Ecohydrological Changes and Resilience of a Shallow Lake Ecosystem under Intense Human Pressure and Recent Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
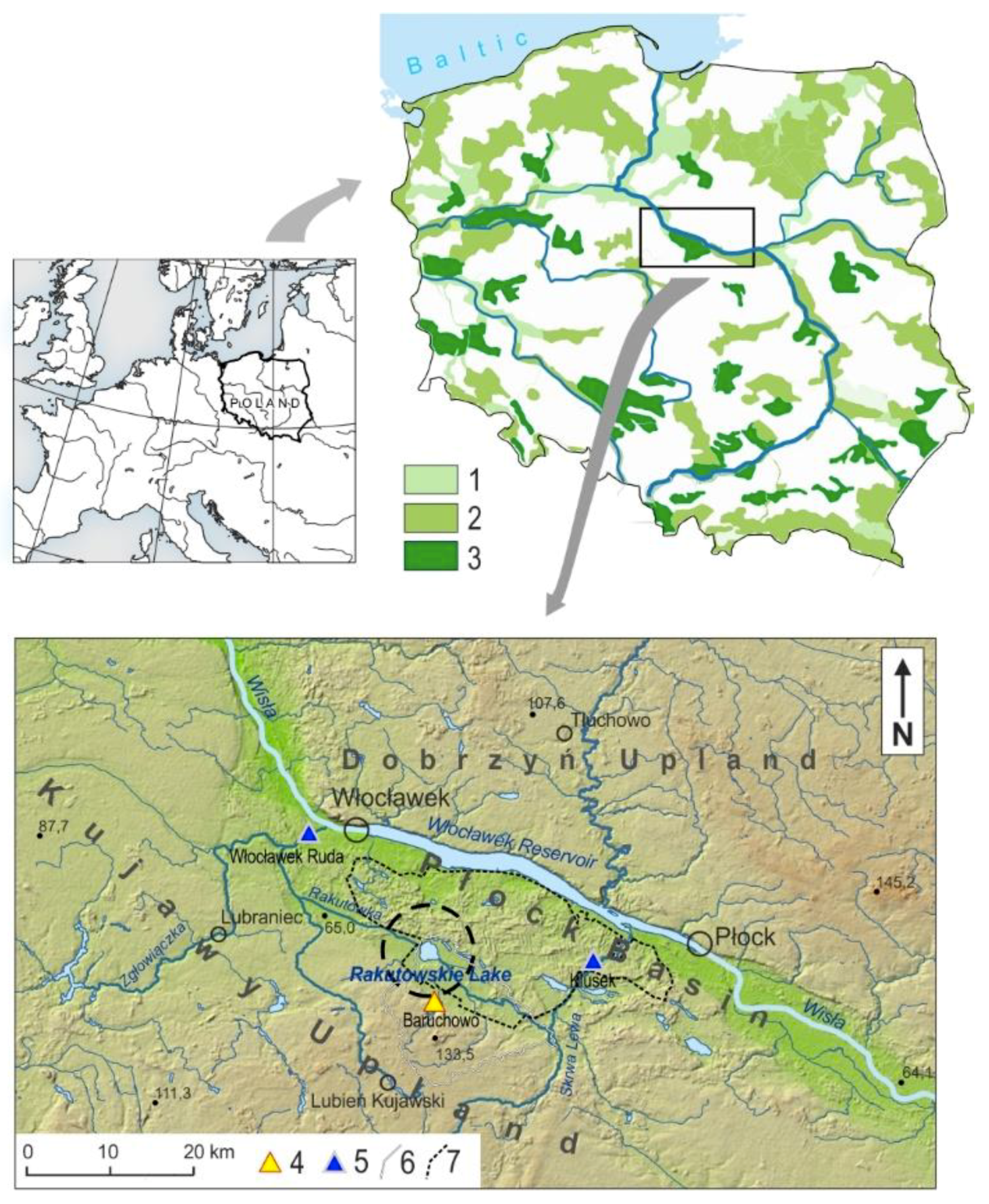
2.1. Study Area
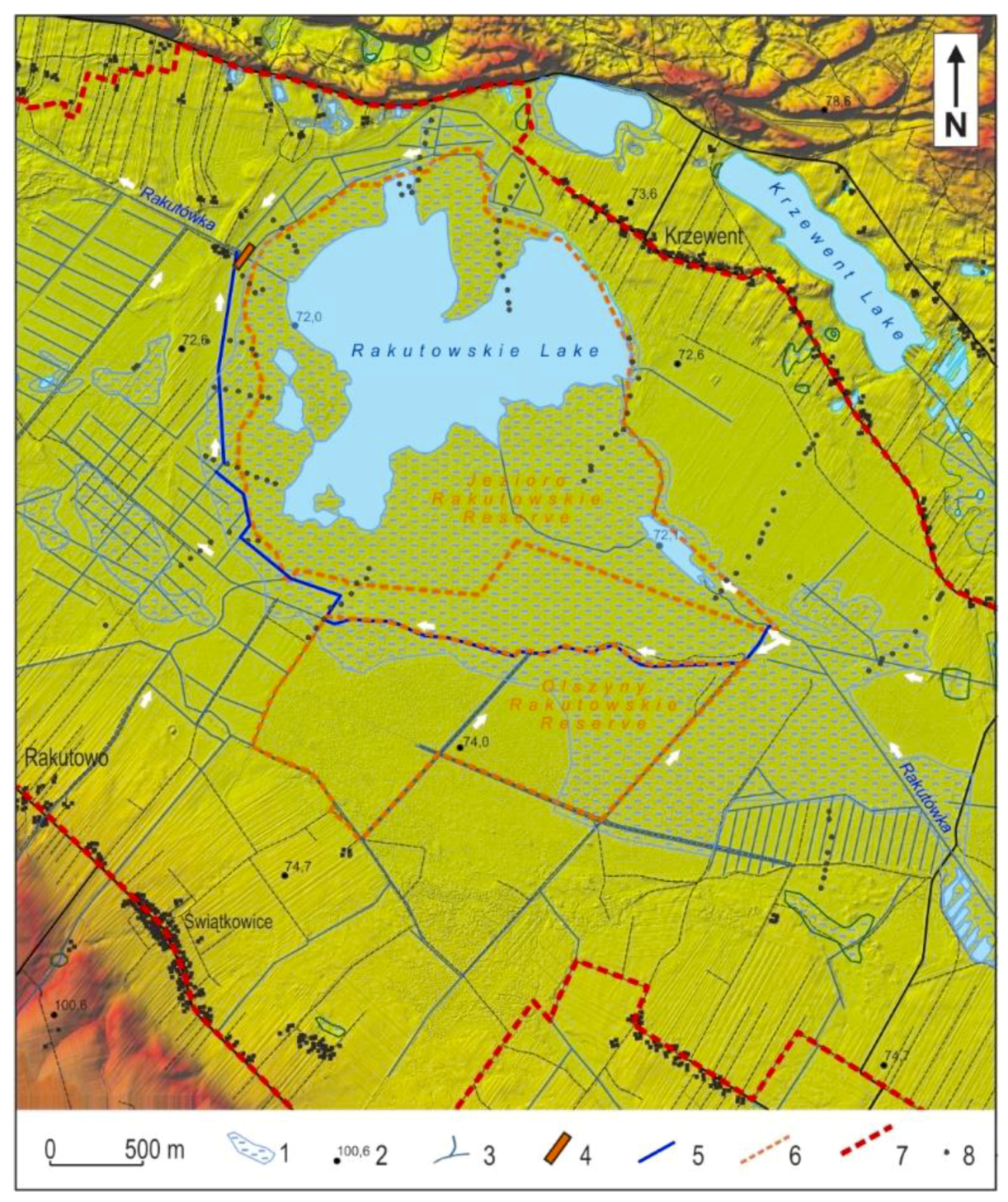
Habitat of Rakutowskie Lake and Rakutówka River
2.2. Methods
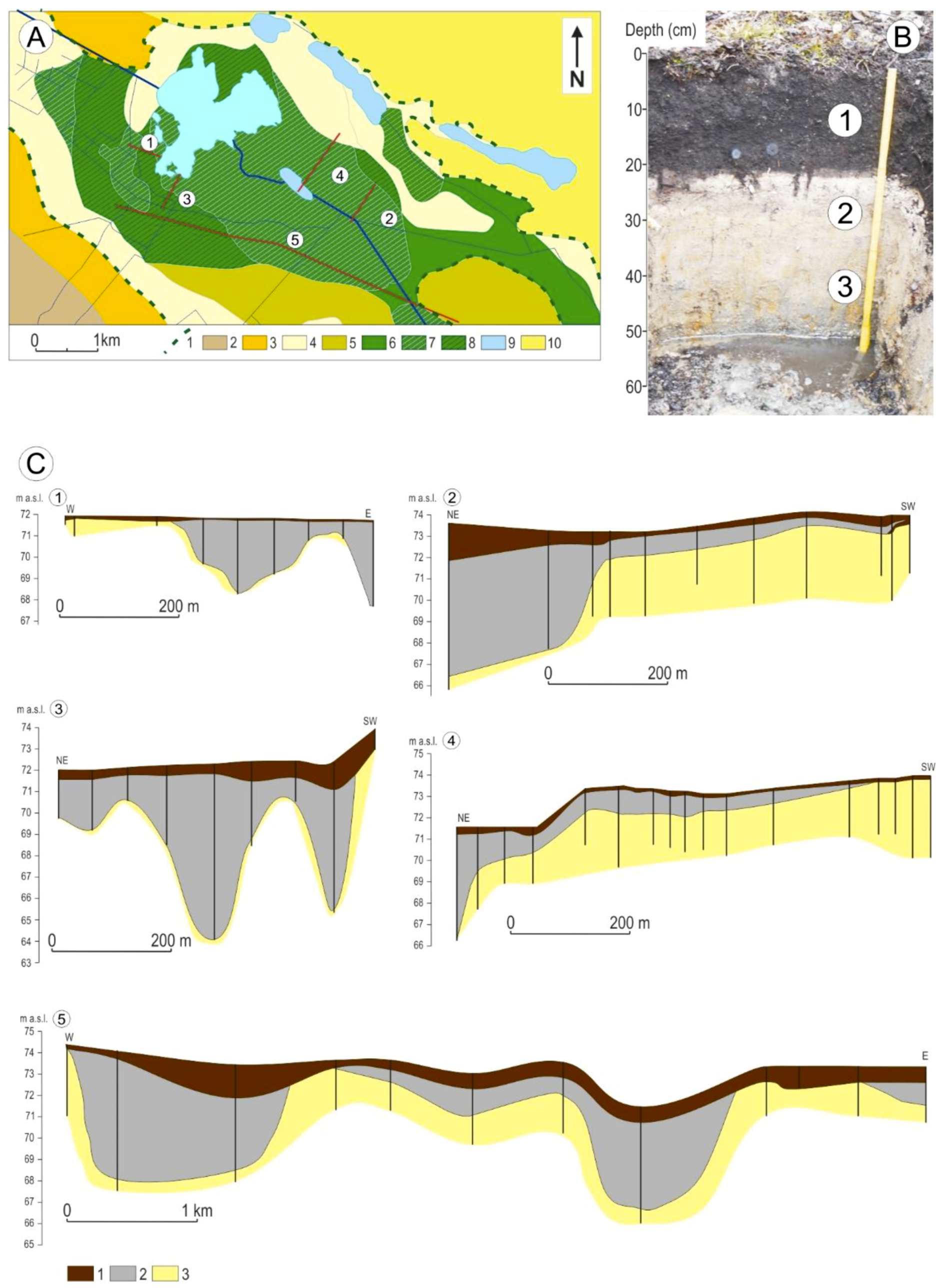
2.2.1. Geology, Morphology of the Area
2.2.2. Cartographic and Photogrammetric Materials, Satellite Images
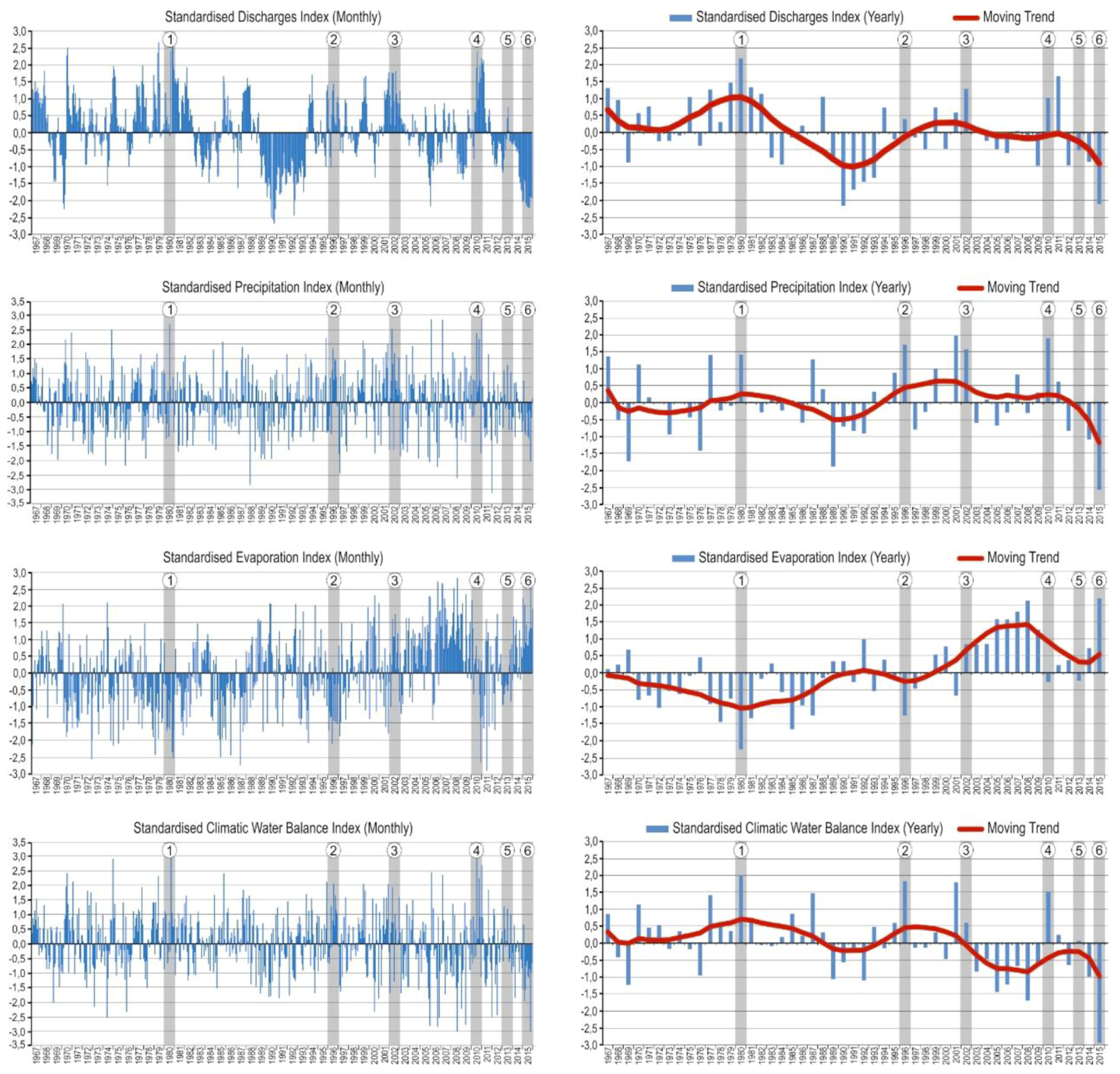
2.2.3. Hydroclimate
3. Results
3.1. Geology, Morphology of the Area
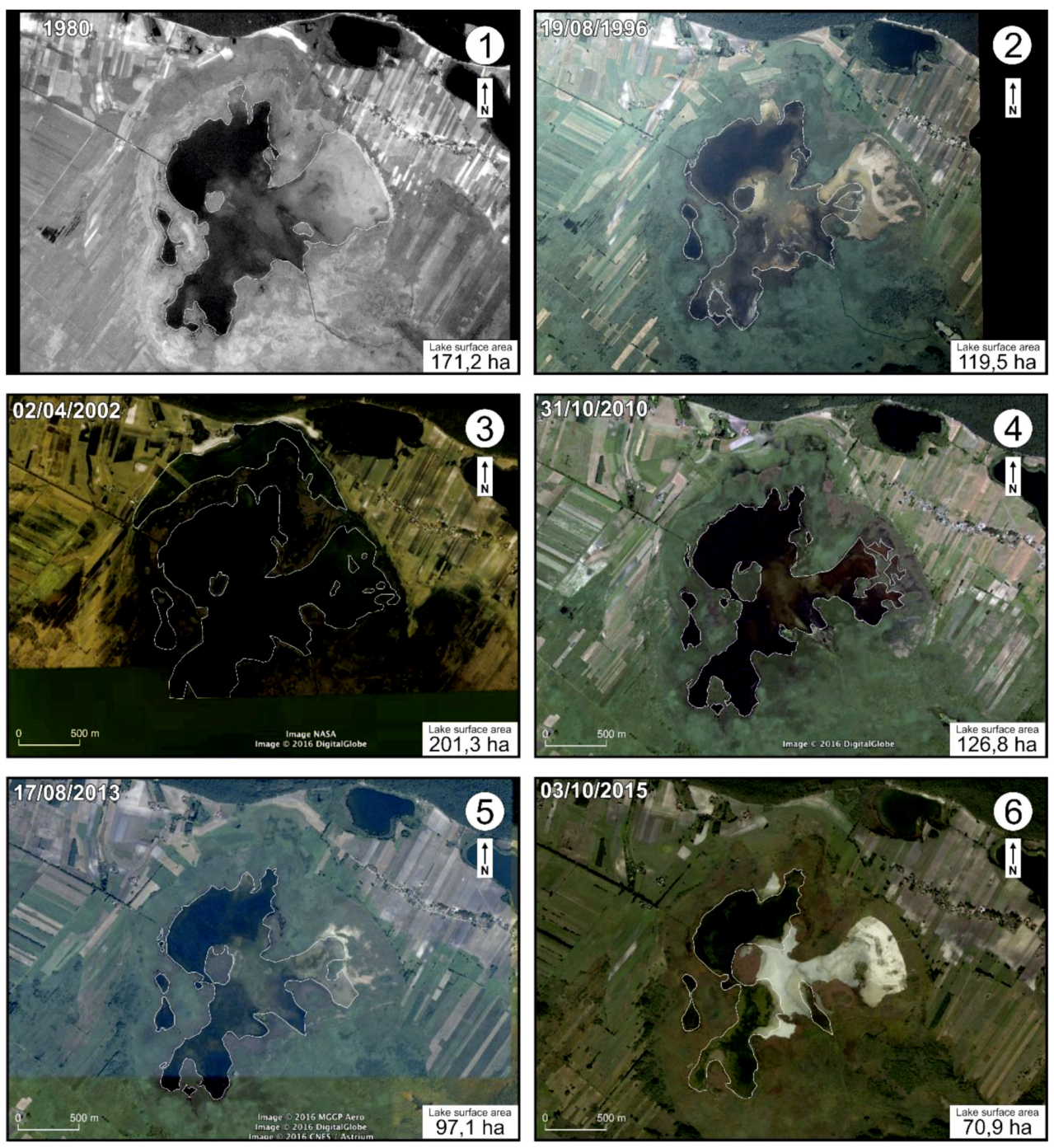
3.2. Cartographic and Photogrammetric Materials, Satellite Images
3.3. Hydroclimate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joosten, H.; Clarke, D. Wise Use of Mires and Peatlands—Background and Principles Including a Framework for Decision-Making; International Peat Society et International Mire Conservation Group: Jyvaskyla, Finland, 2002; p. 304. [Google Scholar]
- Rydin, H.; Jeglum, J.K. The Biology of Peatlands; Oxford university press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Page, S.E.; Baird, A.J. Peatlands and global change: Response and resilience. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turetsky, M.R.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Euskirchen, E.; Talbot, J.; Frolking, S.; McGuire, A.D.; Tuittila, E.S. The resilience and functional role of moss in boreal and arctic ecosystems. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.J.; Shaw, B.; Stenøien, H.K.; Golinski, G.K.; Hassel, K.; Flatberg, K.I.; Carine, M. Pleistocene survival, regional genetic structure and interspecific gene flow among three northern peat-mosses: Sphagnum inexspectatum, S. orientaleands and S. miyabeanum. J. Biogeogr. 2015, 42, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowaciński, Z. Red List of Threatened Animals in Poland; Instytut Ochrony Przyrody PAN: Kraków, Poland, 2002; p. 155. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, M.D.; Rochefort, L. Moss regeneration for fen restoration: Field and greenhouse experiments. Restor. Ecol. 2010, 18, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granath, G.; Moore, P.A.; Lukenbach, M.C.; Waddington, J.M. Mitigating wildfire carbon loss in managed northern peatlands through restoration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. Wetland resources: Status, trends, ecosystem services, and restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmihorski, M.; Pärt, T.; Gustafson, T.; Berg, Å.; Rohr, J. Effects of water level and grassland management on alpha and beta diversity of birds in restored wetlands. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, J. Managing wetland habitats for waterbirds: An international perspective. Wetlands 2010, 30, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodkiewicz, T.; Neubauer, G.; Chylarecki, P.; Sikora, A.; Cenian, Z.; Ostasiewicz, M.; Wylegała, P.; Ławicki, Ł.; Smyk, B.; Betleja, J.; et al. Monitoring populacji ptaków Polski w latach 2012–2013. Biul. Monit. Przyr. 2013, 11, 1–72. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Agency, E.E. Environmental Assessment Report; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2000.
- Eiseltová, M. Restoration of lakes, streams, floodplains, and bogs in Europe. In Principles and Case Studies; Eiseltová, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 3, p. 374. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 688. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z. Zmiany klimatu, ich przyczyny i skutki: Obserwacje i projekcje. Landf. Anal. 2011, 15, 39–49. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bartczak, A. Wieloletnia zmienność odpływu rzecznego z dorzecza Zgłowiączki. Prace Geograficzne IGiPZ PAN 2007, 209, 164. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Gierszewski, P. Charakterystyka środowiska hydrochemicznego wód powierzchniowych zachodniej części kotliny płockiej. Pra. Geogr. IGiPZ PAN 2000, 176, 136. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Fal, B.; Bogdanowicz, E. Zasoby wód powierzchniowych Polski. Wiadom. IMiGW 2002, 25, 3–38. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jokiel, P. Zasoby Wodne Środkowej Polski w XXI Wieku; Wydawnictwo UŁ: Łódź, Poland, 2004. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Błaszkiewicz, M.; Piotrowski, J.A.; Brauer, A.; Gierszewski, P.; Kordowski, J.; Kramkowski, M.; Lamparski, P.; Lorenz, S.; Noryśkiewicz, A.M.; Ott, F.; et al. Climatic and morphological controls on diachronous postglacial lake and river valley evolution in the area of last glaciation, northern Poland. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 109, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rosgen, D.L. Applied River Morphology; Wildland Hydrology: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Słowiński, M.; Błaszkiewicz, M.; Brauer, A.; Noryśkiewicz, B.; Ott, F.; Tyszkowski, S. The role of melting dead ice on landscape transformation in the early holocene in Tuchola pinewoods, north Poland. Quat. Int. 2015, 388, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, S.; Ott, F.; Słowiński, M.; Noryskiewicz, A.M.; Drager, N.; Martin-Puertas, C.; Czymzik, M.; Neugebauer, I.; Dulski, P.; Bourne, A.J.; et al. Tracing the laacher see tephra in the varved sediment record of the Trzechowskie palaeolake in central northern Poland. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 76, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordowski, J. The role of blocks of dead ice in the deposition of late glacial sediments in a large valley: A case study from the Vistula river valley in the Grudziądz basin, north Poland. Geogr. Pol. 2013, 86, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M. Objaśnienia do Szczegółowej Mapy Geologicznej Polski 1:50000, Ark; Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny: Gostynin, Poland, 2011. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Baraniecka, M.D. Objaśnienia do Szczegółowej Mapy Geologicznej Polski 1:50000 Arkusz Lubień Kujawski; PIG: Warszawa, Poland, 1993. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Glazik, R. Wpływ zbiornika wodnego na Wiśle we Włocławku na zmiany stosunków wodnych w dolinie. Dokument. Geog. IGiPZ PAN 1978, 2–3, 119. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bobrek, R.; Hasny, J.; Kajzer-Bonk, J.; Wayda, M.; Springer, S.; Żmuda, A. Międzysezonowa powtarzalność dynamiki jesiennej migracji wróblowych Passeriformes nad Jeziorem Rakutowskim. Orn. Polon. 2016, 57, 39–57. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Przybylak, R.; Vizi, Z.; Araźny, A.; Kejna, M.; Maszewski, R.; Uscka-Kowalkowska, J. Poland’s climate extremes index, 1951–2005. Geogr. Pol. 2007, 80, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Siedlecki, M.; Fortuniak, K.; Pawlak, W. Porównanie wybranych metod określania parowania w Łodzi. Przegl. Geofizyc. 2012, 2, 211–221. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.; Cox, D.R. An analysis of transformations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1964, 26, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.; Cox, D.R. An analysis of transformations revisited, rebutted. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1982, 77, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration times scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Janvier, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; American Meteorological Society: Anaheim, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Guttman, N.B. Accepting the standardized precipitation index: A calculation algorithm. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 35, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bąk, B.; Łabędzki, L. Modification of standardized precipitation index SPI for drought monitoring in Poland, Meteorological services’ tasks in NATO operations, missions and excercises. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Military Meteorology, Poznań, Poland, 29 September–2 October 2003; WAT Warszawa: Poznań, Poland, 2003; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Łabędzki, L.; Bąk, B. Indicator-based monitoring and forecasting water deficit and surplus in agriculture in Poland. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci. Land Reclam. 2015, 47, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łabędzki, L. Problematyka susz w Polsce. Woda Środ. Obsz. Wiej. 2004, 4, 47–66. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Łabędzki, L. Estimation of local drought frequency in central Poland using the standardized precipitation index SPI. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartczak, A.; Glazik, R.; Tyszkowski, S. Czasowe i przestrzenne zróżnicowanie odpływu jednostkowego w zlewni rzeki Zgłowiączki (wschodnia część Kujaw). Sci. Nat. Technol. 2014, 8, 28. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Harasimiuk, A.; Wicik, B.; Grabowski, T. The lake deposits in Płock basin (case studies of Lakes Rakutowskie and Żłoby). Limnol. Rev. 2010, 10, 23–28. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konatowska, M.; Rutkowski, P. Zmiany powierzchni i poziomu lustra wody jeziora Kamińsko (nadleśnictwo doświadczalne Zielonka) na przestrzeni ostatnich 150 lat. Studia i Materiały Centrum Edukacji Przyrodniczo-Leśnej 2008, 10, 205–217. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Miller, P. Ubywa Jezior; Przyroda Polska: Warszawa, Poland, 2003. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Marszelewski, W.; Glazik, R. Uwarunkowania hydrologiczne zlewni Jeziora Rakutowskiego i ich przemiany pod wpływem antropopresji. In Aktywna Ochrona Bioróżnorodności Rezerwatu Jezioro Rakutowskie; Materiały Seminaryjne, Zespół Parków Krajobrazowych Brudzeńskiego i Gostynińsko-Włocławskiego: Kowal, Poland, 2002; Volume 28, pp. 28–37. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bartczak, A.; Birek, E.; Brykała, D.; Gierszewski, P.; Glazik, R. Wpływ wybranych czynników antropogenicznych na zmiany stosunków wodnych w zachodniej części Kotliny Płockiej. In Zintegrowany Monitoring Środowiska Przyrodniczego; Funkcjonowanie Środowiska Przyrodniczego w Okresie Przemian Gospodarczych w Polsce, Biblioteka Monitoringu Środowiska: Szymbark, Poland, 2009; pp. 117–130. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kramkowski, M.; Bartczak, A.; Kaczmarek, H.; Słowiński, M.; Tyszkowski, S. Naturalne i antropogeniczne uwarunkowania przestrzennych zmian obszarów wodno-błotnych na przykładzie Jeziora Rakutowskiego w świetle archiwalnych materiałów kartograficznych i fotogrametrycznych. Problemy Ekologii Krajobrazu 2014, 37, 169–179. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Szurek, J.C. Family farms in polish agricultural policy: 1945–1985. East Eur. Polit. Soc. 1987, 1, 225–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondek, Z. Rozwój przemysłu nawozowego w Polsce. Roczniki Gleboznawcze 1971, 22, 79–87. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kędziora, A. Zagrożenia zasobów wodnych w Wielkopolsce. In Rozwój Rolnictwa w Kierunku Zrównoważonym; Wieland, E., Ed.; Dodatek do miesięcznika Przegląd Komunalny: Poznań, Poland, 1998; pp. 49–63. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Charman, D. Peatlands and Environmental Change; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ptak, M. Zmiany powierzchni jezior na tle zmian lesistości w środkowym i dolnym dorzeczu Warty od końca XIX wieku. In Woda w Badaniach Geograficznych; Ciupa, T., Suligowski, R., Eds.; Gospodarki Przestrzennej UJ: Kraków, Poland, 2010. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Herbst, M.; Kappen, L. The ratio of transpiration versus evaporation in a reed belt as influenced by weather conditions. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 63, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.; Betancourt, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stouffer, R.J. Climate change. Stationarity is dead: Whither water management? Science 2008, 319, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwed, M.; Graczyk, D.; Pińskwar, I.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Projections of climate extremes in Poland. Geogr. Pol. 2007, 80, 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- Gutry-Korycka, M.; Sadurski, A.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Pociask-Karteczka, J.; Skrzypczyk, L. Zasoby wodne a ich wykorzystanie. Nauka 2014, 1, 77–98. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, S.; Xu, Y. Dynamic of Dalinor lakes in the inner Mongolian plateau and its driving factors during 1976–2015. Water 2017, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędziora, A.; Kępińska-Kasprzak, M.; Kowalczak, P.; Kundzewicz, Z.; Miler, A.; Pierzgalski, E.; Tokarczyk, T. Zagrożenia związane z niedoborem wody. Gospodarka Wodna 2014, 1, 373–376. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bartczak, A.; Glazik, R.; Tyszkowski, S. Identyfikacja i ocena intensywności okresów suchych we wschodniej części Kujaw. Nau. Przyr. Technol. 2014, 8, 46. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Szwed, M.; Karg, G.; Pińskwar, I.; Radziejewski, M.; Graczyk, D.; Kędziora, A.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Climate change and its effect on agriculture, water resources and human health sectors in Poland. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


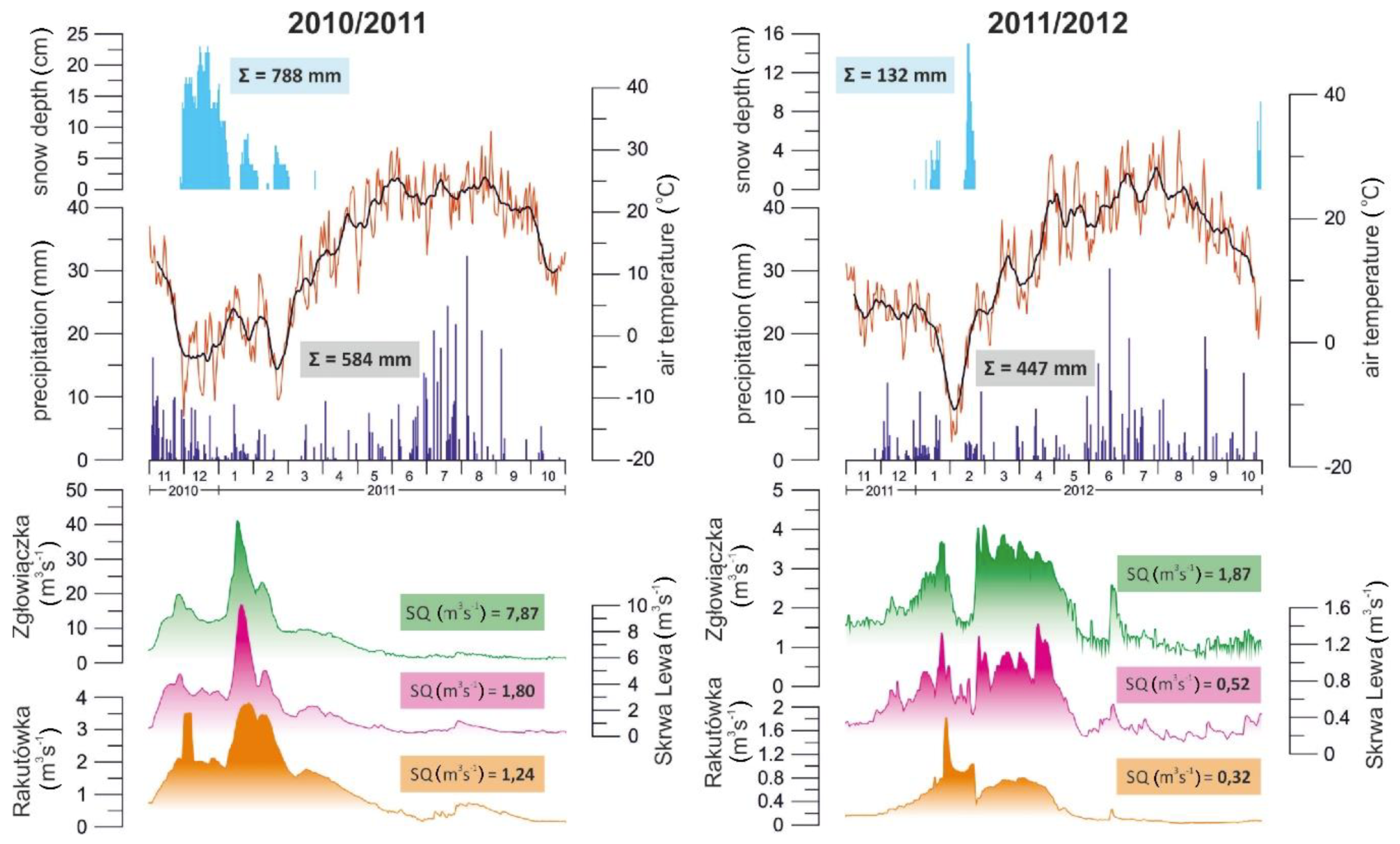
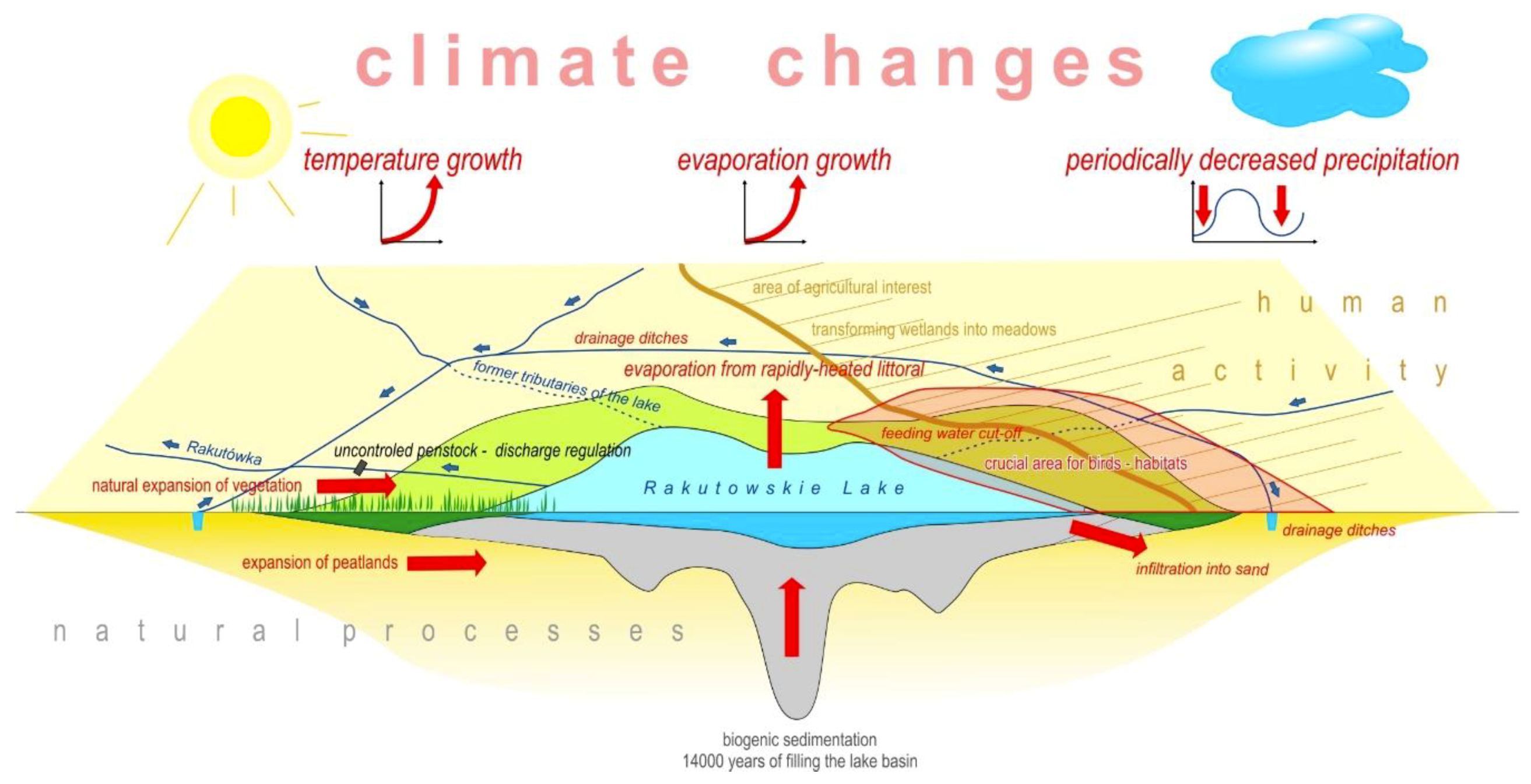
| No. | Name | Year | Scale | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Topograficzna Karta Królestwa Polskiego Topographic Map of the Kingdom of Poland | 1843 | 1:126,000 | based on a topographic photo, scale 1:42,000 |
| B | Reymann’s Specialkarte | Approx. 1845 | 1:200,000 | |
| C | Königlich-Preussische Landesaufnahme | 1902 | 1:300,000 | |
| D | Karte des Westlichen Russlands | 1911 | 1:100,000 | based on Russian maps, scale 1:42,000 and 1:8000 |
| E | Mapa Operacyjna Polski Operational Map of Poland | 1922 | 1:300,000 | executed by the Military Geographical Institute (MGI), based on a German map Übersichtskarte von Mitteleuropa (Outline Map of Central Europe) from 1916 |
| F | Map WIG MGI map | 1930 | 1:100,000 | |
| G | Topographische Karte (Meßtischblatt) | 1941, 1944 | 1:25,000 | |
| H | Karte des Deutschen Reiches-Großblatt/Einheitsblatt | 1945 | 1:100,000 | based on Meßtischblatt from 1930 and aerial maps from June 1941 |
| I | Topographic map | 1983 | 1:10,000 |
| Type | Year | Scale |
|---|---|---|
| panchromatic aerial photos | 1961-09-24 | 1:18,000 |
| panchromatic aerial photos | 1980 | 1:30,000 |
| RGB (Red, Green, Blue) photo | 1996-08-19 | 1:26,000 |
| RGB orthophotomap | 2009-09-09 | 1:5000 |
| SDI, SPI, SCWBI | Classification |
|---|---|
| 2.00 and more | Extremely wet |
| 1.50 ÷ 2.00 | Severely wet |
| 1.00 ÷ 1.50 | Moderately wet |
| 0.50 ÷ 1.00 | Slightly wet |
| −0.50 ÷ 0.50 | Normal |
| −0.50 ÷ −1.00 | Slightly dry |
| −1.00 ÷ (−1.50) | Moderately dry |
| −1.50 ÷ (−2.00) | Severely dry |
| −2.00 and less | Extremely dry |
| SEI | Classification |
|---|---|
| 2.00 and more | Extremely dry |
| 1.50 ÷ 2.00 | Severely dry |
| 1.00 ÷ 1.50 | Moderately dry |
| 0.50 ÷ 1.00 | Slightly dry |
| −0.50 ÷ 0.50 | Normal |
| −0.50 ÷ (−1.00) | Slightly wet |
| -1.00 ÷ (−1.50) | Moderately wet |
| −1.50 ÷ (−2.00) | Severely wet |
| −2.00 and less | Extremely wet |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartczak, A.; Słowińska, S.; Tyszkowski, S.; Kramkowski, M.; Kaczmarek, H.; Kordowski, J.; Słowiński, M. Ecohydrological Changes and Resilience of a Shallow Lake Ecosystem under Intense Human Pressure and Recent Climate Change. Water 2019, 11, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010032
Bartczak A, Słowińska S, Tyszkowski S, Kramkowski M, Kaczmarek H, Kordowski J, Słowiński M. Ecohydrological Changes and Resilience of a Shallow Lake Ecosystem under Intense Human Pressure and Recent Climate Change. Water. 2019; 11(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartczak, Arkadiusz, Sandra Słowińska, Sebastian Tyszkowski, Mateusz Kramkowski, Halina Kaczmarek, Jarosław Kordowski, and Michał Słowiński. 2019. "Ecohydrological Changes and Resilience of a Shallow Lake Ecosystem under Intense Human Pressure and Recent Climate Change" Water 11, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010032
APA StyleBartczak, A., Słowińska, S., Tyszkowski, S., Kramkowski, M., Kaczmarek, H., Kordowski, J., & Słowiński, M. (2019). Ecohydrological Changes and Resilience of a Shallow Lake Ecosystem under Intense Human Pressure and Recent Climate Change. Water, 11(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010032






