Numerical Simulation Study on Salt Release Across the Sediment–Water Interface at Low-Permeability Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
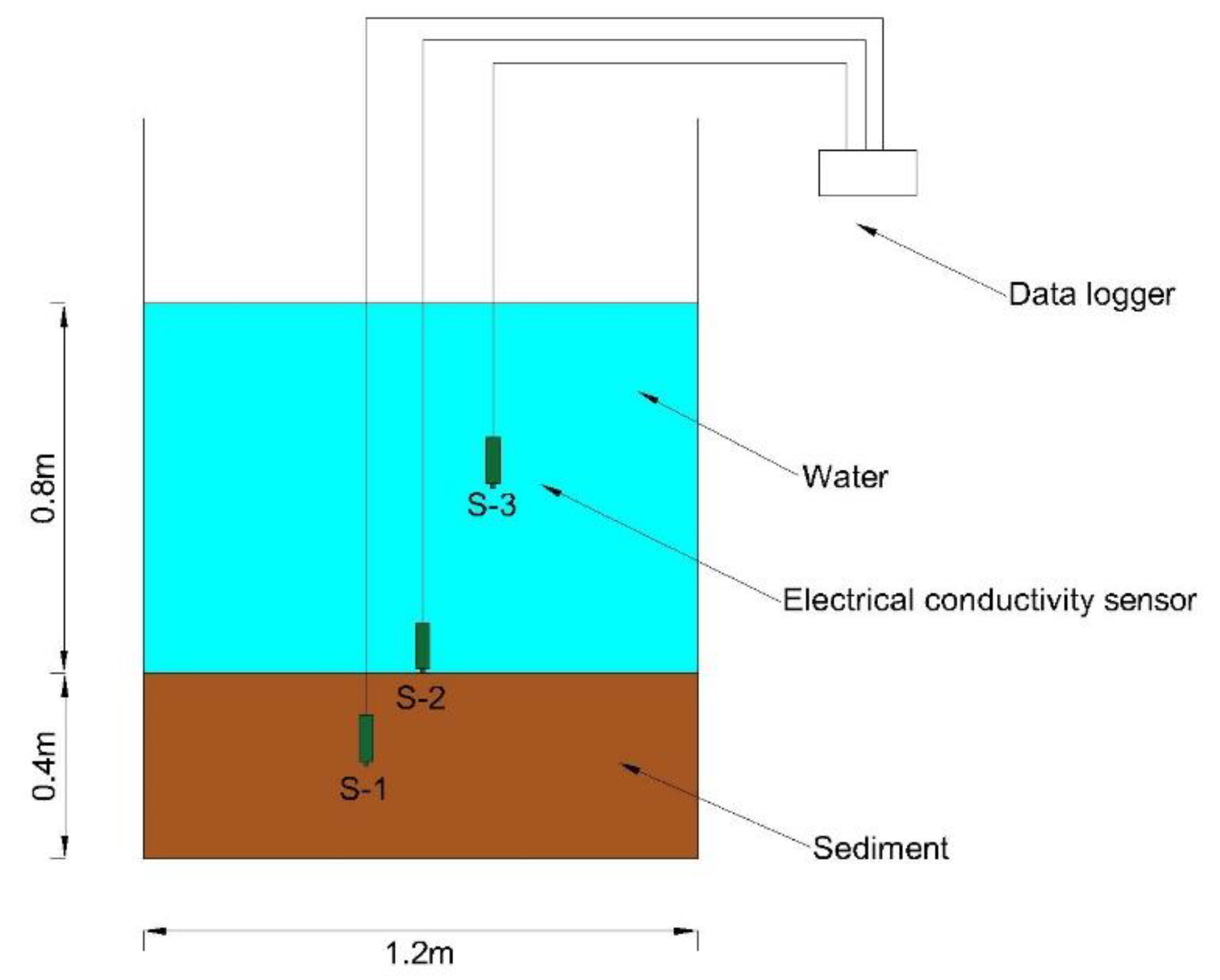
2.2. In Situ Tests and Experiments
2.3. Mathematical Model
2.4. Model Input
2.5. Model Scenarios
3. Results and Discussion
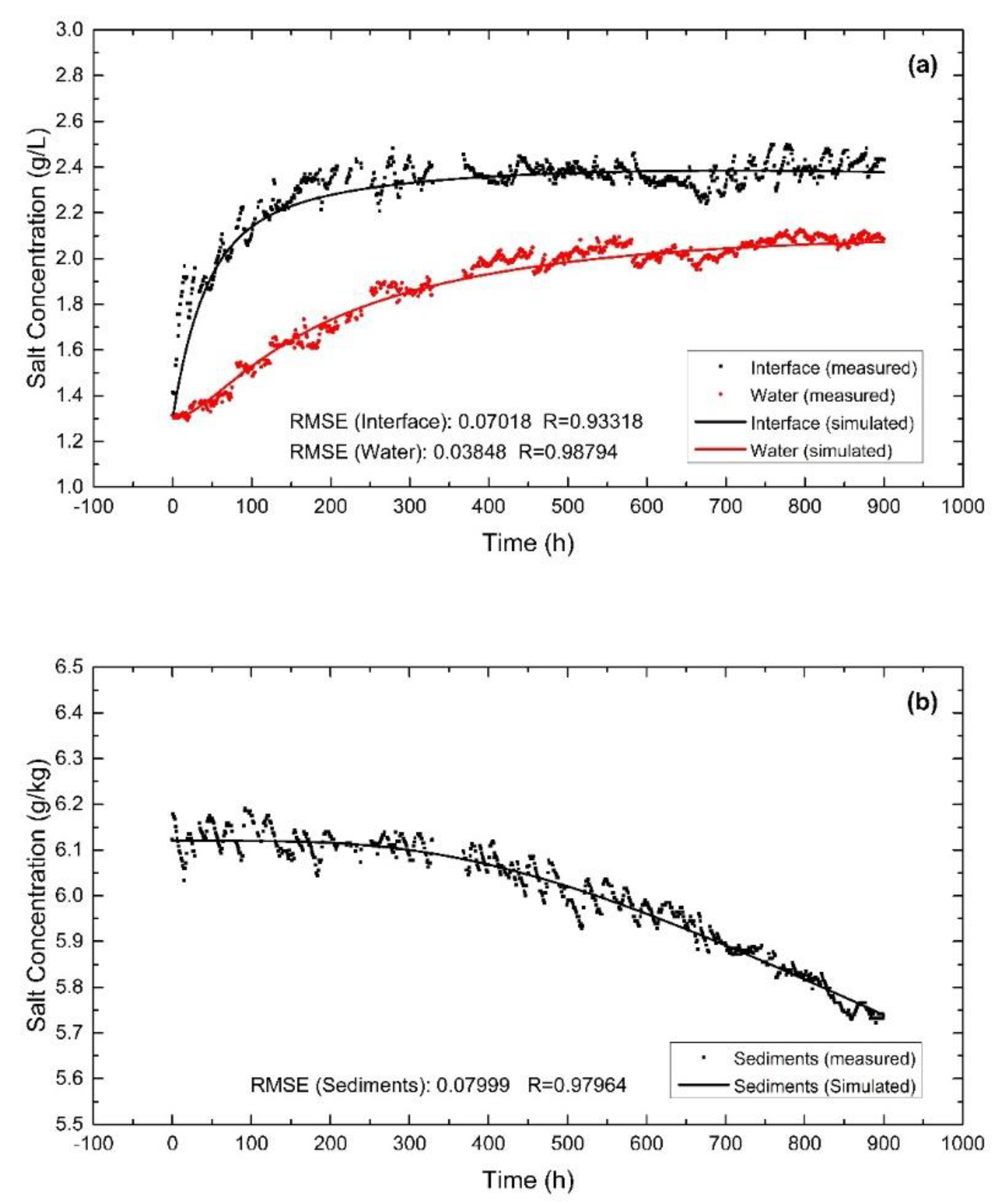
3.1. Parameter Inversion
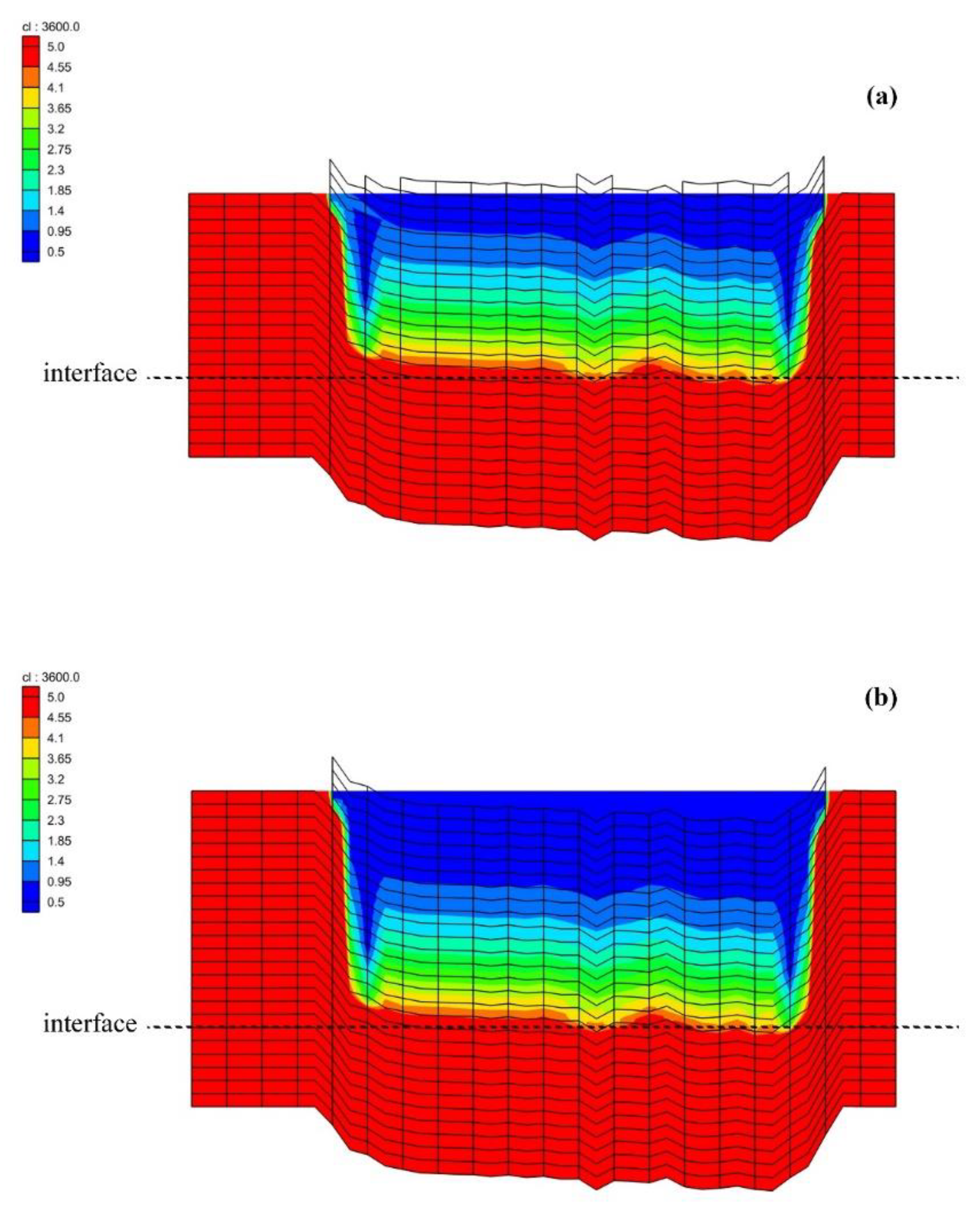
3.2. Model Validation
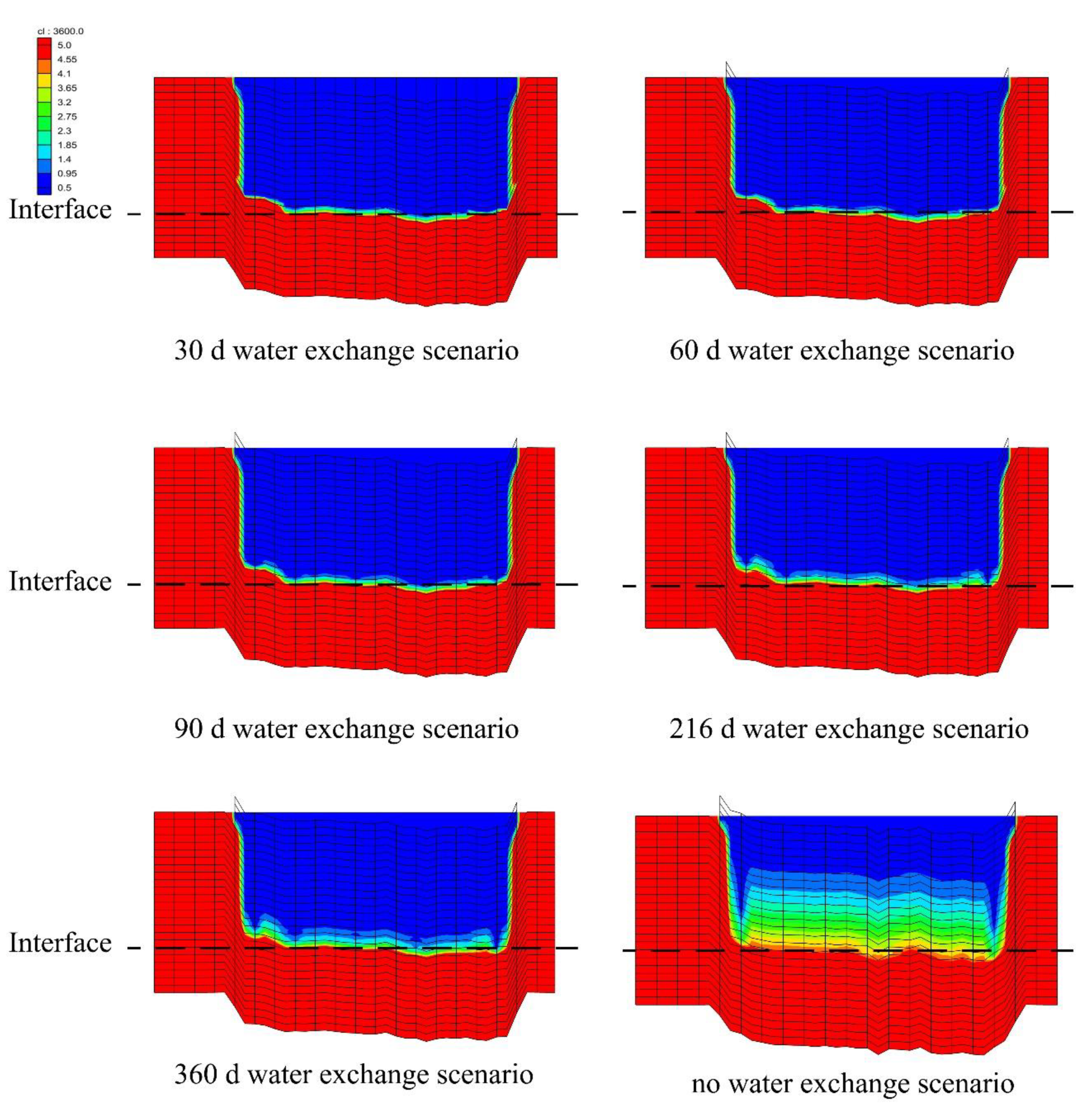
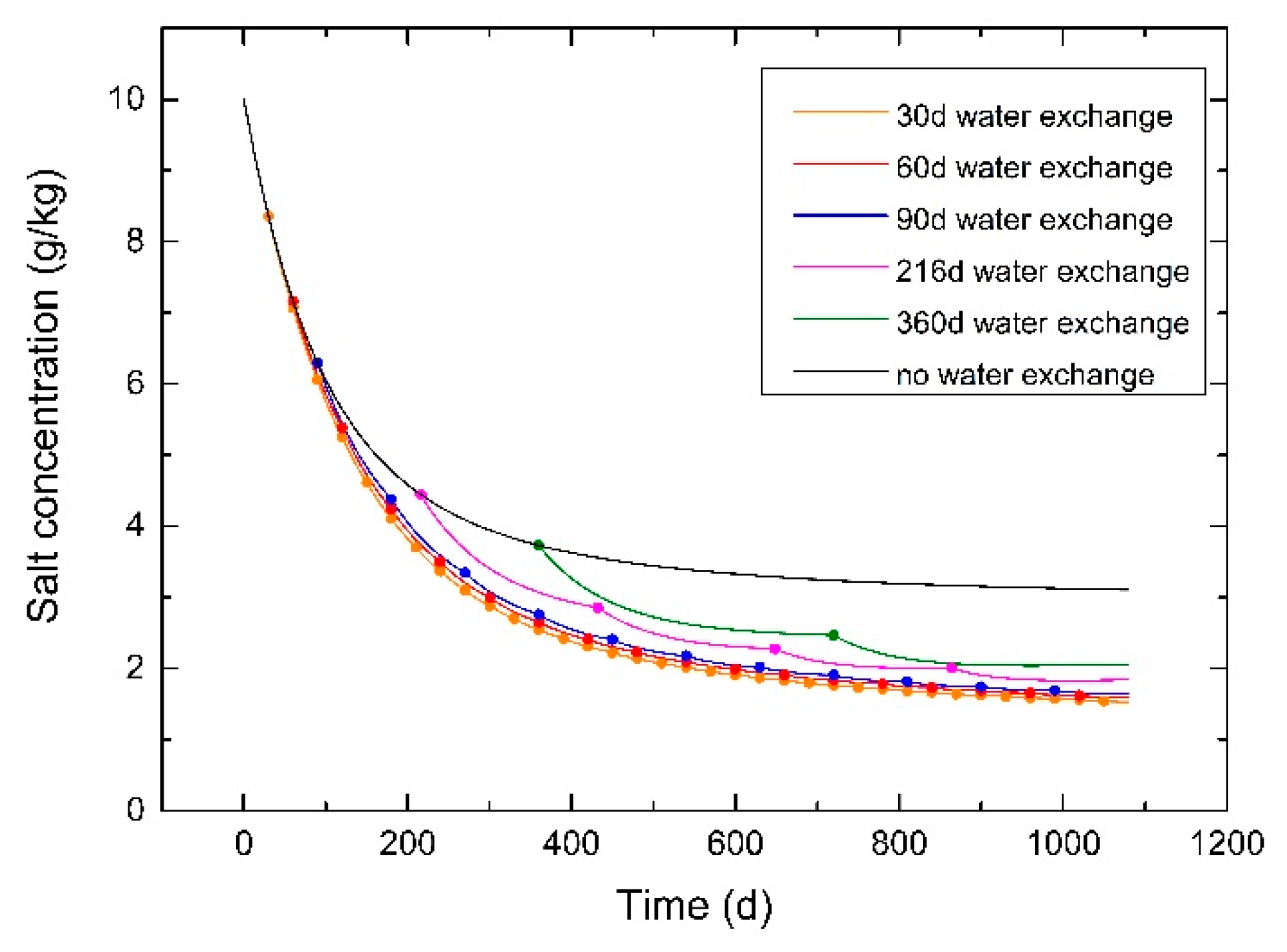
3.3. Salinity Distribution under Water-Exchange Scenarios
3.4. Salinity Distribution under Lake Stage Scenarios
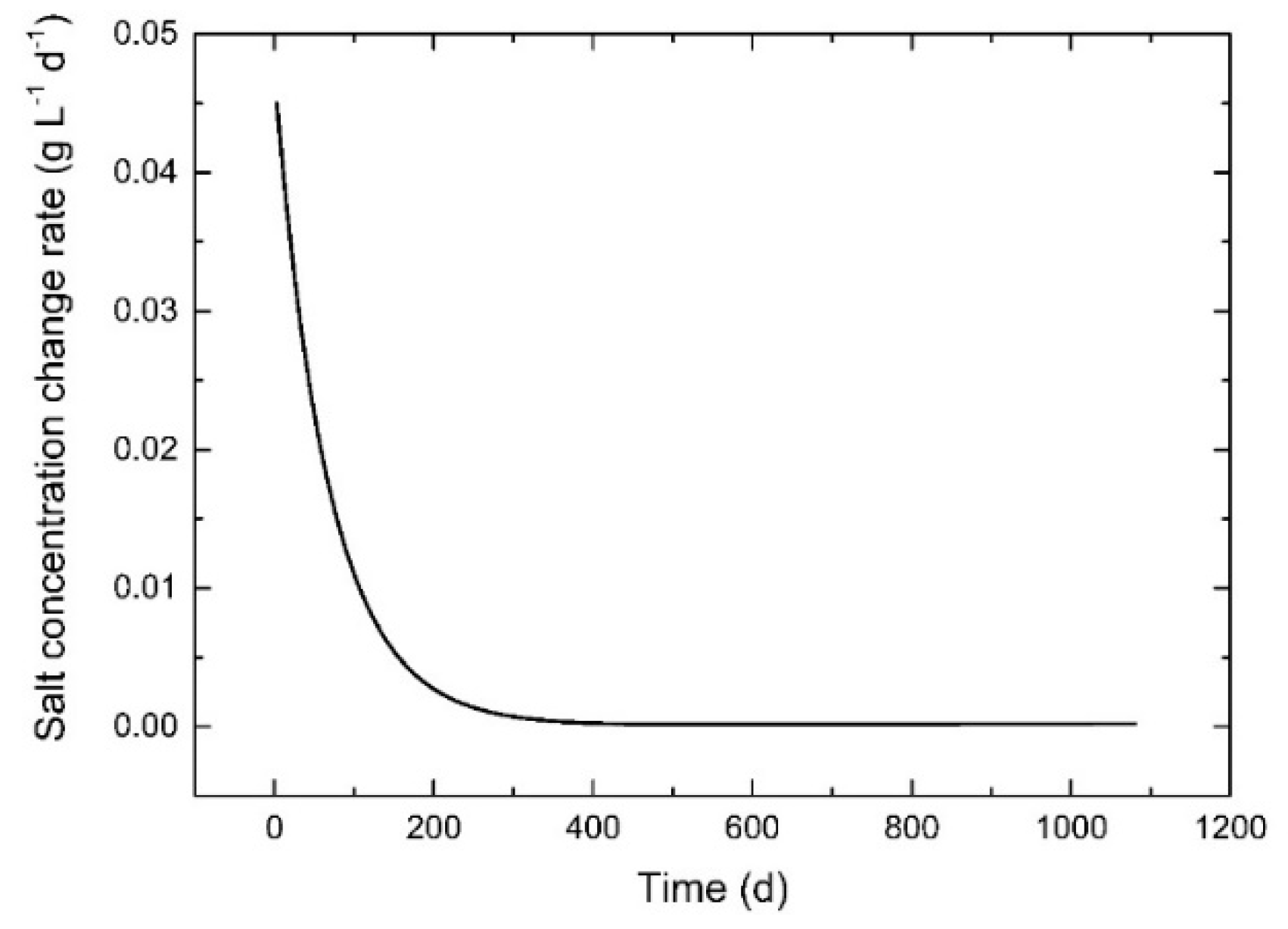
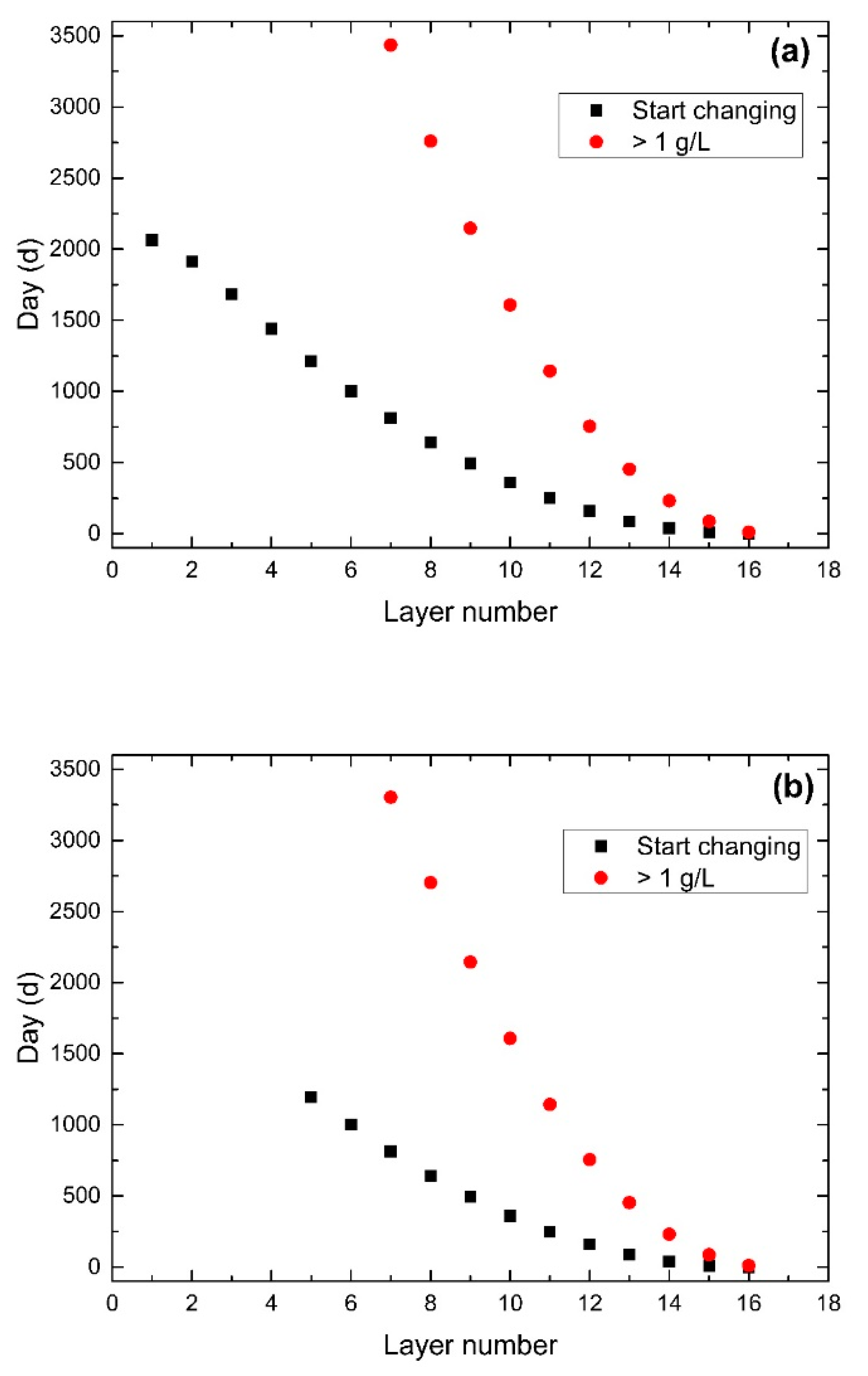
3.5. Effect of Period of Water-Exchange
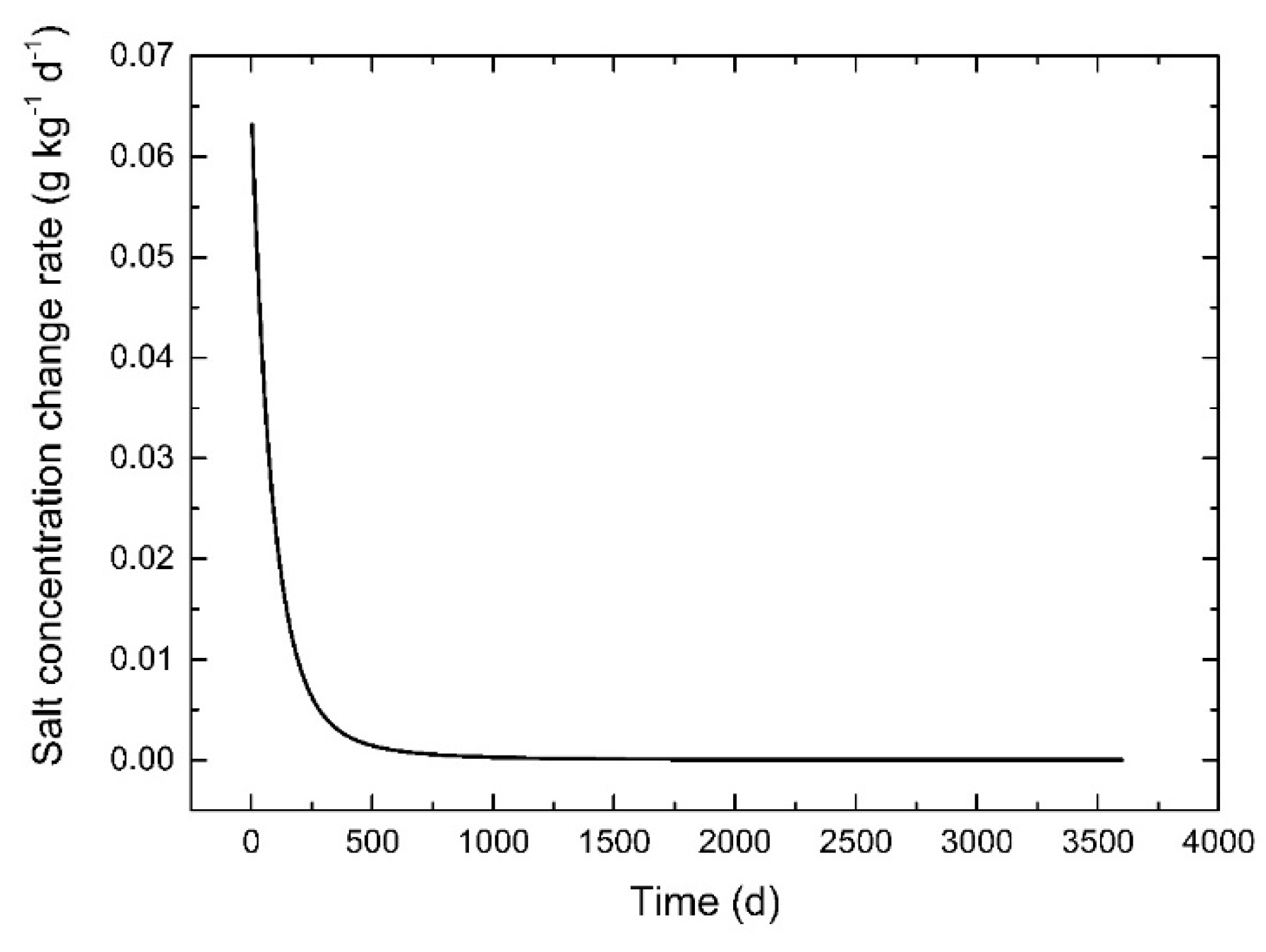
3.6. Effect of Lake Stage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonellini, M.; Mollema, P.N. Impact of groundwater salinity on vegetation species richness in the coastal pine forests and wetlands of Ravenna, Italy. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, E.; Karam, H.; Hemond, H.F.; Harvey, C.F. Transient groundwater dynamics in a coastal aquifer: The effects of tides, the lunar cycle, and the beach profile. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2473–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaruddin, S.; Werner, A.D.; Morgan, L.K. Water table salinization due to seawater intrusion. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 8397–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarthy, T.S. Groundwater in the wetlands of the Okavango Delta, Botswana, and its contribution to the structure and function of the ecosystem. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.C.; Singh, V.P. Hydrochemical analysis of salinization for a tannery belt in Southern India. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurinak, J.J.; Whitmore, J.C.; Wagenet, R.J. Kinetics of salt release from a saline soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, P.A.; Mifflin, M.D. Water from low-permeability sediments and land subsidence. Water Resour. Res. 1965, 1, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Gibbes, B.; Li, L. Driving mechanisms for groundwater flow and salt transport in a subterranean estuary. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L03402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Qun, L.; Shusheng, G.; Zhiming, H.; Hui, X. Pseudo threshold pressure gradient to flow for low permeability reservoirs. Explor. Dev. 2009, 36, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonneea, M.E.; Mulligan, A.E.; Charette, M.A. Climate-driven sea level anomalies modulate coastal groundwater dynamics and discharge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2701–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuzil, C.E. Groundwater flow in low-permeability environments. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 1163–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuzil, C.E. How permeable are clays and shales? Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remenda, V.H.; Kamp, G.; Cherry, J.A. Use of vertical profiles of δ18O to constrain estimates of hydraulic conductivity in a thick, unfractured aquitard. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 2979–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, M.J.; Wassenaar, L.I. Implications of the distribution of δD in pore waters for groundwater flow and the timing of geologic events in a thick aquitard system. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, A.P.; Sonntag, C.; Lippmann, J.; Pearson, F.J.; Gautschi, A. Solute transport in formations of very low permeability: Profiles of stable isotope and dissolved noble gas contents of pore water in the Opalinus Clay, Mont Terri, Switzerland. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, P.; Hunkeler, D. Carbon and chlorine isotopologue fractionation of chlorinated hydrocarbons during diffusion in water and low permeability sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 157, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebbe, L.; Meir, N.V. Hydraulic conductivities of low permeability sediments inferred from a triple pumping test and observed vertical gradients. Groundwater 2000, 38, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cey, B.D.; Barbour, S.L.; Hendry, M.J. Osmotic flow through a Cretaceous clay in southern Saskatchewan, Canada. Can. Geotech. J. 2001, 38, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H. Non-Darcian flow in low-permeability media: Key issues related to geological disposal of high-level nuclear waste in shale formations. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadokostaki, K.G.; Petrou, J.K. Combined experimental and computer simulation study of the kinetics of solute release from a relaxing swellable polymer matrix. I. Characterization of non-fickian solvent uptake. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 2458–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J. Characteristics and mechanism of low permeability clastic reservoir in Chinese petroliferous basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2004, 22, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Gregory, S. Diffusion of ions in seawater and deep sea sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1974, 88, 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rees, K.C.J.; Sudicky, E.A.; Rao, P.S.C.; Reddy, K.R. Evaluation of laboratory techniques for measuring diffusion coefficients in sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, F.S.; Rowe, R.K.; Quigley, R.M. Estimation of chloride diffusion coefficient and tortuosity factor for mudstone. J. Geotech. Eng. 1992, 118, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, M.J.; Barbour, S.L.; Boldt-Leppin, B.E.J.; Reifferscheid, L.J.; Wassenaar, L.I. A comparision of laboratory and field based determinations of molecular diffusion coefficients in a low permeability geologic medium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6730–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Jia, L.; Kamath, J.; Kovscek, A.R. Scaling of counter-current imbibition processes in low-permeability porous media. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2002, 33, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J.A.; Harley , B.M.; Neysadurai, A. Desalination of an Important Estuary. Environment Engineering, Process of the 1985 Specialty Conference; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.L.; Cherry, J.A.; Pankow, J.F. Diffusive contaminant transport in natural clay: A field example and implications for clay-lined waste disposal sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portielje, R.; Lijklema, L. Estimation of sediment-water exchange of solutes in Lake Veluwe, the Netherlands. Water Res. 1999, 33, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malusis, M.A.; Shackelford, C.D. Coupling effects during steady-state solute diffusion through a semipermeable clay membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss, J.W.; Michael, H.A. Saltwater-freshwater mixing dynamics in a sandy beach aquifer over tidal, spring-neap, and seasonal cycles. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6747–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, F.; Simon, E. The simulation of chloride inflows into Lake Kinneret. J. Hydrol. 1992, 138, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S. Estimation of lake hydrologic budget terms using the simultaneous solution of water, heat, and salt balances and a Kalman Filtering Approach: Application to Lake Kinneret. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 3041–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, S.; Lyakhovsky, V.; Gvirtzman, H. Transient salt transport modeling of shallow brine beneath a freshwater lake, the Sea of Galilee, Israel. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, A. The mechanism of Lake Kinneret salinization as a linear reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2003, 281, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadokostaki, K.G. Combined experimental and computer simulation study of the kinetics of solute release from a relaxing swellable polymer matrix. II. Release of an osmotically active solute. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Skaggs, T.H.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Reclamation of saline soils by partial ponding: Simulations for different soils. Vadose Zone J. 2010, 9, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, P.T.; Konikow, L.F.; Hornberger, G.Z. Simulation of solute transport across low-permeability barrier walls. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2006, 85, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Takase, K.; Wang, Y. Numerical simulation of groundwater flow for a coastal plain in Japan: Data collection and model calibration. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, J.S.; Olyphant, G.A. Modeling the hydrologic response of groundwater dominated wetlands to transient boundary conditions: Implications for wetland restoration. J. Hydrol. 2007, 332, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, C.D.; Guo, W. MODFLOW/MT3DMS–based simulation of variable-density ground water flow and transport. Groundwater 2006, 44, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, G.R.; Roelvink, J.A.; Kester, J.A.T.M.V.; Stelling, G.S. Development and validation of a three-dimensional morphological model. Coast. Eng. 2004, 51, 883–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeville, A.N.; O’Connell, P.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V.; Nash, J.E. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part III-The Ray catchment at Grendon Underwood. J. Hydrol. 1970, 11, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, P.E.; Nash, J.E.; Farrell, J.P. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part II-The Brosna catchment at Ferbane. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onta, P.R.; Gupta, A.D. Regional management modeling of a complex groundwater system for land subsidence control. Water Resour. Manag. 1995, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartakovsky, G.D.; Neuman, S.P. Three-dimensional saturated-unsaturated flow with axial symmetry to a partially penetrating well in a compressible unconfined aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Mou, X.; Cui, B.; Ping, F. Regulation of drainage canals on the groundwater level in a typical coastal wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.G. An experimental study on starting pressure gradient of fluids flow in low permeability sandstone porous media. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2002, 29, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
 ) indicates the in situ experiment point, the blue dot (●) indicates the drill-hole test point, and the red dashed line (---) indicates the section line. The salinity distribution of the lake water at the section is described in the Results and Discussion section.
) indicates the in situ experiment point, the blue dot (●) indicates the drill-hole test point, and the red dashed line (---) indicates the section line. The salinity distribution of the lake water at the section is described in the Results and Discussion section.
 ) indicates the in situ experiment point, the blue dot (●) indicates the drill-hole test point, and the red dashed line (---) indicates the section line. The salinity distribution of the lake water at the section is described in the Results and Discussion section.
) indicates the in situ experiment point, the blue dot (●) indicates the drill-hole test point, and the red dashed line (---) indicates the section line. The salinity distribution of the lake water at the section is described in the Results and Discussion section.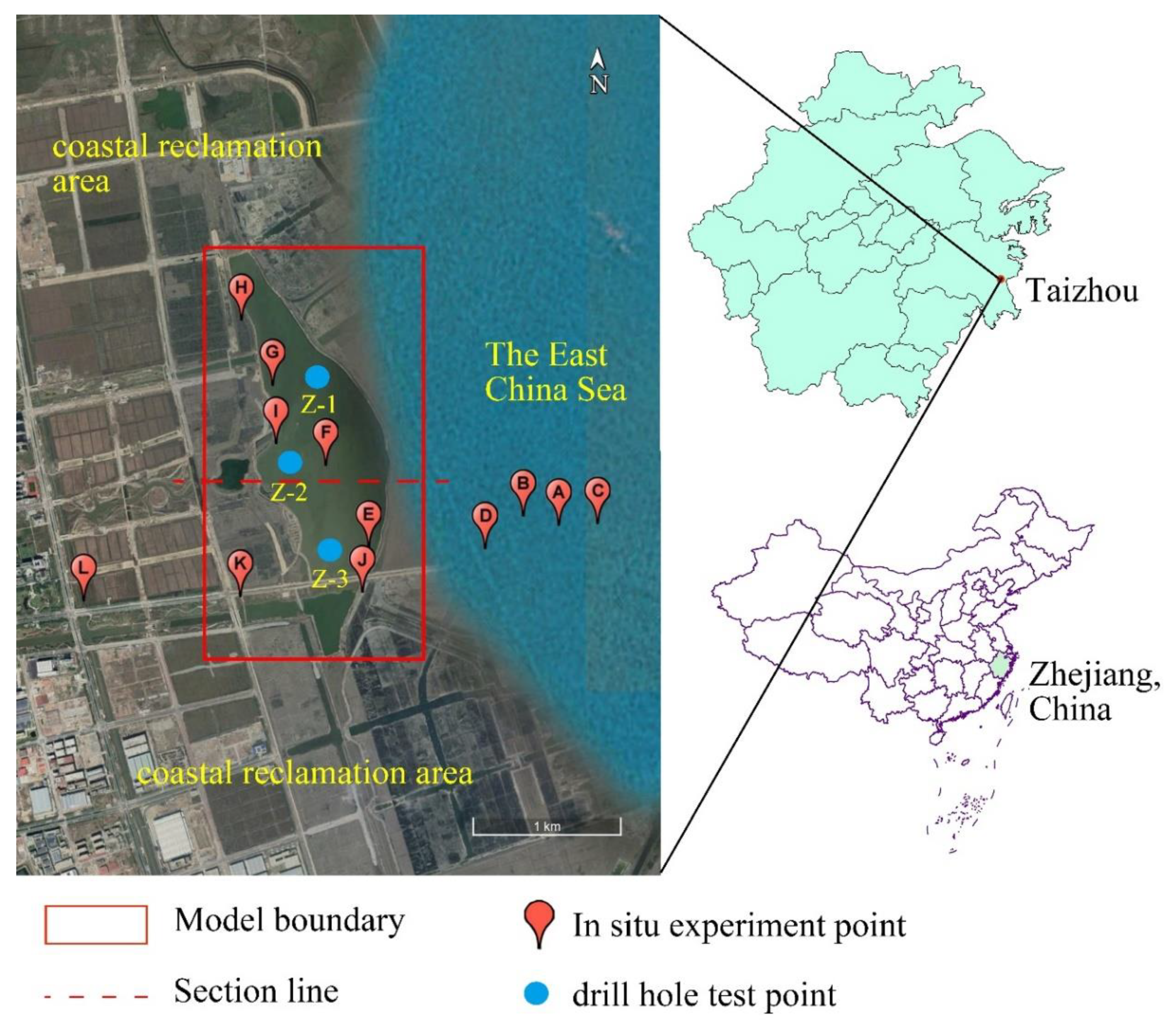


| Depth (m) | Z-1 (g/kg) | Z-2 (g/kg) | Z-3 (g/kg) | Average Salt Concentration (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2–0.5 | 10.70 | 8.20 | 11.90 | 10.27 |
| 0.7–1.0 | 11.80 | 10.80 | 10.10 | 10.90 |
| 1.2–1.5 | 16.70 | 14.80 | 18.70 | 16.73 |
| 1.7–2.0 | 14.10 | 13.00 | 14.50 | 13.87 |
| 2.2–2.5 | 13.80 | 15.40 | 12.70 | 13.97 |
| 2.7–3.0 | 14.60 | 14.90 | 12.70 | 14.07 |
| Serial Number | Kv (m/d) | Serial Number | Kv (m/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SP-A | 0.00201 | SP-G | 0.00087 |
| SP-B | 0.00173 | SP-H | 0.00080 |
| SP-C | 0.00171 | SP-I | 0.00109 |
| SP-D | 0.00174 | SP-J | 0.00109 |
| SP-E | 0.00063 | SP-K | 0.00124 |
| SP-F | 0.00079 | SP-L | 0.00142 |
| Serial Number | Kh (m/d) | Serial Number | Kh (m/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SL-A | 0.0024 | SL-G | 0.0010 |
| SL-B | 0.0020 | SL-H | 0.0010 |
| SL-C | 0.0020 | SL-I | 0.0013 |
| SL-D | 0.0020 | SL-J | 0.0013 |
| SL-E | 0.0010 | SL-K | 0.0015 |
| SL-F | 0.0009 | SL-L | 0.0016 |
| Data Type | Salinity of Lake Water (g/L) | RMSE | R | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interface | 0.25 m | 0.5 m | 0.75 m | 1 m | |||
| Simulation (the 90th day) | 2.79 | 1.02 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.5 | 0.13491 | 0.99892 |
| Measured (the 90th day) | 2.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
| Simulation (the 180th day) | 1.99 | 0.83 | 0.58 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.09316 | 0.99838 |
| Measured (the 180th day) | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhuo, Y.; Yang, D. Numerical Simulation Study on Salt Release Across the Sediment–Water Interface at Low-Permeability Area. Water 2019, 11, 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122503
Li W, Wang J, Chen Z, Yang Y, Liu R, Zhuo Y, Yang D. Numerical Simulation Study on Salt Release Across the Sediment–Water Interface at Low-Permeability Area. Water. 2019; 11(12):2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122503
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Weijian, Jinguo Wang, Zhou Chen, Yun Yang, Ruitong Liu, Yue Zhuo, and Dong Yang. 2019. "Numerical Simulation Study on Salt Release Across the Sediment–Water Interface at Low-Permeability Area" Water 11, no. 12: 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122503
APA StyleLi, W., Wang, J., Chen, Z., Yang, Y., Liu, R., Zhuo, Y., & Yang, D. (2019). Numerical Simulation Study on Salt Release Across the Sediment–Water Interface at Low-Permeability Area. Water, 11(12), 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122503




