Abstract
Modern sawing techniques employed in ornamental stones’ exploitation produce large amounts of slurry that can be potentially diffused into the environment by runoff water. Slurry produced by limestone and marble quarrying can impact local karst aquifers, negatively affecting the groundwater quality and generating a remarkable environmental and economic damage. A very representative case-study is that of the Apuan Alps (north-western Tuscany, Italy) because of the intensive marble quarrying activity. The Apuan Alps region extends over about 650 km2; it hosts several quarries, known all over the world for the quality of the marble extracted, and a karst aquifer producing about 70,000 m3/day of high-quality water used directly for domestic purposes almost without treatments. In addition, Apuan Alps are an extraordinary area of natural and cultural heritage hosting many caves (about 1200), karst springs and geosites of international and national interest. During intense rain events, carbonate slurry systematically reaches the karst springs, making them temporarily unsuitable for domestic uses. In addition, the deterioration of the water quality threatens all the hypogean fauna living in the caves. This paper provides preliminary insights of the hydrological and biological indicators that can offer information about the impact of the marble quarrying activities on groundwater resources, karst habitats and their biodiversity.
1. Introduction
Karst areas constitute about 10% of the land surface worldwide and there is a widespread concern about the effects that human activities have upon karst environments [1,2]. Karst aquifers often host water resources that are very important, in terms of both quantity and quality, usually not requiring any treatment before being distributed through civil aqueducts. For this reason, karst groundwater sources are attaining a growing economic and social value. According to UNESCO’s International Geoscience Programme (IGCP) 513, concerning “karst aquifers and water resources” and their preservation, about 25% of the world’s population relies on drinking water supplies from karst aquifers. On the other hand, karst areas are extremely vulnerable and could be easily (and potentially irreversibly) damaged by human activities such as deforestation, agricultural practices, urbanization, tourism, military activities, water exploitation, mining and quarrying (e.g., [3], and reference therein). Climate change poses an additional risk to karst groundwater, exacerbating the major challenges in the next future.
An unexpectedly high diversity of living forms (micro, meio and macro-organisms) have been discovered in karst aquifers in the second half of the 20th century. Karst stygobionts are often geographically rare and phylogenetically isolated taxa, with ancient origins which date back to the Early Tertiary period [4]. The stygofauna show morphological, physiological and behavioral characteristics suitable for life in absence of light and scarcity of trophic resources (e.g., [5,6,7,8]). The stygofauna of karst habitats are represented by vertebrates as well as by small invertebrates, among which crustaceans are dominant [9,10]. Beyond the importance that such highly specialized fauna have in terms of global biodiversity, stygofauna provides a wide range of ecosystem services, including those related to the degradation of pollutants [11,12].
Known since the Roman age for the extraction of the precious white marble, the Apuan Alps, in north-western Tuscany, are a very peculiar mountain range and an extraordinary region of natural and cultural heritage in the Mediterranean basin, with many geological and biological features of national and international interest. This mountain range, whose maximum elevation is 1942 m a.s.l. at Pisanino Mount, consists of both metamorphosed and non-metamorphosed carbonate rocks belonging to three different tectonic units (Figure 1). Apuan metamorphic unit is mainly represented by meta-dolostone, marble and dolomitic marble (about 115 km2 as outcrops) and by cherty limestones (about 20 km2) ([13] and references therein).
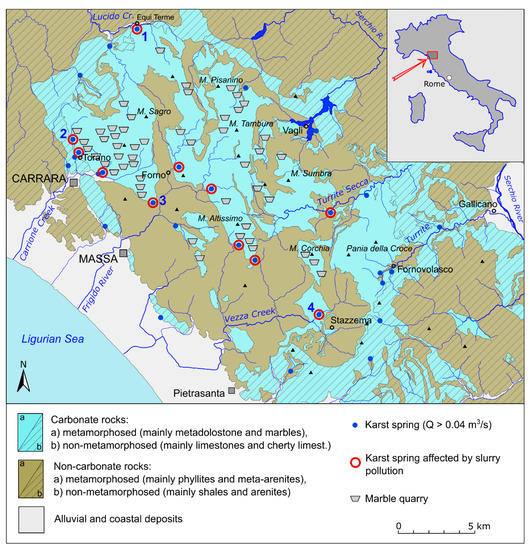
Figure 1.
Hydrogeological sketch map of the Apuan Alps with the location of the major karst springs (average discharge >0.04 m3/s) fed by carbonate aquifers and marble quarries. Numbers refer to monitored karst systems: (1) Equi springs; (2) Carbonera spring; (3) Cartaro spring; (4) Monte Corchia cave stream.
In an area of about 650 km2, the carbonate rock assemblages display very different structural and lithological traits. For this reason, they offer a wide variety of hydrogeological conditions displayed in many springs with very different hydrodynamics and hydro-chemical features [13]. The carbonate rocks contain important groundwater resources due to the high rainfall, and the high infiltration coefficient, that can reach 75% of total precipitation. Most of the major springs drain metamorphic carbonate aquifers, and supply drinking water mainly for inhabitants of the coastal plain (where Carrara and Massa towns are located).
The marble exploitation in the Apuan Alps is presently carried out in about 150 quarries that are frequently located at high altitudes (Figure 2a). Line drilling and sawing are the most modern techniques to produce large rectangular blocks suitable for being cut into smaller, regularly shaped products and slabs (Figure 2b). Sawing can be accomplished by a variety of tools, including wire, belt and chain saws. Pollutants resulting from quarrying, including the marble dust (locally known as “marmettola”) that is a product of rock sawing, easily infiltrate by means of meteoric waters into the underlying karst aquifers through solution cavities. This condition is responsible for the high vulnerability of the groundwater bodies, which is particularly critical for metamorphic carbonate rocks (i.e., marbles and meta-dolostone), due to the absence of retention of pollutants in the unsaturated zone (epikarst and vadose zone) and to the high hydraulic conductivity in the saturated one [14]. As a matter of fact, this fine-grained material is easily mobilized by rainwater and dispersed into and through the subterranean karst systems [15].
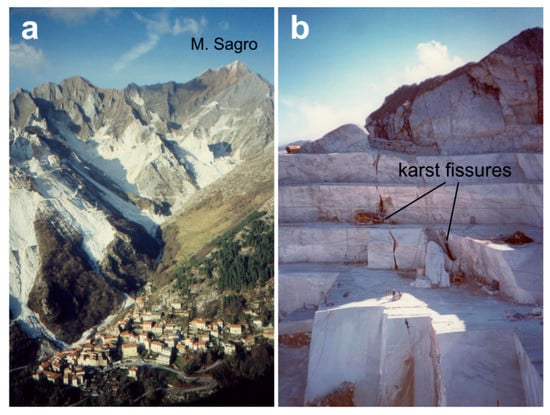
Figure 2.
(a) A view of Colonnata valley, in Northern Apuan Alps, showing the intense quarrying that concerns high-altitude areas too. (b) Quarrying is performed through sawing large blocks with chain or diamond-wire saws; karst fissures or solution pit interception is very frequent (Focolaccia quarry, M. Tambura, central Apuan Alps).
In the last decade, the annual marble production in the Apuan Alps quarries has been about 1.2 Mt/year [16]. The extraction and squaring of marble blocks produce about 4% dust per unit [15], in respect to marble production, which so amounts to about 0.05 Mt/year, or, as volume, about 25,000 m3/year, assuming a porosity of 35%. Most of this powder is disposed on quarry yards and stored in controlled repository areas but a substantial part of it is dispersed into the surrounding areas by wind and runoff before collecting. Furthermore, it is quite frequent that quarries intercept open fissures and solution pits through which marble powder enters the subterranean drainage usually driven by high-intensity rainfall events [17,18].
While the marble quarries in the Apuan Alps have been long and widely studied in many environmental respects, including marble formation volumes [19], rock mass stability [20] and restoration perspectives [21], the real effects of marble slurry pollution, and in particular its impact on groundwater and the processes governing its transport through the karst aquifers, have not yet been systematically examined, despite the fact that this aspect is crucial for the development of management measures aimed at preserving the water quality and the biodiversity of karst systems.
For these reasons, the Apuan Alps can be considered a relevant case-study area, where the impact of slurries produced by marble quarries on karst aquifers can be investigated in order to obtain an indication of general interest and worldwide application. The main purpose of this article is to provide the information available up to now regarding marmettola pollution, including its physical and chemical features, and the potential impacts that this particular waste product can cause on the Apuan Alps karst ecosystem, and more generally, in similar karst areas heavily affected by marble quarrying. The article also provides new data on both the hydro-physical properties of groundwater bodies and their biodiversity.
2. Chemical and Physical Features of Marmettola and Karst Spring Sediments
Marmettola is a fine, white powder produced during the extraction and squaring of marble blocks by way of chain and diamond-wire saws. Minor sources are represented by the dust produced by the intense traffic of heavy trucks, bulldozers and tractors transporting and moving heavy marble blocks along quarry roads and service areas. The chemical composition of the powder reflects the mineralogical constituents of the different marble varieties. The grains are essentially composed by calcite (usually 95–99%), mainly in sand-to-silt sizes, with a small percentage (1–3%) of dolomite [15,22,23]. Silicates, primarily quartz, muscovite and/or chlorite and clay minerals, are often present in minor amounts [15,21].
In order to investigate textural features, we examined some slurry samples collected in 2017, coming from a quarry at Mount Sagro, by scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis. Grains produced by chain saws were very angular in shape and with planar surfaces formed along calcite cleavage planes (Figure 3a). SEM image processing revealed that marble slurry is mainly composed by weight of a fine to very-fine sand (Figure 3b), whereas most of the particle sizes (expressed as equivalent circle diameter = ECD) range between 8 and 32 μm, if we consider the number of particles (Figure 3c). A consistent amount of the finer silt-sized fraction is possibly derived from consumption of larger grains during sawing [15]. The powder produced by diamond-wire cutting is generally finer (most grains <62.5 μm in size) but with grains showing an angular shape like those coming from chain saws [15].
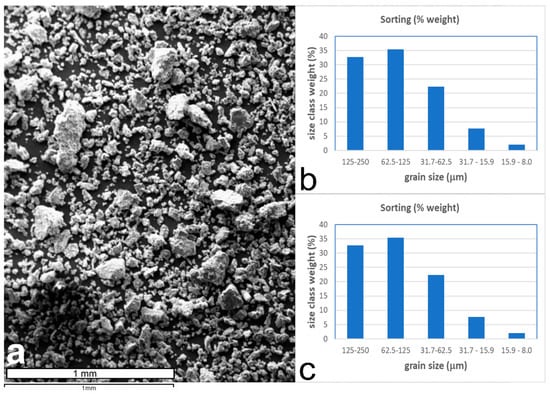
Figure 3.
(a) SEM image of marmettola produced by chain sawing collected at a marble quarry in the Mount Sagro area (note the very angular shape of particles). (b) Weight sorting of the sample collected (weight percent for each grain size class). (c) Frequency sorting (number of grains) of the same sample.
By means of direct investigation of karst systems contaminated by marble slurry, such that of Monte Corchia cave, we realized that suspended sediments found in springs and cave-streams consisted of fine sand and mud having a light grey or ochre color. From a chemical and mineralogical point of view, these deposits had a higher amount of Mg and Si respect to marmettola, due to the occurrence of dolomite and silicates of natural origin. In a sample collected in 2012 at Tana dei Tufi, a captured spring located near Torano village (Carrara marble district) often affected by turbidity, SEM analysis showed that about 75% of the grains were carbonate, the remaining being silicate particles. Grain morphometric analysis performed on SEM images revealed that grains’ ECDs mainly ranged from 15.9 to 62.5 μm, with the silicate particles a little finer than carbonate ones (Figure 4a,b). Other morphometric parameters, such as the aspect ratio (length/breadth ratio of each) and the roundness (calculated as perimeter2/4π * grain area), were similar in both carbonate and silicate grains (Figure 4c–f). SEM images confirmed also that most of this sediment consisted of calcite angular grains like those forming marmettola. Grains finer than 16 μm were poorly represented, probably because they were washed away as suspended load during floods. These preliminary data suggest that the transport through the karst network of the Apuan Alps produces an effective sorting and a mixing with natural sediments.
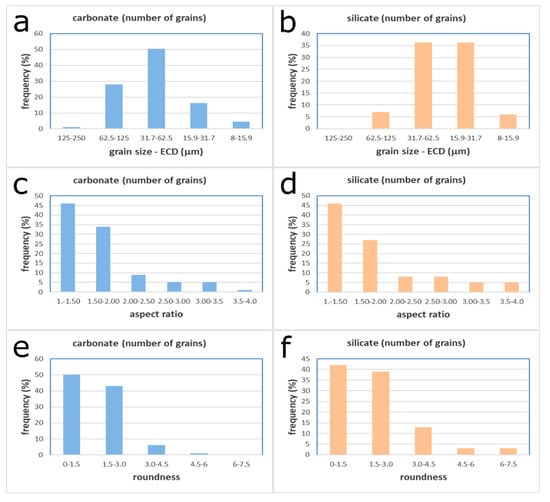
Figure 4.
ECD (equivalent circular diameter; in μm), aspect ratio and roundness of carbonate and silicate fractions of a sediment collected at the Tana dei Tufi karst spring (Torano, Northern Apuan Alps) (see text for explanation).
3. Impact of Marble Slurry on Karst Groundwater
Once marble powder mixes up with water, it produces a fluid mud that rapidly disperses through the karst groundwater network [15,24]. This slurry negatively affects the groundwater quality, and its persistence in the karst system may produce remarkable environmental and economic damage [25,26]. In the Apuan Alps, the marmettola slurry has been observed in cave streams and karst springs (Figure 5).
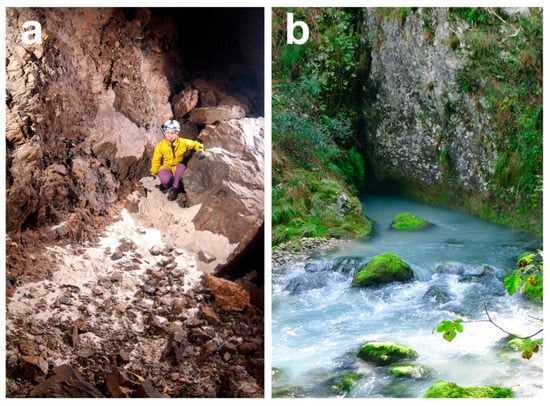

Figure 5.
(a) Marmettola deposited in the occasionally flooded Buca di Equi cave. (b) Whitish, turbid water due to the marble slurry flowing out from the Equi karst spring observed several days after a strong flood in October 2013.
Although several studies have described the environmental impacts of human activities on karst systems [1,27], there are relatively a few papers that specifically refer to the effects from quarrying on karst drainage systems. The relationship between quarrying activities and the environmental damage caused on carbonate rock has been well documented for over sixty years [28]. On the contrary, there are only a few reports that include major discussions of the environmental impacts on the karst aquifer of slurry produced by in-situ stone cutting and almost none referring to the impact on the karst stygofauna [29,30,31].
One of the most effective ways to investigate the dynamics of marble slurry transfer through karst subterranean networks is by monitoring of main spring hydro-physical parameters (flow rate, temperature, electrical conductivity and turbidity) coupled with sampling of suspended load. In the Apuan Alps, the turbidity observed at springs during floods can be often related to the suspended transport of marble slurry produced by quarries [15]. In fact, we have frequently observed that springs whose catchment areas do not embrace quarry districts have usually clear or slightly muddy water even during floods, apart from some springs that are fed by surface sinking water. On the contrary, turbidity due to carbonate slurry is systematically observed in water springs located in quarrying districts (Figure 5b).
In order to study the effects of the marble slurry on the karst aquifers of the Apuan Alps, a monitoring network has been recently (starting from April 2018) installed by the authority in charge for the environmental monitoring in Tuscany (Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale Toscana-ARPAT). The monitoring settlement concerns three karst springs (Carbonera, Cartaro and Equi), and one cave stream (Monte Corchia Cave; see Figure 1 for location). Stream and spring monitoring is performed by automatic probes acquiring water level (resolution 1 mm), water temperature (resolution 0.1 °C), electrical conductivity (accuracy 1%) and turbidity (resolution 1—NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Unit)); data are freely available at http://sira.arpat.toscana.it. Samples of marmettola were collected in quarries, whereas sediments were collected in a cave stream (Monte Corchia Cave) and karst springs, in order to compare the physical features of both marble sawing powder and springs suspended load.
One of the clearest examples of the marble slurry’s impact on the Apuan Alps karst systems is provided by the springs located close to Equi Terme village (Massa) (see Figure 1 for location). Equi springs are fed by the Northern sector of the Apuan Alps karst aquifer, consisting mainly of marble and meta-dolostones. Marble quarries are the main human activity occurring in the catchment area. This multi-spring is characterized by high and very rapid fluctuations of water flow. During the dry season, the discharge can decrease down to 0.03–0.04 m3/s, whereas major floods can increase it to a total flow rate of 15–20 m3/s [32]. During floods and some days after, the water is highly turbid, but a slight whitish opalescence can persist for several days afterwards. Figure 6 shows the flow rate and turbidity diagram from April 2018 to April 2019. Floods are characterized by tight peaks followed by a rapid decrease of flow rate, indicating a quick transmission of hydraulic pressure through the karst network due to massive infiltration [33]. Turbidity peaks, which can reach 400 or more NTU, are not perfectly overlaid to the discharge peaks being shifted some days afterward.
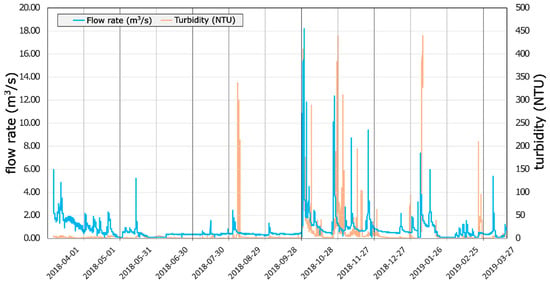
Figure 6.
Flow rate and turbidity of Equi springs from April 2018 to April 2019 (dates are expressed as yyyy-mm-dd).
A detail graph (Figure 7) related to one minor flood (occurred on 1 September 2018 at Equi springs) following a long period of low flow rate, shows some features that clarify the origin of turbidity. The turbidity peak occurred around 48–50 h after the first flow peak, when the discharge decreased almost to the pre-flood level. This means that during minor floods the water remains clear until the marmettola slurry, washed away from the quarries and infiltrated in the catchment area, reaches the spring through a high-conductivity conduits network. In this case, the turbidity is not due to the mobilization of fine sediments contained in the phreatic sector of the aquifer but to the infiltration of surface runoff contaminated by marble slurry.
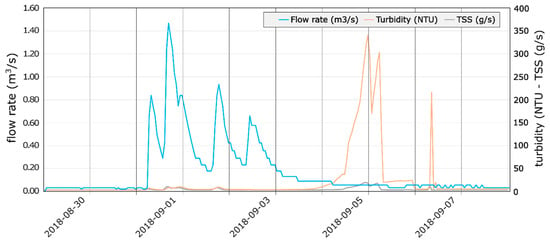
Figure 7.
Flow rate and solid transport diagram of Equi springs during a minor flood on 1 September 2018 (dates are expressed as yyyy-mm-dd). The turbidity peak occurred more than four days after the flow peak.
During major floods, the Equi springs displayed a different behavior of the turbidity parameters with respect to flow rate fluctuation (Figure 8). Turbidity showed a slight but significant increase just a few hours after the discharge rising, whereas the first substantial turbidity peak occurred with a delay of about 48 h after flood. Anyway, we observed that most of the solid load, measured as total suspended sediment (TSS), according to the methods proposed by Drysdale et al. [15], occurred during the maximum flow rate phase. Despite the high values of NTU, the turbidity peaks following with about two days of delay the first flood peak, contributed only for about the 40% to the amount of TSS, since discharge was low. Actually, the total TSS mobilized during this flood was exceptionally high, approaching 37 tons (37,000 kg).
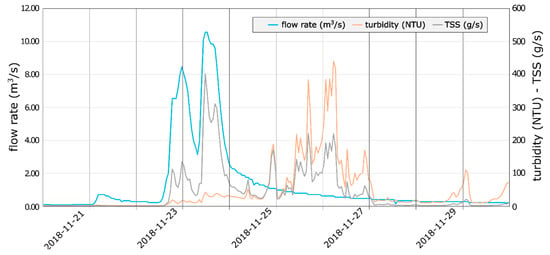
Figure 8.
Flow rate and solid transport diagram of Equi springs during a major flood on 23 November 2018 (dates are expressed as yyyy-mm-dd). The major turbidity peak occurred about three days after the flow rate increase, but the TSS reached its greatest values during the second flood peak.
Comparing the different turbidity responses of these spring group during minor floods (Figure 7) with respect to major floods (Figure 8), we can infer that the TSS mobilized during the phase of major flow rate probably consists of sediments already stored in the phreatic system, which may be dragged away by water only in the case of a high flow velocity.
In conclusion, if we consider the effective TSS load instead of turbidity, we observe two major transport phases, the first during the flood peaks and the second one during the flood decremental phase (Figure 8). Considering the pattern of water and sediment fluxes, it may be argued that the second solid transport wave corresponded to the finest portion of marmettola washed away directly on quarry areas.
4. Impact of Marble Slurry on Karst Stygofauna
It is not an easy task assessing which are the main impacts of marble slurry on the organisms that live in karst aquifers. The main difficulty is the limited accessibility of these environments and the consequent impossibility of directly inspecting the habitats where stygobiotic species dwell [34]. Very appropriately, karst systems have been compared to black boxes in which one can assess exactly the input and the output but cannot directly know what is happening inside [35]. This similitude comes from hydrogeology but actually fits ecology very well. Karst stygofauna may be sampled in the epikarst (mostly caves) or at the karst outlets, through water filtration at the springs. In both cases, however, there is no direct inspection of the habitats except, perhaps, for gours, concretion pools, ponds and rivers, when present.
Despite the sampling difficulties, groundwater ecologists have collected enough information to outline the distributional patterns of many stygobiotic taxa. We know, for instance, that the distribution of stygofauna is not uniform in the aquifer, but that most of the species, which do not have adaptations to withstand fast flows, tend to colonize the habitats where the groundwater flow is low ([36,37,38] and references therein). Most of the species are collected from the small fractures and dissolution fissures (apertures from about one millimeter to a few centimeters) of the karst network, rather than in the fast drains [37,39,40,41]. Groundwater flow is therefore the main organizing factor for karst communities [42] and in extreme cases, such as in the event of an earthquake, the massive earthquake-induced flow discharge can trigger a huge washout of groundwater fauna with a destructive effect on the biological assemblages [36].
In normal conditions, however, groundwater flow acts together with other factors, such as behavioral adaptations. In fact, the occurrence of juveniles of some stygobiotic species at spring-fed karst outlets during a flood event [43] is suggestive of an adaptive strategy: some species release the eggs during the low groundwater level period and use the flood to disperse the juveniles so as to favor the colonization of new habitats [43]. Competition for trophic resources and predation are additional factors that can shape the distribution of communities within karst aquifers, as already observed in previous field and laboratory studies [44]. Finally, the chemical contamination of karst aquifers also influences the distribution of species within the karst network. An organic pollution (indicated by high nitrates and ammonium concentrations and particulate organic matter) may favor, for instance, the permanence of epigean species which, having high metabolic rates, exert a strong competitive pressure on the stygobiotic species, often replacing them completely within the community [45].
Unfortunately, there are no available data on the effect of marble quarry wastes on karst communities. Based on the observations made at Equi springs, we can realistically expect that a substantial quantity of marmettola settles in the smaller fractures of the karst systems, where the flow velocities are low and where, as mentioned above, most species are present. A complete or partial filling of these habitats likely induces chemical variations influencing the availability of oxygen, nutrients and habitat space reduction. This scenario recalls the phenomenon of clogging observed in hyporheic zones (transitional ecotones between surface water and groundwater bodies). In fact, the deposition of fine sediments in the hyporheic zone of the Alpine stream Noce Bianco in Northern Italy due to hydropeaking caused a reduction of the interstitial habitats available to stygobiotic taxa [46]. Similarly, Mori et al. [47] observed that the stygobiotic community of the hyporheic zones of the Sava River (Slovenia) was strongly affected after severe flooding with clogging of interstitial spaces by fine sediments. Microhabitat clogging may select species with certain physiological or trophic characteristics. For instance, in the reduced pore spaces of the hyporheic zones of the River Rhone catchment, only small-sized and slow-moving organisms, mainly copepods, ostracods and cladocerans, occurred [48]. This phenomenon has been confirmed recently by laboratory experiments. Korbel et al. [49] observed that stygobiotic crustaceans, such as the small-sized copepods and the large-sized amphipods and syncarids, are able to move easily in sand substrates (φ = 0.3–0.7 mm) and gravel (φ = 2–4 mm). However, only copepods were able to move in silts (φ < 60 μm), whereas the larger amphipods and syncarids remained on the sediment surface without being able to dig in.
The inability to cope with fine sediments for syncarids and amphipods increases when the groundwater level decreases. In microcosm experiments, none of these animals managed to dig in the mud layers when the overlying water was removed [49]. This phenomenon has serious consequences in terms of loss of ecosystem services. In fact, laboratory experiments have shown that syncarids and amphipods are crucial for maintaining the effective porosity of fine sediment-filled habitats. In the absence of these animals, porosity decreases significantly in two months, causing a further reduction of pore spaces [50]. The diameter of pore spaces in silts is predicted to be <25 μm [51] and the same is expected in quarry waste deposits because most of the particles we measured were from 8 to 32 μm in diameter. The intergranular spaces of marmettola deposits are, therefore, smaller than the smallest dimension of most of stygobiotic crustaceans. Copepods manage to dig in these deposits, and it has to be expected that fine sediments adhere tenaciously to the body of the animal (Figure 9). We do not know how this sort of “coating” will negatively affect the physiology of these organisms, but fissured aquifers filled with marble slurry are likely inhospitable habitats for most of karst stygofauna.
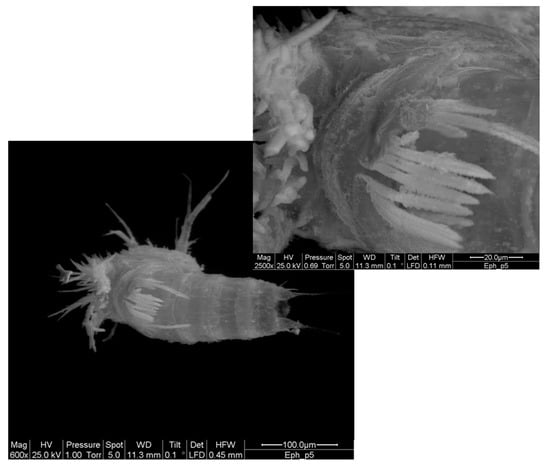
Figure 9.
Silt-coating of an individual of Elaphoidella phreatica (Crustacea Copepoda) from a clay-sandy aquitard in Tuscany (Italy). The photos were obtained by scanning electron microscopy. The grains of silt adhere tenaciously to the body of the animal also covering the setae and appendages. In the detail of the photo, the coating of the fifth thoracic leg involved in mating behavior of these animals is visible.
In order to test this hypothesis, we carried out biological surveys in the Monte Corchia cave, located in one of the most intensely exploited areas with marble quarries in the Apuan Alps. The Monte Corchia karst system is located in the south-western part of the Apuan Alps and is developed inside the carbonate core of a syncline, almost completely enclosed by a low-permeable basement (Figure 1). Monte Corchia cave is about 65 km long and 1185 m deep and it is presently one the largest and deepest caves in Italy [52].
Specimens were collected from the vadose zone of the cave, located between 900 and 800 m a.s.l., which consists of several passages that have been part of the touristic path since 2001. We sampled six percolation water drips with permanent water flow and six concretional pools. The water in the concretional pools was collected by syringes at approximately quarterly intervals from June 2016 to October 2019. Percolation water drips were directed into a 500 mL plastic filtering bottles with partly removed walls covered by a net of 60 μm mesh a few cm above the bottom. The animals coming with the drips were retained in the small amount of water in the filtering bottles and collected on a quarterly basis. Altogether we collected about 700 specimens, 85% of which came from the drips. All the animals were copepods, as also observed in other studies (e.g., [35,53,54]). However, all the animals collected in our surveys belonged to a single taxon, a new undescribed species of the canthocamptid harpacticoid genus Moraria.
This result contrasts with the data of Meleg et al. [55], who reported 11 stygobiotic copepod species from drips and drip pools of five Romanian caves; of Galassi et al. [37], who reported up to eight copepod species from two drips of Frasassi cave; and especially, with the data (up to 33 species per cave) recorded in the Slovenian caves and reviewed by Pipan and Culver [53]. That of Monte Corchia Cave seems, therefore, to be an unusual situation, being similar only to two non-Dinaric caves in Slovenia; namely, Huda luknja, occurring in an isolated karst area, and Snežna jama, an ice cave in the Kamnik–Savinja Alps (two stygobiotic copepod species per cave) [53]. At present, data do not allow us to know whether the persistently low biodiversity observed in Monte Corchia Cave is due to the presence of marmettola and its clogging effects, or to other factors, such as the isolation of the cave that prevents colonization of groundwater similarly to the conditions of Huda luknja in Slovenia [54].
5. Discussion and Conclusions
This study did not aim at proposing strategies to contain the production of marble slurry or to prevent its dispersion in subterranean waterways but had the objective to denounce the fact that too many aspects of this environmental issue have not yet been adequately addressed. For example, the priority issue for the Italian authorities is the correct identification of marmettola as waste or as a by-product. This is not a matter of little importance, since the management regime of by-products is much less restrictive from a legislative point of view. Although the marble powder produced by the quarrying activities in the Apuan Alps is managed as waste, the cross-checks carried out by the competent authorities have highlighted that a relevant amount of it is dispersed in the environment. It would therefore be appropriate to apply an economic sanction that compensates for the environmental damage, including the loss of ecosystem services, consequently to marmettola dispersion. However, the quantification of this penalty, although expressly demanded by the Water Framework Directive in Europe, is difficult to determine now. The main impediment is due to the scarce knowledge of the impacts of marble slurry on the fauna dwelling in karst aquifers. With this review we aimed at disseminating information on the possible biological impacts, and secondly, on the poor biodiversity detected in some parts of the Apuan Alps karst system, such as in Monte Corchia cave. Stygofauna are “out of sight” and it is, therefore, easy to maintain these species as “out of mind” [56].
However, this short-sighted way to perceive karst ecosystems is an oversight before which we cannot remain silent. Fortunately, the turbidity due to marmettola detected at the springs is visible to the naked eye and has an immediate impact on the public, which is shocked by the idea of drinking “dirty” water. The quantification of the environmental impact in this case is easier, since it is possible to estimate the damage caused to the aqueduct filters by the high turbidity or the temporary closure of the distribution network. However, not only the springs presently captured for civil aqueducts but those that can be potentially captured in the future, must be monitored and possibly subjected to safeguarding measures.
Based on a first set of data, this study documented the worsening of the water quality during flood events due to the marmettola transport in the karst system of the Apuan Alps and a supposed negative effect of suspended solid deposition on the local groundwater community. The study highlighted that, although marble slurry does not constitute an immediate danger to public health, it is nevertheless responsible for a serious impact on the Apuan surface and subterranean waterways. We suspect that an unknown amount of marmettola has been already accumulated in the karst aquifers and it is discharged only in conjunction with high-intensity rain events. As already stated, the effects of such a physical pollution, apart the obvious deterioration of the quality of the water intended for human consumption, are still not known in detail. It can be expected that the marble slurry has potentially reduced the water exchanges among karst conduits and fractures and impacted the rock mass porosity, changing the hydrodynamics of the karst networks by also reducing their storage capacity. If so, it could be expected that the local environment will remain damaged (at some extent) for an unknown time period, even if the marmettola dispersion were to be completely stopped. Resilience will be hindered by the depletion of the groundwater biological communities that, otherwise, would be able to provide ecological services of great importance, most of them related to the aquifer self-purification.
In conclusion, the first results of this study have highlighted that the present-day footprint of quarrying activities in the Apuan Alps is greater than that indicated on maps or aerial photographs. It is necessary, therefore, to boost participatory processes involving economic stakeholders and environmental experts, and speleologists who are often the most informed about the conditions within karst systems too. Due to their long history of exploitation, the Apuan Alps represent a red flag that we hope will trigger biological and hydrogeological studies in other areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.P., P.C. and T.D.L.; methodology, L.P., P.C. and T.D.L.; validation, L.P. and D.M.P.G.; formal analysis, L.P.; investigation, L.P., P.C. and T.D.L.; species identification: T.D.L. and D.M.P.G.: resources, D.M.P.G.; data curation, L.P., P.C., T.D.L. and D.M.P.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.P.; writing—review and editing, L.P., P.C., T.D.L. and D.M.P.G.; visualization, L.P.; supervision, L.P. and D.M.P.G.; project administration, L.P. and D.M.P.G.; funding acquisition, D.M.P.G.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the AQUALIFE project LIFE12 BIO/IT/000231 “Development of an innovative and user-friendly indicator system for biodiversity in groundwater dependent ecosystems” of the European commission.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all the institutions that in different ways have encouraged and supported this research, with special mentions to: Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente, Toscana—ARPAT; Parco Regionale delle Alpi Apuane, Federazione Speleologica Toscana.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Williams, P.W. Environmental change and human impact on karst terrains: An introduction. Catena 1993, 25, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beymen, P.; Townsend, K. A disturbance Index for karst environments. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, I.; Margane, A.; Ptak, T.; Wiegand, B.; Sauter, M. Groundwater vulnerability assessment for the karstic aquifers of Tanour and Rasoun springs catchment area (NW-Jordan) using COP and EPIK intrinsic methods. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, J.; Culver, D.C. Assessing and conserving groundwater biodiversity: An introduction. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, J.; Danielopol, D.L.; Stanford, J.A. Groundwater Ecology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 571. [Google Scholar]
- Coineau, N. Adaptations to interstitial groundwater life. In Ecosystems of the World, 30: Subterranean Ecosystems’; Wilkens, H., Culver, D.C., Humphreys, W.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 189–210. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lorenzo, T.; Di Marzio, W.D.; Spigoli, D.; Baratti, M.; Messana, G.; Cannicci, S.; Galassi, D.M.P. Metabolic rates of a hypogean and an epigean species of copepod in an alluvial aquifer. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iepure, S.; Rasines-Ladero, R.; Meffe, R.; Carreno, F.; Mostaza, D.; Sundberg, A.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Barroso, J.L. The role of groundwater crustaceans in disentangling aquifer type features—A case study of the Upper Tagus Basin, central Spain. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, D.M.P.; Stoch, F.; Fiasca, B.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Gattone, E. Groundwater biodiversity patterns in the Lessinian Massif of northern Italy. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 830–847. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lorenzo, T.; Cipriani, D.; Fiasca, B.; Rusi, S.; Galassi, D.M.P. Groundwater drift monitoring as a tool to assess the spatial distribution of groundwater species into karst aquifers. Hydrobiologia 2018, 813, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.; Fenwick, G.; Hancock, P.J.; Harvey, M.S. Biodiversity, functional roles and ecosystem services of groundwater invertebrates. Invertebr. Syst. 2008, 22, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebler, C.; Avramov, M. Groundwater ecosystem services: A review. Freshwat. Sci. 2014, 34, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, M.; Piccini, L.; Menichini, M. Hydrodynamic and geochemical features of metamorphic carbonate aquifers and implications for water management: The Apuan Alps (NW Tuscany, Italy) case study. In Karst Water Environment; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Younos, T., Schreiber, M., Kosic Ficco, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Swizterland, 2019; Volume 68, pp. 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civita, M.; Forti, P.; Marini, P.; Meccheri, M.; Micheli, L.; Piccini, L.; Pranzini, G. Pollution Vulnerability Map for the Aquifers of the Apuane Alps—A Brief Guide; Gr. Naz. per la Difesa dalle Catastrofi Idrogeologiche; NRC: Firenze, Italy, 1991; p. 56.
- Drysdale, R.N.; Pierotti, L.; Piccini, L.; Baldacci, F. Suspended sediments in karst spring waters near Massa (Tuscany), Italy. Environ. Geol. 2001, 40, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Regione Toscana. Praer: Piano Regionale Delle Attività Estrattive. Available online: http://www.regione.toscana.it/-/praer-piano-regionale-delle-attivita-estrattive (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Gunn, J.; Hardman, D.; Lindesay, W. Problems of limestone quarrying in an adjacent to the Peak District National Park. Annales de la Société géologique de Belgique 1985, 108, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ekmekci, M. Impact of Quarries on Karst Groundwater Systems. Hydrogeological Processes in Karst Terranes; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, Oxfordshire, UK, 1993; Volume 207, pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrorocco, G.; Salvini, R.; Vanneschi, C. Fracture mapping in challenging environment: A 3D virtual reality approach combining terrestrial LiDAR and high definition images. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 77, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulli, D.; Pellegri, M.; Marchetti, D. Mechanical behaviour of Carrara marble rock mass related to geo-structural conditions and in-situ stress. In Proceedings of the 15th Pan-American Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (PCSMGE)/8th South American Congress on Rock Mechanics (SCRM), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15–18 November 2015; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Gentili, R.; Sgorbati, S.; Baroni, C. Plant species patterns and restoration perspectives in the highly disturbed environment of the Carrara marble quarries (Apuan Alps, Italy). Restor. Ecol. 2011, 19, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantisani, E.; Fratini, F.; Malesani, P.; Molli, G. Mineralogical and petrophysical characterisation of white Apuan Marble. Periodico di Mineralogia 2005, 74, 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cantisani, E.; Pecchioni, E.; Fratini, F.; Garzonio, C.A.; Malesani, P.; Molli, G. Thermal stress in the Apuan marbles: Relationship between microstructure and petrophysical characteristics. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2009, 46, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantelli, F.; Montigiani, A.; Lotti, L.; Piccini, L.; Bianucci, P.; Malcapi, V. Le acque sotterranee del sistema carsico del M. Corchia: Valorizzazione, salvaguardia e rischi di inquinamento. In Proceedings of the 3 Convegno Nazionale “Protezione e gestione delle acque sotterranee per il III millennio”, Parma, Italy, 13–15 October 1999; pp. 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, G.; D’Agostino, F.; Ercoli, L. Problems of soil and groundwater pollution in the disposable of “marble” slurries in NW Sicily. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.Y.; Sabah, E. Geological and technical characterisation of Iscehisar (Afyon-Turkey) marble deposits and the impact of marble waste on environmental pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.H.H.; Hotzl, H. Karst Hydrogeology and Human Activities: Impact, Consequences, and Implications; IAH International contributions to hydrogeology, 20; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Foose, R.M. Ground-water behavior in the Hershey Valley, Pennsylvania. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1953, 64, 623–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, T. Applying ecology for cave management in China and neighbouring countries. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Silva, M.; Martins, R.P.; Ferreira, R.L. Cave conservation priority index to adopt a rapid protection strategy: A case study in Brazilian Atlantic rain forest. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugai, L.S.M.; Ochoa-Quintero, J.M.; Costa-Pereira, R.; Roque, F.O. Beyond above ground. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 2109–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, S.R.H. How preferential flow delivers pre-event groundwater rapidly to streams. Hydrol. Proc. 2019, 33, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggetti, E.; Lazzaroni, M.; Verole, M.; Piccini, L. Risultati e interpretazione idrodinamica del monitoraggio in continuo delle sorgenti carsiche di Equi Terme (Alpi Apuane). In Proceedings of the 22 Congresso Nazionale di Speleologia, Pertosa, Auletta (Salerno), Italy, 30 May–2 June 2015; pp. 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Korbel, K.; Chariton, A.; Stephenson, S.; Greenfield, P.; Hose, G.C. Wells provide a distorted view of life in the aquifer: Implications for sampling, monitoring and assessment of groundwater ecosystems. Sci. Reports 2017, 7, 40702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangin, A. L’approche systémique du karst, conséquences conceptuelles et méthodologiques. Bulletin de la Société Méridionale de Spéléologie et de Préhistoire 1984, 24, 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Galassi, D.M.P.; Lombardo, P.; Fiasca, B.; Di Cioccio, A.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Petitta, M.; Di Carlo, P. Earthquakes trigger the loss of groundwater biodiversity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, D.M.P.; Fiasca, B.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Montanari, A.; Porfirio, S.; Fattorini, S. Groundwater biodiversity in a chemoautotrophic cave ecosystem: How geochemistry regulates microcrustacean community structure. Aquat. Ecol. 2017, 51, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoch, F.; Fiasca, B.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Porfirio, S.; Petitta, M.; Galassi, D.M.P. Exploring copepod distribution patterns at three nested spatial scales in a spring system: Habitat partitioning and potential for hydrological bioindication. J. Limnol. 2016, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancelj, A. Microdistribution and high diversity of Copepoda (Crustacea) in a small cave in central Slovenia. Hydrobiologia 2002, 477, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancelj, A. Fauna of an unsaturated karstic zone in Central Slovenia: Two new species of Harpacticoida (Crustacea: Copepoda), Elaphoidella millennii n. sp. and E. tarmani n. sp., their ecology and morphological adaptations. Hydrobiologia 2009, 621, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.C.; Christman, M.C.; Sket, B.; Trontelj, P. Sampling adequacy in an extreme environment: Species richness patterns in Slovenian caves. Biodivers. Conserv. 2004, 13, 1209–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, J.; Vervier, P.; Malard, F.; Laurent, R.; Reygrobellet, J.L. Dynamics of communities and ecology of karst ecosystems: Example of three karsts in Eastern and Southern France. In Groundwater Ecology; Gibert, J., Danielopol, D.L., Stanford, J.A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 425–450. [Google Scholar]
- Turquin, M.J. The tactics of dispersal of two species of Niphargus (perennial, Troglobitic amphipoda). In Proceedings of the 8th International Congress of Speleology, Bowling-Green, KY, USA, 18–24 July 1981; Volume 1, pp. 353–355. [Google Scholar]
- Fattorini, S.; Lombardo, P.; Fiasca, B.; Di Cioccio, A.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Galassi, D.M.P. Earthquake-related changes in species spatial niche overlaps in spring communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, F.; Reygrobellet, J.L.; Mathieu, J.; Lafont, M. The use of invertebrate communities to describe groundwater flow and contaminat transport in a fractured rock aquifer. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1994, 131, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, M.C.; Maiolini, B.; Carolli, M.; Silveri, L. Impact of hydropeaking on hyporheic invertebrates in an Alpine stream (Trentino, Italy). Ann. Limnol. 2009, 45, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Simčič, T.; Žibrat, U.; Brancelj, A. The role of river flow dynamics and food availability for the hyporheic microcrustaceans: A reach scale study. Fund. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2012, 180, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descloux, S.; Datry, T.; Usseglio-Polatera, P. Trait-based structure of invertebrates along a gradient of sediment colmation: Benthos versus hyporheos responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbel, K.L.; Stephenson, S.; Hose, G.C. Sediment size influences habitat selection and use by groundwater macrofauna and meiofauna. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpp, C.; Hose, G.C. The impact of water table drawdown and drying on subterranean aquatic fauna in in vitro experiments. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stakman, W.P. Determination of pore size by the air bubbling pressure method. In Proceedings of the Wageningen Symposium “Water in the unsaturated zone”; IASH/AIHS: Unesco, Belgium, 1966; pp. 366–372. Available online: http://hydrologie.org/redbooks/a082/RB082.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Piccini, L.; Zanchetta, G.; Drysdale, R.N.; Hellstrom, J.; Isola, I.; Fallick, A.E.; Leone, G.; Doveri, M.; Mussi, M.; Mantelli, F.; et al. The environmental features of the Monte Corchia cave system (Apuan Alps, central Italy) and their effects on speleothem growth. Int. J. Spel. 2008, 37, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipan, T.; Culver, D.C. Organic carbon in shallow subterranean habitats. Acta Carsologica 2013, 42, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipan, T.; Navodnik, V.; Janzekovic, F.; Novak, T. Studies of the fauna of percolation water of Huda Luknja, a cave in isolated karst in Northeast Slovenie. Acta Carsologica 2008, 37, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleg, I.N.; Moldovan, O.T.; Iepure, S.; Fiers, F.; Brad, T. Diversity patterns of fauna in dripping water of caves from Transylvania. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2011, 47, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.J.; Gunn, J.; Perkins, J. The impact of pollution on aquatic invertebrates within a subterranean ecosystem—Out of sight out of mind. Archiv Fur Hydrobiol. 2002, 155, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).