Contribution of Moisture from Mediterranean Sea to Extreme Precipitation Events over Danube River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ranking of Extreme Precipitation Events
2.2. Lagrangian Analysis of Mediterranean Moisture Contribution to Extreme Precipitation Events in Danube River Basin
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ∑CHIRPS | Daily mean precipitation value from CHIRPS precipitation dataset |
| Anom. CHIRPS | Daily precipitation anomaly value from CHIRPS precipitation dataset |
| CHIRPS | Climate Hazards Group Infra-Red Precipitation with Station data dataset |
| Clim. CHIRPS | Daily climatological precipitation value from CHIRPS precipitation dataset |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecast |
| ERA | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting Re-Analysis |
| FLEXPART | FLEXiblePARTicle dispersion model |
| HydroSHEDS | Hydrological data and maps based on Shuttle elevation derivatives at multiple scales |
| PFLEX | Available moisture from the Mediterranean Sea (E − P < 0 values) obtained via Lagrangian experiment |
| PFLEX-% | The percentage of the Mediterranean contribution for each event calculated by FLEXPART |
| PFLEX-ANOM | Daily anomalous (E − P) < 0 value obtained via Lagrangian experiment |
| PFLEX-CLI | Daily climatological (E − P) < 0 value obtained via Lagrangian experiment |
| PFLEX-EVENT | (E − P) < 0 mean values from the Mediterranean Sea into the Danube River Basin the day/days of extreme precipitation event obtained via Lagrangian experiment |
References
- Dankers, R.; Hiederer, R. Extreme Temperatures and Precipitation in Europe: Analysis of a High-Resolution Climate Change Scenario; JRC Scientific and Technical Reports; European Communities: Luxemburg, 2008; Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.397.1054&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Christensen, J.H.; Christensen, O.B. Severe summertime flooding in Europe. Nature 2003, 421, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, O.B.; Christensen, J.H. Intensification of extreme European summer precipitation in a warmer climate. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2004, 44, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, D.; Stojanovic, M.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Tracking the Origin of Moisture over the Danube River Basin Using a Lagrangian Approach. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekárová, P.; Miklánek, P.; Melo, M.; Halmová, D.; Pekár, J.; Mitková, V. Flood Marks along the Danube River between Passau and Bratislava; VEDA: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2014; Available online: http://147.213.100.3:81/danubeflood/PDF/kniha9VEDA%20small.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2018).
- Brilly, M. Hydrological Processes of the Danube River Basin; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Loczy, D. Geomorphological Impacts of Extreme Weather: Case Studies from Central and Eastern Europe; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 141–146. ISBN 978-94-007-6300-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ionita, M.; Scholz, P.; Chelcea, S. Spatio-temporal variability of dryness/wetness in the Danube River Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4483–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, M.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Moisture Transport Anomalies over the Danube River Basin during Two Drought Events: A Lagrangian Analysis. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosio, A. Climate Change Projections for the Danube River Basin; European Comission, Join Research Centre (JRC): Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: http://drdsi.jrc.ec.europa.eu/data/userstories/ReqNo_JRC92778_reqno_jrc92778_climate_change_projections_for_the_danube_area_final.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Olcina, J.; Pérez Morales, A.; Gil Guirado, S.; López, F.; Rico Amorós, A.M. The significance of vulnerability and exposure in increased flood risk on the mediterranean coast. In Consorseguros Revista Digital; Consorcio de Compensación de Seguros (CCS): Madrid, Spain, 2017; Available online: http://www.consorsegurosdigital.com/almacen/pdf/the-significance-of-vulnerability-and-exposure-in-increased-flood-risk-on-the-mediterranean-coast.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- Schmidli, J.; Frei, C. Trends of Heavy Precipitation and Wet and Dr y Spells in Switzerland during the 20th Centry. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, M. Recent Extreme Floods and Their Transformation along the Danube River. J. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2017, 73, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrow, T.; Thieken, A.H.; Kreibich, H.; Bahlburg, C.H.; Merz, B. Improvements on Flood Alleviation in Germany: Lessons Learned from the Elbe Flood in August 2002. Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliev, O.F.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.; Plate, E.J.; Bolgov, M.V. Extreme Hydrological Events: New Concepts for Security; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 418–420. ISBN 1-4020-5741-5. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F. Climate change hot-spots. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlačova, K.; Lapin, M.; Valent, P.; Szolgay, J.; Kohnova, S.; Rončak, P. Estimation of the impact of climate change-induced extreme precipitation events on floods. Contrib. Geophys. Geod. 2015, 45, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestieri, A.; Arnone, E.; Blenkinsop, S.; Candela, A.; Fowler, H.; Noto, L.V. The impact of climate change on extreme precipitation in Sicily, Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łupikasza, E.B.; Hanselb, S.; Matschullat, J. Regional and seasonal variability of extreme precipitationtrends in southern Poland and central-eastern Germany 1951–2006. Int. J. Clim. 2011, 31, 2249–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, S.C.; Fischer, E.M.; Posselt, R.; Liniger, M.A.; Croci-Maspoli, M.; Knutti, R. Emerging trends in heavy precipitation and hot temperature extremes in Switzerland. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocheva, L.; Marinova, T.; Simeonov, P.; Gospodinov, I. Variability and trends of extreme precipitation events over Bulgaria (1961–2005). Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, D.; Nieto, R.; Ramos, A.M.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. Wet Spells and Associated Moisture Sources Anomalies across Danube River Basin. Water 2017, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Hernández, E.; Gimeno, L. A Lagrangian analysis of the variation in moisture sources related to drier and wetter conditions in regions around the Mediterranean basin. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2307–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Hernández, M.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L.; Garcia-Herrera, R. Variability of moisture sources in the Mediterranean region during the period 1980–2000. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6781–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodemann, H.; Zubler, E. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of the moisture sources for Alpine precipitation during 1995–2002. Int. J. Clim. 2010, 30, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Stohl, A. On the origin of continental precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle. Part I: Method description, validation, and demonstration for the August 2002 flooding in central Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle: Part II: Moisture transports between Earth’s ocean basins and river catchments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Trigo, R.M.; Liberato, M.L.R. A ranking of high-resolution daily precipitation extreme events for the Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2014, 15, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Trigo, R.M.; Liberato, M.L.R. Ranking of multi-day extreme precipitation events over the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittu, S. A study on Atmospheric Dispersion Using the Transport Model FLEXPART. University of Oslo, Department of Geosciences—Meteorology and Oceanography Section, 2011. Available online: https://www.duo.uio.no/bitstream/handle/10852/12594/guttu-master.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 21 August 2018).
- An, X.; Yao, B.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Zhou, L. Tracking source area of Shangdianzi station using Lagrangian particle dispersion model of FLEXPART. Met. Apps 2014, 21, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numaguti, A. Origin and recycling processes of precipitating water over the Eurasian continent: Experiments using an atmospheric general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Forster, C.; Frank, A.; Seibert, P.; Wotawa, G. Technical note: The Lagrangian particle dispersion model FLEXPART version 6.2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L.; Drumond, A.; Hernandez, E. A Lagrangian identification of the main moisture sources and sinks affecting the Mediterranean area. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2010, 5, 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, Z.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. A Lagrangian analysis of the moisture budget over the Fertile Crescent during two intense drought episodes. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. Where Does the Iberian Peninsula Moisture Come from? An Answer Based on a Lagrangian Approach. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L.; Gallego, D.; Trigo, R.M. Contributions to the moisture budget of airmasses over Iceland. Meteorol. Z. 2007, 16, 037–044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. Extreme Sea Ice Loss over the Arctic: An Analysis Based on Anomalous Moisture Transport. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Stohl, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Domínguez, F.; Yoshimura, K.; Yu, L.; Drumond, A.; Durán-Quesada, A.M.; Nieto, R. Oceanic and Terrestrial Sources of Continental Precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivatek-Šahdan, S.; Stanešić, A.; Tudor, M.; Odak Plenković, I.; Janeković, I. Impact of SST on heavy rainfall events on eastern Adriatic during SOP1 of HyMeX. Atmos. Res. 2010, 200, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchia, L.; Scoccimarro, E.; Gualdi, S.; Marson, P.; Ahrens, B.; Berthou, S.; Dubois, C. Mediterranean extreme precipitation: A multi-model assessment. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toreti, A.; Xoplaki, E.; Maraun, D.; Kuglitsch, F.G.; Wanner, H.; Luterbacher, J. Characterisation of extreme winter precipitation in the Mediterranean and associated anomalous atmospheric circulation patterns. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. 2010, 10, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, N.; Otto, F.E.L.; van Oldenborgh, G.J.; Massey, N.R.; Sparrow, S.; Allan, M.R. The heavy precipitation event of May-June 2013 in the upper Danube and Elbe basins. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, S69–S72. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/b7f3/90dab80a8363a3ef415e601df5a63800b6ac.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2018).
- Thévenot, O.; Bouin, M.-N.; Ducrocq, V.; Lebeaupin Brossier, C.; Nuissier, O.; Pianezze, J.; Duffourg, F. Influence of the sea state on Mediterranean heavy precipitation: A case-study from HyMeX SOP1. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 142, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schicker, I.; Radanovics, S.; Seibert, P. Origin and transport of Mediterranean moisture and air. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5089–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toreti, A.; Giannakaki, P.; Martius, O. Precipitation extremes in the Mediterranean region and associated upper-level synoptic-scale flow structures. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 1925–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanescu, G.; Stoleriu, C.C. Exceptional floods in the Prut basin, Romania, in the context of heavy rains in the summer of 2010. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard, D.; Ducrocq, V.; Auger, L. A climatology of mesoscale environment associated with Mediterranean heavy precipitating events over a Northwestern Mediterranean area. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2012, 51, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, L.; Prisi, S.G. Extreme Rainfalls in the Mediterranean Area. In Storminess and Environmental Change: Climate Forcing and Responses in the Mediterranean Region; Diodato, N., Bellocchi, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 17–39. ISBN 978-94-007-7947-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl, S. Characterising the relationship between weather extremes in Europe and synoptic circulation features. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
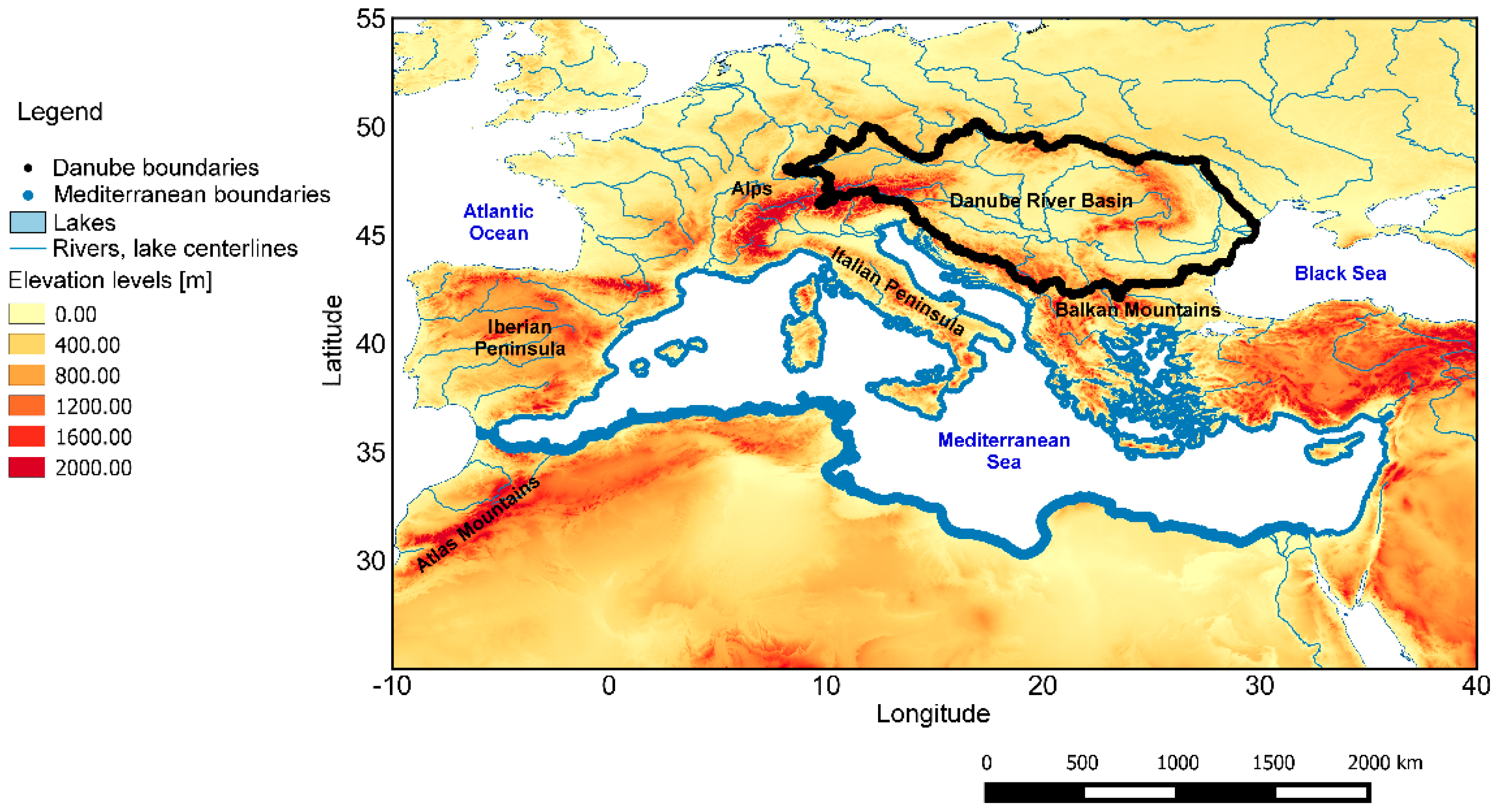
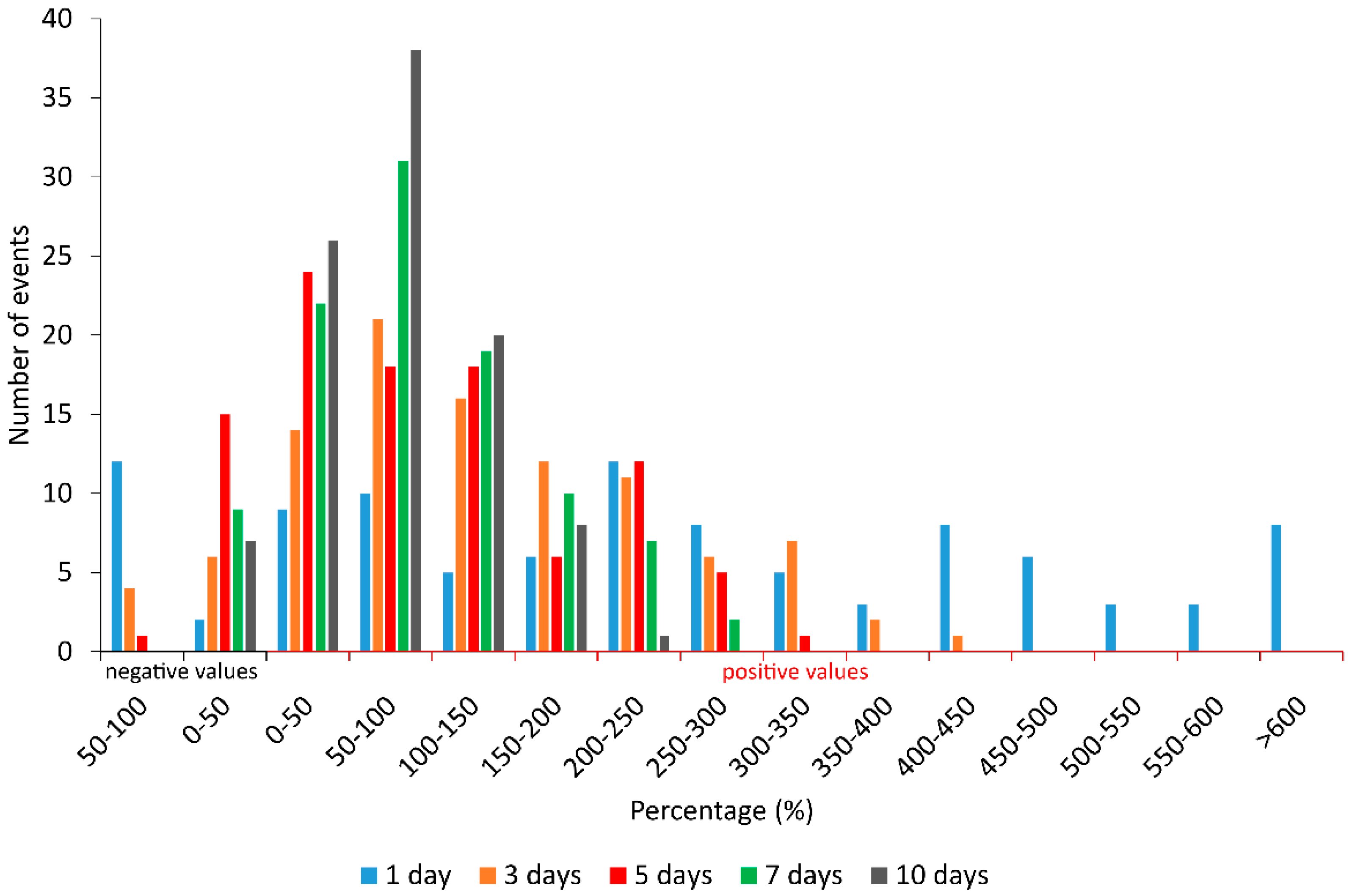
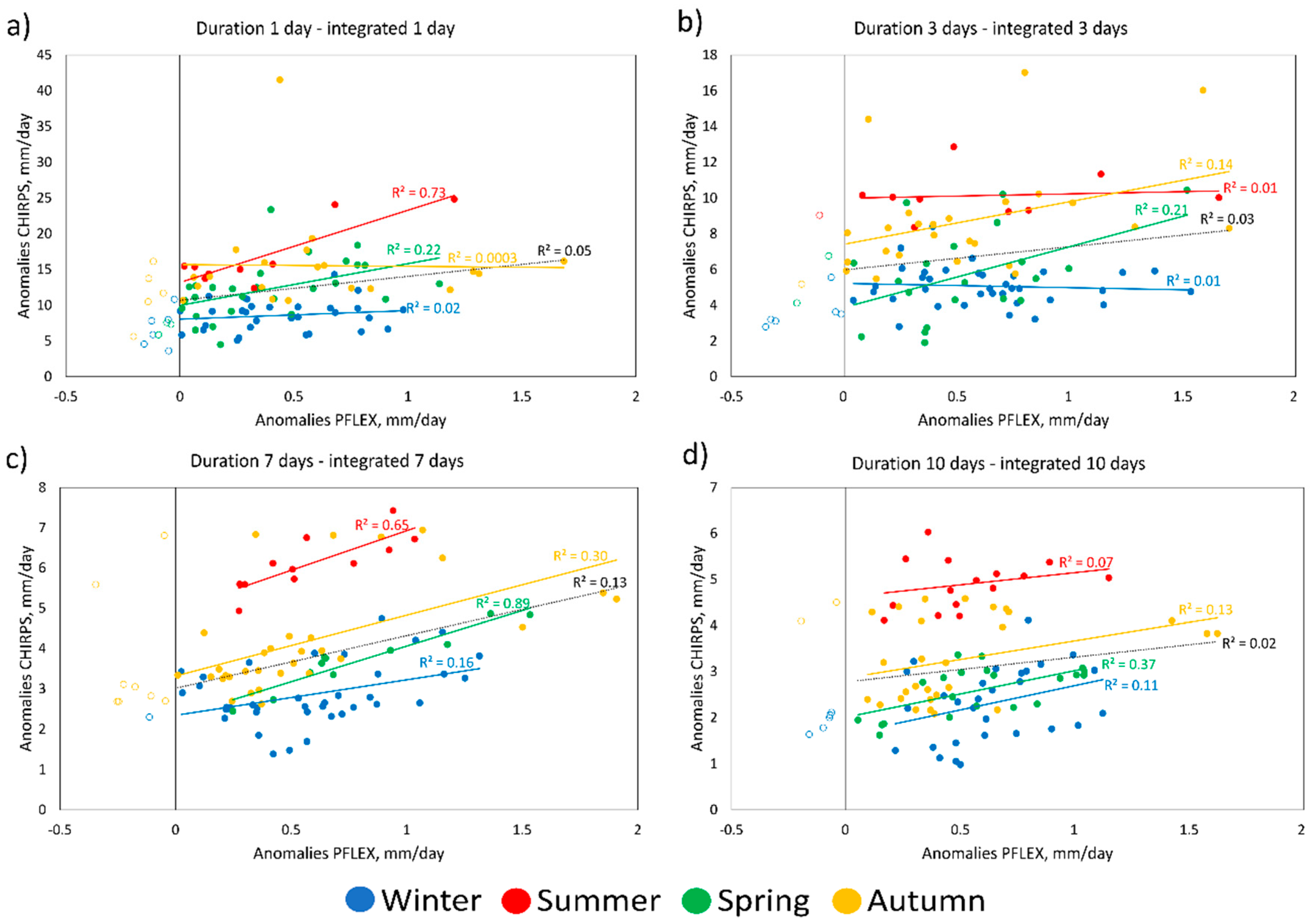
| Position of the Ranking | 1 Day | 3 Days | 5 Days | 7 Days | 10 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 Sep 1996 | 24 Sep 1996 | 24 Sep 1996 | 1 Jan 1996 | 23 Aug 2005 |
| 2 | 28 Dec 2014 | 23 Sep 1996 | 25 Sep1996 | 15 Dec 1990 | 18 Dec 1990 |
| 3 | 6 Nov 1985 | 25 Sep 1996 | 26 Sep 1996 | 2 Jan 1996 | 24 Aug 2005 |
| 4 | 1 Mar 2008 | 11 Feb 1984 | 14 Dec 1990 | 14 Dec 1990 | 4 Jan 1996 |
| 5 | 18 Feb 1994 | 6 Nov 1985 | 23 Jan 1998 | 7 May 1987 | 15 Dec 1990 |
| 6 | 27 Nov 1983 | 8 Jan 2010 | 27 Sep 1996 | 27 Sep 1996 | 17 Dec 1990 |
| 7 | 6 May 1987 | 6 May 1987 | 23 Sep 1996 | 24 Sep 1996 | 16 Dec 1990 |
| 8 | 14 Mar 2013 | 10 Feb 1984 | 22 Jan 1998 | 16 Dec 1990 | 14 Dec 1990 |
| 9 | 2 Mar 2014 | 29 Oct 1990 | 30 Oct 1990 | 28 Sep 1996 | 22 Aug 2005 |
| 10 | 27 Mar 1993 | 31 Oct 1994 | 31 Oct 1990 | 25 Sep 1996 | 12 May 1991 |
| Position of the Ranking | Date Event | Mean ∑CHIRPS | Clim. CHIRPS | Anom. CHIRPS | R | PFLEX-EVENT | PFLEX-CLI | PFLEX-ANOM | PFLEX-% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | |||||||||
| 1 | 23 Sep 1996 | 45.66 | 4.13 | 41.53 | 198.65 | 0.59 | 0.15 | 0.44 | 285.69 |
| 2 | 28 Dec 2014 | 17.76 | 3.45 | 14.31 | 168.81 | 0.82 | 0.14 | 0.68 | 457.93 |
| 3 | 6 Nov 1985 | 19.74 | 1.96 | 17.79 | 156.70 | 0.45 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 118.89 |
| 4 | 1 Mar 2008 | 13.09 | 2.42 | 10.68 | 155.58 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 11.87 |
| 5 | 18 Feb 1994 | 12.05 | 1.18 | 10.87 | 142.60 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 285.92 |
| 6 | 27 Nov 1983 | 16.94 | 1.57 | 15.38 | 140.42 | 0.76 | 0.16 | 0.60 | 383.90 |
| 7 | 6 May 1987 | 26.90 | 3.53 | 23.37 | 138.02 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.40 | 224.24 |
| 8 | 14 Mar 2013 | 14.18 | 1.17 | 13.01 | 137.91 | 1.21 | 0.07 | 1.14 | 1657.75 |
| 9 | 2 Mar 2014 | 9.67 | 2.07 | 7.60 | 136.17 | 0.08 | 0.14 | −0.06 | −41.29 |
| 10 | 27 Mar 1993 | 13.32 | 2.47 | 10.86 | 131.77 | 1.12 | 0.21 | 0.90 | 424.33 |
| 3 days | |||||||||
| 1 | 24 Sep 1996 | 19.61 | 2.59 | 17.02 | 249.95 | 1.37 | 0.57 | 0.80 | 140.94 |
| 2 | 23 Sep 1996 | 18.54 | 2.51 | 16.03 | 228.27 | 2.10 | 0.51 | 1.59 | 312.59 |
| 3 | 25 Sep 1996 | 16.90 | 2.49 | 14.41 | 224.59 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.11 | 18.07 |
| 4 | 11 Feb 1984 | 6.77 | 1.70 | 5.07 | 206.04 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 34.63 |
| 5 | 6 Nov 1985 | 9.50 | 2.03 | 7.46 | 204.39 | 1.12 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 107.29 |
| 6 | 8 Jan 2010 | 6.12 | 1.46 | 4.67 | 198.54 | 0.96 | 0.30 | 0.66 | 217.26 |
| 7 | 6 May 1987 | 13.52 | 3.08 | 10.44 | 198.36 | 2.05 | 0.53 | 1.52 | 284.32 |
| 8 | 10 Feb 1984 | 6.54 | 1.61 | 4.93 | 195.88 | 1.03 | 0.38 | 0.64 | 169.23 |
| 9 | 29 Oct 1990 | 11.82 | 2.03 | 9.79 | 195.15 | 1.07 | 0.35 | 0.71 | 202.75 |
| 10 | 31 Oct 1994 | 10.10 | 2.05 | 8.06 | 193.43 | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.01 | 3.85 |
| 5 days | |||||||||
| 1 | 24 Sep 1996 | 19.61 | 2.59 | 17.02 | 254.85 | 1.92 | 0.74 | 1.18 | 160.01 |
| 2 | 25 Sep1996 | 18.54 | 2.51 | 16.03 | 254.22 | 1.62 | 0.77 | 0.85 | 110.97 |
| 3 | 26 Sep 1996 | 16.90 | 2.49 | 14.41 | 251.71 | 1.14 | 0.79 | 0.36 | 45.42 |
| 4 | 14 Dec 1990 | 6.77 | 1.70 | 5.07 | 237.58 | 1.40 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 222.56 |
| 5 | 23 Jan 1998 | 9.50 | 2.03 | 7.46 | 234.92 | 1.17 | 0.48 | 0.69 | 145.60 |
| 6 | 27 Sep 1996 | 6.12 | 1.46 | 4.67 | 231.42 | 0.60 | 0.79 | −0.20 | −24.68 |
| 7 | 23 Sep 1996 | 13.52 | 3.08 | 10.44 | 230.92 | 2.13 | 0.70 | 1.42 | 201.84 |
| 8 | 22 Jan 1998 | 6.54 | 1.61 | 4.93 | 227.95 | 1.57 | 0.46 | 1.11 | 243.75 |
| 9 | 30 Oct 1990 | 11.82 | 2.03 | 9.79 | 222.08 | 1.14 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 142.65 |
| 10 | 31 Oct 1990 | 10.10 | 2.05 | 8.06 | 221.67 | 1.13 | 0.47 | 0.65 | 138.03 |
| 7 days | |||||||||
| 1 | 1 Jan 1996 | 6.52 | 2.12 | 4.40 | 298.19 | 1.67 | 0.51 | 1.16 | 225.99 |
| 2 | 15 Dec 1990 | 6.41 | 1.67 | 4.74 | 290.71 | 1.41 | 0.51 | 0.89 | 173.84 |
| 3 | 2 Jan 1996 | 5.33 | 1.96 | 3.37 | 277.60 | 1.36 | 0.49 | 0.88 | 180.10 |
| 4 | 14 Dec 1990 | 5.84 | 1.64 | 4.21 | 273.79 | 1.55 | 0.51 | 1.04 | 205.09 |
| 5 | 7 May 1987 | 7.53 | 2.67 | 4.86 | 260.72 | 2.16 | 0.80 | 1.36 | 171.43 |
| 6 | 27 Sep 1996 | 9.15 | 2.32 | 6.83 | 260.69 | 1.24 | 0.89 | 0.35 | 38.74 |
| 7 | 24 Sep 1996 | 9.28 | 2.34 | 6.94 | 258.47 | 1.92 | 0.86 | 1.07 | 124.99 |
| 8 | 16 Dec 1990 | 5.47 | 1.62 | 3.86 | 257.33 | 1.26 | 0.53 | 0.73 | 138.16 |
| 9 | 28 Sep 1996 | 9.07 | 2.26 | 6.81 | 256.91 | 0.86 | 0.90 | −0.05 | −5.41 |
| 10 | 25 Sep 1996 | 9.08 | 2.31 | 6.77 | 256.87 | 1.76 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 102.92 |
| 10 days | |||||||||
| 1 | 23 Aug 2005 | 8.05 | 2.02 | 6.03 | 325.98 | 1.15 | 0.79 | 0.36 | 45.52 |
| 2 | 18 Dec 1990 | 4.82 | 1.76 | 3.06 | 317.66 | 1.22 | 0.56 | 0.66 | 116.23 |
| 3 | 24 Aug 2005 | 7.49 | 2.04 | 5.45 | 315.91 | 1.08 | 0.82 | 0.26 | 31.93 |
| 4 | 4 Jan 1996 | 4.68 | 1.90 | 2.78 | 313.98 | 1.28 | 0.51 | 0.76 | 147.99 |
| 5 | 15 Dec 1990 | 4.99 | 1.63 | 3.36 | 313.50 | 1.55 | 0.55 | 0.99 | 179.03 |
| 6 | 17 Dec 1990 | 4.68 | 1.72 | 2.97 | 301.29 | 1.33 | 0.56 | 0.77 | 136.24 |
| 7 | 16 Dec 1990 | 4.78 | 1.62 | 3.16 | 300.85 | 1.41 | 0.56 | 0.85 | 152.19 |
| 8 | 14 Dec 1990 | 4.69 | 1.66 | 3.03 | 298.32 | 1.64 | 0.55 | 1.09 | 195.89 |
| 9 | 22 Aug 2005 | 7.45 | 2.03 | 5.42 | 298.17 | 1.21 | 0.76 | 0.45 | 58.65 |
| 10 | 12 May 1991 | 6.03 | 2.67 | 3.36 | 290.89 | 1.44 | 0.95 | 0.49 | 51.64 |
| Duration | 1 day | 3 days | 5 days | 7 days | 10 days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | 86% (100) | 90% (100) | 84% (100) | 91% (100) | 93% (100) |
| Winter | 83.33% (36) | 85.71% (42) | 86.96% (46) | 97.44% (39) | 85.29% (43) |
| Spring | 90% (30) | 90.91% (22) | 100% (7) | 100% (11) | 100% (21) |
| Summer | 100% (9) | 90% (10) | 100% (9) | 100% (11) | 100% (15) |
| Autumn | 80% (25) | 96.15% (26) | 73.68% (38) | 79.49% (39) | 93.33% (30) |
| Duration of Extreme Event | 1 Day | 3 Days | 5 Days | 7 Days | 10 Days | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period of integration used for PFLEX-ANOM values | 1 day | 3 days | 5 days | 7 days | 10 days | 3 days | 5 days | 7 days | 10 days | 5 days | 7 days | 10 days | 7 days | 10 days | 10 days |
| Annual | 3.34 * | 1.42 | 0.23 | 1.13 | −0.10 | 1.30 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 1.05 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 1.30 * | 0.09 * | 0.04 |
| Winter | 1.21 | −0.15 | −0.05 | −0.27 | −0.39 | −0.24 | −0.25 | −0.30 | −0.37 | 1.19 | 1.13 | 1.17 | 0.88 * | 1.07 * | 1.05 |
| Spring | 5.83 * | 4.77 * | 1.07 | 0.69 | −0.53 | 3.40 * | 1.72 | 0.10 | 0.83 | 1.22 | 1.29 | 1.29 | 1.77 * | 1.87 * | 1.01 * |
| Summer | 10.10 * | 6.14 | 6.83 | 7.90 * | 7.87 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.27 | −0.42 | −0.64 | −0.85 | 1.97 * | 2.07 * | 0.53 |
| Autumn | −0.25 | −3.18 | −3.27 | −0.31 | −0.87 | 2.38 | 1.04 | 1.48 | 1.53 | 2.15 | 1.36 | 0.86 | 1.51 * | 1.33 * | 0.81 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciric, D.; Nieto, R.; Ramos, A.M.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. Contribution of Moisture from Mediterranean Sea to Extreme Precipitation Events over Danube River Basin. Water 2018, 10, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091182
Ciric D, Nieto R, Ramos AM, Drumond A, Gimeno L. Contribution of Moisture from Mediterranean Sea to Extreme Precipitation Events over Danube River Basin. Water. 2018; 10(9):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091182
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiric, Danica, Raquel Nieto, Alexandre M. Ramos, Anita Drumond, and Luis Gimeno. 2018. "Contribution of Moisture from Mediterranean Sea to Extreme Precipitation Events over Danube River Basin" Water 10, no. 9: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091182
APA StyleCiric, D., Nieto, R., Ramos, A. M., Drumond, A., & Gimeno, L. (2018). Contribution of Moisture from Mediterranean Sea to Extreme Precipitation Events over Danube River Basin. Water, 10(9), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091182









