Endemic Freshwater Fish Range Shifts Related to Global Climate Changes: A Long-Term Study Provides Some Observational Evidence for the Mediterranean Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
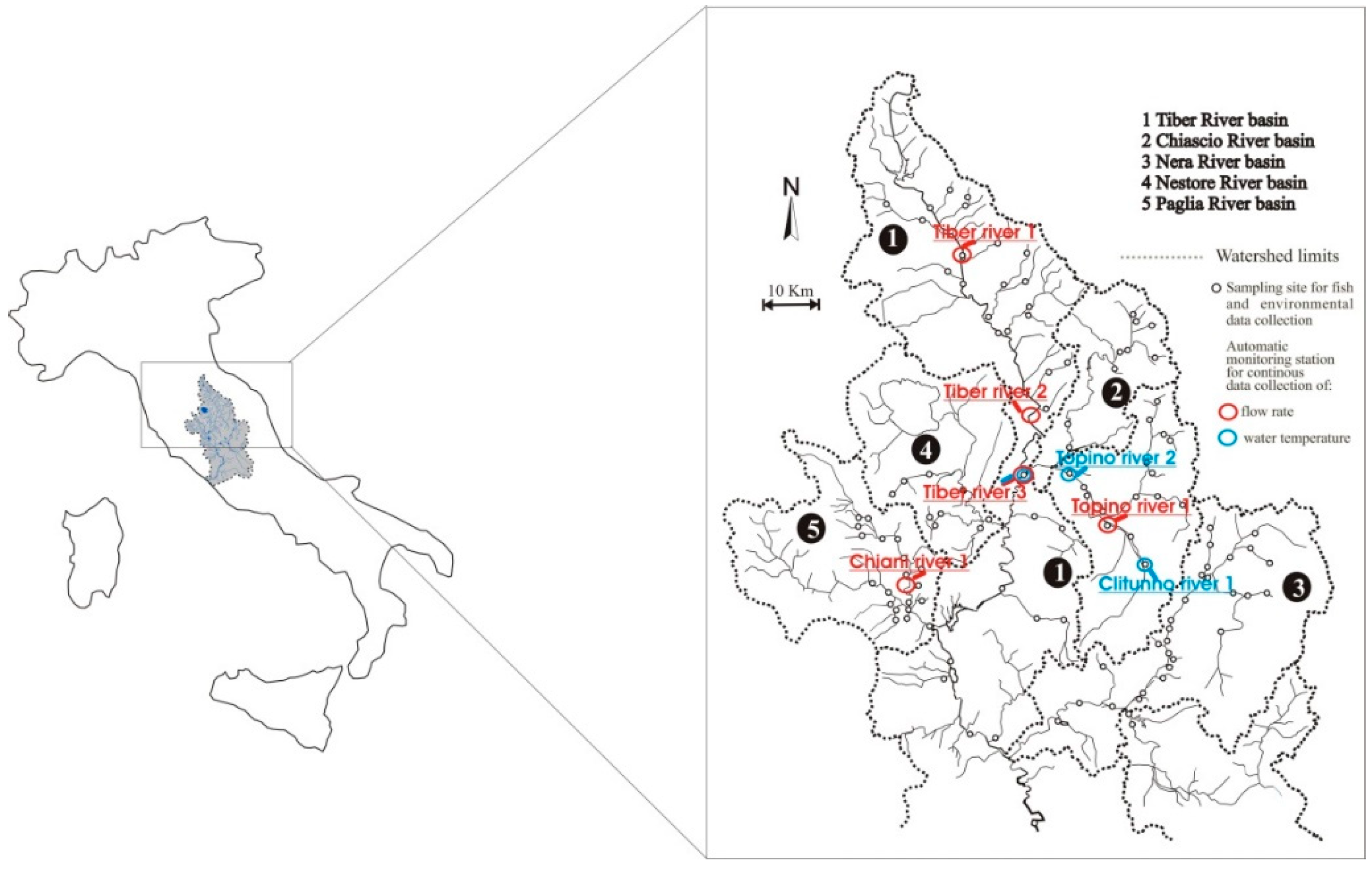
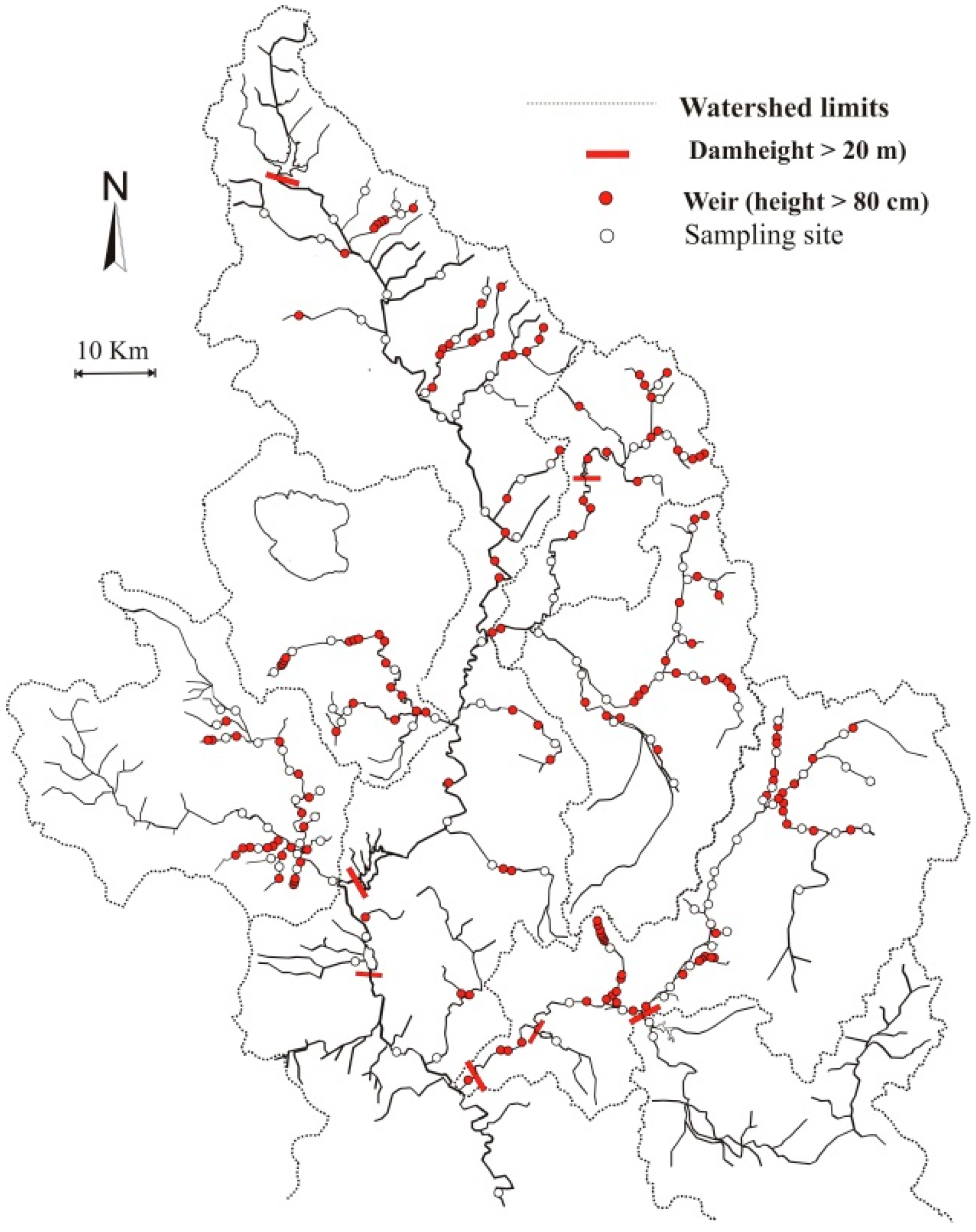
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Body Condition and Size Structure Estimation
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
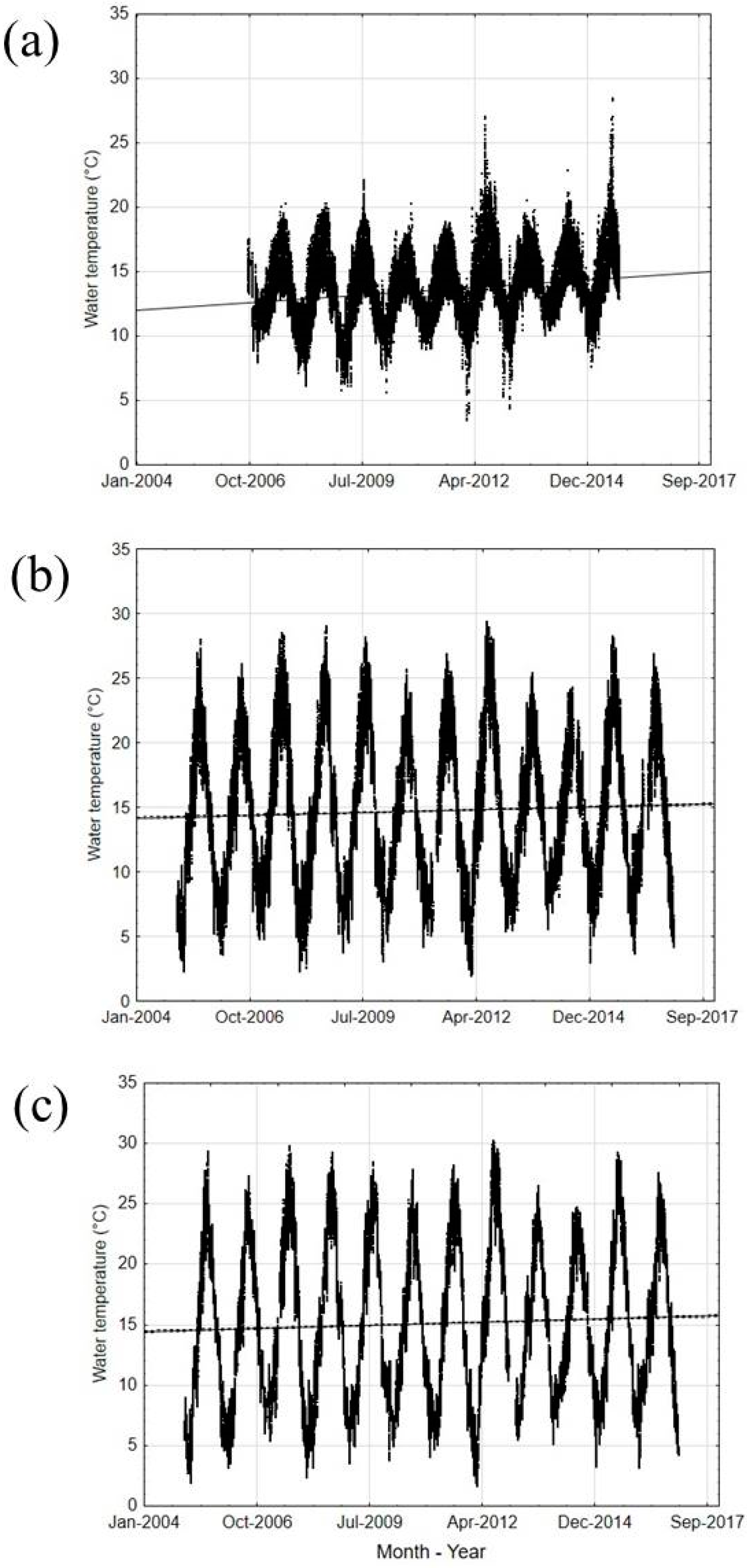
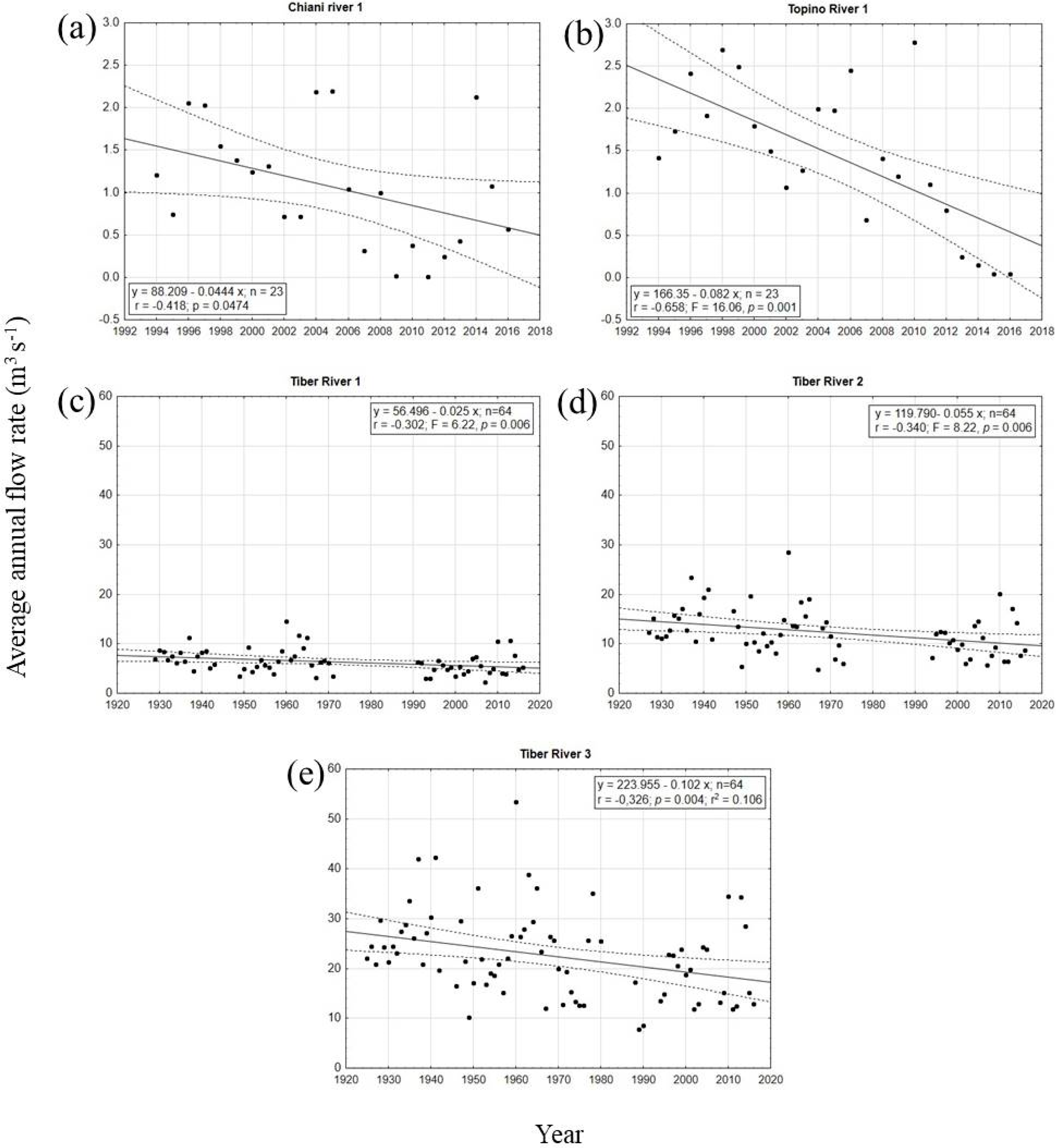
3.1. Climate Changes
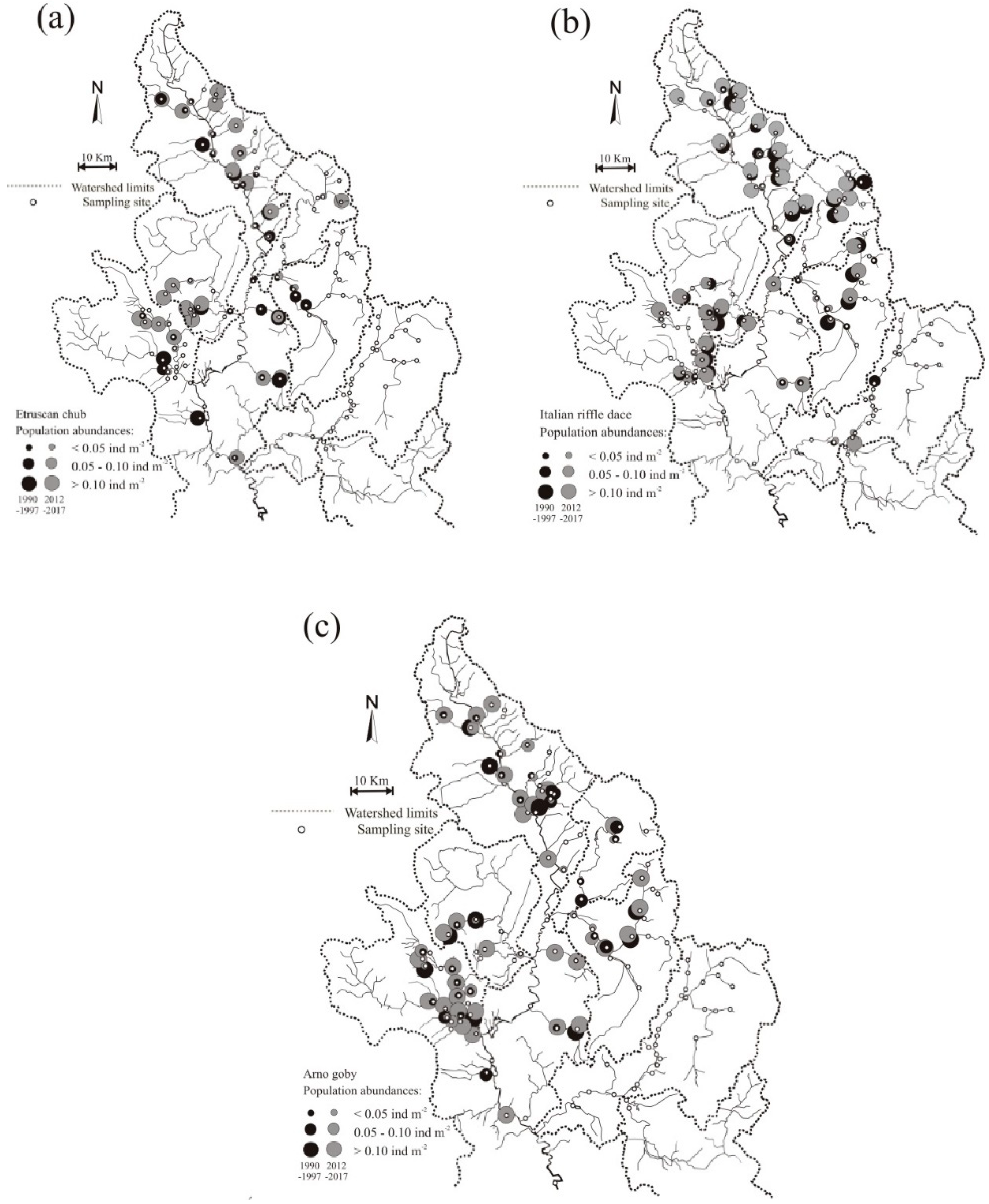
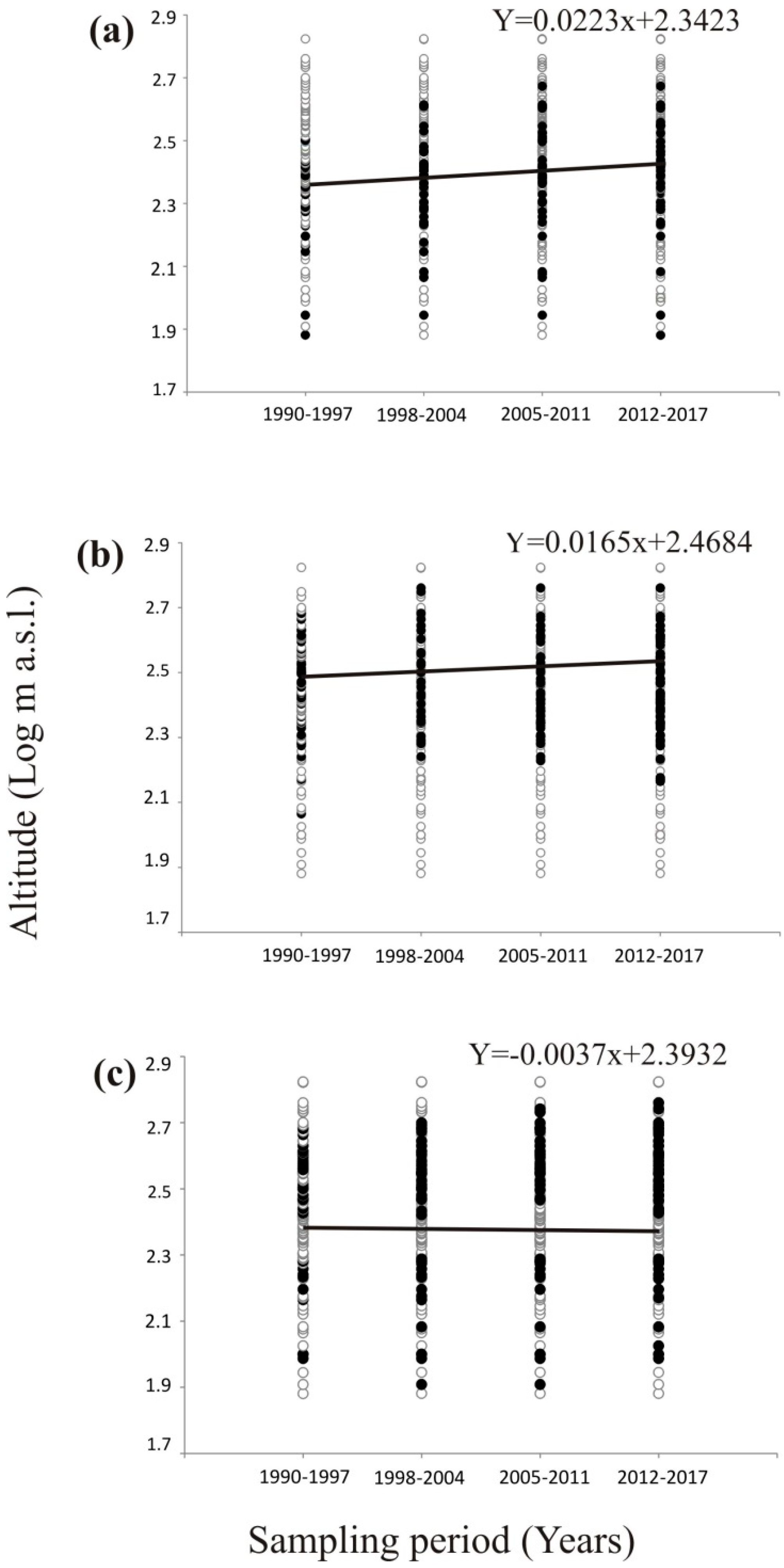
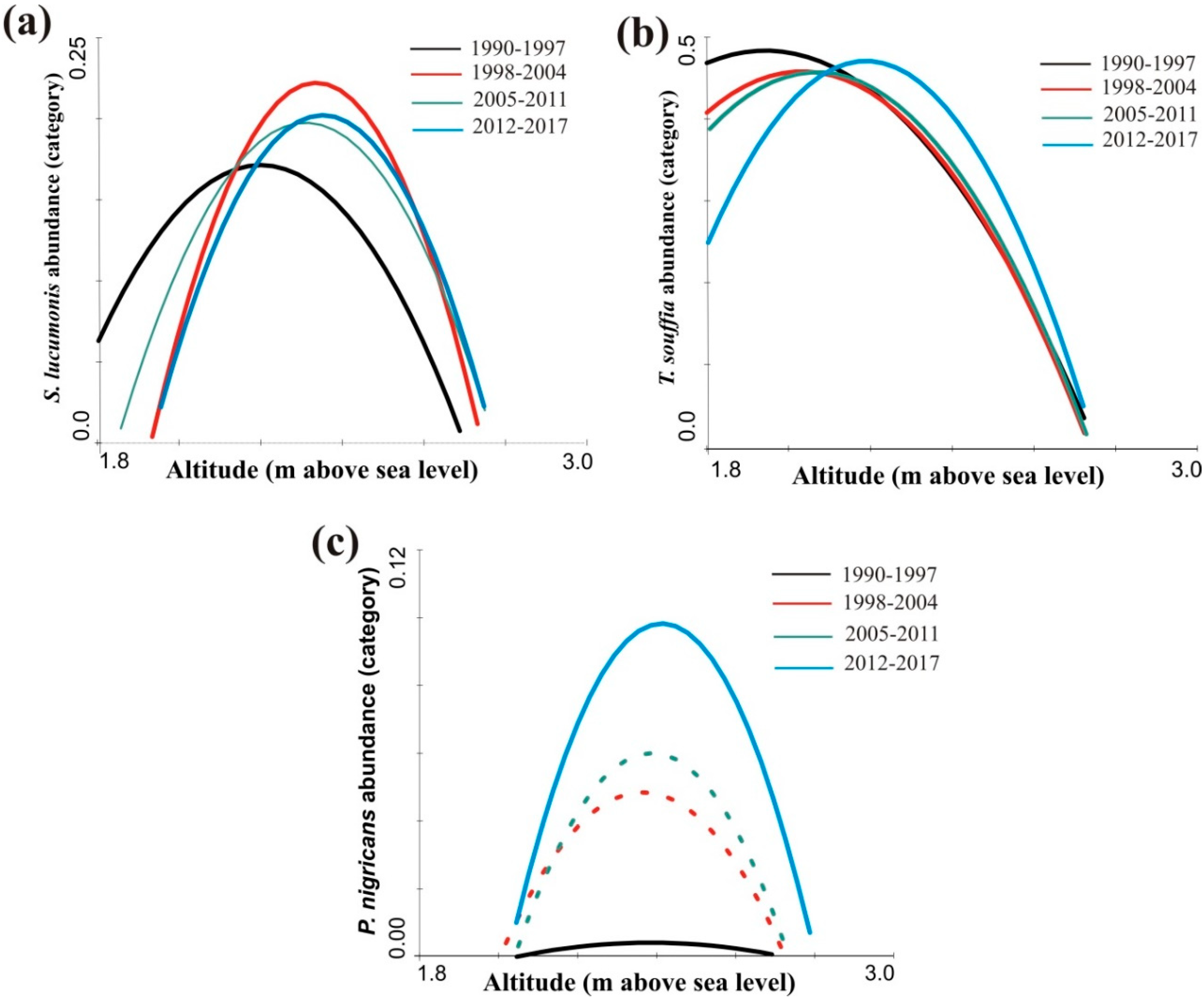
3.2. Distribution Shift
3.3. Population Status
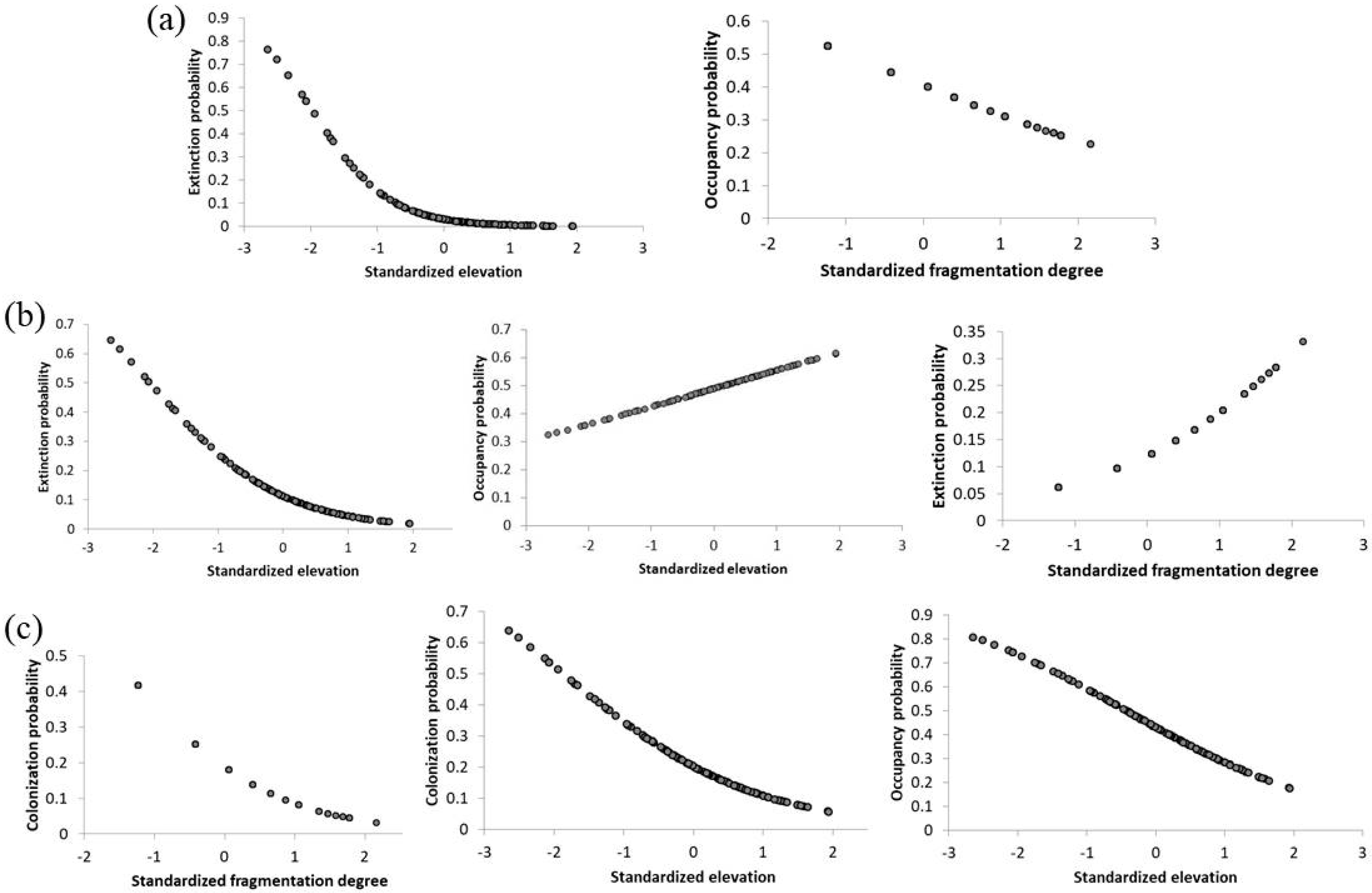
3.4. Occupancy, Colonization, Extirpation and Detection Probabilities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mack, R.N.; Simberloff, D.; Lonsdale, W.; Evans, M.H.; Clout, M.; Bazzaz, F.A. Biotic invasions: Causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttelod, A.; García, N.; Malak, D.A.; Temple, H.J.; Katariya, V. The Mediterranean: A biodiversity hotspot under threat. In Wildlife in a Changing World. An Analysis of the 2008 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Vié, J.C., Hilton-Taylor, C., Stuart, S.N., Eds.; Ingoprint: Barcelona, Spain, 2009; pp. 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, G.S. Freshwater fishes and East Indian zoogeography. Stanf. Ichtyol. Bull. 1951, 4, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Strayer, D.L.; Dudgeon, D. Freshwater biodiversity conservation: Recent progress and future challenges. J. North. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwall, W.; Smith, K.; Allen, D.; Seddon, M.; McGregor, R.G.; Clausnitzer, V.; Kalkman, V. Freshwater biodiversity a hidden resource under threat. In Wildlife in a Changing World. An Analysis of the 2008 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Vié, J.C., Hilton-Taylor, C., Stuart, S.N., Eds.; Ingoprint: Barcelona, Spain, 2009; pp. 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Comte, L.; Buisson, L.; Daufresne, M.; Grenouillet, G.L. Climate-induced changes in the distribution of freshwater fish: Observed and predicted trends. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.; Carrizo, S.; Freyhof, J.; Cid, N.; Lengyel, S.; Scholz, M.; Kasperdius, H.; Darwall, W. Europe’s freshwater biodiversity under climate change: Distribution shifts and conservation needs. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, M.; Barocco, R.; Carosi, A.; Giannetto, D.; Pompei, L. The fish fauna of the Apennine streams related to changes in the regime of wet depositions. Biol. Ambient. 2014, 28, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Xenopoulos, M.A.; Lodge, D.M.; Alcamo, J.; Märker, M.; Schulze, K.; Van Vuuren, D.P. Scenarios of freshwater fish extinctions from climate change and water withdrawal. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.; Perkins, D.M.; Brown, L.E. Climate change and freshwater ecosystems: Impacts cross multiple levels of organization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crozier, L.G.; Hutchings, J.A. Plastic and evolutionary responses to climate change in fish. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Mandrak, N.E.; Minns, C.K. Potential impacts of climate change on the distributions of several common and rare freshwater fishes in Canada. Divers. Distrib. 2005, 11, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foden, W.; Mace, G.; Vié, J.C.; Angulo, A.; Butchart, S.; De Vantier, L.; Dublin, H.; Gutsche, A.; Stuart, S.; Turak, E. Species susceptibility to climate change impacts. In The 2008 Review of the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Vié, J.C., Hilton-Taylor, C., Stuart, S.N., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pratchett, M.S.; Bay, L.K.; Gehrke, P.C.; Koehn, J.D.; Osborne, K.; Pressey, R.L.; Sweatman, H.P.A.; Wachenfeld, D. Contribution of climate change to degradation and loss of critical fish habitats in Australian marine and freshwater environments. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1062–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellard, C.; Bertelsmeier, C.; Leadley, P.; Thuiller, W.; Courchamp, F. Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Godinho, F.N.; Ferreira, M.T. Composition of endemic fish assemblages in relation to exotic species and river regulation in a temperate stream. Biol. Invasions 2000, 2, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletterbauer, F.; Melcher, A.H.; Ferreira, T.; Schmutz, S. Impact of climate change on the structure of fish assemblages in European rivers. Hydrobiologia 2015, 744, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickling, R.; Roy, D.B.; Hill, J.K.; Fox, R.; Thomas, C.D. The distributions of a wide range of taxonomic groups are expanding polewards. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, D.J.; Rieman, B.E. Stream isotherm shifts from climate change and implications for distributions of ectothermic organisms. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.D.; Cameron, A.; Green, R.E.; Bakkenes, M.; Beaumont, L.J.; Collingham, Y.C.; Erasmus, B.F.N.; De Siqueira, M.F.; Grainger, A.; Hannah, L.; et al. Extinction risk from climate change. Nature 2004, 427, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, M.E. Keeping up with a warming world; assessing the rate of adaptation to climate change. Proc. R. Soc. B 2008, 275, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santato, S.; Mysiak, J.; Pérez-Blanco, C.D. The Water Abstraction License Regime in Italy. A case for Reform? Water 2016, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Water Quantity; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/92-9167-205-X/page013.html (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- Lorenzoni, M.; Mearelli, M.; Ghetti, L. Native and exotic fish species in the Tiber river watershed (Umbria—Italy) and their relationship to the longitudinal gradient. Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic. 2006, 382, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carosi, A.; Ghetti, L.; Forconi, A.; Lorenzoni, M. Fish community of the river Tiber basin (Umbria—Italy): Temporal changes and possible threats to native biodiversity. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2015, 416, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, D.; Carosi, A.; Ghetti, L.; Pedicillo, G.; Pompei, L.; Lorenzoni, M. Ecological traits of Squalius lucumonis (Actinopterygii, Cyprinidae) and main differences with those of Squalius squalus in the Tiber River Basin (Italy). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2013, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Kottelat: Cornol, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, Version 2018-1. Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 13 September 2018).
- Tirelli, T.; Pessani, D. Use of decision tree and artificial neural network approaches to model presence/absence of Telestes muticellus in Piedmont (north-western Italy). River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompei, L.; Carosi, A.; Forconi, A.; Giannetto, D.; Lorenzoni, M. Distribution and abundance of Padogobius nigricans (Canestrini, 1867) and P. bonelli (Bonaparte, 1846) in the river Tiber basin (Umbria, central Italy). Ital. J. Freshw. Ichthyol. 2016, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Pompei, L.; Giannetto, D.; Lorenzoni, M. Range expansion of an invasive goby in the River Tiber basin (Central Italy): Effects on the abundance and the shelter occupancy of a congeneric native goby. Aquat. Invasions 2018, 13, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Giovinazzo, G.; Mearelli, M. Presence and distribution of non-native fish species in the Tiber river basin, from the sources to the confluence with the Nera River. Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Mus. Civ. St. Nat. 1997, 137, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, P.A.P. A mathematical theory of animal trapping. Biometrika 1951, 38, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippin, C. An evaluation of the removal method of estimating animal populations. Biometrics 1956, 12, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seber, G.A.F.; Le Cren, E.D. Estimating population parameters from catches larges relative to the population. J. Anim. Ecol. 1967, 36, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyons, J.; Rasmussen, P.; Seelbach, P.; Simon, T.; Wiley, M.; Kanehl, P.; Baker, E.; Scott, N.; Stewart, P.M. Watershed, reach, and riparian influences on stream fish assemblages in the Northern Lakes and Forest Ecoregion, U.S.A. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.A.; Kraft, C.E. Stream fish assemblages in relation to landscape position and local habitat variables. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2005, 134, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agenzia per la Protezione dell’Ambiente e per i servizi Tecnici (APAT); Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR); Istituto di Ricerca sulle Acque (IRSA). Analytical Methods for Water. Manuals and Guidelines. 2003. Available online: http://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/manuali-e-linee-guida/metodi-analitici-per-le-acque (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Waters Works Association (AWWA); Water Pollution Control Federation (WPCF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; Clesceri, L.S., Greenberg, A.E., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Waters Works Association (AWWA); Water pollution Control Federation (WPCF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; Greenberg, A.E., Clesceri, L.S., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti, P.F. I Macroinvertebrati Nell’analisi di Qualità dei Corsi D’acqua; Bertelli: Trento, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Carosi, A.; Ghetti, L.; Lorenzoni, M. Status of Pseudorasbora parva in the Tiber River Basin (Umbria, central Italy) 20 years after its introduction. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2016, 417, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.R.; Brown, M.L.; Springer, T.A. Evaluation of the relative weight (Wr) index, with new applications to walleye. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1990, 10, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, B.G.; Brown, M.L.; Willis, D.W. Relative weight (Wr) status and current use in fisheries assessment and management. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2000, 8, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.L.; Murphy, B.R. Relationship of relative weight (Wr) to proximate composition of juvenile striped bass and hybrid striped bass. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1991, 120, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, V.; Bicchi, A.; Carosi, A.; Pedicillo, G.; Spigonardi, M.P.; Lorenzoni, M. Calculation of standard weight (Ws) for the main fish species in the Tiber basin. Stud. Trent. Sci. Nat. 2010, 87, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Giannetto, D.; Carosi, A.; Franchi, E.; Pedicillo, G.; Pompei, L.; Lorenzoni, M. Proposed standard weight (Ws) equations for Telestes muticellus (Bonaparte, 1837) in the Tiber River basin. Cybium 2011, 35, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Le Cren, E.D. The length relationship and seasonal cycle in gonad weight and condition in the perch (Perca fluviatilis). J. Anim. Ecol. 1951, 20, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish populations. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1975, 191, 1–382. [Google Scholar]
- Gabelhouse, D.W., Jr. A length-categorization system to assess fish stocks. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1984, 4, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedicillo, G.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Ghetti, L. Application of Stock Density Indices as a tool for broad-scale population assessment for four cyprinid species in Central Italy. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2013, 33, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, H.; Tischler, G.; Wanzenböck, J. Ecological integrity assessment of lakes using fish communities-suggestion of new metrics developed in two Austrian prealpine lakes. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2003, 88, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F. Canonical correspondence analysis: A new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 1986, 67, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Šmilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data; University of South Bohemia: Ceské Budejovice, Czech Republic, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.L.; Austen, D.J. Data management and statistical techniques. In Fisheries Techniques; Murphy, B.R., Willis, D.W., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1996; pp. 17–61. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Inference: An Information-Theoretic Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Franchi, E.; Carosi, A.; Ghetti, L.; Pompei, L.; Lorenzoni, M. Changes in the fish community of the upper Tiber River after construction of a hydro-dam. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, J.A.; Link, J.S.; Hare, J.A.; Overholtz, W.J. Changing spatial distribution of fish stocks in relation to climate and population size on the Northeast United States continental shelf. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 393, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lake, P.S. Ecological effects of perturbation by drought in flowing waters. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Erkinaro, J.; Huusko, A.; Luoto, M. Climate change effects on freshwater fishes conservation and management. In Conservation of Freshwater Fishes; Closs, G.P., Krkosek, M., Olden, J.D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 77–106. [Google Scholar]
- Pirisinu, Q.; Natali, M. Gobius nigricans Canestrini (Peisces, Osteichtyes, Gobiidae) endemic species of central Italy. Riv. Idrobiol. 1980, 19, 593–614. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi, G.; Zerunian, S.; Torricelli, P.; Marconato, A. The Fish of Italian Inland Waters; Istituto Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato: Rome, Italy, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Carosi, A.; Mearelli, M.; Giovinazzo, G.; Petesse, M.L.; Lorenzoni, M. Distribution and ecology of the Arno goby (Padogobius nigricans Canestrini) in the river Tiber basin. In Proceedings of the VI AIIAD National Congress, Varese Ligure, Italy, 6–8 June 1996; pp. 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Eby, L.A.; Helmy, O.; Holsinger, L.M.; Young, M.K. Evidence of Climate-Induced Range Contractions in Bull Trout Salvelinus confluentus in a Rocky Mountain Watershed, USA. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenger, S.J.; Isaak, D.J.; Luce, C.H.; Neville, H.M.; Fausch, K.D.; Dunham, J.B.; Dauwalter, D.C.; Young, M.K.; Elsner, M.M.; Rieman, B.E.; et al. Flow regime, temperature, and biotic interactions drive differential declines of trout species under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14175–14180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vila-Gispert, A.; García-Berthou, E.; Moreno-Amich, R. Fish zonation in a Mediterranean stream: Effects of human disturbances. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carosi, A.; Ghetti, L.; Cauzillo, C.; Pompei, L.; Lorenzoni, M. Occurrence and distribution of exotic fishes in the Tiber River basin (Umbria, central Italy). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2017, 33, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzoni, M.; Pace, R.; Pedicillo, G.; Viali, P.; Carosi, A. Growth, catches and reproductive biology of ruffe Gymnocephalus cernuus in Lake Piediluco (Umbria, Italy). Folia Zool. Brno 2009, 58, 420–435. [Google Scholar]
- Carosi, A.; Ghetti, L.; Padula, R.; Lorenzoni, M. Potential effects of global climate change on fisheries in the Trasimeno Lake (Italy), with special reference to the goldfish Carassius auratus invasion and the endemic southern pike Esox cisalpinus decline. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C.; Yohe, G. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 2003, 421, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisan, A.; Thuiller, W. Predicting Species Distribution: Offering more than a simple habitat models. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahel, F.J.; Olden, J.D. Assessing the effects of climate change on aquatic invasive species. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, M. Assessing the effects of environmental stressors on fish populations. Aquat. Toxicol. 1997, 39, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Gandola, E.; Martinoli, M.; Tancioni, L.; Scardi, M. Cascaded neural networks improving fish species prediction accuracy: The role of the biotic information. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalny, G.; Laaha, G.; Melcher, A.; Trimmel, H.; Weihs, P.; Rauch, H.P. The influence of riparian vegetation shading on water temperature during low flow conditions in a medium sized river. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

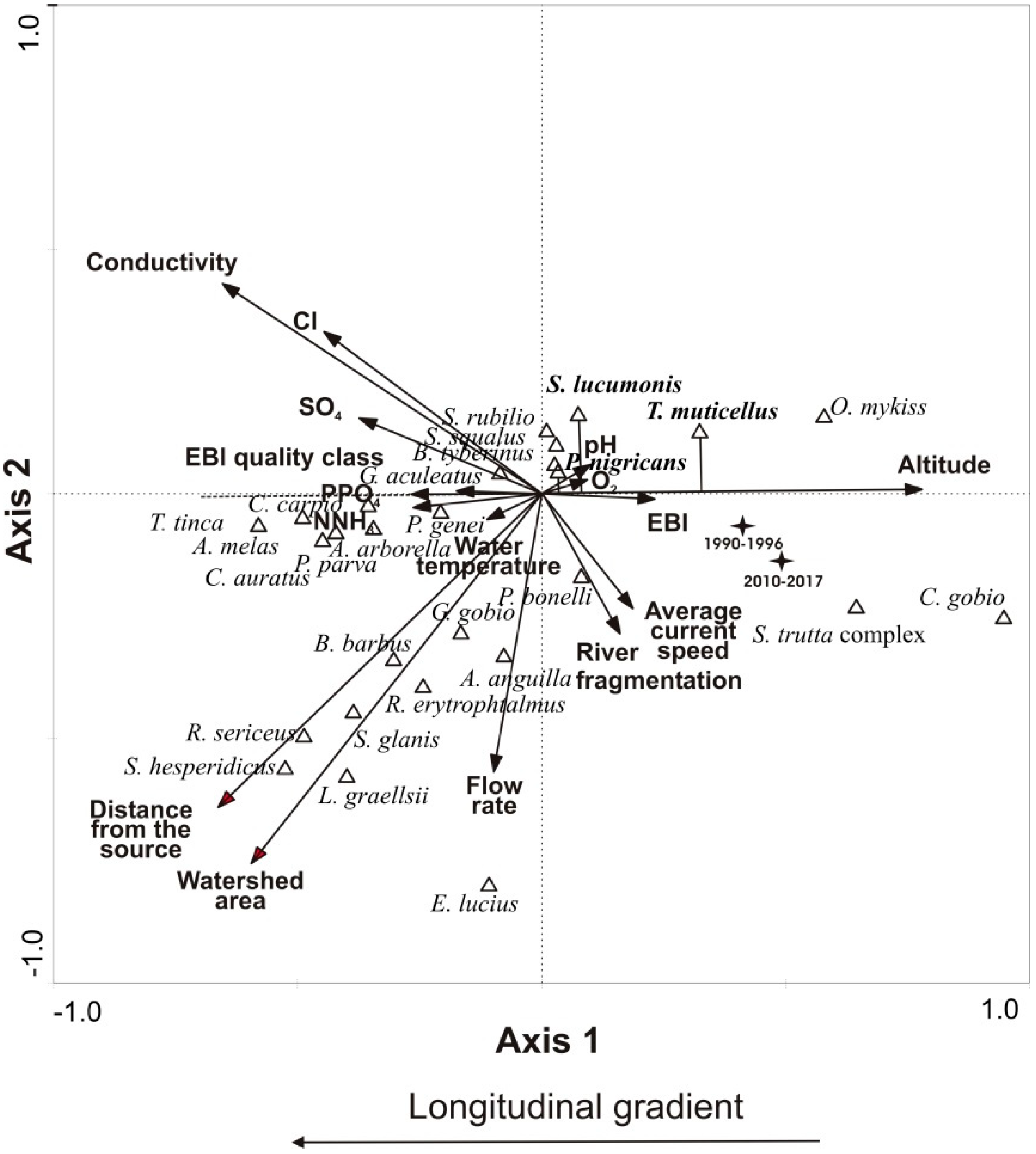

| Environmental Parameters | AX1 | p | AX2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude (m a.s.l.) | 0.802 | 0.000 | −0.225 | 0.000 |
| Average current speed (m s−1) | 0.183 | 0.002 | −0.336 | 0.000 |
| Cl (mg L−1) | −0.719 | 0.000 | 0.477 | 0.000 |
| Conductivity (S cm−1) | −0.738 | 0.000 | 0.399 | 0.000 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg L−1) | 0.193 | 0.001 | −0.004 | 0.943 |
| Distance from the source (km) | −0.652 | 0.000 | −0.544 | 0.000 |
| EBI (units) | 0.537 | 0.000 | −0.111 | 0.061 |
| EBI Quality Class (units) | −0.606 | 0.000 | 0.111 | 0.062 |
| Flow rate (m3 s−1) | −0.135 | 0.023 | −0.619 | 0.000 |
| NNH3 (mg L−1) | −0.317 | 0.000 | 0.021 | 0.728 |
| pH (units) | −0.013 | 0.826 | 0.115 | 0.052 |
| PPO4 (mg L−1) | −0.259 | 0.000 | 0.122 | 0.040 |
| River fragmentation degree (units) | 0.156 | 0.008 | −0.400 | 0.000 |
| SO4 (mg L−1) | −0.593 | 0.000 | 0.127 | 0.033 |
| Water temperature (°C) | −0.249 | 0.000 | −0.097 | 0.104 |
| Watershed area (km−2) | −0.547 | 0.000 | −0.700 | 0.000 |
| Species | Occupancy (ψ) | Colonization (ɣ) | Extirpation (ε) | Detection (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Lucumonis | 0.36 ± 0.06 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.11 ± 0.06 | 0.74 ± 0.04 |
| T. Muticellus | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 0.28 ± 0.08 | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.03 |
| P. Nigricans | 0.40 ± 0.06 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.79 ± 0.03 |
| Species | Detection Probability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Period 1 | Time Period 2 | Time Period 3 | Time Period 4 | |
| 1990–1997 | 1998–2004 | 2005–2010 | 2011–2017 | |
| S. Lucumonis | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 0.82 ± 0.05 | 0.76 ± 0.06 | 0.65 ± 0.07 |
| T. Muticellus | 0.64 ± 0.01 | 0.75 ± 0.05 | 0.69 ± 0.06 | 0.81 ± 0.05 |
| P. Nigricans | 0.61 ± 0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 0.78 ± 0.05 | 0.86 ± 0.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carosi, A.; Padula, R.; Ghetti, L.; Lorenzoni, M. Endemic Freshwater Fish Range Shifts Related to Global Climate Changes: A Long-Term Study Provides Some Observational Evidence for the Mediterranean Area. Water 2019, 11, 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112349
Carosi A, Padula R, Ghetti L, Lorenzoni M. Endemic Freshwater Fish Range Shifts Related to Global Climate Changes: A Long-Term Study Provides Some Observational Evidence for the Mediterranean Area. Water. 2019; 11(11):2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112349
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarosi, Antonella, Rosalba Padula, Lucia Ghetti, and Massimo Lorenzoni. 2019. "Endemic Freshwater Fish Range Shifts Related to Global Climate Changes: A Long-Term Study Provides Some Observational Evidence for the Mediterranean Area" Water 11, no. 11: 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112349
APA StyleCarosi, A., Padula, R., Ghetti, L., & Lorenzoni, M. (2019). Endemic Freshwater Fish Range Shifts Related to Global Climate Changes: A Long-Term Study Provides Some Observational Evidence for the Mediterranean Area. Water, 11(11), 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112349








