Aligning the Freshwater Health Index Indicator System against the Transboundary Water Governance Framework of Southeast Asia’s Sesan, Srepok, and Sekong River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Area and Method
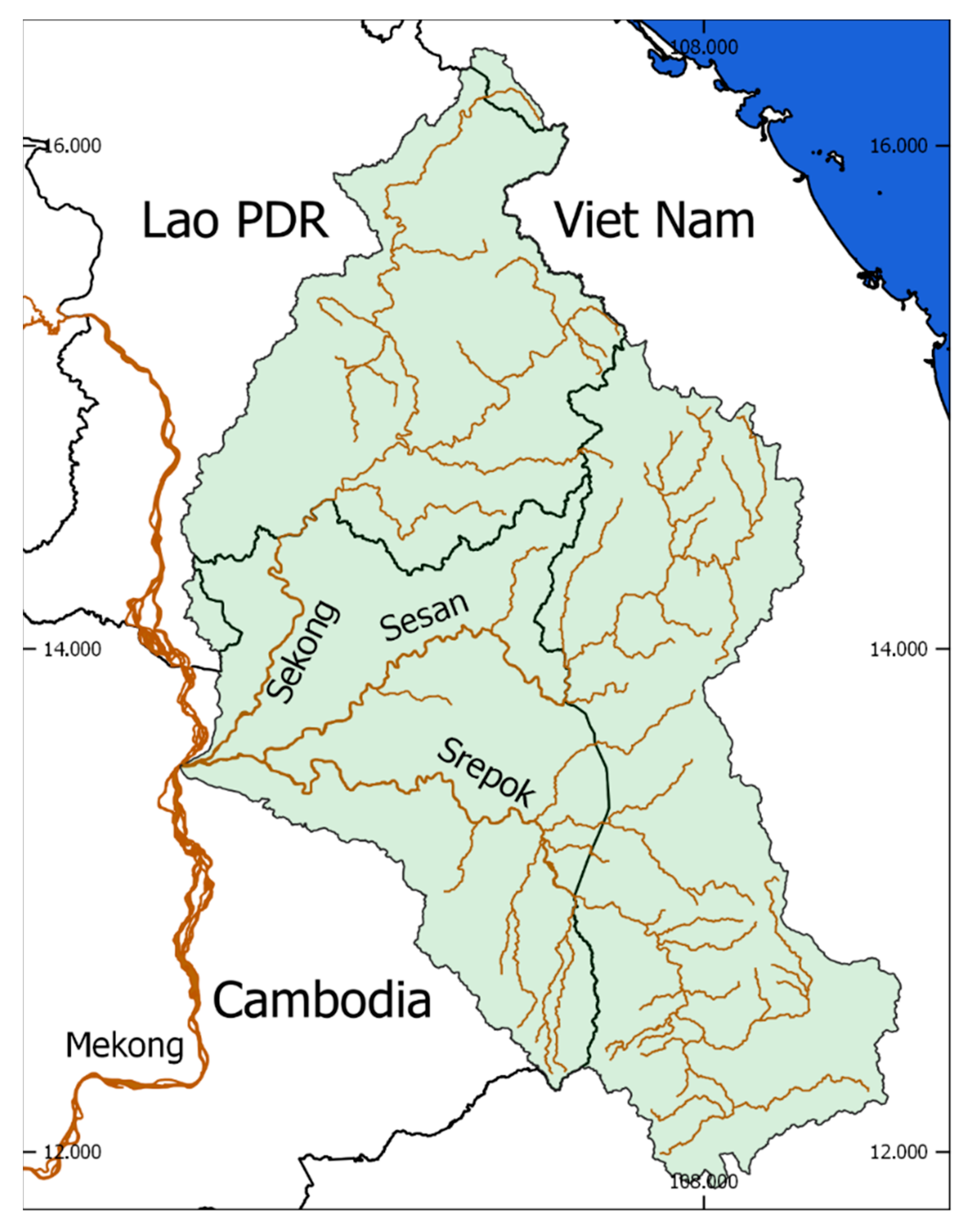
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Method
3. The 3S’ Water Governance Framework
3.1. Global Agendas
3.2. Regional Agencies and Cooperation Mechanisms
3.3. Basin, National and Provincial Governance
4. Alignment of FHI Metrics against Water-Related Legislation in the 3S
4.1. Ecosystem Vitality
4.1.1. Water Quantity
4.1.2. Water Quality
4.1.3. Drainage Basin Condition
4.1.4. Biodiversity
4.2. Ecosystem Services
4.2.1. Provisioning
4.2.2. Regulating and Support
4.2.3. Cultural and Aesthetic Services
4.3. Governance and Stakeholders
4.4. Future Scenarios
4.4.1. Energy Development and Dam Construction
4.4.2. Climate Change
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vollmer, D.; Regan, H.M.; Andelman, S.J. Assessing the sustainability of freshwater systems: A critical review of composite indicators. Ambio 2016, 45, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Foguet, A.; Garriga, R.G. Analyzing water poverty in basins. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gafy, E.D. The water poverty index as an assistant tool for drawing strategies of the Egyptian water sector. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2015, 9, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juwana, I.; Muttil, N.; Perera, B.J. Indicator-based water sustainability assessment—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, S.; Ciuffo, B.; Nijkamp, P. A systemic framework for sustainability assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 119, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, D.W.; Clark, W.C.; Alcock, F.; Dickson, N.M.; Eckley, N.; Guston, D.H.; Jäger, J.; Mitchell, R.B. Knowledge Systems for Sustainable Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8086–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.H.; Dyer, F.; Hairsine, P.; Kennard, M.; Linke, S.; Merrin, L.; Read, A.; Robinson, W.; Ryan, C.; Wilkinson, S.; et al. Australian Water Resources 2005. A Baseline Assessment of Water Resources for the National Water Initiative. Level 2 Assessment River and Wetland Health Theme Assessment of River and Wetland Health: A Framework for Comparative Assessment of the Ecological Condition of Australian Rivers and Wetlands; National Water Commission: Canberra, Austrilia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Birk, S.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Brucet, S.; Courrat, A.; Poikane, S.; Solimini, A.; Van De Bund, W.; Zampoukas, N.; Hering, D. Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: An almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernersson, A.-S.; Carere, M.; Maggi, C.; Tusil, P.; Soldan, P.; James, A.; Sanchez, W.; Dulio, V.; Broeg, K.; Reifferscheid, G.; et al. The European technical report on aquatic effect-based monitoring tools under the water framework directive. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, C.A. Quantifying water vulnerability: A multi-dimensional approach. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2011, 25, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassert, F.; Luck, M.; Landis, M.; Reig, P.; Shiao, T. Aqueduct Global Maps 2.1: Constructing Decision-Relevant Global Water Risk Indicators; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- WBCSD (World Business Council for Sustainable Development). Global Water Tool. Available online: http://www.wbcsd.org/work-program/sector-projects/water/global-water-tool.aspx (accessed on 30 July 2018).
- Souter, N.J.; Shaad, K.; Vollmer, D.; Regan, H.M.; Farrell, T.; Arnaiz, M.; Meynell, P.-J.; Cochrane, T.; Arias, M.E.; Piman, T.; et al. Using the Freshwater Health Index to asses hydropower development scenarios in the Sesan, Srepok and Sekong River basin. 2019. In review. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, P.T.; Rutherfurd, I.D.; Peel, M.C.; Conlan, I.A. The Hydrology of the Mekong River. In The Mekong: Biophysical Environment of an International River Basin; Campbell, I.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Koehnken, L. IKMP Discharge and Sediment Monitoring Programme Review, Recommendations and Data Analysis, Parts 1 & 2. Technical Advice on Water; Lao PDR: Vientiane, Laos, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, E.; Saray, S.; Teoh, S.J.; Tran, T.C. Fish and fisheries in the Sesan, Sekong and Srepok River basins (Mekong watershed). In On Optimizing the Management of Cascades or System of Reservoirs at Catchment Level; ICEM: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ziv, G.; Baran, E.; Nam, S.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, I.; Levin, S.A. Trading-off fish biodiversity, food security, and hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Agency for International Development. Mekong ARCC Climate Change Impact and Adaptation Study for the Lower Mekong Basin: Main Report; ICEM: Bangkok, Thailand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Piman, T.; Lennaerts, T.; Southalack, P. Assessment of hydrological changes in the lower Mekong Basin from Basin-Wide development scenarios. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, T.B.; Loucks, D.P. Managing flow, sediment, and hydropower regimes in the Sre Pok, Se San, and Se Kong Rivers of the Mekong basin. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5141–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, D.; Shaad, K.; Souter, N.J.; Farrell, T.; Dudgeon, D.; Sullivan, C.A.; Fauconnier, I.; Macdonald, G.M.; Mccartney, M.P.; Power, A.G. Integrating the social, hydrological and ecological dimensions of freshwater health: The freshwater health index. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H. Global Freshwater Resources: Soft-Path Solutions for the 21st Century. Science 2003, 302, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Mcintyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Reidy Liermann, C. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Union for Conservation of Nature. A Window of Opportunity for the Mekong Basin: The UN Watercourses Convention as a Basis for Cooperation (A Legal Analysis of How the UN Watercourses Convention Complements the Mekong Agreement); IUCN Asia Regional Office: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rieu-Clarke, A.; Moynihan, R.; Magsig, B.-O. UN Watercourses Convention User’s Guide; IHP-HELP Centre for Water Law, Policy and Science (under the auspices of UNESCO): Dundee, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Tian, F.; Hu, H.; Grey, D.; Gilmont, M. Rivers and reciprocity: Perceptions and policy on international Watercourses. Water Policy 2016, 18, 803–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals Report 2016; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ortigara, A.; Kay, M.; Uhlenbrook, S. A review of the SDG 6 synthesis report 2018 from an education, training, and research perspective. Water 2018, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, P.; Wyatt, A. Negotiating local livelihoods: scales of conflict in the Se San River Basin. Asia Pac. Viewp. 2004, 45, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekong River Commission. Transboundary Water Resources Management Issues in the Sesan and Srepok River Basins of Cambodia and Viet Nam; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Lao PDR, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mekong River Commission. Core Mechanisms of Bilateral Water Cooperation Agreed for Sesan—Srepok and Mekong Delta. Available online: http://www.mrcmekong.org/news-and-events/news/core-mechanisms-of-bilateral-water-cooperation-agreed-for-sesan-srepok-and-mekong-delta/ (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- UN-Water. Status Report on IWRM and Water Efficiency Plans for CSD 16; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.P.L. The Legal Framework of Vietnam’s Water Sector: Update 2013; Braun, J.V., Denich, M., Gerke, S., Hornidge, A.-K., Schetter, C., Eds.; Center for Development Research, University of Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ngor, P.B.; Legendre, P.; Oberdorff, T.; Lek, S. Flow alterations by dams shaped fish assemblage dynamics in the complex Mekong-3S river system. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 88, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, K.; Larsen, H. 2014 Lower Mekong Regional Water Quality Monitoring Report; Mekong River Comission: Vientiane, Laos, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Torell, M.; Salamanca, A.M.; Ratner, B.D. Wetlands Management in Cambodia: Socioeconomic, Ecological, and Policy Perspectives; WorldFish Center: Penang, Malaysia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Souter, N.J.; Shaad, K.; Vollmer, D. Using the Freshwater Health Index to Assess Progress toward Sustainable Development Goal 6, Clean Water and Sanitation, in Cambodia. In Environmental Sustainability in Asia: Progress, Challenges and Opportunities in the Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals, Series 2—Cambodia; Korea Environment Institute: Sejong, Korea, 2019; pp. 80–97. [Google Scholar]
- Dore, J.; Lebel, L. Deliberation and Scale in Mekong Region Water Governance. Environ. Manag. 2010, 46, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| FHI Components, Major Indicators and Sub-Indicators | FHI Score | Number of Relevant Laws, Policies and Plans | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| International | Cambodia | Lao PDR | Viet Nam | ||
| Ecosystem Vitality | 64 | ||||
| Water quantity | 66 | ||||
| Deviation from natural flow regime | 66 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Groundwater storage | - | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Water quality | 81 | ||||
| Suspended solids, total Nitrogen, total Phosphorous, indicators of major concern | 81 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Drainage-basin condition | 85 | ||||
| Extent of channel modification | 96 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Flow connectivity | 78 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Land cover naturalness | 82 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Biodiversity | 38 | ||||
| Changes in number and population size of species of concern | 31 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Changes in number and population size of invasive and nuisance species | 46 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ecosystem Services | 80 | ||||
| Provisioning | 94 | ||||
| Water supply reliability relative to demand | 95 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Biomass for consumption | 94 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Regulation and support | 66 | ||||
| Sediment regulation | 39 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Flood regulation | 81 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Deviation of water quality metrics from benchmarks | 88 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Exposure to water-associated diseases | 67 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Cultural/aesthetic | 83 | ||||
| Conservation/cultural heritage sites | 83 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Recreation | - | ||||
| Governance and Stakeholders | 43 | ||||
| Enabling environment | 42 | ||||
| Water resource management | 50 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Rights to resource use | 45 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Incentives and regulations | 45 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Financial capacity | 42 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Technical capacity | 36 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Stakeholder engagement | 46 | ||||
| Information access and knowledge | 41 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Engagement in decision-making processes | 51 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Vision and adaptive governance | 43 | ||||
| Strategic planning and adaptive governance | 39 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Monitoring and learning mechanisms | 47 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Effectiveness | 43 | ||||
| Enforcement and compliance | 37 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Distribution of benefits from ecosystem services | 42 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Water-related conflict | 45 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Souter, N.J.; Wang, R.Y.; Vollmer, D. Aligning the Freshwater Health Index Indicator System against the Transboundary Water Governance Framework of Southeast Asia’s Sesan, Srepok, and Sekong River Basin. Water 2019, 11, 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112307
Liu X, Souter NJ, Wang RY, Vollmer D. Aligning the Freshwater Health Index Indicator System against the Transboundary Water Governance Framework of Southeast Asia’s Sesan, Srepok, and Sekong River Basin. Water. 2019; 11(11):2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112307
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaofeng, Nicholas J. Souter, Raymond Yu Wang, and Derek Vollmer. 2019. "Aligning the Freshwater Health Index Indicator System against the Transboundary Water Governance Framework of Southeast Asia’s Sesan, Srepok, and Sekong River Basin" Water 11, no. 11: 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112307
APA StyleLiu, X., Souter, N. J., Wang, R. Y., & Vollmer, D. (2019). Aligning the Freshwater Health Index Indicator System against the Transboundary Water Governance Framework of Southeast Asia’s Sesan, Srepok, and Sekong River Basin. Water, 11(11), 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112307





