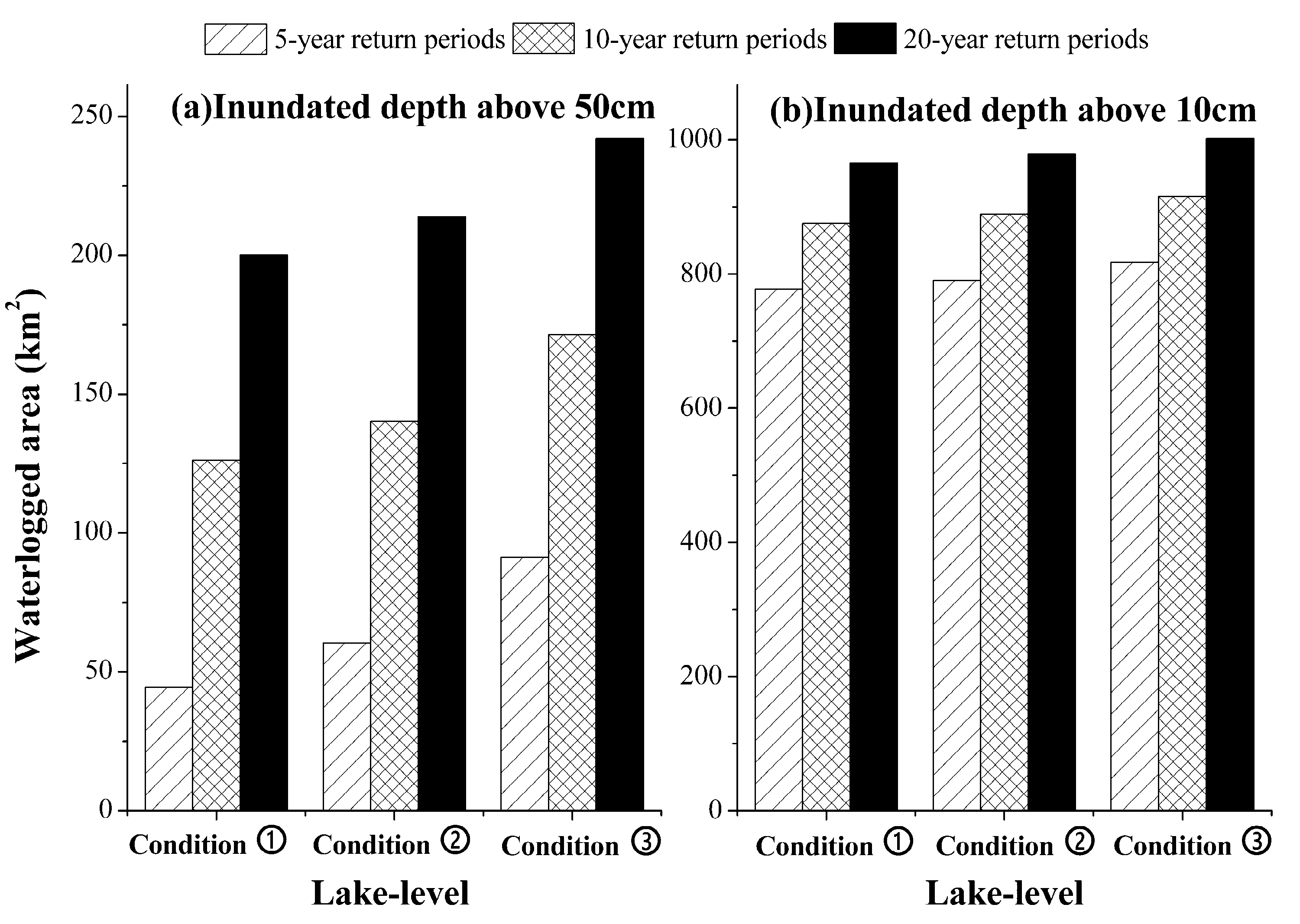
4.2. The Influence of WLFs on the Waterlogged Area Around Lake
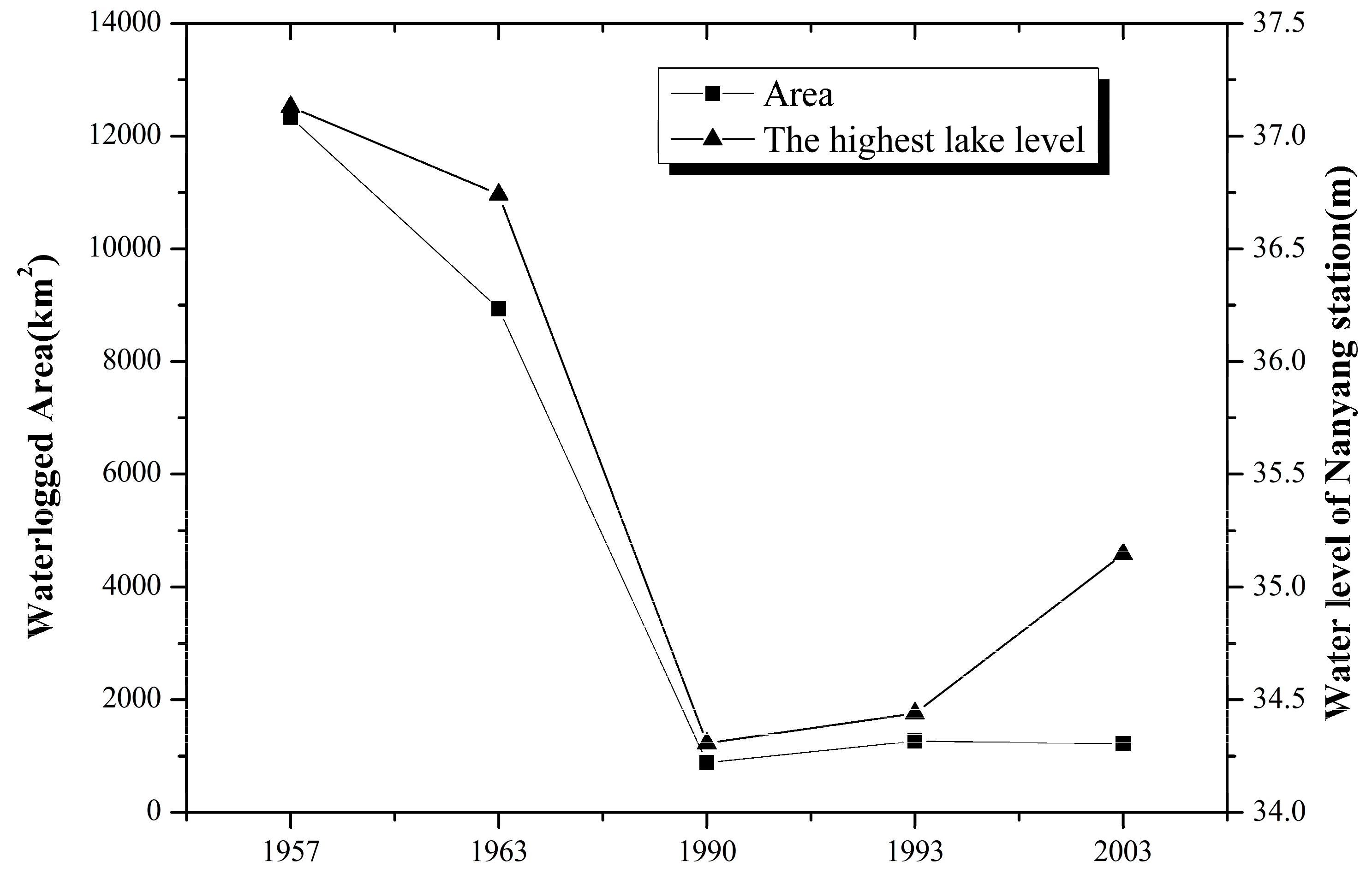
4.3. The Relationship between the Waterlogged Area and the Highest Lake Level During Typical Years in Which Waterlogging Occurred in the Lakeside Area of Nansi Lake
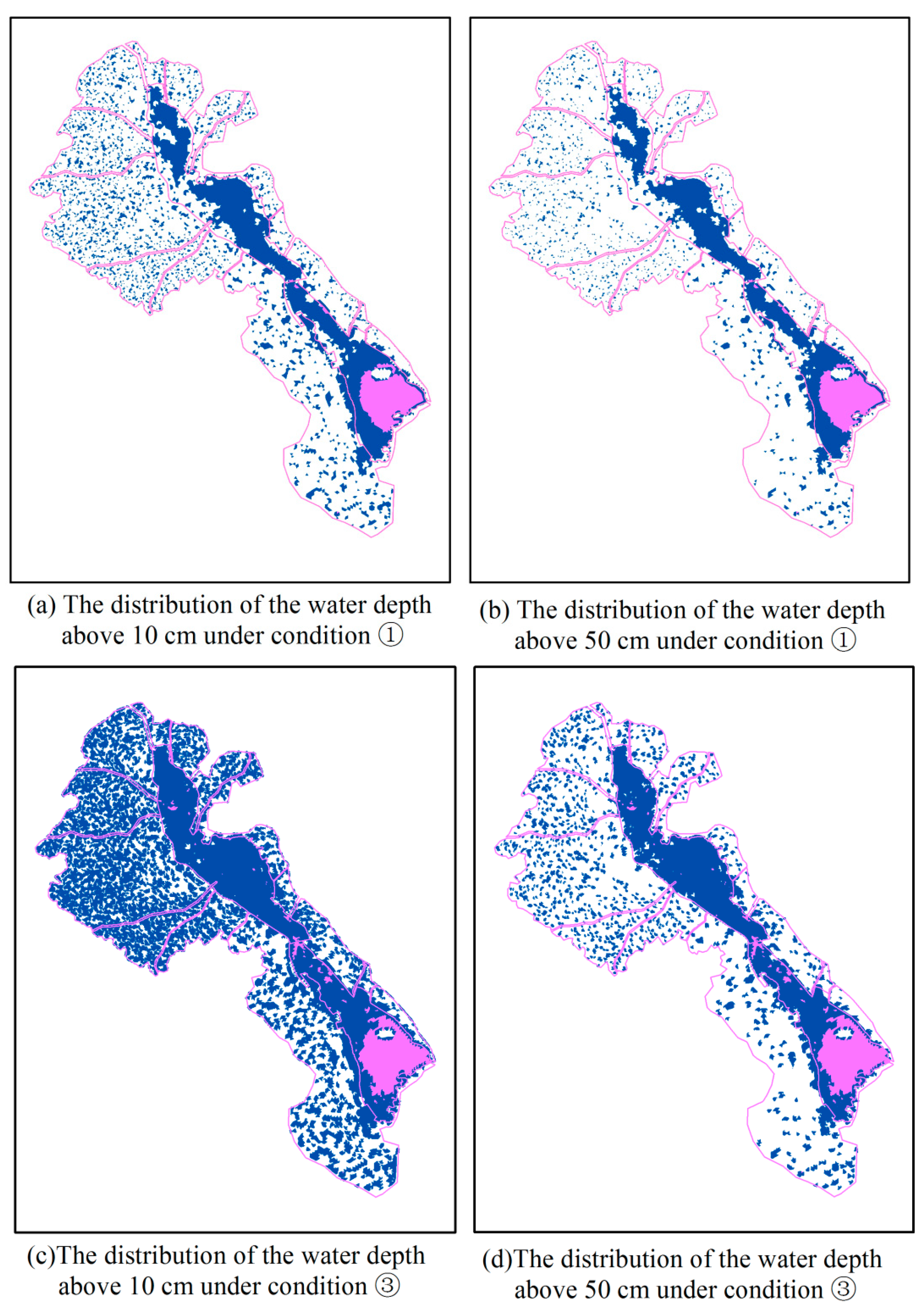
4.4. The Differences in the Waterlogging of Different Areas around Nansi Lake in Response to WLFs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verpoorter, C.; Kutser, T.; Seekell, D.A.; Tranvik, L.J. A global inventory of lakes based on high-resolution satellite imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6396–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, J.; Oltmans, S.J. The global distribution of long-term total ozone variations during the period 1957–1975. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1978, 117, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coops, H.; Beklioglu, M.; Crisman, T.L. The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems—Workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beklioglu, M.; Altinayar, G.; Tan, C.O. Water level control over submerged macrophyte development in five shallow lakes of Mediterranean Turkey. Arch. für Hydrobiol. 2006, 166, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G.O.P, O. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 75, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, J.W. Loons in freshwater lakes. Hydrobiologia 1994, 279, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furey, P.; Nordin, R.; Mazumder, A. Water Level Drawdown Affects Physical and Biogeochemical Properties of Littoral Sediments of a Reservoir and a Natural Lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2004, 20, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlin, W.H.; Davies, J.M.; Nordin, R.N.; Mazumder, A. Effects of water level fluctuation and short-term climate variation on thermal and stratification regimes of a British Columbia reservoir and lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2004, 20, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Öhl, U. Effects of Water-Level Fluctuations on the Littoral Benthic Fish Community in Lakes: A Mesocosm Experiment. Behav. Ecol. 2005, 16, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.S.; Xenopoulos, M.A.; Hogsden, K.; Metcalfe, R.A.; Dillon, P.J. Natural lake level fluctuation and associated concordance with water quality and aquatic communities within small lakes of the Laurentian Great Lakes region. Hydrobiologia 2008, 613, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasid, H.; Hufferd, J. Hazards of living on the edge of water: The case of Minnesota Point, Duluth, Minnesota. Hum. Ecol. 1988, 17, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, J.C.; Johnson, G.D. Lake Level Influences on Sediment and Nutrient Retention in a Lakeside Wetland. J. Environ. Qual. 1990, 19, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, X. Effects of underlying surface changes on drainage modulus in Four-lake Watershed. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416–417, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Variation of floods characteristics and their responses to climate and human activities in Poyang Lake, China. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapalan, M.; Blöschl, G. Transformation of point rainfall to areal rainfall: Intensity-duration-frequency curves. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Yin, J.; Xu, S.; Wen, J. Community-based scenario modelling and disaster risk assessment of urban rainstorm waterlogging. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yu, D.; Chen, Z.; Wilby, R.L. An evaluation of the impacts of land surface modification, storm sewer development, and rainfall variation on waterlogging risk in Shanghai. Nat. Hazard 2012, 63, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, Y.; Pan, G.; Han, L. Impacts of Urbanization on Precipitation in Taihu, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Ye, X. The changing patterns of floods in Poyang Lake, China: Characteristics and explanations. Nat. Hazard 2015, 76, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W. Secular Trends of Precipitation Amount, Frequency, and Intensity in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partal, T.; Kahya, E. Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2011–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.M.; Fairbank, C.A. Is Precipitation in Northern New England Becoming More Extreme? Statistical Analysis of Extreme Rainfall in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Maine and Updated Estimates of the 100-Year Storm. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haylock, M.; Nicholls, N. Trends in Extreme Rainfall Indices for an Updated High Quality Data Set for Australia, 1910–1998. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, D.S.; Chatterjee, C.; Kalakoti, S.; Upadhyay, P.; Sahoo, M.; Panda, A. Modeling urban floods and drainage using SWMM and MIKE URBAN: A case study. Nat. Hazard 2016, 84, 749–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.-S. Rainstorm waterlogging risk assessment in central urban area of Shanghai based on multiple scenario simulation. Nat. Hazard 2014, 73, 1569–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Population vulnerability assessment based on scenario simulation of rainstorm-induced waterlogging: A case study of Xuhui District, Shanghai City. Nat. Hazard 2013, 66, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yu, D.; Yin, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, S. Multiple scenario analyses of Huangpu River flooding using a 1D/2D coupled flood inundation model. Nat. Hazard 2013, 66, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, K.; Wei, Y.M. Regional flood risk assessment via coupled fuzzy c-means clustering methods: an empirical analysis from China’s Huaihe River Basin. Nat. Hazard 2018, 93, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gironás, J.; Roesner, L.A.; Rossman, L.A.; Davis, J. A new applications manual for the Storm Water Management Model (SWMM). Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L. Redevelopment of the US EPA Stormwater Management Model. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2003, 10, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chang, T.J. Inundation simulation for urban drainage basin with storm sewer system. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S. Application of a 2D Hydrodynamic Model for Assessing Flood Risk from Extreme Storm Events. Climate 2013, 1, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, F.; Petheram, C.; Marvanek, S.; Ticehurst, C.; Wallace, J.; Hasan, M. Impact of climate change on floodplain inundation and hydrological connectivity between wetlands and rivers in a tropical river catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1574–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Herath, S.; Musiake, K. A mathematical model for flood loss estimation. J. Hydrol. 2003, 277, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, B.; Wen, J. Scenario-based community flood risk assessment: a case study of Taining county town, Fujian province, China. Nat. Hazard 2016, 82, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.G.; Li, L.H.; Jiang, J.H.; Wan, J.B. Impacts of water level fluctuation on the flood disaster around Poyang Lake. In Proceedings of the 2013 3rd International Conference on Intelligent System Design and Engineering Applications, Hong Kong, China, 10–18 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- She, D.; Xia, J.; Zhu, L.; Lü, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Changes of rainfall and its possible reasons in the Nansi Lake Basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Hook, S.J. Space observations of inland water bodies show rapid surface warming since 1985. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.J.; Morrison, T.; Matheson, L. Initial development of a work-related assessment of dysexecutive syndrome: The Complex Task Performance Assessment. Work 2008, 31, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Iestyn Woolway, R.; Merchant, C.J. Amplified surface temperature response of cold, deep lakes to inter-annual air temperature variability. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- An, W.C.; Li, X.M. Phosphate adsorption characteristics at the sediment--water interface and phosphorus fractions in Nansi Lake, China, and its main inflow rivers. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 148, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DHI. MIKE 11: A Modelling System for Rivers and Channels; User Guide; Danish Hydraulic Institute: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models Part I-A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Waterlogged Disaster in The Huaihe Basin and Its Management; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; ISBN 978-7-03-043690-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wind, H.G.; Nierop, T.M.; de Blois, C.J.; de Kok, J.L. Analysis of flood damages from the 1993 and 1995 Meuse Floods. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3459–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, B.; Thieken, A.H. Flood risk curves and uncertainty bounds. Nat. Hazard 2009, 51, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gauging Station | NSE | RMSE (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2008 | 2007 | 2008 | |
| Nanyang | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Makou | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.09 | 0.05 |
| Erji Lake(downstream) | 0.67 | 0.98 | 0.05 | 0.5 |
| Weishan | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.07 | 0.02 |
| Stations | Data Duration | Rainfall for Three-Day Duration (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 10% | 5% | ||
| Liangshanzha | 1966–2008 | 157.02 | 188.34 | 217.91 |
| Houying | 1951–2008 | 154.67 | 188.07 | 220.11 |
| Huayu | 1967–2009 | 141.74 | 164.42 | 184.77 |
| Wangzhong | 1957–2009 | 148.14 | 175.87 | 202.17 |
| Wanglu | 1967–2009 | 139.31 | 167.49 | 194.4 |
| Xuecheng | 1960–1992 | 172.49 | 226.80 | 282.11 |
| Wanggudui | 1962–2009 | 150.08 | 177.29 | 201.82 |
| Crop | Resistance Inundated Time (h) | Resistance Inundated Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Rice | 72 | 0.5 |
| Cotton | 24 | 0.1 |
| Corn | 24 | 0.1 |
| Soybeans | 48 | 0.1 |
| Scenario Number | Initial Lake Level of NL | Return Periods of the Design Rainfall | Water Depth of NL | Inundated Depth above 0.1 m | Inundated Depth above 0.5 m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (m) | Max (m) | Total Area (km2) | Area Ratio (%) | Total Area (km2) | Area Ratio (%) | |||
| 1 | ①Upper lake 33 m, lower lake 31.3 m | 5 | 1.41 | 4.76 | 777.87 | 22.45 | 44.41 | 1.28 |
| 2 | 10 | 1.45 | 4.85 | 875.54 | 25.27 | 126.20 | 3.64 | |
| 3 | 20 | 1.48 | 4.92 | 965.00 | 27.85 | 200.08 | 5.77 | |
| 4 | ②Upper lake 33.5 m, lower lake 31.8 m | 5 | 1.75 | 5.08 | 790.54 | 22.81 | 60.45 | 1.74 |
| 5 | 10 | 1.79 | 5.15 | 889.27 | 25.66 | 140.25 | 4.05 | |
| 6 | 20 | 182 | 5.21 | 978.51 | 28.24 | 213.96 | 6.17 | |
| 7 | ③Upper lake 34 m, lower lake 32.3 m | 5 | 2.11 | 5.68 | 817.70 | 23.6 | 91.29 | 2.63 |
| 8 | 10 | 2.15 | 5.69 | 915.44 | 26.42 | 171.50 | 4.95 | |
| 9 | 20 | 2.16 | 5.68 | 1001.73 | 28.91 | 242.03 | 6.98 | |
| Return Periods of the Design Rainfall | Area of Inundated Depth Above 0.1 m | Inundated Depth Above 0.5 m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increment (km2) | Relative Increment (%) | Area Ratio Increase | Increment (km2) | Relative Increase (%) | Area Ratio Increase | |
| 5 | 12.67 | 1.63 | 0.37 | 16.04 | 36.12 | 0.46 |
| 10 | 13.73 | 1.57 | 0.40 | 14.05 | 11.13 | 0.41 |
| 20 | 13.51 | 1.40 | 0.39 | 13.88 | 6.94 | 0.40 |
| Return Periods of the Design Rainfall | Area of Inundated Depth Above 0.1 m | Area of Inundated Depth Above 0.5 m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increment (km2) | Relative Increase (%) | Area Ratio Increase | Increment (km2) | Relative Increase (%) | Area ratio Increase | |
| 5 | 27.16 | 3.44 | 3.44 | 30.84 | 51.02 | 0.89 |
| 10 | 26.17 | 2.94 | 0.76 | 31.25 | 22.28 | 0.90 |
| 20 | 23.22 | 2.37 | 0.67 | 28.07 | 13.12 | 0.81 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, K.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Ye, A. Interactions between Lake-Level Fluctuations and Waterlogging Disasters around a Large-Scale Shallow Lake: An Empirical Analysis from China. Water 2019, 11, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020318
Wang Z, Wang K, Liu K, Cheng L, Wang L, Ye A. Interactions between Lake-Level Fluctuations and Waterlogging Disasters around a Large-Scale Shallow Lake: An Empirical Analysis from China. Water. 2019; 11(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020318
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zongzhi, Kun Wang, Kelin Liu, Liang Cheng, Lihui Wang, and Ailing Ye. 2019. "Interactions between Lake-Level Fluctuations and Waterlogging Disasters around a Large-Scale Shallow Lake: An Empirical Analysis from China" Water 11, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020318
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, K., Liu, K., Cheng, L., Wang, L., & Ye, A. (2019). Interactions between Lake-Level Fluctuations and Waterlogging Disasters around a Large-Scale Shallow Lake: An Empirical Analysis from China. Water, 11(2), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020318





