Abstract
In studies on the effect of rainfall on slope stability, soil hydraulic conductivity is usually assumed to be isotropic to simplify the analysis. In the present study, a coupled hydromechanical framework based on transient seepage analysis and slope stability analysis is used to investigate the effects of hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on rainfall infiltration and slope safety at various slope locations (the top of the slope, the slope itself and the toe of the slope). The results show that when the vertical hydraulic conductivity (Ky) is constant, the horizontal hydraulic conductivity (Kx) increases (i.e., anisotropy increases). This occurs because rainfall tends to infiltrate into the interior of the slope, resulting in the soil on top of the slope and on the slope itself being easily influenced by rainfall, leading to soil instability. The change of rainfall infiltration at the slope itself is the most significant. When the anisotropic ratio Kr (=Kx/Ky) increased from 1 to 100, the depth of the wetting zones for loam, silt and clay slopes increased by 23.3%, 33.3% and 50%, respectively. However, increased Kr led to a slower infiltration rate in the vertical direction at the toe of the slope. Compared to the results for Kr = 1 and for Kr = 100, the thickness of the wetting zones at the toe of loam and silt slopes decreased by 23.3% and 30.0%, respectively. For the clay slope, Kr changes did not significantly affect the wetting zones because of poor permeability. The results of this study suggest that the effect of soil hydraulic conductivity anisotropy should be considered when estimating slope stability to better understand the effect of rainfall on slopes.
1. Introduction
Studies on landslides, which occur in many parts of the world, have found that slope stability is influenced by not only internal factors, such as topography, geological structure of the slope and groundwater conditions but also external factors, such as precipitation, earthquakes and human activity [1,2,3,4,5]. Rainwater infiltration is the most common cause of landslides [6,7]. Mountainous areas all over the world are subjected to heavy rainfall in the wet season [8,9]. During rainfall events, rainwater infiltrates into the pores of the soil, increasing the water content of the soil in the dry zone (above the groundwater table and near the surface), which becomes a wetting zone or transient saturated zone [10,11,12,13]. Water that infiltrates into the soil increases the shear stress and the pore water pressure of the soil. When the pore water pressure of the soil increases, the effective stress decreases, resulting in a decrease in the shear strength of the soil and a decrease in slope stability. Therefore, rainfall seepage is considered to be an important factor in slope failure [14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
Numerous studies have focused on the mechanism of rainfall-triggered landslides [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Results show that when rainfall occurs on slopes, the hydraulic properties of soil and rainfall patterns control the seepage behavior. The spatial variability of soil’s properties is also an important factor that can influence rainfall infiltration and slope stability [31,32]. The saturated hydraulic conductivity of soil, Ks, limits the rainfall infiltration rate and rainfall characteristics, such as intensity and duration, control the rainfall amount that can infiltrate into the soil [33,34]. However, most research has assumed that the hydraulic conductivity of soil is isotropic. In a natural environment, the hydraulic conductivity of soil is usually anisotropic; however, few studies have considered the effect of soil hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on slope stability. Studies that discuss hydraulic anisotropy usually define the anisotropic ratio as Kx/Ky to describe soil hydraulic conductivity anisotropy, where Kx and Ky are the hydraulic conductivity in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The values of the anisotropic ratio for alluvium range from 2 to 10 and that for clay soil can be higher than 100 [35]. Dong and Hsu [36] used a numerical model to estimate the effect of hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on the stability of stratified, poorly cemented rock slopes. They showed that neglecting hydraulic conductivity anisotropy resulted in overestimation of the safety factor of the slope by about 40%. Mahmood et al. [37] discussed the effect of anisotropic conductivity on the pore water pressure and reliability index of an unsaturated embankment. When the horizontal conductivity is fixed and the vertical conductivity is reduced, the rainfall infiltration rate in the vertical direction decreases and the slope reliability index remains unchanged. These studies show the significance of hydraulic anisotropy on the mechanism of rainfall-induced landslides. However, previous studies have not clarified the effect of hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on rainfall infiltration and slope stability at various locations on a slope (the top of the slope, the slope itself and the toe of the slope). Therefore, a coupled hydromechanical framework based on transient seepage analysis and slope stability analysis is established in this study to investigate the effects of hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on rainfall infiltration and slope safety at various locations on a slope.
Reliable limit equilibrium methods such as the ordinary method [38], Bishops’ simplified method [39], Janbu’s simplified method [40] and the Morgenstern and Price method [41] are commonly used to investigate slope stability. Although these methods can be used to easily calculate the safety factor of a slope by presuming the slope’s failure surface, it is difficult to identify where the slope failure begin and the real failure surface. Thus, the local factor of safety method [42], which is a new stability analysis method based on the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion, is used in the present study. The advantage of using the local factor of safety (LFS) method is that this method can compute the factor of safety of each soil element, this is helpful to compare the effect of rainfall infiltration on soil stability at various locations or depths of a slope. In this study, a coupled hydromechanical framework based on transient seepage analysis and slope stability analysis is utilized for analyzing the effect of soil hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on slope stability.
2. Methodology
2.1. Seepage Analysis
Transient seepage analysis was conducted using the HYDRUS 2D [43] numerical model. The solution for transient unsaturated flow is based on Richards equation [44]:
where [-] is the volumetric water content, t [T] is the time, h [L] is the pore water pressure or suction head, H [L] is the total head, W [L3T−1] is the boundary flux, K(h) is the hydraulic conductivity function (HCF) and is the soil-water retention curve (SWRC). In this study, the van Genuchten [45] SWRC model—shown in Equation (2)—is used to describe the relationship between soil volumetric water content and soil suction and the Mualem model [46]—shown in Equation (3)—is used for the HCF:
where [-] represents the saturated water content, [-] represents the residual water content, [L−1], n [-] and l [-] are the fitting parameters related to the inverse of the air entry value (suction), pore size distribution of soil and pore connectivity of soil, respectively and m = 1 − 1/n. [LT−1] represents the saturated hydraulic conductivity and [-] is the equivalent degree of saturation, defined as:
2.2. Theory of Effective Stress and Local Factor of Safety
In the stability analysis, the concept of suction stress [47] was used to calculate the soil effective stress. Suction stress includes all the inter-particle stresses such as capillary stress, the electric double-layer force, the van der Waals attractive force and the matric suction of soil. Lu et al. [48] postulated that suction stress represents the energy stored by the soil water and provided the closed-form equations for the effective stress and suction stress in soils, respectively, expressed as:
where is the suction stress [ML−1T−2], is the pore air pressure [ML−1T−2], is the pore water pressure [ML−1T−2], is the matric suction of soil [ML−1T−2] and [L−1] and n [-] are fitting parameters identical to those in the van Genuchten [45] SWRC model.
The local factor of safety method [42] was used in this study to estimate slope stability. This method is based on the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion (Figure 1). It defines the local factor of safety (LFS) as the ratio of the potential Coulomb stress to the current Coulomb stress, shown in Equation (7). In this theory, the solid Mohr circle is assumed to be the current state of stress of a soil element. When the water content of the soil is increased, the solid Mohr circle shifts leftward because of the suction stress increasing. The size of the Mohr circle remains nearly unchanged because it is related to the difference in the principal total stresses , which are determined by the slope geometry and the self-weight of the soil. If the Mohr circle shifting leftward, the Mohr circle is closer to the Mohr-Coulomb failure envelope, then, the state of stress of the soil is closer to the failure condition.
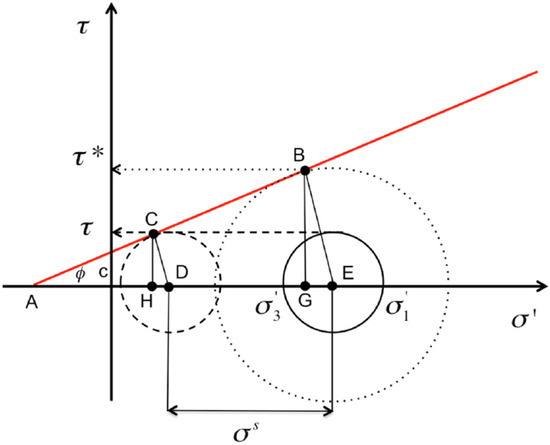
Figure 1.
Illustration of the concept of local factor of safety [49].
In Equation (8), is the shear strength or potential Coulomb stress [ML−1T−2], is the shear stress or current Coulomb stress [ML−1T−2], c is the effective cohesion of the slope material [ML−1T−2], and are the maximum effective stress and minimum effective stress [ML−1T−2], respectively and is the angle of shearing resistance of the slope material [LL−1].
In addition, referring to the effective stress theory of Lu and Likos [47], substituting Equation (5) into Equation (8) yields:
Then, the solution of LFS can be utilized for calculating the stability of the slope and is combined with the finite element method to estimate the safety factor variation with space and time. If the suction stress of the soil is increased, indicating that the LFS of the soil is reduced, which means the stability of the soil is decreased.
2.3. Coupled Hydromechanical Framework
The finite element software HYDRUS 2D [43] and the Slope Cube Module [49] were used to establish a coupled hydromechanical framework to investigate the effect of rainfall infiltration on slope stability. The geometry and boundary conditions of the two-dimensional (2D) slope model are shown in Figure 2. The boundaries of the slope surface (BC, CD and DE boundaries) were set as the rainfall infiltration boundaries and the sides of the slope (AG and FH boundaries) were set as the boundaries of the fixed water level to maintain the depth of the original groundwater level in the slope. BG, EH and AF were the no-flow boundaries; the flux at these three boundaries is zero.
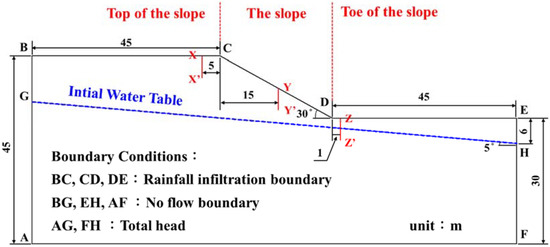
Figure 2.
Illustration of slope model.
In this study, three types of soil were considered, namely loam, silt and clay, representing high to low hydraulic conductivity residual soils. The hydraulic properties of the materials include saturated water content (), saturated hydraulic conductivity () and the fitting parameters and n for SWRC [44], as shown in Table 1. From the theories of SWRC, HCF and suction stress mentioned above, the corresponding pore water pressure, soil water permeability and soil suction stress of the slope materials can be obtained for various water content conditions (Figure 3). Table 2 shows the compiled mechanical characteristic parameters of the soils, where Gs represents the specific weight of the soil, E represents the Young’s modulus of the soil and v is Poisson’s ratio.

Table 1.
Hydraulic properties of slope material [50].
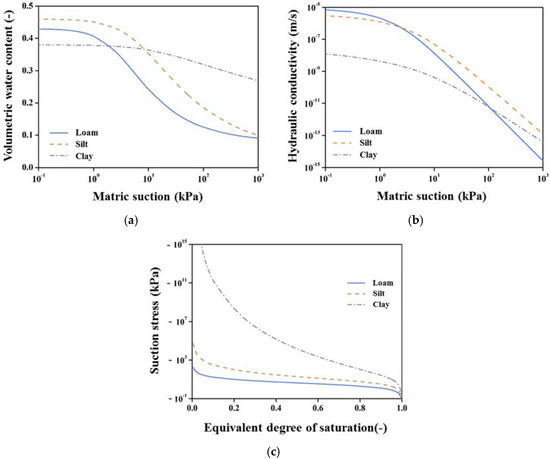
Figure 3.
Hydraulic properties of slope material. (a) Soil water retention curve (SWRC); (b) Hydraulic conductivity function (HCF); (c) Suction stress characteristic curve.

Table 2.
Mechanical properties of slope material [51].
In the coupled hydromechanical framework, the solution for transient unsaturated flow [43] was used to conduct seepage analysis of 2D slopes to examine the effects of rainfall infiltration on the water content, soil suction and soil unit weight in unsaturated slope layers. Then, the solutions of the seepage analysis were input into FEM2D [52] which is one part of code wrote in the Slope Cube Module and is used to compute the soil stresses and displacements by using the field of moist unit weight as the gravity term [49]. A linear momentum balance equation is used to describe the total stress changes in slope materials:
where represents the stress tensor in 2D space, represents the unit weight of the slope material related to water content and b is the unit vector of body forces with two components. The field of soil suction stress and effective stress can be estimated using Equations (5) and (7), respectively, with the solutions of the field of soil saturation, soil suction and total stress. The LFS method can then be used to calculate the soil stability field.
3. Results and Discussion
In a nature environment, soil always sediment by gravity and shows layered distribution, resulting in the hydraulic conductivity of soil in all directions are different (i.e., hydraulic conductivity anisotropy). According to previous studies, the conductivity in the horizontal direction (Kx) is usually higher than that in the vertical direction (Ky) and the anisotropic ratio (Kr = Kx/Ky) ranges from 1 to 100 [35]. The Ky value of slope materials (loam, silt and clay) was defined as constant in this research and the Kx value was varied to design different anisotropic cases for the analysis. The settings of each case are shown in Table 3. The rainfall intensity was set at 14.5 mm/h, which is the threshold value for long-duration extreme events, as defined by the National Science and Technology Center for Disaster Reduction. The rainfall duration is longer than 1 day and the rainfall amount in 1 day is about 350 mm [53]. In this study, the analysis is performed for 48 h (rainfall duration is 48 h) and was average divided into 48 time steps.

Table 3.
Case design for hydraulic conductivity anisotropy.
The analysis results show a significant difference in the rainfall effect on the slope saturation and stability at different locations (Figure 4). When Kr is equal to 100 (high anisotropy case), the thickness of the wetting zone caused by rainfall increases for the slope. However, at the toe of the slope, with increasing anisotropic ratio, the thickness of the wetting zone decreases for a given rainfall intensity. Thus, the results of the X-X,’ Y-Y’ and Z-Z’ sections (Figure 2), representing the top of the slope, the slope itself and the toe of the slope, respectively, are discussed here to clarify the effect of hydraulic conductivity anisotropy.
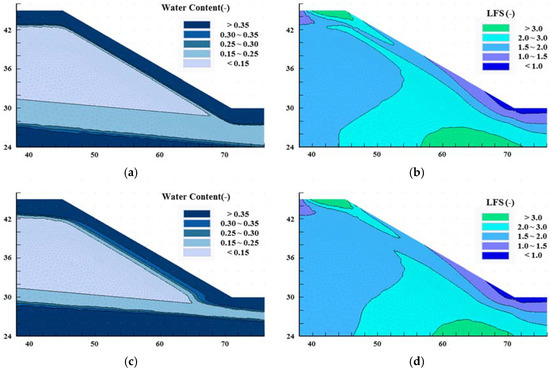
Figure 4.
Effect of soil hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on soil water content and local factor of safety (LFS) distribution (using results for loam slope as an example). (a) Kr = 1 (water content); (b) Kr = 1 (LFS); (c) Kr = 100 (water content); (d) Kr = 100 (LFS).
3.1. Top of Slope (X-X’ Section)
The results of water content, soil suction stress and LFS at the top of the slope (X-X’ section) after a rainfall event in different cases are first discussed. The results for the loam slope show that the thickness of the wetting zone caused by rainfall infiltration increases by about 12.5% when Kr is increased from 1 to 100 (Figure 5). When Kr is increased and Ky remains constant, the soil permeability in the horizontal direction increases. The rainfall in the soil tends to infiltrate in the horizontal direction and thus the rainwater permeates deep into the slope. The soil at the top of the slope is also affected by this phenomenon. The soil water content at depths in the range of 2.8 to 3.2 m is increased in the high anisotropy case and the change of water content also affect soil suction stress and LFS, as shown in Figure 5b,c.
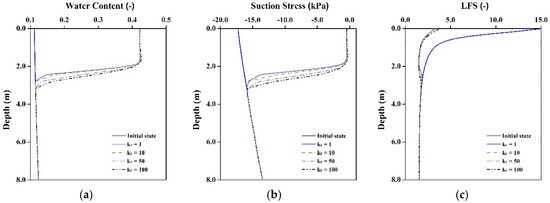
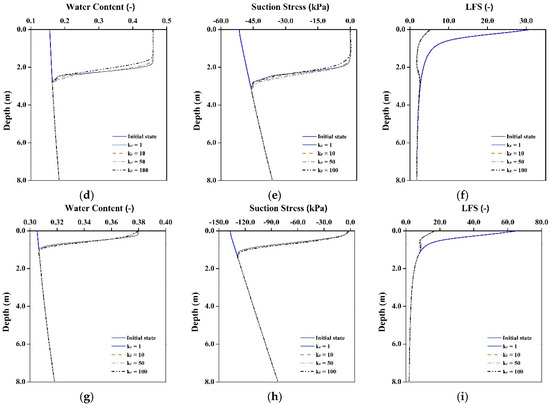
Figure 5.
Results of rainfall infiltration in various hydraulic conductivity anisotropy cases at top of slope (X-X’). Changes in (a,d,g) Water content; (b,e,h) Suction stress; and (c,f,i) LFS for loam, silt and clay slopes, respectively. (a) Loam; (b) Loam; (c) Loam; (d) Silt; (e) Silt; (f) Silt; (g) Clay; (h) Clay; (i) Clay.
For silt and clay slopes, although high Kr increases soil permeability in the horizontal direction, the original hydraulic conductivity of these two slope materials is so small that the results of modeling do not show the effect of anisotropy changes on the saturation and stability at the top of the slope (X-X’ section).
3.2. Slope (Y-Y’ Section)
The results of the Y-Y’ section are used to discuss the effect of anisotropy changes on the saturation and stability of the slope. The results of water content field, suction stress field and LFS field are shown in Figure 6. In each case, the results show that the thickness of the wetting zone caused by precipitation increases with increasing Kr. This is because Kx increases when Kr is increased, rainfall infiltration flow tends to be in the horizontal direction and seepage can easily affect soil saturation and stability. Compared with the Kr = 1 results, the depth of the wetting zone increased by about 23.3%, 33.3% and 50% for loam, silt and clay slopes, respectively, for Kr = 100. It also shows that the LFS tends to easily drop down when Kr is high.
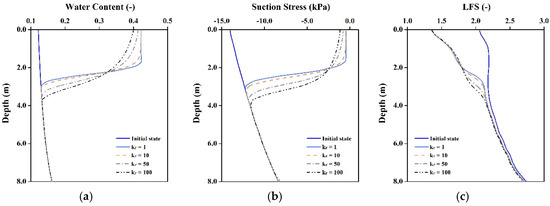
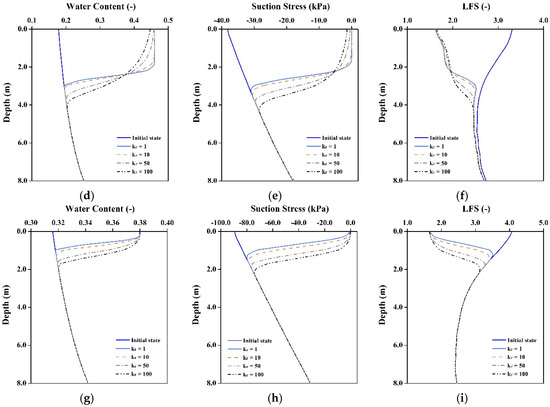
Figure 6.
Results of rainfall infiltration in various hydraulic conductivity anisotropy cases on the slope (Y-Y’). Changes in (a,d,g) Water content; (b,e,h) Suction stress; and (c,f,i) LFS for loam, silt and clay slopes, respectively. (a) Loam; (b) Loam; (c) Loam; (d) Silt; (e) Silt; (f) Silt; (g) Clay; (h) Clay; (i) Clay.
3.3. Toe of Slope (Z-Z’ Section)
For Kr = 100, the soil below depths of 2.8, 3.0 and 5.0 m for the loam, silt and clay slopes, respectively, is affected by groundwater table rises, as shown in Figure 7. The groundwater table was originally inclined by 5°; however, when the horizontal hydraulic conductivity increases, the initial groundwater table is not under a steady state, it tends to become level with time, resulting in a groundwater table rise at the toe of the slope. This study also conducts these analyses without rainfall, the results are the same, show that the groundwater table rising is because of the horizontal hydraulic conductivity increases.
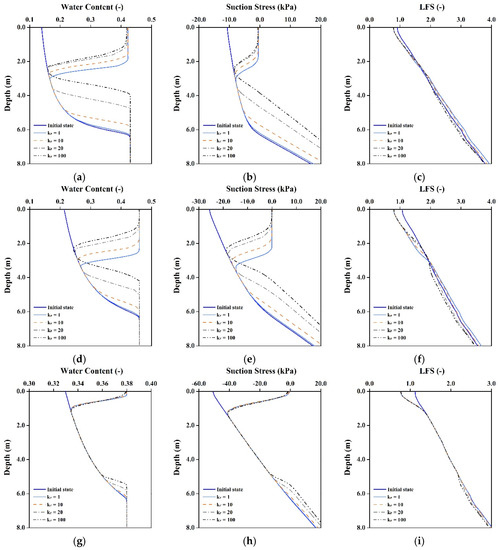
Figure 7.
Results of rainfall infiltration in various hydraulic conductivity anisotropy cases at toe of slope (Z-Z’). Changes in (a,d,g) Water content; (b,e,h) Suction stress; and (c,f,i) LFS for loam, silt and clay slopes, respectively. (a) Loam; (b) Loam; (c) Loam; (d) Silt; (e) Silt; (f) Silt; (g) Clay; (h) Clay; (i) Clay.
As mentioned above, when Kr increases, rainfall tends to infiltrate in the horizontal direction. Thus, the rainwater can flow into the slope body quickly in the horizontal direction in high Kr cases, which decreases the vertical infiltration rate. As shown in the results for the loam and silt slopes, when Kr = 100, the thickness of wetting zone at the toe of the slope (Z-Z’ section) decreases by about 23.3% and 30.0%, respectively, compared with that for Kr = 1. And the changes of the wetting front also affect soil stability, the results show that the safety factor of the soil at 2 m below the surface is higher when Kr increases. The hydraulic conductivity of clay is so small that the anisotropy changes do not affect the soil saturation and stability of the clay slope.
The analysis results show that soil hydraulic conductivity anisotropy can influence the behavior of rainfall infiltration at different locations of the slope, especially when Kr is higher than 10. However, as mentioned above, the values of the anisotropic ratio for alluvium usually range from 2 to 10 and that for clay soil can be much higher. Therefore, slope stability analyses in the further research could consider hydraulic conductivity anisotropy to better understand the impact of rainfall on the slope when the anisotropic ratio is higher than 10. In addition, this study shows the advantages of the LFS method, which allows the effect of rainfall on soil stability to be evaluated at each point within a slope. However, the study considering a slope made up of homogeneous material is a strong limitation that limits the application to real cases of study. In a real slope, the hydrology of a hillslope is usually influenced by the internal discontinuities (layering, bedding, pedology, etc.). Thus, in the future research, conducting geological surveys to determine slope geometry, structure and using probabilistic method to determine soil properties in the numerical model could make the results of the analyses more reliable.
4. Conclusions
A coupled hydromechanical framework was used in this study to investigate the effects of hydraulic conductivity anisotropy on rainfall infiltration and slope safety. Changes in the water content field, suction stress field and LFS field show that the anisotropy of soil permeability has an effect on rainfall infiltration. When the vertical hydraulic conductivity is fixed, an increase in Kr represents an increase in soil seepage mobility in the horizontal direction, making the soil on the slope itself more susceptible to rainfall infiltration, decreasing the soil safety factor. When Kr was increased from 1 to 100, the depth of the wetting zone on the slope itself increased by 23.3%, 33.3% and 50.0% for loam, silt and clay slopes, respectively and resulting in the soil LFS more easily to decrease. Although the results of loam slope also show the effect of anisotropy changes on the saturation and stability at the top of the slope (X-X’ section), the original hydraulic conductivity of silt and clay slope is so small that the results of modeling do not show the effect of anisotropy changes. In addition, when the horizontal hydraulic conductivity increased, the rainfall at the toe of the slope tended to flow into the slope body in the horizontal direction, decreasing the vertical infiltration rate. Compared to the results for Kr = 1, for Kr = 100, the thickness of the wetting zone at the toe of the loam and silt slopes decreased by 23.3% and 30.0%, respectively. Thus, it can be seen that rainfall infiltration behavior was most affected by hydraulic conductivity anisotropy at the slope (Y-Y’ section). The rainfall infiltration behavior at the top of the slope and the toe of the slope was less sensitive to the anisotropy of hydraulic conductivity for slope materials with poor permeability, such as clay. Therefore, hydraulic conductivity anisotropy could be considered in analyses of slope stability to better predict the effect of rainfall infiltration on slope safety, especially when Kr is higher than 10.
However, the study considering a slope made up of homogeneous material is a strong limitation that limits the application to real cases of study. Thus, future research could conduct geological surveys to determine the slope geometry, structure and soil properties in the numerical model to improve the reliability of the study results.
Author Contributions
H.-F.Y. conceived the subject of the article, literature review and contributed to the writing of the paper; Y.-J.T. participated in data processing, elaborated the statistical analysis and figures.
Funding
This research was funded by the Research Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), grant number (106-2625-M-006-014).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support the Headquarters of University Advancement at the National Cheng Kung University, which is sponsored by the Ministry of Education, Taiwan, ROC.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rahardjo, H.; Ong, T.H.; Rezaur, R.B.; Leong, E.C. Factors controlling instability of homogeneous soil slopes under rainfall. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntohar, A.S.; Liao, H.J. Analysis of rainfall-induced infinite slope failure during typhoon using a hydrological–geotechnical model. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tang, W. Stability analysis of rainfall-induced slope failure: A review. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 2011, 164, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.R.; Qian, Y.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhao, B. Analysis of rainfall infiltration law in unsaturated soil slope. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 567250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.E. Prediction of shallow landslide by surficial stability analysis considering rainfall infiltration. Eng. Geol. 2017, 231, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.S.; Sayed Owaise, R.; Ashwin, S.; Jain, R.M.; Prasanth, S.; Venugopalan, R.B. Investigation on infrastructural damages by rainfall-induced landslides during november 2009 in nilgiris, india. Nat. Hazards 2013, 65, 1535–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, H. Models and influencing factors of the delay phenomenon for rainfall on slope stability. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. New NASA Model Finds Landslide Threats in Near Real-Time during Heavy Rains; Greenbelt: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12897 (accessed on 22 March 2018).
- Matsushi, Y.; Hattanji, T.; Matsukura, Y. Mechanisms of shallow landslides on soil-mantled hillslopes with permeable and impermeable bedrocks in the Boso Peninsula, Japan. Geomorphology 2006, 76, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, C.A.; Santi, P.M. Debris flows and their toll on human life: A global analysis of debris-flow fatalities from 1950 to 2011. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuin, Y.; Hotta, N.; Suzuki, M.; Ogawa, K.I. Estimating the effects of heavy rainfall conditions on shallow landslides using a distributed landslide conceptual model. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2012, 49, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Jeong, S.; Kim, G. Gis-based prediction method of landslide susceptibility using a rainfall infiltration-groundwater flow model. Eng. Geol. 2014, 182, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyerdahl, H. Influence of extreme long-term rainfall and unsaturated soil properties on triggering of a landslide—A case study. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 2017, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lee, C.F.; Law, K.T. Causative mechanisms of rainfall-induced fill slope failures. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iryo, T.; Rowe, R.K. Infiltration into an embankment reinforced by nonwoven geotextiles. Can. Geotech. J. 2005, 42, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, S.; Asano, S.; Okamoto, T. Relationship between rain and/or meltwater, pore-water pressure and displacement of a reactivated landslide. Eng. Geol. 2008, 101, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Borden, R.H. Numerical simulation of MSE wall behavior induced by surface-water infiltration. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 2110–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.; Ng, K.Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Li, W.C. Rainfall-induced landslides in Hulu Kelang area, Malaysia. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Vanapalli, S.K. Hydro-mechanical coupling effect on surficial layer stability of unsaturated expansive soil slopes. Comput. Geotech. 2015, 70, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.H.; Uzuoka, R.; Thuo, J.N.; Lin, G.L.; Nakai, Y. Coupled hydro-mechanical analysis of two unstable unsaturated slopes subject to rainfall infiltration. Eng. Geol. 2017, 216, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Shi, Q. A numerical investigation of the stability of unsaturated soil slopes subjected to transient seepage. Comput. Geotech. 1998, 22, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F.; Wang, S.J. Characterization of rainfall-induced landslides. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4817–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, B.D.; Znidarcic, D. Stability analyses of rainfall induced landslides. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Take, W.A.; Bolton, M.D.; Wong, P.C.P.; Yeung, F.J. Evaluation of landslide triggering mechanisms in model fill slopes. Landslides 2004, 1, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Troncone, A. Analytical method for predicting the mobility of slow-moving landslides owing to groundwater fluctuations. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Leong, E.C. Effects of flux boundary conditions on pore-water pressure distribution in slope. Eng. Geol. 2013, 165, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Kim, J.M.; Ashraf, M. The effect of soil type on matric suction and stability of unsaturated slope under uniform rainfall. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Leong, E.C. Effects of rainfall characteristics on the stability of tropical residual soil slope. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, Paris, France, 12–14 September 2016; EDP Sciences: Paris, France, 2016; p. 15004. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, E.; Troncone, A. A performance-based method for the design of drainage trenches used to stabilize slopes. Eng. Geol. 2018, 239, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Donato, A.; Pugliese, L.; Troncone, A. Analysis of the Maierato landslide (Calabria, Southern Italy). Landslides 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Woo, I. Assessment of rainfall-induced shallow landslide susceptibility using a gis-based probabilistic approach. Eng. Geol. 2013, 161, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, V.; Bicocchi, G.; Rossi, G.; Segoni, S.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F. Soil characterization for shallow landslides modeling: A case study in the Northern Apennines (Central Italy). Landslides 2017, 14, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.F.; Wang, J.; Shen, K.L.; Lee, C.H. Rainfall characteristics for anisotropic conductivity of unsaturated soil slopes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8669–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristo, C.; Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A. Effect of variations in rainfall intensity on slope stability in singapore. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D. Groundwater Hydrology; Jon Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.J.; Tu, C.H.; Lee, W.R.; Jheng, Y.J. Effects of hydraulic conductivity/strength anisotropy on the stability of stratified, poorly cemented rock slopes. Comput. Geotech. 2012, 40, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, J.M. Effect of anisotropic conductivity on suction and reliability index of unsaturated slope exposed to uniform antecedent rainfall. Landslides 2013, 10, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellenius, W. Calculation of the stability of earth dams. In Transactions of the 2nd Congress on Large Dams; International Commission on Large Dams: Washington, DC, USA, 1936; Volume 4, pp. 445–463. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, A.W. The principle of effective stress. Teknisk Ukeblad 1959, 39, 859–863. [Google Scholar]
- Janbu, N. Application of composite slip surfaces for stability analysis. Eur. Conf. Stab. Earth Slopes 1955, 3, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern, N.; Price, V.E. The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces. Geotechnique 1965, 15, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Şener-Kaya, B.; Wayllace, A.; Godt, J.W. Analysis of rainfall-induced slope instability using a field of local factor of safety. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. Development and applications of the hydrus and stanmod software packages and related codes. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Likos, W.J. Unsaturated Soil Mechanics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W.; Wu, D.T. A closed-form equation for effective stress in unsaturated soil. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Wayllace, A.; Formetta, G. The Slope Cube Module; Soil Water Retention, LLC: Madison, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carsel, R.F.; Parrish, R.S. Developing joint probability distributions of soil water retention characteristics. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnesota Department of Transportation. MnDOT Pavement Design Manual; Minnesota Department of Transportation: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, J.N. An Introduction to the Finite Element Method; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.Y.; Yen, P.L.; Li, T.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Yu, Y.C. Taiwan Extreme Rainfall Events: Summary of Important Events from 1992 to 2013; National Science and Technology Center for Disaster Reduction: New Taipei, Taiwan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).