N-Nitrosodimethylamine Formation from Treatment of Seasonally and Spatially Varying Source Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
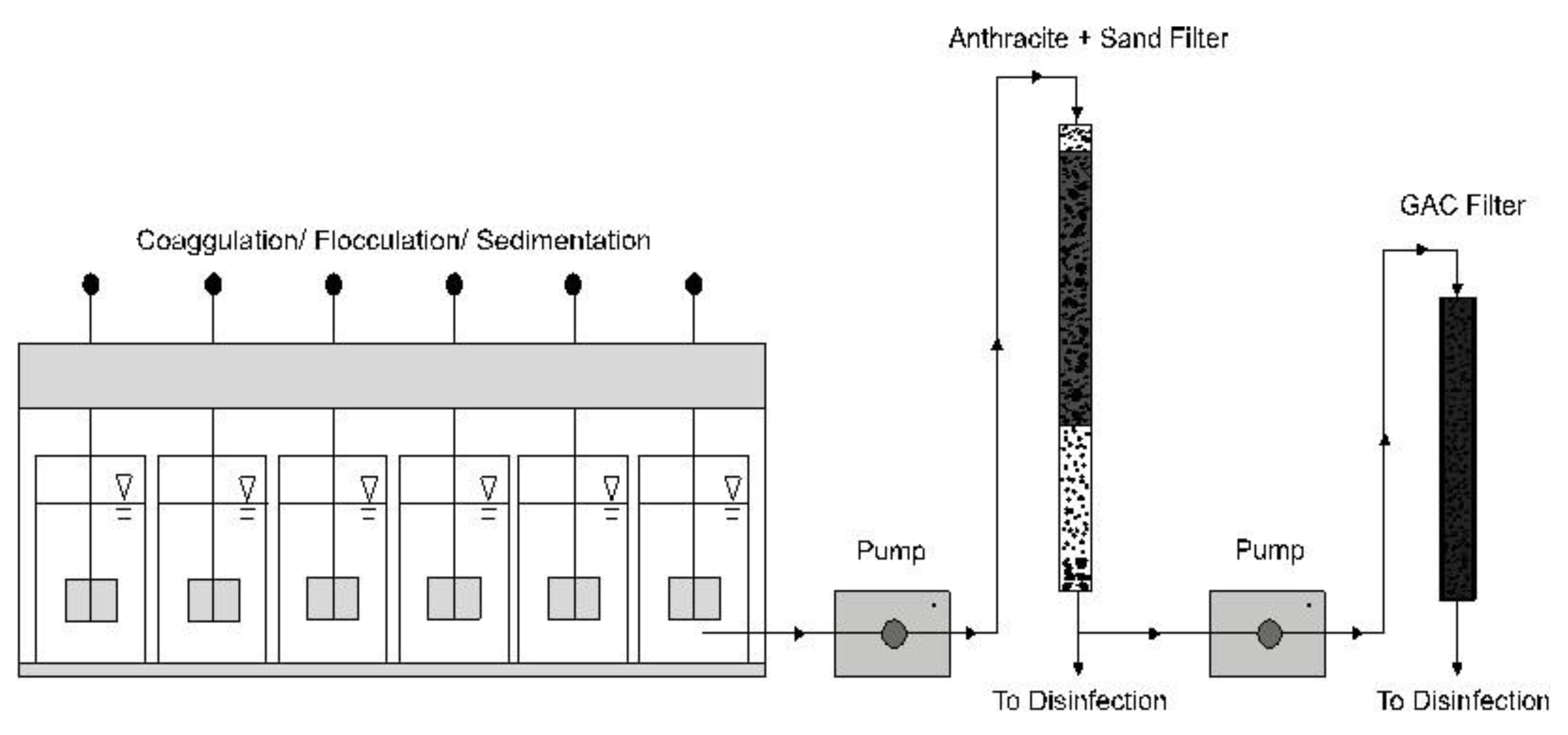
2.1. Field Site Locations
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Monochloramine Disinfection
2.5. NDMA Analysis Preparation
2.6. Analytical Techniques
2.6.1. Precursor Analysis
2.6.2. NDMA Analysis
- (1)
- Separation of NDMA with an octadecylsilyl column as part of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- (2)
- Photolysis of NDMA with UV light irradiation to form peroxynitrite
- (3)
- Chemiluminescence detection of peroxynitrite with luminol solution.
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
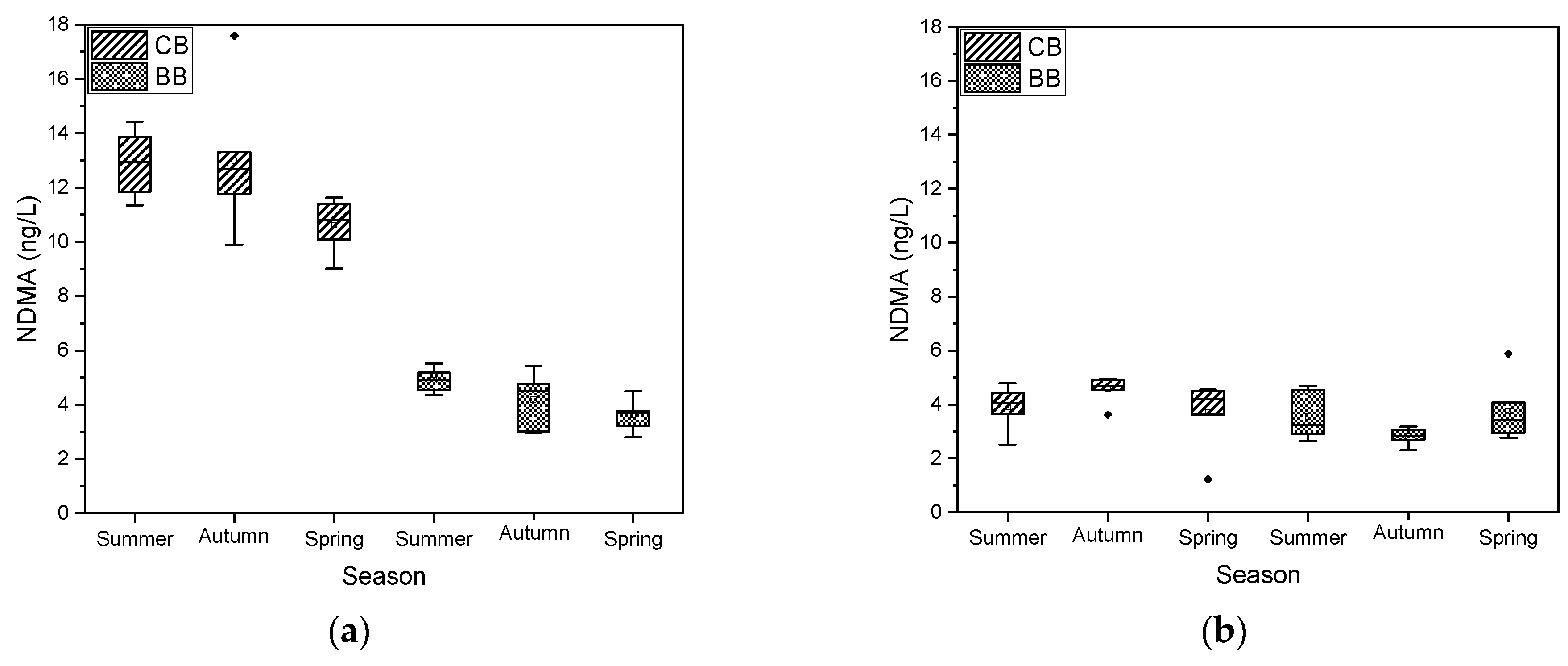
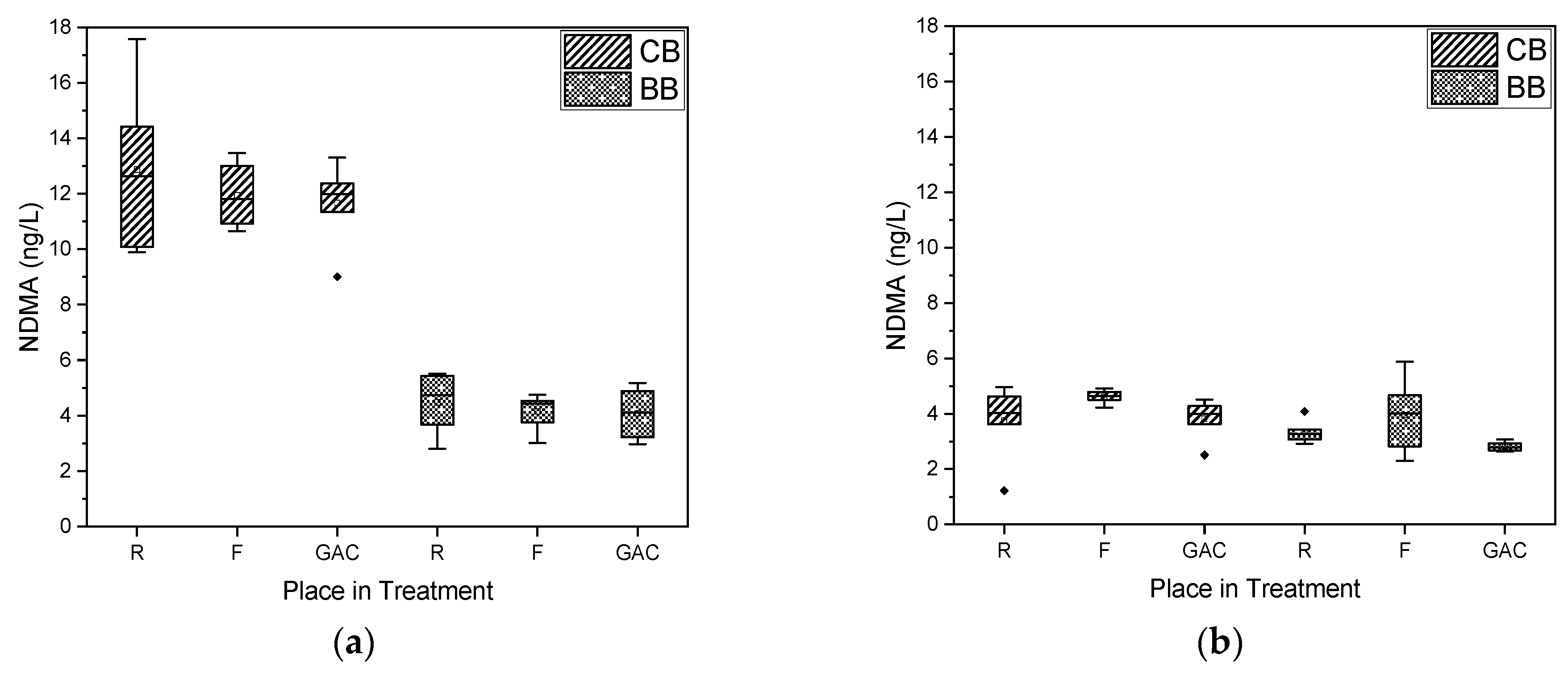
3.1. NDMA Formation
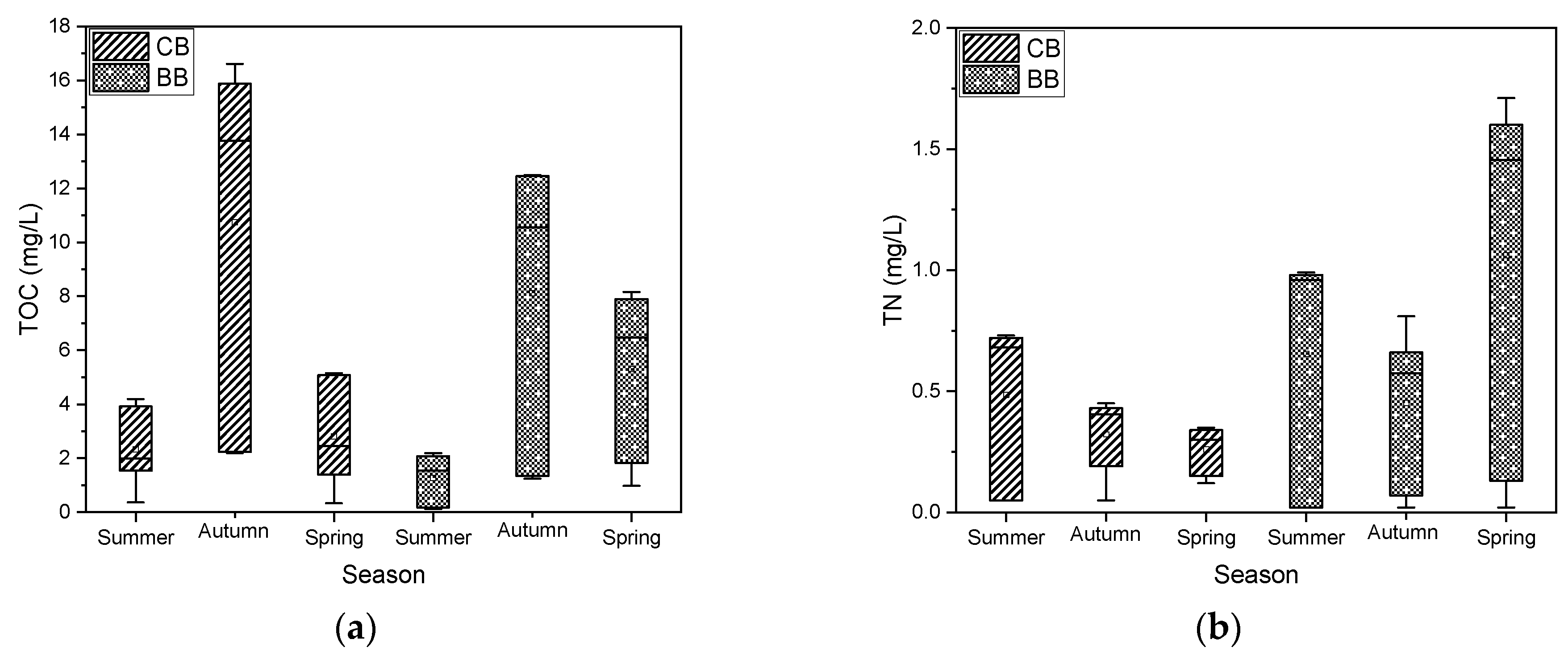
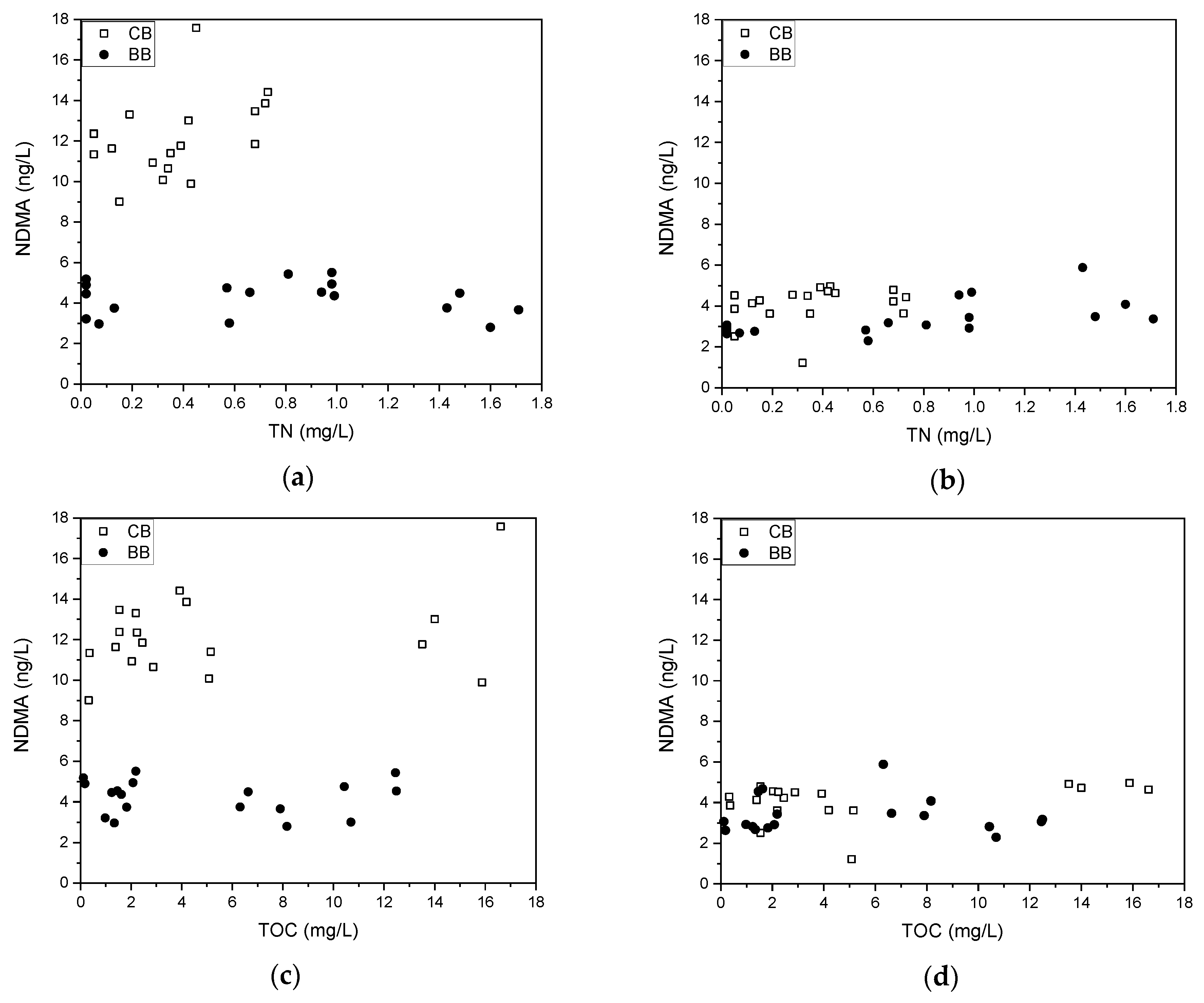
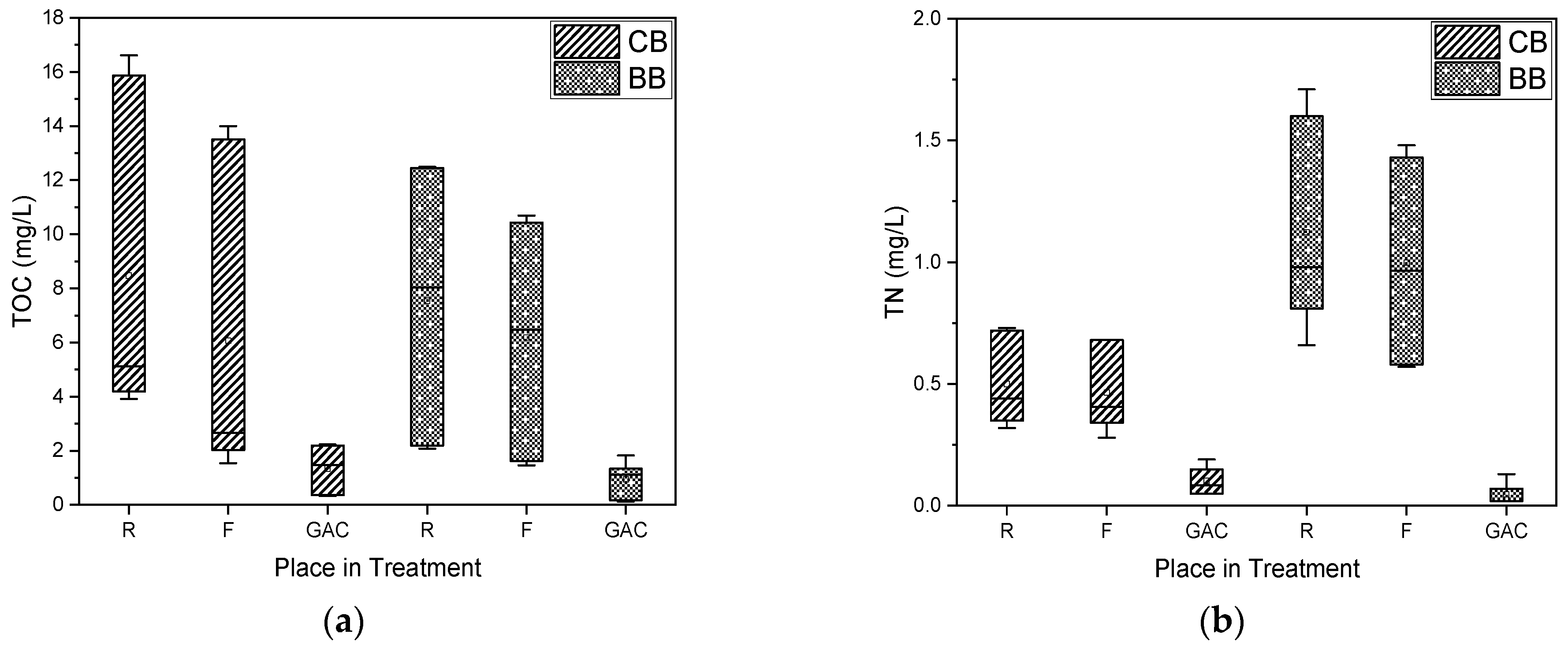
3.2. Seasonal Precursor Presence
3.3. Evaluation of Bench-Top Treatment Efficacy
3.3.1. Precursor Removal
3.3.2. NDMA Formation Potentials
3.3.3. Acceptable NDMA Concentrations
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.; Valentine, R.L. Formation of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) from reaction of monochloramine: A new disinfection by-product. Water Res. 2002, 36, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitch, W.A.; Sedlak, D.L. Formation of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) from dimethylamine during chlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Valentine, R.L. N-nitrosodimethylamine formation by free-chlorine-enhanced nitrosation of dimethlyamine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4871–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, I.M.; Mitch, W.A. Nitrosamine formation pathway revisited: The importance of chloramine speciation and dissolved oxygen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6007–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasner, S.W. The formation and control of emerging disinfection by-products of health concern. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 4077–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, J.; Andrzejewski, P. Nitrosamines and water. J. Hazard. Mater 2011, 189, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, I.A.; Wasserman, A.E. Nitrates, nitrites, and nitrosamines. Science 1972, 177, 15–19. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/1733909 (accessed on 27 March 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.K. Nitrosamines as potential environmental carcinogens in man. Clin. Biochem. 1990, 23, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeppky, R.N. Nitrosamine and N-nitroso compound chemistry and biochemistry. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment; Federal Register: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; pp. 22–58.
- IARC. Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Monographs: Lyon, France, 1987; Volume 7, pp. 1–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 4, pp. 1–541. [Google Scholar]
- A Brief History of NDMA Findings in Drinking Water. Available online: http://www.waterboards.ca.gov/drinking_water/certlic/drinkingwater/NDMAhistory.html (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Drinking Water Standards and Guidelines. Available online: https://www.mass.gov/guides/drinking-water-standards-and-guidelines (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Mitch, W.A.; Sedlak, D.L. Characterization and fate of N-nitrosodimethylamine precursors in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, I.M.; Mitch, W.A. Influence of the order of reagent addition on NDMA formation during chloramination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3811–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, J.M.; Walse, S.S.; Mitch, W.A. Quaternary amines as nitrosamine precursors: A role for consumer products? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Croué, J. Dissolved organic nitrogen as a precursor for chloroform, dichloroacetonitrile, N-nitrosodimethylamine, and trichloronitromethane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5485–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, G. Identification of potential nitrogenous organic precursors for C-, N-DBPs and characterization of their DBPs formation. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3753–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitch, W.A.; Gerecke, A.C.; Sedlak, D.L. A N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) precursor analysis for chlorination of water and wastewater. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Valentine, R.L. Modeling the formation of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) from the reaction of natural organic matter (NOM) with monochloramine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7290–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbes, M.; Beita-Sandí, W.; Kim, D.; Karanfil, T. The role of chloramine species in NDMA formation. Water Res. 2018, 140, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, I.J.; Levallois, P.; Tremblay, H.; Sérodes, J.; Deblois, C.; Charrois, J.; Taguchi, V.; Boyd, J.; Li, X.; Rodriguez, M.J. Spatial and temporal occurrence of N-nitrosamines in seven drinking water supply systems. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7693–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, H.; Kim, D.; Karanfil, T. Seasonal and temporal patterns of NDMA formation potentials in surface waters. Water Res. 2015, 69, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, E.; Liao, X.; Meng, X.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Sheng, D.; Chao, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Identification of nitrosamine precursors from urban drainage during storm events: A case study in southern China. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, M.C.H.; Bowden, W.B.; Shanley, J.B.; Vermilyea, A.; Sleeper, R.; Gold, A.J.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Inamdar, S.P.; Levia, D.F.; Andres, A.S.; et al. High-frequency dissolved organic carbon and nitrate measurements reveal differences in storm hysteresis and loading in relation to land cover and seasonality. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5345–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.A.; Moore, L.A.; Miltner, R.J. Formation and control of non-trihalomethane disinfection by-products. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1989, 81, 54–60. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/41292790 (accessed on 23 June 2019). [CrossRef]
- AWWA. Water chlorination/chloramination practices and principles. AWWA Man. 2006, 2, 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.; Goslan, E.H.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. A critical review of trihalomethane and haloacetic acid formation from natural organic matter surrogates. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2012, 1, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Community Water Treatment. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/drinking/public/water_treatment.html (accessed on 23 June 2019).
- Hanigan, D.; Zhang, J.; Herckes, P.; Krasner, S.W.; Chen, C.; Westerhoff, P. Adsorption of N-nitrosodimethylamine precursors by powdered and granular activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12630–12639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavey-Roback, S.L.; Sugar, C.A.; Krasner, S.W.; Suffet, I.H. NDMA formation during drinking water treatment: A multivariate analysis of factors influencing formation. Water Res. 2016, 95, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazar, S.; Gold, A.J.; Addy, K.; Moatar, F.; Birgand, F.; Schroth, A.; Kellogg, D.Q. Contrasting behavior of nitrate and phosphate flux from high flow events on small agricultural and urban watersheds. Biogeochemistry 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, B.M.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Gold, A.J. Simulating climate change induced thermal stress in coldwater fish habitat using SWAT model. Water 2017, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Information. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/climate-information (accessed on 24 June 2019).
- Silva, M.K.; Wada, T.K. Study of the formation of stable high concentrated monochloramine solutions. Syst. Eng. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kodamatani, H.; Yamazaki, S.; Saito, K.; Amponsaa-Karikari, A.; Kishikawa, N.; Kuroda, N.; Tomiyasu, T.; Komatsu, Y. Highly sensitive method for determination of N-nitrosamines using high-performance liquid chromatography with online UV irradiation and luminol chemiluminescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodamatani, H.; Roback, S.L.; Plumlee, M.H.; Ishida, K.P.; Masunaga, H.; Maruyama, N.; Fujioka, T. An inline ion-exchange system in a chemiluminescence-based analyzer for direct analysis of N-Nitrosamines in treated wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1553, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Ishida, K.P.; Kodamatani, H. A rapid and reliable technique for N-nitrosodimethylamine analysis in reclaimed water by HPLC-photochemical reaction-chemiluminescence. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerecke, A.C.; Sedlak, D.L. Precursors of N-nitrosodimethylamine in natural waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, D.M.; Wu, Q.; Donovan, A.; Shi, H.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J. N-nitrosamine formation by monochloramine, free chlorine, and peracetic acid disinfection with presence of amine precursors in drinking water system. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najm, I.; Trussell, R. NDMA formation in water and wastewater. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2001, 93, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrois, J.W.A.; Boyd, J.M.; Froese, K.L.; Hrudey, S.E. Occurrence of N-nitrosamines in Alberta public drinking-water distribution systems. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 6, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Boyd, J.M.; Woodbeck, M.; Andrews, R.C.; Qin, F.; Hrudey, S.E.; Li, X. Formation of N-nitrosamines from eleven disinfection treatments of seven different surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4857–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, M.J.; Jaén-Gil, A.; Hawkes, J.; Petrovic, M.; Catalán, N. Orbitrap molecular fingerprint of dissolved organic matter in natural waters and its relationship with NDMA formation potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, S.; Finger, N.; Singh, S.; Mitchell, M.; Levia, D.; Bais, H.; Scott, D.; McHale, P. Dissolved organic matter (DOM) concentration and quality in a forested mid-Atlantic watershed, USA. Biogeochemistry 2012, 108, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.; Raymond, P.A. Dissolved organic matter export from a forested watershed during Hurricane Irene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Inamdar, S.; Mitchell, M.; McHale, P. Seasonal pattern of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in watershed sources: Influence of hydrologic flow paths and autumn leaf fall. Biogeochemistry 2014, 118, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Delaney-Newcomb, K.; Kaushal, S.S.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Belt, K.T. Potential effects of leaf litter on water quality in urban watersheds. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, M.G.; Toor, G. Dissolved organic nitrogen in urban streams: Biodegradability and molecular composition studies. Water Res. 2016, 96, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, P.C.; Chang, E.E.; Liang, C.H. NOM characteristics and treatabilities of ozonation processes. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; He, W.; Han, H. Changes in different organic matter fractions during conventional treatment and advanced treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, R.G.; Haines, B.L. Geochemistry of dissolved organic nutrients in water percolating through a forest ecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Kraus, T.E.C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Anastasio, C.; Zasoski, R.J. Contribution of amino compounds to dissolved organic nitrogen in forest soils. Biogeochemistry 2002, 61, 173–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Finished Water Storage Facilities; Office of Ground and Drinking Water: Washington DC, USA, 2002; pp. 1–22.

| Study | Source Water | Result | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDMA precursors in natural water | Natural waters from reservoirs, lakes, and groundwaters (U.S.) | NDMA formation has weak correlation to DOC content (R2 = 0.41), however strength of correlation is source dependent. NDMA precursors are a suite of compounds associated with humic substances and other high molecular weight polymers | [41] |
| NDMA formation in water and wastewater | Untreated natural water (U.S.) | No significant relationship between NDMA formation and natural organic carbon or nitrogen | [43] |
| NDMA survey of drinking water distribution systems | Lakes, rivers, creeks, and groundwater (Canada) | No apparent trends between NDMA concentrations and DOC, NH3-N, NO3−, total Kjedldahl nitrogen (TKN), and organic N | [44] |
| NDMA formation in natural water | Rivers and lakes (U.S. & Canada) | No significant relationships between NDMA formation and total organic carbon (TOC) | [45] |
| NDMA formation in natural water, and precursor fingerprinting | Natural reservoirs (Spain) | After fingerprinting dissolved organic matter (DOM), a positive correlation was found between NDMA formation and aliphatic as well as peptide and lipid-like compounds (r2 = 0.88) | [46] |
| Effect | Mean Square * | P Value |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 1.195 | 0.085 |
| CT | 6.769 | 0.000 |
| Season | 1.700 | 0.035 |
| Treatment * CT | 1.003 | 0.120 |
| Treatment * Season | 0.855 | 0.133 |
| CT * Season | 2.260 | 0.015 |
| Treatment * CT * Season | 0.684 | 0.211 |
| Effect | Mean Square * | P Value |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 1.218 | 0.601 |
| CT | 590.571 | 0.000 |
| Season | 8.471 | 0.047 |
| Treatment * CT | 2.549 | 0.356 |
| Treatment * Season | 1.638 | 0.600 |
| CT * Season | 3.471 | 0.252 |
| Treatment * CT * Season | 0.271 | 0.975 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meadows, M.C.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Fujioka, T.; Kodamatani, H.; Leddy, M.B.; Boving, T.B. N-Nitrosodimethylamine Formation from Treatment of Seasonally and Spatially Varying Source Water. Water 2019, 11, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102019
Meadows MC, Pradhanang SM, Fujioka T, Kodamatani H, Leddy MB, Boving TB. N-Nitrosodimethylamine Formation from Treatment of Seasonally and Spatially Varying Source Water. Water. 2019; 11(10):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102019
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeadows, Maxwell C., Soni M. Pradhanang, Takahiro Fujioka, Hitoshi Kodamatani, Menu B. Leddy, and Thomas B. Boving. 2019. "N-Nitrosodimethylamine Formation from Treatment of Seasonally and Spatially Varying Source Water" Water 11, no. 10: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102019
APA StyleMeadows, M. C., Pradhanang, S. M., Fujioka, T., Kodamatani, H., Leddy, M. B., & Boving, T. B. (2019). N-Nitrosodimethylamine Formation from Treatment of Seasonally and Spatially Varying Source Water. Water, 11(10), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102019







